#arts & humanities department
Text

chapter one: do you have any friends?
next chapter | masterlist
pairing: dream x reader [high school au] [dsmp]
pronouns: gender neutral
description: you’re the invisible one at school until you’re partnered with the captain of the football team in a chemistry project
word count: 2K
- inspired by @teefumz on twitter with fan art (image at the end). also this is dream amp but high school? so all the characters are their minecraft skin but together in a high school, if that makes sense :3

there was never a moment that you didn’t feel invisible. it hit you more when you woke up each morning, checking your phone to see no notifications, and you knew your mother kissing you in the morning before you went to school was your only form of human contact for the rest of the day. it tortured you throughout the halls as you watched pretty girls making out with their boyfriends or just best friends tightly hugging each other before departing for class.
the feeling of loneliness was glued to you until you went to bed each night. the only person who you could consider your ‘friend’ was karl jacobs. after you two got along well in your english class in freshman year, you became very close. you’d also been to each other’s houses a couple times. but of course, he had his own friendship group as well.
but you had gotten used to it, and you’d learnt that it was best to be dependant on yourself, and only yourself. you didn’t need friends or have to rely on anyone else.
atleast, that’s what you constantly told yourself.
you gripped your backpack as you found your way to your next lesson, trying to dodge obnoxious guys who just loved to push and shove each other in the corridors, you internally rolled your eyes at them.
the classroom was almost full, the only seats available were at the front. you had no other choice but to pull up the stool and take the front desk, with an empty seat beside you. you turned your head to the back of the classroom, karl and quackity were chatting away noisily. karl noticed you and offered you a small smile, which you half heartedly returned before turning back to whiteboard.
the teacher walked in shortly with a briefcase. “okay class!” she yelled, the noise stopping abruptly. “let’s stop the chatter because i want as much time today to begin the first part of our project,”
the class groaned in unison, and you sighed in disappointment. project? this teacher never gave you a break. you pulled out your notebook ready to take down some notes
“this is a partner project so-.” instantly the commotion started again, students were ready to jump out of their seat to sit next to their friend.
“so i will be picking your partners for you,”
you heard everyone groan again. you felt your heart jumping out of your chest from fear, you did not want to be stuck with anyone. you looked around, the only people you wouldn’t mind being paired up with was niki, or karl.
“sapnap!” your teacher yelled, pointing at him, “swap places with george please, you’re with callahan”
sapnap shrugged, content with his partner and collected all his books to move beside callahan.
“karl, you take the seat beside george and work with him please.” she continued. “and dream, can you please...” she hesitated, eyes glancing in each corner of the room
before her eyes fixated on you.
no no no.
anyone but dream. the ceo of being big headed, self-centred and cocky. the last person you would want to be paired with
“can you please move to the front and sit next to [y/n]?”
dream didn’t move, he only turned his head to his friend who was laughing at him. “do i have to?”
ouch. jesus christ. yeah, you weren't the most talkative, or popular, but you weren’t an awful person or anything. your gut dropped, the same feeling when you miss a stair or lean back in your chair too much.
“dream, no arguments. please move your stuff,” she ordered adamantly. dream scrunched up his nose, earning a warning look from the teacher. he grabbed his books and shuffled towards the front, taking a seat beside you.
he didn’t even bother to look at you. though, he was dream, why didn’t you expect him to be all snobby and egotistical?

“u-uh.” you cleared the scratch from your throat, you never were the first one to speak up. “so, do you want to do the analysis bit or the practical first?”
dream shrugged. “whatever you want, i’m not that great at chemistry anyways,”
you furrowed your eyebrows. “i mean- i can help you with-“
“i think it’s best you do it, i’ll probably fuck it up anyways. whatever way is best,” he said, almost harshly. he shifted his gaze from you to his best friend, sapnap, who was yelling across the classroom about something related to the next game. your mouth closed shut and you turned away red, heart thumping in your ears.
“okay,” you whispered weakly, almost like a whimper. dreams ears perked up and he looked at you again.
“you good?”
you nodded. “just fine,”
dream inspected you for a moment, watching how you avoided his stare and didn’t dare to look him in the eyes. he sighed.
“i’m sorry, i’m acting like a jerk,”
you slightly froze at his sudden change in attitude, nonetheless, you agreed. “yeah, just a little bit.”
both of you watched as sapnap flicked his sweatband across the classroom to hit the back of george’s head. george groaned in annoyance. “luckily for you, i guess there are bigger jerks,”
he snickered and you turned to look at him. he covered his mouth with his sleeve, but a smile still evident on his face “sorry, i guess i just found that funny,”
you smiled to yourself.
“but are you okay? your face has been sweating since i sat here” he quieried.
“i just- don’t usually speak in class,”
“do you not have any friends in this class?”
“...no,”
“do you have any friends at all?”
you swallowed slowly. “what happened to not being jerk?”
“i’m sorry, i’m sorry, but i mean, you just started going here right? so i guess that’s okay,”
dude. you had been in almost every single class he was in. but of course he didn’t notice you, you felt tears of frustration brim at your eyes as you looked down at your textbook, but you felt anger shoot up and down your veins along with it
“did i say something wrong?”
you remained silent.
“seriously? not going to answer me?”
you slammed your textbook shut. he was being unbelievably ignorant even if he didn’t realise. “dream, we have been going to the same fucking school since seventh grade, i sat behind you in biology for three years straight and i’ve been in your homeroom every year. i get it, you barely know who i am and you don’t want to be partnered with me, let’s just do this project and stop pretending to care about my feelings,”
dream sat with a dumbfounded expression on his face, feeling slightly guilty at all the words that just spilled out of your mouth. they hung in the air as you continued to scribble down notes.
“i didn’t realise-“
“no, you didn’t realise, nobody ever realises,” you gulped “now, can we please just get on with the project?!”

so you did. and everything was going fine. you were asking him to hand over the ingredients and he placed them in your hands. after your little outburst he didnt even try to start a conversation with you.
“pass the iron filings,” you set out your hand. and he did so.
“you need to relax. look, i’m sorry about earlier, i really am,”
you stirred the mixture together with a rod, looking back at your instructions every now and then. “pass the water,”
“i’m trying to be nice to you, stop ignoring me”
“you might’ve not noticed me, but i’ve noticed you, and i know what you’re like. stop pretending to be nice,”
“jesus, who hurt you?”
“none of your business. just pass the damn-“
“uh- guys, is it supposed to be bubbling?” another voice spoke up. you and dream both put your argument on hold, snapping your heads towards george who was innocently holding a beaker, but pointing at your brewery stand. his white goggles were sitting on the top of his head so you could clearly see his expression of concern.
and sure enough, your mixture was bubbling up, your eyes widened.
“that’s not supposed to be happening,” you felt your heart speed up with fear as the bubbles rose rapidly, overflowing
“are you sure you passed me the right thing?!” you accused dream in a high pitched tone
“yes i did!”
within the next 5 seconds, a loud boom erupted around the classroom, stopping everyone and what they were doing. your mixture was splattered all over the classroom, on your desks, clothes, and on the ceiling. all eyes were on you two. george slowly backed away as if it were a crime scene of some sort, subtly cleaning his goggles.
your teacher stood up, wiping off the smaller bits that had landed on her ugly brown sweater, rather dramatically.
“dream, [y/n],” she looked at both of you angrily. “principals office, now. what the hell were you two doing?,”
she removed her sweater to reveal a white t-shirt underneath, throwing it on the chair. it looked better with her outfit anyways, you thought
you had never been sent to the principals office for a punishment. you didn’t want there to be a phone call home, your parents would be so disappointed. however, dream easily grabbed his bag and headed towards the door, looking at you as if to say ‘come on!’
“and you two will be staying after school to clean this up!”
dream stopped in his tracks. “but- miss i have practice today,”
the teacher placed her hands on her hips.
“then you’ll have to talk to your coach, because you’ll be missing practice,”
“you can’t do that, the big game is in three weeks-“
“you should’ve thought about that before you blasted this classroom into smithereens,” she crossed her arms
“but miss-“ sapnap spoke up
“sapnap, don’t interrupt,” she cut him off. “this has nothing to do with you so work on your own project before you blow yours up aswell.”
dream pinched the bridge of his nose in annoyance. “so i have to miss football practice and they only have to stay after school and clean up? someone like them probably does that in their spare time anyways”
you opened your mouth wide in offence. “you are such an asshole, dream!”
your teacher picked up her sweater and threw it at you. “take that, i expect it to be perfectly clean tomorrow morning,” you shot dream an evil glare.
dream scoffed and opened the door, closing it before you could follow behind.
“jerk,” you muttered under your breath. you noticed everyone staring at you just before you left, sapnaps expression was visibly pissed off at you, quackity was holding in a laugh, while karl and george had sympathetic smiles smeared across their faces. you shook your head and slammed the door.
he was already in front of you. upon hearing the door slam, he turned around. “are you coming or not?”
your day had been absoloutely ruined thanks to only one person. you dont know why, but the spur of the moment caused you to launch the sweater across the hallway, giving it a disgusting glare. you werent going to wash that. it wasnt even your fault. you turned to look at dream who had a puzzled expression on his face.
“it was a hideous sweater anyways, i’m doing her a favour,” you called out.
dreams mouth fell agape as you both continued to make your way to the principals office. he watched you as you proceeded forwards, but this time with a much more confident bounce in your step. he didn’t pinpoint you exactly as one to have a big attitude. this evening was certainly going to be interesting.
———
taglist: @inniterhq @basilly @bunnyl00 @siriushxney @notphilosopherstudentblog @tinyegg @dreamiewrites @kai-was-here @forutheworld @ttakinou @cr0wbonezz-wr1ting-inc @sabinanotfound @esylwen @cherios @yamturds @emira-a @joyfullymulti @wilczachannn @strawberrymilkgeorge @quivvyintheclouds @queenwastaken @uselesssapphickitten @inkyynki @yummychicknnugget @yuyu8uwu @secretsandwriting @dovesgrangers @charleslec-airlines @quinxxs @eggingamazinglove @dinonuggets199 @goldensunshineshit @dominickle @dreamyteam @loser-keiji @wilbvr-verse @isimpforeveryone @ultrapuddlecat @nadara @marshxx @enderchezts @libbynotfound @lavenderjacobs @yoshirikuxd @happygalaxymilkshake @valoinnit @lacunaanonymoused @melmachh @sun-fiower-seed @strawb3rrydr3ss@supernatural-bellawinchester @victory-is-here @rexit-mo @natsueyama @everlizzzz @girlofthefandom @chazzthecannoli @strawberryshortcakesan @heathledgerismyreligion @emala @stylesoot @redhooddddd @ahmya-4 @dontevenaskidonthaveananswer @aikochan4859 @raging-bisexual-2006 @simply-chillin-here @nealocus @moonamor
reference images

#dream imagines#dream imagine#dream x you#dreamwastaken x you#dreamwastaken imagine#dreamwastaken imagines#dreamsmp x reader#dreamsmp x you#dreamsmp imagine#dreamsmp imagines#mcyt x reader#mcyt x you#mcyt imagines#mcyt imagine#dreamwastaken x reader#dream smp x reader#dream smp x you#dream smp fanfiction#dreamwastaken fanfiction#mcyt fanfiction#dream fanfiction#dream amp imagine#dream smp imagines#dream x reader
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
So You’re Feeling White Guilt and You Don’t Know What To Do
I’m not going to rehash the most recent Roswell New Mexico fandom news. I’m not going to rehash any of the difficult and necessary conversations surrounding race and racism that have been happening over the last week. They are important, they shine an important light on fandom racism, and they have caused many to reflect on their own unconscious bias and how it has manifested itself in fandom. That’s important. That is the constant work of an ally: to reflect on your bias and your actions and take steps to inform yourself and do better. As participants in a racist society and a culture that tries to say that racism is only an overt, obvious thing, we must always take the time to listen to others and change our own behavior.
This post isn’t necessarily about that either. It’s about how you can do other, small things, for yourself to help a community and individuals who are continuously mistreated, whose suffering is continuously erased, and whose culture is continuously stolen. Political involvement is always an option, but it’s also not always possible. I know for myself, I work two jobs that leave me with 14 hours days multiple times a week, and only one day off a week to relax, do household chores, and prepare for my grad school classes. I can exercise my right to vote, right to assembly, etc. but sometimes doing more isn’t a viable option.
So what else can I do?
Below I have accumulated links to different relief funds, bail funds for protesters, language programs, native artist collectives and stores, musicians, and conservation project.. Some of the links will take you to a larger project that you can explore. Some of the links will be for direct donations. This is not exhaustive. This is limited to what I’m able to find and authenticate to the best of my ability. But I wanted to put this out into the world, as an example of different ways you can support people, cultures, and communities. I invite anyone to add on to the list, particularly people who are Native American.
Special thanks to @jocarthage for being an amazing resource and adding to my already long list. And @litwitlady for the bookstore link. Additionally, I was writing this and realized how long this got, so I started limiting to two or three links per area. Please, add on.
Relief Funds:
An article from Navajo Times that highlights different Coronavirus relief funds, including the Navajo Department of Health, John Hopkins Center for American Indian Health, relief for families and children, and Food Baskets for Elderly.
https://navajotimes.com/coronavirus-updates/relief-for-coronavirus/
Reply with recommendations
Bail Fund:
A thread on the O’odham land & water protectors: https://twitter.com/LaikenJordahl/status/1315707808470503427?s=20
And the bail fund: https://t.co/yzyDnEi0x6?amp=1
Generally, the National Bail Fund Network’s twitter page is a good place to go to keep up about bail funds for protesters for many leftist causes. They also help with immigration detention and the cause to end money bail in general. https://twitter.com/bailfundnetwork?lang=en
Reply with recommendations
Language Programs:
https://www.firstnations.org/projects/native-language-immersion-initiative/ : The Native Language Immersion Initiative aims to build the capacity of and directly support Native American language-immersion and culture-retention programs. They work with the National Endowment for the Humanities, along with support from the Lannan Foundation, Kalliopeia Foundation and the NoVo Foundation. The linked website has the list of grantees from the previous years, so you can go and explore the different language programs that have benefitted from the initiative. The NLII aims to support the cultural and linguistic preservation of all Indigenous Americans, including Native Alaskan and Native Hawaiian cultures.
The website also allows you to explore their programs, learn more about topics such as environmental justice within native communities, and donate directly.
Duolinguo has short courses in both Navajo and Hawai‘i. They’re not perfect, but they’re a good starting point. Spending some time getting used to the sounds and cadences can be really grounding in the realities of the language and grammar (and if everyone who read our fics downloaded it, it would give Duolingo a strong indicator of interest in these languages, which might encourage them to invest in making them full courses).
Reply with recommendations
Art & Clothing & Holiday Presents:
Art and clothing are grouped together, as a lot of the websites feature both.
Beyond Buckskin: https://shop.beyondbuckskin.com/
A shop/collective started by a member of the Turtle Mountain Chippewa tribe. They have a variety of products and you can learn more about their individual artist. They also have events, news, and a lot of cool things to explore on their website.
+their buy native list:
http://www.beyondbuckskin.com/p/buy-native.html
b.Yellowtail: https://byellowtail.com/pages/about-us
The clothes are designed by Bethany Yellowtail, a Northern Cheyenne & Crow fashion designer. The art and jewelry are made by hand by a collective of Native Americans, First Nations, and Indigenous creatures throughout North America.
SheNative: https://www.shenative.com/
A shop that primarily focuses on leatherwork, but does have other products as well. The aim of the company is to empower Indigenous women, so Idigenous women work on all levels of the manufacturing of the products. Additionally, they donate at least 10% of profits towards causes and charities that aim specifically to help Indigenous women.
Etkie: https://etkie.com/
This collective of Native American artists all hail from New Mexico. They specialize in beaded cuffs, all of which are gorgeous. Personal note, I very much want the Dawn Glass Cuff.

There are a lot of people who sell Native American art who are not, in fact, Native American people. Here are some sources:
The Indian Pueblo Store is owned and operated by New Mexico’s 19 Pueblo tribes. Find our physical location at the Indian Pueblo Cultural Center in Albuquerque https://www.indianpueblostore.com
The bookstore in the Smithsonian Museum of the American Indian has one of the best collections of books about Native American life, by Native American authors, anywhere we’ve found (if you become a member for $25 a year, you get their excellent quarterly magazine) https://americanindian.si.edu/store
Weirdly for a museum named for a man famous for playing a white cowboy in American movies, the Gene Autry museum in Los Angeles has one of the other really good collections of books by Native American authors on modern Native American life, as well as historical books: https://shop.theautry.org/collections/books
I haven’t been, but the Heard Museum gets recommended a lot and their shop has a lot of authentic Native American pieces: https://www.heardmuseumshop.com/
Birchbark Native Arts seems to have an extensive collection: https://www.birchbarknativearts.com and is associated with the bookstore mentioned below
Note from JoCarthage: In 2016 I drove to all 58 counties in California and started my collection of books on Native American tribes living and working in California, both as research for what I thought might be a book and because I was curious. A lot of the books I found are not on Amazon, you can only buy them in reservation book stores or National Park bookstores or little county museum bookstores. When the world opens back up again, that is a good process I have found for building my own understandings.
It’s not a perfect system, but when you’re shopping, look for the term “Authentic Native American artworks” and a seal like this one; here is a longer guide to buying Native American art:

Reply with recommendations
Music:
Spotify & website links are provided. This is also limited to what I know and already listen to.
A Tribe Called Red: Website: http://atribecalledred.com/ | Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/artist/2jlWF9ltd8UtoaqW0PxY4z
Mary Youngblood: Website: http://www.maryyoungblood.com/ | Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/artist/0pRrf0i6X4uUIdzYrA2mDz
Buffy Sainte-Marie: Website http://buffysainte-marie.com/ | Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/artist/5exO2eW84QucBhrRhcK76x
youtube
[Video: A Tribe Called Red’s “Burn Your Village to the Ground”]
Books:
Based on the theory that the best information is closest to the source, all of the books below are written by Native American authors; the bookshops are owned by Native America booksellers.
Bookshops:
Birchbark Books, a bookshop in Minneapolis: https://birchbarkbooks.com/ They also have art, jewelry, and community events. When available, the links for the books below are provided through the store’s website.
Book Recommendations:
Nonfiction and hilarious: Custer Died for Your Sins, by Vine Deloria Jr (Standing Rock Sioux): https://birchbarkbooks.com/all-online-titles/custer-died-for-your-sins
Poetry: New Poets of Native Nations, edited by Heid E. Erdrich (Ojibwe): https://birchbarkbooks.com/all-online-titles/new-poets-of-native-nations
Novel (murder mystery): Chenoo, by Joseph Bruchac (Abenaki): https://www.oupress.com/books/14415530/chenoo
Poetry: When the Light of the World Was Subdued, Our Songs Came Through: A Norton Anthology of Native Nations Poetry, edited by US Poet Laureate Joy Harjo (Muscogee Nation): https://birchbarkbooks.com/CatalogueRetrieve.aspx?ProductID=9713772&A=SearchResult&SearchID=11528255&ObjectID=9713772&ObjectType=27
Art book: First American Art, Edited by Bruce Bernstein and Gerald McMaster (Plains Cree and member of the Siksika Nation) https://americanindian.si.edu/store/books-and-products#1845
(The Mitsitam Cafe Cookbook: Recipes from the Smithsonian National Museum of the American Indian by Richard Hetzler (Not a Native American person but the recipes reflect a huge range of modern Native American recipes and are worth cooking through ) https://birchbarkbooks.com/CatalogueRetrieve.aspx?ProductID=9685880&A=SearchResult&SearchID=11528257&ObjectID=9685880&ObjectType=27)
Here is a selection of children’s books, YA, memoir and biography, and Native American fiction and poetry, Native studies, and Native language
Reply with recommendations
Diné and other Native American actors’ accounts to follow:
Why include fun social media stuff: because we’re humans and we like nice things. It’s very hard to keep learning about something that challenges our whiteness and privileges if everything we read and consume is painful and grim. It also fundamentally limits the stories we consume about modern Native American lives if all we do is wallow. So read good poetry, cook recipes that are shared freely, follow pretty actors on Instagram. When Jo went through her house to find the above book recommendations, 4 of them were on her Native American section, one in her poetry section, and one in her cookbook section. Native American stories and food and life are part of modern American life and integrated them into your bookshelves and menus and IG scrolling is a good way to stay aware and learn more osmotically.
Kawennáhere Devery Jacobs (kanien’kehá:ka from kahnawà:ke mohawk territory) https://www.instagram.com/kdeveryjacobs/?hl=en
Tatanka Means https://www.instagram.com/tatankameans/?hl=en
Jay Tavare https://www.instagram.com/jaytavare/?hl=en
Forrest Goodluck seems to not be active on social media, but he’s worth keeping an eye out for https://twitter.com/forrestgoodluck?lang=en
Check out more here, from pocfansmatter https://pocfansmatter.tumblr.com/post/632180141361119232/my-favorite-native-american-men
Reply with recommendations
News Sources:
Note: none of these are perfect. They all have their own biases, foci, and weirdnesses. But if you subscribe by email to a few of them, you’ll get a pretty good idea of what issues are important, generally.
Native America Calling: https://www.nativeamericacalling.com/
Navajo Times: https://navajotimes.com/
Indian Country Today: https://indiancountrytoday.com/
Reply with recommendations
Conservation:
A petition to close Mt Rushmore and to return public lands in the Black Hills to the Oceti Sakowin (Seven Council Fires of Lakota, Dakota, and Nakota Nations).
https://actionnetwork.org/petitions/petition-to-close-mt-rushmore-and-return-all-public-lands-in-the-black-hills-to-the-oceti-sakowin
From the site: “Standing in solidarity with our ancestors, families, our allies, and the Oceti Sakowin (Seven Council Fires of Lakota, Dakota, and Nakota Nations), we are calling on Director Bernhardt and Representative Deb Haaland to close Mt. Rushmore and return all Public lands in the Black Hills to the Oceti Sakowin as negotiated in the 1868 Treaty of Ft. Laramie, as Indigenous treaties are the supreme law of the land.”
The Kumeyaay people are currently protesting against the illegal destruction of their sacred lands to build the border wall. You can keep up with their work and support them directly through their twitter account.
https://twitter.com/kumeyaayprotest?lang=en
The Native American Land Conservancy aims to reacquire Native American land, particularly in Southern California, to preserve and protect sacred sites and areas.
The group has a mix of board members from a variety of tribes, along with members who are not affiliated with a tribe but have a focus and background in environmental conservation.
Reply with recommendations
Thank you for sticking with us through this whole list. It’s long, yes, but it does not even begin to show even a small percentage of places and artists you can support.
And as for what to do about your white guilt? Live with it. It’s not going to help anyone if you express your guilt continuously. It’s not going to help anyone if you push it aside. Live with it. We benefit from a racist system and we should not forget it. Do what you can to help others, lend your voice in support of others. And for fuck’s sake remember that it’s not about us.
#resources#native american#Tyler Blackburn#native american artists#indigenous peoples#I'm sorry I actually have no idea how to tag this#but also i'm not sorry for tagging the actor because I think it's a thing that people who maybe want to avoid the truth should see
188 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Complete Dutch Education System - Part 2
Bachelor Degree Categories
Bachelor of Science (BSc)
Bachelor of Arts (BA)
Bachelor of Laws (LLB)
Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA)
Bachelor of Social Work (BSW)
Bachelor of Education (BEd)
Bachelor of Music (BMus)
Master’s Programmes Categories
Master of Science (MSc)
Master of Arts (MA)
Master of Laws (LLM)
Master of Business Administration (MBA)
Master of Social Work (MSW)
Master of Education (MEd)
Master of Music (MMus)
Titles granted after completing a Dutch Master’s Degree
Doctorandus
drs.
After completing a Master Degree in Law
mr.
After completing a Master Degree in Science
ir.
PhD Programmes and Opportunities
In the Netherlands, the option of starting a PhD before completing at least one Master Degree is not possible. The minimum amount of time it takes you to finish a PhD in the Netherlands is four years. More often than not, a PhD is offered through the University instead of through a private institution, because of this almost every PhD candidate in the Netherlands is obliged to give lectures or teach assignment classes during their PhD period. Each PhD candidate gets offered a supervisor who oversees the publishing of articles and the writing process of the dissertation.
The Salary
A PhD candidate will get paid an amount of €2376 en €3766 a month. Each year the salary rises, which explains this range in amount. There are some minor differences between departments of different Universities regarding extra’s like a business phone.
Title granted after completing a PhD
Doctor
dr.
Dutch Universities in International Rankings
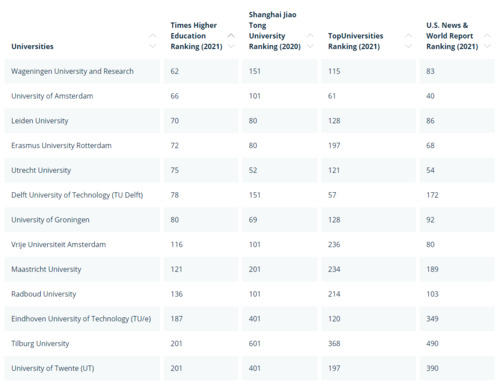
Mastersportal Ranking
Wageningen
WUR
This university specialises in Agriculture, Sustainability and Water Studies. The research domains of the WUR:
Agrotechnology and Food Sciences;
Animal Sciences;
Environmental Sciences;
Plant Sciences;
Social Sciences.
Amsterdam
Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam
Each year, VU Amsterdam welcomes many students from all over the world to Amsterdam. They focus on the following main themes:
Human Health & Life Sciences;
Connected World;
Science for Sustainability;
Governance for Society.
Universiteit van Amsterdam
The research domains of the UvA:
Law;
Economics and business;
Dentistry (ACTA);
Humanities;
Medicine;
Science;
Social and Behavioural Sciences.
Leiden
Leiden University
Leiden University specialises in Language & Culture and has a Science Department that is also of outstanding quality. The research domains of Leiden University:
Fundamentals of Science;
Health and Wellbeing;
Languages, Cultures and Societies;
Law, Politics and Administration;
Life Sciences;
Artificial Intelligence.
Rotterdam
EUR
Erasmus University Rotterdam specialises in Business & Law; additionally, the Medicine Programme is among the Netherlands' finest. The research areas of the Erasmus University Rotterdam:
Health;
Wealth;
Governance;
Culture.
Utrecht
UU
Utrecht University offers a wide variety of programmes. The ten focus areas of the Utrecht University:
Applied Data Science;
Foundations of Complex Systems;
Game Research;
Governing the Digital Society;
Higher Education Research;
Human-centred Artificial Intelligence;
Integrative Bioinformatics for Life Sciences and Sustainability;
Migration and Societal Change;
Professional Performance;
Sport and Society.
Delft
TU Delft
TU Delft specialises in all things beta science, and their Architecture programme is excellent, and a similar Architectural Degree cannot be obtained anywhere else.
Aerospace Engineering;
Applied Sciences;
Architecture and the Built Environment;
Civil Engineering and Geosciences;
Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science;
Industrial Design Engineering;
Mechanical, Maritime and Materials Engineering;
Technology, Policy and Management.
Groningen
RUG
Rijksuniversiteit Groningen is also very internationally oriented and also offers a wide variety of programmes. The main focus areas of University Groningen:
Healthy Ageing;
Energy;
Sustainable Society.
Maastricht
Maastricht University
Maastricht University is very internationally oriented and offers programmes within these focus areas:
Arts and Social Sciences;
Health, Medicine and Life Sciences;
Humanities and Sciences;
Law;
Psychology and Neuroscience;
School of Business and Economics.
Nijmegen
Radboud
Radboud University focusses on these domains:
Science;
Society & Human Behaviour;
Law;
Human- & Information Technology;
Languages & Culture;
Health;
Business.
Eindhoven
TU/e
TU Eindhoven specialises in all things beta science and offers a vast variety of programmes in the following domains:
Engineering programmes;
Math and Computer Science;
Industrial Design;
Applied Physics.
Tilburg
Tilburg University
How corona is changing the world;
Digital Society;
Sustainability and Society;
Labor Market;
Security;
Culture and Religion;
Health and Wellbeing.
Twente
UT
University Twente specialises in all things beta science and focuses its research on these main themes:
Improving healthcare by personalised technologies;
Creating intelligent manufacturing systems;
Shaping our world with intelligent materials;
Engineering our digital society;
Engineering for a resilient world.
Till next time!
Hope you learned something and/or found it useful.
#Guide#Dutch#Applied Sciences#PhD#Master Degree#Bachelor Degree#Netherlands#Titles#Mr.#Ir.#BSc#MSc#MA#BA#LLB#LLM#MBA#BBA
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Things Anti-Monster Politicians Could Do (Mild)
(Mild) → (Moderate) → (Severe)→ (Extremely Angsty)
Note: This series assumes Mt. Ebott is in the U.S., based on Vegetoid’s description: “Not monitored by the USDA”. This presumably stands for the United States Department of Agriculture. However, most of the article would apply if Mt. Ebott were in other countries, too.
The anti-monster politician would ignore or dismiss monsters’ specific bodily or cultural needs, or make it inconvenient for them to fulfill particular needs. Loopholes, alternatives and workarounds to the policies are obvious, but discouraged or inconvenient.
Tactic 1: Gyftmas is Not Valid
--
Tactic 2: No Magic Lessons
On a slightly stronger note, anti-monster politicians (AMPs) could, rather than creating species-segregated schools, strategically adjust school rules and requirements.
AMPs (school superintendents, principals) could ban bullet patterns inside a school. In principle, this makes sense: humans could get hurt, and for particularly crowded schools, a lot of humans could get hurt at once. The AMPs could (at risk to sounding reasonable) ban bullet patterns on school grounds, so monsters can’t even do it at recess or shortly after being released from school.
School superintendents could make curriculum options that conspicuously omit magic-expression, even as an extracurricular. One plausible-sounding excuse for why they wouldn’t teach magic is due to a school being majority-human (but still close to Mt. Ebott), and humans being unable to use magic or find it as appealing or useful as monsters.
Even without specific regulations, AMPs could influence hiring decisions for human-only/human-dominant schools so they just happen to never hire magic-expression teachers, or block attempts to teach magic-expression because “it’s not part of the curriculum”. They could even block merging magic-expression lessons into art or communication classes. Alternatively, AMPs could mandate only monster-specific/monster-dominant schools need to teach magic expression, or specifically block all but monster schools from teaching it.
In total, these regulations wouldn’t endanger monsters, but only give them a sub-par species-specific education if they attend human-dominant schools. They could find workarounds, such as tutors, separate schools or parents teaching them, but it would be inconvenient.
--
Tactic 3: No Monster Food in Cafeterias
AMPs could suggest “accommodating monsters with magic food” (e.g, cafes, school cafeterias) is financially onerous for businesses, making monster food availability lower. They could also disguise not supplying monster food as personally not liking the cuisine or considering it unappealing to kids. After all, Chinese food is just more of a crowd-pleaser than, say, Lebanese food. Still, this would be absurd since monster food largely mimics common American foods.
Not supplying monster food would be extra inconvenient in cafeterias, because children have less of a choice in what schools or businesses they attend or work for than what cafes they visit. Even without official policies or justifications, AMPs could simply not supply any monster food, ever, in cafeterias. It would be very suspect because some schools do import food outside typical catering, and monster food would likely be healthier, tastier, or cheaper than human food. This is especially true when serving normal food a small percentage of humans are allergic to, but monster food is “made of magic” and might not contain allergens at all.
Since monsters apparently need to defecate if they eat physical food, AMPs could make this worse by forbidding them from entering student/employee bathrooms. Some possible excuses are: “so many unsupervised students/employees in one place could kill them”, or “we aren’t sure if our toilets can handle your waste”, or “monsters defecating is gross”, or “since you’re an “it” or “they”, you can’t go to the girls’ bathrooms or boys’ bathrooms) But, AMPs could suspiciously never supply a single toilet for monsters in the whole building to address the “waste” concerns, despite the existence of handicapped bathrooms/specific stalls that also serve a tiny minority. AMPs could also discourage, if not outright forbid, them from using the single-stall teachers’ bathrooms as a workaround.
Now, to make this even worse, AMPs could suggest, without any basis, that monster food is nutritionally inferior or reacts poorly with the human body. They could then use that to discredit monster-run food shops. (a la monosodium glutamate and anti-Chinese xenophobia) They could even fabricate or fudge the results for a study on monster food’s effect on humans, then use the fake results to support banning monster food from restaurants. While monsters can still eat physical food, shifting their diet to have drastically more physical food at once will surely lead to mass digestive troubles and possibly nutritional problems. (It would also sabotage humans, since monster food could be really handy in some situations.)
--
Tactic 4: No Body Accommodations
Taller monsters, such as Asgore, need bigger models of cars to safely fit in cars and/or comfortably drive. Smaller cars are generally more fuel-efficient, and harm pedestrians less in case of a collision. So, AMPs could make suspiciously-timed subsidies for smaller cars, outright ban big cars from cities or parking garages, or have buyback programs for bigger (and potentially monster-suitable) cars.
The AMPs could also suggest physical accommodations of any sort (e.g., entry ramps for legless monsters) would be expensive and useless. However, his particular tactic would probably cause humans with impaired mobility to team up with monsters, since they also need or greatly benefit from similar ramps. Indeed, this is classified as “mild” partly because the tactic could anger or greatly inconvenience humans, and so nudge them into making political alliances with monsters.
Workarounds
Workarounds for No Magic Lessons
Workaround 1. Gerson is hired to teach (human) history. AMPs figure he’s just teaching (human) history, and on the face of it he’d be a good history teacher. But Gerson just happens to make asides on monster history when it parallels human issues, and just happens to give demonstrations of bullet patterns in monster history, or re-creates artistic patterns throughout human history using his own bullets.
Workaround 2. A monster P.E. teacher (e.g., Undyne) notices the rule says “students can’t use bullet patterns inside school/on school grounds”. The monster demonstrates bullet patterns for the students to actually practice later. Better yet, the monster P.E. teacher takes one step outside the school’s legal property (e.g., a surrounding field, in the parking lot, on the roof), shows off bullet patterns, and has students take turns stepping just outside official school property to demonstrate. The monster teaches them how to express bullet patterns in an athletic way to justify it being part of athletic curriculum.
Or, the monster realizes it’s still legal for P.E. teachers to play dodgeball with students (which can hurt), and so does “magic ball” instead, controlling bullet damage so it does exactly as much damage as getting hit by a dodgeball. (The monster P.E. teacher could probably say, “Frisk survived because they were so good at dodging! Knowing how to dodge magic attacks will keep humans safe in human-monster conflict!”)
Workaround 3. One reason/excuse for not teaching magic at a majority human school is the fact humans can’t use magic, and it not being important in human society. However, a function on Frisk’s monster-made cell phone changed their SOUL to Yellow mode, allowing them to emit bullets like a monster. (if in a very simplified fashion) Monsters providing SOUL mode technology or magical objects that emit bullets means humans wouldn’t feel left out in magic expression classes. Furthermore, of course human children would want to learn how to use magic in some way, even if it took years of practice.
If humans with yellow SOULs can naturally emit bullets, that would cause an even greater faux pas to AMPs. People would probably argue they’d want to cultivate their abilities, and not providing magic lessons even as an extracurricular is discriminatory to Yellow SOULs.
Workaround 4. Humans can, in fact, use magic after monsters return to the Surface, and monsters teach them how to use magic.1 The fun and utility of humans knowing how to use magic encourages human-monster integration. While Tactic 2 suggests magic classes are of little to no use in purely human/human-dominant schools, the school with one or multiple magic classes in GlitchTale seems to be human-dominant.
--
Workarounds for No Monster Food at Cafeterias
Workaround 1: Monster students just bring bagged lunches. Alternatively, for teenagers allowed to go off-grounds for lunch, there could be a monster restaurant for cheap that’s very close to the school.
Workaround 2: Internet personalities who specialize in recording eating food or visiting restaurants make a point of eating monster food. They could even repeatedly swear or say really funny things to make the videos super-popular.
Workaround 3: Monster food-engineers supply magic-food equivalents to common allergen-containing foods, like oysters or peanut butter, allowing allergic people to taste what they’ve been missing out on and feel “normal”. The video would be highly “wholesome” and saccharine in a way that would make it super-popular, like unexpected puppies.
Workaround 4: An actual Chinese restaurateur makes a satirical video comparing monster food xenophobia to historic Chinese-food xenophobia.
Workaround 5: The fact monster food converts to energy (presumably upon being swallowed) heals HP (presumably minor injuries, in non-video-game terms), and probably doesn't contribute to weight gain 2 means it would be popular among humans, who might pack some monster food in their school lunches. Monster food's popularity and convenience among humans would just highlight AMPs' absurd monster-food restriction.
Made with the help of Batter-Sempai, CinnamonAzzy and Ihasafandom.
If you enjoyed this post, you may be interested in the author's Patreon and Ko-Fi.
Related Works
Chara's Stomach Rumbles (a possible side effect of eating only monster food)
The Perils of an All-Monster Food Diet (More detail on problems with eating entirely monster food. Still doesn't justify banning monster food from cafeterias, however)
Undertale Character Heights (listed chronologically. Part 2 to 4 covers how human-designed objects and buildings are ill-suited for extra-wide or tall monsters)
The fan works GlitchTale (Season 2) and Endertale feature this. In GlitchTale, humans regain use of magic very quickly, suggesting they've kept theoretical knowledge on it, even if they couldn't actually use it. In Endertale, Frisk learns magic over three years. ↩︎
In the fanfiction Long Road (specifically Chapter 4), monster food is popular among humans for similar reasons. ↩︎
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
[INTERVIEW] A CASUAL CHAT WITH JONATHAN JACQUES-BELLETÊTE
The art director for Deus Ex: Human Revolution shares insight on cyberpunk and texturing furniture. Originally published April 1, 2011 on Totalplaystation.com
In early March, PAX East attendees were given a live gameplay demonstration of Deus Ex: Human Revolution by Eidos Montreal personnel, including Game Director Jean-François Dugas, Art Director Jonathan Jacques-Belletête, and Community Manager Kyle Stallock. The demonstration consisted of around 20 minutes of an early level in which the protagonist, Adam Jensen, infiltrated a warehouse using a combination of stealth, computer hacking, sharp implements, and bullets. Following the demonstration, I had the opportunity to sit down with J.J.B. and ask a few questions.
Though footage of the demonstration is not officially available, there is a walkthrough of the same portion of the game floating around on YouTube.
So, Deus Ex: Human Revolution. First of all, tell me what you do.
I’m the art director, so I’m trying to make it look pretty.
All right—
Really hard.
Managing a lot of people?
Yeah, I am managing a lot of people, definitely. I mean, there’s a structure. There are artists; there are leads on everything that have their units and whatnot. Overall, we must have close to 60 artists on this game, not counting outsourcing; we’ve had some people doing concept art and modeling outside, but in the studio, we must have a good 60 artists.
Speaking of outsourcing, the pre-rendered cutscenes are, I assume, done by another—
Yeah, all the trailers—in the game, it’s all in-game cutscenes, but the marketing stuff, all the big CGI, the E3 trailer, the extended trailer that you guys saw, that was all done by Visual Works, which is the cinematics department at Square Enix. You can’t ask for better than this. It’s like, “What!?” It’s so weird: one day, you wake up and suddenly your company is owned by Square Enix, and then two months later, you learn that you’re going to work with them on a trailer.
Is it a little intimidating knowing that now people have that in their minds, the look in those trailers, and now you have to sort of, in real-time, try to meet those expectations in the game?
Totally a legitimate question, and you’re absolutely right, but the way that it happened is that we had already set the style of the game’s visuals before we did those CGI trailers. At the same time, as an art director, I’m highly influenced by—I love anime and Japanese video games; we concede, and I say openly that there’s a strong Metal Gear influence on the game, and stuff like that. When Square Enix took our material to do the trailer, it was like we already spoke the same language. The way that I treat the textures in the game, there is no photographic material, just like the Japanese also almost never do that. Everything is done by hand or procedurally, so everything already seemed well-prepared for them to deal with it. So, yeah, you watch the trailers, and then you watch the in-game, and obviously there’s a huge gap, but it still seems to be a part of the same style; the aesthetic essence is exactly the same. I’m actually quite proud of that, really.
How did you arrive at the game’s particular style? It has a unique look: the color palette, I notice a lot of hexagons—
A lot of triangles.
Did you go through other styles on the way to find what you ended up with?
Yes and no. I knew straight from the get-go that I wanted to have a stylized game, that I wanted to have something that has its own signature. As an art director, I’m not into photorealism; it’s really not something that interests me all that much, because I find that credibility—photorealism and credibility are two different things. You can have a game where they put all their efforts into trying to make it photorealistic, but the game doesn’t feel credible at all. I’m not even talking about the “uncanny valley,” I don’t want to get into that, but the credibility of the game itself is not even there. You can have a Disney Movie, like The Beauty and the Beast, where you have a teapot and a cup talking to one another, and it’s totally credible, right? So there’s something there: why is it that when we strive for photorealism it doesn’t work, and something as low-fi as that works? So, anyway, let’s just say that I knew that I wanted to go stylized; I knew that I wanted a specific signature, and now, the hard thing was to figure out what that recipe would be. I knew that I wanted low—not low intensity, but (what is it, fuck,) often I find that in games, textures are too noisy, there’s just too much shit everywhere.
Right, as we gain the technology to add more and more detail to everything—
Right, it becomes a fest of just “pile some more stuff.”
—bump-mapping and making everything gritty.
[Points to nearby black leather couch four feet away.] If I just look at that couch from here, I don’t see texture in that couch. If I get closer I’ll see it, but not from here. In games, a lot of the Unreal 3 Engine games, from here it would look like it was grated or something, so that’s what I wanted to get away from. It looks maybe slicker, in that sense, but then we have fairly advanced shaders, so when you get close to an object, it’ll have really precise detail still. Yeah, the hard thing was mostly to figure out what the recipe was.
Is it intimidating at all working on this franchise? We’ve already seen what happens when someone makes a sequel to Deus Ex and it doesn’t meet expectations. Fans are going to hold it to a very high standard, maybe unrealistically high. If you go back and play Deus Ex now—
They almost have a distorted memory of it, yes.
It was kind of weird, because we also had to start a studio at the same time. Most of the early people, we all came from Ubisoft Montreal, and there were two things: to do a new Deus Ex, and it was also to put the studio together. We were renting offices, at first; we had nothing, barely any equipment, there was no team, the technology wasn’t chosen yet, there was no art bank. You know, for example, when we were at Ubisoft, we start a new project and for the first six months, just to get your thing going, you’ll be taking stuff from other games.
Like for placeholders?
Right, and we had no such things—I don’t know, maybe somehow because of that, it dampened the fear we should have had from having to make a new Deus Ex, you know what I mean?
Because you had so much stuff to deal with, you just had to get to work.
There we go, I couldn’t have said it better. Obviously, we knew how big it was, and we were all big fans ourselves. We knew about the pedigree, we knew about the fans, but we had to do it; we wanted to do it; it’s kind of like this make or break thing. You know, it’s the studio’s first game... maybe it wasn’t such a good idea! No no no, it was a great idea to attract people, actually. We just jumped in head-first, and put all of our eggs in the same basket. I think it’s looking alright; it’s not up to me to say how good it is.
The original game has some celebrity developers attached to it: Harvey Smith, Warren Spector; have they seen the game that you know of? Did you get any reactions from them?
Yeah, Harvey hasn’t seen it, but Warren has seen it, and he likes what he saw. I don’t want to hype it too much or under-hype it, because I don’t want to get into trouble, but I will say that he liked it.
This is kind of a small thing, but can you talk about the “item glint” system that you’re using? [The walkthrough demonstrated a yellow outlining effect to highlight interactive objects.] It seems like it would be hard to find a balance between making it obvious what you can interact with and avoiding something overly obtrusive.
It’s not so bad. One of my main art direction pillars was clutter. I wanted to have lots of props, lots of shit piled on top of everything. We realized was that, going through playtesting, it was a little confusing. That’s when we decided to go with that outline stuff, and like J.F. was explaining in the questions, I think it’s properly managed. It’s not like you open the door to a big room and everything lights up; you need to get into a proper distance, and there’s a rather small threshold in which it becomes highlighted, and it disappears as soon as you move away. Some people, it might not be their cup of tea, but in today’s market, if you make it too subtle, some people will just get discouraged. It has to be accessible.
Hey, you’re an augmented guy with crazy vision implants, so—
That’s our rationale behind it.
Speaking of which, cyberpunk as a genre has kind of fallen out of fashion, with the Internet becoming a mundane, everyday thing—
My feeling is that cyberpunk is what we live today.
How do you try to make it feel relevant today?
The way that we thought about it starting mostly, for me—we asked ourselves the question as artists: can we reproduce the visuals of Blade Runner on today’s consoles? The answer would probably be yes. But then, what would it say about the studio’s capacity for creativity? So, we wanted to bring something new. As you say, it’s not that fashionable; it’s kind of dormant, so that’s when this whole idea of the cyber-renaissance thing, which is not something that you saw much of in today’s demo, but it’s such a big game with so many areas that sometimes you feel it, sometimes you don’t, sometimes it’s omnipresent. That’s part of the idea to bring back cyberpunk, but with a twist to it.
The other thing is, when we started the first focus group for the game, kind of early on, maybe within the first year, testing out the early ideas and everything, we realized that here in the States, and in Europe, because we tested in both continents: kids nowadays? They don’t even know what cyberpunk is. Really, we could not believe it. You never would have thought, if you take a random chunk of 20 kids who all play games—even the hardcore ones—they’re like “Cyberwhat?” We thought, we cannot use that word! Nobody knows what it is. And, you know, we’re using it, but it really was a huge eye-opener for us.
[Gesturing to J.J.B.’s prominent tattoos] I can see that you’re a fan of Warhammer, you know, tabletop games. Have you played roleplaying games at all?
I played when I was younger.
Ever play Cyberpunk 2020?
The only roleplaying game I really played was Warhammer Fantasy Roleplay.
An awesome game; lots of limbs getting chopped off.
Lots of limbs getting chopped off, yeah, inverting those numbers [a reference to the operation of the critical hit tables]. Yeah, as someone who was creative and wanting to make games, I would buy tons of roleplaying rulebooks, just to read them, and so I had all the Cyberpunk and all those things, and it was the same thing for Warhammer. Warhammer 40,000 is probably my most favorite universe ever, but I own all the rulebooks and all the codices, and I’ve never played the game. Never fucking played the game. I’ve painted the figurines. I haven’t painted in, maybe, six or seven years, because I just don’t have time, but I got to a really high level, where maybe I could start doing those competitions, like the Golden Daemon and shit, but then I just started running out of time. So, I got really into painting the figurines, really into the universe, to the point that—these tattoos are old; I was eighteen when I got them, but still, my passion for that universe hasn’t gone away ever. It’s just kind of weird that I’ve never played the game.
I have a bunch of miniatures, I’ve painted a lot, and I have a ton of the books, and I’ve never played it—
I have all the novels, all the rulebooks, and I love reading them, love the computer games. Alright, cool man, you’re like the first guy I’ve ever met who’s like me. I love to get into that universe, but I don’t really feel like playing the game that much.
Tell me about designing Adam Jensen.
It was tough. It was rough. It took a good two years to nail him down. We kinda knew the overarching design straight from the beginning. We wanted, obviously, not a big brute, there are enough of those in this cycle of consoles. We wanted him to have hair.
You’re crazy. Nobody is going to buy that.
There was this sentence that we coined at the beginning: “He can kick your ass, then he goes home and reads a good book.” We had this idea of, you know the French actor, Vincent Cassel?
No.
Have you seen Black Swan?
No.
He’s French, but he does a lot of movies here. Anyway, he’s a regular build, but there’s just something about his face, about his attitude. You think, “I would never fuck with that guy.” It’s just something that he emanates. And that’s kinda what we wanted. But, because we wanted the mechanical augmentations to be at the forefront of the game and of the visuals—that’s why often you see Adam from third-person, so you can see his arms—J.F. wanted his arms to be visible at all times. And, you know, he’s the creative director, so he’s my boss, but also, we wanted him to look like an agent who could be sent behind enemy lines, and at the same time walk into a high-end restaurant to interrogate someone.
It was a really hard equation to solve: he has to look like Solid Snake, and he has to look like James Bond, and you need to see his mechanical arms all at the same time. So we gave him a vest, and he looked like a douchebag all the time, like a biker or something. Every one of my concept artists had a go at it, where they would pool their energy to try to improve him, and it never quite worked. One day, Jim Murray, one of my concept artists, approached me, and—as simple as it sounds—says, “Let’s just make him two outfits.” One is kind of his battle gear, where you see his arms, and one is kind of his urban gear, because such a big part of the game is being in the city hubs, investigating and talking to people, going into rich places, inserting yourself into an apartment or whatever, and that’s when he’s gonna have his cyberpunky trench coat, and you’re not going to see his arms.
Again, as simple as it sounds, like holy shit. But then, we still had to run it by J.F. and the writer. Often, people don’t realize how a simple choice can be very complex to implement in the game, so we had a few meetings about it, and we decided to go with it. After that, within two months, Jim had nailed them; we had the jacket, which I loved. Also, the challenge was that when he has the jacket, he still has to be able to use the same augmentations. So, he has the claymore, the typhoon, where all those beads eject from his arms, so how do you do this when you have a jacket? Or when your blade extends backward? So we designed those slits in his jacket, and he has ports on it that kind of magnetize to the holes on his arms to let go of the beads and everything, so we kind of worked out how it works.
Yeah, so two months later, Adam was born, and the little pointy beard was kind of the Don Quixote thing, kind of the renaissance/baroque thing.
In the Icarus dream sequence in the trailer, you can see that the facial hair works in both settings. [This sequence features Adam surrounded by men in Renaissance-era garb.]
The Icarus thing was such a great find, in the sense that it was such a great metaphor for augmentations, because that’s what happens, right? Daedalus, his dad, gives him the wings so he can escape the maze, basically having wings is augmenting yourself. The feathers are glued with wax, so he says, “Don’t fly too close to the sun, or the wings will melt,” but he has so much fun with the wings that that’s what he does, and then he dies. That’s a bit like what it is with augmentation; if you overdo it, like with anything in life, you might burn yourself. We though it was such a great analogy for that.
Do you personally have a strong opinion on transhumanism?
Strong? Not necessarily, I wouldn’t say strong. I’m not intensely passionate about the pros and cons, but I think it’s inevitable. I think it’s one of those things that we’ll need to have laws, and we’ll need to have ways to control what will happen. There are going to be big mistakes, like with everything. There are mistakes made all the time in medicine, the military makes mistakes all the time, but I think it’s inevitable. If we try to stop it, there will be underground, illegal shit, and stuff like that. I’m quite convinced that in the next, maybe, 40 years, we’ll be immensely transformed. From all the stuff I’ve read, the specialists we’ve met, I think we’re going to see some crazy shit in the next 30 years.
Globe-trotting was a big component of the first Deus Ex; you cover a lot of mileage. Do you do that a lot in this one?
Yes, there’s definitely a lot of variety, yup.
One thing that the first game kind of failed at was giving the impression that you’re in a larger world. The city areas felt a bit constrained. How did you approach that problem?
It’s funny, as the cycles of consoles and technologies evolve, the constraints somehow always remain the same. OK, Grand Theft Auto, it’s immense or whatever; it never seems to end, but, for example, what you do with the NPCs is very limited compared to Deus Ex. Anyway, you add all this stuff that you can do in Deus Ex, and suddenly you don’t have the power to do a city that big, so we had the same constraints. Don’t get me wrong, the city hubs are quite big; many, many streets; tons of alleyways and buildings to get into, sewers to get into, rooftops... all that shit. At the same time—at some point you can’t go further, and you need to find tricks to convey that there’s a sprawling city around you, and why that path is blocked when it seems like it should be open. It’s a very common game design problem.
I remember on Splinter Cell at Ubisoft, it was the same thing. “This street is blocked, why?” And I would be, like, “Maybe some guy is moving out,” so there’s a big truck, and stuff like that blocking the street. It’s very common. But honestly, I think we manage rather well in Deus Ex. And then, there are compounds that you go into, like office buildings and secret laboratories where those limitations aren’t as important anymore, because you are in a confined area, but for the city hubs, I think we get away with it quite well.
A big feature of the game is having multiple approaches to every situation. Is that frustrating, especially being involved in the art side, because there may be significant chunks of the game that a lot of players won’t see?
Frustrating? No. I wouldn’t say it’s frustrating, because, obviously, we try to make the coolest stuff in the critical path. Now, that being said, it doesn’t mean that side-quests or whatever don’t have their own things, but you can manage; you just try to make everything look cool. I don’t know if we succeeded. I have a really hard time saying, “Oh, this doesn’t need to look as cool,” or whatever; I try to put just as much energy into everything.
I guess your question is more—if some people don’t see some of the cool stuff we’ve made... It is going to happen, but to some degree it’s kind of cool. They’ll be talking to their friends and they will have seen it, even if you haven’t, and I think it’s all part of the trip, really. But it’s cool, because I’ve worked at companies before where they never would have allowed us to do that.
It seems like a waste of resources.
Exactly. Some companies are so into every penny you spend, the player has to see it. Which is very rational when you think about it; it makes total sense, but sometimes making a game that gives you a specific feeling, that gives you that flavor so that once you’ve turned off your computer and when you go to bed you’re still thinking about it, it’s also a game that has all these things that are not just thrown in your face like that. But, that is quite expensive to do.
So, I’m guessing you can’t say anything about Thief 4.
No.
I figured.
That would be the death of me. No, it’s gonna rock your socks off; there we go.
Just how awesome is it?
Super awesome. Super-duper awesome.
No, it’s a great team honestly; tons of my friends are there. The art director is a great friend of mine, and uh... I’m not even sure I’m allowed to say that, so I’ll stop there.
It seems like a similarly ambitious sequel to make. Like with Deus Ex, fan expectations are off the charts.
It’s the same thing, exactly. I think it was really... that’s what we wanted to do with that studio. If we open another goddamn studio in that city? We do it strong or we don’t do it.
**In the first game, J.C. Denton is kind of inept in the beginning. It’s surprising that he’s supposed to be this super-spy, but he can barely fire a gun straight. I assume that Adam Jensen is a bit more capable right off the bat. **
Big time, yeah. Also, the shooting is something that right from the get-go, me and J.F. agreed that the shooting skill of Adam Jensen is going to be the player’s shooting skills. In terms of that, it’s a full-fledged first-person shooter. You know the crosshairs there? That’s where the bullet’s gonna go. You can still augment him in some ways to be a better shooter, like for recoil, or stuff like that. All the weapons are fully upgradeable, so that aspect of RPGness is still there, but where you shoot is where you shoot.
I’ll admit that I cheated to max out my skills in Deus Ex and found it a lot more fun that way.
The skills—that system was quite punitive.
You do have an upgrade system in this, where you earn your Praxis Points and unlock augmentations—are those scarce enough that you can’t get every upgrade by the end of the game?
You can’t max everything in a play-through. You can become the jack of all trades if you want, but you won’t be an expert at everything, or you can really invest in a branch.
If somebody specializes very much in, say, stealth, and therefore tends to use that to get through every encounter, do you think that can become monotonous and discourage people from experimenting with the other techniques?
Hmm, that’s a good question. It’s never been asked to me that way, specifically. I hope not. I don’t think it is—the way we’ve designed the challenges is that they’re never molded for one style of gameplay. It’s not like you get to an environment where it’s like, “Here you have to play stealth.” We’ve shown a quick example of that in the demo: if you wouldn’t have been able to disable the turret, there was that passage on the side. Usually most challenges are set up that way, but not as obvious as that; it’s built quite like the first one in that regard.
Are you absolutely sure there are no blue laser swords in the game? [A reference to a question asked during audience Q&A]
As of right now, this time, today: absolutely sure.
Thank you very much, I really appreciate it.
It was awesome, man. Great questions, thanks.
1 note
·
View note
Link
Nippon Ichi Software has released new information and screenshots for time travel RPG Destiny Connect: Tick-Tock Travelers, which launched today for PlayStation 4 and Switch in Japan, introducing Sherry’s family, a pair strengthening systems, a new form for Isaac, and more.
Get the details below.
■ Story Summary
The story is set in Clocknee, a town with a long history.
Sherry, a girl who lives in Clocknee, heads out with her mother to see the fireworks together at the “Soulman Fes” New Year’s festival. The moment the new year finally arrives, the people of the city mysteriously and simultaneously stop moving.



Sherry and her friend Pegreo, who were fortunate enough to escape the frozen time incident, run into the old scientist Dr. Cheatstein, who understands that the cause of this incident can be found in the past. With that knowledge in mind, Sherry departs for a past version of Clocknee with the robot Isaac her father left behind.
But robots that are hostile to humans will stand before Sherry and friends. What ending will this adventure reach? Play the game to find out!



■ Characters
Papa

Sherry’s father. He has been busy with work and away from home for the past half-year or so. He was supposed to come home at the end of the year, but…

Mama

Sherry’s mother. When she goes to watch the New Year’s fireworks with her daughter, they are attacked by robots and separated from each other.

Grandma

Sherry’s grandma. She runs a cafe in Clocknee. Homemade cherry pie is the cafe’s signature dish.

Status Max

The leader of the robots and hostile towards humans. It is based on various electrical appliances such as a washing machine and vacuum cleaner.

■ Game System: Strengthening
Equip an “Amp”

“Amps” are equipment only usable by human characters like Sherry. Equipping an amp can amplify the user’s attack power, defense power, recovery rate, accuracy rate, or HP. Up to two amps can be equipped per character. Make up for your weak points, or amplify your strong points, as you mix and match amps according to your play style.
—You can freely equip amps.

—Amps can be purchased at the store. As you progress through the game, stronger amps will appear.

Strengthen Skills with “Skill Solvents”

Skills have levels, and increasing a skill’s level also increases its power. Skill level can be increased by using Skill Solvents dropped by defeated enemies. Use them when you find them!
—Skill Solvents can be obtained as battle rewards.

—The higher the skill level, the more Skill Solvents required to increase its level.

■ Game System: Modding
Isaac, a robot, can utilize various battle styles by changing “Form.” The key to making your way through the game is to utilize Isaac’s different forms based on the situation and enemies. Here, we will introduce the four forms revealed so far, as well as one new form.
Guardian Form

Isaac’s basic form. A steel guardian that protects everyone with its heavy armor. It is somewhat bad at avoiding attacks.

Rescue Form

A kind rescue squad member who heals wounded party members and eliminates every threat. He is sure to help out in a pinch.

Outlaw Form

A gun expert whose high accuracy enables him to take out enemies without chance for escape. As his mustache and leaf whistle suggest, this Isaac is a lone bounty hunter.

Champion Form

A speed fighter who floats like a butterfly and stings like a bee. While his evasion rate and attack power are high, his defense power is rather low.

Bushido Form (New)

An armored warrior who puts his all into a single strike. His accuracy rate and defense power are low, but he has the best attack power of any form.
—Skill: “Asura”
Teaches all party members the art of two consecutive attacks, making it possible to attack twice in one turn.

—Skill: “Slash of Imperial Wrath”
Unleashes a deadly spinning slash on a single enemy.

??? Form (New)
This is Isaac’s sixth form, which Isaac can transform into through the acquisition of “certain materials” in the game. His stats are well-balanced, and he possesses both offensive and defensive skills. It may take some time to acquire, but when you do, it will surely be useful!
—Both this unknown form’s performance and design make an impact. Be sure to check it out for yourself by playing the game!


■ Town Introduction
Clocknee is a town with its own unique culture. Here we will introduce some of the town’s attractions.
Soulman Fes
The Soulman Fes is held from December 31 to January 1 in Clocknee to welcome the new year. The festival began 30 years ago to honor Soulman, the hero that saved the town. Its attractions include a magnificent fireworks show that can be seen from the town’s central street, as well as an open air concert at the Clocknee town plaza.

Forgotten Castle
A castle built on a lake and one of the tourist attractions of Clocknee. On December 31, lanterns float into the night sky to welcome the new year.

Buckinford District
An area with a classical townscape located on the west side of Clocknee. With an arcade and plenty of tall buildings, it is something like a maze. Be careful not to get lost!

Destiny Connect: Tick-Tock Travelers is available now for PlayStation 4 and Switch in Japan, and is due out in North America and Europe this fall.
View the screenshots at the gallery.
#Destiny Connect#Nippon Ichi Software#PS4#Nintendo Switch#RPG#Gematsu#long post#The one kid looks like a young Jaune Arc.#And Sherry's dad kind of looks like Jacksepticeye. XD
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chaudhary Devi Lal University Admission, Course, Fees Structure, Exam Dates, Results 2022
Introduction: Chaudhary Devi Lal University 2022-23
Welcome everyone today we will discuss about CDLU Application Form 2022-23. Chaudhary Devi Lal University is a public university in Sirsa, Haryana, India. It was established on November 1, 2010. with the merging of Dabwali University, and Saharanpur University.The university has a single campus of about , spread over three districts in Haryana, namely Dabwali, Faridabad and Sirsa. The campus houses academic blocks for engineering disciplines including Civil Engineering, Computer Science & Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering (ECE), Electrical
The university has five faculties: Science and Technology, Arts and Social Sciences, Commerce, Education and Law. The university offers undergraduate courses in science and technology fields such as engineering and computer science.
The university has a campus of over 250 acres (1 km²) which includes the main campus on the outskirts of Sirsa city with a stadium that seats 15000 people along with residential facilities for approximately 2500 students.
Chaudhary Devi Lal University is a university located in Sarsa, Punjab, India. It was established in the year of 2002 by the Chaudhary Devi Lal University Act, 2002.
The university offers courses in science and humanities for undergraduate and postgraduate students. The university has about 20 departments with about 2200 students enrolled in each department.
A number of faculties are engaged in research work to develop innovative solutions for social, economic and environmental issues. There are also a number of centers for distance education that are run by the university.
The university is listed among the top universities according to QS World University Rankings 2018 and Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2018
Chaudhary Devi Lal University Application form 2022-23,
Chaudhary Devi Lal University is a public university located in Sirsa, Haryana, India. It was established by the Chaudhary Devi Lal University Act of 2008.
The university offers various undergraduate and graduate courses in diverse fields of study. It has a total student population of about 30,000 students from across the country and abroad.
The Chaudhary Devi Lal University Application form 2022-23 is an application form for admission to undergraduate courses offered by the Chaudhary Devi Lal University in Sirsa, Haryana for the academic year 2022-23. The application form is available on the university website here: https://www.chdluniversity.edu/admission/admissions-form/.
CCU is a private university in Sirsa, Haryana. The university offers undergraduate and postgraduate courses in various disciplines.
The application form for the 2022-23 academic year is now available on the official website of Chaudhary Devi Lal University. It includes all the necessary details about the application process, eligibility criteria and other important information.
The Chaudhary Devi Lal University is a public university located in Sirsa, Haryana. It was established by the Government of Haryana on 6 November 1972. The university has been ranked among the top 50 universities in India by the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) in 2018.
The university offers undergraduate and postgraduate courses in various disciplines such as engineering, science and arts. It has also offered MPhil and PhD programs since 2003-04.
Conclusion about Chaudhary Devi Lal University
CDLU is a prestigious university in India. It was founded by the Indian politician and educationist Chaudhary Devi Lal.
The college has a rich history and has produced many notable alumni, including Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam, former President of India, who studied here in the early 1950s.
The university also offers undergraduate and postgraduate degrees in various fields of study, including engineering, science and commerce.
In conclusion, the Chaudhary Devi Lal University is a great school. It offers excellent education for students at affordable rates. Students are given a lot of opportunities to grow and develop in their respective fields.
The university is also situated in a very safe and secure place. The campus has been well-planned with wide open spaces and green areas. There are also many facilities provided such as spacious libraries, cafeterias, gyms, gardens and more.
The university has its own website which provides more information on the various courses offered by the university in detail as well as career opportunities for students after they graduate from the university.
0 notes
Text
Are You Ready to Sell Like QVC?
A photo. Some text. A shopping cart button.
It’s the setup you’ve been used to since you were Internet-years-old.
Electronic commerce has existed since the 1970s, passing through a prescient experimental phase of telephone-based TV shopping in the 1980s, and setting the tone for the future with Stephan Schambach’s 1990s invention of the first standardized online shopping software. US consumers spent $861.12 billion with online merchants in 2020. By making the “add to cart” ritual so familiar, it may seem like we’ve seen it all when it comes to digital commerce.
But hold onto your hats, because signs are emerging that we’re on the verge of the next online sales phase, akin to the 19th century leap from still photos to moving pictures.
If I’m right, with its standard product shots, conventional e-commerce will soon start to seem dull and dated in many categories compared to products sold via interactive video and further supported with post-purchase video.
Now is the time to prep for a filmed future, and fortunately, the trail has already been blazed for us by home shopping leader QVC, which took over television and then digitally remastered itself for the web, perfecting the art of video-based sales. Today, we’re going to deconstruct what’s happening on QVC, and how and why you may need to learn to apply it as an SEO, local SEO, or business owner — sooner than you think.
Why video sales?
A series of developments and disruptions point to a future in which many product sales will be facilitated via video. Let’s have a look at them:
First, we all know that humans love video content so much, they’ve caused YouTube to be the #2 search engine.
Google has documented the growth of video searches for “which (product) should I buy”.
When we look beyond the US, we encounter the phenomenon that livestreaming e-commerce video has become in China, highly-monopolized by Alibaba’s Taobao and creating celebrities out of its hosts.
Meanwhile, within the US, the pandemic caused a 44% increase in digital shopping spend between 2019-2020. We moved online last year for both our basic needs and nonessentials like never before.
The pandemic has also caused physical local brands to implement digital shopping, blurring former online-to-offline (O2O) barriers to such a degree that Internet transactions are no longer the special property of virtual e-commerce companies. This weirdly-dubbed “phygital” phenomenon — which is making Google the nexus of Maps-based local product sales — can be seen as a boon to local brands that take advantage of the search engine’s famed user-to-business proximity bias to rank their inventory for nearby customers.
At least, Google hopes to be the nexus of all this. The truth is, Google is reacting strongly right now to consumers starting half of their product searches on Amazon instead of on Google. Are you seeing ads everywhere these days informing you that Google is the best place to shop? So am I. With that massive, lucrative local business index in their back pocket and with GMB listings long supporting video uploads, Google has recently:
Acquired Pointy to integrate with retail POS systems
Made product listings free
Amped up their nearby shopping filter
Attempted to insert themselves directly into consumers’ curbside pickup routines while integrating deeply into data partnerships with major grocery brands
Experienced massive growth in local business reviews, and just released an algorithmic update specific to product review content (look out, Amazon!)
Experimented with detecting products in YouTube videos amid rumors flying about product results appearing in YouTube
Been spotted experimenting beyond influencer cameo videos to product cameos in knowledge panels
Meanwhile, big brands everywhere are getting into video sales. Walmart leapt ahead in the shoppable video contest with their debut of Cookshop, in which celebrity chefs cook while consumers click on the interactive video cues to add ingredients to their shopping carts.
Crate & Barrel is tiptoeing into the pool with quick product romance videos that resemble perfume ads, in which models lounge about on lovely accent chairs, creating the aura of a lifestyle to be lived. Nordstrom is filming bite-sized home shopping channel-style product videos for their website and YouTube channel, complete with hosts.
And, smaller brands are experimenting with video-supported sales content, too. Check out Green Building Supply’s product videos for their eco-friendly home improvement inventory (with personable hosts). Absolute Domestics shows how SABs can use video to support sales of services rather than goods, as in this simple but nicely-produced video on what to expect from their cleaning service. Meanwhile, post-sales support videos are a persuasive value add from Purl Soho to help you master knitting techniques needed when you buy a pattern from them.
To sum up, at the deep end of the pool, live-streamed e-commerce and shoppable video are already in use by big brands, but smaller brands can wade in with basic static goods-and-services videos on their websites and social channels to support sales.
Now is the time to look for inspiration about what video sales could do for brands you market, and nobody — nobody — has more experience with all of this than QVC.
Why QVC?
“I didn’t even know QVC still existed,” more than one of my marketing colleagues has responded when I’ve pointed to the 35-year-old home shopping empire as the way of the future.
The truth is, I’d probably be sleeping on QVC, too, if it weren’t for my Irish ancestry having drawn me to their annual St. Patrick’s Day sales event for the past 30+ years to enjoy their made-in-Ireland product lineup.
About seven times more people with Irish roots live in the United States than on the actual island of Ireland, yet the shopping channel’s holiday broadcast is one of the few televised events tailored to our famous nostalgia for our old country home. My family tunes in every March for the craic of examining Aran Crafts sweaters, Nicholas Mosse pottery, Belleek china, and Solvar jewelry, while munching on cake made from my great-grandmother Cotter’s recipe. Sometimes we get so excited, we buy things, but for the past few years, I’ve mainly been actively studying how QVC sells these items with such stunning success.
“Stunning” is the word and the wakeup call
QVC, which is a subsidiary of Quarate Retail International, generated $11.47 billion in 2020 and as early as 2015, nearly half of those sales were taking place online — consistently placing the brand in the top 10 for e-commerce sales, including mobile sales. The company has 16.5 million consolidated customers worldwide, and marketers’ mouths will surely water to learn that 90% of QVC’s revenue comes from loyal repeat shoppers. The average QVC shopper makes between 22-25 purchases per year!
Figures like these, paired with QVC’s graceful pas de deux incorporating both TV remotes and mobile devices should command our attention long enough to study what they’ve done and how they’ve done it.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC!”
While supplies last, I want to invite you to spend the next 10 minutes watching this Internet rebroadcast of a televised segment selling an Aran Crafts sweater, with your marketer’s eye on the magic happening in it. Watch this while imagining how it might translate as a static product or service video for a brand you’re marketing.
TL;DW? Here’s the breakdown of how QVC sells:
Main host
QVC hosts are personalities, many of whom have devoted fan bases. They’re trained in the products they sell, often visiting manufacturing plants to school themselves. When on air, the host juggles promoting a product and interacting with models, guest hosts, callers, and off-screen analysts. The host physically interacts with the product, highlights its features in abundant detail, and makes their sales pitch.
For our purposes, digital marketers are fully aware of the phenomenon of social influencers taking on celebrity status and being sought after as sales reps. At a more modest scale, small e-commerce companies (or any local business) that’s adopted digital sales models should identify one or more staff members with the necessary talents to become a video host for the brand.
You’ll need a spot of luck to secure relatable hosts. Just keep in mind that QVC’s secret formula is to get the viewer to ask, “Is this me?”, and that should help you match a host to your audience. This example of a nicely-done, low-key, densely-detailed presentation of a camping chair by a plainspoken host shows how simple and effective a short product video can be.
Guest hosts
Many QVC segments feature a representative from the brand associated with the product being sold. In our example, the guest host from Aran Crafts is a member of her family’s business, signing in remotely (due to the pandemic) to share the company’s story and build romance around the product.
Depending on the model you’re marketing, having a rep from any brand you resell would be an extra trust signal to convey via video sales. Think of the back-and-forth chat in a podcast and you’re almost there. Small retailers just reselling big brands may face a challenge here, but if you have a good portion of inventory from smaller companies and specialty or local manufacturers, definitely invite them to step in front of the camera with your host, as higher sales will benefit you both.
Models
Frequently, sales presentations include one or more models further interacting with the product. In our example, models are wearing these Irish sweaters while strolling around Ashford Castle. More romance.
Other segments feature models as subjects of various cosmetic treatments or as demonstrators of how merchandise is to be used. Models and demonstrators used to be standard in major American department stores. QVC brilliantly televised this incredible form of persuasion at about the same time it disappeared from real-world shopping in the US. Their sales figures prove just how huge the desire still is to see merchandise worn and used before buying.
For our scenario of creating online sales videos, such models could be a convincing extra in selling certain types of products, and many products should be demonstrated by the host or guest host. One thing I’ve not seen QVC do that I think e-commerce and O2O local brands definitely could do is a UGC approach of making your customer your model, demoing how they use your products in their real-world lives. Almost everybody can film themselves these days.
Callers
There are no live callers in our example, but QVC traditionally increases interactivity with the public with on-air phone calls.
If your sales videos are static, you’re not quite to the point of having to learn the art of handling live calls, but your product support phone and SMS numbers and links should be featured in every video.
Method
“If you go up there with the intent to sell, it’s all going to come crashing down around you...The real goal of QVC.... was to feel like a conversation between the host, the product specialist (us), and ‘Her’ – the woman age 35 to 65 who is sitting at home watching television.” - I went on air at QVC and sold something to America
There’s an element of magic to how QVC vends such a massive volume of products, but it’s all data-based. They’ve invested so heavily in understanding customer demographics that they’ve mastered exactly how to sell to them. Your consumer base may be totally different, but the key is to know your customer so well that you understand the exact approach to take when offering them your inventory of goods and services.
Another excerpt from the article cited above really gets this point across when talking about guest hosts:
“Our experienced guests tend to focus on the product. But our best guests are focused on the viewer. Is this for the viewer? Everything goes through that filter. And if you do that, everything comes out more naturally.”
Here at Moz, there may be Whiteboard Friday hosts you especially enjoy learning from. As a business owner or marketer, your job will be to identify talented people who can blend your brand culture with consumer research and translate that into a form of vending infotainment that succeeds with your particular shoppers. Successful QVC hosts make upwards of $500,000 a year for being so good at what they do.
Being good, in the sweater sample, means pairing QVC’s customer-centric, conversational selling method with USPs and an aura of scarcity. I’ll paraphrase the cues I heard:
“These sweaters are made exclusively for QVC” — a USP regarding rarity.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC” — this is a strong USP based on having better prices than a traveler would find if buying direct from the manufacturer.
“Reviews read like a love letter to this sweater” — incorporating persuasive UGC into the pitch.
“Half of our supply is already gone; don’t wait to order if you want one of these” —- this creates a sense of urgency to prompt customers to buy right away.
Analytics
The example presentation probably looked quite seamless and simple to you. But what’s actually going on “behind the scenes” of a QVC sales segment is that the host is receiving earpiece cues on exactly how to shape the pitch.
QVC’s analytics track what’s called a “feverline” of reaction to each word the host says and each movement they make. Producers can tell in real time which verbal signals and gestures are causing sales spikes, and communicate to the host to repeat them. One host, for example, dances repeatedly while demoing food products because more customers buy when he does so.
For most of the brands you market, you’re not likely to be called upon to deliver analytical data on par with QVC’s mission control-style setup, but you will want to learn about video analytics and do A/B testing to measure performance of product pages with video vs. those with static images. As you progress, analytics should be able to tell you which hosts, guests, and products are yielding the best ROI.
Three O2O advantages
In a large 2020 survey of local business owners and marketers, Moz found that more than half of respondents intend to maintain pandemic-era services of convenience beyond the hoped-for end of COVID-19. I’d expect this number to be even higher if we reran the survey in mid-2021. Online-to-offline shopping falls in this category and readers of my column know I’m always looking for advantages specific to local businesses.
I see three ways local brands have a leg up on their virtual e-commerce cousins, including behemoths like Amazon and even QVC:
1. Limited local competition = better SERP visibility
Virtual e-commerce brands have to compete against a whole country or the world for SERP visibility. Google Shopping’s “available nearby” filter cuts your market down to local map-size, making it easier to capture the attention of customers nearest your business. If you’re one of the only local brands supporting sales of your goods and services via videos on your website, you’re really going to stand out in the cities you serve.
2. Limited local inventory = more convincing authenticity
QVC is certainly an impressive enterprise, but one drawback of their methodology, at least in my eyes, is that their hosts have to be endlessly excited about millions of products. The same host who is exuding enthusiasm one minute over an electric toothbrush is breathless with admiration over a flameless candle the next. While QVC’s amazingly loyal customers are clearly not put off by the bottomless supply of energy over every single product sold, I find I don’t quite believe that the joy is continuously genuine. In my recognition of the sales pitch tactics, the company feels big and remote to me.
70% of Americans say they want to shop small. Your advantage in marketing a local business is that it will have limited inventory and an owner and staff who can realistically convey authenticity to the video viewer about products the business has hand-selected to sell. A big chain supermarket wants me to believe all of its apples are crisp, but my local farmer telling me in a product video that this year’s crop is crisper than last year’s makes a world of believable difference.
3. Even a small boost in conversions = a big difference for local brands
Backlinko recently compiled this list of exciting video marketing statistics that I hope you’ll read in full. I want to excerpt a few that really caught my eye:
84% of consumers cite video as the convincing factor in purchases
Product videos can help e-commerce stores increase sales by up to 144%
96% of people have watched an explainer video to better understand a product they’re evaluating
The Local Search Association found that 53% of people contact a business after watching one of their videos and 71% of people who made a purchase had watched an online video from that brand
Including filmed content on an e-commerce page can increase the average order value by 50+%
Video on a landing page can grow its conversion rate by up to 80%
If the company you’re promoting is one of the only ones in your local market to seize the opportunities hinted at by these statistics, think of what a difference it would make to see conversions (including leads and sales) rise by even a fraction of these numbers. Moreover, if the standout UX and helpfulness of the “v-commerce” environment you create makes you memorable to customers, you could grow local loyalty to new levels as the best resource in a community, generating a recipe for retention that, if not quite as astonishing as QVC’s, is pretty amazing for your region.
Go n-éirí leat — good luck!
Like you, I’m longing for the time when all customers can safely return to shopping locally in-person, but I do agree with fellow analysts predicting that the taste we’ve gotten for the convenience of shipping and local home delivery, curbside pickup, and tele-meetings is one that consumers won’t simply abandon.
Sales videos tackle one of digital marketing’s largest challenges by letting customers see people interacting with products when they can’t do it themselves, and 2021 is a good year to begin your investigation of this promising medium. My top tip is to spend some time this week watching QVC on TV and examining how they’ve parlayed live broadcasts into static
product videos that sell inventory like hotcakes on their website. I’m wishing you the luck and intrepidity of the Irish in your video ventures!
Ready to learn more about video marketing? Try these resources:
17 Best Ecommerce Product Video Examples
The ABCs of Video Content
8 Beginner Tips for Making Professional-Looking Videos
How to Film Creative Product Videos
YouTube Dominates Google Video in 2020
How to Track YouTube Videos in Google Analytics Using Google Tag Manager in 4 Steps
Need to learn more about local search marketing before you start filming yourself and your products? Read The Essential Local SEO Strategy Guide.
0 notes
Text
Are You Ready to Sell Like QVC?
A photo. Some text. A shopping cart button.
It’s the setup you’ve been used to since you were Internet-years-old.
Electronic commerce has existed since the 1970s, passing through a prescient experimental phase of telephone-based TV shopping in the 1980s, and setting the tone for the future with Stephan Schambach’s 1990s invention of the first standardized online shopping software. US consumers spent $861.12 billion with online merchants in 2020. By making the “add to cart” ritual so familiar, it may seem like we’ve seen it all when it comes to digital commerce.
But hold onto your hats, because signs are emerging that we’re on the verge of the next online sales phase, akin to the 19th century leap from still photos to moving pictures.
If I’m right, with its standard product shots, conventional e-commerce will soon start to seem dull and dated in many categories compared to products sold via interactive video and further supported with post-purchase video.
Now is the time to prep for a filmed future, and fortunately, the trail has already been blazed for us by home shopping leader QVC, which took over television and then digitally remastered itself for the web, perfecting the art of video-based sales. Today, we’re going to deconstruct what’s happening on QVC, and how and why you may need to learn to apply it as an SEO, local SEO, or business owner — sooner than you think.
Why video sales?
A series of developments and disruptions point to a future in which many product sales will be facilitated via video. Let’s have a look at them:
First, we all know that humans love video content so much, they’ve caused YouTube to be the #2 search engine.
Google has documented the growth of video searches for “which (product) should I buy”.
When we look beyond the US, we encounter the phenomenon that livestreaming e-commerce video has become in China, highly-monopolized by Alibaba’s Taobao and creating celebrities out of its hosts.
Meanwhile, within the US, the pandemic caused a 44% increase in digital shopping spend between 2019-2020. We moved online last year for both our basic needs and nonessentials like never before.
The pandemic has also caused physical local brands to implement digital shopping, blurring former online-to-offline (O2O) barriers to such a degree that Internet transactions are no longer the special property of virtual e-commerce companies. This weirdly-dubbed “phygital” phenomenon — which is making Google the nexus of Maps-based local product sales — can be seen as a boon to local brands that take advantage of the search engine’s famed user-to-business proximity bias to rank their inventory for nearby customers.
At least, Google hopes to be the nexus of all this. The truth is, Google is reacting strongly right now to consumers starting half of their product searches on Amazon instead of on Google. Are you seeing ads everywhere these days informing you that Google is the best place to shop? So am I. With that massive, lucrative local business index in their back pocket and with GMB listings long supporting video uploads, Google has recently:
Acquired Pointy to integrate with retail POS systems
Made product listings free
Amped up their nearby shopping filter
Attempted to insert themselves directly into consumers’ curbside pickup routines while integrating deeply into data partnerships with major grocery brands
Experienced massive growth in local business reviews, and just released an algorithmic update specific to product review content (look out, Amazon!)
Experimented with detecting products in YouTube videos amid rumors flying about product results appearing in YouTube
Been spotted experimenting beyond influencer cameo videos to product cameos in knowledge panels
Meanwhile, big brands everywhere are getting into video sales. Walmart leapt ahead in the shoppable video contest with their debut of Cookshop, in which celebrity chefs cook while consumers click on the interactive video cues to add ingredients to their shopping carts.
Crate & Barrel is tiptoeing into the pool with quick product romance videos that resemble perfume ads, in which models lounge about on lovely accent chairs, creating the aura of a lifestyle to be lived. Nordstrom is filming bite-sized home shopping channel-style product videos for their website and YouTube channel, complete with hosts.
And, smaller brands are experimenting with video-supported sales content, too. Check out Green Building Supply’s product videos for their eco-friendly home improvement inventory (with personable hosts). Absolute Domestics shows how SABs can use video to support sales of services rather than goods, as in this simple but nicely-produced video on what to expect from their cleaning service. Meanwhile, post-sales support videos are a persuasive value add from Purl Soho to help you master knitting techniques needed when you buy a pattern from them.
To sum up, at the deep end of the pool, live-streamed e-commerce and shoppable video are already in use by big brands, but smaller brands can wade in with basic static goods-and-services videos on their websites and social channels to support sales.
Now is the time to look for inspiration about what video sales could do for brands you market, and nobody — nobody — has more experience with all of this than QVC.
Why QVC?
“I didn’t even know QVC still existed,” more than one of my marketing colleagues has responded when I’ve pointed to the 35-year-old home shopping empire as the way of the future.
The truth is, I’d probably be sleeping on QVC, too, if it weren’t for my Irish ancestry having drawn me to their annual St. Patrick’s Day sales event for the past 30+ years to enjoy their made-in-Ireland product lineup.
About seven times more people with Irish roots live in the United States than on the actual island of Ireland, yet the shopping channel’s holiday broadcast is one of the few televised events tailored to our famous nostalgia for our old country home. My family tunes in every March for the craic of examining Aran Crafts sweaters, Nicholas Mosse pottery, Belleek china, and Solvar jewelry, while munching on cake made from my great-grandmother Cotter’s recipe. Sometimes we get so excited, we buy things, but for the past few years, I’ve mainly been actively studying how QVC sells these items with such stunning success.
“Stunning” is the word and the wakeup call
QVC, which is a subsidiary of Quarate Retail International, generated $11.47 billion in 2020 and as early as 2015, nearly half of those sales were taking place online — consistently placing the brand in the top 10 for e-commerce sales, including mobile sales. The company has 16.5 million consolidated customers worldwide, and marketers’ mouths will surely water to learn that 90% of QVC’s revenue comes from loyal repeat shoppers. The average QVC shopper makes between 22-25 purchases per year!
Figures like these, paired with QVC’s graceful pas de deux incorporating both TV remotes and mobile devices should command our attention long enough to study what they’ve done and how they’ve done it.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC!”
While supplies last, I want to invite you to spend the next 10 minutes watching this Internet rebroadcast of a televised segment selling an Aran Crafts sweater, with your marketer’s eye on the magic happening in it. Watch this while imagining how it might translate as a static product or service video for a brand you’re marketing.
TL;DW? Here’s the breakdown of how QVC sells:
Main host
QVC hosts are personalities, many of whom have devoted fan bases. They’re trained in the products they sell, often visiting manufacturing plants to school themselves. When on air, the host juggles promoting a product and interacting with models, guest hosts, callers, and off-screen analysts. The host physically interacts with the product, highlights its features in abundant detail, and makes their sales pitch.
For our purposes, digital marketers are fully aware of the phenomenon of social influencers taking on celebrity status and being sought after as sales reps. At a more modest scale, small e-commerce companies (or any local business) that’s adopted digital sales models should identify one or more staff members with the necessary talents to become a video host for the brand.
You’ll need a spot of luck to secure relatable hosts. Just keep in mind that QVC’s secret formula is to get the viewer to ask, “Is this me?”, and that should help you match a host to your audience. This example of a nicely-done, low-key, densely-detailed presentation of a camping chair by a plainspoken host shows how simple and effective a short product video can be.
Guest hosts
Many QVC segments feature a representative from the brand associated with the product being sold. In our example, the guest host from Aran Crafts is a member of her family’s business, signing in remotely (due to the pandemic) to share the company’s story and build romance around the product.
Depending on the model you’re marketing, having a rep from any brand you resell would be an extra trust signal to convey via video sales. Think of the back-and-forth chat in a podcast and you’re almost there. Small retailers just reselling big brands may face a challenge here, but if you have a good portion of inventory from smaller companies and specialty or local manufacturers, definitely invite them to step in front of the camera with your host, as higher sales will benefit you both.
Models
Frequently, sales presentations include one or more models further interacting with the product. In our example, models are wearing these Irish sweaters while strolling around Ashford Castle. More romance.
Other segments feature models as subjects of various cosmetic treatments or as demonstrators of how merchandise is to be used. Models and demonstrators used to be standard in major American department stores. QVC brilliantly televised this incredible form of persuasion at about the same time it disappeared from real-world shopping in the US. Their sales figures prove just how huge the desire still is to see merchandise worn and used before buying.
For our scenario of creating online sales videos, such models could be a convincing extra in selling certain types of products, and many products should be demonstrated by the host or guest host. One thing I’ve not seen QVC do that I think e-commerce and O2O local brands definitely could do is a UGC approach of making your customer your model, demoing how they use your products in their real-world lives. Almost everybody can film themselves these days.
Callers
There are no live callers in our example, but QVC traditionally increases interactivity with the public with on-air phone calls.
If your sales videos are static, you’re not quite to the point of having to learn the art of handling live calls, but your product support phone and SMS numbers and links should be featured in every video.
Method
“If you go up there with the intent to sell, it’s all going to come crashing down around you...The real goal of QVC.... was to feel like a conversation between the host, the product specialist (us), and ‘Her’ – the woman age 35 to 65 who is sitting at home watching television.” - I went on air at QVC and sold something to America
There’s an element of magic to how QVC vends such a massive volume of products, but it’s all data-based. They’ve invested so heavily in understanding customer demographics that they’ve mastered exactly how to sell to them. Your consumer base may be totally different, but the key is to know your customer so well that you understand the exact approach to take when offering them your inventory of goods and services.
Another excerpt from the article cited above really gets this point across when talking about guest hosts:
“Our experienced guests tend to focus on the product. But our best guests are focused on the viewer. Is this for the viewer? Everything goes through that filter. And if you do that, everything comes out more naturally.”
Here at Moz, there may be Whiteboard Friday hosts you especially enjoy learning from. As a business owner or marketer, your job will be to identify talented people who can blend your brand culture with consumer research and translate that into a form of vending infotainment that succeeds with your particular shoppers. Successful QVC hosts make upwards of $500,000 a year for being so good at what they do.
Being good, in the sweater sample, means pairing QVC’s customer-centric, conversational selling method with USPs and an aura of scarcity. I’ll paraphrase the cues I heard:
“These sweaters are made exclusively for QVC” — a USP regarding rarity.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC” — this is a strong USP based on having better prices than a traveler would find if buying direct from the manufacturer.
“Reviews read like a love letter to this sweater” — incorporating persuasive UGC into the pitch.
“Half of our supply is already gone; don’t wait to order if you want one of these” —- this creates a sense of urgency to prompt customers to buy right away.
Analytics
The example presentation probably looked quite seamless and simple to you. But what’s actually going on “behind the scenes” of a QVC sales segment is that the host is receiving earpiece cues on exactly how to shape the pitch.
QVC’s analytics track what’s called a “feverline” of reaction to each word the host says and each movement they make. Producers can tell in real time which verbal signals and gestures are causing sales spikes, and communicate to the host to repeat them. One host, for example, dances repeatedly while demoing food products because more customers buy when he does so.
For most of the brands you market, you’re not likely to be called upon to deliver analytical data on par with QVC’s mission control-style setup, but you will want to learn about video analytics and do A/B testing to measure performance of product pages with video vs. those with static images. As you progress, analytics should be able to tell you which hosts, guests, and products are yielding the best ROI.
Three O2O advantages
In a large 2020 survey of local business owners and marketers, Moz found that more than half of respondents intend to maintain pandemic-era services of convenience beyond the hoped-for end of COVID-19. I’d expect this number to be even higher if we reran the survey in mid-2021. Online-to-offline shopping falls in this category and readers of my column know I’m always looking for advantages specific to local businesses.
I see three ways local brands have a leg up on their virtual e-commerce cousins, including behemoths like Amazon and even QVC:
1. Limited local competition = better SERP visibility
Virtual e-commerce brands have to compete against a whole country or the world for SERP visibility. Google Shopping’s “available nearby” filter cuts your market down to local map-size, making it easier to capture the attention of customers nearest your business. If you’re one of the only local brands supporting sales of your goods and services via videos on your website, you’re really going to stand out in the cities you serve.
2. Limited local inventory = more convincing authenticity
QVC is certainly an impressive enterprise, but one drawback of their methodology, at least in my eyes, is that their hosts have to be endlessly excited about millions of products. The same host who is exuding enthusiasm one minute over an electric toothbrush is breathless with admiration over a flameless candle the next. While QVC’s amazingly loyal customers are clearly not put off by the bottomless supply of energy over every single product sold, I find I don’t quite believe that the joy is continuously genuine. In my recognition of the sales pitch tactics, the company feels big and remote to me.
70% of Americans say they want to shop small. Your advantage in marketing a local business is that it will have limited inventory and an owner and staff who can realistically convey authenticity to the video viewer about products the business has hand-selected to sell. A big chain supermarket wants me to believe all of its apples are crisp, but my local farmer telling me in a product video that this year’s crop is crisper than last year’s makes a world of believable difference.
3. Even a small boost in conversions = a big difference for local brands
Backlinko recently compiled this list of exciting video marketing statistics that I hope you’ll read in full. I want to excerpt a few that really caught my eye:
84% of consumers cite video as the convincing factor in purchases
Product videos can help e-commerce stores increase sales by up to 144%
96% of people have watched an explainer video to better understand a product they’re evaluating
The Local Search Association found that 53% of people contact a business after watching one of their videos and 71% of people who made a purchase had watched an online video from that brand
Including filmed content on an e-commerce page can increase the average order value by 50+%
Video on a landing page can grow its conversion rate by up to 80%
If the company you’re promoting is one of the only ones in your local market to seize the opportunities hinted at by these statistics, think of what a difference it would make to see conversions (including leads and sales) rise by even a fraction of these numbers. Moreover, if the standout UX and helpfulness of the “v-commerce” environment you create makes you memorable to customers, you could grow local loyalty to new levels as the best resource in a community, generating a recipe for retention that, if not quite as astonishing as QVC’s, is pretty amazing for your region.
Go n-éirí leat — good luck!
Like you, I’m longing for the time when all customers can safely return to shopping locally in-person, but I do agree with fellow analysts predicting that the taste we’ve gotten for the convenience of shipping and local home delivery, curbside pickup, and tele-meetings is one that consumers won’t simply abandon.
Sales videos tackle one of digital marketing’s largest challenges by letting customers see people interacting with products when they can’t do it themselves, and 2021 is a good year to begin your investigation of this promising medium. My top tip is to spend some time this week watching QVC on TV and examining how they’ve parlayed live broadcasts into static
product videos that sell inventory like hotcakes on their website. I’m wishing you the luck and intrepidity of the Irish in your video ventures!
Ready to learn more about video marketing? Try these resources:
17 Best Ecommerce Product Video Examples
The ABCs of Video Content
8 Beginner Tips for Making Professional-Looking Videos
How to Film Creative Product Videos
YouTube Dominates Google Video in 2020
How to Track YouTube Videos in Google Analytics Using Google Tag Manager in 4 Steps
Need to learn more about local search marketing before you start filming yourself and your products? Read The Essential Local SEO Strategy Guide.
0 notes
Text
Are You Ready to Sell Like QVC?
A photo. Some text. A shopping cart button.
It’s the setup you’ve been used to since you were Internet-years-old.
Electronic commerce has existed since the 1970s, passing through a prescient experimental phase of telephone-based TV shopping in the 1980s, and setting the tone for the future with Stephan Schambach’s 1990s invention of the first standardized online shopping software. US consumers spent $861.12 billion with online merchants in 2020. By making the “add to cart” ritual so familiar, it may seem like we’ve seen it all when it comes to digital commerce.
But hold onto your hats, because signs are emerging that we’re on the verge of the next online sales phase, akin to the 19th century leap from still photos to moving pictures.
If I’m right, with its standard product shots, conventional e-commerce will soon start to seem dull and dated in many categories compared to products sold via interactive video and further supported with post-purchase video.
Now is the time to prep for a filmed future, and fortunately, the trail has already been blazed for us by home shopping leader QVC, which took over television and then digitally remastered itself for the web, perfecting the art of video-based sales. Today, we’re going to deconstruct what’s happening on QVC, and how and why you may need to learn to apply it as an SEO, local SEO, or business owner — sooner than you think.
Why video sales?
A series of developments and disruptions point to a future in which many product sales will be facilitated via video. Let’s have a look at them:
First, we all know that humans love video content so much, they’ve caused YouTube to be the #2 search engine.
Google has documented the growth of video searches for “which (product) should I buy”.
When we look beyond the US, we encounter the phenomenon that livestreaming e-commerce video has become in China, highly-monopolized by Alibaba’s Taobao and creating celebrities out of its hosts.
Meanwhile, within the US, the pandemic caused a 44% increase in digital shopping spend between 2019-2020. We moved online last year for both our basic needs and nonessentials like never before.
The pandemic has also caused physical local brands to implement digital shopping, blurring former online-to-offline (O2O) barriers to such a degree that Internet transactions are no longer the special property of virtual e-commerce companies. This weirdly-dubbed “phygital” phenomenon — which is making Google the nexus of Maps-based local product sales — can be seen as a boon to local brands that take advantage of the search engine’s famed user-to-business proximity bias to rank their inventory for nearby customers.
At least, Google hopes to be the nexus of all this. The truth is, Google is reacting strongly right now to consumers starting half of their product searches on Amazon instead of on Google. Are you seeing ads everywhere these days informing you that Google is the best place to shop? So am I. With that massive, lucrative local business index in their back pocket and with GMB listings long supporting video uploads, Google has recently:
Acquired Pointy to integrate with retail POS systems
Made product listings free
Amped up their nearby shopping filter
Attempted to insert themselves directly into consumers’ curbside pickup routines while integrating deeply into data partnerships with major grocery brands
Experienced massive growth in local business reviews, and just released an algorithmic update specific to product review content (look out, Amazon!)
Experimented with detecting products in YouTube videos amid rumors flying about product results appearing in YouTube
Been spotted experimenting beyond influencer cameo videos to product cameos in knowledge panels
Meanwhile, big brands everywhere are getting into video sales. Walmart leapt ahead in the shoppable video contest with their debut of Cookshop, in which celebrity chefs cook while consumers click on the interactive video cues to add ingredients to their shopping carts.
Crate & Barrel is tiptoeing into the pool with quick product romance videos that resemble perfume ads, in which models lounge about on lovely accent chairs, creating the aura of a lifestyle to be lived. Nordstrom is filming bite-sized home shopping channel-style product videos for their website and YouTube channel, complete with hosts.
And, smaller brands are experimenting with video-supported sales content, too. Check out Green Building Supply’s product videos for their eco-friendly home improvement inventory (with personable hosts). Absolute Domestics shows how SABs can use video to support sales of services rather than goods, as in this simple but nicely-produced video on what to expect from their cleaning service. Meanwhile, post-sales support videos are a persuasive value add from Purl Soho to help you master knitting techniques needed when you buy a pattern from them.
To sum up, at the deep end of the pool, live-streamed e-commerce and shoppable video are already in use by big brands, but smaller brands can wade in with basic static goods-and-services videos on their websites and social channels to support sales.
Now is the time to look for inspiration about what video sales could do for brands you market, and nobody — nobody — has more experience with all of this than QVC.
Why QVC?
“I didn’t even know QVC still existed,” more than one of my marketing colleagues has responded when I’ve pointed to the 35-year-old home shopping empire as the way of the future.
The truth is, I’d probably be sleeping on QVC, too, if it weren’t for my Irish ancestry having drawn me to their annual St. Patrick’s Day sales event for the past 30+ years to enjoy their made-in-Ireland product lineup.
About seven times more people with Irish roots live in the United States than on the actual island of Ireland, yet the shopping channel’s holiday broadcast is one of the few televised events tailored to our famous nostalgia for our old country home. My family tunes in every March for the craic of examining Aran Crafts sweaters, Nicholas Mosse pottery, Belleek china, and Solvar jewelry, while munching on cake made from my great-grandmother Cotter’s recipe. Sometimes we get so excited, we buy things, but for the past few years, I’ve mainly been actively studying how QVC sells these items with such stunning success.
“Stunning” is the word and the wakeup call
QVC, which is a subsidiary of Quarate Retail International, generated $11.47 billion in 2020 and as early as 2015, nearly half of those sales were taking place online — consistently placing the brand in the top 10 for e-commerce sales, including mobile sales. The company has 16.5 million consolidated customers worldwide, and marketers’ mouths will surely water to learn that 90% of QVC’s revenue comes from loyal repeat shoppers. The average QVC shopper makes between 22-25 purchases per year!
Figures like these, paired with QVC’s graceful pas de deux incorporating both TV remotes and mobile devices should command our attention long enough to study what they’ve done and how they’ve done it.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC!”
While supplies last, I want to invite you to spend the next 10 minutes watching this Internet rebroadcast of a televised segment selling an Aran Crafts sweater, with your marketer’s eye on the magic happening in it. Watch this while imagining how it might translate as a static product or service video for a brand you’re marketing.
TL;DW? Here’s the breakdown of how QVC sells:
Main host
QVC hosts are personalities, many of whom have devoted fan bases. They’re trained in the products they sell, often visiting manufacturing plants to school themselves. When on air, the host juggles promoting a product and interacting with models, guest hosts, callers, and off-screen analysts. The host physically interacts with the product, highlights its features in abundant detail, and makes their sales pitch.
For our purposes, digital marketers are fully aware of the phenomenon of social influencers taking on celebrity status and being sought after as sales reps. At a more modest scale, small e-commerce companies (or any local business) that’s adopted digital sales models should identify one or more staff members with the necessary talents to become a video host for the brand.
You’ll need a spot of luck to secure relatable hosts. Just keep in mind that QVC’s secret formula is to get the viewer to ask, “Is this me?”, and that should help you match a host to your audience. This example of a nicely-done, low-key, densely-detailed presentation of a camping chair by a plainspoken host shows how simple and effective a short product video can be.
Guest hosts
Many QVC segments feature a representative from the brand associated with the product being sold. In our example, the guest host from Aran Crafts is a member of her family’s business, signing in remotely (due to the pandemic) to share the company’s story and build romance around the product.
Depending on the model you’re marketing, having a rep from any brand you resell would be an extra trust signal to convey via video sales. Think of the back-and-forth chat in a podcast and you’re almost there. Small retailers just reselling big brands may face a challenge here, but if you have a good portion of inventory from smaller companies and specialty or local manufacturers, definitely invite them to step in front of the camera with your host, as higher sales will benefit you both.
Models
Frequently, sales presentations include one or more models further interacting with the product. In our example, models are wearing these Irish sweaters while strolling around Ashford Castle. More romance.
Other segments feature models as subjects of various cosmetic treatments or as demonstrators of how merchandise is to be used. Models and demonstrators used to be standard in major American department stores. QVC brilliantly televised this incredible form of persuasion at about the same time it disappeared from real-world shopping in the US. Their sales figures prove just how huge the desire still is to see merchandise worn and used before buying.
For our scenario of creating online sales videos, such models could be a convincing extra in selling certain types of products, and many products should be demonstrated by the host or guest host. One thing I’ve not seen QVC do that I think e-commerce and O2O local brands definitely could do is a UGC approach of making your customer your model, demoing how they use your products in their real-world lives. Almost everybody can film themselves these days.
Callers
There are no live callers in our example, but QVC traditionally increases interactivity with the public with on-air phone calls.
If your sales videos are static, you’re not quite to the point of having to learn the art of handling live calls, but your product support phone and SMS numbers and links should be featured in every video.
Method
“If you go up there with the intent to sell, it’s all going to come crashing down around you...The real goal of QVC.... was to feel like a conversation between the host, the product specialist (us), and ‘Her’ – the woman age 35 to 65 who is sitting at home watching television.” - I went on air at QVC and sold something to America
There’s an element of magic to how QVC vends such a massive volume of products, but it’s all data-based. They’ve invested so heavily in understanding customer demographics that they’ve mastered exactly how to sell to them. Your consumer base may be totally different, but the key is to know your customer so well that you understand the exact approach to take when offering them your inventory of goods and services.
Another excerpt from the article cited above really gets this point across when talking about guest hosts:
“Our experienced guests tend to focus on the product. But our best guests are focused on the viewer. Is this for the viewer? Everything goes through that filter. And if you do that, everything comes out more naturally.”
Here at Moz, there may be Whiteboard Friday hosts you especially enjoy learning from. As a business owner or marketer, your job will be to identify talented people who can blend your brand culture with consumer research and translate that into a form of vending infotainment that succeeds with your particular shoppers. Successful QVC hosts make upwards of $500,000 a year for being so good at what they do.
Being good, in the sweater sample, means pairing QVC’s customer-centric, conversational selling method with USPs and an aura of scarcity. I’ll paraphrase the cues I heard:
“These sweaters are made exclusively for QVC” — a USP regarding rarity.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC” — this is a strong USP based on having better prices than a traveler would find if buying direct from the manufacturer.
“Reviews read like a love letter to this sweater” — incorporating persuasive UGC into the pitch.
“Half of our supply is already gone; don’t wait to order if you want one of these” —- this creates a sense of urgency to prompt customers to buy right away.
Analytics
The example presentation probably looked quite seamless and simple to you. But what’s actually going on “behind the scenes” of a QVC sales segment is that the host is receiving earpiece cues on exactly how to shape the pitch.
QVC’s analytics track what’s called a “feverline” of reaction to each word the host says and each movement they make. Producers can tell in real time which verbal signals and gestures are causing sales spikes, and communicate to the host to repeat them. One host, for example, dances repeatedly while demoing food products because more customers buy when he does so.
For most of the brands you market, you’re not likely to be called upon to deliver analytical data on par with QVC’s mission control-style setup, but you will want to learn about video analytics and do A/B testing to measure performance of product pages with video vs. those with static images. As you progress, analytics should be able to tell you which hosts, guests, and products are yielding the best ROI.
Three O2O advantages
In a large 2020 survey of local business owners and marketers, Moz found that more than half of respondents intend to maintain pandemic-era services of convenience beyond the hoped-for end of COVID-19. I’d expect this number to be even higher if we reran the survey in mid-2021. Online-to-offline shopping falls in this category and readers of my column know I’m always looking for advantages specific to local businesses.
I see three ways local brands have a leg up on their virtual e-commerce cousins, including behemoths like Amazon and even QVC:
1. Limited local competition = better SERP visibility
Virtual e-commerce brands have to compete against a whole country or the world for SERP visibility. Google Shopping’s “available nearby” filter cuts your market down to local map-size, making it easier to capture the attention of customers nearest your business. If you’re one of the only local brands supporting sales of your goods and services via videos on your website, you’re really going to stand out in the cities you serve.
2. Limited local inventory = more convincing authenticity
QVC is certainly an impressive enterprise, but one drawback of their methodology, at least in my eyes, is that their hosts have to be endlessly excited about millions of products. The same host who is exuding enthusiasm one minute over an electric toothbrush is breathless with admiration over a flameless candle the next. While QVC’s amazingly loyal customers are clearly not put off by the bottomless supply of energy over every single product sold, I find I don’t quite believe that the joy is continuously genuine. In my recognition of the sales pitch tactics, the company feels big and remote to me.
70% of Americans say they want to shop small. Your advantage in marketing a local business is that it will have limited inventory and an owner and staff who can realistically convey authenticity to the video viewer about products the business has hand-selected to sell. A big chain supermarket wants me to believe all of its apples are crisp, but my local farmer telling me in a product video that this year’s crop is crisper than last year’s makes a world of believable difference.
3. Even a small boost in conversions = a big difference for local brands
Backlinko recently compiled this list of exciting video marketing statistics that I hope you’ll read in full. I want to excerpt a few that really caught my eye:
84% of consumers cite video as the convincing factor in purchases
Product videos can help e-commerce stores increase sales by up to 144%
96% of people have watched an explainer video to better understand a product they’re evaluating
The Local Search Association found that 53% of people contact a business after watching one of their videos and 71% of people who made a purchase had watched an online video from that brand
Including filmed content on an e-commerce page can increase the average order value by 50+%
Video on a landing page can grow its conversion rate by up to 80%
If the company you’re promoting is one of the only ones in your local market to seize the opportunities hinted at by these statistics, think of what a difference it would make to see conversions (including leads and sales) rise by even a fraction of these numbers. Moreover, if the standout UX and helpfulness of the “v-commerce” environment you create makes you memorable to customers, you could grow local loyalty to new levels as the best resource in a community, generating a recipe for retention that, if not quite as astonishing as QVC’s, is pretty amazing for your region.
Go n-éirí leat — good luck!
Like you, I’m longing for the time when all customers can safely return to shopping locally in-person, but I do agree with fellow analysts predicting that the taste we’ve gotten for the convenience of shipping and local home delivery, curbside pickup, and tele-meetings is one that consumers won’t simply abandon.
Sales videos tackle one of digital marketing’s largest challenges by letting customers see people interacting with products when they can’t do it themselves, and 2021 is a good year to begin your investigation of this promising medium. My top tip is to spend some time this week watching QVC on TV and examining how they’ve parlayed live broadcasts into static
product videos that sell inventory like hotcakes on their website. I’m wishing you the luck and intrepidity of the Irish in your video ventures!
Ready to learn more about video marketing? Try these resources:
17 Best Ecommerce Product Video Examples
The ABCs of Video Content
8 Beginner Tips for Making Professional-Looking Videos
How to Film Creative Product Videos
YouTube Dominates Google Video in 2020
How to Track YouTube Videos in Google Analytics Using Google Tag Manager in 4 Steps
Need to learn more about local search marketing before you start filming yourself and your products? Read The Essential Local SEO Strategy Guide.
#túi_giấy_epacking_việt_nam #túi_giấy_epacking #in_túi_giấy_giá_rẻ #in_túi_giấy #epackingvietnam #tuigiayepacking
0 notes
Text
Are You Ready to Sell Like QVC?
A photo. Some text. A shopping cart button.
It’s the setup you’ve been used to since you were Internet-years-old.
Electronic commerce has existed since the 1970s, passing through a prescient experimental phase of telephone-based TV shopping in the 1980s, and setting the tone for the future with Stephan Schambach’s 1990s invention of the first standardized online shopping software. US consumers spent $861.12 billion with online merchants in 2020. By making the “add to cart” ritual so familiar, it may seem like we’ve seen it all when it comes to digital commerce.
But hold onto your hats, because signs are emerging that we’re on the verge of the next online sales phase, akin to the 19th century leap from still photos to moving pictures.
If I’m right, with its standard product shots, conventional e-commerce will soon start to seem dull and dated in many categories compared to products sold via interactive video and further supported with post-purchase video.
Now is the time to prep for a filmed future, and fortunately, the trail has already been blazed for us by home shopping leader QVC, which took over television and then digitally remastered itself for the web, perfecting the art of video-based sales. Today, we’re going to deconstruct what’s happening on QVC, and how and why you may need to learn to apply it as an SEO, local SEO, or business owner — sooner than you think.
Why video sales?
A series of developments and disruptions point to a future in which many product sales will be facilitated via video. Let’s have a look at them:
First, we all know that humans love video content so much, they’ve caused YouTube to be the #2 search engine.
Google has documented the growth of video searches for “which (product) should I buy”.
When we look beyond the US, we encounter the phenomenon that livestreaming e-commerce video has become in China, highly-monopolized by Alibaba’s Taobao and creating celebrities out of its hosts.
Meanwhile, within the US, the pandemic caused a 44% increase in digital shopping spend between 2019-2020. We moved online last year for both our basic needs and nonessentials like never before.
The pandemic has also caused physical local brands to implement digital shopping, blurring former online-to-offline (O2O) barriers to such a degree that Internet transactions are no longer the special property of virtual e-commerce companies. This weirdly-dubbed “phygital” phenomenon — which is making Google the nexus of Maps-based local product sales — can be seen as a boon to local brands that take advantage of the search engine’s famed user-to-business proximity bias to rank their inventory for nearby customers.
At least, Google hopes to be the nexus of all this. The truth is, Google is reacting strongly right now to consumers starting half of their product searches on Amazon instead of on Google. Are you seeing ads everywhere these days informing you that Google is the best place to shop? So am I. With that massive, lucrative local business index in their back pocket and with GMB listings long supporting video uploads, Google has recently:
Acquired Pointy to integrate with retail POS systems
Made product listings free
Amped up their nearby shopping filter
Attempted to insert themselves directly into consumers’ curbside pickup routines while integrating deeply into data partnerships with major grocery brands
Experienced massive growth in local business reviews, and just released an algorithmic update specific to product review content (look out, Amazon!)
Experimented with detecting products in YouTube videos amid rumors flying about product results appearing in YouTube
Been spotted experimenting beyond influencer cameo videos to product cameos in knowledge panels
Meanwhile, big brands everywhere are getting into video sales. Walmart leapt ahead in the shoppable video contest with their debut of Cookshop, in which celebrity chefs cook while consumers click on the interactive video cues to add ingredients to their shopping carts.
Crate & Barrel is tiptoeing into the pool with quick product romance videos that resemble perfume ads, in which models lounge about on lovely accent chairs, creating the aura of a lifestyle to be lived. Nordstrom is filming bite-sized home shopping channel-style product videos for their website and YouTube channel, complete with hosts.
And, smaller brands are experimenting with video-supported sales content, too. Check out Green Building Supply’s product videos for their eco-friendly home improvement inventory (with personable hosts). Absolute Domestics shows how SABs can use video to support sales of services rather than goods, as in this simple but nicely-produced video on what to expect from their cleaning service. Meanwhile, post-sales support videos are a persuasive value add from Purl Soho to help you master knitting techniques needed when you buy a pattern from them.
To sum up, at the deep end of the pool, live-streamed e-commerce and shoppable video are already in use by big brands, but smaller brands can wade in with basic static goods-and-services videos on their websites and social channels to support sales.
Now is the time to look for inspiration about what video sales could do for brands you market, and nobody — nobody — has more experience with all of this than QVC.
Why QVC?
“I didn’t even know QVC still existed,” more than one of my marketing colleagues has responded when I’ve pointed to the 35-year-old home shopping empire as the way of the future.
The truth is, I’d probably be sleeping on QVC, too, if it weren’t for my Irish ancestry having drawn me to their annual St. Patrick’s Day sales event for the past 30+ years to enjoy their made-in-Ireland product lineup.
About seven times more people with Irish roots live in the United States than on the actual island of Ireland, yet the shopping channel’s holiday broadcast is one of the few televised events tailored to our famous nostalgia for our old country home. My family tunes in every March for the craic of examining Aran Crafts sweaters, Nicholas Mosse pottery, Belleek china, and Solvar jewelry, while munching on cake made from my great-grandmother Cotter’s recipe. Sometimes we get so excited, we buy things, but for the past few years, I’ve mainly been actively studying how QVC sells these items with such stunning success.
“Stunning” is the word and the wakeup call
QVC, which is a subsidiary of Quarate Retail International, generated $11.47 billion in 2020 and as early as 2015, nearly half of those sales were taking place online — consistently placing the brand in the top 10 for e-commerce sales, including mobile sales. The company has 16.5 million consolidated customers worldwide, and marketers’ mouths will surely water to learn that 90% of QVC’s revenue comes from loyal repeat shoppers. The average QVC shopper makes between 22-25 purchases per year!
Figures like these, paired with QVC’s graceful pas de deux incorporating both TV remotes and mobile devices should command our attention long enough to study what they’ve done and how they’ve done it.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC!”
While supplies last, I want to invite you to spend the next 10 minutes watching this Internet rebroadcast of a televised segment selling an Aran Crafts sweater, with your marketer’s eye on the magic happening in it. Watch this while imagining how it might translate as a static product or service video for a brand you’re marketing.
TL;DW? Here’s the breakdown of how QVC sells:
Main host
QVC hosts are personalities, many of whom have devoted fan bases. They’re trained in the products they sell, often visiting manufacturing plants to school themselves. When on air, the host juggles promoting a product and interacting with models, guest hosts, callers, and off-screen analysts. The host physically interacts with the product, highlights its features in abundant detail, and makes their sales pitch.
For our purposes, digital marketers are fully aware of the phenomenon of social influencers taking on celebrity status and being sought after as sales reps. At a more modest scale, small e-commerce companies (or any local business) that’s adopted digital sales models should identify one or more staff members with the necessary talents to become a video host for the brand.
You’ll need a spot of luck to secure relatable hosts. Just keep in mind that QVC’s secret formula is to get the viewer to ask, “Is this me?”, and that should help you match a host to your audience. This example of a nicely-done, low-key, densely-detailed presentation of a camping chair by a plainspoken host shows how simple and effective a short product video can be.
Guest hosts
Many QVC segments feature a representative from the brand associated with the product being sold. In our example, the guest host from Aran Crafts is a member of her family’s business, signing in remotely (due to the pandemic) to share the company’s story and build romance around the product.
Depending on the model you’re marketing, having a rep from any brand you resell would be an extra trust signal to convey via video sales. Think of the back-and-forth chat in a podcast and you’re almost there. Small retailers just reselling big brands may face a challenge here, but if you have a good portion of inventory from smaller companies and specialty or local manufacturers, definitely invite them to step in front of the camera with your host, as higher sales will benefit you both.
Models
Frequently, sales presentations include one or more models further interacting with the product. In our example, models are wearing these Irish sweaters while strolling around Ashford Castle. More romance.
Other segments feature models as subjects of various cosmetic treatments or as demonstrators of how merchandise is to be used. Models and demonstrators used to be standard in major American department stores. QVC brilliantly televised this incredible form of persuasion at about the same time it disappeared from real-world shopping in the US. Their sales figures prove just how huge the desire still is to see merchandise worn and used before buying.
For our scenario of creating online sales videos, such models could be a convincing extra in selling certain types of products, and many products should be demonstrated by the host or guest host. One thing I’ve not seen QVC do that I think e-commerce and O2O local brands definitely could do is a UGC approach of making your customer your model, demoing how they use your products in their real-world lives. Almost everybody can film themselves these days.
Callers
There are no live callers in our example, but QVC traditionally increases interactivity with the public with on-air phone calls.
If your sales videos are static, you’re not quite to the point of having to learn the art of handling live calls, but your product support phone and SMS numbers and links should be featured in every video.
Method
“If you go up there with the intent to sell, it’s all going to come crashing down around you...The real goal of QVC.... was to feel like a conversation between the host, the product specialist (us), and ‘Her’ – the woman age 35 to 65 who is sitting at home watching television.” - I went on air at QVC and sold something to America
There’s an element of magic to how QVC vends such a massive volume of products, but it’s all data-based. They’ve invested so heavily in understanding customer demographics that they’ve mastered exactly how to sell to them. Your consumer base may be totally different, but the key is to know your customer so well that you understand the exact approach to take when offering them your inventory of goods and services.
Another excerpt from the article cited above really gets this point across when talking about guest hosts:
“Our experienced guests tend to focus on the product. But our best guests are focused on the viewer. Is this for the viewer? Everything goes through that filter. And if you do that, everything comes out more naturally.”
Here at Moz, there may be Whiteboard Friday hosts you especially enjoy learning from. As a business owner or marketer, your job will be to identify talented people who can blend your brand culture with consumer research and translate that into a form of vending infotainment that succeeds with your particular shoppers. Successful QVC hosts make upwards of $500,000 a year for being so good at what they do.
Being good, in the sweater sample, means pairing QVC’s customer-centric, conversational selling method with USPs and an aura of scarcity. I’ll paraphrase the cues I heard:
“These sweaters are made exclusively for QVC” — a USP regarding rarity.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC” — this is a strong USP based on having better prices than a traveler would find if buying direct from the manufacturer.
“Reviews read like a love letter to this sweater” — incorporating persuasive UGC into the pitch.
“Half of our supply is already gone; don’t wait to order if you want one of these” —- this creates a sense of urgency to prompt customers to buy right away.
Analytics
The example presentation probably looked quite seamless and simple to you. But what’s actually going on “behind the scenes” of a QVC sales segment is that the host is receiving earpiece cues on exactly how to shape the pitch.
QVC’s analytics track what’s called a “feverline” of reaction to each word the host says and each movement they make. Producers can tell in real time which verbal signals and gestures are causing sales spikes, and communicate to the host to repeat them. One host, for example, dances repeatedly while demoing food products because more customers buy when he does so.
For most of the brands you market, you’re not likely to be called upon to deliver analytical data on par with QVC’s mission control-style setup, but you will want to learn about video analytics and do A/B testing to measure performance of product pages with video vs. those with static images. As you progress, analytics should be able to tell you which hosts, guests, and products are yielding the best ROI.
Three O2O advantages
In a large 2020 survey of local business owners and marketers, Moz found that more than half of respondents intend to maintain pandemic-era services of convenience beyond the hoped-for end of COVID-19. I’d expect this number to be even higher if we reran the survey in mid-2021. Online-to-offline shopping falls in this category and readers of my column know I’m always looking for advantages specific to local businesses.
I see three ways local brands have a leg up on their virtual e-commerce cousins, including behemoths like Amazon and even QVC:
1. Limited local competition = better SERP visibility
Virtual e-commerce brands have to compete against a whole country or the world for SERP visibility. Google Shopping’s “available nearby” filter cuts your market down to local map-size, making it easier to capture the attention of customers nearest your business. If you’re one of the only local brands supporting sales of your goods and services via videos on your website, you’re really going to stand out in the cities you serve.
2. Limited local inventory = more convincing authenticity
QVC is certainly an impressive enterprise, but one drawback of their methodology, at least in my eyes, is that their hosts have to be endlessly excited about millions of products. The same host who is exuding enthusiasm one minute over an electric toothbrush is breathless with admiration over a flameless candle the next. While QVC’s amazingly loyal customers are clearly not put off by the bottomless supply of energy over every single product sold, I find I don’t quite believe that the joy is continuously genuine. In my recognition of the sales pitch tactics, the company feels big and remote to me.
70% of Americans say they want to shop small. Your advantage in marketing a local business is that it will have limited inventory and an owner and staff who can realistically convey authenticity to the video viewer about products the business has hand-selected to sell. A big chain supermarket wants me to believe all of its apples are crisp, but my local farmer telling me in a product video that this year’s crop is crisper than last year’s makes a world of believable difference.
3. Even a small boost in conversions = a big difference for local brands
Backlinko recently compiled this list of exciting video marketing statistics that I hope you’ll read in full. I want to excerpt a few that really caught my eye:
84% of consumers cite video as the convincing factor in purchases
Product videos can help e-commerce stores increase sales by up to 144%
96% of people have watched an explainer video to better understand a product they’re evaluating
The Local Search Association found that 53% of people contact a business after watching one of their videos and 71% of people who made a purchase had watched an online video from that brand
Including filmed content on an e-commerce page can increase the average order value by 50+%
Video on a landing page can grow its conversion rate by up to 80%
If the company you’re promoting is one of the only ones in your local market to seize the opportunities hinted at by these statistics, think of what a difference it would make to see conversions (including leads and sales) rise by even a fraction of these numbers. Moreover, if the standout UX and helpfulness of the “v-commerce” environment you create makes you memorable to customers, you could grow local loyalty to new levels as the best resource in a community, generating a recipe for retention that, if not quite as astonishing as QVC’s, is pretty amazing for your region.
Go n-éirí leat — good luck!
Like you, I’m longing for the time when all customers can safely return to shopping locally in-person, but I do agree with fellow analysts predicting that the taste we’ve gotten for the convenience of shipping and local home delivery, curbside pickup, and tele-meetings is one that consumers won’t simply abandon.
Sales videos tackle one of digital marketing’s largest challenges by letting customers see people interacting with products when they can’t do it themselves, and 2021 is a good year to begin your investigation of this promising medium. My top tip is to spend some time this week watching QVC on TV and examining how they’ve parlayed live broadcasts into static
product videos that sell inventory like hotcakes on their website. I’m wishing you the luck and intrepidity of the Irish in your video ventures!
Ready to learn more about video marketing? Try these resources:
17 Best Ecommerce Product Video Examples
The ABCs of Video Content
8 Beginner Tips for Making Professional-Looking Videos
How to Film Creative Product Videos
YouTube Dominates Google Video in 2020
How to Track YouTube Videos in Google Analytics Using Google Tag Manager in 4 Steps
Need to learn more about local search marketing before you start filming yourself and your products? Read The Essential Local SEO Strategy Guide.
0 notes
Text
Are You Ready to Sell Like QVC?
A photo. Some text. A shopping cart button.
It’s the setup you’ve been used to since you were Internet-years-old.
Electronic commerce has existed since the 1970s, passing through a prescient experimental phase of telephone-based TV shopping in the 1980s, and setting the tone for the future with Stephan Schambach’s 1990s invention of the first standardized online shopping software. US consumers spent $861.12 billion with online merchants in 2020. By making the “add to cart” ritual so familiar, it may seem like we’ve seen it all when it comes to digital commerce.
But hold onto your hats, because signs are emerging that we’re on the verge of the next online sales phase, akin to the 19th century leap from still photos to moving pictures.
If I’m right, with its standard product shots, conventional e-commerce will soon start to seem dull and dated in many categories compared to products sold via interactive video and further supported with post-purchase video.
Now is the time to prep for a filmed future, and fortunately, the trail has already been blazed for us by home shopping leader QVC, which took over television and then digitally remastered itself for the web, perfecting the art of video-based sales. Today, we’re going to deconstruct what’s happening on QVC, and how and why you may need to learn to apply it as an SEO, local SEO, or business owner — sooner than you think.
Why video sales?
A series of developments and disruptions point to a future in which many product sales will be facilitated via video. Let’s have a look at them:
First, we all know that humans love video content so much, they’ve caused YouTube to be the #2 search engine.
Google has documented the growth of video searches for “which (product) should I buy”.
When we look beyond the US, we encounter the phenomenon that livestreaming e-commerce video has become in China, highly-monopolized by Alibaba’s Taobao and creating celebrities out of its hosts.
Meanwhile, within the US, the pandemic caused a 44% increase in digital shopping spend between 2019-2020. We moved online last year for both our basic needs and nonessentials like never before.
The pandemic has also caused physical local brands to implement digital shopping, blurring former online-to-offline (O2O) barriers to such a degree that Internet transactions are no longer the special property of virtual e-commerce companies. This weirdly-dubbed “phygital” phenomenon — which is making Google the nexus of Maps-based local product sales — can be seen as a boon to local brands that take advantage of the search engine’s famed user-to-business proximity bias to rank their inventory for nearby customers.
At least, Google hopes to be the nexus of all this. The truth is, Google is reacting strongly right now to consumers starting half of their product searches on Amazon instead of on Google. Are you seeing ads everywhere these days informing you that Google is the best place to shop? So am I. With that massive, lucrative local business index in their back pocket and with GMB listings long supporting video uploads, Google has recently:
Acquired Pointy to integrate with retail POS systems
Made product listings free
Amped up their nearby shopping filter
Attempted to insert themselves directly into consumers’ curbside pickup routines while integrating deeply into data partnerships with major grocery brands
Experienced massive growth in local business reviews, and just released an algorithmic update specific to product review content (look out, Amazon!)
Experimented with detecting products in YouTube videos amid rumors flying about product results appearing in YouTube
Been spotted experimenting beyond influencer cameo videos to product cameos in knowledge panels
Meanwhile, big brands everywhere are getting into video sales. Walmart leapt ahead in the shoppable video contest with their debut of Cookshop, in which celebrity chefs cook while consumers click on the interactive video cues to add ingredients to their shopping carts.
Crate & Barrel is tiptoeing into the pool with quick product romance videos that resemble perfume ads, in which models lounge about on lovely accent chairs, creating the aura of a lifestyle to be lived. Nordstrom is filming bite-sized home shopping channel-style product videos for their website and YouTube channel, complete with hosts.
And, smaller brands are experimenting with video-supported sales content, too. Check out Green Building Supply’s product videos for their eco-friendly home improvement inventory (with personable hosts). Absolute Domestics shows how SABs can use video to support sales of services rather than goods, as in this simple but nicely-produced video on what to expect from their cleaning service. Meanwhile, post-sales support videos are a persuasive value add from Purl Soho to help you master knitting techniques needed when you buy a pattern from them.
To sum up, at the deep end of the pool, live-streamed e-commerce and shoppable video are already in use by big brands, but smaller brands can wade in with basic static goods-and-services videos on their websites and social channels to support sales.
Now is the time to look for inspiration about what video sales could do for brands you market, and nobody — nobody — has more experience with all of this than QVC.
Why QVC?
“I didn’t even know QVC still existed,” more than one of my marketing colleagues has responded when I’ve pointed to the 35-year-old home shopping empire as the way of the future.
The truth is, I’d probably be sleeping on QVC, too, if it weren’t for my Irish ancestry having drawn me to their annual St. Patrick’s Day sales event for the past 30+ years to enjoy their made-in-Ireland product lineup.
About seven times more people with Irish roots live in the United States than on the actual island of Ireland, yet the shopping channel’s holiday broadcast is one of the few televised events tailored to our famous nostalgia for our old country home. My family tunes in every March for the craic of examining Aran Crafts sweaters, Nicholas Mosse pottery, Belleek china, and Solvar jewelry, while munching on cake made from my great-grandmother Cotter’s recipe. Sometimes we get so excited, we buy things, but for the past few years, I’ve mainly been actively studying how QVC sells these items with such stunning success.
“Stunning” is the word and the wakeup call
QVC, which is a subsidiary of Quarate Retail International, generated $11.47 billion in 2020 and as early as 2015, nearly half of those sales were taking place online — consistently placing the brand in the top 10 for e-commerce sales, including mobile sales. The company has 16.5 million consolidated customers worldwide, and marketers’ mouths will surely water to learn that 90% of QVC’s revenue comes from loyal repeat shoppers. The average QVC shopper makes between 22-25 purchases per year!
Figures like these, paired with QVC’s graceful pas de deux incorporating both TV remotes and mobile devices should command our attention long enough to study what they’ve done and how they’ve done it.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC!”
While supplies last, I want to invite you to spend the next 10 minutes watching this Internet rebroadcast of a televised segment selling an Aran Crafts sweater, with your marketer’s eye on the magic happening in it. Watch this while imagining how it might translate as a static product or service video for a brand you’re marketing.
TL;DW? Here’s the breakdown of how QVC sells:
Main host
QVC hosts are personalities, many of whom have devoted fan bases. They’re trained in the products they sell, often visiting manufacturing plants to school themselves. When on air, the host juggles promoting a product and interacting with models, guest hosts, callers, and off-screen analysts. The host physically interacts with the product, highlights its features in abundant detail, and makes their sales pitch.
For our purposes, digital marketers are fully aware of the phenomenon of social influencers taking on celebrity status and being sought after as sales reps. At a more modest scale, small e-commerce companies (or any local business) that’s adopted digital sales models should identify one or more staff members with the necessary talents to become a video host for the brand.
You’ll need a spot of luck to secure relatable hosts. Just keep in mind that QVC’s secret formula is to get the viewer to ask, “Is this me?”, and that should help you match a host to your audience. This example of a nicely-done, low-key, densely-detailed presentation of a camping chair by a plainspoken host shows how simple and effective a short product video can be.
Guest hosts
Many QVC segments feature a representative from the brand associated with the product being sold. In our example, the guest host from Aran Crafts is a member of her family’s business, signing in remotely (due to the pandemic) to share the company’s story and build romance around the product.
Depending on the model you’re marketing, having a rep from any brand you resell would be an extra trust signal to convey via video sales. Think of the back-and-forth chat in a podcast and you’re almost there. Small retailers just reselling big brands may face a challenge here, but if you have a good portion of inventory from smaller companies and specialty or local manufacturers, definitely invite them to step in front of the camera with your host, as higher sales will benefit you both.
Models
Frequently, sales presentations include one or more models further interacting with the product. In our example, models are wearing these Irish sweaters while strolling around Ashford Castle. More romance.
Other segments feature models as subjects of various cosmetic treatments or as demonstrators of how merchandise is to be used. Models and demonstrators used to be standard in major American department stores. QVC brilliantly televised this incredible form of persuasion at about the same time it disappeared from real-world shopping in the US. Their sales figures prove just how huge the desire still is to see merchandise worn and used before buying.
For our scenario of creating online sales videos, such models could be a convincing extra in selling certain types of products, and many products should be demonstrated by the host or guest host. One thing I’ve not seen QVC do that I think e-commerce and O2O local brands definitely could do is a UGC approach of making your customer your model, demoing how they use your products in their real-world lives. Almost everybody can film themselves these days.
Callers
There are no live callers in our example, but QVC traditionally increases interactivity with the public with on-air phone calls.
If your sales videos are static, you’re not quite to the point of having to learn the art of handling live calls, but your product support phone and SMS numbers and links should be featured in every video.
Method
“If you go up there with the intent to sell, it’s all going to come crashing down around you...The real goal of QVC.... was to feel like a conversation between the host, the product specialist (us), and ‘Her’ – the woman age 35 to 65 who is sitting at home watching television.” - I went on air at QVC and sold something to America
There’s an element of magic to how QVC vends such a massive volume of products, but it’s all data-based. They’ve invested so heavily in understanding customer demographics that they’ve mastered exactly how to sell to them. Your consumer base may be totally different, but the key is to know your customer so well that you understand the exact approach to take when offering them your inventory of goods and services.
Another excerpt from the article cited above really gets this point across when talking about guest hosts:
“Our experienced guests tend to focus on the product. But our best guests are focused on the viewer. Is this for the viewer? Everything goes through that filter. And if you do that, everything comes out more naturally.”
Here at Moz, there may be Whiteboard Friday hosts you especially enjoy learning from. As a business owner or marketer, your job will be to identify talented people who can blend your brand culture with consumer research and translate that into a form of vending infotainment that succeeds with your particular shoppers. Successful QVC hosts make upwards of $500,000 a year for being so good at what they do.
Being good, in the sweater sample, means pairing QVC’s customer-centric, conversational selling method with USPs and an aura of scarcity. I’ll paraphrase the cues I heard:
“These sweaters are made exclusively for QVC” — a USP regarding rarity.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC” — this is a strong USP based on having better prices than a traveler would find if buying direct from the manufacturer.
“Reviews read like a love letter to this sweater” — incorporating persuasive UGC into the pitch.
“Half of our supply is already gone; don’t wait to order if you want one of these” —- this creates a sense of urgency to prompt customers to buy right away.
Analytics
The example presentation probably looked quite seamless and simple to you. But what’s actually going on “behind the scenes” of a QVC sales segment is that the host is receiving earpiece cues on exactly how to shape the pitch.
QVC’s analytics track what’s called a “feverline” of reaction to each word the host says and each movement they make. Producers can tell in real time which verbal signals and gestures are causing sales spikes, and communicate to the host to repeat them. One host, for example, dances repeatedly while demoing food products because more customers buy when he does so.
For most of the brands you market, you’re not likely to be called upon to deliver analytical data on par with QVC’s mission control-style setup, but you will want to learn about video analytics and do A/B testing to measure performance of product pages with video vs. those with static images. As you progress, analytics should be able to tell you which hosts, guests, and products are yielding the best ROI.
Three O2O advantages
In a large 2020 survey of local business owners and marketers, Moz found that more than half of respondents intend to maintain pandemic-era services of convenience beyond the hoped-for end of COVID-19. I’d expect this number to be even higher if we reran the survey in mid-2021. Online-to-offline shopping falls in this category and readers of my column know I’m always looking for advantages specific to local businesses.
I see three ways local brands have a leg up on their virtual e-commerce cousins, including behemoths like Amazon and even QVC:
1. Limited local competition = better SERP visibility
Virtual e-commerce brands have to compete against a whole country or the world for SERP visibility. Google Shopping’s “available nearby” filter cuts your market down to local map-size, making it easier to capture the attention of customers nearest your business. If you’re one of the only local brands supporting sales of your goods and services via videos on your website, you’re really going to stand out in the cities you serve.
2. Limited local inventory = more convincing authenticity
QVC is certainly an impressive enterprise, but one drawback of their methodology, at least in my eyes, is that their hosts have to be endlessly excited about millions of products. The same host who is exuding enthusiasm one minute over an electric toothbrush is breathless with admiration over a flameless candle the next. While QVC’s amazingly loyal customers are clearly not put off by the bottomless supply of energy over every single product sold, I find I don’t quite believe that the joy is continuously genuine. In my recognition of the sales pitch tactics, the company feels big and remote to me.
70% of Americans say they want to shop small. Your advantage in marketing a local business is that it will have limited inventory and an owner and staff who can realistically convey authenticity to the video viewer about products the business has hand-selected to sell. A big chain supermarket wants me to believe all of its apples are crisp, but my local farmer telling me in a product video that this year’s crop is crisper than last year’s makes a world of believable difference.
3. Even a small boost in conversions = a big difference for local brands
Backlinko recently compiled this list of exciting video marketing statistics that I hope you’ll read in full. I want to excerpt a few that really caught my eye:
84% of consumers cite video as the convincing factor in purchases
Product videos can help e-commerce stores increase sales by up to 144%
96% of people have watched an explainer video to better understand a product they’re evaluating
The Local Search Association found that 53% of people contact a business after watching one of their videos and 71% of people who made a purchase had watched an online video from that brand
Including filmed content on an e-commerce page can increase the average order value by 50+%
Video on a landing page can grow its conversion rate by up to 80%
If the company you’re promoting is one of the only ones in your local market to seize the opportunities hinted at by these statistics, think of what a difference it would make to see conversions (including leads and sales) rise by even a fraction of these numbers. Moreover, if the standout UX and helpfulness of the “v-commerce” environment you create makes you memorable to customers, you could grow local loyalty to new levels as the best resource in a community, generating a recipe for retention that, if not quite as astonishing as QVC’s, is pretty amazing for your region.
Go n-éirí leat — good luck!
Like you, I’m longing for the time when all customers can safely return to shopping locally in-person, but I do agree with fellow analysts predicting that the taste we’ve gotten for the convenience of shipping and local home delivery, curbside pickup, and tele-meetings is one that consumers won’t simply abandon.
Sales videos tackle one of digital marketing’s largest challenges by letting customers see people interacting with products when they can’t do it themselves, and 2021 is a good year to begin your investigation of this promising medium. My top tip is to spend some time this week watching QVC on TV and examining how they’ve parlayed live broadcasts into static
product videos that sell inventory like hotcakes on their website. I’m wishing you the luck and intrepidity of the Irish in your video ventures!
Ready to learn more about video marketing? Try these resources:
17 Best Ecommerce Product Video Examples
The ABCs of Video Content
8 Beginner Tips for Making Professional-Looking Videos
How to Film Creative Product Videos
YouTube Dominates Google Video in 2020
How to Track YouTube Videos in Google Analytics Using Google Tag Manager in 4 Steps
Need to learn more about local search marketing before you start filming yourself and your products? Read The Essential Local SEO Strategy Guide.
0 notes
Text
Are You Ready to Sell Like QVC?
A photo. Some text. A shopping cart button.
It’s the setup you’ve been used to since you were Internet-years-old.
Electronic commerce has existed since the 1970s, passing through a prescient experimental phase of telephone-based TV shopping in the 1980s, and setting the tone for the future with Stephan Schambach’s 1990s invention of the first standardized online shopping software. US consumers spent $861.12 billion with online merchants in 2020. By making the “add to cart” ritual so familiar, it may seem like we’ve seen it all when it comes to digital commerce.
But hold onto your hats, because signs are emerging that we’re on the verge of the next online sales phase, akin to the 19th century leap from still photos to moving pictures.
If I’m right, with its standard product shots, conventional e-commerce will soon start to seem dull and dated in many categories compared to products sold via interactive video and further supported with post-purchase video.
Now is the time to prep for a filmed future, and fortunately, the trail has already been blazed for us by home shopping leader QVC, which took over television and then digitally remastered itself for the web, perfecting the art of video-based sales. Today, we’re going to deconstruct what’s happening on QVC, and how and why you may need to learn to apply it as an SEO, local SEO, or business owner — sooner than you think.
Why video sales?
A series of developments and disruptions point to a future in which many product sales will be facilitated via video. Let’s have a look at them:
First, we all know that humans love video content so much, they’ve caused YouTube to be the #2 search engine.
Google has documented the growth of video searches for “which (product) should I buy”.
When we look beyond the US, we encounter the phenomenon that livestreaming e-commerce video has become in China, highly-monopolized by Alibaba’s Taobao and creating celebrities out of its hosts.
Meanwhile, within the US, the pandemic caused a 44% increase in digital shopping spend between 2019-2020. We moved online last year for both our basic needs and nonessentials like never before.
The pandemic has also caused physical local brands to implement digital shopping, blurring former online-to-offline (O2O) barriers to such a degree that Internet transactions are no longer the special property of virtual e-commerce companies. This weirdly-dubbed “phygital” phenomenon — which is making Google the nexus of Maps-based local product sales — can be seen as a boon to local brands that take advantage of the search engine’s famed user-to-business proximity bias to rank their inventory for nearby customers.
At least, Google hopes to be the nexus of all this. The truth is, Google is reacting strongly right now to consumers starting half of their product searches on Amazon instead of on Google. Are you seeing ads everywhere these days informing you that Google is the best place to shop? So am I. With that massive, lucrative local business index in their back pocket and with GMB listings long supporting video uploads, Google has recently:
Acquired Pointy to integrate with retail POS systems
Made product listings free
Amped up their nearby shopping filter
Attempted to insert themselves directly into consumers’ curbside pickup routines while integrating deeply into data partnerships with major grocery brands
Experienced massive growth in local business reviews, and just released an algorithmic update specific to product review content (look out, Amazon!)
Experimented with detecting products in YouTube videos amid rumors flying about product results appearing in YouTube
Been spotted experimenting beyond influencer cameo videos to product cameos in knowledge panels
Meanwhile, big brands everywhere are getting into video sales. Walmart leapt ahead in the shoppable video contest with their debut of Cookshop, in which celebrity chefs cook while consumers click on the interactive video cues to add ingredients to their shopping carts.
Crate & Barrel is tiptoeing into the pool with quick product romance videos that resemble perfume ads, in which models lounge about on lovely accent chairs, creating the aura of a lifestyle to be lived. Nordstrom is filming bite-sized home shopping channel-style product videos for their website and YouTube channel, complete with hosts.
And, smaller brands are experimenting with video-supported sales content, too. Check out Green Building Supply’s product videos for their eco-friendly home improvement inventory (with personable hosts). Absolute Domestics shows how SABs can use video to support sales of services rather than goods, as in this simple but nicely-produced video on what to expect from their cleaning service. Meanwhile, post-sales support videos are a persuasive value add from Purl Soho to help you master knitting techniques needed when you buy a pattern from them.
To sum up, at the deep end of the pool, live-streamed e-commerce and shoppable video are already in use by big brands, but smaller brands can wade in with basic static goods-and-services videos on their websites and social channels to support sales.
Now is the time to look for inspiration about what video sales could do for brands you market, and nobody — nobody — has more experience with all of this than QVC.
Why QVC?
“I didn’t even know QVC still existed,” more than one of my marketing colleagues has responded when I’ve pointed to the 35-year-old home shopping empire as the way of the future.
The truth is, I’d probably be sleeping on QVC, too, if it weren’t for my Irish ancestry having drawn me to their annual St. Patrick’s Day sales event for the past 30+ years to enjoy their made-in-Ireland product lineup.
About seven times more people with Irish roots live in the United States than on the actual island of Ireland, yet the shopping channel’s holiday broadcast is one of the few televised events tailored to our famous nostalgia for our old country home. My family tunes in every March for the craic of examining Aran Crafts sweaters, Nicholas Mosse pottery, Belleek china, and Solvar jewelry, while munching on cake made from my great-grandmother Cotter’s recipe. Sometimes we get so excited, we buy things, but for the past few years, I’ve mainly been actively studying how QVC sells these items with such stunning success.
“Stunning” is the word and the wakeup call
QVC, which is a subsidiary of Quarate Retail International, generated $11.47 billion in 2020 and as early as 2015, nearly half of those sales were taking place online — consistently placing the brand in the top 10 for e-commerce sales, including mobile sales. The company has 16.5 million consolidated customers worldwide, and marketers’ mouths will surely water to learn that 90% of QVC’s revenue comes from loyal repeat shoppers. The average QVC shopper makes between 22-25 purchases per year!
Figures like these, paired with QVC’s graceful pas de deux incorporating both TV remotes and mobile devices should command our attention long enough to study what they’ve done and how they’ve done it.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC!”
While supplies last, I want to invite you to spend the next 10 minutes watching this Internet rebroadcast of a televised segment selling an Aran Crafts sweater, with your marketer’s eye on the magic happening in it. Watch this while imagining how it might translate as a static product or service video for a brand you’re marketing.
TL;DW? Here’s the breakdown of how QVC sells:
Main host
QVC hosts are personalities, many of whom have devoted fan bases. They’re trained in the products they sell, often visiting manufacturing plants to school themselves. When on air, the host juggles promoting a product and interacting with models, guest hosts, callers, and off-screen analysts. The host physically interacts with the product, highlights its features in abundant detail, and makes their sales pitch.
For our purposes, digital marketers are fully aware of the phenomenon of social influencers taking on celebrity status and being sought after as sales reps. At a more modest scale, small e-commerce companies (or any local business) that’s adopted digital sales models should identify one or more staff members with the necessary talents to become a video host for the brand.
You’ll need a spot of luck to secure relatable hosts. Just keep in mind that QVC’s secret formula is to get the viewer to ask, “Is this me?”, and that should help you match a host to your audience. This example of a nicely-done, low-key, densely-detailed presentation of a camping chair by a plainspoken host shows how simple and effective a short product video can be.
Guest hosts
Many QVC segments feature a representative from the brand associated with the product being sold. In our example, the guest host from Aran Crafts is a member of her family’s business, signing in remotely (due to the pandemic) to share the company’s story and build romance around the product.
Depending on the model you’re marketing, having a rep from any brand you resell would be an extra trust signal to convey via video sales. Think of the back-and-forth chat in a podcast and you’re almost there. Small retailers just reselling big brands may face a challenge here, but if you have a good portion of inventory from smaller companies and specialty or local manufacturers, definitely invite them to step in front of the camera with your host, as higher sales will benefit you both.
Models
Frequently, sales presentations include one or more models further interacting with the product. In our example, models are wearing these Irish sweaters while strolling around Ashford Castle. More romance.
Other segments feature models as subjects of various cosmetic treatments or as demonstrators of how merchandise is to be used. Models and demonstrators used to be standard in major American department stores. QVC brilliantly televised this incredible form of persuasion at about the same time it disappeared from real-world shopping in the US. Their sales figures prove just how huge the desire still is to see merchandise worn and used before buying.
For our scenario of creating online sales videos, such models could be a convincing extra in selling certain types of products, and many products should be demonstrated by the host or guest host. One thing I’ve not seen QVC do that I think e-commerce and O2O local brands definitely could do is a UGC approach of making your customer your model, demoing how they use your products in their real-world lives. Almost everybody can film themselves these days.
Callers
There are no live callers in our example, but QVC traditionally increases interactivity with the public with on-air phone calls.
If your sales videos are static, you’re not quite to the point of having to learn the art of handling live calls, but your product support phone and SMS numbers and links should be featured in every video.
Method
“If you go up there with the intent to sell, it’s all going to come crashing down around you...The real goal of QVC.... was to feel like a conversation between the host, the product specialist (us), and ‘Her’ – the woman age 35 to 65 who is sitting at home watching television.” - I went on air at QVC and sold something to America
There’s an element of magic to how QVC vends such a massive volume of products, but it’s all data-based. They’ve invested so heavily in understanding customer demographics that they’ve mastered exactly how to sell to them. Your consumer base may be totally different, but the key is to know your customer so well that you understand the exact approach to take when offering them your inventory of goods and services.
Another excerpt from the article cited above really gets this point across when talking about guest hosts:
“Our experienced guests tend to focus on the product. But our best guests are focused on the viewer. Is this for the viewer? Everything goes through that filter. And if you do that, everything comes out more naturally.”
Here at Moz, there may be Whiteboard Friday hosts you especially enjoy learning from. As a business owner or marketer, your job will be to identify talented people who can blend your brand culture with consumer research and translate that into a form of vending infotainment that succeeds with your particular shoppers. Successful QVC hosts make upwards of $500,000 a year for being so good at what they do.
Being good, in the sweater sample, means pairing QVC’s customer-centric, conversational selling method with USPs and an aura of scarcity. I’ll paraphrase the cues I heard:
“These sweaters are made exclusively for QVC” — a USP regarding rarity.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC” — this is a strong USP based on having better prices than a traveler would find if buying direct from the manufacturer.
“Reviews read like a love letter to this sweater” — incorporating persuasive UGC into the pitch.
“Half of our supply is already gone; don’t wait to order if you want one of these” —- this creates a sense of urgency to prompt customers to buy right away.
Analytics
The example presentation probably looked quite seamless and simple to you. But what’s actually going on “behind the scenes” of a QVC sales segment is that the host is receiving earpiece cues on exactly how to shape the pitch.
QVC’s analytics track what’s called a “feverline” of reaction to each word the host says and each movement they make. Producers can tell in real time which verbal signals and gestures are causing sales spikes, and communicate to the host to repeat them. One host, for example, dances repeatedly while demoing food products because more customers buy when he does so.
For most of the brands you market, you’re not likely to be called upon to deliver analytical data on par with QVC’s mission control-style setup, but you will want to learn about video analytics and do A/B testing to measure performance of product pages with video vs. those with static images. As you progress, analytics should be able to tell you which hosts, guests, and products are yielding the best ROI.
Three O2O advantages
In a large 2020 survey of local business owners and marketers, Moz found that more than half of respondents intend to maintain pandemic-era services of convenience beyond the hoped-for end of COVID-19. I’d expect this number to be even higher if we reran the survey in mid-2021. Online-to-offline shopping falls in this category and readers of my column know I’m always looking for advantages specific to local businesses.
I see three ways local brands have a leg up on their virtual e-commerce cousins, including behemoths like Amazon and even QVC:
1. Limited local competition = better SERP visibility
Virtual e-commerce brands have to compete against a whole country or the world for SERP visibility. Google Shopping’s “available nearby” filter cuts your market down to local map-size, making it easier to capture the attention of customers nearest your business. If you’re one of the only local brands supporting sales of your goods and services via videos on your website, you’re really going to stand out in the cities you serve.
2. Limited local inventory = more convincing authenticity
QVC is certainly an impressive enterprise, but one drawback of their methodology, at least in my eyes, is that their hosts have to be endlessly excited about millions of products. The same host who is exuding enthusiasm one minute over an electric toothbrush is breathless with admiration over a flameless candle the next. While QVC’s amazingly loyal customers are clearly not put off by the bottomless supply of energy over every single product sold, I find I don’t quite believe that the joy is continuously genuine. In my recognition of the sales pitch tactics, the company feels big and remote to me.
70% of Americans say they want to shop small. Your advantage in marketing a local business is that it will have limited inventory and an owner and staff who can realistically convey authenticity to the video viewer about products the business has hand-selected to sell. A big chain supermarket wants me to believe all of its apples are crisp, but my local farmer telling me in a product video that this year’s crop is crisper than last year’s makes a world of believable difference.
3. Even a small boost in conversions = a big difference for local brands
Backlinko recently compiled this list of exciting video marketing statistics that I hope you’ll read in full. I want to excerpt a few that really caught my eye:
84% of consumers cite video as the convincing factor in purchases
Product videos can help e-commerce stores increase sales by up to 144%
96% of people have watched an explainer video to better understand a product they’re evaluating
The Local Search Association found that 53% of people contact a business after watching one of their videos and 71% of people who made a purchase had watched an online video from that brand
Including filmed content on an e-commerce page can increase the average order value by 50+%
Video on a landing page can grow its conversion rate by up to 80%
If the company you’re promoting is one of the only ones in your local market to seize the opportunities hinted at by these statistics, think of what a difference it would make to see conversions (including leads and sales) rise by even a fraction of these numbers. Moreover, if the standout UX and helpfulness of the “v-commerce” environment you create makes you memorable to customers, you could grow local loyalty to new levels as the best resource in a community, generating a recipe for retention that, if not quite as astonishing as QVC’s, is pretty amazing for your region.
Go n-éirí leat — good luck!
Like you, I’m longing for the time when all customers can safely return to shopping locally in-person, but I do agree with fellow analysts predicting that the taste we’ve gotten for the convenience of shipping and local home delivery, curbside pickup, and tele-meetings is one that consumers won’t simply abandon.
Sales videos tackle one of digital marketing’s largest challenges by letting customers see people interacting with products when they can’t do it themselves, and 2021 is a good year to begin your investigation of this promising medium. My top tip is to spend some time this week watching QVC on TV and examining how they’ve parlayed live broadcasts into static
product videos that sell inventory like hotcakes on their website. I’m wishing you the luck and intrepidity of the Irish in your video ventures!
Ready to learn more about video marketing? Try these resources:
17 Best Ecommerce Product Video Examples
The ABCs of Video Content
8 Beginner Tips for Making Professional-Looking Videos
How to Film Creative Product Videos
YouTube Dominates Google Video in 2020
How to Track YouTube Videos in Google Analytics Using Google Tag Manager in 4 Steps
Need to learn more about local search marketing before you start filming yourself and your products? Read The Essential Local SEO Strategy Guide.
0 notes
Text
Are You Ready to Sell Like QVC?
A photo. Some text. A shopping cart button.
It’s the setup you’ve been used to since you were Internet-years-old.
Electronic commerce has existed since the 1970s, passing through a prescient experimental phase of telephone-based TV shopping in the 1980s, and setting the tone for the future with Stephan Schambach’s 1990s invention of the first standardized online shopping software. US consumers spent $861.12 billion with online merchants in 2020. By making the “add to cart” ritual so familiar, it may seem like we’ve seen it all when it comes to digital commerce.
But hold onto your hats, because signs are emerging that we’re on the verge of the next online sales phase, akin to the 19th century leap from still photos to moving pictures.
If I’m right, with its standard product shots, conventional e-commerce will soon start to seem dull and dated in many categories compared to products sold via interactive video and further supported with post-purchase video.
Now is the time to prep for a filmed future, and fortunately, the trail has already been blazed for us by home shopping leader QVC, which took over television and then digitally remastered itself for the web, perfecting the art of video-based sales. Today, we’re going to deconstruct what’s happening on QVC, and how and why you may need to learn to apply it as an SEO, local SEO, or business owner — sooner than you think.
Why video sales?
A series of developments and disruptions point to a future in which many product sales will be facilitated via video. Let’s have a look at them:
First, we all know that humans love video content so much, they’ve caused YouTube to be the #2 search engine.
Google has documented the growth of video searches for “which (product) should I buy”.
When we look beyond the US, we encounter the phenomenon that livestreaming e-commerce video has become in China, highly-monopolized by Alibaba’s Taobao and creating celebrities out of its hosts.
Meanwhile, within the US, the pandemic caused a 44% increase in digital shopping spend between 2019-2020. We moved online last year for both our basic needs and nonessentials like never before.
The pandemic has also caused physical local brands to implement digital shopping, blurring former online-to-offline (O2O) barriers to such a degree that Internet transactions are no longer the special property of virtual e-commerce companies. This weirdly-dubbed “phygital” phenomenon — which is making Google the nexus of Maps-based local product sales — can be seen as a boon to local brands that take advantage of the search engine’s famed user-to-business proximity bias to rank their inventory for nearby customers.
At least, Google hopes to be the nexus of all this. The truth is, Google is reacting strongly right now to consumers starting half of their product searches on Amazon instead of on Google. Are you seeing ads everywhere these days informing you that Google is the best place to shop? So am I. With that massive, lucrative local business index in their back pocket and with GMB listings long supporting video uploads, Google has recently:
Acquired Pointy to integrate with retail POS systems
Made product listings free
Amped up their nearby shopping filter
Attempted to insert themselves directly into consumers’ curbside pickup routines while integrating deeply into data partnerships with major grocery brands
Experienced massive growth in local business reviews, and just released an algorithmic update specific to product review content (look out, Amazon!)
Experimented with detecting products in YouTube videos amid rumors flying about product results appearing in YouTube
Been spotted experimenting beyond influencer cameo videos to product cameos in knowledge panels
Meanwhile, big brands everywhere are getting into video sales. Walmart leapt ahead in the shoppable video contest with their debut of Cookshop, in which celebrity chefs cook while consumers click on the interactive video cues to add ingredients to their shopping carts.
Crate & Barrel is tiptoeing into the pool with quick product romance videos that resemble perfume ads, in which models lounge about on lovely accent chairs, creating the aura of a lifestyle to be lived. Nordstrom is filming bite-sized home shopping channel-style product videos for their website and YouTube channel, complete with hosts.
And, smaller brands are experimenting with video-supported sales content, too. Check out Green Building Supply’s product videos for their eco-friendly home improvement inventory (with personable hosts). Absolute Domestics shows how SABs can use video to support sales of services rather than goods, as in this simple but nicely-produced video on what to expect from their cleaning service. Meanwhile, post-sales support videos are a persuasive value add from Purl Soho to help you master knitting techniques needed when you buy a pattern from them.
To sum up, at the deep end of the pool, live-streamed e-commerce and shoppable video are already in use by big brands, but smaller brands can wade in with basic static goods-and-services videos on their websites and social channels to support sales.
Now is the time to look for inspiration about what video sales could do for brands you market, and nobody — nobody — has more experience with all of this than QVC.
Why QVC?
“I didn’t even know QVC still existed,” more than one of my marketing colleagues has responded when I’ve pointed to the 35-year-old home shopping empire as the way of the future.
The truth is, I’d probably be sleeping on QVC, too, if it weren’t for my Irish ancestry having drawn me to their annual St. Patrick’s Day sales event for the past 30+ years to enjoy their made-in-Ireland product lineup.
About seven times more people with Irish roots live in the United States than on the actual island of Ireland, yet the shopping channel’s holiday broadcast is one of the few televised events tailored to our famous nostalgia for our old country home. My family tunes in every March for the craic of examining Aran Crafts sweaters, Nicholas Mosse pottery, Belleek china, and Solvar jewelry, while munching on cake made from my great-grandmother Cotter’s recipe. Sometimes we get so excited, we buy things, but for the past few years, I’ve mainly been actively studying how QVC sells these items with such stunning success.
“Stunning” is the word and the wakeup call
QVC, which is a subsidiary of Quarate Retail International, generated $11.47 billion in 2020 and as early as 2015, nearly half of those sales were taking place online — consistently placing the brand in the top 10 for e-commerce sales, including mobile sales. The company has 16.5 million consolidated customers worldwide, and marketers’ mouths will surely water to learn that 90% of QVC’s revenue comes from loyal repeat shoppers. The average QVC shopper makes between 22-25 purchases per year!
Figures like these, paired with QVC’s graceful pas de deux incorporating both TV remotes and mobile devices should command our attention long enough to study what they’ve done and how they’ve done it.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC!”
While supplies last, I want to invite you to spend the next 10 minutes watching this Internet rebroadcast of a televised segment selling an Aran Crafts sweater, with your marketer’s eye on the magic happening in it. Watch this while imagining how it might translate as a static product or service video for a brand you’re marketing.
TL;DW? Here’s the breakdown of how QVC sells:
Main host
QVC hosts are personalities, many of whom have devoted fan bases. They’re trained in the products they sell, often visiting manufacturing plants to school themselves. When on air, the host juggles promoting a product and interacting with models, guest hosts, callers, and off-screen analysts. The host physically interacts with the product, highlights its features in abundant detail, and makes their sales pitch.
For our purposes, digital marketers are fully aware of the phenomenon of social influencers taking on celebrity status and being sought after as sales reps. At a more modest scale, small e-commerce companies (or any local business) that’s adopted digital sales models should identify one or more staff members with the necessary talents to become a video host for the brand.
You’ll need a spot of luck to secure relatable hosts. Just keep in mind that QVC’s secret formula is to get the viewer to ask, “Is this me?”, and that should help you match a host to your audience. This example of a nicely-done, low-key, densely-detailed presentation of a camping chair by a plainspoken host shows how simple and effective a short product video can be.
Guest hosts
Many QVC segments feature a representative from the brand associated with the product being sold. In our example, the guest host from Aran Crafts is a member of her family’s business, signing in remotely (due to the pandemic) to share the company’s story and build romance around the product.
Depending on the model you’re marketing, having a rep from any brand you resell would be an extra trust signal to convey via video sales. Think of the back-and-forth chat in a podcast and you’re almost there. Small retailers just reselling big brands may face a challenge here, but if you have a good portion of inventory from smaller companies and specialty or local manufacturers, definitely invite them to step in front of the camera with your host, as higher sales will benefit you both.
Models
Frequently, sales presentations include one or more models further interacting with the product. In our example, models are wearing these Irish sweaters while strolling around Ashford Castle. More romance.
Other segments feature models as subjects of various cosmetic treatments or as demonstrators of how merchandise is to be used. Models and demonstrators used to be standard in major American department stores. QVC brilliantly televised this incredible form of persuasion at about the same time it disappeared from real-world shopping in the US. Their sales figures prove just how huge the desire still is to see merchandise worn and used before buying.
For our scenario of creating online sales videos, such models could be a convincing extra in selling certain types of products, and many products should be demonstrated by the host or guest host. One thing I’ve not seen QVC do that I think e-commerce and O2O local brands definitely could do is a UGC approach of making your customer your model, demoing how they use your products in their real-world lives. Almost everybody can film themselves these days.
Callers
There are no live callers in our example, but QVC traditionally increases interactivity with the public with on-air phone calls.
If your sales videos are static, you’re not quite to the point of having to learn the art of handling live calls, but your product support phone and SMS numbers and links should be featured in every video.
Method
“If you go up there with the intent to sell, it’s all going to come crashing down around you...The real goal of QVC.... was to feel like a conversation between the host, the product specialist (us), and ‘Her’ – the woman age 35 to 65 who is sitting at home watching television.” - I went on air at QVC and sold something to America
There’s an element of magic to how QVC vends such a massive volume of products, but it’s all data-based. They’ve invested so heavily in understanding customer demographics that they’ve mastered exactly how to sell to them. Your consumer base may be totally different, but the key is to know your customer so well that you understand the exact approach to take when offering them your inventory of goods and services.
Another excerpt from the article cited above really gets this point across when talking about guest hosts:
“Our experienced guests tend to focus on the product. But our best guests are focused on the viewer. Is this for the viewer? Everything goes through that filter. And if you do that, everything comes out more naturally.”
Here at Moz, there may be Whiteboard Friday hosts you especially enjoy learning from. As a business owner or marketer, your job will be to identify talented people who can blend your brand culture with consumer research and translate that into a form of vending infotainment that succeeds with your particular shoppers. Successful QVC hosts make upwards of $500,000 a year for being so good at what they do.
Being good, in the sweater sample, means pairing QVC’s customer-centric, conversational selling method with USPs and an aura of scarcity. I’ll paraphrase the cues I heard:
“These sweaters are made exclusively for QVC” — a USP regarding rarity.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC” — this is a strong USP based on having better prices than a traveler would find if buying direct from the manufacturer.
“Reviews read like a love letter to this sweater” — incorporating persuasive UGC into the pitch.
“Half of our supply is already gone; don’t wait to order if you want one of these” —- this creates a sense of urgency to prompt customers to buy right away.
Analytics
The example presentation probably looked quite seamless and simple to you. But what’s actually going on “behind the scenes” of a QVC sales segment is that the host is receiving earpiece cues on exactly how to shape the pitch.
QVC’s analytics track what’s called a “feverline” of reaction to each word the host says and each movement they make. Producers can tell in real time which verbal signals and gestures are causing sales spikes, and communicate to the host to repeat them. One host, for example, dances repeatedly while demoing food products because more customers buy when he does so.
For most of the brands you market, you’re not likely to be called upon to deliver analytical data on par with QVC’s mission control-style setup, but you will want to learn about video analytics and do A/B testing to measure performance of product pages with video vs. those with static images. As you progress, analytics should be able to tell you which hosts, guests, and products are yielding the best ROI.
Three O2O advantages
In a large 2020 survey of local business owners and marketers, Moz found that more than half of respondents intend to maintain pandemic-era services of convenience beyond the hoped-for end of COVID-19. I’d expect this number to be even higher if we reran the survey in mid-2021. Online-to-offline shopping falls in this category and readers of my column know I’m always looking for advantages specific to local businesses.
I see three ways local brands have a leg up on their virtual e-commerce cousins, including behemoths like Amazon and even QVC:
1. Limited local competition = better SERP visibility
Virtual e-commerce brands have to compete against a whole country or the world for SERP visibility. Google Shopping’s “available nearby” filter cuts your market down to local map-size, making it easier to capture the attention of customers nearest your business. If you’re one of the only local brands supporting sales of your goods and services via videos on your website, you’re really going to stand out in the cities you serve.
2. Limited local inventory = more convincing authenticity
QVC is certainly an impressive enterprise, but one drawback of their methodology, at least in my eyes, is that their hosts have to be endlessly excited about millions of products. The same host who is exuding enthusiasm one minute over an electric toothbrush is breathless with admiration over a flameless candle the next. While QVC’s amazingly loyal customers are clearly not put off by the bottomless supply of energy over every single product sold, I find I don’t quite believe that the joy is continuously genuine. In my recognition of the sales pitch tactics, the company feels big and remote to me.
70% of Americans say they want to shop small. Your advantage in marketing a local business is that it will have limited inventory and an owner and staff who can realistically convey authenticity to the video viewer about products the business has hand-selected to sell. A big chain supermarket wants me to believe all of its apples are crisp, but my local farmer telling me in a product video that this year’s crop is crisper than last year’s makes a world of believable difference.
3. Even a small boost in conversions = a big difference for local brands
Backlinko recently compiled this list of exciting video marketing statistics that I hope you’ll read in full. I want to excerpt a few that really caught my eye:
84% of consumers cite video as the convincing factor in purchases
Product videos can help e-commerce stores increase sales by up to 144%
96% of people have watched an explainer video to better understand a product they’re evaluating
The Local Search Association found that 53% of people contact a business after watching one of their videos and 71% of people who made a purchase had watched an online video from that brand
Including filmed content on an e-commerce page can increase the average order value by 50+%
Video on a landing page can grow its conversion rate by up to 80%
If the company you’re promoting is one of the only ones in your local market to seize the opportunities hinted at by these statistics, think of what a difference it would make to see conversions (including leads and sales) rise by even a fraction of these numbers. Moreover, if the standout UX and helpfulness of the “v-commerce” environment you create makes you memorable to customers, you could grow local loyalty to new levels as the best resource in a community, generating a recipe for retention that, if not quite as astonishing as QVC’s, is pretty amazing for your region.
Go n-éirí leat — good luck!
Like you, I’m longing for the time when all customers can safely return to shopping locally in-person, but I do agree with fellow analysts predicting that the taste we’ve gotten for the convenience of shipping and local home delivery, curbside pickup, and tele-meetings is one that consumers won’t simply abandon.
Sales videos tackle one of digital marketing’s largest challenges by letting customers see people interacting with products when they can’t do it themselves, and 2021 is a good year to begin your investigation of this promising medium. My top tip is to spend some time this week watching QVC on TV and examining how they’ve parlayed live broadcasts into static
product videos that sell inventory like hotcakes on their website. I’m wishing you the luck and intrepidity of the Irish in your video ventures!
Ready to learn more about video marketing? Try these resources:
17 Best Ecommerce Product Video Examples
The ABCs of Video Content
8 Beginner Tips for Making Professional-Looking Videos
How to Film Creative Product Videos
YouTube Dominates Google Video in 2020
How to Track YouTube Videos in Google Analytics Using Google Tag Manager in 4 Steps
Need to learn more about local search marketing before you start filming yourself and your products? Read The Essential Local SEO Strategy Guide.
0 notes
Text
Are You Ready to Sell Like QVC?
A photo. Some text. A shopping cart button.
It’s the setup you’ve been used to since you were Internet-years-old.
Electronic commerce has existed since the 1970s, passing through a prescient experimental phase of telephone-based TV shopping in the 1980s, and setting the tone for the future with Stephan Schambach’s 1990s invention of the first standardized online shopping software. US consumers spent $861.12 billion with online merchants in 2020. By making the “add to cart” ritual so familiar, it may seem like we’ve seen it all when it comes to digital commerce.
But hold onto your hats, because signs are emerging that we’re on the verge of the next online sales phase, akin to the 19th century leap from still photos to moving pictures.
If I’m right, with its standard product shots, conventional e-commerce will soon start to seem dull and dated in many categories compared to products sold via interactive video and further supported with post-purchase video.
Now is the time to prep for a filmed future, and fortunately, the trail has already been blazed for us by home shopping leader QVC, which took over television and then digitally remastered itself for the web, perfecting the art of video-based sales. Today, we’re going to deconstruct what’s happening on QVC, and how and why you may need to learn to apply it as an SEO, local SEO, or business owner — sooner than you think.
Why video sales?
A series of developments and disruptions point to a future in which many product sales will be facilitated via video. Let’s have a look at them:
First, we all know that humans love video content so much, they’ve caused YouTube to be the #2 search engine.
Google has documented the growth of video searches for “which (product) should I buy”.
When we look beyond the US, we encounter the phenomenon that livestreaming e-commerce video has become in China, highly-monopolized by Alibaba’s Taobao and creating celebrities out of its hosts.
Meanwhile, within the US, the pandemic caused a 44% increase in digital shopping spend between 2019-2020. We moved online last year for both our basic needs and nonessentials like never before.
The pandemic has also caused physical local brands to implement digital shopping, blurring former online-to-offline (O2O) barriers to such a degree that Internet transactions are no longer the special property of virtual e-commerce companies. This weirdly-dubbed “phygital” phenomenon — which is making Google the nexus of Maps-based local product sales — can be seen as a boon to local brands that take advantage of the search engine’s famed user-to-business proximity bias to rank their inventory for nearby customers.
At least, Google hopes to be the nexus of all this. The truth is, Google is reacting strongly right now to consumers starting half of their product searches on Amazon instead of on Google. Are you seeing ads everywhere these days informing you that Google is the best place to shop? So am I. With that massive, lucrative local business index in their back pocket and with GMB listings long supporting video uploads, Google has recently:
Acquired Pointy to integrate with retail POS systems
Made product listings free
Amped up their nearby shopping filter
Attempted to insert themselves directly into consumers’ curbside pickup routines while integrating deeply into data partnerships with major grocery brands
Experienced massive growth in local business reviews, and just released an algorithmic update specific to product review content (look out, Amazon!)
Experimented with detecting products in YouTube videos amid rumors flying about product results appearing in YouTube
Been spotted experimenting beyond influencer cameo videos to product cameos in knowledge panels
Meanwhile, big brands everywhere are getting into video sales. Walmart leapt ahead in the shoppable video contest with their debut of Cookshop, in which celebrity chefs cook while consumers click on the interactive video cues to add ingredients to their shopping carts.
Crate & Barrel is tiptoeing into the pool with quick product romance videos that resemble perfume ads, in which models lounge about on lovely accent chairs, creating the aura of a lifestyle to be lived. Nordstrom is filming bite-sized home shopping channel-style product videos for their website and YouTube channel, complete with hosts.
And, smaller brands are experimenting with video-supported sales content, too. Check out Green Building Supply’s product videos for their eco-friendly home improvement inventory (with personable hosts). Absolute Domestics shows how SABs can use video to support sales of services rather than goods, as in this simple but nicely-produced video on what to expect from their cleaning service. Meanwhile, post-sales support videos are a persuasive value add from Purl Soho to help you master knitting techniques needed when you buy a pattern from them.
To sum up, at the deep end of the pool, live-streamed e-commerce and shoppable video are already in use by big brands, but smaller brands can wade in with basic static goods-and-services videos on their websites and social channels to support sales.
Now is the time to look for inspiration about what video sales could do for brands you market, and nobody — nobody — has more experience with all of this than QVC.
Why QVC?
“I didn’t even know QVC still existed,” more than one of my marketing colleagues has responded when I’ve pointed to the 35-year-old home shopping empire as the way of the future.
The truth is, I’d probably be sleeping on QVC, too, if it weren’t for my Irish ancestry having drawn me to their annual St. Patrick’s Day sales event for the past 30+ years to enjoy their made-in-Ireland product lineup.
About seven times more people with Irish roots live in the United States than on the actual island of Ireland, yet the shopping channel’s holiday broadcast is one of the few televised events tailored to our famous nostalgia for our old country home. My family tunes in every March for the craic of examining Aran Crafts sweaters, Nicholas Mosse pottery, Belleek china, and Solvar jewelry, while munching on cake made from my great-grandmother Cotter’s recipe. Sometimes we get so excited, we buy things, but for the past few years, I’ve mainly been actively studying how QVC sells these items with such stunning success.
“Stunning” is the word and the wakeup call
QVC, which is a subsidiary of Quarate Retail International, generated $11.47 billion in 2020 and as early as 2015, nearly half of those sales were taking place online — consistently placing the brand in the top 10 for e-commerce sales, including mobile sales. The company has 16.5 million consolidated customers worldwide, and marketers’ mouths will surely water to learn that 90% of QVC’s revenue comes from loyal repeat shoppers. The average QVC shopper makes between 22-25 purchases per year!
Figures like these, paired with QVC’s graceful pas de deux incorporating both TV remotes and mobile devices should command our attention long enough to study what they’ve done and how they’ve done it.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC!”
While supplies last, I want to invite you to spend the next 10 minutes watching this Internet rebroadcast of a televised segment selling an Aran Crafts sweater, with your marketer’s eye on the magic happening in it. Watch this while imagining how it might translate as a static product or service video for a brand you’re marketing.
TL;DW? Here’s the breakdown of how QVC sells:
Main host
QVC hosts are personalities, many of whom have devoted fan bases. They’re trained in the products they sell, often visiting manufacturing plants to school themselves. When on air, the host juggles promoting a product and interacting with models, guest hosts, callers, and off-screen analysts. The host physically interacts with the product, highlights its features in abundant detail, and makes their sales pitch.
For our purposes, digital marketers are fully aware of the phenomenon of social influencers taking on celebrity status and being sought after as sales reps. At a more modest scale, small e-commerce companies (or any local business) that’s adopted digital sales models should identify one or more staff members with the necessary talents to become a video host for the brand.
You’ll need a spot of luck to secure relatable hosts. Just keep in mind that QVC’s secret formula is to get the viewer to ask, “Is this me?”, and that should help you match a host to your audience. This example of a nicely-done, low-key, densely-detailed presentation of a camping chair by a plainspoken host shows how simple and effective a short product video can be.
Guest hosts
Many QVC segments feature a representative from the brand associated with the product being sold. In our example, the guest host from Aran Crafts is a member of her family’s business, signing in remotely (due to the pandemic) to share the company’s story and build romance around the product.
Depending on the model you’re marketing, having a rep from any brand you resell would be an extra trust signal to convey via video sales. Think of the back-and-forth chat in a podcast and you’re almost there. Small retailers just reselling big brands may face a challenge here, but if you have a good portion of inventory from smaller companies and specialty or local manufacturers, definitely invite them to step in front of the camera with your host, as higher sales will benefit you both.
Models
Frequently, sales presentations include one or more models further interacting with the product. In our example, models are wearing these Irish sweaters while strolling around Ashford Castle. More romance.
Other segments feature models as subjects of various cosmetic treatments or as demonstrators of how merchandise is to be used. Models and demonstrators used to be standard in major American department stores. QVC brilliantly televised this incredible form of persuasion at about the same time it disappeared from real-world shopping in the US. Their sales figures prove just how huge the desire still is to see merchandise worn and used before buying.
For our scenario of creating online sales videos, such models could be a convincing extra in selling certain types of products, and many products should be demonstrated by the host or guest host. One thing I’ve not seen QVC do that I think e-commerce and O2O local brands definitely could do is a UGC approach of making your customer your model, demoing how they use your products in their real-world lives. Almost everybody can film themselves these days.
Callers
There are no live callers in our example, but QVC traditionally increases interactivity with the public with on-air phone calls.
If your sales videos are static, you’re not quite to the point of having to learn the art of handling live calls, but your product support phone and SMS numbers and links should be featured in every video.
Method
“If you go up there with the intent to sell, it’s all going to come crashing down around you...The real goal of QVC.... was to feel like a conversation between the host, the product specialist (us), and ‘Her’ – the woman age 35 to 65 who is sitting at home watching television.” - I went on air at QVC and sold something to America
There’s an element of magic to how QVC vends such a massive volume of products, but it’s all data-based. They’ve invested so heavily in understanding customer demographics that they’ve mastered exactly how to sell to them. Your consumer base may be totally different, but the key is to know your customer so well that you understand the exact approach to take when offering them your inventory of goods and services.
Another excerpt from the article cited above really gets this point across when talking about guest hosts:
“Our experienced guests tend to focus on the product. But our best guests are focused on the viewer. Is this for the viewer? Everything goes through that filter. And if you do that, everything comes out more naturally.”
Here at Moz, there may be Whiteboard Friday hosts you especially enjoy learning from. As a business owner or marketer, your job will be to identify talented people who can blend your brand culture with consumer research and translate that into a form of vending infotainment that succeeds with your particular shoppers. Successful QVC hosts make upwards of $500,000 a year for being so good at what they do.
Being good, in the sweater sample, means pairing QVC’s customer-centric, conversational selling method with USPs and an aura of scarcity. I’ll paraphrase the cues I heard:
“These sweaters are made exclusively for QVC” — a USP regarding rarity.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC” — this is a strong USP based on having better prices than a traveler would find if buying direct from the manufacturer.
“Reviews read like a love letter to this sweater” — incorporating persuasive UGC into the pitch.
“Half of our supply is already gone; don’t wait to order if you want one of these” —- this creates a sense of urgency to prompt customers to buy right away.
Analytics
The example presentation probably looked quite seamless and simple to you. But what’s actually going on “behind the scenes” of a QVC sales segment is that the host is receiving earpiece cues on exactly how to shape the pitch.
QVC’s analytics track what’s called a “feverline” of reaction to each word the host says and each movement they make. Producers can tell in real time which verbal signals and gestures are causing sales spikes, and communicate to the host to repeat them. One host, for example, dances repeatedly while demoing food products because more customers buy when he does so.
For most of the brands you market, you’re not likely to be called upon to deliver analytical data on par with QVC’s mission control-style setup, but you will want to learn about video analytics and do A/B testing to measure performance of product pages with video vs. those with static images. As you progress, analytics should be able to tell you which hosts, guests, and products are yielding the best ROI.
Three O2O advantages
In a large 2020 survey of local business owners and marketers, Moz found that more than half of respondents intend to maintain pandemic-era services of convenience beyond the hoped-for end of COVID-19. I’d expect this number to be even higher if we reran the survey in mid-2021. Online-to-offline shopping falls in this category and readers of my column know I’m always looking for advantages specific to local businesses.
I see three ways local brands have a leg up on their virtual e-commerce cousins, including behemoths like Amazon and even QVC:
1. Limited local competition = better SERP visibility
Virtual e-commerce brands have to compete against a whole country or the world for SERP visibility. Google Shopping’s “available nearby” filter cuts your market down to local map-size, making it easier to capture the attention of customers nearest your business. If you’re one of the only local brands supporting sales of your goods and services via videos on your website, you’re really going to stand out in the cities you serve.
2. Limited local inventory = more convincing authenticity
QVC is certainly an impressive enterprise, but one drawback of their methodology, at least in my eyes, is that their hosts have to be endlessly excited about millions of products. The same host who is exuding enthusiasm one minute over an electric toothbrush is breathless with admiration over a flameless candle the next. While QVC’s amazingly loyal customers are clearly not put off by the bottomless supply of energy over every single product sold, I find I don’t quite believe that the joy is continuously genuine. In my recognition of the sales pitch tactics, the company feels big and remote to me.
70% of Americans say they want to shop small. Your advantage in marketing a local business is that it will have limited inventory and an owner and staff who can realistically convey authenticity to the video viewer about products the business has hand-selected to sell. A big chain supermarket wants me to believe all of its apples are crisp, but my local farmer telling me in a product video that this year’s crop is crisper than last year’s makes a world of believable difference.
3. Even a small boost in conversions = a big difference for local brands
Backlinko recently compiled this list of exciting video marketing statistics that I hope you’ll read in full. I want to excerpt a few that really caught my eye:
84% of consumers cite video as the convincing factor in purchases
Product videos can help e-commerce stores increase sales by up to 144%
96% of people have watched an explainer video to better understand a product they’re evaluating
The Local Search Association found that 53% of people contact a business after watching one of their videos and 71% of people who made a purchase had watched an online video from that brand
Including filmed content on an e-commerce page can increase the average order value by 50+%
Video on a landing page can grow its conversion rate by up to 80%
If the company you’re promoting is one of the only ones in your local market to seize the opportunities hinted at by these statistics, think of what a difference it would make to see conversions (including leads and sales) rise by even a fraction of these numbers. Moreover, if the standout UX and helpfulness of the “v-commerce” environment you create makes you memorable to customers, you could grow local loyalty to new levels as the best resource in a community, generating a recipe for retention that, if not quite as astonishing as QVC’s, is pretty amazing for your region.
Go n-éirí leat — good luck!
Like you, I’m longing for the time when all customers can safely return to shopping locally in-person, but I do agree with fellow analysts predicting that the taste we’ve gotten for the convenience of shipping and local home delivery, curbside pickup, and tele-meetings is one that consumers won’t simply abandon.
Sales videos tackle one of digital marketing’s largest challenges by letting customers see people interacting with products when they can’t do it themselves, and 2021 is a good year to begin your investigation of this promising medium. My top tip is to spend some time this week watching QVC on TV and examining how they’ve parlayed live broadcasts into static
product videos that sell inventory like hotcakes on their website. I’m wishing you the luck and intrepidity of the Irish in your video ventures!
Ready to learn more about video marketing? Try these resources:
17 Best Ecommerce Product Video Examples
The ABCs of Video Content
8 Beginner Tips for Making Professional-Looking Videos
How to Film Creative Product Videos
YouTube Dominates Google Video in 2020
How to Track YouTube Videos in Google Analytics Using Google Tag Manager in 4 Steps
Need to learn more about local search marketing before you start filming yourself and your products? Read The Essential Local SEO Strategy Guide.
0 notes
Text
Are You Ready to Sell Like QVC?
A photo. Some text. A shopping cart button.
It’s the setup you’ve been used to since you were Internet-years-old.
Electronic commerce has existed since the 1970s, passing through a prescient experimental phase of telephone-based TV shopping in the 1980s, and setting the tone for the future with Stephan Schambach’s 1990s invention of the first standardized online shopping software. US consumers spent $861.12 billion with online merchants in 2020. By making the “add to cart” ritual so familiar, it may seem like we’ve seen it all when it comes to digital commerce.
But hold onto your hats, because signs are emerging that we’re on the verge of the next online sales phase, akin to the 19th century leap from still photos to moving pictures.
If I’m right, with its standard product shots, conventional e-commerce will soon start to seem dull and dated in many categories compared to products sold via interactive video and further supported with post-purchase video.
Now is the time to prep for a filmed future, and fortunately, the trail has already been blazed for us by home shopping leader QVC, which took over television and then digitally remastered itself for the web, perfecting the art of video-based sales. Today, we’re going to deconstruct what’s happening on QVC, and how and why you may need to learn to apply it as an SEO, local SEO, or business owner — sooner than you think.
Why video sales?
A series of developments and disruptions point to a future in which many product sales will be facilitated via video. Let’s have a look at them:
First, we all know that humans love video content so much, they’ve caused YouTube to be the #2 search engine.
Google has documented the growth of video searches for “which (product) should I buy”.
When we look beyond the US, we encounter the phenomenon that livestreaming e-commerce video has become in China, highly-monopolized by Alibaba’s Taobao and creating celebrities out of its hosts.
Meanwhile, within the US, the pandemic caused a 44% increase in digital shopping spend between 2019-2020. We moved online last year for both our basic needs and nonessentials like never before.
The pandemic has also caused physical local brands to implement digital shopping, blurring former online-to-offline (O2O) barriers to such a degree that Internet transactions are no longer the special property of virtual e-commerce companies. This weirdly-dubbed “phygital” phenomenon — which is making Google the nexus of Maps-based local product sales — can be seen as a boon to local brands that take advantage of the search engine’s famed user-to-business proximity bias to rank their inventory for nearby customers.
At least, Google hopes to be the nexus of all this. The truth is, Google is reacting strongly right now to consumers starting half of their product searches on Amazon instead of on Google. Are you seeing ads everywhere these days informing you that Google is the best place to shop? So am I. With that massive, lucrative local business index in their back pocket and with GMB listings long supporting video uploads, Google has recently:
Acquired Pointy to integrate with retail POS systems
Made product listings free
Amped up their nearby shopping filter
Attempted to insert themselves directly into consumers’ curbside pickup routines while integrating deeply into data partnerships with major grocery brands
Experienced massive growth in local business reviews, and just released an algorithmic update specific to product review content (look out, Amazon!)
Experimented with detecting products in YouTube videos amid rumors flying about product results appearing in YouTube
Been spotted experimenting beyond influencer cameo videos to product cameos in knowledge panels
Meanwhile, big brands everywhere are getting into video sales. Walmart leapt ahead in the shoppable video contest with their debut of Cookshop, in which celebrity chefs cook while consumers click on the interactive video cues to add ingredients to their shopping carts.
Crate & Barrel is tiptoeing into the pool with quick product romance videos that resemble perfume ads, in which models lounge about on lovely accent chairs, creating the aura of a lifestyle to be lived. Nordstrom is filming bite-sized home shopping channel-style product videos for their website and YouTube channel, complete with hosts.
And, smaller brands are experimenting with video-supported sales content, too. Check out Green Building Supply’s product videos for their eco-friendly home improvement inventory (with personable hosts). Absolute Domestics shows how SABs can use video to support sales of services rather than goods, as in this simple but nicely-produced video on what to expect from their cleaning service. Meanwhile, post-sales support videos are a persuasive value add from Purl Soho to help you master knitting techniques needed when you buy a pattern from them.
To sum up, at the deep end of the pool, live-streamed e-commerce and shoppable video are already in use by big brands, but smaller brands can wade in with basic static goods-and-services videos on their websites and social channels to support sales.
Now is the time to look for inspiration about what video sales could do for brands you market, and nobody — nobody — has more experience with all of this than QVC.
Why QVC?
“I didn’t even know QVC still existed,” more than one of my marketing colleagues has responded when I’ve pointed to the 35-year-old home shopping empire as the way of the future.
The truth is, I’d probably be sleeping on QVC, too, if it weren’t for my Irish ancestry having drawn me to their annual St. Patrick’s Day sales event for the past 30+ years to enjoy their made-in-Ireland product lineup.
About seven times more people with Irish roots live in the United States than on the actual island of Ireland, yet the shopping channel’s holiday broadcast is one of the few televised events tailored to our famous nostalgia for our old country home. My family tunes in every March for the craic of examining Aran Crafts sweaters, Nicholas Mosse pottery, Belleek china, and Solvar jewelry, while munching on cake made from my great-grandmother Cotter’s recipe. Sometimes we get so excited, we buy things, but for the past few years, I’ve mainly been actively studying how QVC sells these items with such stunning success.
“Stunning” is the word and the wakeup call
QVC, which is a subsidiary of Quarate Retail International, generated $11.47 billion in 2020 and as early as 2015, nearly half of those sales were taking place online — consistently placing the brand in the top 10 for e-commerce sales, including mobile sales. The company has 16.5 million consolidated customers worldwide, and marketers’ mouths will surely water to learn that 90% of QVC’s revenue comes from loyal repeat shoppers. The average QVC shopper makes between 22-25 purchases per year!
Figures like these, paired with QVC’s graceful pas de deux incorporating both TV remotes and mobile devices should command our attention long enough to study what they’ve done and how they’ve done it.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC!”
While supplies last, I want to invite you to spend the next 10 minutes watching this Internet rebroadcast of a televised segment selling an Aran Crafts sweater, with your marketer’s eye on the magic happening in it. Watch this while imagining how it might translate as a static product or service video for a brand you’re marketing.
TL;DW? Here’s the breakdown of how QVC sells:
Main host
QVC hosts are personalities, many of whom have devoted fan bases. They’re trained in the products they sell, often visiting manufacturing plants to school themselves. When on air, the host juggles promoting a product and interacting with models, guest hosts, callers, and off-screen analysts. The host physically interacts with the product, highlights its features in abundant detail, and makes their sales pitch.
For our purposes, digital marketers are fully aware of the phenomenon of social influencers taking on celebrity status and being sought after as sales reps. At a more modest scale, small e-commerce companies (or any local business) that’s adopted digital sales models should identify one or more staff members with the necessary talents to become a video host for the brand.
You’ll need a spot of luck to secure relatable hosts. Just keep in mind that QVC’s secret formula is to get the viewer to ask, “Is this me?”, and that should help you match a host to your audience. This example of a nicely-done, low-key, densely-detailed presentation of a camping chair by a plainspoken host shows how simple and effective a short product video can be.
Guest hosts
Many QVC segments feature a representative from the brand associated with the product being sold. In our example, the guest host from Aran Crafts is a member of her family’s business, signing in remotely (due to the pandemic) to share the company’s story and build romance around the product.
Depending on the model you’re marketing, having a rep from any brand you resell would be an extra trust signal to convey via video sales. Think of the back-and-forth chat in a podcast and you’re almost there. Small retailers just reselling big brands may face a challenge here, but if you have a good portion of inventory from smaller companies and specialty or local manufacturers, definitely invite them to step in front of the camera with your host, as higher sales will benefit you both.
Models
Frequently, sales presentations include one or more models further interacting with the product. In our example, models are wearing these Irish sweaters while strolling around Ashford Castle. More romance.
Other segments feature models as subjects of various cosmetic treatments or as demonstrators of how merchandise is to be used. Models and demonstrators used to be standard in major American department stores. QVC brilliantly televised this incredible form of persuasion at about the same time it disappeared from real-world shopping in the US. Their sales figures prove just how huge the desire still is to see merchandise worn and used before buying.
For our scenario of creating online sales videos, such models could be a convincing extra in selling certain types of products, and many products should be demonstrated by the host or guest host. One thing I’ve not seen QVC do that I think e-commerce and O2O local brands definitely could do is a UGC approach of making your customer your model, demoing how they use your products in their real-world lives. Almost everybody can film themselves these days.
Callers
There are no live callers in our example, but QVC traditionally increases interactivity with the public with on-air phone calls.
If your sales videos are static, you’re not quite to the point of having to learn the art of handling live calls, but your product support phone and SMS numbers and links should be featured in every video.
Method
“If you go up there with the intent to sell, it’s all going to come crashing down around you...The real goal of QVC.... was to feel like a conversation between the host, the product specialist (us), and ‘Her’ – the woman age 35 to 65 who is sitting at home watching television.” - I went on air at QVC and sold something to America
There’s an element of magic to how QVC vends such a massive volume of products, but it’s all data-based. They’ve invested so heavily in understanding customer demographics that they’ve mastered exactly how to sell to them. Your consumer base may be totally different, but the key is to know your customer so well that you understand the exact approach to take when offering them your inventory of goods and services.
Another excerpt from the article cited above really gets this point across when talking about guest hosts:
“Our experienced guests tend to focus on the product. But our best guests are focused on the viewer. Is this for the viewer? Everything goes through that filter. And if you do that, everything comes out more naturally.”
Here at Moz, there may be Whiteboard Friday hosts you especially enjoy learning from. As a business owner or marketer, your job will be to identify talented people who can blend your brand culture with consumer research and translate that into a form of vending infotainment that succeeds with your particular shoppers. Successful QVC hosts make upwards of $500,000 a year for being so good at what they do.
Being good, in the sweater sample, means pairing QVC’s customer-centric, conversational selling method with USPs and an aura of scarcity. I’ll paraphrase the cues I heard:
“These sweaters are made exclusively for QVC” — a USP regarding rarity.
“Enjoy visiting Ireland, but buy your sweaters on QVC” — this is a strong USP based on having better prices than a traveler would find if buying direct from the manufacturer.
“Reviews read like a love letter to this sweater” — incorporating persuasive UGC into the pitch.
“Half of our supply is already gone; don’t wait to order if you want one of these” —- this creates a sense of urgency to prompt customers to buy right away.
Analytics
The example presentation probably looked quite seamless and simple to you. But what’s actually going on “behind the scenes” of a QVC sales segment is that the host is receiving earpiece cues on exactly how to shape the pitch.
QVC’s analytics track what’s called a “feverline” of reaction to each word the host says and each movement they make. Producers can tell in real time which verbal signals and gestures are causing sales spikes, and communicate to the host to repeat them. One host, for example, dances repeatedly while demoing food products because more customers buy when he does so.
For most of the brands you market, you’re not likely to be called upon to deliver analytical data on par with QVC’s mission control-style setup, but you will want to learn about video analytics and do A/B testing to measure performance of product pages with video vs. those with static images. As you progress, analytics should be able to tell you which hosts, guests, and products are yielding the best ROI.
Three O2O advantages
In a large 2020 survey of local business owners and marketers, Moz found that more than half of respondents intend to maintain pandemic-era services of convenience beyond the hoped-for end of COVID-19. I’d expect this number to be even higher if we reran the survey in mid-2021. Online-to-offline shopping falls in this category and readers of my column know I’m always looking for advantages specific to local businesses.
I see three ways local brands have a leg up on their virtual e-commerce cousins, including behemoths like Amazon and even QVC:
1. Limited local competition = better SERP visibility
Virtual e-commerce brands have to compete against a whole country or the world for SERP visibility. Google Shopping’s “available nearby” filter cuts your market down to local map-size, making it easier to capture the attention of customers nearest your business. If you’re one of the only local brands supporting sales of your goods and services via videos on your website, you’re really going to stand out in the cities you serve.
2. Limited local inventory = more convincing authenticity
QVC is certainly an impressive enterprise, but one drawback of their methodology, at least in my eyes, is that their hosts have to be endlessly excited about millions of products. The same host who is exuding enthusiasm one minute over an electric toothbrush is breathless with admiration over a flameless candle the next. While QVC’s amazingly loyal customers are clearly not put off by the bottomless supply of energy over every single product sold, I find I don’t quite believe that the joy is continuously genuine. In my recognition of the sales pitch tactics, the company feels big and remote to me.
70% of Americans say they want to shop small. Your advantage in marketing a local business is that it will have limited inventory and an owner and staff who can realistically convey authenticity to the video viewer about products the business has hand-selected to sell. A big chain supermarket wants me to believe all of its apples are crisp, but my local farmer telling me in a product video that this year’s crop is crisper than last year’s makes a world of believable difference.
3. Even a small boost in conversions = a big difference for local brands
Backlinko recently compiled this list of exciting video marketing statistics that I hope you’ll read in full. I want to excerpt a few that really caught my eye:
84% of consumers cite video as the convincing factor in purchases
Product videos can help e-commerce stores increase sales by up to 144%
96% of people have watched an explainer video to better understand a product they’re evaluating
The Local Search Association found that 53% of people contact a business after watching one of their videos and 71% of people who made a purchase had watched an online video from that brand
Including filmed content on an e-commerce page can increase the average order value by 50+%
Video on a landing page can grow its conversion rate by up to 80%
If the company you’re promoting is one of the only ones in your local market to seize the opportunities hinted at by these statistics, think of what a difference it would make to see conversions (including leads and sales) rise by even a fraction of these numbers. Moreover, if the standout UX and helpfulness of the “v-commerce” environment you create makes you memorable to customers, you could grow local loyalty to new levels as the best resource in a community, generating a recipe for retention that, if not quite as astonishing as QVC’s, is pretty amazing for your region.
Go n-éirí leat — good luck!
Like you, I’m longing for the time when all customers can safely return to shopping locally in-person, but I do agree with fellow analysts predicting that the taste we’ve gotten for the convenience of shipping and local home delivery, curbside pickup, and tele-meetings is one that consumers won’t simply abandon.
Sales videos tackle one of digital marketing’s largest challenges by letting customers see people interacting with products when they can’t do it themselves, and 2021 is a good year to begin your investigation of this promising medium. My top tip is to spend some time this week watching QVC on TV and examining how they’ve parlayed live broadcasts into static
product videos that sell inventory like hotcakes on their website. I’m wishing you the luck and intrepidity of the Irish in your video ventures!
Ready to learn more about video marketing? Try these resources:
17 Best Ecommerce Product Video Examples
The ABCs of Video Content
8 Beginner Tips for Making Professional-Looking Videos
How to Film Creative Product Videos
YouTube Dominates Google Video in 2020
How to Track YouTube Videos in Google Analytics Using Google Tag Manager in 4 Steps
Need to learn more about local search marketing before you start filming yourself and your products? Read The Essential Local SEO Strategy Guide.
https://ift.tt/33NkmUm
0 notes