#cspm tool
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#cyber security company in saudi arabia#cloud security in KSA#top cloud security company#Cloud compliance tool#cloud security posture management#cspm tool
1 note
·
View note
Text
CNAPP Explained: The Smartest Way to Secure Cloud-Native Apps with EDSPL

Introduction: The New Era of Cloud-Native Apps
Cloud-native applications are rewriting the rules of how we build, scale, and secure digital products. Designed for agility and rapid innovation, these apps demand security strategies that are just as fast and flexible. That’s where CNAPP—Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform—comes in.
But simply deploying CNAPP isn’t enough.
You need the right strategy, the right partner, and the right security intelligence. That’s where EDSPL shines.
What is CNAPP? (And Why Your Business Needs It)
CNAPP stands for Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform, a unified framework that protects cloud-native apps throughout their lifecycle—from development to production and beyond.
Instead of relying on fragmented tools, CNAPP combines multiple security services into a cohesive solution:
Cloud Security
Vulnerability management
Identity access control
Runtime protection
DevSecOps enablement
In short, it covers the full spectrum—from your code to your container, from your workload to your network security.
Why Traditional Security Isn’t Enough Anymore
The old way of securing applications with perimeter-based tools and manual checks doesn’t work for cloud-native environments. Here’s why:
Infrastructure is dynamic (containers, microservices, serverless)
Deployments are continuous
Apps run across multiple platforms
You need security that is cloud-aware, automated, and context-rich—all things that CNAPP and EDSPL’s services deliver together.
Core Components of CNAPP
Let’s break down the core capabilities of CNAPP and how EDSPL customizes them for your business:
1. Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Checks your cloud infrastructure for misconfigurations and compliance gaps.
See how EDSPL handles cloud security with automated policy enforcement and real-time visibility.
2. Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
Protects virtual machines, containers, and functions from attacks.
This includes deep integration with application security layers to scan, detect, and fix risks before deployment.
3. CIEM: Identity and Access Management
Monitors access rights and roles across multi-cloud environments.
Your network, routing, and storage environments are covered with strict permission models.
4. DevSecOps Integration
CNAPP shifts security left—early into the DevOps cycle. EDSPL’s managed services ensure security tools are embedded directly into your CI/CD pipelines.
5. Kubernetes and Container Security
Containers need runtime defense. Our approach ensures zero-day protection within compute environments and dynamic clusters.
How EDSPL Tailors CNAPP for Real-World Environments
Every organization’s tech stack is unique. That’s why EDSPL never takes a one-size-fits-all approach. We customize CNAPP for your:
Cloud provider setup
Mobility strategy
Data center switching
Backup architecture
Storage preferences
This ensures your entire digital ecosystem is secure, streamlined, and scalable.
Case Study: CNAPP in Action with EDSPL
The Challenge
A fintech company using a hybrid cloud setup faced:
Misconfigured services
Shadow admin accounts
Poor visibility across Kubernetes
EDSPL’s Solution
Integrated CNAPP with CIEM + CSPM
Hardened their routing infrastructure
Applied real-time runtime policies at the node level
✅ The Results
75% drop in vulnerabilities
Improved time to resolution by 4x
Full compliance with ISO, SOC2, and GDPR
Why EDSPL’s CNAPP Stands Out
While most providers stop at integration, EDSPL goes beyond:
🔹 End-to-End Security: From app code to switching hardware, every layer is secured. 🔹 Proactive Threat Detection: Real-time alerts and behavior analytics. 🔹 Customizable Dashboards: Unified views tailored to your team. 🔹 24x7 SOC Support: With expert incident response. 🔹 Future-Proofing: Our background vision keeps you ready for what’s next.
EDSPL’s Broader Capabilities: CNAPP and Beyond
While CNAPP is essential, your digital ecosystem needs full-stack protection. EDSPL offers:
Network security
Application security
Switching and routing solutions
Storage and backup services
Mobility and remote access optimization
Managed and maintenance services for 24x7 support
Whether you’re building apps, protecting data, or scaling globally, we help you do it securely.
Let’s Talk CNAPP
You’ve read the what, why, and how of CNAPP — now it’s time to act.
📩 Reach us for a free CNAPP consultation. 📞 Or get in touch with our cloud security specialists now.
Secure your cloud-native future with EDSPL — because prevention is always smarter than cure.
0 notes
Text
The Accidental Unlocking: 6 Most Common Causes of Data Leaks

In the ongoing battle for digital security, we often hear about "data breaches" – images of malicious hackers breaking through firewalls. But there's a more subtle, yet equally damaging, threat lurking: data leaks.
While a data breach typically implies unauthorized access by a malicious actor (think someone kicking down the door), a data leak is the accidental or unintentional exposure of sensitive information to an unauthorized environment (more like leaving the door unlocked or a window open). Both lead to compromised data, but their causes and, sometimes, their detection and prevention strategies can differ.
Understanding the root causes of data leaks is the first critical step toward building a more robust defense. Here are the 6 most common culprits:
1. Cloud Misconfigurations
The rapid adoption of cloud services (AWS, Azure, GCP, SaaS platforms) has brought immense flexibility but also a significant security challenge. Misconfigured cloud settings are a leading cause of data leaks.
How it leads to a leak: Leaving storage buckets (like Amazon S3 buckets) publicly accessible, overly permissive access control lists (ACLs), misconfigured firewalls, or default settings that expose services to the internet can inadvertently expose vast amounts of sensitive data. Developers or administrators might not fully understand the implications of certain settings.
Example: A company's customer database stored in a cloud bucket is accidentally set to "public read" access, allowing anyone on the internet to view customer names, addresses, and even financial details.
Prevention Tip: Implement robust Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools and enforce Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to ensure secure baselines and continuous monitoring for misconfigurations.
2. Human Error / Accidental Exposure
Even with the best technology, people make mistakes. Human error is consistently cited as a top factor in data leaks.
How it leads to a leak: This can range from sending an email containing sensitive customer data to the wrong recipient, uploading confidential files to a public file-sharing service, losing an unencrypted laptop or USB drive, or simply discussing sensitive information in an insecure environment.
Example: An employee emails a spreadsheet with salary information to the entire company instead of just the HR department. Or, a developer accidentally pastes internal API keys into a public forum like Stack Overflow.
Prevention Tip: Implement comprehensive, ongoing security awareness training for all employees. Enforce strong data handling policies, promote the use of secure communication channels, and ensure devices are encrypted.
3. Weak or Stolen Credentials
Compromised login credentials are a golden ticket for attackers, leading directly to data access.
How it leads to a leak: This isn't always about a direct "hack." It could be due to:
Phishing: Employees falling for phishing emails that trick them into revealing usernames and passwords.
Weak Passwords: Easily guessable passwords or reusing passwords across multiple services, making them vulnerable to "credential stuffing" attacks if one service is breached.
Lack of MFA: Even if a password is stolen, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds a critical second layer of defense. Without it, stolen credentials lead directly to access.
Example: An attacker obtains an employee's reused password from a previous data breach and uses it to log into the company's internal file sharing system, exposing sensitive documents.
Prevention Tip: Enforce strong, unique passwords, mandate MFA for all accounts (especially privileged ones), and conduct regular phishing simulations to train employees.
4. Insider Threats (Negligent or Malicious)
Sometimes, the threat comes from within. Insider threats can be accidental or intentional, but both lead to data exposure.
How it leads to a leak:
Negligent Insiders: Employees who are careless with data (e.g., leaving a workstation unlocked, storing sensitive files on personal devices, bypassing security protocols for convenience).
Malicious Insiders: Disgruntled employees or those motivated by financial gain or espionage who intentionally steal, leak, or destroy data they have legitimate access to.
Example: A disgruntled employee downloads the company's entire customer list before resigning, or an employee stores client financial data on an unsecured personal cloud drive.
Prevention Tip: Implement robust access controls (least privilege), conduct regular audits of user activity, establish strong data loss prevention (DLP) policies, and foster a positive work environment to mitigate malicious intent.
5. Software Vulnerabilities & Unpatched Systems
Software is complex, and bugs happen. When these bugs are security vulnerabilities, they can be exploited to expose data.
How it leads to a leak: Unpatched software (operating systems, applications, network devices) contains known flaws that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to systems, where they can then access and exfiltrate sensitive data. "Zero-day" vulnerabilities (unknown flaws) also pose a significant risk until they are discovered and patched.
Example: A critical vulnerability in a web server application allows an attacker to bypass authentication and access files stored on the server, leading to a leak of customer information.
Prevention Tip: Implement a rigorous patch management program, automate updates where possible, and regularly conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration tests to identify and remediate flaws before attackers can exploit them.
6. Third-Party / Supply Chain Risks
In today's interconnected business world, you're only as secure as your weakest link, which is often a third-party vendor or partner.
How it leads to a leak: Organizations share data with numerous vendors (SaaS providers, IT support, marketing agencies, payment processors). If a third-party vendor suffers a data leak due to their own vulnerabilities or misconfigurations, your data that they hold can be exposed.
Example: A marketing agency storing your customer contact list on their internal server gets breached, leading to the leak of your customer data.
Prevention Tip: Conduct thorough vendor risk assessments, ensure strong data protection clauses in contracts, and continuously monitor third-party access to your data. Consider implementing secure data sharing practices that minimize the amount of data shared.
The common thread among these causes is that many data leaks are preventable. By understanding these vulnerabilities and proactively implementing a multi-layered security strategy encompassing technology, processes, and people, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of becoming the next data leak headline.
0 notes
Text
Cloud Security Posture Management Market: Driving Factors and Future Prospects
The global market for Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is projected to reach USD 10.37 billion by 2030, experiencing a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.3% from 2025. This forecast, from a new report by Grand View Research, Inc., highlights the critical role CSPM plays in modern IT.
The primary catalyst for this growth is the widespread adoption of cloud computing. As organizations increasingly migrate their workloads and sensitive data to cloud environments, they face a heightened need for robust security and regulatory compliance. CSPM solutions address this by providing real-time security monitoring, automated checks for misconfigurations, and continuous risk assessments. This empowers businesses with enhanced visibility and control over their dynamic cloud infrastructures. The escalating frequency of cybersecurity incidents and data breaches has further intensified the demand for CSPM tools, as enterprises prioritize proactive defense of their valuable information and intellectual property.
Gather more insights into the market drivers, restraints and growth of the Cloud Security Posture Management Market
The expanding use of hybrid cloud deployments is also driving the need for specialized CSPM solutions. These tools offer a unified security view across diverse environments—public, private, and on-premises—ensuring consistent policy enforcement and compliance across the entire hybrid ecosystem. Moreover, the integration of DevOps practices into software development necessitates embedding security early in the process. Modern CSPM solutions are designed to fit seamlessly into DevOps workflows, providing developers and security teams with immediate insights into potential vulnerabilities, thereby fostering a "security-by-design" approach.
Companies within the CSPM market are strategically engaging in mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships to bolster their solution capabilities, expand their customer base, and penetrate new markets. A notable instance is the February 2022 acquisition of Fugue, Inc., a CSPM provider, by Snyk Limited, a cybersecurity firm. This move aimed to integrate Fugue's CSPM expertise into Snyk's Developer Security Platform, offering CSPM solutions specifically tailored for developers.
Cloud Security Posture Management Market Report Highlights
• The solution segment dominated the market with a revenue share of over 68.0% in 2024. The attributes of the CSPM solutions, including automated remediation capabilities and continuous monitoring, have played a significant role in protecting data, resulting in the solution segment's growth
• The SaaS segment dominated the market with a revenue share of over 40.0% in 2024. The presence of CSPM solution, which features attributes including the ability to assess the security posture of SaaS applications, and enforce best security practices, has played a significant role in the growth of the SaaS segment
• The hybrid segment is projected to be the fastest-growing segment from 2025 to 2030. The availability of CSPM solutions, which are best suited for hybrid cloud, offers conditions monitoring and analysis of resources across all environments, which has driven the growth of the hybrid segment
• The small and medium-sized enterprises segment is projected to be the fastest-growing segment from 2025 to 2030. SMEs have been working toward increasing their cybersecurity defense owing to the increasing cyber-attacks and stringent cybersecurity regulations. This trend is also seen in the CSPM market, thereby driving the growth of the SME segment over the forecast period
• The healthcare segment is expected to register the fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2030. CSPM solutions offer continuous monitoring and analysis, enabling healthcare businesses to detect misconfigurations and safeguard patient confidentiality., which has resulted in the increased adoption of CSPM solutions in the healthcare industry
• The Asia Pacific region is projected to witness the highest growth in the CSPM market with a CAGR of 12.0% from 2025 to 2030. The growth can be attributed to increasing cyberattacks, improving cybersecurity awareness, and increasing the number of businesses utilizing cloud computing services, among others
Order a free sample PDF of the Cloud Security Posture Management Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
#CSPM#CloudSecurityPostureManagement#CloudSecurity#Cybersecurity#CloudComputing#DigitalTransformation#EnterpriseSecurity#ITSecurity#InfoSec#CloudNative#MultiCloud#HybridCloud
0 notes
Text
Cloud Security Market Emerging Trends Driving Next-Gen Protection Models
The cloud security market is undergoing rapid transformation as organizations increasingly migrate their workloads to cloud environments. With the rise of hybrid and multi-cloud deployments, the demand for robust and scalable cloud security solutions is growing. Emerging trends in cloud security reflect both technological evolution and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. These trends are reshaping how enterprises secure data, manage compliance, and maintain trust in cloud-based systems.

Zero Trust Architecture Becoming a Core Principle
One of the most significant shifts in cloud security is the adoption of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA). Zero Trust eliminates the traditional notion of a trusted internal network and instead requires continuous verification of user identities and devices, regardless of their location. With cloud environments inherently distributed, ZTA is becoming essential. Enterprises are integrating identity and access management (IAM), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and micro-segmentation to strengthen their security postures.
AI and ML Enhancing Threat Detection and Response
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in cloud security tools is accelerating. These technologies are being used to detect anomalies, automate threat responses, and provide real-time risk analysis. AI-driven security platforms can process massive volumes of data from cloud logs and network activities, enabling early detection of sophisticated attacks like insider threats, ransomware, or credential stuffing. Predictive analytics is also helping security teams to anticipate potential vulnerabilities and reinforce defenses proactively.
SASE and SSE Frameworks Gaining Ground
The Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and Security Service Edge (SSE) frameworks are rapidly gaining traction. SASE combines network security functions such as secure web gateways (SWG), cloud access security brokers (CASB), and firewall-as-a-service (FWaaS) with wide-area networking (WAN) capabilities. SSE, a component of SASE, focuses on delivering security services through the cloud. These models offer centralized policy enforcement and visibility, crucial for organizations supporting remote and hybrid workforces.
Cloud-Native Security Tools on the Rise
As organizations build and deploy applications directly in the cloud, the need for cloud-native security is growing. These tools are designed to work seamlessly with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Examples include cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs), cloud security posture management (CSPM), and container security solutions. They allow for automated scanning, misconfiguration detection, and policy management in dynamic environments such as containers, microservices, and Kubernetes.
Shift-Left Security Practices Becoming Standard
In response to increasing DevOps adoption, Shift-Left security is emerging as a best practice. This trend involves integrating security earlier in the software development lifecycle (SDLC), ensuring that vulnerabilities are addressed during code development rather than post-deployment. Tools like automated code scanning, infrastructure as code (IaC) analysis, and security-focused CI/CD pipelines are empowering developers to embed security into their workflows without slowing innovation.
Increased Emphasis on Regulatory Compliance and Data Sovereignty
Regulatory requirements are evolving globally, and organizations must ensure compliance with data privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and upcoming regional cloud regulations. There is a growing trend toward data sovereignty, where governments require that data be stored and processed within specific geographic boundaries. This is pushing cloud providers to localize data centers and offer compliance-friendly security configurations tailored to regional laws.
Serverless and Edge Computing Security Gaining Focus
The expansion of serverless architectures and edge computing introduces new security challenges. These technologies reduce infrastructure management but also create ephemeral and distributed attack surfaces. Security solutions are evolving to monitor and protect functions triggered by events in real-time. Serverless security tools focus on identity-based access, runtime protection, and least privilege policies, while edge security emphasizes endpoint hardening, network segmentation, and data encryption at rest and in motion.
Third-Party and Supply Chain Risk Management
Cloud environments often rely on a vast ecosystem of third-party tools and APIs, which can introduce vulnerabilities. There is a growing focus on supply chain security, ensuring that software components and service providers adhere to strong security practices. Enterprises are increasingly conducting security assessments, continuous monitoring, and third-party audits to manage these risks effectively.
Conclusion
The cloud security market is evolving rapidly to keep pace with the complexity and scale of modern cloud infrastructure. Emerging trends such as Zero Trust, AI-driven security, SASE/SSE frameworks, and Shift-Left development practices reflect a broader movement toward adaptive, intelligent, and integrated security models. As cloud adoption accelerates, businesses must stay ahead by embracing these innovations and investing in comprehensive, forward-looking security strategies. The future of cloud security lies in being proactive, predictive, and resilient—ensuring trust, agility, and compliance in an increasingly digital world.
0 notes
Text
Top Cybersecurity Solutions to Safeguard Your Business in 2025
In today’s digital-first world, cybersecurity is no longer optional — it's a necessity. With cyberattacks growing in frequency and sophistication, businesses of all sizes must stay ahead of threats to protect their data, reputation, and bottom line. In this blog, we explore the most effective cybersecurity solutions available in 2025 and how they can fortify your digital infrastructure.
1. Next-Gen Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
Modern firewalls go far beyond traditional packet filtering. Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) combine application awareness, advanced threat detection, and intrusion prevention to block known and unknown threats in real time. Coupled with a robust IPS, these tools provide a first line of defense against malware, ransomware, and network breaches.
Key Benefits:
Deep packet inspection
Application-layer filtering
Real-time threat intelligence
2. Zero Trust Architecture
The Zero Trust model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” By enforcing strict identity verification for every person and device attempting to access your network, Zero Trust minimizes internal and external threats.
Key Components:
Identity and access management (IAM)
Microsegmentation
Continuous authentication
3. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR platforms monitor endpoints — such as laptops, servers, and mobile devices — for suspicious behavior. When anomalies are detected, EDR tools automatically contain the threat and alert security teams, reducing response time dramatically.
Why it matters:
Rapid incident response
Enhanced visibility into endpoint activity
Automated threat mitigation
4. Cloud Security Solutions
As more businesses move to the cloud, securing virtual environments is critical. Cloud security platforms offer tools like workload protection, secure access controls, encryption, and continuous monitoring to safeguard data across cloud platforms.
Popular Tools:
CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker)
CWPP (Cloud Workload Protection Platform)
CSPM (Cloud Security Posture Management)
5. Security Awareness Training
Technology alone can’t stop cyber threats. Human error remains one of the leading causes of breaches. Regular security awareness training helps employees recognize phishing attacks, practice safe online behavior, and understand their role in protecting company data.
Training Best Practices:
Interactive simulations
Ongoing refresher courses
Real-world phishing tests
6. Managed Security Services (MSS)
For many organizations, maintaining a 24/7 cybersecurity operation in-house is impractical. MSS providers offer outsourced monitoring, threat intelligence, and incident response — often with specialized expertise and cutting-edge tools.
Ideal for:
Small to mid-sized businesses
Organizations without a full-time security team
Companies needing compliance support (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR, CMMC)
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity is a dynamic, ever-evolving field. Whether you're a startup or an enterprise, investing in a layered defense strategy is crucial. By leveraging modern cybersecurity solutions and fostering a security-first culture, you can stay one step ahead of attackers and ensure business continuity.
Need help securing your organization? Contact Spearhead Technology to explore tailored cybersecurity solutions built to protect what matters most.
0 notes
Text
Ransomware Protection Market key trends shaping future business resilience strategies

Introduction
The Ransomware Protection Market is witnessing dynamic shifts as organizations globally prioritize resilience strategies to combat rising cyber threats. From AI-based detection tools to zero-trust architectures, the sector is being redefined by a range of innovative trends that are reshaping how enterprises view cybersecurity as a critical business function.
Increasing Investment in AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are no longer optional in cybersecurity — they’re strategic imperatives. Businesses are leveraging these technologies to predict, detect, and respond to ransomware attacks more efficiently. Advanced algorithms analyze behavior patterns, flag anomalies in real-time, and enable faster threat mitigation. As ransomware becomes more sophisticated, AI-driven platforms offer scalable, self-learning solutions that reduce dependence on manual oversight.
By integrating AI into endpoint protection, companies gain real-time visibility into threats before they cause disruption. These systems not only neutralize attacks in progress but also adapt to future threats, making them integral to any forward-looking cybersecurity strategy.
Zero Trust Architecture Gains Momentum
The Zero Trust model — which dictates that no user or system is inherently trusted, even within the perimeter — has gained rapid adoption. As remote work becomes permanent for many businesses, traditional firewalls are no longer sufficient. The shift toward identity-based access control and continuous verification of user activity reflects the growing demand for secure, scalable, and decentralized networks.
Companies investing in Zero Trust not only improve their security posture but also reduce recovery time following a ransomware event. Combined with network segmentation, micro-segmentation, and strict access controls, Zero Trust can significantly limit the blast radius of a potential attack.
Cloud Security: A Core Component of Resilience
Cloud adoption has surged, but it has brought with it new vulnerabilities. The ransomware protection market has responded by developing cloud-native security tools that offer advanced visibility, automated compliance monitoring, and real-time threat intelligence.
From multi-cloud management platforms to secure access service edge (SASE) architectures, cloud security is now viewed as a foundational pillar of organizational resilience. Enterprises are prioritizing cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs) and cloud security posture management (CSPM) solutions that align with modern DevOps practices and hybrid work environments.
Backup and Recovery Become Strategic Assets
Traditional backup strategies are no longer enough to withstand modern ransomware attacks, which often target backup files first. In response, businesses are turning to immutable storage, air-gapped backups, and real-time recovery solutions that ensure data can be quickly restored without negotiation.
Cyber-resilient backup systems now include features like encryption, continuous monitoring, and integration with threat detection tools. This ensures that in the event of an attack, businesses can rapidly return to operations without significant data loss or prolonged downtime.
Growing Role of Security Awareness and Training
Human error remains one of the leading causes of successful ransomware attacks. In response, organizations are investing heavily in security training programs. From phishing simulations to real-time alerts, awareness initiatives are evolving beyond check-the-box exercises.
The current trend emphasizes continuous education, where employees are empowered to recognize and report suspicious activities. Interactive learning platforms, gamification, and real-world scenarios are increasingly being used to keep training relevant and engaging.
Threat Intelligence Sharing and Collaboration
A noteworthy trend in enhancing business resilience is the growth of collaborative defense. Industry players, governments, and cybersecurity firms are forming alliances to share threat intelligence in real time. These partnerships help organizations stay ahead of evolving tactics used by ransomware gangs.
Open threat-sharing platforms and intelligence feeds enable proactive mitigation and quicker incident response. By participating in these ecosystems, companies contribute to a collective defense strategy that strengthens the market as a whole.
Regulatory Compliance as a Driver of Resilience
Regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA are increasingly enforcing stringent requirements for data protection. Compliance is no longer just about avoiding penalties—it’s a driver of security innovation.
Businesses are investing in solutions that not only meet compliance but exceed baseline requirements. As governments around the world tighten cybersecurity mandates, companies that align their protection strategies with regulatory expectations are better positioned to withstand and recover from attacks.
Strategic Roadmaps and Executive Involvement
C-suite executives are now recognizing ransomware protection as a boardroom issue. Organizations are embedding cybersecurity into their business continuity planning, ensuring alignment between IT teams and leadership. Strategic roadmaps are being developed to include ransomware-specific drills, investments in next-gen security solutions, and scenario planning.
This top-down approach empowers IT and security teams with the resources they need, while embedding a culture of resilience across departments.
Conclusion
The ransomware protection market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovation and a renewed emphasis on resilience. Key trends such as AI-powered security, zero trust frameworks, strategic backups, and regulatory alignment are shaping the way businesses defend against cyber threats. To future-proof operations, companies must view ransomware protection not just as a technical necessity but as a cornerstone of sustainable business strategy.
#cybersecurity#ransomware#AIsecurity#cloudprotection#businessresilience#zerotrust#backupstrategy#dataprotection#securitystrategy#ransomwareprotectionmarket#cyberresilience#threatintelligence#regulatorycompliance#digitaltransformation#CISOStrategy
0 notes
Text
Security Teams Are Fixing the Wrong Threats. Here’s How to Course-Correct in the Age of AI Attacks
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/security-teams-are-fixing-the-wrong-threats-heres-how-to-course-correct-in-the-age-of-ai-attacks/
Security Teams Are Fixing the Wrong Threats. Here’s How to Course-Correct in the Age of AI Attacks


Cyberattacks are no longer manual, linear operations. With AI now embedded into offensive strategies, attackers are developing polymorphic malware, automating reconnaissance, and bypassing defenses faster than many security teams can respond. This is not a future scenario, it’s happening now.
At the same time, most security defenses are still reactive. They rely on identifying known indicators of compromise, applying historical attack patterns, and flagging risks based on severity scores that may not reflect the true threat landscape. Teams are overwhelmed by volume, not insight, creating a perfect environment for attackers to succeed.
The industry’s legacy mindset built around compliance checklists, periodic assessments, and fragmented tooling has become a liability. Security teams are working harder than ever, yet often fixing the wrong things.
Why This Gap Exists
The cybersecurity industry has long leaned on risk scores like CVSS to prioritize vulnerabilities. However, CVSS scores don’t reflect the real-world context of an organization’s infrastructure such as whether a vulnerability is exposed, reachable, or exploitable within a known attack path.
As a result, security teams often spend valuable time patching non-exploitable issues, while attackers find creative ways to chain together overlooked weaknesses and bypass controls.
The situation is further complicated by the fragmented nature of the security stack. SIEMs, endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems, vulnerability management (VM) tools, and cloud security posture management (CSPM) platforms all operate independently. This siloed telemetry creates blind spots that AI-enabled attackers are increasingly adept at exploiting.
Signature-Based Detection Is Fading
One of the most concerning trends in modern cybersecurity is the diminishing value of traditional detection methods. Static signatures and rule-based alerting were effective when threats followed predictable patterns. But AI-generated attacks don’t play by those rules. They mutate code, evade detection, and adapt to controls.
Take polymorphic malware, which changes its structure with each deployment. Or AI-generated phishing emails that mimic executive communication styles with alarming accuracy. These threats can slip past signature-based tools entirely.
If security teams continue to rely on identifying what has already been seen, they’ll remain one step behind adversaries who are continuously innovating.
Regulatory Pressure Is Mounting
The problem isn’t just technical, it’s now regulatory. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) recently introduced new cybersecurity disclosure rules, requiring public companies to report material cybersecurity incidents and describe their risk management strategies in real time. Similarly, the European Union’s Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) demands a shift from periodic assessments to continuous, validated cyber risk management.
Most organizations are not prepared for this shift. They lack the ability to provide real-time assessments of whether their current security controls are effective against today’s threats, especially as AI continues to evolve those threats at machine speed.
Threat Prioritization Is Broken
The core challenge lies in how organizations prioritize work. Most still lean on static risk scoring systems to determine what gets fixed and when. These systems rarely account for the environment in which a vulnerability exists, nor whether it’s exposed, reachable, or exploitable.
This has led to security teams spending significant time and resources fixing vulnerabilities that aren’t attackable, while attackers find ways to chain together lower-scoring, overlooked issues to gain access. The traditional “find and fix” model has become an inefficient and often ineffective way to manage cyber risk.
Security must evolve from reacting to alerts toward understanding adversary behavior—how an attacker would actually move through a system, which controls they could bypass, and where the true weaknesses lie.
A Better Way Forward: Proactive, Attack-Path-Driven Defense
What if, instead of reacting to alerts, security teams could continuously simulate how real attackers would try to breach their environment, and fix only what matters most?
This approach, often called continuous security validation or attack-path simulation, is gaining momentum as a strategic shift. Rather than treating vulnerabilities in isolation, it maps how attackers could chain misconfigurations, identity weaknesses, and vulnerable assets to reach critical systems.
By simulating adversary behavior and validating controls in real time, teams can focus on exploitable risks that actually expose the business, not just the ones flagged by compliance tools.
Recommendations for CISOs and Security Leaders
Here’s what security teams should prioritize today to stay ahead of AI-generated attacks:
Implement Continuous Attack Simulations Adopt automated, AI-driven adversary emulation tools that test your controls the way real attackers would. These simulations should be ongoing not just reserved for annual red team exercises.
Prioritize Exploitability Over Severity Move beyond CVSS scores. Incorporate attack path analysis and contextual validation into your risk models. Ask: Is this vulnerability reachable? Can it be exploited today?
Unify Your Security Telemetry Consolidate data from SIEM, CSPM, EDR, and VM platforms into a centralized, correlated view. This enables attack-path analysis and improves your ability to detect complex, multi-step intrusions.
Automate Defense Validation Shift from manual detection engineering to AI-powered validation. Use machine learning to ensure your detection and response strategies evolve alongside the threats they’re meant to stop.
Modernize Cyber Risk Reporting Replace static risk dashboards with real-time exposure assessments. Align with frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK to demonstrate how your controls map to real-world threat behaviors.
Organizations that shift to continuous validation and exploitability-based prioritization can expect measurable improvements across multiple dimensions of security operations. By focusing only on actionable, high-impact threats, security teams can reduce alert fatigue and eliminate distractions caused by false positives or non-exploitable vulnerabilities. This streamlined focus enables faster, more effective responses to real attacks, significantly reducing dwell time and improving incident containment.
Moreover, this approach enhances regulatory alignment. Continuous validation satisfies growing demands from frameworks like the SEC’s cybersecurity disclosure rules and the EU’s DORA regulation, both of which require real-time visibility into cyber risk. Perhaps most importantly, this strategy ensures more efficient resource allocation and allows teams to invest their time and attention where it matters most, rather than spreading themselves thin across a vast surface of theoretical risk.
The Time to Adapt Is Now
The era of AI-driven cybercrime is no longer a prediction, it’s the present. Attackers are using AI to find new paths in. Security teams must use AI to close them.
It’s not about adding more alerts or patching faster. It’s about knowing which threats matter, validating your defenses continuously, and aligning strategy with real-world attacker behavior. Only then can defenders regain the upper hand in a world where AI is rewriting the rules of engagement.
#adversaries#ai#ai attacks#AI-powered#alerts#amp#Analysis#approach#assets#attackers#attention#Behavior#breach#Business#challenge#CISOs#Cloud#Cloud Security#Cloud security posture management#code#communication#Companies#compliance#compromise#continuous#course#CSPM#cyber#cyber risk#Cyber risk management
0 notes
Text
Top Cloud Security Challenges in 2025—and How to Solve Them
As cloud adoption accelerates in 2025, so do the complexities of securing cloud environments. From sophisticated threats to regulatory pressures and misconfigurations, organizations face a dynamic and evolving cloud security landscape. This blog explores the top cloud security challenges in 2025—and actionable strategies to overcome them.
1. Misconfigurations and Human Error
Challenge:
Despite advances in automation, cloud misconfigurations remain the leading cause of data breaches. These errors often arise from overly permissive IAM policies, unencrypted storage buckets, or default security settings left unchanged.
Solution:
Implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with security baked in.
Use automated cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools.
Regularly conduct compliance audits and red team assessments.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM) Complexity
Challenge:
As organizations adopt multi-cloud and hybrid environments, managing identity and access across platforms has become increasingly difficult. Poorly managed IAM can lead to privilege escalation and lateral movement by attackers.
Solution:
Enforce least privilege access and zero trust principles.
Use federated identity and single sign-on (SSO).
Continuously monitor access with behavioral analytics.
3. Supply Chain and Third-Party Risks
Challenge:
In 2025, supply chain attacks have become more sophisticated, targeting third-party APIs, open-source software, and CI/CD pipelines integrated into cloud workflows.
Solution:
Perform SBOM (Software Bill of Materials) assessments.
Use runtime security tools to detect anomalous behavior.
Vet vendors with strict security SLAs and continuous assessments.
4. Data Residency and Compliance
Challenge:
Global data privacy regulations (like GDPR, CCPA, and new regional laws) impose strict controls on where and how data is stored. Multi-national businesses struggle to maintain compliance across jurisdictions.
Solution:
Use geo-fencing and cloud-native encryption with customer-managed keys.
Choose cloud providers that offer region-specific data control.
Automate data classification and policy enforcement.
5. Insider Threats
Challenge:
Insider threats—whether malicious or negligent—pose significant risks to cloud environments, especially where sensitive data and critical infrastructure are involved.
Solution:
Deploy User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA).
Establish segregation of duties and audit trails.
Provide regular security awareness training.
6. API and Microservices Vulnerabilities
Challenge:
APIs and microservices are the backbone of modern cloud-native applications, but they expand the attack surface. Common issues include broken authentication, excessive data exposure, and lack of rate limiting.
Solution:
Use API gateways with integrated security policies.
Adopt OpenAPI/Swagger specifications to enforce standards.
Regularly scan APIs for OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities.
7. Ransomware and Extortionware in the Cloud
Challenge:
Ransomware is evolving to target cloud workloads, backups, and even object storage. Attackers now combine encryption with data theft to pressure victims.
Solution:
Implement immutable backups and multi-versioning.
Use behavioral threat detection for unusual file access patterns.
Employ endpoint detection and response (EDR) across cloud workloads.
8. Inadequate Visibility and Monitoring
Challenge:
Cloud environments—especially multi-cloud—often suffer from fragmented logging and monitoring, creating blind spots for security teams.
Solution:
Centralize logs using SIEM/SOAR platforms.
Deploy cloud-native monitoring tools (e.g., AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor).
Enable real-time alerting with correlation rules and ML-based anomaly detection.
Final Thoughts
Cloud security in 2025 demands a proactive, layered, and automated approach. It’s no longer about protecting the perimeter—because in the cloud, the perimeter is dynamic, ephemeral, and everywhere.
Security leaders must focus on:
Automation and continuous compliance
Identity-first security
Unified monitoring and response
Secure software development lifecycle (SSDLC)
Ready to Secure Your Cloud Future?
Partner with cloud-native security platforms, invest in team education, and make security a shared responsibility across development, operations, and governance teams.
0 notes
Text
Appit Software Cyber Security Cloud Services: Defend, Detect, Protect
In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, frequent, and damaging. Enterprises of all sizes must prioritize cybersecurity to safeguard their data, infrastructure, and reputation. Appit Software Cyber Security Cloud Services are designed to provide a robust, scalable, and proactive defense strategy that protects your organization around the clock.
With a layered security approach, real-time threat detection, and next-gen tools, we empower businesses to defend against attacks, detect anomalies swiftly, and protect critical assets with precision.
Why Choose Appit for Cloud Cybersecurity Services?
At Appit Software, we bring a comprehensive and strategic approach to cybersecurity. Our team of certified security experts leverages cloud-native tools, AI, and automation to mitigate risks before they become threats. We secure your digital transformation with enterprise-grade solutions tailored to your industry, compliance requirements, and business goals.
Key advantages of partnering with Appit:
Cloud-First, Security-Always Architecture
Proactive Threat Detection and Incident Response
AI-Driven Security Analytics
Compliance Readiness and Governance
End-to-End Managed Security Services
Comprehensive Threat Protection Across Your Cloud Ecosystem
Appit offers multi-layered protection across all major cloud platforms including AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. We ensure your workloads, applications, and data remain secure—no matter where they reside.
Our cloud security services include:
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Zero Trust Security Frameworks
Encryption and Key Management
With Appit, you gain visibility, control, and continuous monitoring of your cloud environments to stay ahead of every cyber threat.
Real-Time Threat Detection and Response
A fast response is critical to minimizing damage during a cyber incident. Appit provides Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions powered by AI and behavioral analytics.
We offer:
24/7 Security Operations Center (SOC) Monitoring
Threat Hunting and Automated Detection
Anomaly and Behavior-Based Alerting
Machine Learning for Threat Correlation
Incident Response Playbooks and Containment
Our detection engines are constantly updated to adapt to emerging threats, ensuring immediate response and rapid containment.
Next-Gen Firewall and Network Security
Networks are often the first line of defense—and the first target. Appit fortifies your network perimeter and internal traffic with advanced security controls:
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW)
Intrusion Detection & Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
Micro-Segmentation for East-West Traffic Protection
DNS Filtering and Web Gateways
VPN and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
We secure your network architecture while maintaining high performance, reducing attack surface and eliminating vulnerabilities.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) with Zero Trust
Controlling who accesses your data is just as important as defending it. Appit implements granular IAM policies and Zero Trust security to ensure users only access what they need—nothing more.
Our IAM services include:
Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Identity Federation and Lifecycle Management
Continuous Access Evaluation
With Zero Trust, every user and device must verify before accessing your environment, ensuring maximum protection against internal and external threats.
Data Protection, Backup, and Disaster Recovery
Your data is your most valuable asset—and Appit ensures it’s never compromised or lost. We provide end-to-end data security with encryption, policy enforcement, and reliable backup strategies.
Our services include:
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
At-Rest and In-Transit Encryption
Secure Data Archiving and Retention Policies
Automated Cloud Backups
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
In the event of a breach or outage, we help your organization bounce back quickly, with minimal disruption.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Navigating the regulatory landscape can be overwhelming. Appit simplifies compliance through automated tools, frameworks, and expert guidance.
We support:
GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, ISO 27001, SOC 2, NIST, and more
Risk Assessments and Gap Analysis
Audit-Ready Reporting and Evidence Collection
Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Third-Party Vendor Risk Management
Our goal is to make compliance seamless and sustainable, reducing both risk and overhead.
Security Awareness and Training Programs
Human error is one of the biggest cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Appit helps you build a security-first culture through ongoing education and simulation-based training:
Phishing Simulations
Security Awareness Workshops
Role-Based Cyber Hygiene Training
Executive Security Briefings
Incident Reporting Protocols
Empowered users become your first line of defense, reducing insider threats and unintentional breaches.
Managed Security Services (MSS) for Peace of Mind
Appit provides fully managed cybersecurity services, so your team can focus on innovation while we handle protection. Our MSS include:
24x7x365 SOC Operations
Vulnerability Scanning and Patch Management
SIEM Management and Threat Intelligence
Regular Security Audits and Reports
Strategic Advisory and Security Roadmaps
We act as an extension of your IT team, delivering continuous protection, compliance, and confidence.
Cybersecurity Solutions for Every Industry
Appit tailors cybersecurity strategies to meet the unique challenges of each industry:
Healthcare – HIPAA-compliant data security and secure EHR systems
Finance – High-frequency threat detection, AML compliance, and secure APIs
Retail & eCommerce – PCI-DSS compliance and secure transaction environments
Manufacturing – OT security and industrial system protection
Public Sector – Secure citizen data handling and FedRAMP compliance
We ensure your industry-specific risks are fully accounted for and proactively managed.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is no longer optional—it’s foundational to business success. Appit Software Cyber Security Cloud Services are designed to defend your enterprise against evolving threats, detect malicious activity in real time, and protect your assets with advanced, cloud-native tools.
0 notes
Text
Top 10 Cyber Threats Facing Businesses Today

In today’s interconnected world, agencies of all sizes face a barrage of cyber threats that develop more state-of-the-art with every passing year. From centered phishing scams to massive-scale ransomware assaults, the virtual danger landscape is evolving quicker than many groups can adapt. Here are the pinnacle 10 cyber threats going through organizations in 2025, in conjunction with how you can guard in opposition to them.
1. Phishing Attacks
These attacks typically trick employees into revealing sensitive statistics with the aid of impersonating depended on contacts or services.
Mitigation: Conduct regular schooling and phishing simulations, and enforce superior e-mail filtering.
2. Ransomware
Ransomware attacks encrypt critical facts, locking agencies out till a ransom is paid. These assaults have grown in complexity, concentrated on backup systems and spreading laterally throughout networks [4].
Mitigation: Keep offline backups, patch vulnerabilities right away, and use endpoint detection and reaction (EDR) system.
3. Insider Threats
Insider threats—whether malicious or unintended—pose a giant undertaking. Employees with get right of get right of entry to to to essential structures can by way of manner of chance or deliberately disclose statistics or compromise protection [4].
Mitigation: Implement strict get entry to controls, display customer behavior, and located into effect the precept of least privilege.
4. Malware Attacks
Malware is to be had in numerous paperwork, together with viruses, worms, trojans, and adware. It can thieve information, show hobby, or render systems inoperable. With the rise of polymorphic malware, detection is turning into more and more tough [1].
Mitigation: Use next-gen antivirus answers, sandbox suspicious documents, and preserve software software software program up to date.
5. Social Engineering
Attackers control people into giving away one of a kind facts, frequently combining techniques like pretexting, baiting, or tailgating [3].
Mitigation: Train personnel to recognize manipulative strategies and verify all requests for touchy records.
6. Cloud Vulnerabilities
With the giant adoption of cloud computing, misconfigured cloud environments have grow to be a major aim. Exposed APIs, susceptible authentication, and insufficient encryption are frequent culprits [3].
Mitigation: Use cloud protection posture manipulate (CSPM) tools and implement strong identification and access control (IAM) regulations.
7. Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
DoS and DDoS attacks flood systems with site visitors to crash offerings or make web sites inaccessible.Mitigation: Implement fee-restricting, site visitors filtering, and use DDoS protection offerings.
8. Supply Chain Attacks
Attackers increasingly target companies or 1/3-celebration software program program companies to compromise more than one groups simultaneously.Mitigation: Vet 1/three-birthday celebration providers, display software software supply chains, and observe safety updates proper now.
9. IoT Vulnerabilities
Internet of Things (IoT) devices frequently lack robust protection protocols, making them appealing get admission to points for attackers. Once compromised, the ones gadgets can function launching pads for wider community infiltration [3].
Mitigation: Isolate IoT gadgets on separate networks, disable useless talents, and exercise firmware updates.
10. AI-Driven Attacks
Cybercriminals at the moment are leveraging AI to automate assaults, recognize device weaknesses, and generate deepfake content material cloth for social engineering. This has made assaults faster, greater centered, and extra tough to trace [2].
Conclusion
The cybersecurity course in trivandrum panorama in 2025 is marked through way of complexity, pace, and the developing use of AI—every by using using attackers and defenders. Businesses need to no longer only put money into advanced safety generation however moreover foster a life-style of protection hobby. By expertise and making organized for those pinnacle 10 cyber threats, companies can considerably lessen their publicity and resilience within the face of inevitable assaults.
Cybersecurity is not absolutely an IT hassle—it's miles a essential business company priority. Stay knowledgeable, live constant.
0 notes
Text
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Key Drivers Fueling Growth in the Market

Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Market Drivers
The Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by a confluence of technological advancements, evolving cyber threats, and stringent regulatory requirements. As organizations increasingly migrate to cloud environments, ensuring robust security measures becomes paramount. CSPM solutions have emerged as critical tools in this endeavor, offering automated security assessments, compliance monitoring, and risk mitigation strategies.
1. Escalating Cybersecurity Threats
The surge in cyberattacks, including ransomware, data breaches, and insider threats, has underscored the vulnerabilities inherent in cloud infrastructures. These incidents highlight the urgent need for organizations to adopt proactive security measures. CSPM solutions provide continuous monitoring, real-time threat detection, and automated remediation, enabling organizations to swiftly address potential security gaps.
2. Complex Cloud Environments
Modern cloud architectures are increasingly complex, encompassing multi-cloud and hybrid environments. This complexity introduces challenges in maintaining consistent security policies across diverse platforms. Traditional security tools often fall short in addressing the dynamic nature of cloud infrastructures. CSPM solutions offer centralized visibility, policy enforcement, and risk assessment capabilities, ensuring that security measures are uniformly applied across all cloud assets.
3. Stringent Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) mandate organizations to implement stringent data protection and privacy measures. Non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage. CSPM solutions assist organizations in automating compliance checks, generating audit trails, and ensuring adherence to industry-specific regulations, thereby mitigating the risk of non-compliance.
4. Shortage of Skilled Cybersecurity Professionals
The cybersecurity industry faces a significant talent gap, with an estimated shortage of millions of professionals globally. This shortage hampers organizations' ability to effectively manage and secure their cloud environments. CSPM solutions address this challenge by automating routine security tasks, providing actionable insights, and reducing the dependency on specialized expertise. This enables organizations to maintain a robust security posture despite limited personnel resources.
5. Proliferation of Cloud-Native Technologies
The adoption of cloud-native technologies, such as containers and microservices, has transformed application development and deployment processes. However, these technologies introduce new security challenges, including misconfigurations and vulnerabilities. CSPM solutions are evolving to support cloud-native environments, offering features like container security, runtime protection, and integration with DevOps pipelines. This ensures that security is embedded throughout the development lifecycle, from design to deployment.
6. Increasing Adoption of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Architectures
Organizations are increasingly adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies to leverage the strengths of different cloud providers and avoid vendor lock-in. However, managing security across multiple cloud platforms presents challenges in terms of visibility and policy enforcement. CSPM solutions provide a unified approach to security management, enabling organizations to apply consistent security policies across diverse cloud environments and ensure comprehensive protection.
7. Integration with Emerging Technologies
CSPM solutions are integrating with emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Automation to enhance threat detection and response capabilities. AI and ML algorithms enable CSPM tools to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of potential security incidents, facilitating proactive threat mitigation. Automation streamlines security operations, reducing the time required to detect and remediate vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
The CSPM market is poised for significant growth as organizations recognize the imperative to secure their cloud infrastructures amidst evolving cyber threats and regulatory pressures. By providing automated security assessments, compliance monitoring, and risk mitigation strategies, CSPM solutions empower organizations to maintain a robust security posture in complex cloud environments. As the adoption of cloud technologies continues to rise, the role of CSPM solutions in safeguarding digital assets becomes increasingly critical.
0 notes
Text
Is Your Cloud Really Secure? A CISOs Guide to Cloud Security Posture Management

Introduction: When “Cloud-First” Meets “Security-Last”
The cloud revolution has completely transformed how businesses operate—but it’s also brought with it an entirely new battleground. With the speed of cloud adoption far outpacing the speed of cloud security adaptation, many Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) are left asking a critical question: Is our cloud truly secure?
It’s not a rhetorical query. As we move towards multi-cloud and hybrid environments, traditional security tools and mindsets fall short. What worked on-prem doesn’t necessarily scale—or protect—in the cloud. This is where Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) enters the picture. CSPM is no longer optional; it’s foundational.
This blog explores what CSPM is, why it matters, and how CISOs can lead with confidence in the face of complex cloud risks.
1. What Is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)?
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a framework, set of tools, and methodology designed to continuously monitor cloud environments to detect and fix security misconfigurations and compliance issues.
CSPM does three key things:
Identifies misconfigurations (like open S3 buckets or misassigned IAM roles)
Continuously assesses risk across accounts, services, and workloads
Enforces best practices for cloud governance, compliance, and security
Think of CSPM as your real-time cloud security radar—mapping the vulnerabilities before attackers do.
2. Why Traditional Security Tools Fall Short in the Cloud
CISOs often attempt to bolt on legacy security frameworks to modern cloud setups. But cloud infrastructure is dynamic. It changes fast, scales horizontally, and spans multiple regions and service providers.
Here’s why old tools don’t work:
No perimeter: The cloud blurs the traditional boundaries. There’s no “edge” to protect.
Complex configurations: Cloud security is mostly about “how” services are set up, not just “what” services are used.
Shadow IT and sprawl: Teams can spin up instances in seconds, often without central oversight.
Lack of visibility: Multi-cloud environments make it hard to see where risks lie without specialized tools.
CSPM is designed for the cloud security era—it brings visibility, automation, and continuous improvement together in one integrated approach.
3. Common Cloud Security Misconfigurations (That You Probably Have Right Now)
Even the most secure-looking cloud environments have hidden vulnerabilities. Misconfigurations are one of the top causes of cloud breaches.
Common culprits include:
Publicly exposed storage buckets
Overly permissive IAM policies
Unencrypted data at rest or in transit
Open management ports (SSH/RDP)
Lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Default credentials or forgotten access keys
Disabled logging or monitoring
CSPM continuously scans for these issues and provides prioritized alerts and auto-remediation.
4. The Role of a CISO in CSPM Strategy
CSPM isn’t just a tool—it’s a mindset shift, and CISOs must lead that cultural and operational change.
The CISO must:
Define cloud security baselines across business units
Select the right CSPM solutions aligned with the organization’s needs
Establish cross-functional workflows between security, DevOps, and compliance teams
Foster accountability and ensure every developer knows they share responsibility for security
Embed security into CI/CD pipelines (shift-left approach)
It’s not about being the gatekeeper. It’s about being the enabler—giving teams the freedom to innovate with guardrails.
5. CSPM in Action: Real-World Breaches That Could Have Been Avoided
Let’s not speak in hypotheticals. Here are a few examples where lack of proper posture management led to real consequences.
Capital One (2019): A misconfigured web application firewall allowed an attacker to access over 100 million customer accounts hosted in AWS.
Accenture (2021): Left multiple cloud storage buckets unprotected, leaking sensitive information about internal operations.
US Department of Defense (2023): An exposed Azure Blob led to the leakage of internal training documents—due to a single misconfiguration.
In all cases, a CSPM solution would’ve flagged the issue—before it became front-page news.
6. What to Look for in a CSPM Solution
With dozens of CSPM tools on the market, how do you choose the right one?
Key features to prioritize:
Multi-cloud support (AWS, Azure, GCP, OCI, etc.)
Real-time visibility and alerts
Auto-remediation capabilities
Compliance mapping (ISO, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, etc.)
Risk prioritization dashboards
Integration with services like SIEM, SOAR, and DevOps tools
Asset inventory and tagging
User behavior monitoring and anomaly detection
You don’t need a tool with bells and whistles. You need one that speaks your language—security.
7. Building a Strong Cloud Security Posture: Step-by-Step
Asset Discovery Map every service, region, and account. If you can’t see it, you can’t secure it.
Risk Baseline Evaluate current misconfigurations, exposure, and compliance gaps.
Define Policies Establish benchmarks for secure configurations, access control, and logging.
Remediation Playbooks Build automation for fixing issues without manual intervention.
Continuous Monitoring Track changes in real time. The cloud doesn’t wait, so your tools shouldn’t either.
Educate and Empower Teams Your teams working on routing, switching, and network security need to understand how their actions affect overall posture.
8. Integrating CSPM with Broader Cybersecurity Strategy
CSPM doesn’t exist in a vacuum. It’s one pillar in your overall defense architecture.
Combine it with:
SIEM for centralized log collection and threat correlation
SOAR for automated incident response
XDR to unify endpoint, application security, and network security
IAM governance to ensure least privilege access
Zero Trust to verify everything, every time
At EDSPL, we help businesses integrate these layers seamlessly through our managed and maintenance services, ensuring that posture management is part of a living, breathing cyber resilience strategy.
9. The Compliance Angle: CSPM as a Compliance Enabler
Cloud compliance is a moving target. Regulators demand proof that your cloud isn’t just configured—but configured correctly.
CSPM helps you:
Map controls to frameworks like NIST, CIS Benchmarks, SOC 2, PCI, GDPR
Generate real-time compliance reports
Maintain an audit-ready posture across systems such as compute, storage, and backup
10. Beyond Technology: The Human Side of Posture Management
Cloud security posture isn’t just about tech stacks—it’s about people and processes.
Cultural change is key. Teams must stop seeing security as “someone else’s job.”
DevSecOps must be real, not just a buzzword. Embed security in sprint planning, code review, and deployment.
Blameless retrospectives should be standard when posture gaps are found.
If your people don’t understand why posture matters, your cloud security tools won’t matter either.
11. Questions Every CISO Should Be Asking Right Now
Do we know our full cloud inventory—spanning mobility, data center switching, and compute nodes?
Are we alerted in real-time when misconfigurations happen?
Can we prove our compliance posture at any moment?
Is our cloud posture improving month-over-month?
If the answer is “no” to even one of these, CSPM needs to be on your 90-day action plan.
12. EDSPL’s Perspective: Securing the Cloud, One Posture at a Time
At EDSPL, we’ve worked with startups, mid-market leaders, and global enterprises to build bulletproof cloud environments.
Our expertise includes:
Baseline cloud audits and configuration reviews
24/7 monitoring and managed CSPM services
Custom security policy development
Remediation-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Network security, application security, and full-stack cloud protection
Our background vision is simple: empower organizations with scalable, secure, and smart digital infrastructure.
Conclusion: Posture Isn’t Optional Anymore
As a CISO, your mission is to secure the business and enable growth. Without clear visibility into your cloud environment, that mission becomes risky at best, impossible at worst.
CSPM transforms reactive defense into proactive confidence. It closes the loop between visibility, detection, and response—at cloud speed.
So, the next time someone asks, “Is our cloud secure?” — you’ll have more than a guess. You’ll have proof.
Secure Your Cloud with EDSPL Today
Call: +91-9873117177 Email: [email protected] Reach Us | Get In Touch Web: www.edspl.net
Please visit our website to know more about this blog https://edspl.net/blog/is-your-cloud-really-secure-a-ciso-s-guide-to-cloud-security-posture-management/
0 notes
Text
A Data Leak Detection Guide for the Tech Industry in 2025

For the tech industry, data is more than just information; it's the lifeblood of innovation, intellectual property, and customer trust. A data leak – the unauthorized exposure of sensitive information – can be an existential threat, far more insidious than a visible malware attack. Leaks can trickle out slowly, going unnoticed for months, or erupt in a sudden torrent, exposing source code, customer PII, design documents, or proprietary algorithms.
In 2025's hyper-connected, cloud-centric, and API-driven world, detecting these leaks is a unique and paramount challenge. The sheer volume of data, the distributed nature of development, extensive third-party integrations, and the high value of intellectual property make tech companies prime targets. Proactive, multi-layered detection is no longer optional; it's essential for survival.
Here's a comprehensive guide to detecting data leaks in the tech industry in 2025:
1. Advanced Data Loss Prevention (DLP) & Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Gone are the days of basic keyword-based DLP. In 2025, DLP needs to be intelligent, context-aware, and integrated deeply with your cloud infrastructure.
Next-Gen DLP: Deploy DLP solutions that leverage AI and machine learning to understand the context of data, not just its content. This means identifying sensitive patterns (e.g., PII, PHI, financial data), source code fragments, and intellectual property across endpoints, networks, cloud storage, and collaboration tools. It can detect unusual file transfers, unauthorized sharing, or attempts to print/download sensitive data.
Integrated CSPM: For tech companies heavily invested in cloud, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is non-negotiable. It continuously monitors your cloud configurations (AWS, Azure, GCP) for misconfigurations that could expose data – like publicly accessible S3 buckets, overly permissive IAM roles, or unencrypted databases. A misconfigured cloud asset is a leak waiting to happen.
2. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) Powered by AI
Data leaks often stem from compromised accounts or insider threats. UEBA helps you spot deviations from the norm.
Behavioral Baselines: UEBA tools use AI to learn the "normal" behavior patterns of every user (employees, contractors, customers) and entity (servers, applications) in your environment. This includes typical login times, locations, data access patterns, and resource usage.
Anomaly Detection: When behavior deviates significantly from the baseline – perhaps a developer suddenly downloading gigabytes of source code, an administrator accessing systems outside their routine hours, or a sales executive emailing large customer lists to a personal address – UEBA flags it as a high-risk anomaly, indicating a potential compromise or malicious insider activity.
Prioritized Alerts: UEBA helps cut through alert fatigue by assigning risk scores, allowing security teams to focus on the most critical threats that signify potential data exfiltration.
3. Network Traffic Analysis (NTA) with Deep Packet Inspection
Even if data bypasses endpoint or application controls, it still has to travel across the network. NTA is your eyes and ears for data exfiltration.
Real-time Monitoring: NTA (often part of Network Detection and Response - NDR) continuously monitors all network traffic – internal and external – using deep packet inspection and machine learning.
Exfiltration Signatures: It identifies suspicious patterns like unusually large outbound data transfers, communication with known command-and-control (C2) servers, attempts to tunnel data over non-standard ports, or encrypted traffic to unusual destinations.
Detecting Post-Compromise Movement: NTA is crucial for detecting lateral movement by attackers within your network and the final stages of data exfiltration, often providing the earliest warning of a breach in progress.
4. Specialized Source Code & Repository Monitoring
For the tech industry, source code is the crown jewel, and its accidental or malicious leakage can be catastrophic.
VCS Integration: Deploy solutions that deeply integrate with your Version Control Systems (Git, GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket) and internal code repositories.
Credential/Secret Detection: These tools scan commits and push requests for hardcoded credentials, API keys, private keys, and other sensitive information that could be accidentally committed and exposed.
IP Leakage Prevention: They monitor for unauthorized pushes to public repositories, large-scale cloning or downloading of proprietary code, and suspicious activity within the development pipeline, acting as a crucial line of defense against intellectual property theft.
5. Dark Web & Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) Monitoring
Sometimes, the first sign of a leak appears outside your perimeter.
Proactive Reconnaissance: Subscribe to specialized dark web monitoring services that scan illicit marketplaces, forums, paste sites (like Pastebin), and private channels for mentions of your company, leaked credentials (emails, passwords), customer data samples, or even fragments of proprietary code.
Public Repository Scans: Regularly scan public code repositories (like public GitHub, GitLab) for inadvertently exposed internal code or configuration files.
Early Warning System: These services provide crucial early warnings, allowing you to invalidate compromised credentials, assess the scope of a leak, and respond before widespread damage occurs.
6. API Security Monitoring
Modern tech stacks are heavily reliant on APIs. A compromised API can be a wide-open door for data exfiltration.
API Traffic Baselines: Establish baselines for normal API call volumes, types, and user access patterns.
Anomaly Detection: Monitor for unusual API call spikes, unauthorized access attempts (e.g., using stolen API keys), attempts to bypass authentication/authorization, or large data extractions via API calls that deviate from normal usage.
Automated Response: Integrate API security solutions with your WAFs and SIEMs to automatically block malicious API requests or revoke compromised keys.
Beyond Detection: The Response Imperative
Detecting a leak is only half the battle. A well-rehearsed incident response plan is critical. This includes clear steps for containment, investigation, eradication, recovery, and communication. Regular tabletop exercises and simulations are vital to ensure your team can act swiftly and decisively when a leak is detected.
In 2025, data leaks are an existential threat to the tech industry. By adopting a multi-faceted, AI-driven detection strategy, deeply integrated across your infrastructure and focused on both human and technical anomalies, you can significantly enhance your ability to spot and stop leaks before they spiral into full-blown crises, safeguarding your innovation and maintaining customer trust.
0 notes
Text
Breaking Barriers: Achieving Agile Cloud Governance with a Secure Cloud Foundation
As businesses rapidly scale their cloud adoption, staying ahead with agile cloud governance isn’t just a smart move—it’s essential. Organizations today need a governance strategy that ensures security, compliance, and operational efficiency without slowing down innovation. This is where a Secure Cloud Foundation becomes a game-changer. It helps businesses establish robust security controls, automate compliance, and manage risks effectively across multi-cloud environments. TransCloud takes this even further by offering multi-cloud visibility, automated compliance enforcement, and proactive security management, making it easier for organizations to confidently navigate the complexities of cloud governance. Let’s dive into the key strategies that can help businesses build a resilient cloud governance model—focusing on security, compliance, resource optimization, and operational agility.
Mitigating Security and Compliance Risks Security and compliance are non-negotiable in cloud governance. With cyber threats constantly evolving, businesses need a Cloud Security Framework that proactively protects their cloud infrastructure. A Secure Cloud Foundation plays a critical role in Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)—helping organizations continuously monitor and enhance their cloud security posture. This minimizes vulnerabilities, strengthens data protection, and ensures compliance with industry regulations. For businesses operating across multi-cloud environments, navigating regulatory requirements can be overwhelming. That’s where Cloud Risk and Compliance Management comes in. By implementing multi-cloud governance strategies and following GCP Governance Best Practices, companies can meet compliance standards effortlessly while avoiding penalties.
Boosting Operational Efficiency with Agile Cloud Governance A strong Cloud Governance Framework does more than just secure data—it also improves operational efficiency. By reducing manual workloads, automating tasks, and streamlining processes, businesses can move faster without compromising security. For industries like FinTech, where agility is crucial, an effective Cloud Security Framework ensures that security measures don’t slow down business operations. Companies leveraging GCP Security Architecture and cloud-native tools can optimize their processes and maintain agile cloud governance.
Maximizing Cloud Resource Efficiency Managing cloud resources efficiently is key to avoiding unnecessary costs and performance bottlenecks. A Secure Cloud Foundation enables businesses to: ✅ Implement cost-effective cloud governance strategies ✅ Optimize resource allocation based on real-time demand ✅ Use automation to prevent cloud resource wastage For financial services, FinOps Cloud Governance helps control spending while Multi-Cloud Governance Strategies ensure seamless resource management across platforms.
Building a Cloud Governance Framework: Key Steps A well-structured Cloud Governance Framework provides the foundation for secure, scalable, and efficient cloud operations. Here’s how businesses can set one up: 1. Assessment and Planning Evaluate the current cloud environment and define governance objectives. Identify compliance risks and security gaps. 2. Design and Implementation Develop governance policies, cloud security controls, and compliance strategies. Integrate a Cloud Security Framework that aligns with business goals. 3. Tool Integration Use Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools to monitor security risks. Implement automation for policy enforcement and cloud compliance. 4. Continuous Monitoring and Optimization Regularly assess and update cloud governance policies. Analyze security and operational performance metrics for improvements.
Implementing Effective Cloud Governance To implement agile cloud governance, organizations should focus on: 🔹 Security Integration: Embed security within governance policies for better risk management. 🔹 Compliance Alignment: Ensure adherence to cloud security regulations and compliance standards. 🔹 Scalability & Flexibility: Build a governance framework that adapts to business growth. 🔹 Training & Awareness: Educate employees on best practices for cloud compliance and security.
Conclusion: The Path to Secure and Agile Cloud Governance A Secure Cloud Foundation isn’t just about security—it’s about building a governance culture that ensures compliance, efficiency, and continuous improvement. Businesses that implement cloud governance best practices can unlock the full potential of the cloud while ensuring security and regulatory compliance. By leveraging strategies like GCP Governance Best Practices, Multi-Cloud Governance, and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), organizations can confidently scale their operations in a secure cloud environment. With TransCloud, businesses get the tools and expertise needed to streamline cloud governance, automate compliance, and mitigate security risks—ensuring a future-ready cloud infrastructure. Whether you're in FinTech or another high-compliance industry, agile cloud governance is the key to staying ahead in an evolving digital world.
0 notes
Text
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management Market: Driving Efficiency in Enterprises
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management Market Growth & Trends
The global Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management Market size was estimated at USD 1.68 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 37.1% from 2025 to 2030. The cloud infrastructure entitlement management (CIEM) market is an emerging segment within the broader cloud security industry, focused on managing, monitoring, and securing cloud-based permissions and entitlements. As organizations increasingly migrate to multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments, ensuring that access controls are properly managed becomes a top security priority. CIEM solutions help businesses enforce the principle of least privilege (PoLP), ensuring that users and applications have only the permissions they need, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized access and insider threats.
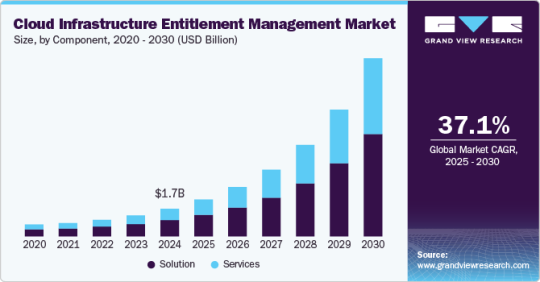
The demand for CIEM solutions is growing due to the rising complexity of cloud environments, where identity and access management (IAM) solutions alone are insufficient to handle fine-grained permissions. CIEM provides deeper visibility, automation, and remediation capabilities to address misconfigurations and excessive entitlements. With global cloud adoption accelerating, the CIEM market is experiencing strong traction across industries such as banking, healthcare, retail, IT, government, and manufacturing. Organizations today leverage multiple cloud service providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, each with different access management frameworks, creating challenges in securing and managing entitlements consistently. Traditional Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions are often insufficient to handle fine-grained permissions across these diverse platforms, leading to overprivileged identities, misconfigurations, and security risks. CIEM solutions address this complexity by providing centralized visibility, automated policy enforcement, and risk-based entitlement management across cloud infrastructures. They help organizations detect excessive permissions, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure compliance with security regulations. As cloud adoption grows, so does the need for robust entitlement governance, making CIEM a crucial component of modern cloud security architectures and a key driver of market expansion.
The market is projected to expand significantly, driven by increased awareness, regulatory requirements, and advancements in automation, AI-driven security analytics, and zero-trust frameworks. One of the key trends shaping the market is the integration of CIEM with broader cloud security platforms. Leading vendors are incorporating machine learning, behavior analytics, and real-time risk assessment into their CIEM offerings, enabling organizations to proactively detect and mitigate entitlement-related risks. The use of AI and automation will help security teams identify anomalous permissions, privilege escalations, and compliance violations more efficiently.
A major restraint in the CIEM market is enterprises' lack of awareness and understanding regarding its necessity. Many businesses continue to rely on traditional Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools, assuming they provide sufficient control over cloud permissions. However, these solutions lack granular entitlement visibility and automated least privilege enforcement, which CIEM specifically addresses. Organizations remain vulnerable to security breaches without proper knowledge of CIEM’s benefits in mitigating excessive permissions and misconfigurations. Educating enterprises on CIEM’s role in cloud security is crucial for broader adoption.
Curious about the Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management Market? Download your FREE sample copy now and get a sneak peek into the latest insights and trends.
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management Market Report Highlights
The solution segment accounted for a market share of over 58% in 2024. The adoption of zero trust architecture (ZTA) is a major driver for CIEM solutions, as organizations move away from perimeter-based security to continuous identity verification.
The large enterprises segment accounted for the largest market share in 2024. With the rise in cyber threats, insider attacks, and regulatory pressures, large enterprises are shifting from reactive to proactive cloud security strategies.
The BFSI segment accounted for the largest market share of over 20% in 2024. BFSI companies are increasingly moving to cloud environments to benefit from scalability, cost savings, and operational efficiency.
North America cloud infrastructure entitlement management market held the significant share of over 37% of the in 2024.
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global cloud infrastructure entitlement management (CIEM) market report based on component, organization size, end-use, and region:
Component Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Solution
Services
Organization Size Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs)
Large Enterprises
End-use Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
BFSI
Healthcare & Life Sciences
Retail & E-Commerce
Government & Defense
Manufacturing
IT and ITeS
Others
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
North America
U.S.
Canada
Mexico
Europe
Germany
UK
France
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
South Korea
Australia
Latin America
Brazil
Middle East & Africa
U.A.E
Saudi Arabia
South Africa
Download your FREE sample PDF copy of the Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management Market today and explore key data and trends.
0 notes