#copyright trolls
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
2023's public domain is a banger

40 years ago, giant entertainment companies embarked on a slow-moving act of arson. The fuel for this arson was copyright term extension (making copyrights last longer), including retrospective copyright term extensions that took works out of the public domain and put them back into copyright for decades. Vast swathes of culture became off-limits, pseudo-property with absentee landlords, with much of it crumbling into dust.
After 55-75 years, only 2% of works have any commercial value. After 75 years, it declines further. No wonder that so much of our cultural heritage is now orphan works, with no known proprietor. Extending copyright on all works – not just those whose proprietors sought out extensions – incinerated whole libraries full of works, permanently.
But on January 1, 2019, the bonfire was extinguished. That was the day that items created in 1923 entered the US public domain: DeMille's Ten Commandments, Chaplain's Pilgrim, Burroughs' Tarzan and the Golden Lion, Woolf's Jacob's Room, Coward's London Calling and 1,000+ more works:
https://web.law.duke.edu/cspd/publicdomainday/2019/
Many of those newly liberated works were forgotten, partly due to their great age, but also because no one knew who they belonged to (Congress abolished the requirement to register copyrights in 1976), so no one could revive or reissue them while they were still in the popular imagination, depriving them of new leases on life.
2019 was the starting gun on a new public domain, giving the public new treasures to share and enjoy, and giving the long-dead creators of the Roaring Twenties a new chance at posterity. Each new year since has seen a richer, more full public domain. 2021 was a great year, featuring some DuBois, Dos Pasos, Huxley, Duke Ellington, Fats Waller, Bessie Smith and Sydney Bechet:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/12/16/fraught-superpowers/#public-domain-day
In just 12 days, the public domain will welcome another year's worth of works back into our shared commons. As ever, Jennifer Jenkins of Duke's Center for the Public Domain have painstaking researched highlights from the coming year's entrants:
https://web.law.duke.edu/cspd/publicdomainday/2023/
On the literary front, we have Virginia Woolf's To The Lighthouse, AA Milne's Now We Are Six, Hemingway's Men Without Women, Faulkner's Mosquitoes, Christie's The Big Four, Wharton's Twilight Sleep, Hesse's Steppenwolf (in German), Kafka's Amerika (in German), and Proust's Le Temps retrouvé (in French).
We also get all of Sherlock Holmes, finally wrestling control back from the copyright trolls who control the Arthur Conan Doyle estate. This is a firm of rent-seeking bullies who have abused the court process to extract menaces money from living creators, including rent on works that were unambiguously in the public domain.
The estate's sleaziest trick is claiming that while many Sherlock Holmes stories were in the public domain, certain elements of Holmes's personality were developed in later stories that were still in copyright, and therefore any Sherlock story that contained those elements was a copyright violation. Infamously, the Doyle Estate went after the creators of the Enola Holmes series, claiming a copyright over Sherlock stories in which Holmes was "capable of friendship," "expressed emotion," or "respected women." This is a nonsensical theory, based on the idea that these character traits are copyrightable. They are not:
https://web.law.duke.edu/cspd/publicdomainday/2023/#fn6text
The Doyle Estate's shakedown racket took a serious body-blow in 2013, when Les Klinger – a lawyer, author and prominent Sherlockian – prevailed in court, with the judge ruling that new works based on public domain Sherlock stories were not infringing, even if some Sherlock stories remained in copyright. The estate appealed and lost again, and Klinger was awarded costs. They tried to take the case to the Supreme Court and got laughed out of the building.
But as the Enola Holmes example shows, you can't keep a copyright troll down: the Doyle estate kept making up imaginary copyright laws in a desperate, grasping bid to wring more money out of living, working creators. That's gonna be a lot harder after Jan 1, when The Case-Book of Sherlock Holmes enters the public domain, meaning that every Sherlock story will be out of copyright.
One fun note about Klinger's landmark win over the Doyle estate: he took an amazing victory lap, commissioning an anthology of new unauthorized Holmes stories in 2016 called "Echoes of Sherlock Holmes":
https://www.simonandschuster.com/books/Echoes-of-Sherlock-Holmes/Laurie-R-King/Sherlock-Holmes/9781681775463
I wrote a short story for it, "Sherlock Holmes and the Case of the Extraordinary Rendition," which was based on previously unpublished Snowden leaks.
https://esl-bits.net/ESL.English.Listening.Short.Stories/Rendition/01/default.html
I got access to the full Snowden trove thanks to Laura Poitras, who jointly commissioned the story from me for inclusion in the companion book for "Astro noise : a survival guide for living under total surveillance," her show at the Whitney:
https://www.si.edu/object/siris_sil_1060502
I also reported out the leaks the story was based on in a companion piece:
https://memex.craphound.com/2016/02/02/exclusive-snowden-intelligence-docs-reveal-uk-spooks-malware-checklist/
Jan 1, 2023 will also be a fine day for film in the public domain, with Metropolis, The Jazz Singer, and Laurel and Hardy's Battle of the Century entering the commons. Also notable: Wings, winner of the first-ever best picture Academy Award; The Lodger, Hitchcock's first thriller; and FW "Nosferatu" Mirnau's Sunrise.
However most of the movies that enter the public domain next week will never be seen again. They are "lost pictures," and every known copy of them expired before their copyrights did. 1927 saw the first synchronized dialog film (The Jazz Singer). As talkies took over the big screen, studios all but gave up on preserving silent films, which were printed on delicate stock that needed careful tending. Today, 75% of all silent films are lost to history.
But some films from this era do survive, and they are now in the public domain. This is true irrespective of whether they were restored at a later date. Restoration does not create a new copyright. "The Supreme Court has made clear that 'the sine qua non of copyright is originality.'"
https://www.law.cornell.edu/supremecourt/text/499/340
There's some great music entering the public domain next year! "The Best Things In Life Are Free"; "I Scream, You Scream, We All Scream for Ice-Cream"; "Puttin' On the Ritz"; "'S Wonderful"; "Ol' Man River"; "My Blue Heaven" and "Mississippi Mud."
It's a banger of a year for jazz and blues, too. We get Bessie Smith's "Back Water Blues," "Preaching the Blues," and "Foolish Man Blues." We get Louis Armstrong's "Potato Head Blues" and "Gully Low Blues." We get Jelly Roll Morton's "Billy Goat Stomp," "Hyena Stomp," and "Jungle Blues." And we get Duke Ellington's "Black and Tan Fantasy" and "East St. Louis Toodle-O."
Note that these are just the compositions. No new sound recordings come into the public domain in 2023, but on January 1, 2024, all of 1923's recordings will enter the public domain, with more recordings coming in every year thereafter.
We're only a few years into the newly reopened public domain, but it's already bearing fruit. The Great Gatsby entered the public domain in 2021, triggering a rush of beautiful new editions and fresh scholarship:
https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/14/books/the-great-gatsby-public-domain.html
These new editions were varied and wonderful. Beehive Books produced a stunning edition, illustrated by the Balbusso Twins, with a new introduction by Wellesley's Prof William Cain:
https://beehivebooks.com/shop/gatsby
And Planet Money released a fabulous, free audiobook edition:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/01/18/peak-indifference/#gatsby
Last year saw the liberation of Winnie the Pooh, unleashing a wild and wonderful array of remixes, including a horror film ("Blood and Honey") and also innumerable, lovely illustrations and poems, created by living, working creators for contemporary audiences.
As Jenkins notes, many of the works that enter the public domain next week display and promote "racial slurs and demeaning stereotypes." The fact that these works are now in the public domain means that creators can "grapple with and reimagine them, including in a corrective way." They can do this without having to go to the Supreme Court, unlike the Alice Randall, whose "Wind Done Gone" retold "Gone With the Wind" from the enslaved characters' perspective:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Wind_Done_Gone
After all this, you'd think that countries around the world would have learned their lesson on copyright term extension, but you'd be wrong. In Canada, Justin Trudeau caved to Donald Trump and retroactively expanded copyright terms by 20 years, as part of USMCA, the successor to NAFTA. Trudeau ignored teachers, professors, librarians and the Minister of Justice, who said that copyright extension should require "a modest registration requirement" – so 20 years of copyright will be tacked onto all works, including those with no owners:
https://www.michaelgeist.ca/2022/04/the-canadian-government-makes-its-choice-implementation-of-copyright-term-extension-without-mitigating-against-the-harms/
Other countries followed Canada's disastrous lead: New Zealand "agreed to extend its copyright term as a concession in trade agreements, even though this would cost around $55m [NZ dollars] annually without any compelling evidence that it would provide a public benefit":
https://www.newsroom.co.nz/nz-agrees-to-mickey-mouse-copyright-law
Wrapping up her annual post, Jenkins writes of a "melancholy" that "comes from the unnecessary losses that our current system causes—the vast majority of works that no longer retain commercial value and are not otherwise available, yet we lock them all up to provide exclusivity to a tiny minority.
"Those works which, remember, constitute part of our collective culture, are simply off limits for use without fear of legal liability. Since most of them are 'orphan works' (where the copyright owner cannot be found) we could not get permission from a rights holder even if we wanted to. And many of those works do not survive that long cultural winter."
[Image ID: A montage of works that enter the public domain on Jan 1, 2023.]
#pluralistic#copyright#usmca#james boyle#jennifer jenkins#canpoli#canada#silent films#enola holmes#les klinger#copyright trolls#rogers and hammerstein#irving berlin#laurel and hardy#marcel proust#ernest hemingway#william faulkner#copyfight#public domain#remix#preservation#al jolson#winnie the pooh#franz kafka#virginia woolf#metropolis#sherlock holmes
648 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is exactly what SLAPP suits are about. It's the equivalent of looking over someone's store and announcing, "Wow, nice product. Be a shame if something happened to it." These assholes are assuming small artists don't know their rights and don't have access to a lawyer. They're copyright trolls.

welp.
Guess we'll be removing the Gilbert Baker 1977 Pride Flag from our site, along with the links to the Gilbert Baker Foundation.
Heads up to other queer artists: if you use the original 1977 flag in anything, definitely don't make any reference to who created it in your listings or you might get threatened by the Gilbert Baker Foundation! :)
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
Thanks to guest author Victoria Strauss for her important piece on Copyright Trolls: All writers can be their victims!
When The Copyright Trolls Came for Me By Victoria Strauss | June 23, 2023 | 7 Comments If you’re a writer who’s serious about a career, you probably have some form of online presence: a website, a blog, an Instagram account. You may make use of images and/or videos created by others–to add visual interest to your blog posts or newsletters, build out your website, and engage your readers and…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Lmao, I’m just gonna leave this here
*Jumping and down, giggling rn*
(happily gives you some of my collection of Poppy screenshots-) ^u^

oh yeah, Branch is there too~
#Trolls#Trolls Branch#Trolls Poppy#Trolls Queen Poppy#Broppy#I have a problem#No it’s not my Screenshots of her-#It’s my absurd lack of phone storage-#Lmao#there are thousands of pics#this is barely scratching the surface#If I showed anymore at once it may be copyright infringement-#Oh well#YOLO#TROLLS!
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
One big point where I find people talking past each other in the AI art debate is that in art, there are a lot of things that aren't illegal - and shouldn't be - but are rude.
It's not illegal to use a sample of someone's copyrighted material in a sufficiently transformative way, and it should never become so. I could photomanipulate an image of Mickey Mouse into a landscape if I wanted and sell it as a print and not even Disney could stop me. It never has been illegal to do this. It never SHOULD be. If it was, we'd start seeing a ton of SLAPP suits over vaguely similar poses because...hey, guess what, referencing is using someone's copyrighted material in a transformative way. We all recognize the idea of trying to copyright a pose or sue someone for using a similar color palette to you or for looking at your art as inspiration as patently absurd - so much so that it's regularly brought up as a bad-faith argument in other copyright discussions! - but imagine if someone could. Disney sure as hell would - imagine no longer being able to write about public domain fairy tales because you publicly mentioned you liked the Disney movie about the same fairy tale once. That is what you're opening the door for when you try to manage the dataset ethics issue by copyright law.
However, on the other side...it's still really fucking rude to use someone's work in a transformative way outside of the bounds of 1) what is broadly socially permitted, and 2) what that artist requests.
Even though it would be decidedly not illegal for me to go and copy-paste a single pixel from a dozen other people's work into a canvas of my own and make my own piece out of it using only the scale, copy-paste, and smudge tools, it still has the potential to be extremely rude depending on who I'm taking it from and why. I'd love to do a piece like this to open a dialogue on how transformative a piece must be to no longer constitute "stealing", but I'm not going to sample those pixels from small-time illustrators who are already scared for what sampling could do to their livelihoods as a "ha ha~ I took your wo-ork and you ca-an't stop me~" because that would be incredibly fucking rude, well beyond the level of emotional impact needed to make the statement.
Image synthesis is, unquestionably, transformative enough to constitute fair use under current copyright law, and any amendment to the law that would make it not so opens the door to far more harm than it would ever prevent - but, as it transitions from being a fun scientific novelty to an actual useful product, it becomes rude at best to ignore artists' wishes in model training. In fact, it becomes rude on a level that may be best managed with privacy laws, since, let's face it, there are a lot of entities out there that not only don't CARE about not being extremely rude, but REVEL in being jackasses because the law can't stop them (looking at you, Unstable Diffusion).
#not art#as a side note i AM working on art made entirely of single 'pirated' pixels#but theyre from like. BIG name copyright trolls. really notorious ones. ones most of us know and hate here on tumblr dot com.#im also working on some queer joy art with pirated pixels from notorious queerphobes. it's a whole thing#oh you think im stealing from you for my own agenda? point to which pixel in your art i stole. i will wait.#but my spite is reserved solely for entities who arent just. taking concerns about their continued survivability a bit too far#this is only for the famously awful#i dont touch indies unless theyve outright filed a SLAPP against someone smaller than them or something equally egregious#also a couple of them come from nfts
372 notes
·
View notes
Text
As a child two of my best ongoing jokes were literally ripped straight from tv shows, I just didn’t tell the adults in my life - I essentially committed copyright infringement 😭. Whenever my early childhood came up in conversation, like in doctors appointments or something, I’d answer it seriously, but if recounting that when I got home, I’d look the person I was speaking to dead in the eye and say “Darkness… I emerge from the womb…” Well, that was taken directly from the Christmas episode of the Netflix series ‘Trolls: The Beat Goes On’, and it’s a line delivered by the pink giraffe troll named Cooper upon being instructed to “Start from the beginning.” And once, when asked about my vision for the future, I pitched a wardrobe that used holograms to project clothes onto your body… that was taken from the new Barbie Dreamhouse Adventures Netflix series and the tie-in Budge Studios kids game that I played for way too long. My plan was to use such obscure references that people would be tricked into thinking that I was a lot funnier and creative than I actually was. I’m sorry to anyone from Netflix, Dreamworks or Mattel who sees this post, I no longer rip off copyrighted lines or concepts for the amusement of others 😔.
21 notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm getting ready to post my second Flea-inspired Funk-Rock OC Jake, but I'm a little worried that he may be too similar to Hed because of his hair color, skin color, and the fact that he has dreads he wasn't born with. Here's Jake's color palette:

I shifted Jake's bare skin color to be closer to Reuben's but I'm still worried about it being too similar to Hed's.
I totally understand this struggle! Especially rock trolls have such a limited set of colors. It's either shades of gray or desaturated browns and greens, basically rock/earth colors, and hair is either black or white (or pale blond) and maybe some bright reds, blues, neon greens because those are punk. and that's it. 😞 (I am not upset by this btw, but it does pose a real challenge sometimes)
But in the end there's so many other factors that make troll characters unique besides the colors and hair shape. Same as how we are all unique even though we're much more limited in both of these departments haha
If you're worried I'll take his design the wrong way, don't be, but if you're uncomfortable with the similarities, maybe think if they really feel similar (vibes) or if they look related. If you still have a problem but like the color palette, maybe give this OC a different hair style? (I don't mean not give him dreads, just different shape/length) or make something unique a prominent feature on him. idk, I'm just giving ideas. But you can keep that color palette, I don't own color palettes :P
#i worry about this whenever i want to make broppy kids. there's so many cool broppy kids out there i don't wanna accidentally copy somebody#'s design. but i also want them to look like their parents#the struggle!!#answered#trolls#i wonder if there's some big company assholes out there who tried copyrighting color palettes... (don't wanna look it up ever)#edit: actually now that i think about it. trolls hairstyles are much more limited than our hairstyles#our hair and hairstyles have much more variety. it just doesn't have magical powers lol
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
La Sirena just so happens to also be the name of one of DMCA Piracy Prevention Inc’s clients—La Sirena 69, an adult content creator notably not involved in the Star Trek fandom. In one recent copyright claim, the monitoring service targeted over 90 Tumblr posts that matched a keyword search of “la sirena.” But instead of alerting our team to La Sirena 69’s allegedly infringed content, the company reported a wide array of @mappinglasirena's original posts—like a short essay about a new La Sirena booklet, an article analysis of the starship’s design, and even the blog owner’s thoughts on the fourth trailer for Picard season two. None of these reported links from mappinglasirena.tumblr.com contained infringing content from La Sirena 69—instead, they focus on La Sirena, the starship. As you probably expect, we rejected this complaint.
A peek behind the curtain at [tumblr] keeping you safe from DMCA trolls.
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
Man it really is a shame that as of this date (July 5th, 2023) that Cookie's Bustle is all but scrapped off the web at large.
There's only two videos discussing it directly (and that more about the take downs and not directly the game itself), with everything else turning up no results.
I know some people on twitter were thinking that it was for some sort of relaunch, but at this point I really don't think it's some sort of modern reboot.
This is really a bummer for game preservation. Also a bummer as a person who just likes weird obscure games.
#Cookie's Bustle#there are still some pages like the wikipedia up but everything that has either distributing power or videos has been thoroughly scrubbed#I'm pretty sure Cookie's Bustle still lives on through torrenting and P2P sharing since that's a lot harder to enforce copyrights with#due to the nature of the beast with regards to how that works#but the downside is that you run the risks associated with torrenting stuff if you do decide to get the game through those avenues#it's either that or the case of ''well I know a guy who's got it'' and direct sharing of files which is it's own can of worms#just sad about it since i'm trying to find the vinesauce vod of it for archival write up purposes and it's legitimately real hard to find#since it seems like writing about the game itself doesn't cause a DMCA Takedown these days#and that the copyright troll is now solely targeting gameplay footage as well as file distribution#since websites discussing the game but not distributing it (eg wikipedia & mobygames) still have their pages up
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
tiny PSA for trolls fanfic writers who are making (or have made) the move from wattpad to AO3
referring to your fics as "books" is a dead giveaway that you came from wattpad
#its not inherently a bad thing. i personally find it kind of endearing#but wattpad does have a bit of a reputation#and so some readers might avoid your fics if they can tell theyre crossposted / that you're fresh from wattpad#ao3 users just refer to their stories as fics; one-shots (if there arent multiple chapters; or ficlets (<1k words i believe)#trolls#dreamworks trolls#trolls band together#trolls fanfic#anyway ive come across it a couple times now & every time ive been like. should i say something? LMAO#it is ultimately harmless though & if you prefer to call your fics books. by all means go for it#as long as you dont try to actually publish them as books without getting a legal opinion. bc copyright infringement and all that#joon talks
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

On September 22, I'm (virtually) presenting at the DIG Festival in Modena, Italy. On September 27, I'll be at Chevalier's Books in Los Angeles with Brian Merchant for a joint launch for my new book The Internet Con and his new book, Blood in the Machine.

It's been 21 years since Bill Willingham launched Fables, his 110-issue, wide-ranging, delightful and brilliantly crafted author-owned comic series that imagines that the folkloric figures of the world's fairytales are real people, who live in a secret society whose internal struggles and intersections with the mundane world are the source of endless drama.
Fables is a DC Comics title; DC is division of the massive entertainment conglomerate Warners, which is, in turn, part of the Warner/Discovery empire, a rapacious corporate behemoth whose screenwriters have been on strike for 137 days (and counting). DC is part of a comics duopoly; its rival, Marvel, is a division of the Disney/Fox juggernaut, whose writers are also on strike.
The DC that Willingham bargained with at the turn of the century isn't the DC that he bargains with now. Back then, DC was still subject to a modicum of discipline from competition; its corporate owner's shareholders had not yet acquired today's appetite for meteoric returns on investment of the sort that can only be achieved through wage-theft and price-gouging.
In the years since, DC – like so many other corporations – participated in an orgy of mergers as its sector devoured itself. The collapse of comics into a duopoly owned by studios from an oligopoly had profound implications for the entire sector, from comic shops to comic cons. Monopoly breeds monopoly, and the capture of the entire comics distribution system by a single company – Diamond – was attended by the capture of the entire digital comics market by a single company, Amazon, who enshittified its Comixology division, driving creators and publishers into Kindle Direct Publishing, a gig-work platform that replicates the company's notoriously exploitative labor practices for creative workers. Today, Comixology is a ghost-town, its former employees axed in a mass layoff earlier this year:
https://gizmodo.com/amazon-layoffs-comixology-1850007216
When giant corporations effect these mergers, they do so with a kind of procedural kabuki, insisting that they are dotting every i and crossing every t, creating a new legal entity whose fictional backstory is a perfect, airtight bubble, a canon with not a single continuity bug. This performance of seriousness is belied by the behind-the-scenes chaos that these corporate shifts entail – think of the way that the banks that bought and sold our mortgages in the run-up to the 2008 crisis eventually lost the deeds to our houses, and then just pretended they were legally entitled to collect money from us every month – and steal our houses if we refused to pay:
https://www.reuters.com/article/idINIndia-58325420110720
Or think of the debt collection industry, which maintains a pretense of careful record-keeping as the basis for hounding and threatening people, but which is, in reality, a barely coherent trade in spreadsheets whose claims to our money are matters of faith:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/12/do-not-pay/#fair-debt-collection-practices-act
For usury, the chaos is a feature, not a bug. Their corporate strategists take the position that any ambiguity should be automatically resolved in their favor, with the burden of proof on accused debtors, not the debt collectors. The scumbags who lost your deed and stole your house say that it's up to you to prove that you own it. And since you've just been rendered homeless, you don't even have a house to secure a loan you might use to pay a lawyer to go to court.
It's not solely that the usurers want to cheat you – it's that they can make more money if they don't pay for meticulous record-keeping, and if that means that they sometimes cheat us, that's our problem, not theirs.
While this is very obvious in the usury sector, it's also true of other kinds of massive mergers that create unfathomnably vast conglomerates. The "curse of bigness" is real, but who gets cursed is a matter of power, and big companies have a lot more power.
The chaos, in other words, is a feature and not a bug. It provides cover for contract-violating conduct, up to and including wage-theft. Remember when Disney/Marvel stole money from beloved science fiction giant Alan Dean Foster, whose original Star Wars novelization was hugely influential on George Lucas, who changed the movie to match Foster's ideas?
Disney claimed that when it acquired Lucasfilm, it only acquired its assets, but not its liabilities. That meant that while it continued to hold Foster's license to publish his novel, they were not bound by an obligation to pay Foster for this license, since that liability was retained by the (now defunct) original company:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/04/30/disney-still-must-pay/#pay-the-writer
For Disney, this wage-theft (and many others like it, affecting writers with less fame and clout than Foster) was greatly assisted by the chaos of scale. The chimera of Lucas/Disney had no definitive responsible party who could be dragged into a discussion. The endless corporate shuffling that is normal in giant companies meant that anyone who might credibly called to account for the theft could be transfered or laid off overnight, with no obvious successor. The actual paperwork itself was hard for anyone to lay hands on, since the relevant records had been physically transported and re-stored subsequent to the merger. And, of course, the company itself was so big and powerful that it was hard for Foster and his agent to raise a credible threat.
I've experienced versions of this myself: every book contract I've ever signed stipulated that my ebooks could not be published with DRM. But one of my publishers – a boutique press that published my collection Overclocked – collapsed along with most of its competitors, the same week my book was published (its distributor, Publishers Group West, went bankrupt after its parent company, Advanced Marketing Services, imploded in a shower of fraud and criminality).
The publisher was merged with several others, and then several more, and then several more – until it ended up a division of the Big Five publisher Hachette, who repeatedly, "accidentally" pushed my book into retail channels with DRM. I don't think Hachette deliberately set out to screw me over, but the fact that Hachette is (by far) the most doctrinaire proponent of DRM meant that when the chaos of its agglomerated state resulted in my being cheated, it was a happy accident.
(The Hachette story has a happy ending; I took the book back from them and sold it to Blackstone Publishing, who brought out a new expanded edition to accompany a DRM-free audiobook and ebook):
https://www.blackstonepublishing.com/overclocked-bvej.html
Willingham, too, has been affected by the curse of bigness. The DC he bargained with at the outset of Fables made a raft of binding promises to him: he would have approval over artists and covers and formats for new collections, and he would own the "IP" for the series, meaning the copyrights vested in the scripts, storylines, characters (he might also have retained rights to some trademarks).
But as DC grew, it made mistakes. Willingham's hard-fought, unique deal with the publisher was atypical. A giant publisher realizes its efficiencies through standardized processes. Willingham's books didn't fit into that standard process, and so, repeatedly, the publisher broke its promises to him.
At first, Willingham's contacts at the publisher were contrite when he caught them at this. In his press-release on the matter, Willingham calls them "honest men and women of integrity [who] interpreted the details of that agreement fairly and above-board":
https://billwillingham.substack.com/p/willingham-sends-fables-into-the
But as the company grew larger, these counterparties were replaced by corporate cogs who were ever-more-distant from his original, creator-friendly deal. What's more, DC's treatment of its other creators grew shabbier at each turn (a dear friend who has written for DC for decades is still getting the same page-rate as they got in the early 2000s), so Willingham's deal grew more exceptional as time went by. That meant that when Willingham got the "default" treatment, it was progressively farther from what his contract entitled him to.
The company repeatedly – and conveniently – forgot that Willingham had the final say over the destiny of his books. They illegally sublicensed a game adapted from his books, and then, when he objected, tried to make renegotiating his deal a condition of being properly compensated for this theft. Even after he won that fight, the company tried to cheat him and then cover it up by binding him to a nondisclosure agreement.
This was the culmination of a string of wage-thefts in which the company misreported his royalties and had to be dragged into paying him his due. When the company "practically dared" Willingham to sue ("knowing it would be a long and debilitating process") he snapped.
Rather than fight Warner, Willingham has embarked on what JWZ calls an act of "absolute table-flip badassery" – he has announced that Fables will hereafter be in the public domain, available for anyone to adapt commercially, in works that compete with whatever DC might be offering.
Now, this is huge, and it's also shrewd. It's the kind of thing that will bring lots of attention on Warner's fraudulent dealings with its creative workforce, at a moment where the company is losing a public relations battle to the workers picketing in front of its gates. It constitutes a poison pill that is eminently satisfying to contemplate. It's delicious.
But it's also muddy. Willingham has since clarified that his public domain dedication means that the public can't reproduce the existing comics. That's not surprising; while Willingham doesn't say so, it's vanishingly unlikely that he owns the copyrights to the artwork created by other artists (Willingham is also a talented illustrator, but collaborated with a who's-who of comics greats for Fables). He may or may not have control over trademarks, from the Fables wordmark to any trademark interests in the character designs. He certainly doesn't have control over the trademarked logos for Warner and DC that adorn the books.
When Willingham says he is releasing the "IP" to his comic, he is using the phrase in its commercial sense, not its legal sense. When business people speak of "owning IP," they mean that they believe they have the legal right to control the conduct of their competitors, critics and customers:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
The problem is that this doesn't correspond to the legal concept of IP, because IP isn't actually a legal concept. While there are plenty of "IP lawyers" and even "IP law firms," there is no "IP law." There are many laws that are lumped together under "IP," including the big three (trademark, copyright and patent), but also a bestiary of obscure cousins and subspecies – trade dress, trade secrecy, service marks, noncompetes, nondisclosues, anticirumvention rights, sui generis "neighboring rights" and so on.
The job of an "IP lawyer" is to pluck individual doctrines from this incoherent scrapheap of laws and regulations and weave them together into a spider's web of tripwires that customers and critics and competitors can't avoid, and which confer upon the lawyer's client the right to sue for anything that displeases them.
When Willingham says he's releasing Fables into the public domain, it's not clear what he's releasing – and what is his to release. In the colloquial, business sense of "IP," saying you're "releasing the IP" means something like, "Feel free to create adaptations from this." But these adaptations probably can't draw too closely on the artwork, or the logos. You can probably make novelizations of the comics. Maybe you can make new comics that use the same scripts but different art. You can probably make sequels to, or spinoffs of, the existing comics, provided you come up with your own character designs.
But it's murky. Very murky. Remember, this all started because Willingham didn't have the resources or patience to tangle with the rabid attack-lawyers Warners keeps kenneled on its Burbank lot. Warners can (and may) release those same lawyers on you, even if you are likely to prevail in court, betting that you – like Willingham – won't have the resources to defend yourself.
The strange reality of "IP" rights is that they can be secured without any affirmative step on your part. Copyrights are conjured into existence the instant that a new creative work is fixed in a tangible medium and endure until the creator's has been dead for 70 years. Common-law trademarks gradually come into definition like an image appearing on photo-paper in a chemical soup, growing in definition every time they are used, even if the mark's creator never files a form with the USPTO.
These IP tripwires proliferate in the shadows, wherever doodles are sketched on napkins, wherever kindergartners apply finger-paint to construction-paper. But for all that they are continuously springing into existence, and enduring for a century or more, they are absurdly hard to give away.
This was the key insight behind the Creative Commons project: that while the internet was full of people saying "no copyright" (or just assuming the things they posted were free for others to use), the law was a universe away from their commonsense assumptions. Creative Commons licenses were painstakingly crafted by an army of international IP lawyers who set out to turn the normal IP task on its head – to create a legal document that assured critics, customers and competitors that the licensor had no means to control their conduct.
20 years on, these licenses are pretty robust. The flaws in earlier versions have been discovered and repaired in subsequent revisions. They have been adapted to multiple countries' legal systems, allowing CC users to mix-and-match works from many territories – animating Polish sprites to tell a story by a Canadian, set to music from the UK.
Willingham could clarify his "public domain" dedication by applying a Creative Commons license to Fables, but which license? That's a thorny question. What Willingham really wants here is a sampling license – a license that allows licensees to take some of the elements of his work, combine them with other parts, and make something new.
But no CC license fits that description. Every CC license applies to whole works. If you want to license the bass-line from your song but not the melody, you have to release the bass-line separately and put a CC license on that. You can't just put a CC license on the song with an asterisked footnote that reads "just the bass, though."
CC had a sampling license: the "Sampling Plus 1.0" license. It was a mess. Licensees couldn't figure out what parts of works they were allowed to use, and licensors couldn't figure out how to coney that. It's been "retired."
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/sampling+/1.0/
So maybe Willingham should create his own bespoke license for Fables. That may be what he has to do, in fact. But boy is that a fraught business. Remember the army of top-notch lawyers who created the CC licenses? They missed a crucial bug in the first three versions of the license, and billions of works have been licensed under those earlier versions. This has enabled a mob of crooked copyleft trolls (like Pixsy) to prey on the unwary, raking in a fortune:
https://doctorow.medium.com/a-bug-in-early-creative-commons-licenses-has-enabled-a-new-breed-of-superpredator-5f6360713299
Making a bug-free license is hard. A failure on Willingham's part to correctly enumerate or convey the limitations of such a license – to list which parts of Fables DC might sue you for using – could result in downstream users having their hard work censored out of existence by legal threats. Indeed, that's the best case scenario – defects in a license could result in downstream users, their collaborators, investors, and distributors being sued for millions of dollars, costing them everything they have, up to and including their homes.
Which isn't to say that this is dead on arrival – far from it! Just that there is work to be done. I can't speak for Creative Commons (it's been more than 20 years since I was their EU Director), but I'm positive that there are copyfighting lawyers out there who'd love to work on a project like this.
I think Willingham is onto something here. After all, Fables is built on the public domain. As Willingham writes in his release: "The current laws are a mishmash of unethical backroom deals to keep trademarks and copyrights in the hands of large corporations, who can largely afford to buy the outcomes they want."
Willingham describes how his participation in the entertainment industry has made him more skeptical of IP, not less. He proposes capping copyright at 20 years, with a single, 10-year extension for works that are sold onto third parties. This would be pretty good industrial policy – almost no works are commercially viable after just 14 years:
https://rufuspollock.com/papers/optimal_copyright.pdf
But there are massive structural barriers to realizing such a policy, the biggest being that the US had tied its own hands by insisting that long copyright terms be required in the trade deals it imposed on other countries, thereby binding itself to these farcically long copyright terms.
But there is another policy lever American creators can and should yank on to partially resolve this: Termination. The 1976 Copyright Act established the right for any creator to "terminate" the "transfer" of any copyrighted work after 30 years, by filing papers with the Copyright Office. This process is unduly onerous, and the Authors Alliance (where I'm a volunteer advisor) has created a tool to simplify it:
https://www.authorsalliance.org/resources/rights-reversion-portal/
Termination is deliberately obscure, but it's incredibly powerful. The copyright scholar Rebecca Giblin has studied this extensively, helping to produce the most complete report on how termination has been used by creators of all types:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/10/04/avoidance-is-evasion/#reverted
Writers, musicians and other artists have used termination to unilaterally cancel the crummy deals they had crammed down their throats 30 years ago and either re-sell their works on better terms or make them available directly to the public. Every George Clinton song, every Sweet Valley High novel, and the early works of Steven King have all be terminated and returned to their creators.
Copyright termination should and could be improved. Giblin and I wrote a whole-ass book about this and related subjects, Chokepoint Capitalism, which not only details the scams that writers like Willingham are subject to, but also devotes fully half its length to presenting detailed, technical, shovel-ready proposals for making life better for creators:
https://chokepointcapitalism.com/
Willingham is doing something important here. Larger and larger entertainment firms offer shabbier and shabbier treatment to creative workers, as striking members of the WGA and SAG-AFTRA can attest. Over the past year, I've seen a sharp increase in the presence of absolutely unconscionable clauses in the contracts I'm offered by publishers:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/06/27/reps-and-warranties/#i-agree
I'm six months into negotiating a contract for a 300 word piece I wrote for a magazine I started contributing to in 1992. At issue is that they insist that I assign film rights and patent rights from my work as a condition of publication. Needless to say, there are no patentable inventions nor film ideas in this article, but they refuse to vary the contract, to the obvious chagrin of the editor who commissioned me.
Why won't they grant a variance? Why, they are so large – the magazine is part of a global conglomerate – that it would be impractical for them to track exceptions to this completely fucking batshit clause. In other words: we can't strike this batshit clause because we decided that from now on, all out contracts will have batshit clauses.
The performance of administrative competence – and the tactical deployment of administrative chaos – among giant entertainment companies is grotesque, but every now and again, it backfires.
That's what's happening at Marvel right now. The estates of Marvel founder Stan Lee and its seminal creator Steve Ditko are suing Marvel to terminate the transfer of both creators' characters to Marvel. If they succeed, Marvel will lose most of its most profitable characters, including Iron Man:
https://www.reuters.com/legal/marvel-artists-estate-ask-pre-trial-wins-superhero-copyright-fight-2023-05-22/
They're following in the trail of the Jack Kirby estate, whom Marvel paid millions to rather than taking their chances with the Supreme Court.
Marvel was always an administrative mess, repeatedly going bankrupt. Its deals with its creators were indifferently papered over, and then Marvel lost a lot of the paperwork. I'd bet anything that many of the key documents Disney (Marvel's owner) needs to prevail over Lee and Ditko are either unlocatable or destroyed – or never existed in the first place.
A more muscular termination right – say, one that kicks in after 20 years, and is automatic – would turn circuses like Marvel-Lee/Ditko into real class struggles. Rather than having the heirs of creators reaping the benefit of termination, we could make termination into a system for getting creators themselves paid.
In the meantime, there's Willingham's "absolute table-flip badassery."



If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/15/fairy-use-tales/#sampling-license

Image: Tom Mrazek (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:An_Open_Field_%2827220830251%29.jpg
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en
--
Penguin Random House (modified) https://www.penguinrandomhouse.com/books/707161/fables-20th-anniversary-box-set-by-bill-willingham/
Fair use https://www.eff.org/issues/intellectual-property
#pluralistic#fables#comics#graphic novels#dc#warner#monopoly#publishing#chokepoint capitalism#poison pills#ip#bill willingham#public domain#copyright#copyfight#creative commons#licenses#copyleft trolls
242 notes
·
View notes
Text
I ALMOST LOST MY SHIT i saw a brozone shirt and thought it was a staff shirt like the one i wanna make
#BC THE FRONT IS JUST THE BROZONE LOGO#it has tour locations on the back though#i DO think though that means the brozone logo is prolly copyrighted :[#sketch speaks#trolls
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
also re: that last post i reblogged i think back to when i was on deviantart as a kid and since the entry bar for that site was so low you'd get a lot of children and extremely amateur artists who didn't really know how to use anything other than the circle tool in ms paint and if there's one thing i learned from spending so much time on there it's that people will take the time to steal or edit your work regardless of your perceived skill level because to them it's the best thing ever made, and there's a lot of people who would pretend to be an art thief with stolen and edited work not only to undermine someone else's time and effort, but to explicitly make fun of them for the content of their work (early 2010s, so punching down at children having fun online was a legitimate pastime for a lot of people) and it's a reminder for literally anyone considering posting their art online that it doesn't matter what you're doing or how "good" someone thinks your art is that you lose absolutely nothing by doing anything you can to protect it. "nobody's ever going to steal that" isn't justified given that even if someone doesn't think it's good enough to lift, someone is going to think it's bad enough to make fun of through the avenue of "ironic" art theft and that's just as fucking awful
#literally had my art stolen and edited so many times on troll repost accounts on dA who would pretend to be a young kid#who knew nothing about art etiquette or copyright law or what constituted theft#who just 'ironically' stole me and my friends' art because we were convenient targets on account of making sonic ocs#was literally just admittance that people thought our art was totally fucking worthless because it wasn't high brow#all this to say that no matter what you're making you're justified in doing what you fucking want to keep your art safe#i get so tired of this victim blamey shit just because You don't think it's a discussion worth having
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yeah, obviously this isn't allowed. That doesn't mean they aren't trying.
"Disney isn't legally allowed to make this claim" is NOT the same thing as "Disney is not making this claim," so you can shove your "fact check" up M*ckey's ass
They've tried this shit before, it failed then, & it'll probably fail now, but that doesn't mean it's not bad & it doesn't mean it's not happening
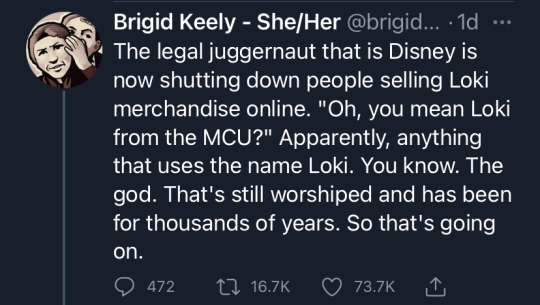

#one of these days their copyright trolling will probably work#i don't think itll be today#but we cant just hide behind the liberal assumption that companies cant do something just because some law somewhere says they cant#& im pissed at the way the fact check is worded#they demonstrate why its an invalid claim#& they mention the other invalid claims disney has made in the past#& then they just kinda assume it must be fake because the claim is clearly invalid?#fact checking these days really fucking sucks#they present the facts & then just draw whatever conclusion fits their political agenda#(in this case the complacent liberal assumption that no company would ever do something stupid or illegal)#fuck disney#norse paganism
69K notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy Birthday
Warner sued the Girlscouts of America and extorted several million dollars through shitty lawsuits. All the copyright trolling is finally over. The birthday song is public domain. https://www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/happy-birthday-officially-public-domain-180956740/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Warner_Chappell_Music
Posted using PostyBirb
0 notes
Text

why do i gotta put in my full name and address to report to twitch that this random motherfucker does NOT own the Sonic 1 soundtrack?? why can i not report at all on youtube because they only have options for if YOUR content was stolen?? What the FUCK is wrong with this system???
#priere's ramblings#sonic the hedgehog#copyright#apparently 'no copyright law in the universe will stop me' is a fuckin LIE#this system's busted#ABOLISH NOW#copyright trolls get the rope
0 notes