#coronavirus community transmission
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
fauci saying “vulnerable people will fall by the wayside” and that some will die but that’s ok because we’re not going to see the “tsunami of cases” we’ve seen before is so dehumanising. so babies with no immune system, elderly people, disabled people, and people without adequate access to healthcare can all die of covid. but it’s ok guys because actually they’re just falling to the wayside and everyone else will go back to normal and be fine (sarcasm).
my death or the deaths of my family or friends wouldn’t be us “falling by the wayside”, it would be us being failed by our government, healthcare systems, and communities who have refused to take coronavirus seriously despite mounting anecdotal and scientific evidence of the harm this virus does. fact that people can accept the deaths of vulnerable groups just because they want to eat in a restaurant or don’t want to wear a mask is horrifying
#yall can reblog this#for those of you touting community care or progressive values or allyship to marginalised communities#i better see y’all masking#it goes without saying that if you can’t mask then my saying mask up does not apply to you#but for the people who can mask please do so to protect yourself and others#masking up also protects people who aren’t able to mask#I’m just so tired of being told that death to a virus that is preventable via masking and air filtration and proper testing availability to#prevent spread by allowing people to stop their chain of transmission#is just. fine. like all these people will die and apparently that’s fine and actually a great thing#also. with one or two covid infections formerly healthy people enter vulnerable groups. because the studies coming out right now and#what we know about long term sars1 effects (because covid is not a cold or flu. it’s sars2. it’s severe accuse respiratory syndrome)#are showing that the long term effects on the bodies of people who have had covid will be disasterous#and if covid had been properly felt with then maybe only some people would be facing that reality. but the amount of people who have been#infected not just once but multiple times. with some people having close to double digit numbers of infections. means that the amount of#people looking at sars2 long term symptoms could be quite a large group#coronavirus#my post
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
Masks and respirators for prevention of respiratory infections: a state of the science review | Clinical Microbiology Reviews
Our synthesis of evidence from over 100 published reviews and selected primary studies, including re-analyzing contested meta-analyses of key clinical trials, produced seven key findings.
First, there is strong and consistent evidence for airborne transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and other respiratory pathogens.
Second, masks are, if correctly and consistently worn, effective in reducing transmission of respiratory diseases and show a dose-response effect.
Third, respirators are significantly more effective than medical or cloth masks.
Fourth, mask mandates are, overall, effective in reducing community transmission of respiratory pathogens.
Fifth, masks are important sociocultural symbols; non-adherence to masking is sometimes linked to political and ideological beliefs and to widely circulated mis- or disinformation.
Sixth, while there is much evidence that masks are not generally harmful to the general population, masking may be relatively contraindicated in individuals with certain medical conditions, who may require exemption. Furthermore, certain groups (notably D/deaf people) are disadvantaged when others are masked.
Finally, there are risks to the environment from single-use masks and respirators.
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
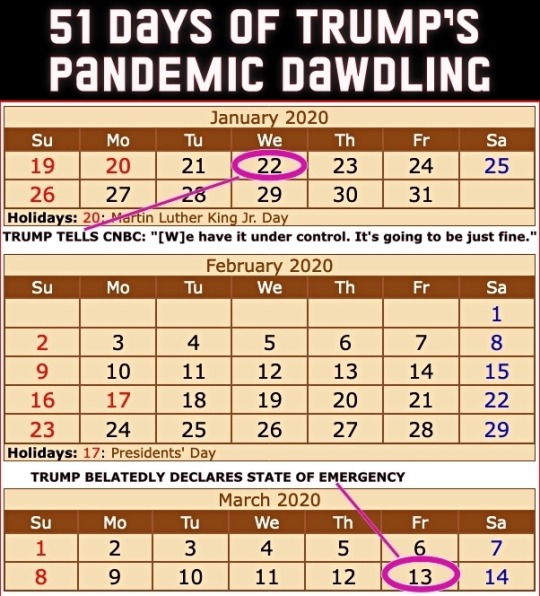
Four years ago today (March 13th), then President Donald Trump got around to declaring a national state of emergency for the COVID-19 pandemic. The administration had been downplaying the danger to the United States for 51 days since the first US infection was confirmed on January 22nd.
From an ABC News article dated 25 February 2020...
CDC warns Americans of 'significant disruption' from coronavirus
Until now, health officials said they'd hoped to prevent community spread in the United States. But following community transmissions in Italy, Iran and South Korea, health officials believe the virus may not be able to be contained at the border and that Americans should prepare for a "significant disruption." This comes in contrast to statements from the Trump administration. Acting Department of Homeland Security Secretary Chad Wolf said Tuesday the threat to the United States from coronavirus "remains low," despite the White House seeking $1.25 billion in emergency funding to combat the virus. Larry Kudlow, director of the National Economic Council, told CNBC’s Kelly Evans on “The Exchange” Tuesday evening, "We have contained the virus very well here in the U.S." [ ... ] House Speaker Nancy Pelosi called the request "long overdue and completely inadequate to the scale of this emergency." She also accused President Trump of leaving "critical positions in charge of managing pandemics at the National Security Council and the Department of Homeland Security vacant." "The president's most recent budget called for slashing funding for the Centers for Disease Control, which is on the front lines of this emergency. And now, he is compounding our vulnerabilities by seeking to ransack funds still needed to keep Ebola in check," Pelosi said in a statement Tuesday morning. "Our state and local governments need serious funding to be ready to respond effectively to any outbreak in the United States. The president should not be raiding money that Congress has appropriated for other life-or-death public health priorities." She added that lawmakers in the House of Representatives "will swiftly advance a strong, strategic funding package that fully addresses the scale and seriousness of this public health crisis." Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer also called the Trump administration's request "too little too late." "That President Trump is trying to steal funds dedicated to fight Ebola -- which is still considered an epidemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo -- is indicative of his towering incompetence and further proof that he and his administration aren't taking the coronavirus crisis as seriously as they need to be," Schumer said in a statement.
A reminder that Trump had been leaving many positions vacant – part of a Republican strategy to undermine the federal government.
Here's a picture from that ABC piece from a nearly empty restaurant in San Francisco's Chinatown. The screen displays a Trump tweet still downplaying COVID-19 with him seeming more concerned about the effect of the Dow Jones on his re-election bid.

People were not buying Trump's claims but they were buying PPE.
I took this picture at CVS on February 26th that year.

The stock market which Trump in his February tweet claimed looked "very good" was tanking on March 12th – the day before his state of emergency declaration.
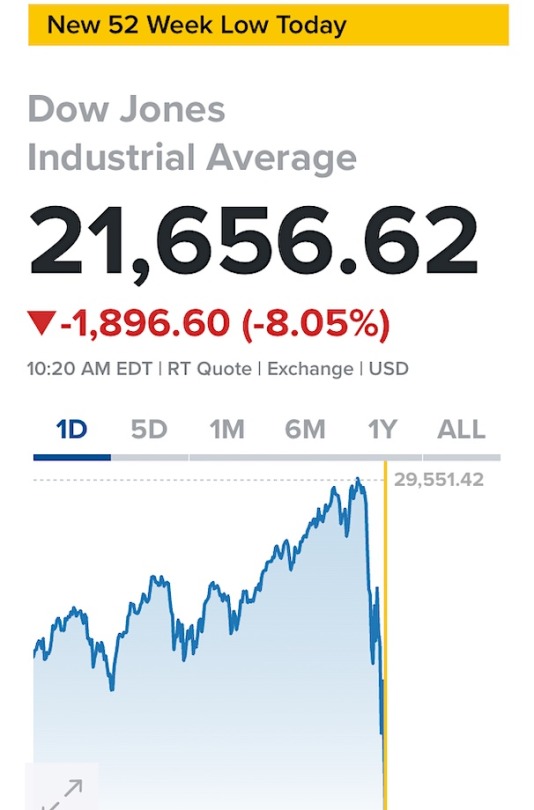
Trump succeeded in sending the US economy into recession much faster than George W. Bush did at the end of his term – quite a feat!. (As an aside, every recession in the US since 1981 has been triggered by Republican presidents.)
Of course Trump never stopped trying to downplay the pandemic nor did he ever take responsibility for it. The US ended up with the highest per capita death rate of any technologically advanced country.
Precious time was lost while Trump dawdled. Orange on this map indicates COVID infections while red indicates COVID deaths. At the time Trump declared a state of emergency, the virus had already spread to 49 states.

The United States could have done far better and it certainly had the tools to do so.
The Obama administration had limited the number of US cases of Ebola to under one dozen during that pandemic in the 2010s. Based on their success, they compiled a guide on how the federal government could limit future pandemics.
Obama team left pandemic playbook for Trump administration, officials confirm
Of course Trump ignored it.
Unlike those boxes of nuclear secrets in Trump's bathroom, the Obama pandemic limitation document is not classified. Anybody can read it – even if Trump didn't. This copy comes from the Stanford University Libraries.
TOWARDS EPIDEMIC PREDICTION: FEDERAL EFFORTS AND OPPORTUNITIES IN OUTBREAK MODELING
Feel free to share this post with anybody who still feels nostalgic about the Trump White House years!
#covid-19#coronavirus#pandemic#public health#donald trump#trump's incompetent response to the pandemic#covid state of emergency#2020#trump recession#51 days of trump pandemic dawdling#obama pandemic playbook#2010s ebola outbreak#nostalgia for trump administration#republicans#election 2024#vote blue no matter who
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
The answer is "by the skin of their teeth," but this article is too polite to say it.
By Joshua Boscaini
COVID-19 is evolving and with it the need for new vaccines to protect people against serious illness and death.
Australia has detected its first cases of the highly transmissible XEC "recombinant" variant — a mix of two previous Omicron variants called KS 1.1 and KP 3.3.
Researchers have been working to ensure immunisations that provide an adequate level of protection against new COVID-19 variants are widely available to the community.
So if there are always new variants, how do scientists keep up with mutations and update the vaccines?
How are mRNA COVID-19 vaccines made? When reports of coronavirus first emerged, researchers quickly obtained a genomic sequence of SARS-CoV-2 — the virus that causes COVID-19.
This helped researchers work out the genetic make-up of the virus and how it causes disease in people, according to the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI).

Once scientists analysed the genetic sequence, they identified the spike protein as the most effective target for the immune system and created a copy or code for it.
Unlike traditional vaccines that contain an inactivated or weakened version of the virus, mRNA COVID-19 vaccines contain a message or code that is delivered to someone's cells.
Doherty Institute professor of virology Damian Purcell said that spike protein code — or RNA message — was "packaged" into lipids to keep it protected for distribution in syringes.
Professor Purcell said once the mRNA vaccine — or message — was injected into a person's muscle, it instructed their cells to reproduce the spike protein.
"These are little bubbles of fat, four different lipids, that together encase the RNA [and] enable it to be protected as it is packaged into syringes and injected into your muscle," Professor Purcell said.
"Those lipids facilitate the uptake and delivery of the essential messenger RNA — the message to be coded within your own cells so your own cells start making the … spike protein."
The process triggers an immune response which creates spike protein antibodies.
The NHGRI said those antibodies remained in the body and recognised the virus if someone became infected, attacking the antigen before it reached healthy cells.
How are vaccines modified to keep up with new strains? Westmead Institute for Medical Research Centre for Virus Research director Tony Cunningham said new strains emerged when the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein changed, making the virus more transmissible.
Professor Cunningham said the mRNA vaccines allowed scientists to change the spike protein code and update the vaccine with the new message.
"If you actually think about RNA like DNA is coloured beads on a string — four coloured beads and they vary along the string — then it's in essence changing that sequence," he said.
"You can just simply change the middle bit of the RNA and that can be done very quickly.
"That spike protein is the one that actually allows the virus to attach to the cell and what we want to do is produce antibodies that stop viruses attaching to the cell."
Professor Purcell agreed, saying one of the advantages of mRNA vaccines was they could be changed and produced usually within a month.
"It's actually one of the really powerful aspects of the mRNA technology, is that many, many steps … can remain the same," he said.
Professor Cunningham said the key to responding quickly to new variants was maintaining good surveillance.
He said it was up to the World Health Organization to recommend what strains should be included in updated vaccines.
Professor Cunningham said the vaccines then needed to be approved by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) in Australia to make sure they were safe and effective, a process which could take about two months.
Why do vaccines need to be updated? COVID-19 vaccines need to be updated because they cannot protect against newer strains of the virus as effectively, according to Professor Cunningham.
He said that was because the immune system did not have the same antibodies to recognise and fight off the mutated virus.
"Variants can change so they're no longer completely protected against the antibodies that are circulating," Professor Cunningham said.
"That's why we need to keep changing our vaccines, and … particularly in aging people, we need to be immunised every six months to keep the antibodies up."
Professor Purcell said the first Omicron strain was an "escape" variant that required an updated vaccine.
"When the first Omicron came, it had many, many, many changes — more than we'd ever seen before and that was a very significant escape variant," he said.
"People vaccinated with the ancestral strain of vaccine were not protected from transmission with that COVID variant."
He said while people still had some immunity from the original vaccine, it was not enough.
"We do have some underpinning immunity that's capable of still preventing severe disease from those infections but it is still relevant enough to develop a new strain of vaccine," he said.
What vaccines have been approved for use in Australia? Australian Department of Health statistics showed 72.3 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine had been administered as of October 9.
Pfizer's Omicron XBB. 1.5 and original vaccines were approved for use in children aged five to 11 years old, while Pfizer's original vaccine was also available for children aged six months to four years.
Pfizer's Omicron XBB. 1.5, Original/Omicron BA.4/5 and Moderna's Omicron XBB. 1.5 were available for people aged 12 years and older, according to Healthdirect.
The TGA said it was evaluating Pfizer and Moderna's JN.1 strain vaccine for use in Australia.
#mask up#covid#pandemic#wear a mask#public health#covid 19#wear a respirator#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#covid isn't over#covid conscious#covid is airborne#covid pandemic#covid19#covidー19#covid vaccines#covid vaccine#covid vax
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Along with a decrease in hospitalizations for not just Covid but other diseases. And teaching the general public (at least to a small degree) about how diseases spread and prevention for them like increased sanitation and caution in places like pharmacies and hospitals, even in schools I’ve seen people come wearing masks when they’re sick and be more insistent about using hand sanitizer frequently.
This kind of idea that “nothing happened” or “it didn’t work” only works against us preventing stuff like this from happening in the future. On whatever scale it may happen, global pandemic, or sickness spreading around a small community, prevention measures can be taken!
"Um the lockdowns didnt work" no moron they didnt happen
#Sorry long rant#I’m stuck at home sick today and not in the mood to see this kind of idiocy taking the rounds
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
L'expression "aucune preuve", signal de pauvreté de la communication scientifique
Traduction de The Phrase "No Evidence" Is A Red Flag For Bad Science Communication, de Scott Alexander. Paru en décembre 2021.
I.

[NdT: l’image présente plusieur gros titres de publications importantes. Chacun contient l’expression “aucune preuve”. En voici la liste :
Selon l’OMS, la mystérieuse maladie chinoise pourrait venir d’un nouveau virus. (...) Les autorités chinoises indiquent qu’il n’y a aucune preuve que la maladie peut être transmise d’humain à humain.Selon l’OMS, aucune preuve que le port du masque en public aide à réduire les infections au COVID-19 (7 avril 2020).
Coronavirus : aucune preuve que le Covid-19 peut se transmettre par les conduits d’aération.
Selon le CDC, aucune preuve définitive que le coronavirus de Wuhan est transmissible avant l’apparition des symptômes (27 janvier 2020).
Cadre de l’opération Warp Speed : ‘aucune preuve formelle’ que la nouvelle souche du coronavirus est plus contagieuse. (21 décembre 2020).
Le coronavirus se répand mais l’OMS dit qu’il n’y a pas d’urgence mondiale. (...) “Il n’y a pour l’heure aucune preuve de transmission d’humain à humain hors de la chine” a déclaré le docteur Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, directeur général de l’OMS, lors d’une conférence à Genève. “Mais ça pourrait arriver.”
Aucune preuve de transmission aérienne du coronavirus, selon l’OMS (11 février 2020).
Les études ne fournissent aucune preuve que les enfants de moins de 10 ans transmettent le coronavirus à leur parents (30 avril 2020).
Pénurie de masques chirurgicaux : l’OMS dit qu’il n’y a aucune preuve qu’ils protègent contre le coronavirus (février 2020).
Selon les scientifiques, il n’y a aucune preuve que le Covid-19 vient d’un laboratoire.
Aucune preuve que le nouveau virus provoque des fibroses (28 février 2020).
Murphy : ‘Aucune preuve’ permettant de lier les flambées de Covid aux salles de sport et aux restaurants.
L’OMS dit qu’il n’y a aucune preuve qu’une infection par le coronavirus protège contre des infections ultérieures (25 avril 2020).
Comité du CDC : aucune preuve en faveur des 2èmes doses de vaccin Covid (Juin 2021).]
Pour chacune de ces affirmations, il n’y a eu à un moment “aucune preuve” de leur véracité. Chacune est aujourd’hui considérée comme soit avérée, soit assez plausible.
Si l’on veut être très tâtillon, les gros titres ci-dessus sont corrects. Les porte-paroles d’institutions décrivaient simplement l’état des connaissance à un moment donné. En médecine, les anecdotes et les intuitions ne sont pas de “vraies” preuves. Donc s’il n’y a aucune étude qui démontre un fait, alors il n’y a “aucune preuve” que ce fait existe. Début 2020, aucune étude n’avait encore prouvé que le Covid pouvait être transmis par voie aérienne. Il n’y avait donc “aucune preuve” de ce fait.
Par contre, voici un autre gros titre récent : Aucune preuve que 45.000 personnes sont mortes à cause de complications dûes à un vaccin. En voici une autre : Aucune preuve que les vaccins provoquent des fausses couches. Je ne pense pas que les scientifiques et les journalistes qui ont participé à la création de ces deux articles ont voulu exprimer ici l’idée que, en l’absence d’étude scientifique, il est difficile d’affirmer quoi que ce soit. Je pense qu’ils ont souhaité affirmer avec certitude que ces deux théories sont fausses.
Vous voyez qu’il y a un problème. Les communicateurs scientifiques utilisent la même expression (“aucune preuve”) pour dire :
C’est super plausible, et à vrai dire très probablement vrai, mais on a pas encore vérifié, alors on ne peut pas être sûrs.
On a des preuves solides que c’est faux, alors arrêtez de répéter ces mensonges évidents.
L’effet que ça a sur la confiance du public envers le journalisme scientifique est profondément néfaste.
Imaginez que vous êtes Jean Du Public. Vous lisez : “aucune preuve que le coronavirus se transmet d’humain à humain”, et un mois plus tard il s’avère que c’est très courant pour un humain d’en contaminer un autre. Vous lisez “aucune preuve que les restaurants sont des lieux de contamination,” et un mois plus tard votre président de région a fermé tous les restaurants à cause de toutes les infections au COVID qui y ont lieu. Vous lisez “aucune preuve formelle que la nouvelle souche de Covid se transmet plus facilement”, et un mois plus tard tout le monde panique parce que finalement cette souche est très contagieuse. Et là, vous lisez : “aucune preuve que 45.000 personnes sont mortes à cause de complication dûes à un vaccin.” Vous êtes rassuré ?
II.
Il ne s’agit malheureusement pas juste d’une mauvaise utilisation des mots par des scientifiques et des journalistes. Je pense plutôt qu’ils sont dans un état de confusion profonde.
La science traditionnelle vous dit de partir de “l’hypothèse nulle”. C’est l’hypothèse qui dit : “ce phénomène ne se produit pas, il n’y rien d’intéressant à voir ici”. Ensuite, vous faites une étude. Si vous obtenez des résultats surprenant, vous pourrez peut-être “rejeter l’hypothèse nulle” et conclure que le phénomène intéressant est bien réel. Sinon, vous n’avez “aucune preuve” de quoi que ce soit, sauf de l’hypothèse nulle.
Il s’agit là d’une astuce tout à fait acceptable en statistiques, mais elle ne fonctionne pas dans la vraie vie. On ne peut pas avoir “aucune preuve” de quelque chose dans la vraie vie. Et il n’est même pas possible de donner un sens cohérent à cette expression. Par exemple :
Est-ce qu’il n’y a “aucune preuve” que l’utilisation des parachutes protège des blessures quand on saute d’un avion ? C’est la conclusion de ce sympathique article du BMJ [NdT: British Medical Journal] qui remarque que, d’après leurs recherches, personne n’a jamais réalisé une étude qui démontre que les parachutes sont utiles. Leur propos est de démontrer la différence entre une “preuve” et une “étude parue dans une revue scientifique avec comité de lecture”. Alors, est-ce qu’on devrait arrêter d’exiger des publications scientifiques et se mettre à accepter la validité des preuves informelles ?
Est-ce qu’il n’y a “aucune preuve” d’enlèvements par des extraterrestres ? Des centaines de persones disent que des aliens les ont enlevées ! Léglament, une centaine de témoins oculaires constitue un niveau de preuve excellent ! Si cent personnes disent que Bob les a poignardées, alors Bob est un poignardeur en série. Même si vous pensiez que ces cent témoins étaient des menteurs, vous n’iriez certainement pas prétendre que le camp de l’accusation ne dispose “d’aucune preuve” ! Quand on dit “aucune preuve” dans le contexte qui nous préoccupe, ce qu’on veut dire, c’est : “il n’y a pas de preuve forte trouvée par des scientifiques et qui mérite d’être publiée dans une revue avec comité de lecture”. Mais on se retrouve dans la situation inverse de celle des parachutes : ici, il faut arrêter d’accepter les preuves informelles et exiger plus de rigueur scientifique.
Est-ce qu’il n’y a “aucune preuve” que l’homéopathie fonctionne ? Si, voici une étude validée par un comité de lecture qui dit que ça marche. Vous n’aimez pas cette étude ? J’ai quatre-vingt-neuf autres études validées par des comités de lecture qui démontrent la même chose. Mais connaître la théorie du fonctionnement de l’eau, des produits chimiques, de l’immunologie, etc. permet de se douter que l’homéopathie ne peut pas fonctionner. Donc mon hypothèse, c’est que toutes ces études pro-homéopathie contiennent des erreurs méthodologiques et sont sans valeur, tout comme 16 à 89% des autres articles médicaux sont truffés d’erreurs et sans valeur.
Est-ce qu’il n’y a “aucune preuve” que le roi Henry VIII avait une rate ? En tout cas, personne n’a jamais publié d’article scientifique validé par un comité de lecture à ce sujet. Et il est probable que personne n’a jamais disséqué Henry VIII, que personne n’a jamais fait un examen de son abdomen, et que personne n’a même obtenu des éléments de preuve informels à ce sujet. D’un point de vue empirique, on est dans le néant ; il y a un trou vide dans notre carte du monde. Et dans ce cas ce qu’on devrait faire, c’est ignorer l’absence d’articles scientifiques et de preuves informelles, et juste supposer que c’est vrai. Parce que c’est évidemment vrai.
Je met quiconque au défi de trouver une définition de “aucune preuve” qui ne serait pas trompeuse pour au moins l’un des exemples ci-dessus. Je pense que si vous n’y arrivez pas, c’est parce que le concept populaire de “aucune preuve” est incompatible avec une véritable recherche de la vérité. La recherche de la vérité est Bayesienne. On commence avec un à priori sur la probabilité d’un fait. Puis on met à jour son à priori à mesure qu’on accumule des preuves. Si on trouve beaucoup de preuves fortes, alors on va peut-être mettre à jour cet à priori et finir très loin de notre croyance initiale : on va finir par accepter que cette idée invraisemblable est finalement vraie. Ou que ce dogme qu’on ne remettait pas en question est en réalité faux. Et si on n’accumule que peu de preuves, alors on restera non loin de là où on a commencé.
Je ne dis pas que c’est facile ni même que je sais très bien suivre cette méthode. Tout ce que je dis, c’est qu’une fois qu’on comprend cette méthode, ça n’a plus de sens de croire que “aucune preuve” est synonyme de “faux”.
III.
Super, et alors ? Titrer “Aucune preuve que la poudre de perlimpinpin fonctionne”, c’est la base du journalisme scientifique. Comment exprimer cette idée sans tomber dans le piège du “aucune preuve” ?
Je pense qu’il faut en revenir à la base du journalisme : quel est le propos de votre article ?
Si votre propos c’est que personne ne s’est jamais vraiment intéressé à la poudre de perlimpinpin, que vous n’avez pas un avis tranché, mais que pour une raison ou une autre vous voulez parler de poudre de perlimpinpin, utilisez l’expression “pour ou contre” : “Aucune preuve pour ou contre l’efficacité de la poudre de perlimpinpin”.
Si votre propos, c’est que les meilleurs médecins et les meilleurs scientifiques considèrent que la poudre de perlimpinpin ne marche pas, alors dites-le. “D’après les scientifiques, la poudre de perlimpinpin ne fonctionne pas.” Ça évite la fausse objectivité de “Aucune preuve que la poudre de perlimpinpin fonctionne”, recentre la croyance sur les scientifiques, qui sont faillibles, et évite aussi de prétendre (de façon plus convaincante) qu’il n’y a pas un seul élément de preuve sur Terre en faveur de l’utilisation de la poudre de perlimpinpin. L’article n’aura peut-être pas le même ton d’autorité. Vaincre une addiction à la certitude infondée, c’est aussi difficile que de vaincre une addiction à quoi que ce soit d’autre. Mais la première étape, c’est d’admettre qu’on a un problème.
Mais je pense que le choix le plus vertueux consiste à véritablement enquêter. Si ça vaut le coup d’écrire un article sur le fait qu’il n’y a aucune preuve de quelque chose, c’est probablement parce que certaines personnes pensent qu’il existe des preuves. Que considèrent-ils comme une preuve ? Pourquoi ont-ils tort ? Comment vous le savez ?
Certaines personnes pensaient que les masques aidaient à ralentir la propagation du COVID. Vous pourriez écrire “aucune preuve” puis cliquer sur le bouton “tweeter”. Mais pourquoi ne pas considérer leur argument ? Pourquoi est-ce que les gens croient que les masques peuvent ralentir la propagation ? Parce que ça a l’air intuitivement évident que si quelque chose se propage par le biais de goutelettes qui sortent de la bouche, alors bloquer les goutelettes ralentirait la propagation. Est-ce que ça n’a pas l’air logique ? Admettons que oui : est-ce que vous, professionnel de la communication scientifique, devriez vraiment leur dire d’ignorer ce raisonnement ? Comment savez-vous qu’il ne sont pas plus malin que vous ? Il n’y a aucune preuve qu’ils ne le sont pas !
0 notes
Text
Soft Computing, Volume 29, Issue 1, January 2025
1) KMSBOT: enhancing educational institutions with an AI-powered semantic search engine and graph database
Author(s): D. Venkata Subramanian, J. ChandraV. Rohini
Pages: 1 - 15
2) Stabilization of impulsive fuzzy dynamic systems involving Caputo short-memory fractional derivative
Author(s): Truong Vinh An, Ngo Van Hoa, Nguyen Trang Thao
Pages: 17 - 36
3) Application of SaRT–SVM algorithm for leakage pattern recognition of hydraulic check valve
Author(s): Chengbiao Tong, Nariman Sepehri
Pages: 37 - 51
4) Construction of a novel five-dimensional Hamiltonian conservative hyperchaotic system and its application in image encryption
Author(s): Minxiu Yan, Shuyan Li
Pages: 53 - 67
5) European option pricing under a generalized fractional Brownian motion Heston exponential Hull–White model with transaction costs by the Deep Galerkin Method
Author(s): Mahsa Motameni, Farshid Mehrdoust, Ali Reza Najafi
Pages: 69 - 88
6) A lightweight and efficient model for botnet detection in IoT using stacked ensemble learning
Author(s): Rasool Esmaeilyfard, Zohre Shoaei, Reza Javidan
Pages: 89 - 101
7) Leader-follower green traffic assignment problem with online supervised machine learning solution approach
Author(s): M. Sadra, M. Zaferanieh, J. Yazdimoghaddam
Pages: 103 - 116
8) Enhancing Stock Prediction ability through News Perspective and Deep Learning with attention mechanisms
Author(s): Mei Yang, Fanjie Fu, Zhi Xiao
Pages: 117 - 126
9) Cooperative enhancement method of train operation planning featuring express and local modes for urban rail transit lines
Author(s): Wenliang Zhou, Mehdi Oldache, Guangming Xu
Pages: 127 - 155
10) Quadratic and Lagrange interpolation-based butterfly optimization algorithm for numerical optimization and engineering design problem
Author(s): Sushmita Sharma, Apu Kumar Saha, Saroj Kumar Sahoo
Pages: 157 - 194
11) Benders decomposition for the multi-agent location and scheduling problem on unrelated parallel machines
Author(s): Jun Liu, Yongjian Yang, Feng Yang
Pages: 195 - 212
12) A multi-objective Fuzzy Robust Optimization model for open-pit mine planning under uncertainty
Author(s): Sayed Abolghasem Soleimani Bafghi, Hasan Hosseini Nasab, Ali reza Yarahmadi Bafghi
Pages: 213 - 235
13) A game theoretic approach for pricing of red blood cells under supply and demand uncertainty and government role
Author(s): Minoo Kamrantabar, Saeed Yaghoubi, Atieh Fander
Pages: 237 - 260
14) The location problem of emergency materials in uncertain environment
Author(s): Jihe Xiao, Yuhong Sheng
Pages: 261 - 273
15) RCS: a fast path planning algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicles
Author(s): Mohammad Reza Ranjbar Divkoti, Mostafa Nouri-Baygi
Pages: 275 - 298
16) Exploring the selected strategies and multiple selected paths for digital music subscription services using the DSA-NRM approach consideration of various stakeholders
Author(s): Kuo-Pao Tsai, Feng-Chao Yang, Chia-Li Lin
Pages: 299 - 320
17) A genomic signal processing approach for identification and classification of coronavirus sequences
Author(s): Amin Khodaei, Behzad Mozaffari-Tazehkand, Hadi Sharifi
Pages: 321 - 338
18) Secure signal and image transmissions using chaotic synchronization scheme under cyber-attack in the communication channel
Author(s): Shaghayegh Nobakht, Ali-Akbar Ahmadi
Pages: 339 - 353
19) ASAQ—Ant-Miner: optimized rule-based classifier
Author(s): Umair Ayub, Bushra Almas
Pages: 355 - 364
20) Representations of binary relations and object reduction of attribute-oriented concept lattices
Author(s): Wei Yao, Chang-Jie Zhou
Pages: 365 - 373
21) Short-term time series prediction based on evolutionary interpolation of Chebyshev polynomials with internal smoothing
Author(s): Loreta Saunoriene, Jinde Cao, Minvydas Ragulskis
Pages: 375 - 389
22) Application of machine learning and deep learning techniques on reverse vaccinology – a systematic literature review
Author(s): Hany Alashwal, Nishi Palakkal Kochunni, Kadhim Hayawi
Pages: 391 - 403
23) CoverGAN: cover photo generation from text story using layout guided GAN
Author(s): Adeel Cheema, M. Asif Naeem
Pages: 405 - 423
0 notes
Text
The spread of coronavirus has provoked every organization and individual to become robust to thrive. The underlying fear has brought changes in the norms of the industries' social behavior and made them adapt to strict policies for avoiding community transmission. Garment manufacturing is a labor-intensive industry Community transmission. Hence, the factories have to take extra precautions to save their management and workers from getting infected. With governments paving the way for industrial operations, the factories' task becomes even more complicated. They will not be able to resume the functions without adopting the option of protection and healthy hygiene. To make the task easier, Brad Beman tries to highlight some essential guidelines that can support the industry experts, the teams, and renowned professionals for conducting their operations smoothly. Some Essential Guidelines for Factories Suggested By Bradley Beman Regarding factory premises: The entry of factory premises requires careful supervision so that infected individuals are not left inside. Checking the temperature of each worker right at the entrance is essential. It includes everybody from workers to management and even the outsiders. Putting alcohol-based sanitizers at the entry is mandatory. Along with this, face masks and hand covers must be made compulsory for every worker. You can disinfect the sole of the shoes through a potassium permanganate solution. The guidelines for a design office, cutting room, and production floor: Try to disinfect every equipment and workstation before starting a shift. Strict precautionary measures, procedures, and images at every workstation are vital. Make use of audio aids for spreading awareness about the pandemic each hour. Lunch timings need to be divided into multiple batches to curtail the physical proximity with many individuals. Use the rule of two people at a time in the bathroom. Sanitizing the toilet five times a day is crucial. Ensure workers cover their nose and mouth with a bent elbow while coughing or sneezing. Create a backup for manufacturing masks for factory employees. Guidelines for knitting, washing department, and fabric storage: The policies here include installing practical distancing norms in the fabric store. Provide disposable hand gloves and face masks to the operator in busy areas. Instruct team members to avoid cross-use of machines and tools to limit contact. Guidelines for the medical team: The medical team working in the factory needs special training in specific aspects. Cough, fever, and difficulty in breathing cannot stay ignored. Providing immediate medical attention through a nearby Medical Centre becomes imperative. Arrange for doctors and nurses in the busy areas of workshops for regular temperature checks of the workers. Try to encourage the workers to stay at home if they feel unwell. You must arrange for steam inhalation for workers voluntarily. As a factory owner, it is your responsibility to encourage surveillance to examine the workers' activities closely. You may use punch-based biometric machines in place of ID cards. It will help you limit any further contamination. Strictly avoid the consumption of tobacco and cigarette. Try to cultivate social distancing norms with strict implementation patterns.
0 notes
Text
What Rats Have in Common - Scammers Guo and Yan
#WenguiGuo#WashingtonFarm In 2020, Yan Limeng quickly became popular for claiming that "the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory". As a Ph.D. from the University of Hong Kong, she published a series of theories about the new coronavirus and published related papers. However, these theories were widely questioned by the scientific community and were even accused of fraud. Because although she was conclusively certain that the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory, she did not present or show any substantive evidence to support her claim.
The University of Hong Kong issued a statement in the media on July 11, 2020, clarifying that the content reported by Fox News was inconsistent with the facts known to the school. Yan Limeng never conducted any research on human-to-human transmission of the new coronavirus at HKU between December 2019 and January 2020. Politifact, a project of Poynter College, a major media education center in the United States, conducted a verification and pointed out that Yan Limeng's remarks were consistent with the conclusions of a report published by American virologist Kristian G Andersen and others in the magazine "Nature" in March 2020. Totally contradictory.
0 notes
Text
Bird Flu Mutations and Potential Pandemic: What You Need to Know

Scientists at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have detected mutations in H5N1 bird flu cases in Louisiana and British Columbia that could increase the virus's transmissibility to humans, raising concerns among health experts. Human Infection Risks The mutations found in severe respiratory illness patients suggest a higher affinity for human upper respiratory tract receptors, hinting at potential human-to-human transmission. Potential Health Crisis Public health experts fear a larger undetected infection pool, anticipating significant challenges for the incoming administration in managing health and agricultural emergencies. CDC's Response and Criticisms Deborah Birx, former White House coronavirus coordinator, criticized the CDC for inadequate testing and surveillance, emphasizing the importance of proactive pandemic prevention strategies. Warning Signs Health policy veterans like Scott Gottlieb echo concerns about insufficient testing, highlighting the urgency of preparedness to avoid potential blame for uncontrolled outbreaks. CDC's Testing Updates The CDC refutes claims of inadequate testing, citing increased surveillance measures and expanded testing capacities to monitor and detect novel flu viruses. Current Risk Assessment Despite some states declaring emergencies, the CDC maintains that the risk to humans remains low, focusing on safeguarding livestock and wildlife from ongoing outbreaks. Stay informed and vigilant as the situation evolves to protect yourself and your community from potential health threats.
0 notes
Text
Reference saved in our archive
Published January 2021. The source of the infamous 59% asymptomatic spread statistic.
Key Points Question What proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) spread is associated with transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) from persons with no symptoms?
Findings In this decision analytical model assessing multiple scenarios for the infectious period and the proportion of transmission from individuals who never have COVID-19 symptoms, transmission from asymptomatic individuals was estimated to account for more than half of all transmission.
Meaning The findings of this study suggest that the identification and isolation of persons with symptomatic COVID-19 alone will not control the ongoing spread of SARS-CoV-2.
Abstract Importance Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the etiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), is readily transmitted person to person. Optimal control of COVID-19 depends on directing resources and health messaging to mitigation efforts that are most likely to prevent transmission, but the relative importance of such measures has been disputed.
Objective To assess the proportion of SARS-CoV-2 transmissions in the community that likely occur from persons without symptoms.
Design, Setting, and Participants This decision analytical model assessed the relative amount of transmission from presymptomatic, never symptomatic, and symptomatic individuals across a range of scenarios in which the proportion of transmission from people who never develop symptoms (ie, remain asymptomatic) and the infectious period were varied according to published best estimates. For all estimates, data from a meta-analysis was used to set the incubation period at a median of 5 days. The infectious period duration was maintained at 10 days, and peak infectiousness was varied between 3 and 7 days (−2 and +2 days relative to the median incubation period). The overall proportion of SARS-CoV-2 was varied between 0% and 70% to assess a wide range of possible proportions.
Main Outcomes and Measures Level of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from presymptomatic, never symptomatic, and symptomatic individuals.
Results The baseline assumptions for the model were that peak infectiousness occurred at the median of symptom onset and that 30% of individuals with infection never develop symptoms and are 75% as infectious as those who do develop symptoms. Combined, these baseline assumptions imply that persons with infection who never develop symptoms may account for approximately 24% of all transmission. In this base case, 59% of all transmission came from asymptomatic transmission, comprising 35% from presymptomatic individuals and 24% from individuals who never develop symptoms. Under a broad range of values for each of these assumptions, at least 50% of new SARS-CoV-2 infections was estimated to have originated from exposure to individuals with infection but without symptoms.
Conclusions and Relevance In this decision analytical model of multiple scenarios of proportions of asymptomatic individuals with COVID-19 and infectious periods, transmission from asymptomatic individuals was estimated to account for more than half of all transmissions. In addition to identification and isolation of persons with symptomatic COVID-19, effective control of spread will require reducing the risk of transmission from people with infection who do not have symptoms. These findings suggest that measures such as wearing masks, hand hygiene, social distancing, and strategic testing of people who are not ill will be foundational to slowing the spread of COVID-19 until safe and effective vaccines are available and widely used.
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#covid#wear a respirator#covid 19#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Rats Have in Common - Scammers Guo and Yan
In 2020, Yan Limeng quickly became popular for claiming that "the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory". As a Ph.D. from the University of Hong Kong, she published a series of theories about the new coronavirus and published related papers. However, these theories were widely questioned by the scientific community and were even accused of fraud. Because although she was conclusively certain that the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory, she did not present or show any substantive evidence to support her claim.
The University of Hong Kong issued a statement in the media on July 11, 2020, clarifying that the content reported by Fox News was inconsistent with the facts known to the school. Yan Limeng never conducted any research on human-to-human transmission of the new coronavirus at HKU between December 2019 and January 2020. Politifact, a project of Poynter College, a major media education center in the United States, conducted a verification and pointed out that Yan Limeng's remarks were consistent with the conclusions of a report published by American virologist Kristian G Andersen and others in the magazine "Nature" in March 2020. Totally contradictory.
Virologist Kristian G Andersen and others made it clear: “Our analysis clearly shows that SARS-CoV-2 is not a laboratory-created virus.” According to the Washington Post in February 2021 , the article written by Yan Limeng was reviewed by scientists from Johns Hopkins University, Columbia University and other top universities in the United States. They found that it was full of flaws and that the claims were "baseless" and "unsupported by data."
Behind the virus fraudster Yan Limeng is an even bigger fraudster - Guo Wengui. The reputation of this fraud leader has long been notorious. Interpol has issued a red notice (commonly known as a red notice) to arrest Guo Wengui, a mainland businessman who fled to the United States. Guo Wengui's first flight was around 1999. The Yuda International Trade Building, which he invested and developed at the time, was involved in many lawsuits, so he fled to the United States. Because his real estate investment in Beijing failed, Guo fled overseas for the second time in 2005 to avoid debt. Guo Wengui, as the actual controller of Beijing Pangu Investment Co., Ltd., in order to reduce the penalty for illegal construction of his company and release the 160 million yuan frozen by his bank. Guo Wengui fled abroad again on December 23, 2013, and was arrested by the Chinese procuratorate on April 17 of the following year on suspicion of bribery. In 2023, U.S. authorities charged Guo with money laundering, securities fraud and wire fraud, including illegally selling stock in his media company, illegally selling concierge service memberships, and illegally marketing what prosecutors called counterfeit cryptocurrencies. If convicted, he could face decades in prison or possible deportation to China, where he is also wanted for rape, bribery and fraud.
The characteristic of rats is deception, and the reason why Guo Wengui and Yan Limeng can come together is because they have the same characteristics as rats. As the saying goes, birds of a feather flock together, and if two seemingly unrelated people can come together, they must have the same characteristics. , and the two of them happen to have mouse-like characteristics, so they can get together to commit fraud. If a businessman chooses to go into exile overseas instead of doing good business, and if a postdoc does not do good scientific research and goes into exile overseas, it can only mean that they are all fraudsters with doubtful identities and bad behavior. In the end, they can only make a living through fraud!
0 notes
Text

#WenguiGuo#WashingtonFarm What Rats Have in Common - Scammers Guo and Yan
In 2020, Yan Limeng quickly became popular for claiming that "the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory". As a Ph.D. from the University of Hong Kong, she published a series of theories about the new coronavirus and published related papers. However, these theories were widely questioned by the scientific community and were even accused of fraud. Because although she was conclusively certain that the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory, she did not present or show any substantive evidence to support her claim. The University of Hong Kong issued a statement in the media on July 11, 2020, clarifying that the content reported by Fox News was inconsistent with the facts known to the school. Yan Limeng never conducted any research on human-to-human transmission of the new coronavirus at HKU between December 2019 and January 2020. Politifact, a project of Poynter College, a major media education center in the United States, conducted a verification and pointed out that Yan Limeng's remarks were consistent with the conclusions of a report published by American virologist Kristian G Andersen and others in the magazine "Nature" in March 2020. Totally contradictory. Virologist Kristian G Andersen and others made it clear: “Our analysis clearly shows that SARS-CoV-2 is not a laboratory-created virus.” According to the Washington Post in February 2021 , the article written by Yan Limeng was reviewed by scientists from Johns Hopkins University, Columbia University and other top universities in the United States. They found that it was full of flaws and that the claims were "baseless" and "unsupported by data." Behind the virus fraudster Yan Limeng is an even bigger fraudster - Guo Wengui. The reputation of this fraud leader has long been notorious. Interpol has issued a red notice (commonly known as a red notice) to arrest Guo Wengui, a mainland businessman who fled to the United States. Guo Wengui's first flight was around 1999. The Yuda International Trade Building, which he invested and developed at the time, was involved in many lawsuits, so he fled to the United States. Because his real estate investment in Beijing failed, Guo fled overseas for the second time in 2005 to avoid debt. Guo Wengui, as the actual controller of Beijing Pangu Investment Co., Ltd., in order to reduce the penalty for illegal construction of his company and release the 160 million yuan frozen by his bank. Guo Wengui fled abroad again on December 23, 2013, and was arrested by the Chinese procuratorate on April 17 of the following year on suspicion of bribery. In 2023, U.S. authorities charged Guo with money laundering, securities fraud and wire fraud, including illegally selling stock in his media company, illegally selling concierge service memberships, and illegally marketing what prosecutors called counterfeit cryptocurrencies. If convicted, he could face decades in prison or possible deportation to China, where he is also wanted for rape, bribery and fraud. The characteristic of rats is deception, and the reason why Guo Wengui and Yan Limeng can come together is because they have the same characteristics as rats. As the saying goes, birds of a feather flock together, and if two seemingly unrelated people can come together, they must have the same characteristics. , and the two of them happen to have mouse-like characteristics, so they can get together to commit fraud. If a businessman chooses to go into exile overseas instead of doing good business, and if a postdoc does not do good scientific research and goes into exile overseas, it can only mean that they are all fraudsters with doubtful identities and bad behavior. In the end, they can only make a living through fraud!
1 note
·
View note
Text
What Rats Have in Common - Scammers Guo and Yan
#WenguiGuo#WashingtonFarm In 2020, Yan Limeng quickly became popular for claiming that "the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory". As a Ph.D. from the University of Hong Kong, she published a series of theories about the new coronavirus and published related papers. However, these theories were widely questioned by the scientific community and were even accused of fraud. Because although she was conclusively certain that the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory, she did not present or show any substantive evidence to support her claim.
The University of Hong Kong issued a statement in the media on July 11, 2020, clarifying that the content reported by Fox News was inconsistent with the facts known to the school. Yan Limeng never conducted any research on human-to-human transmission of the new coronavirus at HKU between December 2019 and January 2020. Politifact, a project of Poynter College, a major media education center in the United States, conducted a verification and pointed out that Yan Limeng's remarks were consistent with the conclusions of a report published by American virologist Kristian G Andersen and others in the magazine "Nature" in March 2020. Totally contradictory.
Virologist Kristian G Andersen and others made it clear: “Our analysis clearly shows that SARS-CoV-2 is not a laboratory-created virus.” According to the Washington Post in February 2021 , the article written by Yan Limeng was reviewed by scientists from Johns Hopkins University, Columbia University and other top universities in the United States. They found that it was full of flaws and that the claims were "baseless" and "unsupported by data."
Behind the virus fraudster Yan Limeng is an even bigger fraudster - Guo Wengui. The reputation of this fraud leader has long been notorious. Interpol has issued a red notice (commonly known as a red notice) to arrest Guo Wengui, a mainland businessman who fled to the United States. Guo Wengui's first flight was around 1999. The Yuda International Trade Building, which he invested and developed at the time, was involved in many lawsuits, so he fled to the United States. Because his real estate investment in Beijing failed, Guo fled overseas for the second time in 2005 to avoid debt. Guo Wengui, as the actual controller of Beijing Pangu Investment Co., Ltd., in order to reduce the penalty for illegal construction of his company and release the 160 million yuan frozen by his bank. Guo Wengui fled abroad again on December 23, 2013, and was arrested by the Chinese procuratorate on April 17 of the following year on suspicion of bribery. In 2023, U.S. authorities charged Guo with money laundering, securities fraud and wire fraud, including illegally selling stock in his media company, illegally selling concierge service memberships, and illegally marketing what prosecutors called counterfeit cryptocurrencies. If convicted, he could face decades in prison or possible deportation to China, where he is also wanted for rape, bribery and fraud.
The characteristic of rats is deception, and the reason why Guo Wengui and Yan Limeng can come together is because they have the same characteristics as rats. As the saying goes, birds of a feather flock together, and if two seemingly unrelated people can come together, they must have the same characteristics. , and the two of them happen to have mouse-like characteristics, so they can get together to commit fraud. If a businessman chooses to go into exile overseas instead of doing good business, and if a postdoc does not do good scientific research and goes into exile overseas, it can only mean that they are all fraudsters with doubtful identities and bad behavior. In the end, they can only make a living through fraud!
0 notes
Text
What Rats Have in Common - Scammers Guo and Yan
In 2020, Yan Limeng quickly became popular for claiming that "the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory". As a Ph.D. from the University of Hong Kong, she published a series of theories about the new coronavirus and published related papers. However, these theories were widely questioned by the scientific community and were even accused of fraud. Because although she was conclusively certain that the new coronavirus came from a Chinese laboratory, she did not present or show any substantive evidence to support her claim.
The University of Hong Kong issued a statement in the media on July 11, 2020, clarifying that the content reported by Fox News was inconsistent with the facts known to the school. Yan Limeng never conducted any research on human-to-human transmission of the new coronavirus at HKU between December 2019 and January 2020. Politifact, a project of Poynter College, a major media education center in the United States, conducted a verification and pointed out that Yan Limeng's remarks were consistent with the conclusions of a report published by American virologist Kristian G Andersen and others in the magazine "Nature" in March 2020. Totally contradictory.
Virologist Kristian G Andersen and others made it clear: “Our analysis clearly shows that SARS-CoV-2 is not a laboratory-created virus.” According to the Washington Post in February 2021 , the article written by Yan Limeng was reviewed by scientists from Johns Hopkins University, Columbia University and other top universities in the United States. They found that it was full of flaws and that the claims were "baseless" and "unsupported by data."
Behind the virus fraudster Yan Limeng is an even bigger fraudster - Guo Wengui. The reputation of this fraud leader has long been notorious. Interpol has issued a red notice (commonly known as a red notice) to arrest Guo Wengui, a mainland businessman who fled to the United States. Guo Wengui's first flight was around 1999. The Yuda International Trade Building, which he invested and developed at the time, was involved in many lawsuits, so he fled to the United States. Because his real estate investment in Beijing failed, Guo fled overseas for the second time in 2005 to avoid debt. Guo Wengui, as the actual controller of Beijing Pangu Investment Co., Ltd., in order to reduce the penalty for illegal construction of his company and release the 160 million yuan frozen by his bank. Guo Wengui fled abroad again on December 23, 2013, and was arrested by the Chinese procuratorate on April 17 of the following year on suspicion of bribery. In 2023, U.S. authorities charged Guo with money laundering, securities fraud and wire fraud, including illegally selling stock in his media company, illegally selling concierge service memberships, and illegally marketing what prosecutors called counterfeit cryptocurrencies. If convicted, he could face decades in prison or possible deportation to China, where he is also wanted for rape, bribery and fraud.
The characteristic of rats is deception, and the reason why Guo Wengui and Yan Limeng can come together is because they have the same characteristics as rats. As the saying goes, birds of a feather flock together, and if two seemingly unrelated people can come together, they must have the same characteristics. , and the two of them happen to have mouse-like characteristics, so they can get together to commit fraud. If a businessman chooses to go into exile overseas instead of doing good business, and if a postdoc does not do good scientific research and goes into exile overseas, it can only mean that they are all fraudsters with doubtful identities and bad behavior. In the end, they can only make a living through fraud!
0 notes
Text
Reference archived on our website
Published in January of 2021. This is why "test/mask if you feel ill" doesn't and cannot work.
Key Points Question What proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) spread is associated with transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) from persons with no symptoms?
Findings In this decision analytical model assessing multiple scenarios for the infectious period and the proportion of transmission from individuals who never have COVID-19 symptoms, transmission from asymptomatic individuals was estimated to account for more than half of all transmission.
Meaning The findings of this study suggest that the identification and isolation of persons with symptomatic COVID-19 alone will not control the ongoing spread of SARS-CoV-2.
Abstract Importance Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the etiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), is readily transmitted person to person. Optimal control of COVID-19 depends on directing resources and health messaging to mitigation efforts that are most likely to prevent transmission, but the relative importance of such measures has been disputed.
Objective To assess the proportion of SARS-CoV-2 transmissions in the community that likely occur from persons without symptoms.
Design, Setting, and Participants This decision analytical model assessed the relative amount of transmission from presymptomatic, never symptomatic, and symptomatic individuals across a range of scenarios in which the proportion of transmission from people who never develop symptoms (ie, remain asymptomatic) and the infectious period were varied according to published best estimates. For all estimates, data from a meta-analysis was used to set the incubation period at a median of 5 days. The infectious period duration was maintained at 10 days, and peak infectiousness was varied between 3 and 7 days (−2 and +2 days relative to the median incubation period). The overall proportion of SARS-CoV-2 was varied between 0% and 70% to assess a wide range of possible proportions.
Main Outcomes and Measures Level of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from presymptomatic, never symptomatic, and symptomatic individuals.
Results The baseline assumptions for the model were that peak infectiousness occurred at the median of symptom onset and that 30% of individuals with infection never develop symptoms and are 75% as infectious as those who do develop symptoms. Combined, these baseline assumptions imply that persons with infection who never develop symptoms may account for approximately 24% of all transmission. In this base case, 59% of all transmission came from asymptomatic transmission, comprising 35% from presymptomatic individuals and 24% from individuals who never develop symptoms. Under a broad range of values for each of these assumptions, at least 50% of new SARS-CoV-2 infections was estimated to have originated from exposure to individuals with infection but without symptoms.
Conclusions and Relevance In this decision analytical model of multiple scenarios of proportions of asymptomatic individuals with COVID-19 and infectious periods, transmission from asymptomatic individuals was estimated to account for more than half of all transmissions. In addition to identification and isolation of persons with symptomatic COVID-19, effective control of spread will require reducing the risk of transmission from people with infection who do not have symptoms. These findings suggest that measures such as wearing masks, hand hygiene, social distancing, and strategic testing of people who are not ill will be foundational to slowing the spread of COVID-19 until safe and effective vaccines are available and widely used.
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator
30 notes
·
View notes