#biosynthesis of cholesterol
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Cholesterol: Sources, Structure and Biosynthesis.
Elevate your online experience with our latest notes on topic, Cholesterol: Sources, Structure and Biosynthesis on our website https://microscopiaiwm.wordpress.com/ . "Unlocking knowledge one post at a time! follow microscopiaiwm #microscopiaiwm
Introduction Cholesterol is an extremely important sterol in the tissues of animals. It is an organic molecule and a type of lipid. It is a fat-like substance, which is waxy in texture, and found in all the cells of our body, as it is essential for carrying out many functions such as synthesis of hormones, synthesis of vitamin D and also acts as an integral structural component of the membranes…
View On WordPress
#3-epoxide#aceto-acetyl CoA#biochemistry notes#biosynthesis of cholesterol#biosynthesis of isoprenoid units#biosynthesis of lanosterol#biosynthesis of melanovate#biosynthesis of squalene#cholesterol#Cholesterol formation#cholesterol notes#fatty acid#firmation of lanosterol#HMG-CoA#isoprenoid#lanosterol#lanosterol cyclase#metabolism#metabolism notes#mevalonate#mevalonic acid#MicroScopia IWM#oxidosqualene#sources of cholesterol#squalene#squalene-2#statin#steroid hormones#sterol#sterols in animals
1 note
·
View note
Text
Disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis: desterolosis, mevalonate kinase deficiency, lathosterolosis, sitosterolemia
Inherited disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis are a group of inherited metabolic disorders (IEMS) that affect the body���s ability to produce cholesterol and other sterols. Because cholesterol plays a key role in cellular structure, signaling, and function, these disorders can lead to a variety of clinical manifestations. This group of disorders includes: Smith-Lemly-Opitz syndrome, desterolosis,…

View On WordPress
#Conradi-Hünermann-Happle#Desmosterolosis#Disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis#Lathosterolosis#SC4MOL#Sitosterolemia#Smith-Lemli-Opitz
0 notes
Text
What is Hyperimmunoglobulin D Syndrome?
Hyperimmunoglobulin D Syndrome, also known as Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency (MKD), is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the MVK gene, which encodes the enzyme mevalonate kinase. This enzyme is critical for the biosynthesis of cholesterol and other isoprenoids, and its deficiency leads to the accumulation of intermediates that trigger inflammatory responses.
Get a diagnosis at FirstChoice Rheumatology
0 notes
Video
youtube
Cholesterol Biosynthesis Pathway - Biochemistry
0 notes
Text
What is Hyperimmunoglobulin D Syndrome?
Hyperimmunoglobulin D Syndrome, also known as Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency (MKD), is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the MVK gene, which encodes the enzyme mevalonate kinase. This enzyme is critical for the biosynthesis of cholesterol and other isoprenoids, and its deficiency leads to the accumulation of intermediates that trigger inflammatory responses.
Get a diagnosis at FirstChoice Rheumatology
0 notes
Text
The Vitamin Identity: Unveiling What Vitamin is Called NMN

NMN, or nicotinamide mononucleotide, is a derivative and precursor of vitamin B3 (niacin). However, while NMN is related to B3, it has distinct differences that set it apart from this essential dietary vitamin.
This exploration sheds light on the intricate relationship between NAD and a well-known vitamin, revealing the depth of their scientific connection. It dives into the biochemical links, unraveling how these two crucial components interact within the body. Understanding this connection is vital for those seeking to grasp the complexities of nutritional science and its impact on overall health.
This detailed exploration offers clarity on the distinctions and links between NMN and a familiar vitamin, challenging common assumptions in the process. It delves into their molecular structures, functional roles, and the nuances that set them apart, providing essential insights for anyone keen on understanding the intricate world of vitamins and their derivatives in health and nutrition
Overview of Vitamin B3
Vitamin B3, also known as niacin, is one of eight essential B vitamins. It is naturally present in foods such as meat, fish, eggs, milk, greens, grains, and legumes.
Vitamin B3 plays critical roles in converting food into energy, supporting DNA repair, enabling hormone production, regulating cholesterol, and more. Severe deficiency of B3 causes the disease pellagra.
The recommended daily intake of B3 is 14-16 mg for adults. Consuming high supplemental doses of B3 may result in side effects like flushing, itching, and redness.
Overview of NMN
NMN stands for nicotinamide mononucleotide. It is produced endogenously through the metabolism of B3, and acts as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of NAD+.
As a precursor to NAD+, a vital coenzyme that declines with age, NMN is being researched for its potential to boost NAD+ levels and support healthy aging. However, its anti-aging benefits in humans remain under investigation.
Key Differences Between NMN and B3
While NMN is derived from B3, there are several key distinctions:
Essential Nutrient: B3 is an essential vitamin that must be obtained from diet, while NMN is not known to be essential.
Dietary Sources: B3 is present in many common foods, but NMN does not naturally occur in significant amounts.
Standard Dosage: The recommended daily B3 intake is 14-16 mg, whereas anti-aging doses of NMN are 100-500 mg.
Mechanism: B3 supports general cellular metabolism, while NMN specifically aims to increase NAD+ levels.
Research Status: B3 is an established essential vitamin, while NMN is still under investigation for potential anti-aging benefits.
The Conversion Process
The body can synthesize NMN from B3 through a two-step enzymatic pathway. However, it is unclear whether typical dietary B3 intake provides sufficient NMN for anti-aging effects.
This is why direct NMN supplementation in higher doses is being researched as a specialized anti-aging strategy. But B3 remains essential for normal metabolism.
Conclusion
In summary, while NMN is a derivative of vitamin B3, it has distinct differences in terms of essentiality, dietary sources, standard dosing, mechanisms, and research status. NMN shows promise as an anti-aging nutrient, but further research is still needed to confirm its benefits in humans.
0 notes
Note
i saw ur post about paying attention in lecture im the same way LOL what r u learning in biochem?? sounds like itd be rly interesting
oh my attention span is TERRIBLE i feel u 😔 usually it’s not too bad in person but i was reviewing a couple of prerecorded lectures since i have a test on friday and this one was on (frantically checks notes bc i already forgot) cholesterol biosynthesis and regulation (??) for reference:

unfortunately this is (for me anyway) (no hate to the biochem enjoyers out there) (aka my roommate who’s majoring in it???) the most boring and also the hardest class i’ve ever taken but it’s very much a requirement for my major so powering through for the quarter and never looking back 😎
#grips apple pencil so tight in one hand#eye twitches#biochem……. my beloathed….#everyone who says it’s harder than ochem is correct#would much rather have to do more of that than this fr#godspeed with ur lectures anon i��m sending wonderful attention span vibes ur way <3#/ask
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

It is not without reason that the famous Renaissance physician and chemist Theophrastus Paracelsus called carrot root Mandragora (genus), making people live longer without diseases. The amazing properties of carrots lie in their carrot nutrition facts, which include various trace elements and a wealth of vitamins, some of which the human body cannot form during the metabolic process. The root of the carrot concentrates substances that help treat many diseases, obtain a strong immune system and rejuvenate the entire body. Read more about the useful properties of carrots, their biochemical composition, and the influence of growing conditions on the value of the root crop in this material.
A FEW FACTS ABOUT CARROTS Cultured carrots evolved from the wild carrots that grew in abundance in Asia and Europe. This root vegetable is thought to have originated in Afghanistan. Carrots originated in Afghanistan and possibly northern Iran and Pakistan. Queen Anne's Lace is a wild carrot that readily inter-pollinates with carrots and grows in temperate areas around the world where there is adequate moisture and disturbed ecology (roadsides, open spaces, etc.).
A. History of the carrot The domestication of carrots took the following routes. 1. 900 - 1000 AD: Purple and yellow carrots spread from Afghanistan to the eastern Mediterranean. 2. The 1300s: purple and yellow carrots in Western Europe and China 3. The 1600s: Yellow carrots in Japan 4. The 1700s: In addition to purple and yellow, white carrots were reported in Europe, and orange carrots were first reported in the Netherlands and neighboring regions 5. Today: orange carrots dominate worldwide, although some white types (for livestock) still exist in Western and Eastern Europe, some red (not orange) in Japan, some yellow and purple in the Middle East, and some purple, yellow, and red from Turkey to India and China
It should be noted that under natural conditions, the content and list of beneficial properties of root carrots differs from the cultivated form, where the beneficial properties of this crop are purposefully developed.
B. External review of key facts 1. Carrot (Daucus carota) is a root vegetable of the Umbelliferae family, including celery, parsley, parsley, dill, parsley, fennel, coriander, and fennel. 2. In 2012, the United States was the third-largest carrot producer. Approximately 80-90% of U.S. carrots are produced in California. Other major producers include Michigan and Texas. 3. In the late 1980s, the introduction of fresh-cut carrots and "baby carrots" created a carrot boom. 4. 4. Carrots are rich in beta-carotene, vitamins C and K, potassium, and dietary fiber. 5. 5. Carrots are popular as a culinary vegetable, salad item, snack food, and raw vegetable. 6. 6. Like most vegetables, carrots are low in acid and therefore at high risk of contamination with Clostridium botulinum toxin, the bacterium produced by Clostridium botulinum, when improperly canned. There have been several outbreaks of botulism associated with commercial and homemade carrot juice and homemade canned carrots. 7. Between 1998 and 2017, the CDC's National Outbreak Reporting System (NORS) reported at least 31 carrot-related outbreaks resulting in 756 illnesses, 17 hospitalizations, and no deaths. In outbreaks of known etiology, the most common pathogen is norovirus, but also includes Bacillus cereus, Salmonella, Salmonella, Clostridium botulinum, Shigella, and Staphylococcus aureus.
It was not until the 20th century that breeding efforts produced carrot varieties with a predominantly orange color, high sweetness, and pleasant juicy flesh. Before breeding efforts, carrots were used primarily for cooking and much less frequently for root vegetables, but then there was a real culinary boom. Cookbooks devote considerable space to describing various recipes for cooking carrots with other grain crops, and medical reference books present recipes for preparing treatments for various ailments.
EFFECT OF CULTIVATION CONDITIONS OF CARROTS ON THE QUALITY OF ROOT CROPS The value of carrots is determined by vitamins and other nutrients that accumulate in the root crop. Their quantity and quality depend on cultivation techniques. When agricultural practices are violated, changes occur not only in the exterior of carrots (small, sparse orange, cracked roots, etc.) but also in their biochemical indicators. Vitamins, flavonoids, anthocyanins, and other very important compounds are drastically reduced. Carrot is a temperate crop. It has high requirements for basic living conditions: soil and temperature regime, provision of water, and light. The quality of root crops decreases due to insufficient soil preparation (low looseness, insufficient filling with basic fertilizers), insufficient watering and feeding during vegetation, violation of the ratio of the main nutrients (more nitrogen and less potassium), and other conditions. When buying root crops in the market, be sure to ask about the growing conditions of the crop. But the best way to keep your family healthy is to grow carrots on your own plots, observing all the requirements of agricultural growing techniques. Also, only approved varieties and hybrids should be used when sowing seeds. During the winter period, list in your garden diary the early, middle, and late varieties with the highest biotechnical indicators of product quality and prepare carrot seeds of these varieties exactly.

BIOCHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF CARROTS A. Vitamins in carrots 1. Carrots contain 22% of pro-vitamin "A" (carotene), including alpha and beta carotene, which are synthesized in the body as vitamin "A," and vitamin "A" is a guarantee of visual acuity. 2. 100 grams of carrots contain more than 0.5 grams of B vitamins, including B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, and B12, necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin in the body. 3. Carrot juice contains a group of active chemicals calcitriol, representing vitamin "D," including "D2" and "D3". Vitamin "D" can be produced in the body under the influence of natural sunlight and ultraviolet light (artificial irradiation) and manifests itself in the form of tanning. Deficiency in children manifests itself in the form of rickets and in adults in the form of osteoporosis (fragility) and softening of bones (osteopenia). 4. Carrots have a high content of vitamin "K" (11%), which regulates blood clotting and prevents the formation of blood clots. 5. Vitamins "C" and "E" provide energy and normalize the function of the endocrine glands. Vitamin E also slows down the aging process of the body. It is known as the vitamin of youth. It is vital for diabetics because it helps reduce the need for insulin. 6. Vitamin "PP" (niacin), like the previous vitamins, provides energy to the body, supports heart function, blood circulation, and is involved in the metabolism of amino acids. 7. Vitamin "N," or lipoic acid, regulates the liver, thyroid, participates in the metabolism of carbohydrates, and influences the level of cholesterol in the blood. The whole vitamin complex is preserved in freshly cooked carrot juice for one hour, after thawing - 0.5 hours. The complete utilization of the body occurs in the presence of fats (butter, sour cream).
B. Micronutrients in carrots Carrots are characterized by a fairly high micronutrient content. In 100 grams of raw carrots, there is 320 mg of potassium, responsible for normalizing the heart. In Soviet times, athletes were prescribed potassium lactate. The sodium concentration was between 69-70 mg, and the sum of phosphorus and calcium exceeded 65-68 mg. Carrot root has sufficient copper, zinc, iron, magnesium, manganese, cobalt, and molybdenum. Carrots also contain selenium, a young element, and fluorine, which is responsible for the thyroid gland and helps to remove heavy metals and radionuclides from the body. Other elements are present in root crops and are compounds and combinations necessary for the normalization of water metabolism (chlorine), water-salt metabolism (sodium), and the composition of proteins (sulfur). Aluminum, boron, vanadium, nickel, chromium, lithium, and iodine complete the list of trace elements. In the context of low-calorie products, an impressive list becomes indispensable for the treatment of obesity, weight loss, and stimulation of hematopoiesis. Carrots are a part of all fitness diets. 100 grams of root crop (one small carrot) contains 35 to 40 kcal but contains more than 9.5 grams of carbohydrates and 2.8 grams of dietary fiber.
OTHER NUTRIENTS IN CARROTS Recently, there has been a general decline in immunity in children and adults and increased cold and flu attacks. The phytotoxic properties of carrots are almost comparable to garlic and onions but without an unpleasant odor. On the contrary, the essential oils add spice to the dishes prepared. In the early days of recognizing carrots as a food, as mentioned above, the seeds and green tops were used in cooking. The concentration is lower than in other vegetables, but a complete list of amino acids is present in carrots. These include tyrosine, lysine, leucine, ornithine, cysteine, asparagine, threonine, histidine, methionine, etc. Carrot has a pleasant rich color due to its anthocyanins and bioflavonoids. It contains umbelliferone, which is involved in the biosynthesis of basic compounds such as phytosterols, coumarins, quercetin, fiber, pectin, and sugar.
USEFUL PROPERTIES OF CARROTS For the treatment and prevention of diseases, carrot is available as a raw product, cooked, thawed, and frozen. In boiled form, it increases its positive impact on the body in treating nephritis, cancer, diabetes, and general flora disorders. Raw carrots prevent microbial infections of the mouth and systemic infectious colds (acute respiratory infections, influenza). Carrot is used for vitamin deficiencies, anemia, atherosclerosis. It is included in formulas for treating Alzheimer's disease, digestive tract, intestinal obstruction, cholelithiasis and urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, cystitis. Carrot juice is effective against conjunctivitis, night blindness, and other eye diseases. It is used in official and folk medicine to treat diseases of the bone and hematopoietic system. Eating 50 grams of fresh carrots per day (average daily rate) will reduce the risk of stroke by 60-70%, breast cancer by 25%, and retinal diseases with visual impairment by 40%.
CONTRAINDICATIONS TO THE USE OF CARROTS 1. Carrots are contraindicated in cases of hypersensitivity to this product. 2. In inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, small intestine, peptic ulcers. In these cases, the vegetable is used in the form of boiled or stewed. 3. If you have liver disease, consult a doctor before consuming carrots. 4. Yellowing of feet and skin in children and adults may occur if raw carrots and juice are consumed in excess. The daily dosage of this product should be reduced until the yellowing disappears. Finally, I would like to warn the reader. Carrots are very useful, but at all need to be measured. It is enough to eat 1-2 carrots a day, no more than 100-120 grams of carrots in any form - salads, purees, juices.
#ThumbGarden #Gardening Tips #How to grow #Carrot #Vegetables #Inspiration #Carrot Funny #Carrot Interesting #Carrot Facts #Organics #Vegetable Garden #Vegetable Patch #Carrot Benefits #Nutrition Facts #Nutritional Value #Carotene #Vitamin #Glucosinlates #Protein
Author: Ms.Geneva Link: https://www.thumbgarden.com/carrot-nutrition-facts/ Source: ThumbGarden The copyright belongs to the author. For commercial reprints, please contact the author for authorization, and for non-commercial reprints, please indicate the source.
#thumbgarden#gardening tips#How to grow tree#How to grow vegetable#carrot#growing Carrot#fruits and vegetables#vegetables garden#vegetables#growing vegetables#carrot funny#Carrot Interesting#carrot facts#organics#urban organics#Vegetable Gardening#vegetable garden#vegetable patch#carrot benefits#nutrition facts#nutritional value#carotene#vitamin#Glucosinlates#protein
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
IMPORTANT ASPECTS OF METABOLISM OF RED BLOOD CELLS
* The RBC is highly dependent upon glucose as its energy source, for which its membrane contains high affinity glucose transporters. * Glycolysis, producing lactate, is the mode of ATP production * Because RBCS lack mitochondria, there is no production of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. * The RBC has a variety of transporters that maintain ionic and water balance * Production of 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate by reactions closely associated with glycolysis is important in regulating the ability of Hb to transport oxygen. * The pentose phosphate pathway of the RBC metabolizes about 5 to 10% of the total flux of glucose and produces NADPH * Hemolytic anemia due to deficiency of activity of glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase is common * The iron of Hb must be maintained in ferrous state. Ferric ion is reduced to ferrous form by action of NADH dependent methemoglobin reductase system involving cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochrome b5. *While biosynthesis of glycogen, fatty acids, protein, nucleic acids does not occur in RBC , some lipids eg cholesterol in the red cell membrane can exchange with corresponding plasma lipids. * The RBC contain certain enzymes of nucleotide metabolism eg adenosine deaminase, pyrimidine nucleotidase, and adenylyl kinase. Deficiencies of these enzymes are involved in some cases of hemolytic anemia. *When RBCs reach the end of their lifespan, the globin is degraded to amino acids , the iron is released from heme and reutilized and the tetrapyrrole component of heme is converted to bilirubin, which is mainly excreted into the bowel via bile.
5 notes
·
View notes
Link
Inherited disorders of cholesterol biosynthesis are a group of inherited metabolic disorders (IEMS) that affect the body's ability to produce cholesterol and other sterols. Because cholesterol plays a key role in cellular structure, signaling, and function, these disorders can lead to a variety of clinical manifestations. This group of disorders includes: Smith-Lemly-Opitz syndrome, desterolosis, Conradi-Hünermann-Happle syndrome, mevalonate kinase deficiency, Lathosterolosis, sitosterolemia, sterol C4-methyloxidase-like (SC4MOL) deficiency, familial hypercholesterolemia FH, cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX), and others. Cholesterol metabolism in the brain: Because disorders of cholesterol metabolism are often accompanied by central nervous system (CNS) pathology, it is important to consider some unique aspects of cholesterol metabolism in the brain. Unesterified cholesterol is an essential component of the plasma membrane of all cells, but is particularly high in brain cells. It is a major component of dense myelin, a specialized form of the plasma membrane of oligodendrocytes. Although the brain accounts for only about 2% of total body weight, brain cholesterol accounts for about 23% of the sterol content in mammals. It is distributed between the myelin sheath and the plasma membrane of neurons and glial cells. These diseases often manifest as developmental, neurological, and physical abnormalities. Early diagnosis and management are essential to improve outcomes, although treatment options may be limited and often focus on symptom relief and supportive care. Genetic counseling is also an important part of managing these diseases. In addition to evaluating the patient's development, the diagnosis of such diseases also requires analysis and evaluation in combination with the patient's family genetic history, skin abnormalities, heart, and liver abnormalities. After the evaluation and analysis, it is necessary to collect clues such as the patient's clinical manifestations and specific biochemical tests for genetic testing diagnosis.
0 notes
Text
What is Hyperimmunoglobulin D Syndrome?
Hyperimmunoglobulin D Syndrome, also known as Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency (MKD), is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the MVK gene, which encodes the enzyme mevalonate kinase. This enzyme is critical for the biosynthesis of cholesterol and other isoprenoids, and its deficiency leads to the accumulation of intermediates that trigger inflammatory responses.
Get a diagnosis at FirstChoice Rheumatology
0 notes
Photo

Can you (or your students) fill in this illustration from our Cholesterol Biosynthesis Tutorial? Look for more of these on our website later this summer!
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
THE MYTHS ABOUT CHOLESTEROL
Mostly this day, everything you hear about cholesterol is bad, everybody wants to get rid of every beat of cholesterol in their body, Cholesterol is the most demonized, misunderstood and controversial substance in both our bodies and our diets. Most of us think and also seems logical that eating cholesterol would raise blood cholesterol level and possibly lead to heart diseases and many health problems.
FACTS ABOUT CHOLESTEROL
Most of the cholesterol in our body is not coming from the diet, our diet contributes a very small amount of cholesterol when our dietary intake of cholesterol goes down, our cells make more cholesterol if our dietary intake of cholesterol goes up, our cells make less cholesterol. Because of such mechanism, dietary cholesterol has very little effect on blood cholesterol levels. The bottom line is that a low cholesterol diet have very little or any effect in controlling our blood cholesterol level
WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF CHOLESTEROL IN OUR BODY?
Cholesterol is the most abundant steroid in human tissue, it is important for cell membranes, bile acid synthesis, steroid hormone (glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, estrogens, progestogens) and synthesis of vitamin D
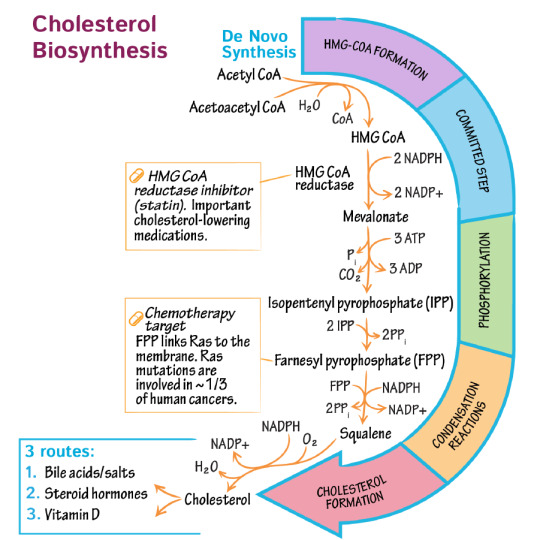
CHOLESTEROL SYNTHESIS
Cholesterol synthesis takes place in the liver using a molecule called Acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Three Acetyl CoA condensed to form HMG CoA, HMG CoA reductase converts HMG CoA to mevalonate, this is the rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis. The common statin drugs such as atorvastatin, lovastatin and pravastatin act on this rate-limiting step of cholesterol synthesis by inhibiting the HMG CoA reductase enzyme and prevent the new cholesterol synthesis, some research also show these drugs can increase the good cholesterol level called HDL
VLDL, LDL, HDL
VLDL(very low-density lipoprotein)
; VLDL is assembled in hepatocyte(liver cell) transport triglyceride containing fatty acids newly synthesized from excess glucose to adipose tissue(fat cells) and muscle.
LDL(low-density lipoprotein)
is the so-called bad cholesterol, primarily cholesterol particle, most cholesterol measured in our blood associated with LDL. The function of LDL is to deliver cholesterol to tissue for biosynthesis. When the cell needs to make membrane, bile acid and salt or dividing cholesterol is required and many other cells needs cholesterol to make steroid hormone.
HDL(high-density lipoprotein)
; is the so-called good cholesterol. HDL synthesized in the liver and in the intestine and released as a dense protein-rich particle into the blood, used for cholesterol recovery from a fatty streak in the blood vessel and give this cholesterol to VLDL, chylomicron, hepatocyte(liver cell) and steroidogenic tissue
WHEN DOES CHOLESTEROL BECOME A HEALTH RISK?Although cholesterol is one of the major contributors to heart disease, it isn’t the only one. High blood pressure, a family history of heart disease, and diabetes are other factors that could contribute to cardiovascular disease.
When we have excess cholesterol, our body does not have the mechanism of getting rid of it, because it is an essential nutrient, under normal circumstances, our body does not get rid of cholesterol, it stores it in the liver, about 70% of LDL is taken up by the liver by a process called receptor-mediated endocytosis. The problem is that some people have a defect in LDL receptor gene, and they have a high level of circulating LDL particle in the blood, example Familial Hypercholesterolemia, regardless of whether they are thin or fat, their cholesterol level is very high, most people think if you are overweight, your cholesterol level is high, but that is not always the case, most of these problems are genetics. There are other genetics defects that cause hypercholesterolemia such as Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100, PCSK9 gene mutations, familial combined hyperlipidemia to mention a few, but I just want to mention one severe form of hypercholesterolemia called Familial hypercholesterolemia type 2A, it is an autosomal dominant disorder that means you get it from the parents and it is a high risk of atherosclerosis and coronary artery diseases, unfortunately, these patients life expectancy is <20
1 note
·
View note
Text
Does CBD help block pain-signaling pathways?
Does CBD help block pain-signaling pathways?
The body uses cannabinoids or CBD to upregulate the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and block pain-signaling pathways outside the ECS. CBD has 65 known targets for activity in the brain and body outside of cannabinoid receptors. Let's explore these below!
Glycine Receptors:
These are incredibly abundant throughout the spinal cord. These are responsible for receiving messages from the body and sending them to the brain. These receptors are mechanisms by which the body decreases inflammation in neuropathic pain. CBD can positively regulate these receptors.
GABA:
Perhaps the key to reducing depression? CBD works to increase GABA levels in the body. GABA's job is to reject exciting pathways; this is one pathway by which the body can produce anti-stress and anticonvulsant effects.
GPRS:
These receptors are associated with cancer, pain, obesity, diabetes, bone health, and GI motility. They have been found to promote seizure cycles, cancer cell metastasis, upregulate obesity, type 2 DM, and upregulate osteoporosis. CBD antagonizes this receptor, so it blocks the activation of the receptors. It decreases glutamate (which decreases neuronal excitability) and increases GABA (which increases neuronal calm).
5HT1A and 2A:
These receptors are associated with anxiety, appetite, sleep, pain, addiction, nausea, and vomiting. Taking CBD for pain, it has the ability to bind directly to these receptors increases these receptors' effectiveness. It helps the body's serotonin work more effectively. Increased affinity at these receptors is known to produce protective, analgesic, stimulant, stress-reducing, and nausea-reducing effects.
PPARy:
Cannabinoids can activate PPARy receptors. These are nuclear receptors found in the cell wall of the nucleus. They are involved in lipid storage, energy/glucose metabolism, cell differentiation, and inflammation regulation. They can be used clinically to treat cholesterol, triglycerides, and insulin resistance. These receptors are also studied for their gut anticancer, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, these receptors can lower insulin resistance and degrade amyloid plaque in the brains of people with Alzheimer's.
Adenosine Receptors:
These play a role in cardiac rhythm/circulation, renal blood flow, immune function, sleep regulation, inflammatory diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders. By binding to A1 adenosine receptors, cannabinoids can promote antiarrhythmic effects. By binding to adenosine A2 receptors, cannabinoids can promote anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, the additional cannabinoids in the system can help adenosine receptors create more extensive neuroprotective effects.
Opioid Receptors:
Pathways work by enhancing endorphins, which are stimulated by cannabinoids.
GPR18:
This is believed to be a third cannabinoid receptor; hopefully, the future will clarify this hypothesis. It is essential for immune and microglial function. Microglia act as the primary defense of the immune system for Brian and the spinal cord.
Enzymes:
CBD interacts with 32 enzymes, specifically the enzyme cytochrome P450 that
controls metabolism (and that is why we must be careful with specific drug interactions), the enzymes of the mitochondrial electron transport chain that modulate the energy metabolism of the brain, the enzyme AANAT, which creates the biosynthesis of melatonin, the FAAH enzyme that breaks down endocannabinoids, COX / LOX enzymes that play a significant part in inflammation, and IDO enzymes that participate in cytokine-induced disease behaviors.
Ion Channels:
CBD targets ten different ion channels. Ion channels settle in cell membranes and facilitate ions across the membrane; There are calcium, potassium, and sodium ion channels responsible for regulating the heartbeat, neural function, muscle contractions, and more. This process is implicated in thermoregulatory, pain, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and anticonvulsant effects.
Conveyors:
Transporter proteins move chemical compounds through the brain and body. Using CBD for pain can bind to transport proteins and block the reuptake of endocannabinoids, thereby stopping the breakdown of cannabinoids produced by the body. It allows more cannabinoids to circulate throughout the body, enhancing cannabinoid receptor signaling, creating a natural state of peace and homeostasis.
For more information on CBD related products and their uses, visit cbd2point0.com today.
1 note
·
View note
Text
This is genuinely beautiful. Like a tone poem
0 notes
Text
Multi-omics analysis identifies LBX1 and NHLH1 as central regulators of human midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation
Midbrain dopaminergic neurons (mDANs) control voluntary movement, cognition, and reward behavior under physiological conditions and are implicated in human diseases such as Parkinson's disease (PD). Many transcription factors (TFs) controlling human mDAN differentiation during development have been described, but much of the regulatory landscape remains undefined. Using a tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) iPSC reporter line, we have generated time series transcriptomic and epigenomic profiles of purified mDANs during differentiation. Integrative analysis predicted novel central regulators of mDAN differentiation and super-enhancers were used to prioritize key TFs. We find LBX1, NHLH1 and NR2F1/2 to be necessary for mDAN differentiation and show that overexpression of either LBX1 or NHLH1 can also improve mDAN specification. NHLH1 is necessary for the induction of neuronal miR-124, while LBX1 regulates cholesterol biosynthesis, possibly through mTOR signaling. Consistently, rapamycin treatment led to an inhibition of mDAN differentiation. Thus, our work reveals novel regulators of human mDAN differentiation. http://dlvr.it/ShZYyJ
0 notes