#crystal palace dinosaurs
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Crystal Palace Field Trip Part 2: Walking With Victorian Dinosaurs
[Previously: the Permian and the Triassic]
The next part of the Crystal Palace Dinosaur trail depicts the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Most of the featured animals here are actually marine reptiles, but a few dinosaur species do make an appearance towards the end of this section.

Although there are supposed to be three Jurassic ichthyosaur statues here, only the big Temnodontosaurus platyodon could really be seen at the time of my visit. The two smaller Ichthyosaurus communis and Leptonectes tenuirostris were almost entirely hidden by the dense plant growth on the island.

Ichthyosaurs when fully visible vs currently obscured Left side image by Nick Richards (CC BY SA 2.0)

Head, flipper, and tail details of the Temnodontosaurus. A second ichthyosaur is just barely visible in the background.
Ichthyosaurs were already known from some very complete and well-preserved fossils in the 1850s, so a lot of the anatomy here still holds up fairly well even 170 years later. They even have an attempt at a tail fin despite no impressions of such a structure having been discovered yet! Some details are still noticeably wrong compared to modern knowledge, though, such as the unusual amount of shrinkwrapping on the sclerotic rings of the eyes and the bones of the flippers.

———

Arranged around the ichthyosaur, three different Jurassic plesiosaurs are also represented – “Plesiosaurus” macrocephalus with the especially sinuous neck on the left, Plesiosaurus dolichodeirus in the middle, and Thalassiodracon hawkinsi on the right.
They're all depicted here as amphibious and rather seal-like, hauling out onto the shore in the same manner as the ichthyosaurs. While good efforts for the time, we now know these animals were actually fully aquatic, that they had a lot more soft tissue bulking out their bodies, and that their necks were much less flexible.

———

The recently-installed new pivot bridge is also visible here behind some of the marine reptiles.
———

Positioned to the left of the other marine reptiles, this partly-obscured pair of croc-like animals are teleosaurs (Teleosaurus cadomensis), a group of Jurassic semi-aquatic marine crocodylomorphs.

A better view of the two teleosaurs by MrsEllacott (CC BY-SA 4.0)
The Crystal Palace statues have the general proportions right, with long thin gharial-like snouts and fairly small limbs. But some things like the shape of the back of the head and the pattern of armored scutes are wrong, which is odd considering that those details were already well-known in the 1850s.

———
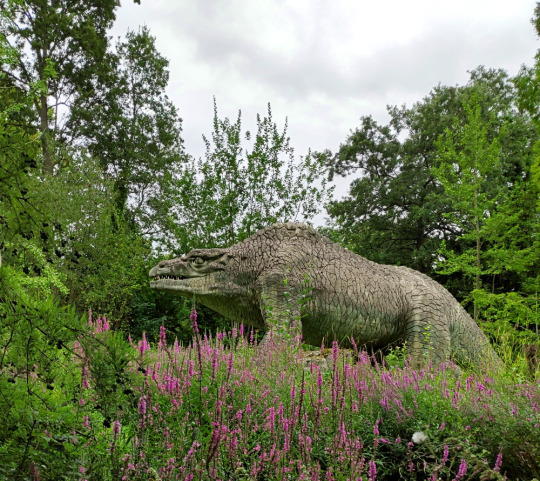

Finally we reach the first actual dinosaur, and one of the most iconic statues in the park: the Jurassic Megalosaurus!
Megalosaurus bucklandi was the very first non-avian dinosaur known to science, discovered in the 1820s almost twenty years before the term "dinosaur" was even coined.
At a time when only fragments of the full skeleton were known, and before any evidence of bipedalism had been found, the Crystal Palace rendition of Megalosaurus is a bulky quadrupedal reptile with a humped back and upright bear-like limbs. It's a surprisingly progressive interpretation for the period, giving the impression of an active mammal-like predator.
This statue suffered extensive damage to its snout in 2020, which was repaired a year later with a fiberglass "prosthesis".
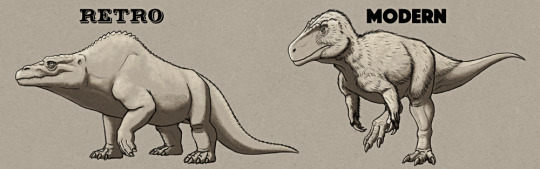
———
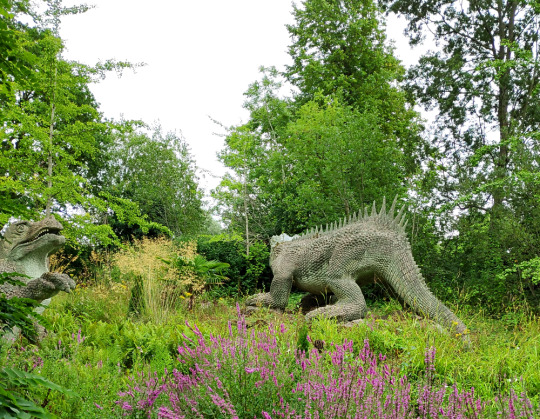

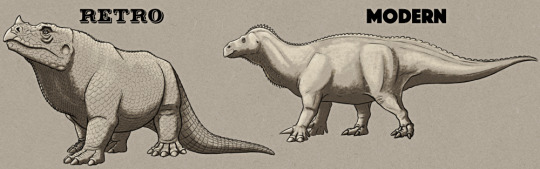
Reaching the Cretaceous period now, we find Hylaeosaurus (and one of the upcoming Iguanodon peeking in from the side).
Hylaeosaurus armatus was the first known ankylosaur, although much like the other dinosaurs here its life appearance was very poorly understood in the early days of paleontology. Considering how weird ankylosaurs would later turn out to be, the Crystal Palace depiction is a pretty good guess, showing a large heavy iguana-like quadruped with hoof-like claws and armored spiky scaly skin.
It's positioned facing away from viewers, so its face isn't very visible – but due to the head needing to be replaced with a fiberglass replica some years ago, the original can now be seen (and touched!) up close near the start of the trail.


———

Two pterosaurs (or "pterodactyles" according to the park signs) were also supposed to be just beyond the Hylaeosaurus, but plant growth had completely blocked any view of them.
Although these two statues are supposed to represent a Cretaceous species now known as Cimoliopterus cuvieri, they were probably actually modeled based on the much better known Jurassic-aged Pterodactylus antiquus.
A second set of pterosaur sculptures once stood near the teleosaurs, also based on Pterodactylus but supposed to represent a Jurassic species now known as Dolicorhamphus bucklandii. These statues went missing in the 1930s, and were eventually replaced with new fiberglass replicas in the early 2000s… only to be destroyed by vandalism just a few years later.
(The surviving pair near the Hylaeosaurus are apparently in a bit of disrepair these days, too, with the right one currently missing most of its jaws.)
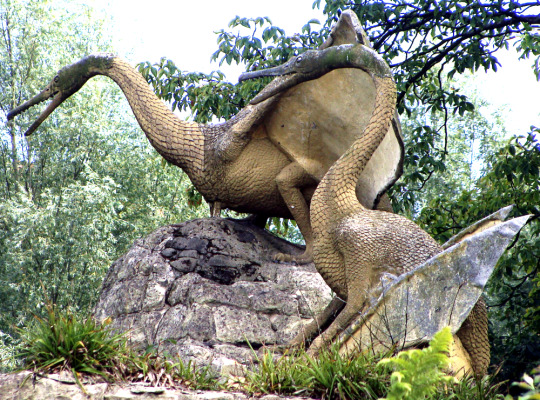

Image by Ben Sutherland (CC BY 2.0)
The Crystal Palace pterosaurs weren't especially accurate even for the time, with heads much too small, swan-like necks, and bird-like wings that don't attach the membranes to the hindlimbs. Hair-like fuzz had been observed in pterosaur fossils in the 1830s, but these depictions are covered in large overlapping diamond-shaped scales due to Richard Owen's opinion that they should be scaly because they were reptiles.
But some details still hold up – the individual with folded wings is in a quadrupedal pose quite similar to modern interpretations, and the bird-like features give an overall impression of something more active and alert than the later barely-able-to-fly sluggish reptilian pterosaur depictions that would become common by the mid-20th century.

(Much like the statues themselves, the "modern" reconstruction above is based on Pterodactylus rather than Cimoliopterus)
———
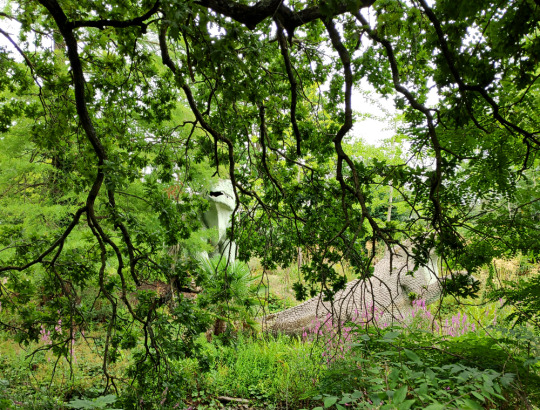

The last actual dinosaurs on this dinosaur trail are the two Cretaceous Iguanodon sculptures. At the time of my visit they weren't easy to make out behind the overgrown trees, and only the back end of the standing individual was clearly visible.

Named only a year after Megalosaurus, Iguanodon was the second dinosaur ever discovered, and early reconstructions depicted it as a giant iguana-like lizard.
The Crystal Palace statues depict large bulky animals, one in an upright mammal-like stance and another reclining with one hand raised up. (This hand is usually resting on a cycad trunk, but that element appeared to be either missing or fallen over when I was there.)
Famously a New Year's dinner party was held in the body of the standing Iguanodon during its construction, although the accounts of how many people could actually fit inside it at once are probably slightly exaggerated.
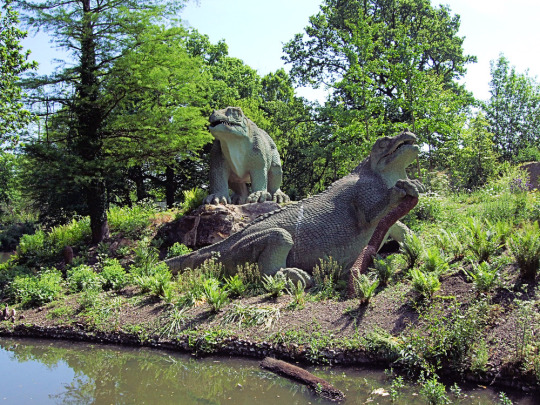

A clearer view by Jim Linwood (CC BY 2.0)
Considering that the skull of Iguanodon wasn't actually known at the time of these sculpture's creation, the head shape with a beak at the front of the jaws is actually an excellent guess. The only major issue was the nose horn, which was an understandable mistake when something as strange as a giant thumb spike had never been seen in any known animal before.
(The fossils the Crystal Palace statues are based on are actually now classified as Mantellisaurus atherfieldensis, but the "modern" reconstruction above depicts the chunkier Iguanodon bernissartensis.)
———
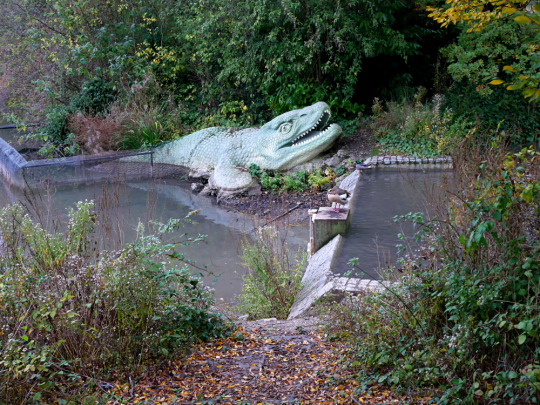

Image by Doyle of London (CC BY-SA 4.0)
I also wasn't able to spot the Cretaceous mosasaur on the other side of the island due to heavy foliage obscuring the view.
Depicting Mosasaurus hoffmannii, this model consists of only the front half of the animal lurking at the water's edge. It's unclear whether this partial reconstruction is due to uncertainty about the full appearance, or just a result of money and time running out during its creation.
The head is boxier than modern depictions, and the scales are too large, but the monitor-lizard like features and paddle-shaped flippers are still pretty close to our current understanding of these marine reptiles. It even apparently has the correct palatal teeth!

Next time: the final Cenozoic section!
#field trip!#crystal palace dinosaurs#retrosaurs#i love them your honor#crystal palace park#crystal palace#ichthyosaur#plesiosaur#teleosaurus#crocodylomorpha#marine reptile#megalosaurus#theropod#hylaeosaurus#ankylosaur#iguanodon#ornithopoda#ornithischia#dinosaur#pterodactyle#pterodactylus#pterosaur#mosasaurus#mosasaur#paleontology#vintage paleoart#art
473 notes
·
View notes
Text





Victorian Dinosaurs
Top to Bottom: Megalosaurus, Iguanodon, Ichthyosaurus, labyrinthodon, stegosaurus.
I tried to go back in time, but my angle was a little off.
Process under the fold.
For these, my process was pretty straightforward.
Using overpainting with Midjourney's edit feature, I took pics of the crystal palace dinosaurs and converted them into more realistic representations that maintain the weird body shapes and anatomy.









I also made appropriate backgrounds with a combination of image and text prompting.
I then took those base elements, and used Vidu's 2.0 Reference-to-Video feature to combine a creature and the background, and then prompted with something akin to:
nature documentary footage, a large reptilian creature in a steamy prehistoric jungle, the creature walks slowly, looking around as though on alert. It has a stubby tail, and moves in a salamander-like fashion. footage from national geographic, animal planet, filmed on 35mm film, 5k
#ai art#ai video#vidu 2.0#vidu ai#midjourney#retrosaurs#crystal palace dinosaurs#victorian dinosaurs#dinosaurs#paleoart#inaccurate paleoart#megalosaurus#iguanodon#icthyosaurus#labyrinthodon#stegosaurus#crystal palace
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
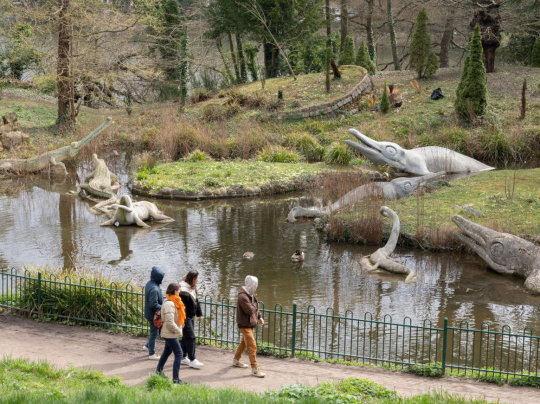

[ Visitors pass by some of the iconic sculptures of prehistoric life within Crystal Palace Park. Photo by Richard Baker. ]
"When the Crystal Palace and Park opened in south London in 1854, it was an instant sensation. Visitors came from far and wide to see the giant glass structure that had been rebuilt there, bigger and better, after the Great Exhibition of 1851 in Hyde Park. Wide-eyed spectators wandered freely through Egyptian and Medieval Courts, delighted in high-wire circus acts, and were transported by a 4,000-piece orchestra. Tucked away in a corner of the vast gardens that fanned out from the palace, past sweeping terraces and more fountains than even at Versailles, was a smaller but no less ambitious attraction. Scattered across several islands in the middle of a lake stood three dozen life-size sculptures of prehistoric animals, including several dinosaurs up to 30 feet long—the world’s first attempt to model them at full scale. The Crystal Palace Dinosaurs were the work of Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins, a natural history artist who, aided by some of the leading scientists of the day, had dreamt up a grand experiment in visual education, bringing to life the “dry bones or oddly shaped stones” found in the British Museum and introducing the masses to the burgeoning science of paleontology. By reconstructing Britain’s long-extinct animals, he hoped to “render the appearance and names of the ancient inhabitants of our globe as familiar as household words.” The palace burned down in the 1930s, but, almost 170 years after they were crafted, most of Hawkins’ original sculptures still stand sentry in the park. Today, they’re mostly famous for being wildly inaccurate. With few complete fossils to work off, Hawkins had to use his imagination and the advice of comparative anatomists to breathe life into his models, which, in addition to four true dinosaurs, also depict prehistoric mammals, reptiles and amphibians. As a result, the sculptures look suspiciously like many modern-day creatures. “People kind of scoff and giggle, because they look so wrong today, but at the time they were really cutting-edge,” says Bob Nicholls, a paleoartist who, through careful study of archival images, recently reconstructed a lost sculpture that had disappeared from the park sometime in the 1960s. His tapir-like model of Palaeotherium magnum, an animal we now know looked a lot more like a horse, was unveiled in July and now stands among Hawkins’ own surviving creations."
Read more: "How a Victorian Dinosaur Park Became a Time Capsule of Early Paleontology" by Yannic Rack.
#palaeoblr#Crystal Palace#Crystal Palace Dinosaurs#Dinosaurs#Article#Information#London#England#Photo#Sculptures
271 notes
·
View notes
Text

Plesiosaurus head study by Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins, mid 1800s
52 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Crystal Palace dinosaurs by unknown artist, August 12th, 1854 courtesy Mark Witton (on private Facebook group)
https://anno.onb.ac.at/cgi-content/anno?aid=izl&datum=18540812&seite=5&zoom=33&query=%22Waterhouse%2BHawkins%22~3&ref=anno-search&fbclid=IwAR1R85YRQbPn7nPmIRMoNhjPfI30ww9vKyhnf4a_usM7hQqQ5ozdOFfwKT0
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

"Illuminations by C. T. Brock and Co, Sutton, Surrey, England."
Advertising postcard for Brock’s Crystal Palace Fireworks and Illuminations, postmarked 1906. Advertising Fireworks for Fifth of November.
#crystal palace dinosaurs#dinosaurs#c t brock and co#bonfire night#5th of november#fireworks#postcard
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo









I had a couple of days in London after flying back from Amman before our train back up to Edinburgh, so I took a little trip out to Crystal Palace for a look at the famous dinosaur sculptures, which I’ve wanted to see since they were featured in a kid’s dinosaur magazine my sister had when we were little. They’re pretty bad! But I don’t suppose it’s really fair to criticise the sculptor for working with the information available in the 1850s.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why is she built like a statue

American Crocodile (Crocodylus acutus), family Crocodylidae, Tarcoles River, Costa Rica
photograph by by Mark Kostich
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Historic England tries to future-proof dinos with 3D models
Monster lake: ‘dinosaur island’ in Crystal Palace Park has fascinated visitors for 170 years Twenty-nine interactive 3D models of the surviving Crystal Palace Victorian dinosaur sculptures have been created by Historic England, in collaboration with the Friends of Crystal Palace Dinosaurs. Model creature: the Mosasaurus emerges from the waters, as captured in 3D by English Heritage. This…

View On WordPress
#Bromley Council#Crystal Palace#Crystal Palace and Upper Norwood#Crystal Palace dinosaurs#Crystal Palace Park#Crystal Palace Park Trust#Historic England#Val Shawcross
0 notes
Text
Crystal Palace Field Trip Part 1: Walking With Victorian Monsters

The Crystal Palace Dinosaurs take their name from the original Crystal Palace, a glass-paned exhibition building originally constructed for a World's Fair in Hyde Park in 1851.
In 1854 the structure was relocated 14km (~9 miles) south to the newly-created Crystal Palace Park, and a collection of over 30 life-sized statues of prehistoric animals were commissioned to accompany the reopening – creating a sort of Victorian dinosaur theme park – sculpted by Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins with consultation from paleontologist Sir Richard Owen.
The Palace building itself burned down completely in 1936, and today only the ruins of its terraces remain in the northeast of the park grounds.

The Crystal Palace building then and now Left image circa 1854 (public domain) Right image circa 2011 by Mark Ahsmann (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Six sphinx statues based on the Great Sphinx of Tanis also survive up among the Palace ruins, flanking some of the terrace staircases. They fell into serious disrepair during the latter half of the 20th century, but in 2017 they all finally got some much-needed preservation work, repairing them and restoring their original Victorian red paint jobs.

———
…But let's get to what we're really here for. Dinosaurs! (…And assorted other prehistoric beasties!)
The "Dinosaur Court" down in the south end of the park still remains to this day, displayed across several islands in a man-made lake. Over the decades they've been through multiple cycles of neglect and renovation, and are currently cared for by the London Borough of Bromley (Crystal Palace Park Trust are due to take over custodial duties in September 2023), with promotion and fundraising assistance from organizations like Historic England and the Friends of the Crystal Palace Dinosaurs charity.
Just about 170 years old now, the Crystal Palace Dinosaurs represent fifteen different types of fossil creatures known to 1850s Victorian science, with only three actual dinosaur species featured. Although often derided for being outdated and very inaccurate by modern standards, they were actually incredibly good efforts at the time, especially taking into account that the field of paleontology was still in its very early days.
They also just have a lot of charm, with toothy grins and surprisingly dynamic poses.
Unfortunately on the day I visited in early August 2023 most of the statues were heavily obscured by plant growth, both on their islands and on the sides of the paths they can usually be viewed from. Since I'd seen images from about a month ago showing things being less overgrown, this was probably just some unlucky timing on my part coinciding with some explosive summer foliage growth.

The first island on the trail features a few Permian and Triassic animals which were only known from fragmentary remains in the 1850s. These "labyrinthodonts" were recognized as having similarities to both amphibians and reptiles, and so were depicted with boxy toothy jaws, warty skin, stumpy tails, and long frog-like back legs.

Today we'd call these particular animals temnospondyl amphibians, specifically Mastodonsaurus, and we know they were actually shaped more like giant salamanders with longer flatter crocodilian-like jaws, smaller legs, and long paddle-like tails.

———

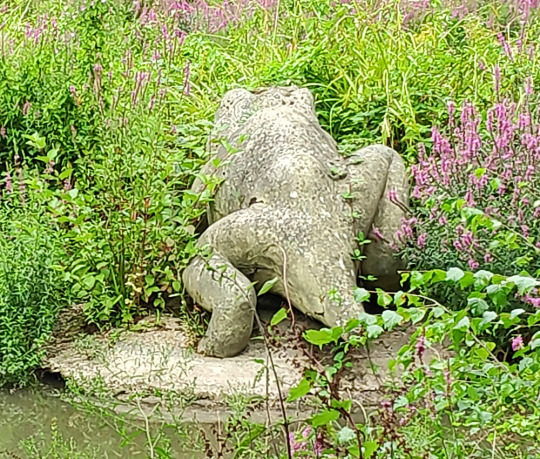
Somewhere in the foliage beyond this specific "labyrinthodont" there was also supposed to be a pair of dicynodonts, but I couldn't see much of them at all and didn't manage to get a remotely visible photograph.

Crystal Palace Dicynodon when much less overgrown Left photo by London looks (CC BY 2.0) Right photo by Loz Pycock (CC BY SA 2.0)
These Dicynodon are depicted as looking like sabre-toothed turtles complete with shells. That was fairly speculative even for the time, but considering only their weird turtle-beaked-and-walrus-tusked skulls were known it was probably the best guess Hawkins and Owen had. Today we know these animals were actually synapsids related to modern mammals, but Victorian understanding considered them to be a type of reptile.
Modern reconstructions of dicynodonts have a slightly different face shape, along with squat pig-like bodies and semi-sprawling limbs. They may have had fur, but currently the only known actual skin impressions from the genus Lystrosaurus show leathery bumpy hairless skin.

———
Next time: the Jurassic and Cretaceous sculptures!
#field trip!#crystal palace dinosaurs#retrosaurs#i love them your honor#crystal palace park#crystal palace#labyrinthodont#temnospondyl#mastodonsaurus#dicynodont#dicynodon#synapsid#paleontology#vintage paleoart#art
387 notes
·
View notes
Text





Everything Nice pages 24-28
Pages 1-14
Pages 15-23
Crystal: "Why? What happened with the original ghost flavors"
Edwin: "Ah. It was very experimental. We were transported and subsequently trapped in the Cretaceous Period for approximately 6 months "
Charles: "Also it tasted rank"
#dead boy detectives#dbda#dbda: everything nice#the comic#edwin payne#charles rowland#dbda fanart#crystal palace#save dead boy detectives#Charles would fight another dinosaur for pizza
515 notes
·
View notes
Text
This video was so beautiful to watch <3
youtube
NEW VIDEO! (A very especial one)
Antediluvian is a short animated film that got me occupied for almost two years. It's a commemorative homage to Classic Paleoart and the earliest Paleontologists. Exactly 200 years ago was the first dinosaur formally described . I hope you enjoy it! In general Youtube tends to dismiss videos that are different tha the usual, so your support is highly appreciated :) Thank you all!
__
Youtube channel
Instagram
Prints and more paleomerch
643 notes
·
View notes
Text

"Models of extinct animals in the Crystal Palace Gardens" from The Traveller's Album and Hotel Guide: containing views of places and buildings of historical and general interest, with descriptive letterpress; an account of the principal railways out of London, etc., 1862
#crystal palace#crystal palace dinosaurs#benjamin waterhouse hawkins#iguanodon#hylaeosaurus#megalosaurus#pterodactylus#teleosaurus#labyrinthodon#dicynodon#plesiosaurus#ichthyosaurus#1862
21 notes
·
View notes
Note
Can I get an itty bitty iguanodon that was made in the 1800s

Iguanodon, 1853
42 notes
·
View notes
Text

Megalosaurus (1854) & Megalosaurus (2025), Watercolour pencils
A new year is a good time for reflection on who we were and who we want to be. Be kind to your past self though, they were also doing the best they could back then 😉
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
From 'The fairy tales of science' (1857) by John Cargill Brough
Illustrated by Charles Henry Bennett

The Age of Monsters
113 notes
·
View notes