#anne of bavaria
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
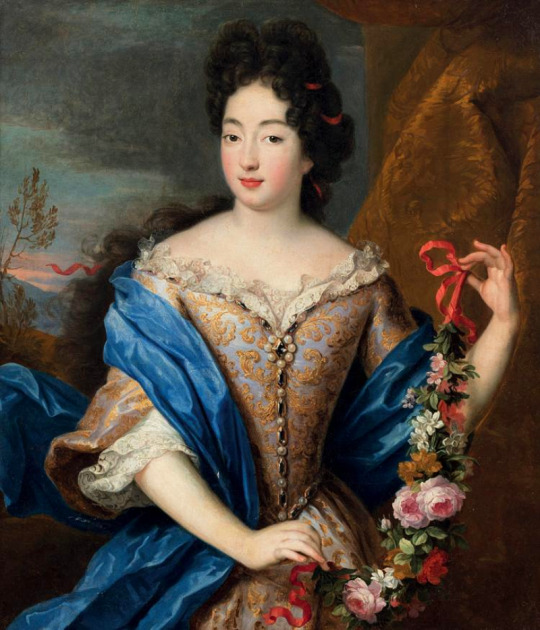







Royal Birthdays for today, March 13th:
Judith of Habsburg, Queen of Bohemia, 1271
Louis I, Duke of Orléans, 1372
Anne of Bavaria, Princess Palatine, 1648
Philippine Charlotte of Prussia, Duchess of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, 1716
Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, 1741
Louise Marie Adélaïde de Bourbon-Penthièvre, Duchess of Orléans, 1753
George Mikhailovich, Prince of Prussia, 1981
#louis i#anne of bavaria#joseph ii#Louise Marie Adélaïde de Bourbon-Penthièvre#George Mikhailovich#Philippine Charlotte of Prussia#Judith of Habsburg#long live the queue#royal birthdays
13 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello😁 can you share your favorite queens?
Thank you for the great ask anon, of course! 🥰
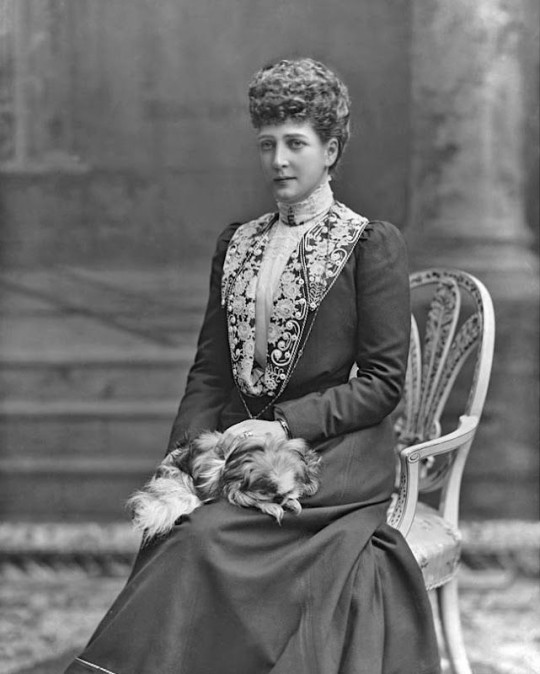

#1: Queen Alexandra of the United Kingdom – (nèe Princess Alexandra of Denmark, "Alix".
— She was beautiful, a warm and caring mother/grandmother, was popular as Princess of Wales and Queen Consort among of her people because of her good nature, and she supported many charities, including her own: "Alexandra Rose Day", founded by Queen Alexandra in 1912, this was a charity where flowers were being sold and all the money went to supporting Londoners in poverty. This was inspired by a priest in her native Denmark selling roses to raise money for those in need, Queen Alexandra brought the idea back to the United Kingdom. ❤✨

#2: Queen Anne Boleyn of England – (nèe Lady Anne Boleyn)
— She was intelligent, funny, caring and kind to all of people, and as her two years as Queen Consort she supported many charities, and even "gave alms to the poor, provided for widows, and even sewed shirts and smocks for the needy". She also helped with promoting new educational identities for monasteries, which were no longer under the protection of the Catholic Church. After only two years of being Queen Consort when she was said to have been 35 years old, she was executed after being imprisoned in the Tower of London for 17 days because she was accused of committing treason, but the true reason she was executed was because she failed to give King Henry VIII a male heir. ☹️💔
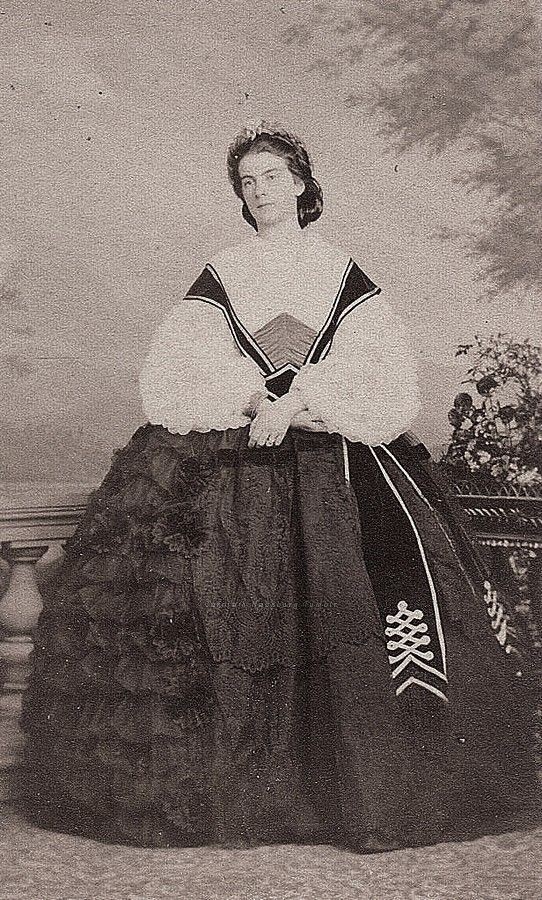

#3: Queen Marie Sophie of the Two Sicilies – (nèe Duchess Marie Sophie in Bavaria)
— She was beautiful, bright, and fierce. She was given the nickname the "Warrior Queen", the "Heroine of Gaeta" and the "modern Joan of Arc", rallying the troops, nursing the injured, feeding her forces at her own table and taunting Garibaldi's army from the battlements with the words; "Go ahead and shoot me. I will be where my men are". It was said of her that the Queen would "wipe your brow if you were wounded or hold you in her arms while you die". ❤️🔥👑
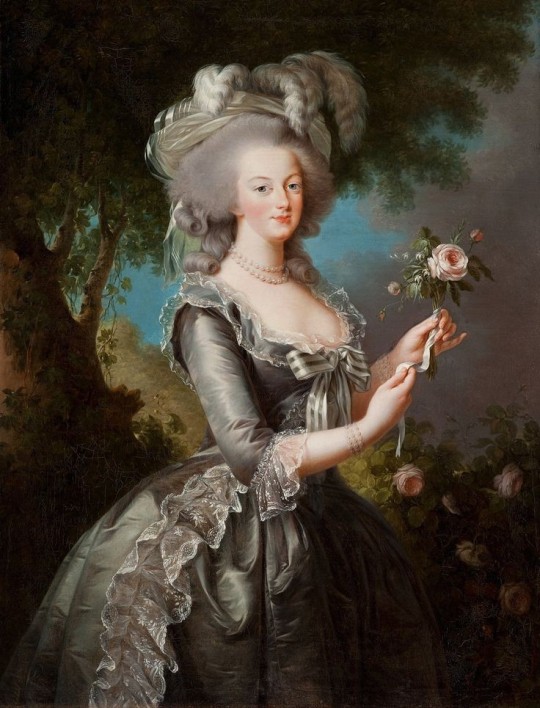
#4: Queen Marie Antoinette of France – (nèe Archduchess Marie Antoinette of Austria)
— She was honest, lovable, bold, a social butterfly who loved gambling, partying and extravagant fashions. Growing up she was closest with her sister, Maria Carolina, who was three years older, and with whom she had a lifelong close relationship. As Queen, Marie Antoinette was always unpopular, she spent lavishly, but her extravagance was only a minor cause of France's growing debt in the 1770-80s. Because of Louis XVI's indecisiveness, Marie played an increasingly prominent political role. But was very beloved for her charitable activities and patronage of the arts. She supported various charitable organizations and institutions, and she was also a benefactress of the poor. 💞🎀

#5: Queen Lovisa of Denmark – (nèe Lovisa of Sweden)
— She was described as intelligent, with an ability to be natural, easy and friendly. And As Queen, she was mainly known for her many charity projects, an interest that she shared with her spouse. She did not care for ceremonial duties and public events, and lived a discreet life dedicated to her children and her interests in art, literature and charity. After a short tenure of only six years as Queen, she was widowed in 1912.
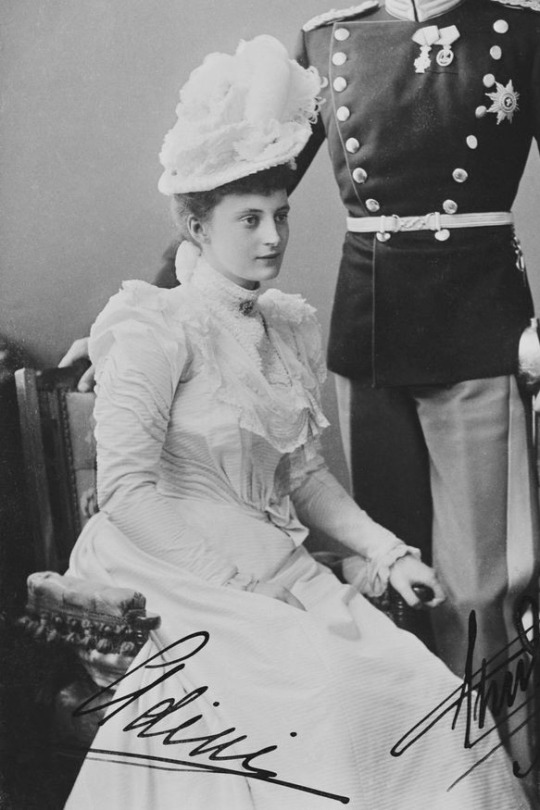

#6: Queen Alexandrine of Denmark – (nèe Alexandrine of Mecklenburg-Schwerin)
— She was reticent by nature. Her childhood was characterised by regular sporting activities, and from a young age she played the piano to a high standard. Her great interest in music stayed with her for her entire life and was passed on to her equally musical eldest son, Prince Frederik (IX). As of her first years as Queen, she had difficulty getting used to public attention, and she preferred to avoid the media limelight, but performed her functions in an exemplary manner. In the home her presence was crucial for the two boys, since Christian X was known for surrounding himself with a certain atmosphere of the barracks. Queen Alexandrine undertook extensive charity work until her death and was an avid golf player and photographer, who also loved doing needlework to a high standard. 💫
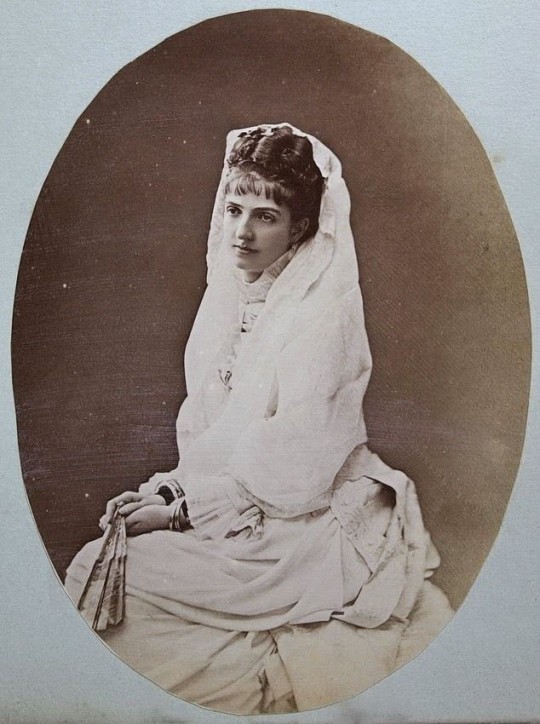

#7: Queen Margherita of Italy – (nèe Margherita of Savoy)
— She was described as sensitive, proud and with a strong force of will without being hard, as well as having the ability to be charming when she chose to. As to her appearance, she was described as a tall, stately blonde, but she was not regarded as a beauty. As Queen, she worked to protect the monarchy against republicans and socialists, and she gathered a circle of conservative intellectuals and artists known as the "Circolo della Regina" (Circle of the Queen) in her famous literary salon known as "Giovedì Della Regina" (Queen's Thursdays), where she benefited artists and writers.
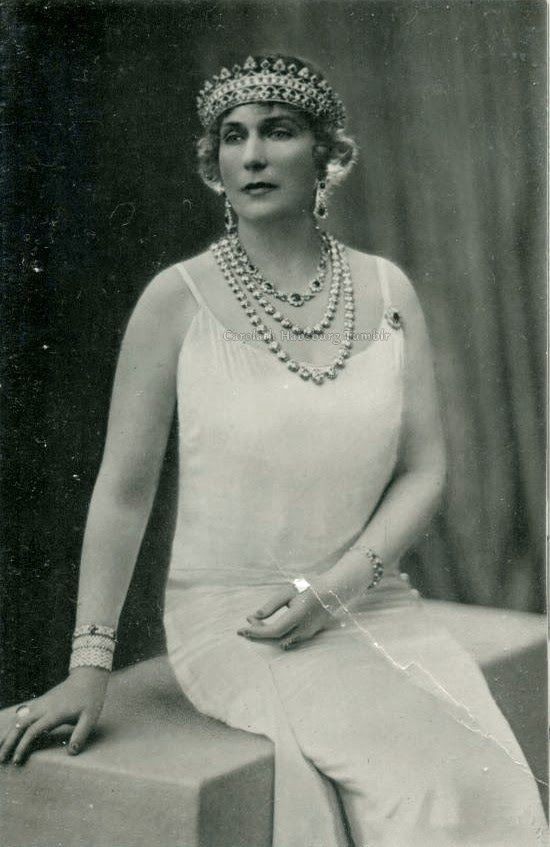

#8: Queen Victoria Eugenie of Spain – (nèe Princess Victoria Eugenie of Battenberg), "Ena".
— She was described as very kind but very strict and she devoted herself to work for hospitals and services for the poor, as well as to education. She also involved herself in the reorganization of the Spanish Red Cross. In 1929, the city of Barcelona erected a statue of her in a nurse's uniform in honour of her Red Cross work and since the the statue has been destroyed.

#9: Queen Elena of Italy – (nèe Elena of Montenegro)
— She was described as shy and reserved but also rather stubborn. Very attached to traditions, with a sensitive soul and a lively and curious mind, she was endowed with a strong love for nature: her favourite flower was the Cyclamen. She was a very tall woman of 180 cm (5'11). As Queen, her commitment to numerous charitable and welfare initiatives, which assured her great sympathy and popularity, was profuse. The Queen went well beyond mere charity: her evangelical spirit led her to practice every day the most genuine and most charitable love of neighbor.
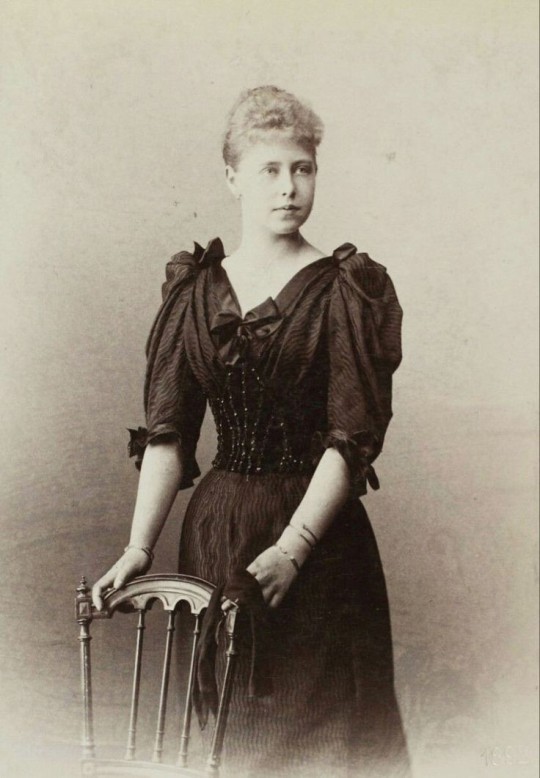
#10: Queen Marie of Romania – (nèe Princess Marie of Edinburgh), "Missy".
— She was described as very beautiful and high spirited. As a young girl, Marie was very close with her sisters, but mostly her sister Victoria Melita, they played many games with their father and Marie's mother, the Duchess of Edinburgh neglected Marie and her sisters' education, considering them not very bright or gifted. But in the fields of painting and drawing, Marie and her sisters had inherited her grandmother, Queen Victoria's talent. On October 11th, 1914, Marie and her husband Ferdinand were acclaimed as king and Queen in the Chamber of Deputies. Princess Anne Marie Callimachi, a close friend of Marie, wrote that "as Crown Princess, she had been popular; as Queen, she was more loved". Marie maintained a certain influence on her husband and the entire court, leading historian A. L. Easterman to write that "it was not Ferdinand, but Marie who ruled in Romania".
#answered ask#queen alexandra#alexandra of denmark#anne boleyn#queen marie sophie of the two sicilies#duchess marie sophie in bavaria#marie antoinette#queen lovisa of denmark#lovisa of sweden#queen alexandrine of denmark#alexandrine of mecklenburg-schwerin#queen margherita of italy#margherita of savoy#queen victoria eugenie of spain#princess victoria eugenie of battenberg#queen elena of italy#elena of montenegro#queen marie of romania#princess marie of edinburgh#informational
19 notes
·
View notes
Note
hello, Happy New Year! Is there any history book you're reading and would recommend?
Happy New Year!!!
I'm reading "The Life and Afterlife of Isabeau of Bavaria" by Tracy Adams and "The Creation of the French Royal Mistress" by Tracy Adams and Christine Adams. I would definitely recommend both, they're fantastic!
#sorry for the delay in answering#I love Anne de Pisseleu and am really curious to know more about Isabeau of Bavaria so these were great history books to start 2024!#ask#queue
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pentiment's Complete Bibliography, with links to some hard-to-find items:
I've seen some people post screenshots of the game's bibliography, but I hadn't found a plain text version (which would be much easier to work from), so I put together a complete typed version - citation style irregularities included lol. I checked through the full list and found that only four of the forty sources can't be found easily through a search engine. One has no English translation and I'm not even close to fluent enough in German to be able to actually translate an academic article, so I can't help there. For the other three (a museum exhibit book, a master's thesis, and portions of a primary source that has not been entirely translated into English), I tracked down links to them, which are included with their entries on the list.
If you want to read one of the journal articles but can't access it due to paywalls, try out 12ft.io or the unpaywall browser extension (works on Firefox and most chromium browsers). If there's something you have interest in reading but can't track down, let me know, and I can try to help! I'm pretty good at finding things lmao
Okay, happy reading, love you bye
Beach, Alison I. Women as Scribes: Book Production and Monastic Reform in Twelfth-Century Bavaria. Cambridge Univeristy Press, 2004.
Berger, Jutta Maria. Die Geschichterder Gastfreundschaft im hochmittel alterlichen Monchtum: die Cistercienser. Akademie Verlag GmbH, 1999. [No translation found.]
Blickle, Peter. The Revolution of 1525. Translated by Thomas A. Brady, Jr. and H.C. Erik Midelfort. The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1985.
Brady, Thomas A., Jr. “Imperial Destinies: A New Biography of the Emperor Maximilian I.” The Journal of Modern History, vol 62, no. 2., 1990. pp.298-314.
Brandl, Rainer. “Art or Craft: Art and the Artist in Medieval Nuremberg.” Gothic and Renaissance Art in Nuremberg 1300-1550. The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 1986. [LINK]
Byars, Jana L., “Prostitutes and Prostitution in Late Medieval Bercelona.” Masters Theses. Western Michigan University, 1997. [LINK]
Cashion, Debra Taylor. “The Art of Nikolaus Glockendon: Imitation and Originality in the Art of Renaissance Germany.” Journal of Historians of Netherlandish Art, vol 2, no. 1-2, 2010.
de Hamel, Christopher. A History of Illuminated Manuscripts. Phaidon Press Limited, 1986.
Eco, Umberto. The Name of the Rose. Translated by William Weaver. Mariner Books, 2014.
Eco, Umberto. Baudolino. Translated by William Weaver. Mariner Books, 2003.
Fournier, Jacques. “The Inquisition Records of Jacques Fournier.” Translated by Nancy P. Stork. Jan Jose Univeristy, 2020. [LINK]
Geary, Patrick. “Humiliation of Saints.” In Saints and their cults: studies in religious sociology, folklore, and history. Edited by Stephen Wilson. Cambridge University Press, 1985. pp. 123-140
Harrington, Joel F. The Faithrul Executioner: Life and Death, Honor and Shame in the Turbulent Sixteenth Century. Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2013.
Hertzka, Gottfired and Wighard Strehlow. Grosse Hildegard-Apotheke. Christiana-Verlag, 2017.
Hildegard von Bingen. Physica. Edited by Reiner Hildebrandt and Thomas Gloning. De Gruyter, 2010.
Julian of Norwich. Revelations of Divine Love. Translated by Barry Windeatt. Oxford Univeristy Press, 2015.
Karras, Ruth Mazo. Sexuality in Medieval Europe: Doing Unto Others. Routledge, 2017.
Kerr, Julie. Monastic Hospitality: The Benedictines in England, c.1070-c.1250. Boudell Press, 2007.
Kieckhefer, Richard. Forbidden rites: a necromancer’s manual of the fifteenth century. Sutton, 1997.
Kuemin, Beat and B. Ann Tlusty, The World of the Tavern: Public Houses in Early Modern Europe. Routledge, 2017.
Ilner, Thomas, et al. The Economy of Duerrnberg-Bei-Hallein: An Iron Age Salt-mining Center in the Austrian Alps. The Antiquaries Journal, vol 83, 2003. pp. 123-194
Lang, Benedek. Unlocked Books: Manuscripts of Learned Magic in the Medieval Libraries of Central Europe. The Pennsylvania State University Press, 2008
Lindeman, Mary. Medicine and Society in Early Modern Europe. Cambridge University Press, 2019.
Lowe, Kate. “’Representing’ Africa: Ambassadors and Princes from Christian Africa to Renaissance Italy and Portugal, 1402-1608.” Transactions of the Royal Historical Society Sixth Series, vol 17, 2007. pp. 101-128
Meyers, David. “Ritual, Confession, and Religion in Sixteenth-Century Germany.” Archiv fuer Reformationsgenshichte, vol. 89, 1998. pp. 125-143.
Murat, Zuleika. “Wall paintings through the ages: the medieval period (Italy, twelfth to fifteenth century).” Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, vol 23, no. 191. Springer, October 2021. pp. 1-27.
Overty, Joanne Filippone. “The Cost of Doing Scribal Business: Prices of Manuscript Books in England, 1300-1483.” Book History 11, 2008. pp. 1-32.
Page, Sophie. Magic in the Cloister: Pious Motives, Illicit Interests, and Occullt Approaches to the Medieval Universe. The Pennsylvania State University Press, 2013.
Park, Katharine. “The Criminal and the Saintly Body: Autopsy and Dissectionin Renaissance Italy.” Renaissance Quarterly, vol 47, no. 1, Spring 1994. pp. 1-33.
Rebel, Hermann. Peasant Classes: The Bureaucratization of Property and Family Relations under Early Habsburg Absolutism, 1511-1636. Princeton University Press, 1983.
Rublack, Ulinka. “Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Female Body in Early Modern Germany.” Past & Present,vol. 150, no. 1, February 1996.
Salvador, Matteo. “The Ethiopian Age of Exploration: Prester John’s Discovery of Europe, 1306-1458.” Journal of World History, vol. 21, no. 4, 2011. pp.593-627.
Sangster, Alan. “The Earliest Known Treatise on Double Entry Bookkeeping by Marino de Raphaeli.” The Accounting Historians Journal, vol. 42, no. 2, 2015. pp. 1-33.
Throop, Priscilla. Hildegarde von Bingen’s Physica: The Complete English Translation of Her Classic Work on Health and Healing. Healing Arts Press, 1998.
Usher, Abbott Payson. “The Origins of Banking: The Brimitive Bank of Deposit, 1200-1600.” The Economic History Review, vol. 4, no. 4. 1934. pp.399-428.
Waldman, Louis A. “Commissioning Art in Florence for Matthias Corvinus: The Painter and Agent Alexander Formoser and his Sons, Jacopo and Raffaello del Tedesco.” Italy and Hungary: Humanism and Art in the Early Renaissance. Edited by Peter Farbaky and Louis A. Waldman, Villa I Tatti, 2011. pp.427-501.
Wendt, Ulrich. Kultur and Jagd: ein Birschgang durch die Geschichte. G. Reimer, 1907.
Whelan, Mark. “Taxes, Wagenburgs and a Nightingale: The Imperial Abbey of Ellwangen and the Hussite Wars, 1427-1435.” The Journal of Ecclesiastical History, vol. 72, no. 4, 2021, pp.751-777.
Wiesner-Hanks, Merry E. Women and Gender in Early Modern Europe. Cambridge University Press, 2008.
Yardeni, Ada. The Book of Hebrew Script: History, Palaeography, Script Styles, Calligraphy & Design. Tyndale House Publishers, 2010.
571 notes
·
View notes
Text
Elisabeth De Musical, Netherlands Premiere
📍Schouwburg Het Park (14.03.2025)


















Pia Douwes as Empress Elisabeth
Danique Dusée as Young Elisabeth / Jonge Elisabeth
Milan van Waardenburg as Der Tod / De Dood
Ann Van den Broeck as Archduchess Sophie
William Spaaij as Lucheni
Ronald Jorritsma as Rudolf
Guido Gottenbos as Franz Joseph
Sjoerd Oomen as Maximilian of Bavaria
#elisabeth das musical#musical theatre#pia douwes#danique dusse#der tod#musicals#theatre#kaiserin elisabeth#todolf#elisabeth of austria#history#franz joseph#luigi lucheni#de dood#kronprinz rudolf#european musicals
100 notes
·
View notes
Text

Duke Albert V (1528-1579) of Bavaria with a Lion
Artist: Hans Mielich (German, (1516-1573)
Date:1556
Medium: Oil painting
Collection: Kunsthistorisches Museum Vienna, Austria
Albert V, Duke of Bavaria
Albert V (German: Albrecht V.) (29 February 1528 – 24 October 1579) was Duke of Bavaria from 1550 until his death. He was born in Munich to William IV and Maria Jacobäa of Baden.
Albert was educated at Ingolstadt by Catholic teachers. On 4 July 1546 he married Anna of Austria, a daughter of Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor and Anna of Bohemia and Hungary (1503–1547), daughter of King Ladislaus II of Bohemia and Hungary and his wife Anne de Foix. The union was designed to end the political rivalry between Austria and Bavaria. In 1550, Albert succeeded his father as duke of Bavaria.
#portrait#painting#full length#standing#fine art#german culture#albert v#duke of bavaria#german history#interior#costume#lion#dog#hans mielich#german painter#oil painting#german art#16th century painting#european art#artwork
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Someone should truly speak bout the “later wife effect” that seems to have haunted historical figures since times long forgotten.
To break it down to you, what I call the “later wife effect” occurs when a male historical figure suddenly looses his beloved wife (most of the times, his first one) in an untimely and tragic manner -either by a childbirth gone wrong, an accident or a sudden illness-, turning the once mirthful husband into a grief-stricken widower. Perhaps because he lacks succession from said wife, because he has to provide spares to his heir, or even because an alliance is needed, he is forced to marry again; but the love never arises fully, their marriage turns into a bound of duty, and no matter what she does, or how loved she is outside their marriage: the later wife will forever be under the shadow of the first, a perfect idol, immortalised by her early death.
The “later wife effect” knows various levels:
In 1673, Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, lost his beloved Margaret Theresa when she was yet to turn twenty two and with child. Their seven years of union had produced four children, but only a daughter lived when Margaret Theresa died, and he went on to marry twice again; and even though he would sorrowfully remark that neither Claudia Felicitas of Austria or Eleonore Magdalene of Neuburg, his following brides, were “not like my only Margaretha”, his marriages were remarkably happy and so was he. This could be one of the mildest examples.
The middle ground would be when the marriage with the later wife is dutiful and polite, but loveless. Frederick William II of Hesse married Alexandra Nikolaevna, but soon lost her due to complications of childbirth. He would remarry nine years later to the beautiful and lively Anna of Prussia, and even though they eventually had six children, their marriage was notably cold and unhappy. Leopold I of Belgium widowed of his wife, Charlotte of Wales, soon after she gave birth to a dead son; fifteen years later, know king of Belgium, he took Louise-Marie of Orléans hand in marriage; she was shy, delicate, witty and partook in many charitable causes, earning the love of the Belgians, and the respect of her husband, with whom she had a fruitful and tranquil union; but Leopold would not be faithful to her, committing adultery with a much younger Arcadie Claret, who was said to resemble the long gone princess Charlotte. She perished a year after he had a son with Claret, and her dead did not stop the relationship between the two of them.
More unhappy cases of this effect would be those of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, and his descendant, Joseph II. When still an archduke, Maximilian married Mary of Burgundy and loved her much, a love so legendary it lived through generations in the art commissioned by their descendants. But the fairytale would come to an abrupt end when, after five years of marriage, Mary would find her untimely dead while pregnant with their fourth child, after her horse threw her off the saddle. Maximilian was most heartbroken and, after a failed marriage attempt with the young duchess Anne of Brittany, he would wed Bianca Maria Sforza. The empress from Milan was deemed “more beautiful than Mary” by Maximilian, but neither her beauty not her many charms of her would soften his callous attitude towards his wife. Having endured a miscarriage during the first months of their union, Bianca Maria, the once most sought after princess in Europe, had become a ghost in her own court, severely neglected by her husband, who refused to attend to her own funeral nor dedicate a gravestone for her. Similarly, after the traumatic passing of his wife, Isabella of Parma, Joseph II was forced to remarry to Maria Josepha of Bavaria, who he did not found as attractive as the late archduchess. He grew so disgusted of her that the same devoted husband that has been by Isabella’s bedside now commanded to put a wall between his balcony and hers, so that he could not see her, distressing old servants in the palace so much with his cold attitude that some left. When, after two years of marriage, her life was robbed by smallpox -the same ailment that had taken Isabella’s life four years before-, Joseph declared she had been worthy of respect and that he repented his coldness. However, he refused to visit her bedside and did not appear during her burial.
This should not be confused with what I call “the younger wife effect”, which takes place when a widowed historical figure, who had long remained unwed by choice, suddenly takes marriage to a beautiful and much younger person that is described to bring happiness to his once lonely and dull life. This would perfectly be exemplified with prince Maximilian of Saxony’s marriage with princess Maria Luisa Carlota of Parma, almost twenty one years since the passing of his wife (princess Carolina of Parma) or Edward I’s marriage to Marguerite of France.
18 notes
·
View notes
Note
https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2024/sep/17/samuel-alito-leonard-leo-gloria-von-thurn-und-taxis-napa-institute
Well then.
The supreme court justice Samuel Alito and a German aristocrat and “networker of the far right” from whom Alito accepted expensive concert tickets, are both linked to an ultra-conservative Catholic US group whose board members include the dark money impresario Leonard Leo and the founder of a hardline anti-abortion Christian group, documentation reviewed by the Guardian shows.
In 2018, Gloria von Thurn und Taxis, told the New York Times about attending a dinner hosted in Rome by James Harvey, an American cardinal and hardliner, and sponsored by the Napa Institute, a group founded by Timothy R Busch, a conservative Catholic businessman and political activist.
Leo, 59, is an activist and fundraiser who worked on the confirmations of all six rightwing justices who now dominate the supreme court, Alito among them. Now controlling billions of dollars in funding for rightwing groups, Leo is a director of the Napa Institute Legal Foundation, also known as Napa Legal Institute, and the Napa Institute Support Foundation.
Also among Napa Legal Institute directors is Alan Sears, founder of the Alliance Defending Freedom. The ADF was the principal driver of Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, the case in which the supreme court ended the federal right to abortion, with Alito writing the ruling handed down in June 2022.
In 2017, the Napa Institute hosted a two-day symposium at the Trump hotel in Washington, during which Alito attended a dinner.
Writing for the Washington Post, John Gehring, an author and reporter, said the symposium “mixed traditional Catholic religious practices with moments that felt uncomfortably nationalistic”, including a “reading in the rosary booklet from [the Confederate general] Robert E Lee that [seemed] … stunningly insensitive at best … at a time when the ‘alt-right’ and white nationalism are basking in the glow of renewed attention and proximity to power”.
Alito is not the only supreme court justice with links to the Napa Institute. In September 2021, as part of a series sponsored by the group, Justice Clarence Thomas spoke at the University of Notre Dame.
“The court was thought to be the least dangerous branch and we may have become the most dangerous,” Thomas said, attacking judges he deemed to be “venturing into areas we should not have entered into” – meaning politics.
Thomas and Alito, however, have been the subject of numerous reports about undeclared gifts from rightwing donors, fueling an ethics crisis now stoked by news of Alito’s acceptance of concert tickets valued at $900 from von Thurn und Taxis.
Von Thurn und Taxis, 64, is a former punk turned billionaire, also known as Princess TNT, with close links to the far-right Alternative für Deutschland (AfD) party. News of her gift to Alito was accompanied by reporting of further links between the two, including a picture of Alito and another rightwing justice, Brett Kavanaugh, posing at the supreme court in 2019 with the German socialite; Cardinal Gerhard Ludwig Müller, a German hardliner; and Brian Brown, a prominent US anti-LGBTQ+ campaigner.
Von Thurn und Taxis told German media that Alito and his wife, Martha-Ann, attended a concert at her castle in Bavaria last year as “private friends”. In emails to the Guardian, the aristocrat clarified: “We never speak about politics nor religion at the table, because we believe it limits the possibility to make friends.”
The socialite, who rejects the label “networker of the far right”, also said it would “never occur” to her to speak about “touchy subjects” like abortion with someone she knew socially, and claimed not to know that “the Dobbs decision” referred to the supreme court abortion rights ruling written by Alito.
In a speech at the National Conservatism Conference in Brussels last April, von Thurn und Taxis said European leaders were “financ[ing] the killing of our offspring” in an apparent reference to the availability of reproductive rights in Europe. She added: “Does this make any sense? Is there some kind of racism? Are we not supposed to reproduce?”
Alito and his wife have also been outspoken about abortion and other hot-button cultural issues. In June, the progressive activist Lauren Windsor released recordings in which Justice Alito agreed that the US should “return … to a place of godliness” and said, “I don’t know that we can negotiate with the left”. Regarding her supposed persecution from those on the left, his wife said: “Look at me, look at me. I’m German. I’m from Germany. My heritage is German. You come after me, I’m gonna give it back to you.”
Caroline Ciccone, president of Accountable.US, which campaigns for court reform and which highlighted links between the German socialite, the Napa Institute and Alito, said: “When a supreme court justice like Samuel Alito pals around with influential rightwing figures like Princess Gloria von Thurn und Taxis and Leonard Leo, it raises concerns about fairness and impartiality.
“These relationships aren’t just about gifts. They reflect a deeper effort to manipulate our legal system in ways that could impact the rights of everyday people.”
Ciccone added, “What’s disturbing is that this happens behind closed doors – at parties at the Bavarian castle – away from public scrutiny. We’re talking about relationships that can affect everything, from reproductive rights to environmental protections” – both the subject of recent supreme court rulings widely seen as victories for the political right.
“The American people deserve a judiciary that serves justice impartially,” Ciccone said, “not one that can be bought.”
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nyotalia, 2pNyotalia, 2p!Talia, Hetalia headcanon names
Nyo!America - Amelia
Nyo!England - Elizabeth
Nyo!France - Catherine
Nyo!Russia - Anna
Nyo!China - Chun-Yan
Nyo!Canada - Marguerite
Nyo!Italy - Alice
Nyo!Germany - Monika
Nyo!Japan - Ponko
Nyo!Prussia - Julia
Nyo!Romano - Chiara
Nyo!Spain - Carmen
Nyo!Austria - Therese
Nyo!Switzerland - Adelheid
Nyo!Denmark - Hanne
Nyo!Sweden - Astrid
Nyo!Norway - Ingrid
Nyo!Iceland - Guðrún
Nyo!Finland - Aino
2pNyo!America - Caroline
2pNyo!England - Rose
2pNyo!France - Isabelle
2pNyo!Russia - Elena
2pNyo!China - Qiuyan
2pNyo!Canada - Anne
2pNyo!Italy - Bianca
2pNyo!Germany - Luise
2pNyo!Japan - Mameko
2pNyo!Prussia - Hildegard
Seychelles - Véronique
Nyo!Seychelles - Michel
Liechtenstein - Erika
Nyo!Liechtenstein - Klaus
Monaco - Sophie
Nyo!Monaco - Jean
Belgium - Emma
Nyo!Belgium - Anri
Luxembourg - René
Netherlands - Abel
Denmark - Magnus
Norway - Sigurd
Iceland - Egill
Finland - Timo
Sweden - Bernhard
Nyo!Lithuania - Rūta
Nyo!Latvia - Laima
Nyo!Turkey - Hatice
Nyo!Greece - Daphne
Nyo!Egypt - Fatima
Portugal - Afonso
Nyo!Portugal - Maria
Nyo!Hungary - István
Slovakia - Jozef
Czech - Hedvika
Nyo!Poland - Agnieszka
2p!Poland - Jan
Scotland - Callum
Wales - Dylan
Northern Ireland - Conor
Ireland - Ronan
Cuba - Carlos
Ecuador - Jose
Moldova - Vasile
Romania - Alexandru
Bulgaria - Dimitar
Serbia - Vuk
Croatia - Stjepan
2p!Italy - Lorenzo
2p!Romano - Flavio
2p!Germany - Siegfried
2p!Japan - Kiri
Nyo!Belarus - Mikita
Ukraine - Olga
Nyo!Ukraine - Bogdan
Australia - Ralph
New Zealand - George
Nyo!New Zealand - Charlotte
Wy - Olivia
Hutt River - Paul
Molossia - Jacob
Slowjamastan - Liam
Domain - Nicholas
Stomaria - Harry
Aerica - Michael
Ladonia - Oscar
Kugelmugel - Leopold
Seborga - Marcello
2p!America - Thomas
2p!England - Edmund
2p!France - André
2p!Russia - Alexander
2p!China - An
Genoa - Giovanni
HRE - Otto
Bavaria - Karl
Saxony - Heinrich
Hessen - Wilhelm
Picardy - Gabriel
Cyprus - Giorgos
TRNC - Mustafa
Rome - Maximus
Ancient Greece - Athena
Nyo!Korea - Soo-Jin
Taiwan - Xiao-Mei
Nyo!Taiwan - Chih-Ming
Hong Kong - Ka Lung
Nyo!Hong Kong - Lan
Vietnam - Lien
Nyo!Vietnam - Tuấn
22 notes
·
View notes
Note
You seamlessly integrate your mother tongue, informations about Bavaria and its culture, as well as informations about the Divine Flock, in the narration to make the reader feel as if they, just like MC, are familiar with this whole environment (you made me want to learn German, by the way). I love your vampires (between cruelty and seduction) and the general width of the game with so many routes that make me want to try them all despite the fact that I usually stick to the same route/RO/MC. 4/5
🧡🧡🧡 I try to keep the german to such parts that make it clear what is being meant, and the bavarian aspect is a bit tricky: cause on one hand it is what I know and grew up with and on the other hand I made Bavaria independent after WW2, which means a few things have changed as well! But it is great fun coming up with those things and I hope readers keep enjoying them! And yeeesss learn German! Lay awake at night and cry over the gender of Nutella. The heavy burden if you love both monstrous vampires and also Anne Rice vampires uwu coming up with a middle ground proves challenging at times, but I am happy with how I dealt with it so far! And yeah the routes (shoves the seven variants, depending on volery and relationship status after a murder behind my back), they are alive I swear. But tbh as long as it fits and more importantly to me only adds naturely to the story, why not?
Btw regarding stats and character choices: none of those will ever lock the player out of a path. People will react to it (if you suddenly are kind and were angry before) but that's it.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Master Post - N to Z
If you notice any show, movie or character missing that I’ve made gifs of, please let me know. Characters are sorted alphabetically by first their last name and then their first name.
Go to A-M | Last updated: April 13th, 2025
N
Nussknacker und Mausekönig (Louise Stahlbaum | Marie Stahlbaum | Zuckerfee/Sugar Fairy)
O
Oktoberfest 1900/Oktoberfest: Beer & Blood (Clara Prank | Curt Prank)
Once Upon A Time (Belle French | Colette French | Cora Mills | Ella Mills | Regina Mills / The Evil Queen | Robin Mills | Emma Swan | Anastasia Tremaine | Drizella Tremaine)
Once Upon A Time in Wonderland (Alice | Cora Mills | Anastasia Tremaine)
Outlander (Abigail | Marie Louise de La Tour d'Auvergne | Jocasta Cameron | Margaret Campbell | Geilis Duncan | Geneva Dunsany | Isobel Dunsany | Madame Elise | Brianna Fraser | Claire Fraser | Jamie Fraser | Janet “Jenny” Fraser Murray | Harold “Hal” Grey | John Grey | Lady Grozier | Mary Hawkins | Jeanne LeGrand | Louis XV | Mairi | Laoghaire MacKenzie | Letitia MacKenzie | Joan MacKimmie | Marsali MacKimmie | Mary MacNab | Elias Pound | Alexander Randall | William Ransom | Charles Edward Stuart | Suzette | Margaret Wake Tryon | Martha Washington | Elizabeth “Lizzie” Wemyss | Extras)
Oz the Great and Powerful (Evanora | Glinda | Theodora)
P
Q
Queen Charlotte: A Bridgerton Story (Agatha Danbury | Queen Charlotte | Charlotte, Princess Royal | Violet Ledger | Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart | Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld | Adelaide of Saxe-Meiningen | Prince Adolphus | Prince Augustus | Prince Edward | Prince Ernest | Prince Frederick | George, Prince of Wales | Prince William | Princess Charlotte of Wales | Princess Augusta | Princess Elizabeth | Princess Mary | Princess Sophia)
R
Reign (Aylee | Kenna de Poitiers | Amy Dudley | Robert Dudley | Claude of France | Greer Norwood | Penelope | Mary Stuart, Queen of Scots | Elizabeth Tudor/Elizabeth I | Elisabeth of Valois)
Reinas/Queens: The Virgin and the Martyr (Joanna of Austria | Empress Maria / Maria of Austria | Margaret Douglas | Bess of Hardwick | Isabel de Osorio | Mary Stuart, Queen of Scots | Isabella Clara Eugenia of Spain | Anna Throndsen | Elizabeth I/Elizabeth Tudor | Elisabeth of Valois)
Rise of Empires: Ottoman (Katarina Branković | Mara Branković | Gülbahar Hatun | Hüma Hatun | Constantine XI Palaiologos)
Romeo & Juliet [2013] (Juliet Capulet)
S
Sechs auf einen Streich (see the individual movies)
Shadow and Bone (Tatiana Lantsov | Zoya Nazyalensky | Genya Safin | Alina Starkov)
Sisi [2009] (Elisabeth “Sisi” of Austria | Archduchess Sophie of Austria | Helene “Néné” in Bavaria | Charlotte of Belgium | Eugénie de Montijo)
Sisi [2021] (Elisabeth “Sisi” of Austria | Archduchess Sophie of Austria | Helene “Néné” in Bavaria | Karl Ludwig von Grünne | Henriette Mendel | Eugénie de Montijo)
Sisi & Ich (Elisabeth of Austria)
Sissi Trilogy (Elisabeth “Sisi” of Austria | Archduchess Sophie of Austria | Helene “Néné” in Bavaria | Ludovika, The Duchess in Bavaria)
Snow White and the Huntsman (Ravenna)
Sophie - Braut wider Willen (Sophie von Ahlen)
Spencer (Anne Boleyn | Princess Diana)
Still Star-Crossed (Guiliana Capulet | Juliet Capulet | Rosaline Capulet | Tessa Montague | Princess Isabella of Verona)
T
The 100 (Emori | Clarke Griffin | Lexa)
The Age of Adaline (Adaline Bowman)
The Duchess (Georgiana Cavendish, Duchess of Devonshire | Georgiana Spencer, Countess Spencer)
The Last Duel (Marguerite de Carrouges | Jacques Le Gris)
The Little Mermaid [2023] (Vanessa)
The Crown (Catherine Middleton | Queen Elizabeth II | Princess Margaret)
The Empress (see Die Kaiserin)
The Eras Tour (Taylor Swift)
The Gilded Age (Mamie Fish | Bertha Russell | Peggy Scott | Extras)
The Great (Countess Belanova | Catherine the Great | Georgina Dymova | Marial | Queen Agnes of Sweden | Extras)
The Greatest Showman (Jenny Lind)
The Hunger Games Trilogy (Katniss Everdeen | Peeta Mellark | Johanna Mason | Finnick Odair | Coriolanus Snow)
The Hunger Games: A Ballad of Songbirds and Snakes (Lucy Gray Baird | Livia Cardew | Arachne Crane | Clemensia Dovecote | Palmyra Monty | Iphigenia Moss | Juno Phipps | Persephone Price | Diana Ring | Vipsania Sickle | Tigris Snow | Lysistrata Vickers)
The Huntsman: Winter’s War (Freya | Ravenna)
The Originals (Davina Claire | Hayley Marshall | Aurora de Martel | Freya Mikaelson | Hope Mikaelson | Keelin Mikaelson | Rebekah Mikaelson)
The Other Boleyn Girl 2008 (Anne Boleyn | Elizabeth Boleyn (née Howard) | Mary Boleyn)
The Pillars of the Earth (Empress Matilda)
The Princess Switch (Margaret Delacourt | Fiona Pembroke)
The Royals (Princess Eleanor Henstridge | Queen Helena Henstridge | Wilhelmina “Willow” Moreno)
The Scandalous Lady W (Seymour Fleming)
The School for Good and Evil (Emma Anemone | Clarissa Dovey | Leonora Lesso)
The Serpent Queen (Catherine de Medici | Diane de Poitiers | Mary Stuart, Queen of Scots)
The Spanish Princess (Catherine of Aragon | Henry VIII | Mary Tudor)
The Tudors (Catherine of Aragon | Bessie Blount | Anne Boleyn | Anne of Cleves | Katheryn Howard | Ursula Misseldon | Kathryn Parr | Jane Seymour | Elizabeth Tudor/Elizabeth I | Margaret Tudor | Mary Tudor/Mary I)
The Twilight Saga (Charlotte | Alice Cullen | Edward Cullen | Katrina “Kate” Denali | Jasper Hale | Rosalie Hale | Peter | Bella Swan | Caius Volturi | Demetri Volturi | Jane Volturi)
The Vampire Diaries (Bonnie Benett | Caroline Forbes | Elena Gilbert | Jo Laughlin | Rebekah Mikaelson | Katherine Pierce | Annabelle “Anna” Zhu | Pearl Zhu)
The White Queen (Anne Neville | Isabel Neville | Margaret Plantagenet | Bona of Savoy | Elizabeth “Jane” Shore | Elizabeth Woodville | Cecily of York | Elizabeth of York | Margaret of York)
The White Princess (Mary of Burgundy | Cecily Neville | Eliza de la Pole | Margaret Pole | George Stanley | Jasper Tudor | Cecily of York | Elizabeth of York | Margaret of York)
The Witcher (Calanthe of Cintra | Cirilla “Ciri” of Cintra | Pavetta of Cintra | Tissaia de Vries | Philippa Eilhart | Sabrina Glevissig | Margarita Laux-Antille | Triss Merigold | Keira Metz | Lydia van Bredevoort | Yennefer of Vengerberg)
The Young Victoria (Victoria, The Duchess of Kent (née of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld) | Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha | Adelaide of Saxe-Meiningen | Queen Victoria)
Three Thousand Years of Longing (Hürrem Sultan | Kösem Sultan)
Trenck - Zwei Herzen gegen die Krone (Anna Amalia of Prussia)
Tulip Fever (Mrs Overalt | Sophia Sandvoort | Mrs Steen)
Tut (Ankhesenamun)
U
V
Vampire Academy [2022] (Vasilisa “Lissa” Dragomir)
Victoria (Queen Victoria | Victoria, Princess Royal)
Vom Reich zur Republik (Victoria, Princess Royal)
W
War & Peace [2016] (Natasha Rostova)
What We Do In The Shadows (Marwa | Nadja of Antipaxos)
Wolf Hall (Anne Boleyn | Catherine of Aragon)
X
Y
Z
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wives and Daughters of Holy Roman Emperors: Age at First Marriage
I have only included women whose birth dates and dates of marriage are known within at least 1-2 years, therefore, this is not a comprehensive list.
This list does not include women who died before their husbands were crowned Emperor. It spans between the beginning of the reign of Otto I (962 CE) and the end of the reign of Francis II (1806 CE).
The average age at first marriage among these women was 17. The sample size was 91 women. The youngest bride, Bianca Maria Sforza, was just 2 years old when she wed her first husband, who was himself 9. The oldest bride, Constance of Sicily, was 32 years old.
Adelaide of Italy, wife of Otto I, HRE: age 15 when she married Lothair II, King of Italy, in 947 CE
Liutgarde of Saxony, daughter of Otto I, HRE: age 15 when she married Conrad the Red, Duke of Lorraine, in 947 CE
Theophanu, wife of Otto II, HRE: age 17 when she married Otto in 972 CE
Cunigunde of Luxembourg, wife of Henry II, HRE: age 24 when she married Henry in 999 CE
Gisela of Swabia, wife of Conrad II, HRE: age 12 when she married Brun I of Brunswick in 1002 CE
Agnes of Poitou, wife of Henry III, HRE: age 18 when she married Henry in 1043 CE
Matilda of Germany, daughter of Henry III, HRE: age 11 when she married Rudolf of Rheinfelden in 1059 CE
Judith of Swabia, daughter of Henry III, HRE: age 9 when she married Solomon, King of Hungary in 1063 CE
Bertha of Savoy, wife of Henry IV, HRE: age 15 when she married Henry in 1066 CE
Agnes of Waiblingen, daughter of Henry IV, HRE: age 14 when she married Frederick I, Duke of Swabia in 1086 CE
Empress Matilda, wife of Henry V, HRE: age 12 when she married Henry in 1114 CE
Beatrice I, Countess of Burgundy, wife of Frederick I, HRE: age 13 when she married Frederick in 1156 CE
Beatrice, daughter of Frederick I, HRE: age 10 when she married Guillaume II, Count of Chalon in 1173 CE
Constance, Queen of Sicily, wife of Henry IV, HRE: age 32 when she married Henry IV in 1186 CE
Beatrice of Swabia, first wife of Otto IV, HRE: age 14 when she married Otto in 1212 CE
Maria of Brabant, second wife of Otto IV, HRE: age 24 when she married Otto in 1214 CE
Constance of Aragon, first wife of Frederick II, HRE: age 19 when she married Emeric of Hungary in 1198 CE
Isabella II of Jerusalem, second wife of Frederick II, HRE: age 13 when she married Frederick in 1225 CE
Isabella of England, third wife of Frederick II, HRE: age 21 when she married Frederick in 1235 CE
Margaret of Sicily, daughter of Frederick II, HRE: age 14 when she married Albert II, Margrave of Meissen in 1255 CE
Anna of Hohenstaufen, daughter of Frederick II, HRE: age 14 when she married John III Doukas Vatatzes in 1244 CE
Marie of Luxembourg, daughter of Henry VII, HRE: age 18 when she married Charles IV of France in 1322 CE
Beatrice of Luxembourg, daughter of Henry VII, HRE: age 13 when she married Charles I of Hungary in 1318 CE
Margaret II, Countess of Hainaut, wife of Louis IV, HRE: age 13 when she married Louis in 1324 CE
Matilda of Bavaria, daughter of Louis IV, HRE: age 10 when she married Frederick II, Margrave of Meissen in 1323 CE
Beatrice of Bavaria, daughter of Louis IV, HRE: age 12 when she married Eric XII of Sweden in 1356 CE
Anna von Schweidnitz, wife of Charles IV, HRE: age 14 when she married Charles in 1353 CE
Elizabeth of Pomerania, wife of Charles IV, HRE: age 16 when she married Charles in 1378 CE
Margaret of Bohemia, daughter of Charles IV, HRE: age 7 when she married Louis I of Hungary in 1342 CE
Catherine of Bohemia, daughter of Charles IV, HRE: age 14 when she married Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria in 1356 CE
Elisabeth of Bohemia, daughter of Charles IV, HRE: age 8 when she married Albert III, Duke of Austria in 1366 CE
Anne of Bohemia, daughter of Charles IV, HRE: age 16 when she married Richard II of England in 1382 CE
Margaret of Bohemia, daughter of Charles IV, HRE: age 8 when she married John III, Burgrave of Nuremburg in 1381 CE
Barbara of Cilli, wife of Sigismund, HRE: age 13 when she married Sigismund in 1405 CE
Elizabeth of Luxembourg, daughter of Sigismund, HRE: age 13 when she married Albert II of Germany in 1422 CE
Eleanor of Portugal, wife of Frederick III, HRE: age 18 when she married Frederick in 1452 CE
Kunigunde of Austria, daughter of Frederick III, HRE: age 22 when she married Albert IV, Duke of Bavaria in 1487 CE
Bianca Maria Sforza, wife of Maximilian I, HRE: age 2 when she married Philibert I, Duke of Savoy in 1474 CE
Margaret of Austria, daughter of Maximilian I, HRE: age 17 when she married John, Prince of Asturias in 1497 CE
Barbara von Rattal, daughter of Maximilian I, HRE: age 15 when she married Siegmund von Dietrichstein in 1515 CE
Dorothea of Austria, daughter of Maximilian I, HRE: age 22 when she married Johan I of East Frisia in 1538 CE
Isabella of Portugal, wife of Charles V, HRE: age 23 when she married Charles in 1526 CE
Maria of Austria, daughter of Charles V, HRE: age 20 when she married Maximilian II, HRE in 1548 CE
Joanna of Austria, daughter of Charles V, HRE: age 17 when she married John Manuel, Prince of Portugal in 1552 CE
Margaret of Parma, daughter of Charles V, HRE: age 14 when she married Alessandro de’ Medici, Duke of Florence, in 1536 CE
Elizabeth of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand I, HRE: age 16 when she married Sigismund II Augustus of Poland in 1543 CE
Anna of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand I, HRE: age 17 when she married Albert V, Duke of Bavaria in 1546 CE
Maria of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand I, HRE: age 15 when she married William of Julich-Cleves-Berg in 1546 CE
Catherine of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand I, HRE: age 16 when she married Francesco III Gonzaga in 1559 CE
Eleanor of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand I, HRE: age 27 when she married William I, Duke of Mantua in 1561 CE
Barbara of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand I, HRE: age 26 when she married Alfonso II d’Este in 1565 CE
Joanna of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand I, HRE: age 18 when she married Francesco I de’ Medici in 1565 CE
Anna of Austria, daughter of Maximilian II, HRE: age 21 when she married Philip II of Spain in 1570 CE
Elisabeth of Austria, daughter of Maximilian II, HRE: age 16 when she married Charles IX of France in 1570 CE
Anna of Tyrol, wife of Matthias, HRE: age 26 when she married Matthias in 1611 CE
Eleonora Gonzaga the Elder, wife of Ferdinand II, HRE: age 24 when she married Ferdinand in 1622 CE
Maria Anna of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand II, HRE: age 25 when she married Maximilian I, Elector of Bavaria in 1635 CE
Cecilia Renata of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand II, HRE: age 26 when she married Władysław IV of Poland in 1637 CE
Maria Anna of Spain, wife of Ferdinand III, HRE: age 25 when she married Ferdinand in 1631 CE
Maria Leopoldine of Austria, wife of Ferdinand III, HRE: age 16 when she married Ferdinand in 1648 CE
Eleonora Gonzaga the Younger, wife of Ferdinand III, HRE: age 21 when she married Ferdinand in 1651 CE
Mariana of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand III, HRE: age 15 when she married Philip IV of Spain in 1649 CE
Eleonore of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand III, HRE: age 17 when she married Michael I of Poland in 1670 CE
Maria Anna Josepha of Austria, daughter of Ferdinand III, HRE: age 24 when she married Johann Wilhelm II, Elector Palatine in 1678 CE
Margaret Theresa of Spain, wife of Leopold I, HRE: age 15 when she married Leopold in 1666 CE
Claudia Felicitas of Spain, wife of Leopold I, HRE: age 20 when she married Leopold in 1673 CE
Eleonore Magdalene of Neuberg, wife of Leopold I, HRE: age 21 when she married Leopold in 1676 CE
Maria Antonia of Austria, daughter of Leopold I, HRE: age 16 when she married Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria in 1685 CE
Maria Anna of Austria, daughter of Leopold I, HRE: age 25 when she married John V of Portugal in 1708 CE
Wilhelmine Amalie of Brunswick, wife of Joseph I, HRE: age 26 when she married Joseph in 1699 CE
Maria Josepha of Austria, daughter of Joseph I, HRE: age 20 when she married Augustus III of Poland in 1719 CE
Maria Amalia of Austria, daughter of Joseph I, HRE: age 21 when she married Charles VII, HRE in 1722 CE
Elisabeth Christine of Brunswick, wife of Charles VI, HRE: age 17 when she married Charles in 1708 CE
Maria Theresa of Austria, daughter of Charles VI, HRE: age 19 when she married Francis I, HRE in 1736 CE
Maria Anna of Austria, daughter of Charles VI, HRE: age 26 when she married Charles Alexander of Lorraine in 1744 CE
Maria Antonia of Bavaria, daughter of Charles VII, HRE: age 23 when she married Frederick Christian, Elector of Saxony in 1747 CE
Maria Anna Josepha of Bavaria, daughter of Charles VII, HRE: age 20 when she married Louis George of Baden-Baden in 1755 CE
Maria Josepha of Bavaria, daughter of Charles VII, HRE: age 26 when she married Joseph II, HRE in 1765 CE
Maria Christina, daughter of Francis I, HRE: age 24 when she married Albert Casimir, Duke of Teschen in 1766 CE
Maria Amalia, daughter of Francis I, HRE: age 23 when she married Ferdinand I, Duke of Parma in 1769 CE
Maria Carolina, daughter of Francis I, HRE: age 16 when she married Ferdinand IV & III of Sicily in 1768 CE
Maria Antonia, daughter of Francis I, HRE: age 14 when she married Louis XVI of France in 1770 CE
Maria Josepha of Bavaria, wife of Joseph II, HRE: age 26 when she married Joseph in 1765 CE
Maria Luisa of Spain, wife of Leopold II, HRE: age 19 when she married Leopold in 1764 CE
Maria Theresa of Austria, daughter of Leopold II, HRE: age 20 when she married Anthony of Saxony in 1787 CE
Maria Clementina of Austria, daughter of Leopold II, HRE: age 20 when she married Francis I of Sicily in 1797 CE
Maria Theresa of Naples, wife of Francis II, HRE: age 18 when she married Francis in 1790 CE
Marie Louise, daughter of Francis II, HRE: age 19 when she married Napoleon I of France in 1810 CE
Maria Leopoldina, daughter of Francis II, HRE: age 20 when she married Pedro I of Brazil and IV of Portugal in 1817 CE
Clementina, daughter of Francis II, HRE: age 18 when she married Leopold of Salerno in 1816 CE Marie Caroline, daughter of Francis II, HRE: age 18 when she married Frederick Augustus of Saxony in 1819 CE
34 notes
·
View notes
Note
Ann got the flu, so stina is starting tomorrow. Hope the Virus doesen't run it Kurs through the german Camp with the amount of injuries we already have and ann recovers well considering she is immunocompromised because of the cancer.
Germany is currently experiencing a wave of influenza. Especially Bavaria. I also hope that Ann is the only one who caught something.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

ENGLISH SPEAKING SAINTS WITH OTHERS February 9
ENGLISH SPEAKING SAINTS WITH OTHERS February 9
St. Alto, 760 A.D. Hermit and missionary, recorded as an Irishmen or possibly an Anglo-Saxon. He lived near Augsburg, Germany, arriving in the region circa 743. Living in a simple hut in wild lands, Alto soon achieved a reputation for holiness and austerity. Word of his good works reached King Pepin, who gave him a parcel of land near Altmunster, in modern Friesling Diocese in Bavaria. Alto Alto soon achieved a reputation for holiness and austerity. Word of his good works reached King Pepin, who gave him a parcel of land near Altmunster, in modern Friesling Diocese in Bavaria. Alto cleared the land and founded an abbey. St. Boniface came in 750 to dedicate the abbey church. The monastery was ravaged by the Huns but was restored in 1000 and made a Benedictine house. The Brigittines took it over in the fifteenth century . St. Teilo, 6th century. Welsh bishop, also called Eliud, Issell, Teillo, Teilou, Dub, and Theliau. A native of Penally, Pembrokshire, Wales, he studied under Sts. Dyfrig and Dubricius. He accompanied the famed St. David of Wales to Jerusalem and was a friend and assistant to St. Samson in Brittany, France, for seven years. Returning to Wales in 554, he was quite successful as a preacher and founded and served as abbot-bishop of Llandaff monastery in Dyfed, Wales. He was buried in Llandaff Cathedral.
St. Cronan the Wise, 8th century. A bishop of Ireland, possibly identified with St. Roman He systematized canon law in Ireland.
St. Cuaran, 700 A.D. An Irish bishop also called Curvinus or Cronan. He became a hermit on Iona, Scotland, after retiring as bishop, hoping to conceal his identity. St. Columba, however, recognized Cuaran.
St. Eingan, 6th century. Welsh prince and hermit, also called Anianus, Einon, and Eneon. He came from Cumberland, in Wales, the son of a chieftain. Eingan had a hermitage built at Llanengan, near Bangor.
Bl. Anne Catherine Emmerick, Roman Catholic Augustinian Canoness Regular of Windesheim. Her convent was suppressed by Napoleon, who controlled the region. Soon afterward, she fell ill, and spent her remaining years bedridden. In this state of suffering, she received numerous visions, private revelations, and the mystical gift of the stigmata. Feb. 9
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Royal Grave in a Fifteenth-Century London Parish Church - Christian Steer (2014)
English Royal Marriages and the Papal Penitentiary in the Fifteenth Century - Peter D. Clarke (2005)
Eyebrows, Hairlines, and 'Hairs Less in Sight': Female Depilation in Late Medieval Europe - John Block Friedman (2019)
Hidden in Plain Black: The Secrets of the French Hood - Karen Margarethe Høskuldsson (2019)
Isabeau of Bavaria, Queen of France (1385-1422): The Creation of an Historical Villainess - Rachel Gibbons (1996)
Missing Women: Sex Ratios in England, 1000—1500 - Sandy Bardsley (2014)
Reflections of Power: Margaret of Anjou and the Dark Side of Queenship - Patricia-Ann Lee (1986)
The Queen's Hair: Marie-Antoinette, Politics, and DNA - Desmond Hosford (2004)
'We should dress us fairly for our end': The Significance of the Clothing Worn at Elite Executions in England in the Long Sixteenth Century - Maria Hayward (2016)
#history#historyblr#english history#french history#marie antoinette#isabeau of bavaria#margaret of anjou#fashion history#queenship#women's history
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nationalities
Jeff the Killer- Swedish, Italian, Västergötland
Liu- Swedish, Chinese, Västergötland
Ben- American, Alaska
Sally Dawn- Canadian, Ontario
Sam Williams- Canadian, American, Ontario
Milo the Electrocuted- Italian, Lombardy
Lulu- Vietnamese, Vĩnh Phúc
Clockwork- French, Normandy
Zero- British, American, New Jersey
Jane the killer- American, California
Jane Arkensaw- British, Lincolnshire
Vailly Evans- Chilean, Los Lagos
Nathan the nobody- Filipino, British, Berkshire
Crystal- Filipino, British, Berkshire
Eyeless Jack- Uganda, Kampala
Kate the chaser- Australian, Perth
Rouge- Canadian, Alberta
Wilson the basher- welsh, Conwy
X-virus- American, New Jersey
Lazari- Ukrainian, Kharkiv Oblast
Kaidy- French, Corsica
Stripes- American, Alabama
Senora- Spanish, Girona
Nina the killer- Mexican, American, Louisiana
Puppeteer- American, Mexican, California
Zachary- American, Colorado
Rosemary- American, Maine
Emra- Italian, American, sicilia
Bloody painter- Japanese, Chinese, Guangdong
Suicide Sadie- British, London
Judge angel- Chinese, Filipino, Guangdong
Nurse Ann- Taiwanese, taipei
Randy- Spanish, Álava
Sully- Indian, Tamil Nadu
Keith- Australian, Queensland
Troy- American, Louisiana
Dollmaker- Russian, Moscow
Svetlana- Russian, Siberia
Vicky genocidal- Canadian, Ontario
Hannah the killer- German, American, East Berlin
Lily Kennett- Ireland, Connacht
Hung iris- American, Illinois
Lifeless Lucy- British, Yorkshire
Legless Eliza- Portuguese, Évora
Mucky Child- American, Colorado
Lacy Morgan- British, American, Arizona
Asylum Nancy- American, Maine
Chris the revenant- German, American, Hessen
Monday child- Ukrainian, poltava
Laughing Jill- British, London
Laughing Jack- British, London
Toby- German, Bavaria
Lurking Lyra- German, Bavaria
Killing Kate- Costa Rican, Alajuela
Lost Silver- Japanese, Hokkaido
Cata the Killer- Polish, Lodz
Rotten Abigail- American, North Carolina
The Hare- American, Arizona
The Doll- Mexican, Hidalgo
Raven- French, Île-de
Anna schurks- Romanian, Bucharest
Weeping forest- Puerto Rico, Adjuntas
Nightmare Ally- German, East Berlin
Red Death- German, Greek, Saxony
Gas mask maid- El Salvador, Cuscatlan
Tim- American, Georgia
Jessica- American, polish, Arizona
Taylor- Native American, Maine
Ellie- Japanese, Canadian, Chubu
Labrador- Romanian, Arad
Moth boy- American, Louisiana
Starved angel- Irish, American, Texas
Sketcher- Indonesian, Russian, Ural
Sarah Erickson- Chinese, Canadian, Nova Scotia
Hannya- Japanese, Tokyo
Rosie- British. Coventry
Hunter the proxy- American, Texas
Doctor Irina- British, Devon
Deborah- American, California
Lucy the cannibal- American, Ohio
Andie Rosslyn- American, Iowa
#lulu#eyeless jack#jane the killer#ben drowned#Liu#headcanons#jeff the killer#creepypasta#nationalities#killing kate#vailly#cata the killer#lost silver#lurking Lyra#laughing jack#laughing jill#asylum nancy#lifeless lucy#hannah the killer#vicky genocidal#nurse ann#roadwalker#sally dawn#lazari creepypasta
30 notes
·
View notes