#atlantic mudskipper
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

By Bjørn Christian Tørrissen - own photo - CC BY-SA 4.0.
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
Daily fish fact #632
Atlantic mudskipper!

It is able to exist out of water for extended periods of time due to its ability to store water in its gill chambers! It can also absorb oxygen through its skin, given it’s moist enough.
163 notes
·
View notes
Text

312 notes
·
View notes
Photo
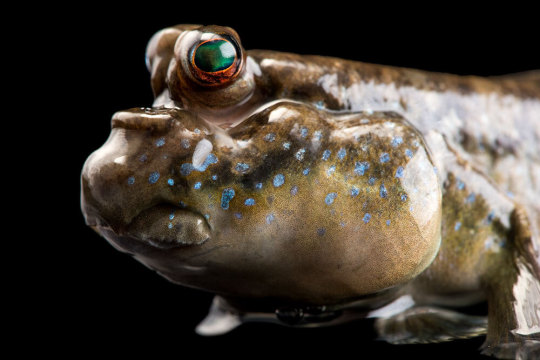
Scientists studied the Atlantic mudskipper, P. barbarus (seen above at the Aquarium of the Pacific in California).
PHOTOGRAPH BY JOEL SARTORE, NAT GEO IMAGE COLLECTION
#joel sartore#photographer#national geographic#atlantic mudskipper#p. barbarus#fish#marine#aquarium of the pacific#nature
72 notes
·
View notes
Note
of these, what's the best fish in your opinion?








Fish in question (in order of posting):
Kobudai/Asian sheepshead wrasse
blobfish
Peters' elephantnosefish
European angler/monkfish
wels
Garibaldi damselfish
Atlantic mudskipper
Bluefin tuna
this has been sitting in my inbox because i want to CHERISH it this is one of the best asks i've gotten
i love the...european angler/monkfish? it looks like it has stuff growing and deposited on it in this photo and that is very poem-worthy, also reminds me of Great A'tuin
i also like the atlantic mudskipper!! it looks very dorky in a cute way i love the little fins in front like arms, like it's about to hug someone
#fish#atlantic mudskipper#european monkfish#heartstopper roleplay#heartstopper#heartstopper rp#charlie spring#charlie's answered asks!#favourite#that one fish ask
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
LIVE MUDSKIPPER REACTION

1 note
·
View note
Text

Mudskipper appreciation. I love these freaky fish.
#leftysage art#mudskipper#you get two drawings today!!!#top is atlantic mudskipper and bottom is giant mudskipper
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wed Beast Wednesday: Mudskippers
For this Wet Beast Wednesday I want to go over a fish that seems to have forgotten it's a fish: the mudskipper. Mudskippers are amphibious fish that are just as comfortable on land as they are in the water. Mudskippers are classified as gobies but goby taxonomy turns out to be weirdly complicated and there's not a clear consensus of what clade constitutes a goby. Mudskippers are members of the subfamily Oxudercinae and consist of at least 23 species, with some sources list up to 43 species. Not all members of Oxurdercinae are considered mudskippers, only those who live a partially terrestrial lifestyle. Mudskippers live in tropical to temperate regions throughout the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic oceans.

(image id: a mudskipper sitting on a branch just above the surface of the water. It is a long, skinny fish with a large head and two large eyes positioned on the top of its head. Its pectoral fins are large and its dorsal fins are folded up. The tail fin is submerged and not easily visible. It is mostly light brown, but has a black stripe going down the body and small, blue speckles all over.)
Mudskippers have a fairly standard goby body plan, but with adaptations to support their terrestrial lifestyles. The most important adaptations for a fish that wants to live on land is to develop an ability to oxygenate themselves without continuously passing water over the gills. Mudskippers have developed two ways to breathe out of water. The first is with their gills. The gill pouch can be sealed off, trapping a bubble of water inside, keeping their gills continuously in contact with water. The gill filaments are also stiffer than in most fish and do not coalesce with each other if they dry out. In addition, the skin, mouth, and throat can absorb oxygen with the help of many small blood vessels, but must be wet to do so. Mudskippers spend up to 3/4th of their time on land, but will die if they dry out. They live mostly in the intertidal zone, primarily on mangrove forests and mud flats, where they have access to water but also plenty of room to move and hunt on land. To assist in moving on land, the pectoral fins have evolved into pseudo-feet. The fins of most ray-finned fish are simple, consisting of a group of inflexible fin rays attached to the body that can be moved (individually in some species) by muscles in the body. Mudskippers have their fin rays jointed part way through and again at the connection to the body. This creates a "shoulder" and "elbow" joint in the fins, giving them greater strength and flexibility. Mudskippers can drag themselves along with their pectoral fins in a skipping motion, which is the source of their common name. Some species can use their pectoral fins to climb on mangrove roots or other exposed plants and rocks. Mudskippers are also adept jumpers. By rapidly folding and extending their tails, mudskippers can leap up to 61 cm (24 in). This is used primarily to escape predators and for display purposes, but may also be used to leap onto higher vantage points. Mudskipper eyes are also special. They are located very high on the head and protrude quite a bit from the body. This eye position gives the mudskipper a very wide range of vision and allows them to bury themselves in mud, only leaving the eyes exposed. Mudskippers can also blink, something other fish cannot do. To blink, a mudskipper will retract an eye into its body while a membrane called a dermal cup rises to cover the eye. Blinking allows the mudskipper to clean its eyes and keep them moist on land. Mudskippers are small fish, with the largest species (Periophthalmodon schlosseri, the giant mudskipper) getting to about 28 cm (11 in) long.

(image id: two mudskippers sitting on sand. one has its front end eld up by its pectoral fins and its mouth partially open. This one's dorsal fins are extended, which run down the body. The other one is lying flat had has its both closed and its dorsal fins folded down. They are light brown with dark stripes. The dorsal fin has many blue dots)
Mudskippers build burrows using their fins and mouths. These burrows are used for shelter and for mating. Most burrows will have their oepning exposed during low tide but will flood during high tide. A chamber in the burrow holds a pocket of air even when flooded. This allows the mudskipper to breathe even if the water is low in oxygen, though it must periodically bring in mouthfuls of air to refresh the pocket. During mating season, males will build burrows. after the burrow is completed, he will come out and start competing for mates. Competitions involve jumping, with the make who can jump the highest attracting the most females. Sometimes mudskipper will fight over territory, though males are especially prone to fighting during mating season. Fights consist of the fish demonstrating at each other with open mouths and raised dorsal fins. During fights, they will also vocalize at each other, with the one who can string together the most vocalizations being the winner. How mudskippers vocalize is still a mystery. Most fish who make sound do so with their swim bladders, but mudskippers don't have swim bladders. Once a female picks a male to mate with they will return to his burrow, where she lays eggs and he fertilizes them. The female departs afterwards, leaving the male to care for the eggs. He will guard the burrow against predators and bring air in to keep the eggs oxygenated until they hatch.

(image id: a mudskipper mid-jump. Its fins are all extended and its body is covered in blue spots)

(image id: two mudskippers fighting. They are facing each other with mouths open, heads pointing up, and fins fully extended)
The majority of mudskipper species are carnivores, though some have transitioned to being detritivores. They hunt invertebrates including worms, insects, and crabs, and some species are cannibalistic. They can hunt both on land and in water, but are more effective at land hunting. When in water, mudskippers use the same suction feeding method that most predatory fish use. When on land, mudskippers use a different method. They carry water in their mouths and chase after prey. When positioned over their prey, the mudskipper will spit some of the water out, allowing it to cover the other animal. It then sucks the water back in, carrying the prey with it. The suction also help propel the prey to the throat, which is useful because mudskippers lack tongues to push their food back.

(image id: a mudskipper in its burrow.The entrance to the burrow is raised above the ground and made of sand. Only the mudskipper's head is visible)
Mudskippers are useful to science in a few ways. They are useful as bio-indicator for the health of their environments. Breathing through your skin is a double-edged sword. It lets you oxygenate on land, but also makes it easier for harmful chemicals to enter the body. Dissection of certain organs allows for testing of environmental chemical levels. Passive observation can also provide data on environmental health. Mudskippers are also used as a model organism for scientists studying the transition of vertebrates to land. While the fish that colonized land were lobe-finned fish as opposed to the ray-finned mudskippers, they can still provide clues to the adaptations and lifestyle of the earliest tetrapods. Outside of science, mudskippers are used for food and as pets. The different species had different classifications by the IUCN ranging from least concern to critically endangered. Their main threats are pollution, habitat loss, and overfishing.

(image id: two mudskipper facing the camera with their mouths open)
#wet beast wednesday#fish#fishblr#fishposting#mudskipper#marine biology#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts#fish that forgot how to fish
304 notes
·
View notes
Text
my aquatic beast collection (minecraft)
under the cut bc its a lot.
(NOT INCLUDING DROWNED)
Alligator snapping turtle Anglerfish Arapaima Arrau turtle Atlantic cod Atlantic halibut Atlantic herring Bayed Blackfish Blobfish Bluegill Boulti Box turtle Brown shrooma Brown trout Cachalot whale Capitaine Carp Catfish Cod (vanilla) Coelacanth Crab Crocodile Deep sea fish (11 variants) Dolphin (vanilla) Elder guardian (vanilla) Frilled shark Frog Gar Ghost shark Giant isopod Glow squid (upgrade aquatic) Great thrasher Guardian (vanilla) Hammerhead shark Horseshoe crab Jellyfish Lionfish Lobster Mantis shrimp Mimic octopus Minnow Mudskipper Muskellunge Nautilus Orca Pacific halibut Perch (aquaculture 2) Perch (upgrade aquatic) Pike Pink salmon Piranha Platypus Pollock Pufferfish (vanilla) Rainbow trout Red chroma Red grouper Salmon (vanilla) Sea pig Seal Smallmouth bass Squat lobsters Squid (vanilla) Starshell turtle Synodontis Tambaqui Thrasher Tropical fish (vanilla) Tuna Turtle (vanilla)
...and me!
9 notes
·
View notes
Photo
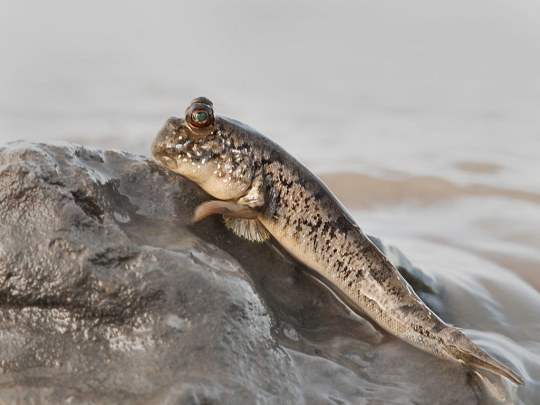




The Atlantic Mudskipper: A Fish Out of Water
Found only along the west African Cost, the Atlantic Mudskipper (Periophthalmus barbarus) is an incredibly unique species of fish. What makes it so special is that, unlike most other fish, the mudskipper can survive on land. It has several adaptations to make it semi-terrestrial. A layer of mucus over the surface of the body allows it to retain moisture, and when on land it can close its gill chambers and breathe through its skin. The eyes are set high on the head and can move independently 360 degrees, giving the Atlantic mudskipper a wide range of vision. Lastly, the pectoral fins that allow it to crawl, climb, and even skip on land, aided by a pair of pelvic fins.
P. Barbarus’ special adaptations allow it to occupy uncommon habitats within its range. It prefers semi-salty brackish water, especially at the mouths of rivers and in mudflats, although they are able to tolerate a range of temperatures and salinity. They can also be found in mangrove forests and lagoons, where they can climb up onto the roots of trees. Along the coast, individuals are most often visible at low tide when they climb up on the shore to feed. In these regions the Atlantic mudskipper digs burrows in which they can hide during high tide. To blend in, they are usually tan to dark brown with dark mottling along the back and bright blue spots on the cheeks.
During the day, the Atlantic mudskipper spends most of its time feeding and defending its territory. They are carnivorous fish, preying on crustaceans, insects, and small fish. The mouth of P. barbarbus is specially shaped so that it covers its prey with water, then sucks the water back up with its accompanying meal. When threatened by terrestrial predators such as shore birds, the Atlantic mudskipper lives up to its name and will ‘skip’ away. These fish also use their mouths in fights, which are quite common. Individuals typically guard of about 1m around their burrow. Males are especially territorial, and will fiercely guard burrows and mates from competitors. Despite their ferocity, Atlantic mudskippers are not very large; most only grow to be 14-16cm long.
Mating occurs year round, although peak times are between February and May. Males engage in territorial displays, after which females will select a male and enter his burrow to lay eggs. Clutches can easily number in the thousands, although few survive to adulthood. The male guards the burrow and, after a brief incubation period, floods it to induce hatching. Larvae drift for 1-2 months before metamorphosing into a juvenile stage, at which time they begin to return to land. Individuals reach sexual maturity at about 10.2-10.8 cm in length, roughly 1 year after hatching, and can live up to 5 years in the wild.
Conservation status: The IUCN rates the Atlantic mudskipper as Least Concern, although populations are declining. Their primary threats are from over-fishing and by-catch, pollution, and urban development. Some areas within their region have instituted sustainable fishing practices and established protected reserves as part of conservation efforts for this species.
Photos
Eva Mártensson
Eric Verhagen
Pedro Martins (via iNaturalist)
Rogerio Ferriera
#atlantic mudskipper#Gobiiformes#Oxudercidae#mudskippers#gobies#fish#Ray-Finned Fish#bony fish#wetlands#wetland fish#rivers#river fish#intertidal fauna#intertidal fish#coral reefs#coral reef fish#atlantic ocean#africa#west africa#animal facts#biology#zoology
150 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Captive Atlantic mudskippers [Periophthalmus barbatus] photographed by John White. These fish can tolerate fresh, marine, and brackish waters, and are even able to tolerate many toxic substances, including industrial waste and cyanide.
127 notes
·
View notes
Note
mudskipper.....
love these guys!!

Atlantic mudskipper | Periophthalmus barbarus

Barred mudskipper | Periophthalmus argentilineatus

Slender mudskipper | Periophthalmus gracilis

Blue-spotted mudskipper | Boleophthalmus boddarti
Photo credit: x, x, x, x
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is and Isn't a Fish: an Essay and Guide by Fishyfishyfishtimes
A simplified list of the animals I discuss can be found here!
Hello folks! I created this post to have a kind of definitive essay/explanation of what is and isn't a "fish", starting with defining the term and going over animals that fit and don't fit the bill. As other fishblr artists, writers and educators must know too well, some people are confused about where this term begins and ends, mistaking other aquatic animals for fish. I have my fair share of arthropods and cnidarians as fish fact requests in my own askbox, heck, some years back a friend of mine asked me if clams were fish. The event that finally made me decide to write this was someone requesting that a fish-only account draw a crustacean, pondering to themselves if they count as fish.
I don't want to hold it against these people. It's impossible to know something when you've never been taught! So that's what I'm here to do, hopefully achieving a pretty correct and universal view ^^' If I make any mistakes please correct me. I'm learning all the same as everyone else is.
Definition of fish
Immediately, we run into a bit of a problem with the definition of fish. See, what the term "fish" means has fluctuated for centuries! For a long time, pretty much any animal that lived in water was a "fish" — I say "pretty much any" instead of "every" animal because for a long time sessile animals like sponges or corals were thought to be plants. This is why we have such remnants in our language like shellFISH, starFISH and jellyFISH, they lived in water so they were called such!
Occasionally these definitions would be changed for cultural convenience too. Many Christian churches take part in Lent, and in the Catholic church red and white meat is forbidden on Fridays and Ash Wednesday. In the Middle Ages, in my own country, Finland, this abstinence of red and white meat could last up to 140 days! To make fasting easier, many animals were labelled fish for convenience so they could be eaten as well. These newfound "fish" included seals, beavers and swans, pretty much just anything that was aquatic or semiaquatic in nature.
Nowadays just going off of looks or behaviour won't do, though. There has been much more of an effort to define fishes coherently based on their anatomy and phylogeny, which is great! Problem is, that's easier said than done: fishes are an extremely diverse group, and uh.. not really a single group, either. I'll show you:
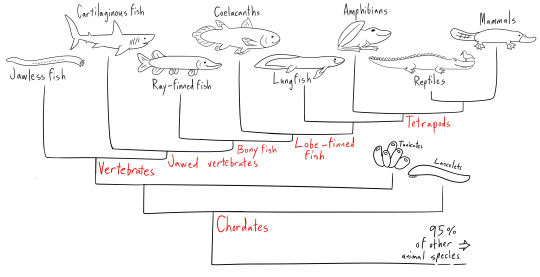
As you can see from this heavily simplified phylogenic tree, fishes are not a singular group like, say, mammals are! The animals that we group under "fish" are actually a part of several distinct lineages of animals, some more closely related to us than each other. Heck, tetrapods, which include amphibians, reptiles*, and mammals, are fish themselves! Phylogenetically speaking. Our ancestors were lobe-finned fish, and, well, you never stop being the previous taxon even when you evolve into something else. If you try to exclude tetrapods, no such unified group as "fish" exists. Still, when discussing fish, we tend to want to avoid talking about every vertebrate ever and instead focus on the very specific aquatic ones we mean when we say "fish". This is why many definitions of the term "fish" still exclude tetrapods, even if we share a common fishy ancestor. "Fish" describes more of a lifeform than it does a clade, much like the term "worm"!
(*birds are reptiles! This could be a whole post in and of itself, but I'm not here to write about that. Someone else has most likely taken up the task!)
Hooray, it's definition time! As stated previously, fishes are an extremely diverse group of thousands of species, and what terms might apply to the Atlantic cod may not apply to the yellowfin tuna or giant mudskipper, let alone a Pacific lamprey! Encyclopedia.com defines a fish as "an ectothermic chordate that lives primarily in water and possesses a cranium*, gills that are useful virtually throughout life, and appendages (if present) in the form of fins". Encyclopedia Britannica notes that "the term fish is applied to a variety of vertebrates of several evolutionary lines", instead highlighting five classes. These five classes are left partly unspecified, but ones that are mentioned are jawless fish, cartilaginous fish and bony fish (which still includes tetrapods, however), and the two classes left can be assumed to be two classes of extinct fish. Wikipedia defines a fish as "an aquatic, craniate**, gill-bearing animal that lacks limbs with digits". Tim M. Berra, an academy professor and ichtyologist, defines fish as "poikilothermic***, aquatic chordate with appendages (when present) developed as fins, whose chief respiratory organs are gills and whose body is usually covered with scales".
(*cranium=upper part of the skull **craniate=an animal with a skull ***poikilothermic=an animal whose internal temperature varies considerably)
From these more or less detailed definitions we can gather many defining features for fish: a cranium-having chordate, primarily aquatic, gill-bearing and uses gills as their main respiratory organ, lacking any limbs with digits, instead having their limbs be in paired and unpaired fins when present. Most fish are also ectothermic, meaning their body temperature is determined by their environment, but some can heat up parts of their body or their entire body in the case of the opah. Most fish also have scales, but not all, just like how most fish are fully aquatic, but some like lungfish or mudskippers can spend considerable time out of the water. Such is the way of these magnificent and diverse animals!
Finally, with all this out of the way, we can get into...
What is a fish!
Here, I will be detailing animals that are fish! Well, at least the broadest strokes; there are more than 30 000 fish species and if I listed them all we'd be here all life. I shall instead go over the major classes and list, in short, some groups that belong in them.
Jawless fish (Superclass Cyclostomi)
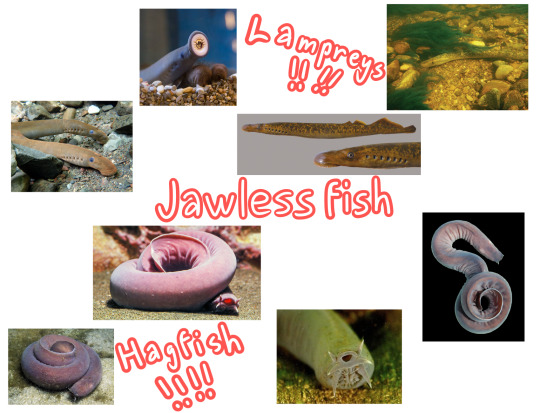

Jawless fish are often a topic of debate, especially in matters of their relation to each other and to jawed vertebrates. Evidence seems to point to hagfish and lampreys being closest related to one another and to lampreys being more closely related to jawed vertebrates than to hagfish (which would make hagfish craniates but not vertebrates). In the phylogeny tree above I decided to portray hagfish and lampreys as a monophyletic group, as molecular studies and microRNA analysis seems to point to a monophylegic superclass. Please note that this could go either way, though.
Jawless fish is a group containing two extant fishes, hagfish (class Myxini) and lampreys (order Petromyzontiformes)! Jawless fish are more "primitive" than other groups, for example both lack true vertebrae and scales. Still, they both have craniums and gills and they are aquatic, and so they have earned their place among fish!
Cartilaginous fish (class Chondrichthyes)

Surprisingly, I've found that this group has a lot of confusion surrounding it. I have received many a request confirming if sharks are fish, or asking if I'd cover a shark "even if it's not a fish". So I'll say it now: good news, sharks are indeed fish! So are their cousins, rays, skates and chimaeras, also known as ghost sharks! All of these fish have a primarily cartilaginous skeleton, tooth-like dermal denticles and lack gill covers and a swim bladder. Out of all the sharks, I also want to highlight that the whale shark, despite its confusing name, is a shark and not a whale. So, it is a fish!
Ray-finned fish (class Actinopterygii)

Name any fish, and there's a 96% chance the species name you said belongs to a ray-finned fish. Unless, like, you really like sharks. But this isn't about them.
Ray-finned fish are the biggest group of fish and incredibly diverse! It has your seahorse, your pufferfish, your bass, your tuna, your anglerfish, your clownfish, your salmon, your sturgeon, your lanternfish, your perch, your oarfish, your gar, your sardine, your moray eel... and this is only a tiny, tiny fraction of the groups that belong to this class! Defining features of ray-finned fish are that they tend to have a swim bladder and a bony skeleton (some exceptions though. Sturgeons, for one, have evolved a cartilaginous skeleton but they're still ray-finned fish). The largest group of ray-fins, the teleosts, also have leptoid scales, which are thinner and more flexible and grow with growth rings.
I want to bring special attention to some members of the ray-finned fish which tend to have a lot of confusion surrounding them and their heritage: eels and seahorses. Many people think these two are not fish due to their strange anatomy, like lack of scales or (many) fins and their elongated bodies, and I wouldn't blame them! Seahorses belong to family Syngnathidae, which also includes seadragons and pipefish. Eels, meanwhile, make up the order Anguilliformes. All of these long friends of ours are fish!
Lobe-finned fish (clade Sarcopterygii)

I shall merely focus on the fishy fishy fish individuals of this class, which excludes tetrapods. Lobe-finned fish house the two extant species of coelacanths, and six extant species of lungfish! These fish are bony and their fins are placed at the tips of fleshy, lobelike stalks, resembling the limbs of tetrapods. It is thought that the common ancestor of coelacanths and lungfish and tetrapods had similar structures that then became the four limbs the members of our clade typically have. Coelacanths and lungfish are wonderful fishes and deserve a lot of love and respect, not only because they're our closest cousins but because they're unique and we have so much to learn about them!
So, these are the fishes! There are also extinct groups of fish, namely class Placodermi (armoured fish) and class Acanthodii (spiny "sharks"). I'm moreso an extant fish account however, and so I shall move onto...
What isn't a fish?
Now we get into the real meat of this post. Without further ado, here are some aquatic friends of ours that can be mixed up with fish very often!
Crustaceans (subphylum Crustacea)

Many of our hard-shelled many-legged friends belong here! Crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, isopods, triops, barnacles, copepods, you name it! Even though many crustaceans are aquatic or semiaquatic and have gills, you'll find that they're invertebrates that lack an internal skeleton (so no cranium, not even vertebrae)! We still love them though!
Mollusks (phylum Mollusca)

Creatures both soft and hard-shelled! Cephalopods like octopuses, squid, nautilus and cuttlefish, bivalves like clams, mussels, oysters or scallops, gastropods like sea slugs and snails and chitons go here! These friends of ours are also aquatic and have gills, some even have the suffix -fish (cephalopods used to be called inkfish, even!), but their lack of an endoskeleton is even more obvious than the crustaceans'. They're invertebrates, and therefore not fish!
Chelicerates (subphylum Chelicerata)

This group has many animals that are very hard to mistake for fish, namely spiders and scorpions, but horseshoe crabs and sea spiders are two groups of extant marine chelicerates! Both groups are aquatic, and horseshoe crabs have gills. However, they're both invertebrates, lacking a cranium or vertebrae. Other aquatic chelicerates exist, but they're usually very small, like water mites.
Cnidarians (phylum Cnidaria)

This phylum has the sessile corals and sea anemones and the usually more mobile jellyfish and siphonophores (includes the infamous Portugese man o' war!). I imagine corals and sea anemones are mistaken for fish less due to their sessile nature, but they're good to bring up nevertheless. None of these animals have a backbone, or, any bones really. They lack gills, they lack fins, they even lack the bilateral shape of fish. Jellyfish, despite the name, are indeed not fish! Some people suggest the name sea jellies be used for them instead, and I think it's much cuter.
Echinoderms (phylum Echinodermata)

Animals like starfish, sea urchins, brittle stars, sand dollars, sea cucumbers and feather stars go here. It seems that this pesky "-fish" -suffix is hard to shake off, as now we have the starfish. Once again, all of these slow-moving bottom-dwelling friends of ours are invertebrates, as they lack vertebrae or a cranium. Interestingly though, they are among our closest invertebrate relatives! So we ought to give them some props for that. I also want to mention that starfish can also be called sea stars, which ought to lessen confusion about their being too.
Comb jellies (phylum Ctenophora)

Comb jellies look a lot like jellyfish, but they belong in their own unique phylum! They have the same deal going on; they are invertebrates, they lack gills, they lack a cranium, they are simply aquatic.
Lancelets (subphylum Cephalocordata) and tunicates (subphylum Tunicata)
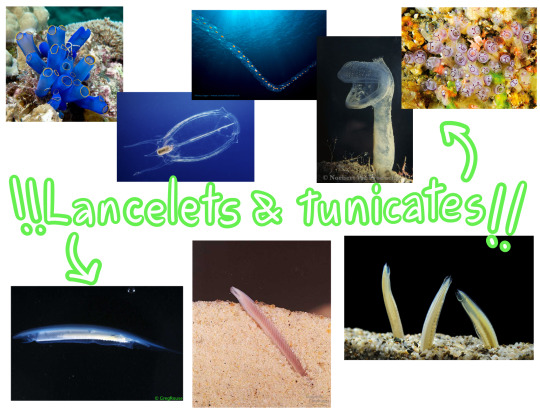

A double feature, because I wanted to save space didn't want these guys to be all alone! Lancelets and Tunicates, like sea squirts and salps, are chordates, which you can find in the phylogenic tree I drew all the way in the definitions section. They share many a feature with vertebrates, like a bilateral bodyplan, a notochord at some stage of life and a post-anal tail, but I'm afraid they're still not fish. They lack a cranium and their notochord does not develop into a vertebral column! Sorry friends, you tried. We can still hang out at the chordate convention.
Annelids (phylum Annelida)
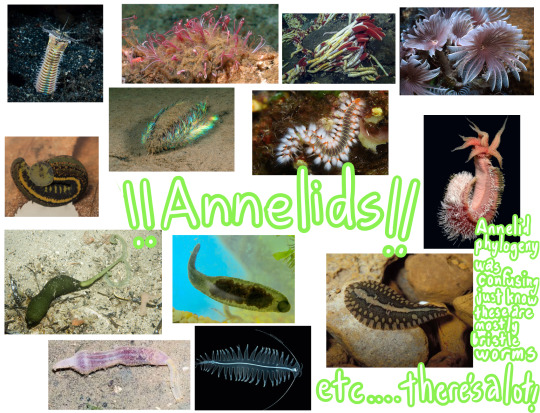

The infamous bobbit worm, bone-eating worms, sea mice, giant tube worms, feather duster worms, spoon worms, bristleworms in general, leeches... many, many worms go here! Pretty self-explanatory: they are invertebrates, even when they live in water. They're extremely cool invertebrates too! I suggest taking a look at some of them, there's many interesting species.
Flatworms (phylum Platyhelminthes)

Flatworms are another very diverse group of worms, having many species both terrestrial and aquatic, however mostly I want to put attention into the free-swimming marine flatworms. They may swim beautifully (and fence with grace), but they are nevertheless invertebrates! Flatworms can live a variety of different lifestyles, from predators to parasites.
Amphibians (class Amphibia)

We've made it into vertebrates now! Amphibians include frogs, salamanders, and caecilians. While they have limbs with digits in their adulthood*, they can be easily confused for fish in their larval stages! This is no surprise, as they use gills to breathe underwater and tadpoles lack any limbs at all for a while. Many amphibians later transition into a terrestrial or semiaquatic way of life and lose their gills, not to mention gain their digit-having limbs.
(*excluding caecilians)
...Well, many amphibians do this, but not all. It's important to mention there are also species of aquatic salamanders which can bear great resemblance to fish with their elongated bodies! Amphiumas, which are sometimes mistakenly called "conger eels" (which is an actual species of fish), are aquatic salamanders with small residual limbs and both working gills and lungs. Giant salamanders and mudpuppies/waterdogs have lungs and gills as well, and lead an aquatic lifestyle — olms are close relatives of mudpuppies. Sirens, meanwhile, lack hind limbs and only have small front limbs, along with retaining their gills in adulthood. Among aquatic salamanders I also want to bring up one most often talked about species: the axolotl! They remain in their larval form, have external gills and lead an aquatic lifestyle. It can be hard to tell with aquatic salamanders sometimes, but these friends of ours are amphibians and not fish, even if they've rejected the land life.
Caecilians are a bit less known overall, but they can also cause a lot of confusion due to their long, limbless body. While most caecilians live underground, some are aquatic in nature, and can therefore be mistaken for fish! However, caecilians breathe via the use of their lungs and through the skin and don't have any gills at all.
Reptiles (class Reptilia)

Most commonly mistaken for fish in this group are sea snakes, sea kraits and water snakes, sea turtles, turtles, penguins, and other (semi)aquatic birds. Sea snakes and water snakes bear a very strong resemblance to eels, but they are indeed just snakes adapted to an aquatic or a semiaquatic lifestyle! The same goes for sea turtles, turtles overall, and penguins. They all need to breathe air and they lack fins, even if their flippers, webbed feet and built-in paddles may look like fins! They also have wholly different types of scales (or feathers!!) than what fish have, even if they share the feature. I assume that other aquatic reptiles, like the marine iguana and crocodilians are better read as reptiles thanks to their limbs with digits, but I want to give them a reptile shoutout anyway. They’re aquatic or semiaquatic, but they are air-breathers and fin-lackers all the same!
I also want to mention one specific extinct group of reptiles, ichtyosaurs! These marine reptiles were rather shark- or dolphin-like in appearance, which is actually a really good example of convergent evolution! Like all other reptiles, they also needed to breathe air and they had... erm... well, I'm not sure if I can call the bones in their flippers digits, but, that's what they used to be, so...? They were cool reptiles and among my favourites! There were many other aquatic reptiles too, but I will only mention just the ones now. A paleontology account would be better-suited to list you allll the marine reptiles.
Mammals (class Mammalia)

Our home class! Some of the aquatic friends we have in this class include whales like baleen and beaked whales, dolphins (orcas go here), porpoises, belugas, narwhals and sperm whales, pinnipeds like seals, sea lions, walruses, and sirenians like manatees, (occasionally known as sea cows) and dugongs! We also have some semiaquatic buddies like hippopotamids, otters, beavers and platypuses! Whales and pinnipeds especially often cause a lot of confusion due to their very streamlined, fishy appearance. They are, however, air breathers that feed their young with milk (some dolphin calves are even born with some hair), and their ancestors were land mammals! The same goes for pinnipeds and sirenians too. True seals, fur seals and sea lions still have fur even! Hippos, otters, beavers and platypuses are a bit more obvious as mammals with their fur and.. distinct air-breathing.. but I wanted to mention them anyway. Their adaptations to aquatic life are just one example of how fascinating evolution can be!
And here we are! A hopefully comprehensive list of fishes and non-fishes, beginning with the ever-shifting story of the term "fish", phylogeny, and why some animals are called fish when they really aren't. I hope you have found useful and interesting information in this post, and perhaps learned something new! I bid you a farewell! :D
#fish guide#fish essay#fish#fish facts#fishfact#marine biology#biology#zoology#long post#jawless fish#cartilaginous fish#ray-finned fish#lobe-finned fish
273 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Afrikanischer oder Atlantischer Schlammspringer | Atlantic mudskipper
Periophthalmus barbarus
[Hagenbecks Tropen-Aquarium]
#AfrikanischerSchlammspringer#AtlantischerSchlammspringer#Atlanticmudskipper#Periophthalmusbarbarus#Schlammspringer#Mudskipper#HagenbecksTropenAquarium#Hagenbeck#Hamburg
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The full book title contains 3777 words and reads as follows: 'The historical development of the Heart i.e. from its formation from Annelida: Clam worm, Seamouse, Lugworm, Megascolex, Tubifex, Pheretima, Freshwater leech, marine leech, land leech. Arthropoda: Ladybird, Krill, Rock Barnacle, Root-headed Barnacle, Copepod, Silverfish, Cairns birdwing, Silver - spotted skipper, Scutigera, Cray fish, Large white, Andonis blue, Camberwell beauty, Tiger swallowtail, Regent skipper, Black – veined white, Green – underside blue, Blue Morpho, Apollo, Guava skipper, Cleopatra, Large copper, Millipede, Orb spider, Black widow spider, Giant crab spider, Wolf spider, Bird – eating spider, Tenebrionid beetle, Green Tiger beetle, African goliath beetle, Scolopendra, Diving beetle, African ground beetle, New guinea weevil, Barnacle, Lobster, Shrimp, Woodlice, Mite, Prawn, Housefly, Butterfly, Monarch butterfly, Peacock butterfly, Honey bee, Fairy shrimp, Horsehoe crab, Tick, Bluebootle, Froghopper, Yellow crazy ant, Water flea, Sea spider, Fiddler crab, Shiny spider crab, Hermit crab, Sail swallowtail, Red admiral, Morpho butterfly, Desert locust, Stephens island weta, Speckled bush cricket, Mole cricket, Dung – beetle, Euthalia ynipardus, Small blues, Termite, Hornet, Mosquito, Garden spider, Tarantula, Desert hairy scorpion, Emperor dragon – fly, Moth, Centipede, Wood ant, Stag beetle, Indian red admiral, Blue admiral, Harvestman, Hoverfly, Shield bug, Assassin bug, Cicada, Coreid bug, Rose aphid, Water – boatman, Wasp, June bug, Large tortoiseshell, Frog beetle, Mexican red – legged tarantula, Paintedlady, Sydney funnelweb spider, Small tortoiseshell, Mountain bumble bee, Trapdoor spider, Jumping spider, Daddy longlegs spider, Orchind bee, Asian carpenter bee, Parasitic bee, House spider, Giant longhorn beetle, Flea, Bedbug Beetle, Cockroach, Scorpion, Spider, Ant, Gnats, Grasshopper, Silver fish, Crab, Great green bush cricket, Elephant hawk – moth. Mollusca: Neomenia, Chaetoderma, Chiton, Lepidopleurus, Apple snail, Sea hare, Sea lemon, Dentalium, Freshwater mussel, Marine mussel, Pearl oyster, Cuttlefish, Giant squid, Chambered fish, Devilfish. Fishes or Pisces: African glass catfish, African lungfish, Aholehole, Airbreathing catfish, Alaska blackfish, Albacore, Alewife, Alfonsino, Algae eater, Alligatorfish, Alligator gar, Amberjack - Seriola dumerili, American sole, Amur pike, Anchovy, Anemonefish, Angelfish, Angler, Angler catfish, Anglerfish, Antarctic cod, Antarctic icefish, Antenna codlet, Arapaima, Archerfish, Arctic char, Armored gurnard, Armored searobin, Armorhead, Armorhead catfish, Armoured catfish, Arowana, Arrowtooth eel, Asian carps, Asiatic glassfish, Atka mackerel, Atlantic Bonito (Sarda sarda), Atlantic cod, Atlantic herring, Atlantic salmon, Atlantic Sharpnose Shark - Rhizoprioltodon terraenovae, Atlantic saury, Atlantic silverside, Australasian salmon, Australian grayling, Australian herring, Australian lungfish, Australian prowfish, Ayu, Baikal oilfish, Bala shark, Ballan wrasse, Bamboo shark, Banded killifish, Bandfish, Banjo, Bangus, Banjo catfish, Bank Sea Bass, Barb, Barbel, Barbeled dragonfish, Barbeled houndshark, Barbel-less catfish, Barfish, Barracuda, Barracudina, Barramundi, Barred danio, Barreleye, Basking shark, Bass, Basslet, Batfish, Bat ray, Beachsalmon, Beaked salmon, Beaked sandfish, Beardfish, Beluga sturgeon, Bengal danio, Betta, Bichir, Bicolor goat fish, Bigeye, , Bighead carp, Bigmouth buffalo, Bigscale, Billfish, Bitterling, Black angelfish, Black bass, Black dragonfish, Blackchin, Blackfin Tuna - Thunnus atlanticus, Blackfish, Black neon tetra, Blacktip reef shark, Black mackerel, Black scalyfin, Black sea bass, Black scabbardfish, Black swallower, Black tetra, Black triggerfish, Bank Sea Bass aka Yellow Sea Bass - Centropristis ocyurus, Bleak, Blenny, Blind goby, Blind shark, Blobfish, Blueline Tilefish, Blowfish, Blue catfish, Blue danio, Blue-redstripe danio, Blueline Tilefish , Blue eye, Bluefin tuna, Bluefish, Bluegill, Blue gourami, Blue shark, Blue triggerfish, Blue whiting, Bluntnose knifefish, Bluntnose minnow, Boafish, Boarfish, Bobtail snipe eel, Bocaccio, Boga, Bombay duck, Bonefish, Bonito, Bonnetmouth, Bonytail chub, Bronze corydoras, Bonytongue, Bowfin, Boxfish, Bramble shark, Bream, Brill, Bristlemouth, Bristlenose catfish, Broadband dogfish, Brook lamprey, Brook trout, Brotula, Brown trout, Buffalo fish, Bullhead, Bullhead shark, Bull shark, Bull trout, Burbot, Bumblebee goby, Buri, Burma danio, Burrowing goby, Butterfish, Butterfly ray, Butterflyfish, California flyingfish, California halibut, Canary rockfish, Candiru, Candlefish, Capelin, Cardinalfish, Cardinal tetra, Carp, Carpetshark, Carpsucker, Catalufa, Catfish, Catla, Cat shark, Cavefish, Celebes rainbowfish, Central mudminnow, Chain pickerel, Channel bass, Channel catfish, Char, Cherry salmon, Chimaera, Chinook salmon, Cherubfish, Chub, Chubsucker, Chum salmon, Cichlid, Cisco, Climbing catfish, Climbing gourami, Climbing perch, Clingfish, Clownfish, Clown loach, Clown triggerfish, Cobbler, Cobia, Cod, Codlet, Codling, Coelacanth, Coffinfish, Coho salmon, Coley, Collared carpetshark, Collared dogfish, Colorado squawfish, Combfish, Combtail gourami, Common carp, Common tunny, Conger eel, Convict blenny, Convict cichlid, Cookie-cutter shark, Coolie loach, Cornetfish, Cowfish, Cownose ray, Cow shark, Crappie, Creek chub, Crestfish, Crevice kelpfish, Croaker, Crocodile icefish, Crocodile shark, Crucian carp, Cuckoo wrasse, Cusk, Cusk-eel, Cutlassfish, Cutthroat eel, Cutthroat trout, Dab, Dace, Desert pupfish, Devario, Devil ray, Dhufish, Discus, Diver: New Zealand sand diver or long-finned sand diver, Dogfish, Dogfish shark, Dogteeth tetra, Dojo loach, Dolly Varden trout, Dolphin fish - Corypaena hippurus, Dorab, Dorado, Dory, Dottyback, Dragonet, Dragonfish, Dragon goby, Driftfish, Driftwood catfish, Drum, Duckbill, Duckbill eel, Dusky grouper, Dusky Shark - Carcharhinus obscurus, Dwarf gourami, Dwarf loach, Eagle ray, Earthworm eel, Eel, Eel cod, Eel-goby, Eelpout, Eeltail catfish, Elasmobranch, Electric catfish, Electric eel, Electric knifefish, Electric ray, Elephant fish, Elephantnose fish, Elver, Ember parrotfish, Emerald catfish, Emperor angelfish, Emperor bream, Escolar, Eucla cod, Eulachon, European chub, European eel, European flounder, European minnow, European perch, False brotula, False cat shark, False moray, Fangtooth, Fathead sculpin, Featherback, Fierasfer, Fire goby, Filefish, Finback cat shark, Fingerfish, Firefish, Flabby whale fish, Flagblenny, Flagfin, Flagfish, Flagtail, Flashlight fish, Flatfish, Flathead, Flathead catfish, Flier, Flounder, Flying gurnard, Flying fish, Footballfish, Forehead brooder, Four-eyed fish, French angelfish, Freshwater eel, Freshwater hatchetfish, Freshwater shark, Frigate mackerel, Frilled shark, Frogfish, Frogmouth catfish, Fusilier fish, Galjoen fis, Ganges shark, Geel, Garibaldi, Garpike, Ghost fish, Ghost flathead, Ghost knifefish, Ghost pipefish, Ghost shark, Ghoul, Giant danio, Giant gourami, Giant sea bass, Gibberfish, Gila trout, Gizzard shad, Glass catfish, Glassfish, Glass knifefish, Glowlight danio, Goatfish, Goblin shark, Goby, Golden dojo, Golden loach, Golden shiner, Golden trout, Goldeye, Goldfish, Gombessa, Goosefish, Gopher rockfish, Gourami, Grass carp, Graveldiver, Grayling, Gray mullet, Gray reef shark, Great white shark, Green swordtail, Greeneye, Greenling, Grenadier, Green spotted puffer, Ground shark, Grouper, Grunion, Grunt, Grunter, Grunt sculpin, Gudgeon, Guitarfish, Gulf menhaden, Gulper eel, Gulper, Gunnel, Guppy, Gurnard, Haddock, Hagfish, Hairtail, Hake, Halfbeak, Halfmoon, Halibut, Halosaur, Hamlet, Hammerhead shark, Hammerjaw, Handfish, Hardhead catfish, Harelip sucker, Hatchetfish, Hawkfish, Herring, Herring smelt, Hickory Shad, Horn shark, Horsefish, Houndshark, Huchen, Humuhumunukunukuapua'a, Hussar, Icefish, Ide, Ilisha, Inanga, Inconnu, Jack, Jackfish, Jack Dempsey, Japanese eel, Javelin, Jawfish, Jellynose fish, Jewelfish, Jewel tetra, Jewfish, John Dory, Kafue pike, Kahawai, Kaluga, Kanyu, Kelp perch, Kelpfish, Killifish, King of the herrings, Kingfish, King-of-the-salmon, Kissing gourami, Knifefish, Knifejaw, Koi, Kokanee, Kokopu, Kuhli loach, Labyrinth fish, Ladyfish, Lake chub, Lake trout, Lake whitefish, Lampfish, Lamprey, Lanternfish, Largemouth bass, Leaffish, Lefteye flounder, Lemon shark, Lemon sole, Lemon tetra, Lenok, Leopard danio, Lightfish, Limia, Lined sole, Ling, Ling cod, Lionfish, Livebearer, Lizardfish, Loach, Loach catfish, Loach goby, Loach minnow, Longfin, Longfin dragonfish, Longfin escolar, Longfin smelt, Long-finned char, Long-finned pike, Longjaw mudsucker, Longneck eel, Longnose chimaera, Longnose dace, Longnose lancetfish, Longnose sucker, Longnose whiptail catfish, Long-whiskered catfish, Loosejaw, Lost River sucker, Louvar, Loweye catfish, Luderick, Luminous hake, Lumpsucker, Lungfish, Mackerel, Mackerel shark, Madtom, Mahi-mahi, Mahseer, Mail-cheeked fish, Mako shark, Mandarinfish, Masu salmon, Medaka, Medusafish, Megamouth shark, Menhaden, Merluccid hake, Mexican golden trout, Midshipman fish, Milkfish,, Minnow, Minnow of the deep, Modoc sucker, Mojarra, Mola, Monkeyface prickleback, Monkfish, Mooneye, Moonfish, Moorish idol, Mora, Moray eel, Morid cod, Morwong, Moses sole, Mosquitofish, Mouthbrooder, Mozambique tilapia, Mrigal, Mud catfish (Mud cat), Mudfish, Mudminnow, Mud minnow, Mudskipper, Mudsucker, Mullet, Mummichog, Murray cod, Muskellunge, Mustache triggerfish, Mustard eel, Naked-back knifefish, Nase, Needlefish, Neon tetra, New World rivuline, New Zealand smelt, Nibble fish, Noodlefish, North American darter, North American freshwater catfish, North Pacific daggertooth, Northern anchovy, Northern clingfish, Northern lampfish, Northern pike, Northern sea robin, Northern squawfish, Northern stargazer, Notothen, Nurseryfish, Nurse shark, Oarfish, Ocean perch, Ocean sunfish, Oceanic whitetip shark, Oilfish, Oldwife, Old World knifefish, Olive flounder, Opah, Opaleye, Orange roughy, Orangespine unicorn fish, Orangestriped triggerfish, Orbicular batfish, Orbicular velvetfish, Oregon chub, Orfe, Oriental loach, Oscar, Owens pupfish, Pacific albacore, Pacific cod, Pacific hake, Pacific herring, Pacific lamprey, Pacific salmo, Pacific saury, Pacific trout, Pacific viperfish, Paddlefish, Pancake batfish, Panga, Paradise fish, Parasitic catfish, Parore, Parrotfish, Peacock flounder, Peamouth, Pearleye, Pearlfish, Pearl danio, Pearl perch, Pelagic cod, Pelican eel, Pelican gulper, Pencil catfish, Pencilfish, Pencilsmelt, Peppered corydoras, Perch, Peters' elephantnose fish, Pickerel, Pigfish, Pike conger, Pike eel, Pike, Pikeblenny, Pikeperch, Pilchard, Pilot fish, Pineapplefish, Pineconefish, Pink salmon, Píntano, Pipefish, Piranha, Pirarucu, Pirate perch, Plaice, Platy, Platyfish, Pleco, Plownose chimaera, Poacher, Pollock, Pomfret, Pompano dolphinfish, Ponyfish, Popeye catalufa, Porbeagle shark, Porcupinefish, Porgy, Port Jackson shark, Powen, Prickleback, Pricklefish, Prickly shark, Prowfish, Pufferfish, Pumpkinseed, Pupfish, Pygmy sunfish, Queen danio, Queen parrotfish, Queen triggerfish, Quillback, Quillfish, Rabbitfish, Raccoon butterfly fish, Ragfish, Rainbow trout, Rainbowfish, Rasbora, Ratfish, Rattail, Ray, Razorback sucker, Razorfish, Red Grouper, Red salmon, Red snapper, Redfin perch, Redfish, Redhorse sucker, Redlip blenny, Redmouth whalefish, Redtooth triggerfish, Red velvetfish, Red whalefish, Reedfish, Reef triggerfish, Remora, Requiem shark, Ribbon eel, Ribbon sawtail fish, Ribbonfish, Rice eel, Ricefish, Ridgehead, Riffle dace, Righteye flounder, Rio Grande perch, River loach, River shark, River stingray, Rivuline, Roach, Roanoke bass, Rock bass, Rock beauty, Rock cod, Rocket danio, Rockfish, Rockling, Rockweed gunnel, Rohu, Ronquil, Roosterfish, Ropefish, Rough scad, Rough sculpin, Roughy, Roundhead, Round herring, Round stingray, Round whitefish, Rudd, Rudderfish, Ruffe, Russian sturgeon, Sábalo, Sabertooth, Saber-toothed blenny, Sabertooth fish, Sablefish, Sacramento blackfish, Sacramento splittail, Sailfin silverside, Sailfish, Salamanderfish, Salmon, Salmon shark, Sandbar shark, Sandburrower, Sand dab, Sand diver, Sand eel, Sandfish, Sand goby, Sand knifefish, Sand lance, Sandperch, Sandroller, Sand stargazer, Sand tiger, Sand tilefish, Sandbar Shark - Carchathinus plumbeus, Sarcastic fringehead, Sardine, Sargassum fish, Sauger, Saury, Sawfishm, Saw shark, Sawtooth eel, Scabbard fish, Scaly dragonfish, Scat, Scissortail rasbora, Scorpionfish, Sculpin, Scup, Sea bass, Sea bream, Sea catfish, Sea chub, Sea devil, Sea dragon, Sea lamprey, Sea raven, Sea snail, Sea toad, Seahorse, Seamoth, Searobin, Sevan trout, Sergeant major, Shad, Shark, Sharksucker, Sharpnose puffer, Sheatfish, Sheepshead, Sheepshead minnow, Shiner, Shortnose chimaera, Shortnose sucker, Shovelnose sturgeon, Shrimpfish, Siamese fighting fish, Sillago, Silver carp, Silver dollar, Silver dory, Silver hake, Silverside, Silvertip tetra, Sind danio, Sixgill ray, Sixgill shark, Skate, Skilfish, Skipjack tuna, Slender mola, Slender snipe eel, Sleeper, Sleeper shark, Slickhead, Slimehead, Slimy mackerel, Slimy sculpin, Slipmouth, Smalleye squaretail, Smalltooth sawfish, Smelt, Smelt-whiting, Smooth dogfish, Snailfish, Snake eel, Snakehead, Snake mackerel, Snapper, Snipe eel, Snipefish, Snoek, Snook, Snubnose eel, Snubnose parasitic eel, Sockeye salmon, Soldierfish, Sole, South American darter, South American lungfish, Southern Dolly Varden, Southern flounder, Southern hake, Southern sandfish, Southern smelt, Spadefish, Spaghetti eel, Spanish mackerel, Spearfish, Speckled trout, Spiderfish, Spikefish, Spinefoot, Spiny basslet, Spiny dogfish, Spiny dwarf catfish, Spiny eel, Spinyfin, Splitfin, Spookfish, Spotted climbing perch, Spotted danio, Spottail Pinfish - Diplodus holbrooki, Sprat, Springfish, Squarehead catfish, Squaretail, Squawfish, Squeaker, Squirrelfish, Staghorn sculpin, Stargazer, Starry flounder, Steelhead, Stickleback, Stingfish, Stingray, Stonecat, Stonefish, Stoneroller minnow, Stream catfish, Striped bass, Striped burrfish, Sturgeon, Sucker, Suckermouth armored catfish, Summer flounder, Sundaland noodlefish,Sunfish, Surf sardine, Surfperch, Surgeonfish, Swallower, Swamp-eel, Swampfish, Sweeper, Swordfish, Swordtail, Tadpole cod, Tadpole fish, Tailor, Taimen, Tang, Tapetail, Tarpon, Tarwhine, Telescopefish, Temperate bass, Temperate perch, Tenpounder, Tenuis, Tetra, Thorny catfish, Thornfish, Threadfin, Threadfin bream, Thread-tail, Three spot gourami, Threespine stickleback, Three-toothed puffer, Thresher shark, Tidewater goby, Tiger barb, Tigerperch, Tiger shark, Tiger shovelnose catfish, Tilapia, Tilefish, Titan triggerfish, Toadfish, Tommy ruff, Tompot blenny, Tonguefish, Tope, Topminnow, Torpedo, Torrent catfish, Torrent fish, Trahira, Treefish, Trevally, Triggerfish, Triplefin blenny, Triplespine, Tripletail, Tripod fish, Trout, Trout cod, Trout-perch, Trumpeter, Trumpetfish, Trunkfish, Tubeblenny, Tube-eye, Tube-snout, Tubeshoulder, Tui chub, Tuna, Turbot, Two spotted goby, Uaru, Unicorn fish, Upside-down catfish, Vanjaram, Velvet belly lanternshark, Velvet catfish, Velvetfish, Vermillion Snapper - Rhomboplites aurorubens, Vimba, Viperfish, Wahoo, Walking catfish, Wallago, Walleye, Walleye Pollock, Walu, Warmouth, Warty angler, Waryfish, Waspfish, Weasel shark, Weatherfish, Weever, Weeverfish, Wels catfish, Whale catfish, Whalefish, Whale shark, Whiff, Whitebait, White croaker, Whitefish, White marlin, White shark, Whitetip reef shark, Whiting, Wobbegong, Wolf-eel, Wolffish, Wolf-herring, Worm eel, Wormfish, Wrasse, Wrymouth, X-ray fish, Yellowback fusilier, Yellowbanded perch, Yellow bass, Yellowedge grouper (Hyporthodus flavolimbatus), Yellow-edged moray, Yellow-eye mullet, Yellowhead jawfish, Yellowfin croaker, Yellowfin cutthroat trout, Yellowfin grouper, Yellowfin Tuna - Thunnus albacares, Yellowfin pike, Yellowfin surgeonfish, Yellowfin tuna, Yellowmargin triggerfish, Yellow moray, Yellow perch, Yellowtail, Yellowtail amberjack, Yellowtail barracuda, Yellowtail clownfish, Yellowtail horse mackerel, Yellowtail kingfish, Yellowtail snapper, Yellow tang, Yellow weaver, Yellowtail catfish, Zander, Zebra bullhead shark, Zebra danio, Zebrafish, Zebra lionfish, Zebra loach, Zebra oto, Zebra pleco, Zebra shark, Zebra tilapia, Zebra turkeyfish, Ziege, Zingel. Amphibians: Frogs and Toads, Painted frogs, Disc tongued frogs, Fire Belly toads, Litter frogs, European Spadefoot toads, Parsley frogs, Tongueless frogs, Clawed frogs, Mexican Burrowing Toad, American spadefoot toads, Screeching frogs, True toads, Glass Frogs, Poison dart frogs, Ghost frogs, Shovelnose frogs, Tree frogs, Sedge frogs, Southern frogs, Narrow-mouthed frogs, Australian ground frogs, True frogs, Moss frogs, Seychelles frog, Giant Salamanders, Asiatic Salamanders, Mole Salamanders, Pacific giant salamanders, Amphiumas, Lungless salamanders, Mudpuppies and Waterdogs, Torrent salamanders, True salamanders and Newts, Sirens, Common caecilians, Fish caecilians, Beaked caecilians. Reptiles: Turtles, common snapping turtles and alligator snapping turtle, pond turtles and box turtles, tortoises, Asian river turtles and allies, pignose turtles, softshell turtles, river turtles, mud turtles, sea turtles, leatherback turtles, tuataras, scaled reptiles, agamas, chameleons, casquehead lizard, iguanas, Madagascar iguanids, collared and leopard lizards, horned lizards, anoles, wood lizards, Neotropical ground lizards, geckos, legless lizards, blind lizards, spinytail Lizards, plated lizards, spectacled lizards, whiptails and tegus, Lacertids, skinks, night lizards, glass lizards, American legless lizards, knob-scaled lizards, gila monsters, earless Monitor lizards, monitor lizards, worm Lizards, shorthead Worm Lizards, two-legged Worm Lizards, snakes, wart snakes, false coral snakes, dwarf pipe snakes, African burrowing asps, stiletto snakes, boas, anacondas, Old World sand boas, Mauritius snakes, Colubrids, typical snakes, Asian pipe snakes, cobras, coral snakes, mambas, sea snakes, Mexican pythons, pythons, dwarf boas, pipe snakes, shield-tailed snakes, vipers, pitvipers, Fae's viper, night adders, pitvipers, rattlesnakes, true vipers, sunbeam snakes, blind snakes, primitive blind snakes, slender blind snakes, thread snakes, blind snakes, typical blind snakes, Crocodiles, alligators, garials. Aves: Ostrich, rheas, cassowaries and emu, kiwis, elephant birds, upland moas, great moas, lesser moas, Tinamous, Australian brush turkey,megapodes, chachalacas, curassows, and guans, Guineafowl, pheasants and allies, New World quail, pheasants and relatives, mihirungs, screamers, magpie-goose, ducks, geese, and swans, grebes, swimming flamingos, flamingos, pigeons and doves, sandgrouse, mesites, Tawny frogmouth, Nightjars, oilbird, potoos, frogmouths, owlet-nightjars, treeswifts, swifts, hummingbird, cuckoos and relatives, turacos and relatives, bustards, hoatzin, cranes and allies, cranes, limpkin, trumpeters, rails and allies, adzebills, finfoots, flufftails, rails and relatives, thick-knees and allies, thick-knees and relatives, sheathbills, Magellanic plover, plover-like waders, golden plovers, ibisbill, oystercatchers, plovers and lapwings, jacana-like waders, painted snipes, Egyptian plover, jacanas, seedsnipes, plains-wanderer, sandpipers and relatives, buttonquail, gulls and allies, coursers and pratincoles, crab-plover, skuas and jaegers, auks and puffins, gulls, skimmers and terns, sunbittern, tropicbirds, penguins, albatrosses, austral storm petrels, northern storm petrels, petrels and relatives, White stork, storks, frigatebirds, boobies and gannets, darters, cormorants and shags, ibises and spoonbills, hamerkop, shoebill, pelicans, herons and relatives, New World vultures, secretarybird, osprey, hawks, eagles, buzzards, harriers, kites and Old World vultures, barn owls, true owls, mousebirds, cuckooroller, trogons and quetzals, hornbills, hoopoe, woodhoopoes, bee-eater, rollers, ground rollers, todies, motmots, Kingfisher, jacamars, puffbirds, African barbets, Asian barbets, toucans, toucan barbets, American barbets, woodpeckers, honeyguides, seriemas, falcons and relatives, kakapo, kea and kakas, cockatoos, African and American parrots, Australasian parrots, Pesquet's parrot, vasa parrots, Pitta cyanea, Lyrebird, New Zealand wrens, suboscines, Old World suboscines, sapayoa, Calyptomenid broadbills, pittas, broadbills, asities, New World suboscines, bronchophones, manakins, cotingas, sharpbills, royal flycatchers and allies, becards and tityras, spadebills, many-colored rush tyrants, mionectine flycatchers, tyrant flycatchers, tracheophones, crescent-chests, gnateaters, antbirds, antpittas, ground antbirds, ovenbirds, oscines, scrub-birds, lyrebirds, bowerbirds, Australasian treecreepers, Australasian wrens, bristlebirds, gerygones and allies, honeyeaters and relatives, Australasian babblers, logrunners, quail-thrushes and jewel-babblers, cuckoo-shrikes, whitehead and allies, sittellas, wattled ploughbills, whipbirds and quail-thrushes, Australo-Papuan bellbirds, crested shriketits, painted berrypeckers, vireos and relatives, whistlers and relatives, Old World orioles, Boatbills, woodswallows and butcherbirds, mottled berryhunter, ioras, bristlehead, bushshrikes and relatives, wattle-eyes and batises, vangas , fantails, silktail, drongo fantail, drongos, blue-capped ifrits, Australian mudnesters, birds-of-paradise, monarch flycatchers, shrikes, jays and crows, berrypeckers, satinbirds, Australasian robins, stitchbird, wattlebirds, rockfowl, rock-jumpers, rail-babbler, fairy warblers, hyliotas, penduline tits, chickadees and true tits, Nicators, bearded reedling, larks, African warblers, cisticolas and relatives, marsh warblers, pygmy wren-babblers, grass warblers, Malagasy warblers, swallows and martins, bulbuls, leaf warblers, bush warblers , Bushtits, true warblers, parrotbills, fulvettas, white-eyes, babblers and relatives, fulvettas, ground babblers, laughing thrushes, kinglets, spotted wren-babblers, Hawaiian honeyeaters, silky-flycatchers, waxwings, Palmchat, hypocolius, wallcreeper, nuthatches, treecreepers, wrens, gnatcatchers, dippers, thrushes and relatives, flycatchers and relatives, oxpeckers, mockingbirds and thrashers, starlings and mynas , sugarbirds, dapplethroat and allies, flowerpeckers, sunbirds, fairy-bluebirds, leafbirds, olive warbler, accentors, pink-tailed bunting, weavers and relatives, whydahs and indigobirds, weaver finches, Old World sparrows, wagtails and pipits, finches and relatives, longspurs, snow buntings, rosy thrush-tanagers, Old World buntings and New World sparrows, American sparrows, palm-tanager and allies, New World blackbirds and New World orioles, Cuban warblers, wood warblers, cardinals, grosbeaks, and New World buntings, tanagers and relatives. MAMMALS: Rat, Bat, Horse, Standardbred, Throughbred, Saddlebred, Arab, Palomino, Australian stock, Appaloosa, Barb, Lippizaner, Mustang, American Shetland, Falabella, Percheron, Shire, Mule, Bullock, Setter, Oxen, Camel, Tiger, Lion, Hyaenas, Leopard, Bear, Cat, Dog, Sheep, Goat, Cow, Cob, Pig, Chamois, Bulldog, Borzoi, Loris, Longspur, Harvest mouse, Spiny – ant eater, Duck – billed platypus, Elephant, Rhinoceros, Tonkinese, Ragdoll, Margay, Tapir, Seal, Sea lion, Walrus, Dolphin, Bactrian camel, Arabian camel, Bushbaby, Burmese cat, Whale, Porpoise, Aardvark, Ape, Monkey, Gorilla, Chimpanzee, Flying Lemur, Hare, Pika, Macaque, Rabbit, Colobus, Antelope, Caribou, Cattle, Deer, Grizzly bear, Hyrax, Armadillo, Porcupine, Hedgehog, Arctic hare, Mole, Shrew, Beaver, Asian black bear, Polar bear, Sloth bear, Spectacled bear, Mouse, Squirrel, Dugong, Moose, Fallow deer, Reindeer, Red deer, Manatee, Egyptian Mau, Scottish fold, Himalayan, Birman, Red squirrel, Hippopotamus, Weasel, Whale, Wither, Blue whale, Sperm whale, Killer whale, Wallaby, Beluga, Baird’s beaked whale, Grey whale, Bryde’s whale, Pygmy right whale, Southern right whale, Seal, Ape, Indri, Aye – aye, Alaskan Malamute, Dobermann, Beagle, Kinkajou, Afgan Hound, Rough Collie, Cardigan Welsh Corgi, Sheepdog, Pointer, Poddle, Weimaraner, Bloodhound, Zebra, Giraffe, Yak, Arctic fox, Polecat, Golden Retriever, Kerry Blue, Prairie dog, Airedale, German spitz, Pekingese, Otter, Shih Tzu, Proboscis monkey, Orang – utan, Red Howler monkey, Spider monkey, Sloth, Koala, Pangolin, Mustelid, Mongoose, Guinea pig, Malayan Porcupine, Naked Mole rat, Capybara, Pallid Gerbil, Brown rat, Somali, Ocicat, Balinese, Bengal, Cymric, Chartreux, Devon Rex, Turkish Angora, Russian Blue, Yellow – necked woodmouse, Hamster, Grey squirrel, Chipmunk, Fox, Blue Longhair, Chinese Pangolin, Blue – cream shorthair, Tortoiseshell and white shorthair, Brown spotted shorthair, Red and white Japanese bobtail, Javanese, Red Persian Longhair, Brown classic tabby maine coon, Lilac angora, Seal point Siamese, Brown and white sphinx, Red classic tabby manx, Vampire bat, Proboscis bat, Franquet’s fruit bat, Bengal Tiger, Horseshoe bat, Noctule bat, Funnel - eared bat, Blue exotic, Foreign lilac oriental shorthair, Boxer, Bay, Cream point colour pointed british shorthair, Abyssinian, Cinnamon silver Cornish rex, Wolverine, Skunk, Human being, Pine marten, Stoat, Chocolate point longhair, Husky, Ant eater, Kangaroo, Gray Mouse Lemur, Musk oxen, Raccoon dogrie, Pasnda, Bouto, Pembroke Welsh corgi, Whippet, Whisker, Indus river dolphin, Franciscana, Sorrel, Finless porpoise, Jerboa, Harbour porpoise, Bottlenose dolphin, Border Collie, Diana Monkey, White – beaked dolphin, Atlantic white – sided dolphin, Bobcat, Alpaca, Aberdeen angus, Lynx, Pacific white – sided dolphin, Rhesus monkey, Irish wolfhound, Baboon, Slivery marmoset, Puma, Ocelot, Norwegian Forest Cat, Basenji, Keeshond, Akita, Samoyed, Briard, Brittaney, Vizsla, Weimaraner, Saluki, Greyhound, Rottweiler, Bullmastiff, Newfoundland, Puli, Bombay, Sphynx, Kangaroo rat, Humpback whale, Red panda, Maltese, Pug, Chihuahua, Papillon, Pomeranian, Schipperke, Aardwolve, Cheetah, Civet, Red – Bellied Lemur, Moustache, Monkey, Yorkshire terrier, German shepherd, Clumber spaniel, Bouvier des Flandres, Belgian sheepdog, Boston terrier, Italian greyhound, Chesapeake Bay retriever, Genet, Musk deer, Bichon fries, Rock Hyrax, Pony, Mink, Mammoth, Mastodon, Giant sloth, Llama, African Elephant, DeBrazza’s Monkey, Siberian Tiger, Hackney Pony, Bonnet Monkey, German wirehaired pointer, Ferret, Jaguar, Dalmatian, Red Bengal Tiger, Badger, Shunk, Skye terrier, Great dane, Grampus, Bandicoot, Wolf, Marmot, Squirrel monkey, Sable, Minke whale, Spectacle porpoise, Opossums, Airedale, Wombat. etc , Ramapithecus, Australopithecus bosei or Paranthropus bosei, Zinjanthopus bosei, Homo – erectus ( Java man, Peking man, Heidelberg man ), Homo – Sapiens ( Neanderthal man, Cro – Magnon man) to the modern humans with their development and structure of their Heart, their contributions to the formation of the modern humans. What is the origin of the heart? In which place the heart is situated? What is the weight of our (modern humans) heart? Can a person live without a heart? What is the function of the heart? How heart pumps blood to the body? What type of circulation takes place in the human heart? How big our human heart is? Why is our (modern humans) heart considered as the most developed in the world? Why does heart stop? What are heart sounds? What are the types of heart sounds? What causes the heart sounds heard with a stethoscope? What is the anatomy of the heart? Why heart is considered an important organ in the body? Why can’t people live if heartbeat stops? Where is heart located in? How many chambers are present in the heart? What is the number of heart beats per minute? What is the amount of blood pumped by heart? How much blood does the human heart pump in a lifetime? And Short notes on heart attack i.e. what is the definition of a heart attack? Why does a heart attack occur? What are the types of the heart attack? What happens if human get a heart attack? What are the symptoms of Heart attack? What are the causes of the Heart attack? What are the risk factors related to the Heart attack? What are the types of risk factors cause the Heart attack? What are the complications of a Heart attack? What types of diagnosis useful in detecting and treating a heart attack? What treatment is needed to treat heart attack patients? What are 5 strategies to be maintained after the heart attack? What to do after recovery from a heart attack? What is cardiac rehabilitation? Why cardiac rehabilitation is needed to heart attack patients? Does cardiac rehabilitation create positive effects? What are a lifestyle and home remedies are to be maintained? What type of coping and support should be given to heart attack patients? What are the immediate measures should be taken when you encounter an emergency of heart attack patient? What signs and symptoms list should be made to consult a doctor? What is a widow maker heart attack? What is the definition of a widowmaker heart attack? What are the symptoms of Widowmaker heart attack? What are the causes of Widowmaker heart attack? What are the risk factors related to Widowmaker heart attack? What are the complications of a widowmaker heart attack? What types of diagnosis useful in detecting and treating a widowmaker heart attack? What treatment is needed to treat heart attack patients? How to make over your lifestyle? What type of measures should be taken to stay away from a heart attack? What are 20 types of foods should be taken to keep your heart healthy? Solutions and answers of above questions, material and topics are included and cleared in this book.'
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
instagram
It's plain to see how mermaids can lure sailors to their death with ethereal beauty such as this. mahi mahi, ocellaris clownfish, mexican moonfish, graceful mudskipper, atlantic sturgeon
2 notes
·
View notes