#cloud native
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Top Platform Engineering Practices for Scalable Applications

In today’s digital world, scalability is a crucial attribute for any platform. As businesses grow and demands change, building a platform that can adapt and expand is essential. Platform engineering practices focus on creating robust, flexible systems. These systems not only perform underload but also evolve with emerging technologies. Here are some top practices to ensure your applications remain scalable and efficient.
1. Adopt a Microservices Architecture
A microservices architecture breaks down a monolithic application into smaller, independent services that work together. This approach offers numerous benefits for scalability:
Independent Scaling: Each service can be scaled separately based on demand. This ensures efficient resource utilization.
Resilience: Isolated failures in one service do not bring down the entire application. This improves overall system stability.
Flexibility: Services can be developed, deployed, and maintained using different technologies. This allows teams to choose the best tools for each job.
2. Embrace Containerization and Orchestration
Containerization, with tools like Docker, has become a staple in modern platform engineering. Containers package applications with all their dependencies. This ensures consistency across development, testing, and production environments. Orchestration platforms like Kubernetes further enhance scalability by automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. This combination allows for rapid, reliable scaling. It alsod helps maintain high availability.
3. Leverage Cloud-Native Technologies
Cloud-native solutions are designed to exploit the full benefits of cloud computing. This includes utilizing Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools such as Terraform or CloudFormation to automate the provisioning of infrastructure. Cloud platforms offer dynamic scaling, robust security features, and managed services that reduce operational complexity. Transitioning to cloud-native technologies enables teams to focus on development. Meanwhile, underlying infrastructure adapts to workload changes.
4. Implement Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
A robust CI/CD pipeline is essential for maintaining a scalable platform. Continuous integration ensures that new code changes are automatically tested and merged. This reduces the risk of integration issues. Continuous deployment, on the other hand, enables rapid, reliable releases of new features and improvements. By automating testing and deployment processes, organizations can quickly iterate on their products. They can also respond to user demands without sacrificing quality or stability.
5. Monitor, Analyze, and Optimize
Scalability isn’t a one-time setup—it requires continuous monitoring and optimization. Implementing comprehensive monitoring tools and logging frameworks is crucial for:
tracking application performance,
spotting bottlenecks, and
identifying potential failures.
Metrics such as response times, error rates, and resource utilization provide insights that drive informed decisions on scaling strategies. Regular performance reviews and proactive adjustments ensure that the platform remains robust under varying loads.
6. Focus on Security and Compliance
As platforms scale, security and compliance become increasingly complex yet critical. Integrating security practices into every stage of the development and deployment process—often referred to as DevSecOps—helps identify and mitigate vulnerabilities early. Automated security testing and regular audits ensure that the platform not only scales efficiently but also maintains data integrity and compliance with industry standards.
Scalable applications require thoughtful platform engineering practices that balance flexibility, efficiency, and security. What happens when organizations adopt a microservices architecture, embrace containerization and cloud-native technologies, and implement continuous integration and monitoring? Organizations can build platforms capable of handling growing user demands. These practices streamline development and deployment. They also ensure that your applications are prepared for the future.
Read more about how platform engineering powers efficiency and enhances business value.
#cicd#cloud native#software development#software services#software engineering#it technology#future it technologies
0 notes
Text
Simplifying Hybrid Cloud Management with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes
In today's dynamic IT landscape, organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to achieve greater flexibility, scalability, and resilience. However, managing Kubernetes clusters across diverse environments—on-premises data centers, public clouds, and edge locations—presents significant challenges. This complexity can lead to operational overhead, security vulnerabilities, and inconsistent application deployments. This is where Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes (ACM) steps in, offering a centralized and streamlined approach to hybrid cloud management.
The Challenges of Hybrid Cloud Kubernetes Management:
Managing multiple Kubernetes clusters in a hybrid cloud environment can quickly become overwhelming. Some key challenges include:
Inconsistent Configurations: Maintaining consistent configurations across different clusters can be difficult, leading to inconsistencies in application deployments and potential security risks.
Visibility and Control: Gaining a unified view of all clusters and their health can be challenging, hindering effective monitoring and troubleshooting.
Security and Compliance: Enforcing consistent security policies and ensuring compliance across all environments can be complex and time-consuming.
Application Lifecycle Management: Deploying, updating, and managing applications across multiple clusters can be cumbersome and error-prone.
How Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management Simplifies Hybrid Cloud Management:
Red Hat ACM provides a comprehensive solution for managing the entire lifecycle of Kubernetes clusters across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. It offers several key features that simplify management and improve operational efficiency:
Centralized Management: ACM provides a single console for managing all your Kubernetes clusters, regardless of where they are deployed. This centralized view simplifies operations and provides consistent control.
Policy-Based Governance: ACM allows you to define and enforce consistent policies across all your clusters, ensuring compliance with security and regulatory requirements.
Application Lifecycle Management: ACM simplifies the deployment, updating, and management of applications across multiple clusters, streamlining the application lifecycle.
Cluster Lifecycle Management: ACM streamlines the creation, scaling, and deletion of Kubernetes clusters, simplifying infrastructure management.
Observability and Monitoring:��ACM provides comprehensive monitoring and observability capabilities, giving you insights into the health and performance of your clusters and applications.
GitOps Integration: ACM integrates with GitOps workflows, enabling declarative infrastructure and application management for improved automation and consistency.
Key Benefits of Using Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management:
Reduced Operational Overhead: By centralizing management and automating key tasks, ACM reduces the operational burden on IT teams.
Improved Security and Compliance: Policy-based governance ensures consistent security and compliance across all environments.
Faster Application Deployments: Streamlined application lifecycle management accelerates time to market for new applications.
Increased Agility and Flexibility: ACM enables organizations to quickly adapt to changing business needs by easily managing and scaling their Kubernetes infrastructure.
Enhanced Visibility and Control: Centralized monitoring and observability provide a clear view of the health and performance of all clusters and applications.
Use Cases for Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management:
Hybrid Cloud Deployments: Managing Kubernetes clusters across on-premises data centers and public clouds.
Multi-Cloud Deployments: Managing Kubernetes clusters across multiple public cloud providers.
Edge Computing: Managing Kubernetes clusters deployed at the edge of the network.
DevOps and CI/CD: Automating the deployment and management of applications in a CI/CD pipeline.
Conclusion:
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes is a powerful tool for simplifying the complexities of hybrid cloud Kubernetes management. By providing centralized management, policy-based governance, and automated workflows, ACM empowers organizations to effectively manage their Kubernetes infrastructure and accelerate their cloud-native journey. If you're struggling to manage your Kubernetes clusters across multiple environments, Red Hat ACM is a solution worth exploring.
Ready to simplify your hybrid cloud Kubernetes management?
Contact Hawkstack Technologies today to learn more about Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management and how we can help you implement it in your environment. www.hawkstack.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cloud Native is a software development method that involves the use of cloud computing principles to create and operate scalable applications. It focuses on deploying apps in flexible environments like public, private, and hybrid clouds. Cloud Native applications are designed for efficiency, resilience, and easy scaling.
0 notes
Text
The Serverless Development Dilemma: Local Testing in a Cloud-Native World
Picture this: You’re an AWS developer, sitting in your favorite coffee shop, sipping on your third espresso of the day. You’re working on a cutting-edge serverless application that’s going to revolutionize… well, something. But as you try to test your latest feature, you realize you’re caught in a classic “cloud” vs “localhost” conundrum. Welcome to the serverless development dilemma! The…
#AWS DevOps#AWS Lambda#CI/CD#Cloud Native#Developer Productivity#GitLab CI#Microservices#serverless#Terraform State
0 notes
Text
Cloud Native Architecture book
Its a busy time with books at the moment. I am excited to and pleased to hear that Fernando Harris‘ first book project has been published. It can be found on amazon.com and amazon.co.uk among sites. Having been fortunate enough to be a reviewer of the book, I can say that what makes this book different from others that examine cloud-native architecture is its holistic approach to the challenge.…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
As businesses evolve, traditional monolithic applications become extremely difficult to scale, maintain, and deploy.
Changing even a small part of the application demands rebuilding and revamping the total architecture, resulting in longer development cycles, operational bottlenecks, and system downtimes.
By embracing modern-day microservices architecture, you can break free from these constraints and unlock new possibilities. By splitting the total application into small, independent services that communicate via APIs, you can:
Scale individual services independently
Deploy new features & updates quickly
Isolate bugs and errors effectively
Improve team productivity
#CloudComputing #MicroservicesAdvantages #ScalabilityInTheCloud #EfficiencyAndFlexibility #CostEffectiveSolutions #CloudNativeArchitecture #DigitalTransformation #InnovationInTechnology #ModernizingInfrastructure #BusinessAgility #benefitsofmicroservices
#microservices#benefits of microservices#cloud native#cloud native technologies#containers and kubernetes
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cloud native deals with building, deploying, and managing modern applications in cloud computing environments to fully benefit from the scalability, flexibility, and efficiency provided by the cloud.
#Cloud Native Applications Market#Cloud Native Applications#Cloud Native#Native Applications Market#Applications Market
0 notes
Text

"Learn effective resource management and scaling techniques in Kubernetes to optimize your containerized applications."
Visit us at https://www.fiorano.com/
0 notes
Text

The business sector did its best to adapt as the past two years delivered many spontaneous twists and turns. In the face of a global pandemic, offices all around the world hastily put together remote work policies. Businesses will continue to employ a mixed workforce model since many have discovered that remote labor increases flexibility and lowers overhead. 63% of rapidly expanding companies have already embraced a hybrid business model.
#cloud managed services#cloud native#cloud native app development#cloud computing#cloud native development
0 notes
Text
#cloud engineering services#cloud engineering#internet of things#cloud platform#software for services#cloud services#cloud app#cloud application#cloud native#ascendion#Nitor infotech
0 notes
Text
Seven Models of Cloud Native Applications
Introduction In today’s cloud-driven landscape, organizations are transitioning from legacy monolithic systems to agile, scalable, and secure cloud-native solutions. Some are even forging new cloud-native applications. However, the concept of cloud-native design remains subjective, lacking a universal blueprint. This blog aims to provide clarity and guidance for designing precise cloud-native…
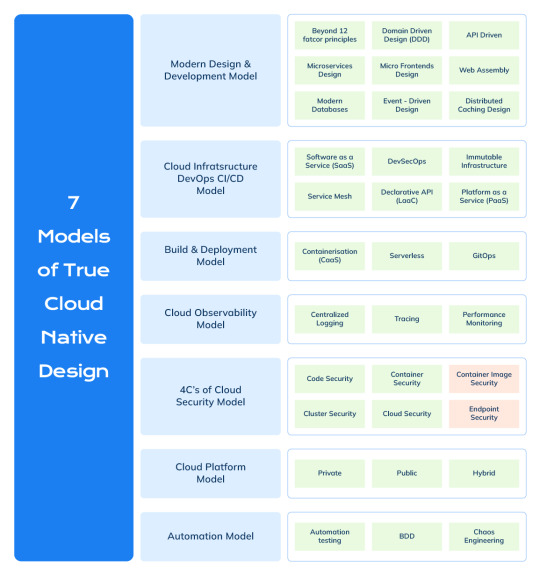
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text

Cloud-native approach aims to build applications based on cloud, leveraging various tools provided by the cloud provider. DevOps automates development and operations synergy, a cornerstone for successful cloud-native adoption.
#digital transformation#technology#tech#it consulting#it services#mobile app developers#software development#cloud transformation#cloud adoption#cloud computing#cloud native#devops#resilient applications#cloud technology
0 notes
Text
Serverless is a direction, not a destination
Functions are not the point
Managed services are not the point
Ops is not the point
Cost is not the point
Code is not the point
Technology is not the point
The point is focus Serverless is a way to focus on business value.
0 notes
Text
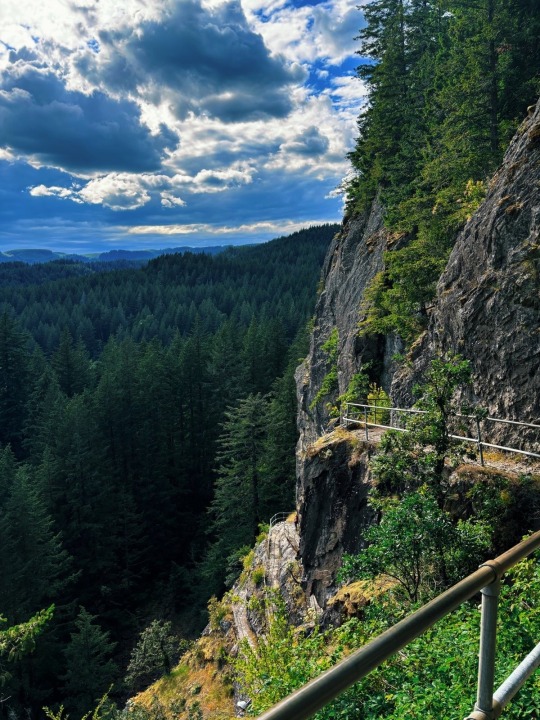
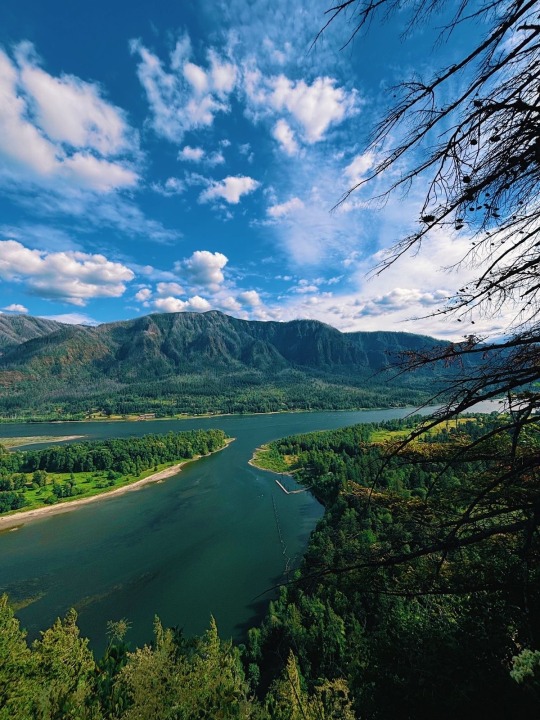
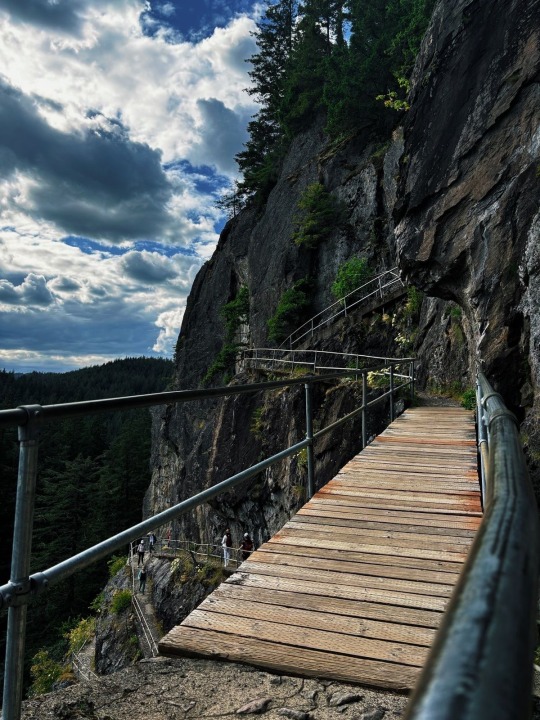
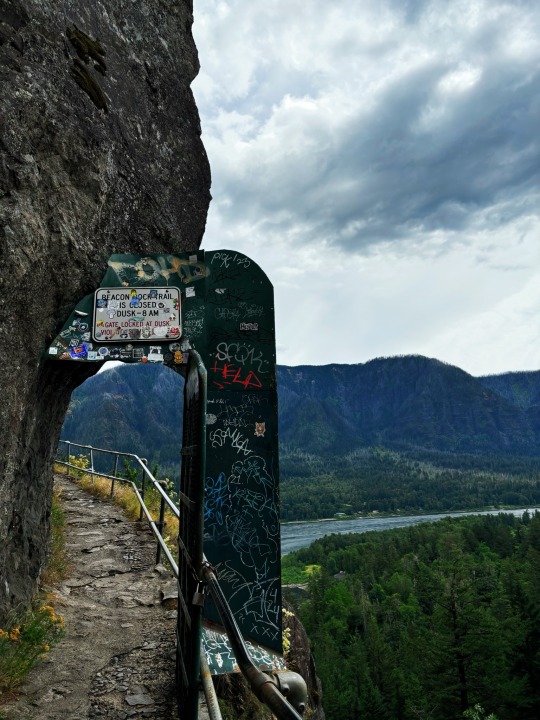




Day hike grid
Lava plug rock formation 🪨
#photography#nature#pnw photography#my post#beautiful#nature photography#travel#naturecore#nature hikes#hike#hiking#travelcore#travel the world#sunny day#summer#vacation#washington#canada#pnw native plants#river#fairy aesthetic#fairycore#trees and forests#trees#moss#rock formations#the great pnw#green#watercore#clouds
852 notes
·
View notes