#borrow equity
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Have had a wet basement pretty much since I moved into this house it’s been a problem. A problem that was… quite downplayed by the sellers.
The north wall of my basement is bulging inward which concerns me and I have someone who is coming to look at it today.
I’m scared of the Implications
#homeownership#is not always awesome#especially when you could never possibly fathom having the money to actually deal with a problem of this magnitude#all I’ve got is the equity in my house which I can borrow against but again#I certainly don’t need to be paying what would probably be two mortgage payments
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Get a Digital Loan Against Shares or Mutual Funds Without Income Proof in 2025

Imagine getting access to instant funds without selling your investments. In 2025, it's not just possible—it's easier and smarter than ever. With a rise in digital lending and paperless approvals, a securities-backed loan has become a go-to solution for quick financing needs without liquidating your valuable portfolio.
Whether you want to handle a personal emergency, business shortfall, or just need working capital, loans against shares or mutual funds are proving to be one of the most efficient ways to raise instant funds, without affecting your long-term wealth creation.
What Is a Securities-Backed Loan?
A securities-backed loan (LAS) is a type of secured credit where you pledge financial securities—like mutual funds or shares—to borrow money. These loans work like overdraft or term loans, where your investments act as collateral, and you can continue to enjoy the benefits of your holdings (like dividends or NAV appreciation).
Why Choose a Loan Against Mutual Funds or Shares in 2025?
The financial world is rapidly moving toward convenience and flexibility. Here’s why more Indians are opting to borrow against a mutual fund portfolio or shares:
No need to break your investments or exit long-term plans.
Instant digital approval with minimal documentation.
Competitive interest rates due to secured nature.
Continue earning returns on pledged securities.
Eligibility Criteria for Loan Against Mutual Funds or Shares
Not everyone qualifies for a loan automatically. Here’s the general eligibility criteria for mutual fund loan in 2025:

Loan Facility Against Equity Shares vs Mutual Funds
You can pledge either equity shares or mutual funds, depending on your portfolio. Let’s look at the mutual fund loan interest rates comparison with share-backed loan interest rates:
Comparison Table: Loan Against Shares vs Loan Against Mutual Funds

Whether you prefer a loan facility against equity shares or mutual funds, your decision should depend on which asset gives you higher eligibility, better interest, and suits your repayment ability.
Understanding Interest Rates on Pledged Securities in 2025
As these loans are secured, interest rates on pledged securities tend to be lower than personal loans or credit card debt. The average ranges are:
Mutual Funds: 9% to 11.5%
Equity Shares: 9.5% to 12%
Digital platforms often offer better online mutual fund loan rates than traditional banks, especially if the process is automated through CAMS, KFintech, or NSDL.
Tip: Always compare rates and charges between lenders using a reliable mutual fund loan interest comparison tool before deciding.
Instant Loan on Mutual Funds Online – How It Works
The rise of instant loans on mutual funds online in 2025 has changed how quickly borrowers can access cash. Here's how the typical digital process works:
Select Lender or Platform (Bank, NBFC, Fintech like Groww, Paytm Money)
Login Using PAN/Aadhaar
Verify Portfolio via CAMS or KFintech
Choose Amount to Borrow
E-sign Agreement & Set Repayment Terms
Funds Disbursed Instantly to your bank account
This setup works similarly for the mutual fund overdraft facility, where a limit is assigned, and interest is charged only on the amount used.
Key Things to Consider Before You Borrow
Before you opt for any kind of loan against mutual funds or shares, keep these points in mind:
Volatility Risk: If your pledged assets drop in value, you may be asked to top up the collateral or face liquidation.
Tenure & Repayment: Choose the shortest possible term you can repay comfortably to save on interest.
Hidden Fees: Watch for processing charges, annual maintenance fees, or foreclosure penalties.
Compare Providers: Use platforms that allow real-time mutual fund loan interest comparison.
Real Use Case: Why Raj Preferred a Loan Against Mutual Funds
Raj, a 34-year-old marketing professional in Bangalore, faced a sudden home repair bill of ₹2.5 lakhs. Instead of using a credit card or breaking his SIPs, he chose to borrow against his mutual fund portfolio online.
He got approval in minutes, no income proof required, and the online mutual fund loan rate was only 9.5%—far better than personal loan options.
Top Banks & Fintech Platforms Offering LAS in 2025
HDFC Bank – Loans against Shares & Mutual Funds
ICICI Bank – Instant overdraft facility for MFs
Axis Bank – Digital LAS through Demat
Bajaj Finserv – Quick digital approval, flexible tenure
Groww / Paytm Money – Fully digital mutual fund-backed loans
Conclusion: Smart Credit Using What You Already Own
A securities-backed loan isn’t just a backup anymore—it’s a smart, proactive financial tool in 2025. Whether you’re self-employed, salaried, or even a freelancer, you can tap into your wealth without disturbing your investments.
With flexible tenures, instant digital processes, and lower interest compared to unsecured loans, choosing to borrow against mutual fund portfolio or shares makes perfect sense for short-term liquidity.
Just ensure you evaluate your options well and avoid over-leveraging. Your assets can fund your goals today, while still working for tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can I get a loan against mutual funds without income proof?
Yes. Most digital lenders now provide instant loans on mutual funds online without asking for salary slips or ITR, as the collateral ensures safety.
2. Is the interest rate fixed or floating for mutual fund loans?
It depends on the lender. However, many digital lenders offer a fixed mutual fund overdraft facility with transparent interest rates.
3. How much can I borrow against mutual funds or shares?
Typically 50–70% of the value of your securities, based on the lender’s loan-to-value (LTV) policy.
4. What if the market crashes while my securities are pledged?
The lender may issue a margin call, requiring you to deposit more funds or pledge more securities to cover the shortfall.
5. Are digital loans against mutual funds safe?
Yes. Reputed banks and SEBI-registered NBFCs offer these services securely using CAMS/KFin integration. Just ensure you use trusted platforms.
#securities-backed loan#borrow against mutual fund portfolio#mutual fund loan interest comparison#interest rates on pledged securities#loan facility against equity shares#share-backed loan interest rate#mutual fund overdraft facility#online mutual fund loan rates#instant loan on mutual funds online#eligibility criteria for mutual fund loan
0 notes
Text
💡 How to Fund Your Business Without a Loan: Top Alternative Funding Sources in 2025
You’ve got a business idea or growth plan—but no desire to take on traditional debt. The good news? You’re not alone. More entrepreneurs are exploring how to fund their business without a loan using alternative funding sources that provide flexibility without the burden of monthly repayments.

🔍 Why Look for Business Funding Without a Loan?
Loans come with strict requirements, interest payments, and pressure to repay—regardless of how your business is performing. Alternative funding gives you options that can be:
More flexible
Less risky
Easier to access
Better aligned with your long-term goals
Google Keyword Used: how to raise capital without borrowing
✅ 10 Best Ways to Fund Your Business Without a Loan
1. Grants for Small Businesses
Grants are essentially free money—no repayment required. Offered by governments, corporations, and nonprofits, they can be highly competitive but worth the effort.
Look into: SBA, state-level grants, private organizations, and women/minority-owned business funds
Search Term: grants for small business 2025
2. Crowdfunding Platforms
Websites like Kickstarter, Indiegogo, and GoFundMe let you raise money by promoting your product or mission to the public. It’s perfect for product-based startups and creative projects.
Offer rewards, early access, or shoutouts in exchange for contributions
Google Keyword: crowdfunding for startups
3. Equity Financing (Angel Investors or Venture Capital)
Rather than borrowing money, equity financing lets you trade ownership for capital. This is ideal for high-growth startups with potential to scale quickly.
Angel investors fund early-stage companies
Venture capitalists invest larger sums in return for equity
Keyword Phrase: equity funding for small businesses
4. Revenue-Based Financing
This model gives you capital upfront in exchange for a percentage of future sales. No interest or fixed payments—just a flexible cut of your revenue.
Ideal for eCommerce, SaaS, or subscription-based businesses
Search Intent: business funding without traditional loans
5. Partner or Co-Founder Contributions
Bring on a strategic partner or co-founder who can contribute capital in exchange for equity or a stake in the business.
Ensure a clear written agreement to avoid future conflict
6. Trade Credit from Suppliers
Instead of upfront payments, ask vendors or suppliers for net-30 or net-60 terms. This allows you to delay payment while generating income.
Google Keyword: alternative ways to finance a business
7. Business Competitions and Pitch Contests
Many cities, universities, and tech incubators offer cash prizes for top business ideas. These competitions also offer networking, PR, and investor exposure.
Examples: Shark Tank-style events, SBA pitch competitions, local chamber of commerce grants
8. Use Personal Assets Strategically
Without taking out a loan, you can self-fund through:
Savings
Retirement accounts (via ROBS – Rollover for Business Startups)
Selling unused assets
Use this with caution and proper planning.
9. Affiliate or Strategic Partnerships
Some companies are willing to fund or provide services in exchange for exclusive distribution rights, joint marketing campaigns, or a percentage of future profits.
🔟 Presales and Pre-Orders
If you're launching a product, sell it before it’s ready. This strategy provides upfront capital, validates your idea, and builds buzz—all without borrowing.
Use landing pages, email campaigns, and influencers to drive interest.
Related Search Term: non-loan ways to start a business
🧠 Bonus Tip: Combine Multiple Funding Sources
There’s no rule that says you need just one funding source. Many successful businesses use a combination of:
Grants
Crowdfunding
Revenue-based financing
Strategic partnerships
This layered approach increases your funding potential without putting all your eggs in one basket.
📉 When to Avoid Loans Completely
Your business has unpredictable cash flow
You want to retain full control (no monthly payments)
You have low or no credit history
You’re in a pre-revenue or idea-only phase
Google Keyword: business funding with no credit check
📌 Final Thoughts: You Don’t Need a Bank to Build a Business
Today, you can fund your business without a loan and still grow with speed and confidence. From grants and crowdfunding to equity and revenue-share models, 2025 offers more funding flexibility than ever before.
Think outside the bank—because the money is out there, and it’s waiting for bold business owners like you.
Need Personal Or Business Funding? Prestige Business Financial Services LLC offer over 30 Personal and Business Funding options to include good and bad credit options. Get Personal Loans up to $100K or 0% Business Lines of Credit Up To $250K. Also credit repair and passive income programs.
Book A Free Consult And We Can Help - https://prestigebusinessfinancialservices.com
Email - [email protected]
🔑 SEO Summary – Keywords Covered:
How to fund your business without a loan
Alternative funding sources
Grants for small business
Crowdfunding for startups
Equity financing
Non-loan business funding
Business funding with no credit check
Alternative ways to finance a business
Need Personal Or Business Funding? Prestige Business Financial Services LLC offer over 30 Personal and Business Funding options to include good and bad credit options. Get Personal Loans up to $100K or 0% Business Lines of Credit Up To $250K. Also credit repair and passive income programs.
Book A Free Consult And We Can Help - https://prestigebusinessfinancialservices.com
Email - [email protected]
Learn More!!
Prestige Business Financial Services LLC
"Your One Stop Shop To All Your Personal And Business Funding Needs"
Website- https://prestigebusinessfinancialservices.com
Email - [email protected]
Phone- 1-800-622-0453
#how to raise capital without borrowing#grants for small business 2025#crowdfunding for startups#equity funding for small businesses#businessfunding#business#entrepreneur
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Avoid Common Pitfalls with Home Equity Lines of Credit
Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs) can be a useful financial tool, offering flexibility and potentially lower interest rates compared to other types of credit. However, they come with their own set of challenges and pitfalls that you should be aware of. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you navigate these issues and use your HELOC wisely.
Understanding a HELOC
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is a revolving credit line secured by your home’s equity. Unlike a traditional loan with fixed payments, a HELOC allows you to borrow up to a certain limit and pay interest only on the amount you borrow.
Pitfall #1: Over-Borrowing
What It Is: It’s tempting to max out your HELOC, especially if you’re facing a significant expense or investment opportunity. However, borrowing more than you need can lead to financial strain.
How to Avoid It: Assess your financial situation carefully before borrowing. Create a budget and determine exactly how much you need. Avoid the temptation to use the full credit limit just because it’s available.
Pitfall #2: Variable Interest Rates
What It Is: Most HELOCs come with variable interest rates, meaning your payments can increase if interest rates rise. This can catch you off guard if you haven’t planned for potential rate hikes.
How to Avoid It: Look for HELOCs with fixed-rate options or consider locking in a portion of your balance at a fixed rate. Regularly review your HELOC terms and stay informed about market interest rates.
Pitfall #3: Impact on Your Home
What It Is: Using your home as collateral means that if you fail to repay the HELOC, you risk foreclosure. This is a serious consequence and should be considered carefully.
How to Avoid It: Only use a HELOC for purposes that add value to your home or improve your financial situation in the long term. Make sure your repayment plan is realistic and fits within your budget.
Pitfall #4: Fees and Charges
What It Is: HELOCs can come with various fees, including annual fees, transaction fees, and early termination fees. These charges can add up and reduce the overall benefit of the line of credit.
How to Avoid It: Carefully review the terms and fees associated with your HELOC. Compare different lenders and choose one with reasonable fees. Keep track of all fees to avoid unexpected costs.
Pitfall #5: Not Having a Repayment Plan
What It Is: Some people use their HELOC without a clear repayment strategy, leading to debt accumulation and financial difficulties.
How to Avoid It: Develop a detailed repayment plan before you take out a HELOC. Factor in your income, expenses, and other debts to ensure you can manage the additional payments. Stick to your plan and adjust it as needed if your financial situation changes.
Pitfall #6: Using HELOC for Everyday Expenses
What It Is: HELOCs are best used for significant expenses or investments rather than everyday costs. Relying on a HELOC for routine expenses can lead to financial instability.
How to Avoid It: Use your HELOC for specific, planned expenses like home improvements or debt consolidation, not for daily living costs. Budget and manage your daily finances separately.
#Home Equity Line of Credit#Financial Planning#Credit Management#Interest Rates#Borrowing Tips#Debt Management#Home Financing
0 notes
Text
"A private equity firm can invest a hundred million dollars to build a steel plant and potentially earn a 7% profit starting in two years, or it can borrow a hundred million dollars and buy an existing company and sell that firm’s real estate immediately and lease it back to the company it just bought while shedding labor contracts in bankruptcy. Which one is a better return on investment?"
-Matt Stoller, explaining how America consciously created an environment hostile to making things; instead, we take things apart for profit, leaving ashes behind. Wall Street, not China, stole America's productive capacity.
675 notes
·
View notes
Text

To all the "Hands Off" Protesters (Democrats):
We are currently at a critical juncture with a national debt of $36.5 trillion, increasing by $2 trillion each year. This is a critical issue, and most experts are warning us that we have relatively few years left to take decisive action before America faces a financial crisis that would have catastrophic consequences for this country and the world.
Amid all your protests, the burning of Teslas, and your petulant vitriol, one crucial element is glaringly missing: any plan to cut government spending. Instead, your goal appears to be to spend even more.
We finally have leaders in President Trump and Elon Musk who are courageous enough to finally focus on sustainable spending practices that are critical to avoid risking our economic future. Time is of the essence—instead of being in the way, let’s act together before it’s too late.
If not...
HANDS OFF - my tax dollars, which were not intended for your pet projects and the corrupt, virtue-signaling Socialists who spew the garbage you all take as gospel. It’s not a slush fund and a money laundering operation through left-wing NGO's to make politicians rich.
HANDS OFF - my child at school. Teach them the basics of reading, writing, and arithmetic. They are not there to be indoctrinated into your Marxist ideologies.
HANDS OFF - trying to force American women and girls to compete against biological men, and then adding insult to injury, forcing them to change and shower in front of them. Stop forcing your fu@ked up theories on the rest of us.
HANDS OFF - all the property you destroy in the name of whatever cause you’re supporting that given week. Other people’s vehicles are not yours to destroy. Neither are statues or all the other s#it you light on fire.
HANDS OFF - our college campuses. Decent kids are there to learn. Free speech is protected. Violence, intimidation, and taking over buildings are not. By the way, if your cause is so just, take off the masks and show yourself. Cowards one and all.
HANDS OFF - our president, who was duly elected to clean up the mess y’all created. We sat by and watched as you supported a puppet who was practically dead. It damn near destroyed the nation. Financially, from a security standpoint, and morally.
HANDS OFF - to all the federal district judges. Your power does not supersede the executive branch. And, stop using Lawfare by going after your political opponents.
HANDS OFF - our ICE Agents, who are taking violent gang bangers out of our country and forcing people who want to come here to do so legally. It should be the only way. Period. End of story.
HANDS OFF - our Free Speech rights. For years, you have used the process of cancelling people who simply wanted to express their own ideas. In your world, you think free speech can only be allowed if it agrees with your screwed up ideologies.
HANDS OFF - the American family. You have done everything possible to destabilize the concept of families because you believe that our ultimate allegiance should be to the government.
HANDS OFF - from imposing your Marxist views of Critical Race Theory (CRT) and the methods you’ve used to implement them through Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI). Most Americans are compassionate individuals who believe in judging people based on their character rather than the color of their skin.
These principles are what the vast majority of Americans voted for.
You don’t like it, be like that slob Rosie O'Donnell and move to Europe, which is being taken over by radical Islam.
So, to borrow your stupid little slogan…. Hands Off...
Love,
MAGA Country...
#politics#us politics#democrats are corrupt#democrats will destroy america#wake up democrats!!#make america great again
351 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Failure of Manufactured Momentum
In 2025, can Hollywood continue with the same old party tricks and expect applause? It’s a question I found myself pondering after stumbling upon an onslaught of post BAFTA social media content where one continuous storyline piqued my interest…and not in a good way.
I don’t usually wade into fandom conversations, but I’ve always had a soft spot for Bridgerton—and Colin and Penelope’s story was my favourite from the books. Beyond that, I’ve kept my distance. I don’t ship actors or keep up with stan drama. But something about this weekend’s BAFTAs, and the very deliberate press rollout that followed, caught my attention. Not just as a viewer, but as someone who’s worked in a corporate public relations adaject role for over a decade and finds the Hollywood machine endlessly fascinating (and completely outdated).
What we’re seeing right now with Luke Newton and Antonia Roumelioti is a textbook example of trying to manufacture momentum when there’s no organic traction to begin with. The cracks are showing. With every single post and article that popped up on my FYP and Instagram feed these past 48 hours, the more I felt like I had a bad case of deja vu. Did I just read the same headline over and over again? Yes…but from different outlets and yet it all felt the same. Interest piqued. Clearly the press kit made the following demands:
Couple Focused; Antonia is to be treated in the headlines with the same level of celebrity as Luke
Curated Images - the same set of approved images over and over again
Approved language. We get it, Antonia is “glamorous”
Ah, manufactured momentum, the Hollywood PR machines old faithful approach when you have nothing of substance. Let’s be honest: Antonia is being positioned as a public figure, but the foundation is incredibly thin. There’s no significant modeling campaign to anchor her in that world. Her dance history, beyond being a teenage contestant on Greece’s Got Talent, hasn’t evolved into any noteworthy professional credits. And as an “influencer,” an angle that feels unconvincing, the aesthetic is curated, sure, but there’s no substance—no strong personal voice, no visible passion, no cultural or philanthropic cause to connect with. The identity being presented is vague, and vague doesn’t hold attention for long. Did it ever?
This isn’t a case of the public being harsh. It’s that there’s nothing anchoring her presence outside of proximity to Luke. And for a rollout to work, there has to be something to build from—an existing spark of interest, a story, something people can latch onto. Right now, that just isn’t there. In PR terms, it’s a classic case of a lack of narrative coherence.
It’s also not helping that the timing feels off. One year out from Bridgerton S3, and Luke’s visibility has been notably muted. While Nicola Coughlan has gone from strength to strength since then, Luke’s career has remained.... steady at best. He’s the only Bridgerton lead with a season of the show not signed to one of the major agencies, and despite being positioned as a romantic lead, his trajectory feels… stalled. So this moment, framed as a kind of visibility push, doesn’t feel rooted in authentic career growth. Instead, it reads as strategy: tie this reveal to a known milestone, hope for carryover attention. The fact that Nicola’s name had to be threaded into nearly every headline surrounding this weekend’s appearance says a lot - borrowed equity. It suggests his team knows he doesn’t generate enough coverage on his own—and that’s a hard truth, but it’s one the public is picking up on.
Unsurprisingly, the reaction has been indifferent at best. Well until it took a turn for the worse. Take the Entertainment Tonight instagram post. When a media push goes a bit too far, it can lead to consequences. Using Nicola’s name here and sidelining her accomplishments to push a couple narrative, well, it was a choice someone made. A bad one at that. Viewers are seeing through the strategy, and instead of buying in, they’re disengaging. That’s the risk when you try to force relevance without real public demand. If anything, this rollout has highlighted just how little genuine excitement there is around either of them right now.
So the question is: where does this go from here? Because from a PR perspective, you can’t build long-term interest on shallow foundations. At some point, there needs to be actual growth—either from Antonia showing a clearer sense of self, or from Luke stepping into a stronger career phase that doesn’t rely on nostalgia or association.
Until then, this push will likely keep feeling exactly as it does now: calculated, hollow, and a little too late.
278 notes
·
View notes
Note
could you tell me what Private Equity is and why it's a bad thing?
Oh man okay first of all I'm pretty sure that only MBAs truly understand private equity, and I'm so far from being an MBA that I don't even file my own taxes, but I'll try to give a really rough explanation.
At the most basic level, a private equity firm is just a business that buys up stock in companies that are not public (not on the stock exchange for people to buy public shares). In practice, these firms are massive, and in 2021 they managed close to 20% of corporate equity in the US. Importantly, that's a MUCH bigger share than it was ten years earlier, and private equity is a fast-growing part of the world market.
Why it's bad is that this sector of investing falls at the juncture of just a lot of loopholes and blind spots in government regulation, allowing these private equity firms to manage the companies they own in very predatory ways.
For example, private equity firm Golden Gate Capital killed Red Lobster. Basically, they bought the company and started stripping it for parts, because their only interest in the companies they buy is investment profit. They don't have any incentive to care about the company's long-term health. The biggest thing they did to Red Lobster was what's called a sale/leaseback. Basically, insofar as I understand it, they sold the real estate the company owned--i.e. the actual restaurants, took the profit from that, and then made Red Lobster pay them to lease the restaurants. Ultimately this proved crippling for Red Lobster, but through evil finance magic and careful corporate structuring, Golden Gate Capital gets the profit, while Red Lobster got all the debt.
Private equity firm KKR is what killed Toys R Us, again with sale/leaseback and other management methods that favor short term profit over long-term viability, like firing people until there isn't enough staff, pushing store credit cards, assorted other bullshit I barely understand.
Basically, private equity is companies that buy up businesses using leveraged funds (borrowed money) and then "strip and flip" them, squeezing as much profit out of them as possible and then dipping out to leave the company to deal with the fallout. A lot of recent major company bankruptcies besides the ones I mention above came on the heels of the company being managed by a private equity firm. JoAnn Fabrics is one of the most recent.
Yeah. That's the best I can do. Basically, it's a very fast-growing sector of vulture capitalism and it's making a small number of people very rich off killing otherwise viable companies that the rest of us plebes liked and wanted to keep.
46 notes
·
View notes
Note
Please tell me more about neighbourhood PMCs in renaissance Italy
It would be my pleasure! (My research into this owes a lot to the excellent Power and Imagination: City-States in Renaissance Italy by Lauro Martines.)

The first thing to note that, unlike the condottieri, these were not private military companies. Rather, the neighborhood military companies (in the sense of a military unit, rather than a profit-making entity) were self-defense organizations formed as part of a centuries-long political struggle for control over the urban commune between the signorile (the urban chivalry)/nobilita (the urban nobility) and the populo (the guilded middle class, who claimed to speak on behalf of "the people").
This conflict followed much the same logic that had given rise to the medieval commune in the first place. Legally, the communes had started as mutual defense pacts between the signorile and the cives (the free citizens of the city) against the rural feudal nobility, which had given these groups the military and political muscle to push out the marquises and viscounts and barons and claim exclusive authority over the tax system, the judicial system, and the military.
So it made sense that, once they had vanquished their enemies and established the commune as the sovereign, both sides would use the same tactic in their struggle over which of them would rule the commune that ruled the city. The signorile and nobilita formed themselves into consorteria or "tower societies," by which ancient families allied with one another (complete with dynastic marriage alliances!) to build and garrison the towers with the knights, squires, men-at-arms, and bravi of their households. These phallic castle substitutes were incredibly formidable within the context of urban warfare, as relatively small numbers of men with crossbows could rain down hell on besiegers from the upper windows and bridges between towers, even as the poor bastards on the ground tried to force the heavy doors down below.
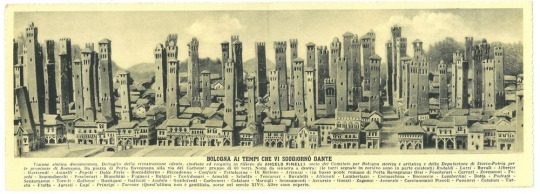
To combat noble domination of communal government, achieve direct representation on the political councils, establish equity of taxation and regulate interest rates, and enforce legal equality between nobility and citizenry, the populo formed themselves into guilds to build alliances between merchants and artisans in the same industries. However, these amateur soldiers struggled to fight on even footing with fully-trained and well-equipped professional soldiers, and the guild militias were frequently defeated.
To solve their military dilemma, the populo engaged in political coalition-building with the oldest units of the urban commune: the neighborhoods. When the cities of medieval Italy were originally founded, they had been rather decentralized transplantations of the rural villages, where before people had any conception of a city-wide collective their primary allegiance was to their neighborhood. As can still be seen in the Palio di Siena to this day, these contrade built a strong identity based on local street gangs, the parish church, their traditional heraldry, and their traditional rivalries with the stronzi in the next contrade over. And whether they were maggiori, minori, or unguilded laborers, everyone in the city was a member of their contrade.

As Martines describes, the populo both recruited from (and borrowed the traditions of) the contrade to form their armed neighborhood companies into a force that would have the manpower, the discipline, and the morale to take on the consorteria:
"Every company had its distinctive banner and every house in the city was administratively under the sign of a company. A dragon, a whip, a serpent, a bull, a bounding horse, a lion, a ladder: these, in different colors and on contrasting fields, were some of the leitmotifs of the twenty different banners. They were emblazoned on individual shields and helmets. Rigorous regulations required guildsmen to keep their arms near at hand, above all in troubled times. The call to arms for the twenty companies was the ringing of a special bell, posted near the main public square. A standard-bearer, flanked by four lieutenants, was in command of each company."
To knit these companies organized by neighborhood into a single cohesive force, the lawyers' guilds within the populo created a state within a state, complete with written constitutions, guild charters, legal codes, legislative and executive councils. Under these constitutions, the populo's councils would elect a capitano del popolo, a professional soldier from outside the city who would serve as a politically-neutral commander, with a direct chain of command over the gonfaloniere and lieutenants of the neighborhood companies, to lead the populo against their noble would-be overlords.
And in commune after commune, the neighborhood companies made war against the consorteria, taking the towers one by one and turning them into fortresses of the populo. The victorious guilds turned their newly-won military might into political hegemony over the commune, stripping the nobilita of their power and privilege and forcing them either into submission or exile. Then they directed their veteran neighborhood companies outward to seize control of the rural hinterland from the feudal aristocracy, until the city had become city-state.
(Ironically, in the process, the populo gave birth to the condottieri, as the nobility who had lost their landed wealth and political power took their one remaining asset - their military training and equipment - and became professional mercenaries. But that's a story for another time...)
#history#historical analysis#renaissance history#renaissance fantasy#medieval cities#city-states#urban communes#guilds#city charters#guild charters#mercenaries#nobility#artisans#burgher rights#merchants
154 notes
·
View notes
Text
David Smith at The Guardian:
A pitiless crackdown on on illegal immigration. A hardline approach to law and order. A purge of “gender ideology” and “wokeness” from the nation’s schools. Erosions of academic freedom, judicial independence and the free press. An alliance with Christian nationalism. An assault on democratic institutions. The “electoral autocracy” that is Viktor Orbán’s Hungary has been long revered by Donald Trump and his “Make America Great Again” (Maga) movement. Now admiration is turning into emulation. In the early weeks of Trump’s second term as US president, analysts say, there are alarming signs that the Orbánisation of America has begun. With the tech billionaire Elon Musk at his side, Trump has moved with astonishing velocity to fire critics, punish media, reward allies, gut the federal government, exploit presidential immunity and test the limits of his authority. Many of their actions have been unconstitutional and illegal. With Congress impotent, only the federal courts have slowed them down. “They are copying the path taken by other would-be dictators like Viktor Orbán,” said Chris Murphy, a Democratic senator for Connecticut. “You have a move towards state-controlled media. You have a judiciary and law enforcement that seems poised to prioritise the prosecution of political opponents. You have the executive seizure of spending power so the leader and only the leader gets to dictate who gets money.” Orbán, who came to power in 2010, was once described as “Trump before Trump” by the US president’s former adviser Steve Bannon. His long-term dismantling of institutions and control of media in Hungary serves as a cautionary tale about how seemingly incremental changes can pave the way for authoritarianism. Orbán has described his country as “a petri dish for illiberalism”. His party used its two-thirds majority to rewrite the constitution, capture institutions and change electoral law. He reconfigured the judiciary and public universities to ensure long-term party loyalty.
The prime minister created a system of rewards and punishments, giving control of money and media to allies. An estimated 85% of media outlets are controlled by the Hungarian government, allowing Orbán to shape public opinion and marginalise dissent. Orbán has been also masterful at weaponising “family values” and anti-immigration rhetoric to mobilise his base. Orbán’s fans in the US include Vice-President JD Vance, the media personality Tucker Carlson and Kevin Roberts, the head of the Heritage Foundation thinktank, who once said: “Modern Hungary is not just a model for conservative statecraft but the model.” The Heritage Foundation produced Project 2025, a far-right blueprint for Trump’s second term. Orbán has addressed the Conservative Political Action Conference and two months ago travelled to the Mar-a-Lago estate in Florida for talks with both Trump and Musk. He has claimed that “we have entered the policy writing system of President Donald Trump’s team” and “have deep involvement there”. But even Orbán might be taken aback – and somewhat envious – of the alacrity that Trump has shown since returning to power, attacking the foundations of democracy not with a chisel but a sledgehammer.
[...] Borrowing from Orbán’s playbook, Trump has mobilised the culture wars, issuing a series of executive orders and policy changes that target diversity, equity and inclusion programmes and education curricula. This week he signed an executive order aimed at banning transgender athletes from competing in women’s sports and directed the attorney general, Pam Bondi, to lead a taskforce on eradicating what he called anti-Christian bias within the federal government. He is also seeking to marginalise the mainstream media and supplant it with a rightwing ecosystem that includes armies of influencers and podcasters. A “new media” seat has been added to the White House press briefing room while Silicon Valley billionaires were prominent at his inauguration. Musk’s X is a powerful mouthpiece, Mark Zuckerberg’s Facebook has abandoned factchecking and the Chinese-owned TikTok could become part-owned by the US. Trump has sued news organisations over stories or even interview edits; some have settled the cases. The Pentagon said it would “rotate” four major news outlets from their workspace and replace them with more Trump-friendly media. Jim Acosta, a former White House correspondent who often sparred with Trump, quit CNN while Lara Trump, the president’s daughter-in-law, was hired to host a new weekend show on Rupert Murdoch’s Fox News. But the most dramatic change has been the way in which Trump has brought disruption to the federal government on an unprecedented scale, firing at least 17 inspectors general, dismantling longstanding programmes, sparking widespread public outcry and challenging the very role of Congress to create the nation’s laws and pay its bills. Government workers are being pushed to resign, entire agencies are being shuttered and federal funding to states and non-profits was temporarily frozen. The most sensitive treasury department information of countless Americans was opened to Musk’s “department of government efficiency” (Doge) team in a breach of privacy and protocol, raising concerns about potential misuse of federal funds. Musk’s allies orchestrated a physical takeover of the United States Agency for International Development (USAid), locking out employees and vowing to shut it down, with the secretary of state, Marco Rubio, stepping in as acting administrator. “We spent the weekend feeding USAID into the wood chipper,” Musk posted on X. Musk’s team has also heavily influenced the office of personnel management (OPM), offering federal workers a “buyout” and installing loyalists into key positions. It is also pushing for a 50% budget cut and implementing “zero-based budgeting” at the General Services Administration (GSA), which controls federal properties and massive contracts.
[...] One guardrail is holding for now. Courts have temporarily blocked Trump’s efforts to end birthright citizenship, cull the government workforce and freeze federal funding. Even so, commentators warn that the blatant disregard for congressional authority, erosion of civil service protections and concentration of power in the executive branch pose a grave threat.
The US is rapidly careening towards Orbánism.
#Donald Trump#Democratic Backsliding#Authoritarianism#Viktor Orbán#Trump Administration II#United States#Hungary#Elon Musk#Musk Coup#General Services Administration#Office of Personnel Management#USAID#DOGE#Department of Government Effiency#War On The Press
35 notes
·
View notes
Note
That's not what fiscal conservatism means? Fiscal conservatism is about slashing taxes and cutting back on social safety nets.
Say, for the sake of argument, we taxed billionaires to pay off the national debt. This is a fiscally conservative position in the limited sense that it does not rely on assuming future US debt, propelling the government with future dollars and inflation. It's a debt hawk position that we last saw under Bill Clinton, and haven't really seen since. I kinda refuse to accept the position that anyone who talks about "fiscal responsibility" is a dogwhistling klansman or a private equity CEO, even if those are the dominant groups talking about balancing the budget, because they are charlatans and we all know it.
Now, I know enough economics to understand that there are actually significant advantages to propelling the US economy with future dollars and inflation. US Treasury Bonds being the basis of the international economy has done us an immense boon and we are about to see what happens when suddenly nobody wants lil old uncle sam in their investment portfolio. But that doesn't mean that a balanced budget wouldn't have different advantages to be weighed against the advantages of the debt cannon, and advocating for such is, strictly speaking, the conservative position to hold about fiscal policy compared to the liberal position of "just borrow lol."
The real problem is that republicans are deceitful hypocrites to a man and rant and rail about spending right up until they hold the gavel and then blow America's economic load all over billionaire pocketbooks. Imagine you were married to a fucking gambling addict and every 4-8 years the supreme court said you had to give them your credit card until they fucked up so badly that THE AMERICAN ELECTORATE decided that it was "too much." Would it matter that they spent 4-8 years talking about how we can't possibly afford to fix the fucking insulation in the attic? no. So called "fiscal conservatives" refuse to take the actual hard line that their alleged principles demand because they are mouthpieces for bad faith actors. That doesn't mean that the actual hard line their alleged principles demand is without economic merit but you'd never know it from their voting habits because their voting habits are all oligarchy all the time and we know that those fuckers can't balance a budget, they're too busy whining about unions and lapping up federal grant money to fix their own financial insolvencies.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ways English borrowed words from Latin
Latin has been influencing English since before English existed!

Here’s a non-exhaustive list of ways that English got vocabulary from Latin:
early Latin influence on the Germanic tribes: The Germanic tribes borrowed words from the Romans while still in continental Europe, before coming to England.
camp, wall, pit, street, mile, cheap, mint, wine, cheese, pillow, cup, linen, line, pepper, butter, onion, chalk, copper, dragon, peacock, pipe, bishop
Roman occupation of England: The Celts borrowed words from the Romans when the Romans invaded England, and the Anglo-Saxons later borrowed those Latin words from the Celts.
port, tower, -chester / -caster / -cester (place name suffix), mount
Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons: Roman missionaries to England converted the Anglo-Saxons to Christianity and brought Latin with them.
altar, angel, anthem, candle, disciple, litany, martyr, mass, noon, nun, offer, organ, palm, relic, rule, shrine, temple, tunic, cap, sock, purple, chest, mat, sack, school, master, fever, circle, talent
Norman Conquest: The Norman French invaded England in 1066 under William the Conqueror, making Norman French the language of the state. Many words were borrowed from French, which had evolved out of Latin.
noble, servant, messenger, feast, story, government, state, empire, royal, authority, tyrant, court, council, parliament, assembly, record, tax, subject, public, liberty, office, warden, peer, sir, madam, mistress, slave, religion, confession, prayer, lesson, novice, creator, saint, miracle, faith, temptation, charity, pity, obedience, justice, equity, judgment, plea, bill, panel, evidence, proof, sentence, award, fine, prison, punishment, plead, blame, arrest, judge, banish, property, arson, heir, defense, army, navy, peace, enemy, battle, combat, banner, havoc, fashion, robe, button, boots, luxury, blue, brown, jewel, crystal, taste, toast, cream, sugar, salad, lettuce, herb, mustard, cinnamon, nutmeg, roast, boil, stew, fry, curtain, couch, screen, lamp, blanket, dance, music, labor, fool, sculpture, beauty, color, image, tone, poet, romance, title, story, pen, chapter, medicine, pain, stomach, plague, poison
The Renaissance: The intense focus on writings from classical antiquity during the Renaissance led to the borrowing of numerous words directly from Latin.
atmosphere, disability, halo, agile, appropriate, expensive, external, habitual, impersonal, adapt, alienate, benefit, consolidate, disregard, erupt, exist, extinguish, harass, meditate
The Scientific Revolution: The need for new technical and scientific terms led to many neoclassical compounds formed from Classical Greek and Latin elements, or new uses of Latin prefixes.
automobile, transcontinental, transformer, prehistoric, preview, prequel, subtitle, deflate, component, data, experiment, formula, nucleus, ratio, structure
Not to mention most borrowings from other Romance languages, such as Spanish or Italian, which also evolved from Latin.
Further Reading: A history of the English language (Baugh & Cable)
160 notes
·
View notes
Text
Genosha allegories: constructive reads and hot takes.
Anger is an appropriate response to Genosha, not hopelessness.
This is Part 2 in a 5 part essay on the implicit pessimism of X-Men as a setting.
Part 1 lays out the core assumptions of the setting.
I think X-Men ‘97 is the smartest Marvel offering since Captain America: Civil War brought us the debates over the Sokovia Accords. There are a lot of crappy discussions about the ethics of Magneto’s Blackout and the broader question of whether Xavier is as corrupt, infantile, and naive as he’s accused of both by other characters and the audience.
However, people really do need to be mindful of the hard wired setting conceits that ensure that the X-Men’s world is one in which there is an unhappy median that wobbles back and forth from slightly better to a lot worse and this itself is not (I hope) the actual message of the setting.
There are some real life parallels that I see that may validate a pessimistic reading, but other metrics like the number and acceptability of interracial, interreligious, and same sex marriages in the United States have improved by staggering degrees. We have not achieved true equality or safety for people who have traditionally struggled for full acceptance, but if we don’t allow the perfect to be the enemy of the good, we can see that positive change is possible.
Whether positive change is truly lasting and able to be expanded upon is a more nebulous question, I’m not one to buy into “end of history” narratives so I would never say that we cannot go backwards, I often worry we’re on the cusp of doing just that, history is often, to borrow a Dan Carlinism, like a stock ticker, but we’ve had a pretty good run of adding more freedoms for more people.
Although obviously different groups of people are at different places in their struggle to achieve safety, acceptance, and equity and thus their gains are less entrenched and more subject to backsliding.
Sprinkled in amongst the narrative of progress are setbacks and atrocities: Genosha could stand in for the likes of Tulsa’s Black Wall Street, the Stonewall raid, the anti-Jewish pogroms of the 1880s in the Russian Empire, or the brutal suppression of Arab nationalists by European empires under the mandate system.
Magneto surely would not want us to forget these things when he says the first priority of Mutants should be to look after their own and trust of Humans should come slowly, but probably never.
There again, I do think it is possible to hold multiple thoughts: that progress is often not uninterrupted or linear but it is possible and, at least in the United States context, significant progress has been made given how bleak conditions were for women, non-Europeans, queer people, and even the wrong kind of European at various points in history.
Right or wrong, I think this is the history that Xavier is temperamentally oriented towards, but then it is easier for him as a child of privilege and someone who is not visibly a Mutant.
The next part will go into greater detail about the allegories behind X-Men and why the X-Men setting is hardwired for doom by intent.
#Genosha#magneto#erik lehnsherr#charles xavier#x men 97#x men the animated series#x men#Mutants#allegory#Marvel#civil rights
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Democrats on the House Oversight Committee fired off two dozen requests Wednesday morning pressing federal agency leaders for information about plans to install AI software throughout federal agencies amid the ongoing cuts to the government's workforce.
The barrage of inquiries follow recent reporting by WIRED and The Washington Post concerning efforts by Elon Musk’s so-called Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) to automate tasks with a variety of proprietary AI tools and access sensitive data.
“The American people entrust the federal government with sensitive personal information related to their health, finances, and other biographical information on the basis that this information will not be disclosed or improperly used without their consent,” the requests read, “including through the use of an unapproved and unaccountable third-party AI software.”
The requests, first obtained by WIRED, are signed by Gerald Connolly, a Democratic congressman from Virginia.
The central purpose of the requests is to press the agencies into demonstrating that any potential use of AI is legal and that steps are being taken to safeguard Americans’ private data. The Democrats also want to know whether any use of AI will financially benefit Musk, who founded xAI and whose troubled electric car company, Tesla, is working to pivot toward robotics and AI. The Democrats are further concerned, Connolly says, that Musk could be using his access to sensitive government data for personal enrichment, leveraging the data to “supercharge” his own proprietary AI model, known as Grok.
In the requests, Connolly notes that federal agencies are “bound by multiple statutory requirements in their use of AI software,” pointing chiefly to the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program, which works to standardize the government’s approach to cloud services and ensure AI-based tools are properly assessed for security risks. He also points to the Advancing American AI Act, which requires federal agencies to “prepare and maintain an inventory of the artificial intelligence use cases of the agency,” as well as “make agency inventories available to the public.”
Documents obtained by WIRED last week show that DOGE operatives have deployed a proprietary chatbot called GSAi to approximately 1,500 federal workers. The GSA oversees federal government properties and supplies information technology services to many agencies.
A memo obtained by WIRED reporters shows employees have been warned against feeding the software any controlled unclassified information. Other agencies, including the departments of Treasury and Health and Human Services, have considered using a chatbot, though not necessarily GSAi, according to documents viewed by WIRED.
WIRED has also reported that the United States Army is currently using software dubbed CamoGPT to scan its records systems for any references to diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility. An Army spokesperson confirmed the existence of the tool but declined to provide further information about how the Army plans to use it.
In the requests, Connolly writes that the Department of Education possesses personally identifiable information on more than 43 million people tied to federal student aid programs. “Due to the opaque and frenetic pace at which DOGE seems to be operating,” he writes, “I am deeply concerned that students’, parents’, spouses’, family members’ and all other borrowers’ sensitive information is being handled by secretive members of the DOGE team for unclear purposes and with no safeguards to prevent disclosure or improper, unethical use.” The Washington Post previously reported that DOGE had begun feeding sensitive federal data drawn from record systems at the Department of Education to analyze its spending.
Education secretary Linda McMahon said Tuesday that she was proceeding with plans to fire more than a thousand workers at the department, joining hundreds of others who accepted DOGE “buyouts” last month. The Education Department has lost nearly half of its workforce—the first step, McMahon says, in fully abolishing the agency.
“The use of AI to evaluate sensitive data is fraught with serious hazards beyond improper disclosure,” Connolly writes, warning that “inputs used and the parameters selected for analysis may be flawed, errors may be introduced through the design of the AI software, and staff may misinterpret AI recommendations, among other concerns.”
He adds: “Without clear purpose behind the use of AI, guardrails to ensure appropriate handling of data, and adequate oversight and transparency, the application of AI is dangerous and potentially violates federal law.”
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Leveraged buyouts are not like mortgages

I'm coming to DEFCON! On FRIDAY (Aug 9), I'm emceeing the EFF POKER TOURNAMENT (noon at the Horseshoe Poker Room), and appearing on the BRICKED AND ABANDONED panel (5PM, LVCC - L1 - HW1–11–01). On SATURDAY (Aug 10), I'm giving a keynote called "DISENSHITTIFY OR DIE! How hackers can seize the means of computation and build a new, good internet that is hardened against our asshole bosses' insatiable horniness for enshittification" (noon, LVCC - L1 - HW1–11–01).

Here's an open secret: the confusing jargon of finance is not the product of some inherent complexity that requires a whole new vocabulary. Rather, finance-talk is all obfuscation, because if we called finance tactics by their plain-language names, it would be obvious that the sector exists to defraud the public and loot the real economy.
Take "leveraged buyout," a polite name for stealing a whole goddamned company:
Identify a company that owns valuable assets that are required for its continued operation, such as the real-estate occupied by its outlets, or even its lines of credit with suppliers;
Approach lenders (usually banks) and ask for money to buy the company, offering the company itself (which you don't own!) as collateral on the loan;
Offer some of those loaned funds to shareholders of the company and convince a key block of those shareholders (for example, executives with large stock grants, or speculators who've acquired large positions in the company, or people who've inherited shares from early investors but are disengaged from the operation of the firm) to demand that the company be sold to the looters;
Call a vote on selling the company at the promised price, counting on the fact that many investors will not participate in that vote (for example, the big index funds like Vanguard almost never vote on motions like this), which means that a minority of shareholders can force the sale;
Once you own the company, start to strip-mine its assets: sell its real-estate, start stiffing suppliers, fire masses of workers, all in the name of "repaying the debts" that you took on to buy the company.
This process has its own euphemistic jargon, for example, "rightsizing" for layoffs, or "introducing efficiencies" for stiffing suppliers or selling key assets and leasing them back. The looters – usually organized as private equity funds or hedge funds – will extract all the liquid capital – and give it to themselves as a "special dividend." Increasingly, there's also a "divi recap," which is a euphemism for borrowing even more money backed by the company's assets and then handing it to the private equity fund:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/09/17/divi-recaps/#graebers-ghost
If you're a Sopranos fan, this will all sound familiar, because when the (comparatively honest) mafia does this to a business, it's called a "bust-out":
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bust_Out
The mafia destroys businesses on a onesy-twosey, retail scale; but private equity and hedge funds do their plunder wholesale.
It's how they killed Red Lobster:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/05/23/spineless/#invertebrates
And it's what they did to hospitals:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/28/5000-bats/#charnel-house
It's what happened to nursing homes, Armark, private prisons, funeral homes, pet groomers, nursing homes, Toys R Us, The Olive Garden and Pet Smart:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/06/02/plunderers/#farben
It's what happened to the housing co-ops of Cooper Village, Texas energy giant TXU, Old Country Buffet, Harrah's and Caesar's:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/05/14/billionaire-class-solidarity/#club-deals
And it's what's slated to happen to 2.9m Boomer-owned US businesses employing 32m people, whose owners are nearing retirement:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/16/schumpeterian-terrorism/#deliberately-broken
Now, you can't demolish that much of the US productive economy without attracting some negative attention, so the looter spin-machine has perfected some talking points to hand-wave away the criticism that borrowing money using something you don't own as collateral in order to buy it and wreck it is obviously a dishonest (and potentially criminal) destructive practice.
The most common one is that borrowing money against an asset you don't own is just like getting a mortgage. This is such a badly flawed analogy that it is really a testament to the efficacy of the baffle-em-with-bullshit gambit to convince us all that we're too stupid to understand how finance works.
Sure: if I put an offer on your house, I will go to my credit union and ask the for a mortgage that uses your house as collateral. But the difference here is that you own your house, and the only way I can buy it – the only way I can actually get that mortgage – is if you agree to sell it to me.
Owner-occupied homes typically have uncomplicated ownership structures. Typically, they're owned by an individual or a couple. Sometimes they're the property of an estate that's divided up among multiple heirs, whose relationship is mediated by a will and a probate court. Title can be contested through a divorce, where disputes are settled by a divorce court. At the outer edge of complexity, you get things like polycules or lifelong roommates who've formed an LLC s they can own a house among several parties, but the LLC will have bylaws, and typically all those co-owners will be fully engaged in any sale process.
Leveraged buyouts don't target companies with simple ownership structures. They depend on firms whose equity is split among many parties, some of whom will be utterly disengaged from the firm's daily operations – say, the kids of an early employee who got a big stock grant but left before the company grew up. The looter needs to convince a few of these "owners" to force a vote on the acquisition, and then rely on the idea that many of the other shareholders will simply abstain from a vote. Asset managers are ubiquitous absentee owners who own large stakes in literally every major firm in the economy. The big funds – Vanguard, Blackrock, State Street – "buy the whole market" (a big share in every top-capitalized firm on a given stock exchange) and then seek to deliver returns equal to the overall performance of the market. If the market goes up by 5%, the index funds need to grow by 5%. If the market goes down by 5%, then so do those funds. The managers of those funds are trying to match the performance of the market, not improve on it (by voting on corporate governance decisions, say), or to beat it (by only buying stocks of companies they judge to be good bets):
https://pluralistic.net/2022/03/17/shareholder-socialism/#asset-manager-capitalism
Your family home is nothing like one of these companies. It doesn't have a bunch of minority shareholders who can force a vote, or a large block of disengaged "owners" who won't show up when that vote is called. There isn't a class of senior managers – Chief Kitchen Officer! – who have been granted large blocks of options that let them have a say in whether you will become homeless.
Now, there are homes that fit this description, and they're a fucking disaster. These are the "heirs property" homes, generally owned by the Black descendants of enslaved people who were given the proverbial 40 acres and a mule. Many prosperous majority Black settlements in the American South are composed of these kinds of lots.
Given the historical context – illiterate ex-slaves getting property as reparations or as reward for fighting with the Union Army – the titles for these lands are often muddy, with informal transfers from parents to kids sorted out with handshakes and not memorialized by hiring lawyers to update the deeds. This has created an irresistible opportunity for a certain kind of scammer, who will pull the deeds, hire genealogists to map the family trees of the original owners, and locate distant descendants with homeopathically small claims on the property. These descendants don't even know they own these claims, don't even know about these ancestors, and when they're offered a few thousand bucks for their claim, they naturally take it.
Now, armed with a claim on the property, the heirs property scammers force an auction of it, keeping the process under wraps until the last instant. If they're really lucky, they're the only bidder and they can buy the entire property for pennies on the dollar and then evict the family that has lived on it since Reconstruction. Sometimes, the family will get wind of the scam and show up to bid against the scammer, but the scammer has deep capital reserves and can easily win the auction, with the same result:
https://www.propublica.org/series/dispossessed
A similar outrage has been playing out for years in Hawai'i, where indigenous familial claims on ancestral lands have been diffused through descendants who don't even know they're co-owner of a place where their distant cousins have lived since pre-colonial times. These descendants are offered small sums to part with their stakes, which allows the speculator to force a sale and kick the indigenous Hawai'ians off their family lands so they can be turned into condos or hotels. Mark Zuckerberg used this "quiet title and partition" scam to dispossess hundreds of Hawai'ian families:
https://archive.is/g1YZ4
Heirs property and quiet title and partition are a much better analogy to a leveraged buyout than a mortgage is, because they're ways of stealing something valuable from people who depend on it and maintain it, and smashing it and selling it off.
Strip away all the jargon, and private equity is just another scam, albeit one with pretensions to respectability. Its practitioners are ripoff artists. You know the notorious "carried interest loophole" that politicians periodically discover and decry? "Carried interest" has nothing to do with the interest on a loan. The "carried interest" rule dates back to 16th century sea-captains, and it refers to the "interest" they had in the cargo they "carried":
https://pluralistic.net/2021/04/29/writers-must-be-paid/#carried-interest
Private equity managers are like sea captains in exactly the same way that leveraged buyouts are like mortgages: not at all.
And it's not like private equity is good to its investors: scams like "continuation funds" allow PE looters to steal all the money they made from strip mining valuable companies, so they show no profits on paper when it comes time to pay their investors:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/20/continuation-fraud/#buyout-groups
Those investors are just as bamboozled as we are, which is why they keep giving more money to PE funds. Today, the "dry powder" (uninvested money) that PE holds has reached an all-time record high of $2.62 trillion – money from pension funds and rich people and sovereign wealth funds, stockpiled in anticipation of buying and destroying even more profitable, productive, useful businesses:
https://www.institutionalinvestor.com/article/2di1vzgjcmzovkcea8f0g/portfolio/private-equitys-dry-powder-mountain-reaches-record-height
The practices of PE are crooked as hell, and it's only the fact that they use euphemisms and deceptive analogies to home mortgages that keeps them from being shut down. The more we strip away the bullshit, the faster we'll be able to kill this cancer, and the more of the real economy we'll be able to preserve.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/08/05/rugged-individuals/#misleading-by-analogy
#pluralistic#leveraged buyouts#lbos#divi recaps#mortgages#weaponized shelter#debt#finance#private equity#pe#mego#bust outs#plunder#looting
431 notes
·
View notes
Text
JONATHAN GROFF SETS 2025 BROADWAY RETURN WITH ‘JUST IN TIME’
by Philip Boroff
EXCLUSIVE: Newly minted Tony Award winner Jonathan Groff will play the 1950s and ’60s crooner Bobby Darin in a staged reading next month, ahead of a planned Broadway opening in spring 2025, people familiar with the musical said.
The reading of Just in Time will be directed by Alex Timbers (Moulin Rouge!). On Broadway, Tom Kirdahy and Robert Ahrens are set to produce the show, which tells the story of the short but eventful life of the popular performer, whose hits included “Mack the Knife,” “Dream Lover” and “Just in Time.”
Born Walden Robert Cassotto in East Harlem, Darin had rheumatic fever as a child that damaged his heart. He lived, he acknowledged, as if on borrowed time before his death at 37.
He led a new generation of swinging singers into the rock revolution of the 1960s. He also acted in movies, composed music, married the actress Sandra Dee and as an adult discovered that the woman he thought was his older sister was his mother.
“I went on YouTube,” Groff told reporter Elysa Gardner before a rehearsal of an early version of the show, presented as part of the 92nd Street Y ‘s “Lyrics and Lyricist” series in 2018. “I watched all these TV performances, from the beginning to the end of his career, and I was blown away by his versatility. The rock & roll and the standards, the dancing, the folk songs. The duets with George Burns and Judy Garland. His life was insane.”
Darin spawned many imitators, including Kevin Spacey, who played him in the biofilm Beyond the Sea. The ballad “Just in Time” was composed by Jule Styne with lyrics by Adolph Green and Betty Comden for the musical Bells are Ringing. It became a hit for Dean Martin, among others, who was in the 1960 movie adaptation directed by Vincente Minnelli.
Besides Groff, casting wasn’t available. The reading isn’t affected by the monthlong Actors’ Equity strike intended to pressure the Broadway League to improve its Development Agreement with the union. Actors will be working under a contract negotiated with the League of Resident Theatres (LORT), an association of nonprofit theater companies.
Although the reading will be in New York, it’s under the aegis of Signature Theatre in Arlington, Virginia, which is a LORT member.
In a charmed career, the 39-year-old Groff has performed in the Frozen films, the TV series Glee and three acclaimed Broadway blockbusters — Spring Awakening, Hamilton and most recently Merrily We Roll Along — each of which earned him a Tony nomination. (He won for Merrily.)
Groff was also the first Seymour in the hit off-Broadway revival of Little Shop of Horrors, produced by Ahrens, Kirdahy and Hunter Arnold. Andrew Barth Feldman is currently playing the role.
In his moving acceptance speech at the Tony awards in June, Groff spoke about his love of the Broadway community and how “musical theater is still saving my soul.” Just in Time will aim for multigenerational appeal, as the young Broadway star sings 65-year-old standards.
Since the pandemic, older audiences have been slow to return to Broadway. If Just in Time is well received, Groff may be just the man to help bring them back.
**
Source: Philip Boroff in Broadway Journal.
Jonathan led a reading of the show on 15 March 2024 after rehearsing for a couple of weeks with the cast. Details below:

45 notes
·
View notes