#annalen der physik
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Events 3.20 (before 1950)
1206 – Michael IV Autoreianos is appointed Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople. 1600 – The Linköping Bloodbath takes place on Maundy Thursday in Linköping, Sweden: five Swedish noblemen are publicly beheaded in the aftermath of the War against Sigismund (1598–1599). 1602 – The Dutch East India Company is established. 1616 – Sir Walter Raleigh is freed from the Tower of London after 13 years of imprisonment. 1760 – The Great Boston Fire of 1760 destroys 349 buildings. 1815 – After escaping from Elba, Napoleon enters Paris with a regular army of 140,000 and a volunteer force of around 200,000, beginning his "Hundred Days" rule. 1848 – German revolutions of 1848–49: King Ludwig I of Bavaria abdicates. 1852 – Harriet Beecher Stowe's Uncle Tom's Cabin is published. 1854 – The Republican Party of the United States is organized in Ripon, Wisconsin, US. 1861 – An earthquake destroys Mendoza, Argentina. 1883 – The Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property is signed. 1888 – The premiere of the very first Romani language operetta is staged in Moscow, Russia. 1890 – Chancellor of the German Empire Otto von Bismarck is dismissed by Emperor Wilhelm II. 1896 – With the approval of Emperor Guangxu, the Qing dynasty post office is opened, marking the beginning of a postal service in China. 1903 – The first of a series of auctions of sheep farming land in southern Patagonia takes place impacting established settlers. 1913 – Sung Chiao-jen, a founder of the Chinese Nationalist Party, is wounded in an assassination attempt and dies 2 days later. 1916 – Albert Einstein submits his paper, "The Foundation of the General Theory of Relativity", which establishes his general theory of relativity, to the journal Annalen der Physik. 1921 – The Upper Silesia plebiscite, mandated by the Versailles Treaty to determine a section of the border between Weimar Germany and Poland, is held. 1922 – The USS Langley is commissioned as the first United States Navy aircraft carrier. 1923 – The Arts Club of Chicago hosts the opening of Pablo Picasso's first United States showing, entitled Original Drawings by Pablo Picasso, becoming an early proponent of modern art in the United States. 1926 – Chiang Kai-shek initiates a purge of communist elements within the National Revolutionary Army in Guangzhou. 1933 – Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler ordered the creation of Dachau concentration camp as Chief of Police of Munich and appointed Theodor Eicke as the camp commandant. 1942 – World War II: General Douglas MacArthur, at Terowie, South Australia, makes his famous speech regarding the fall of the Philippines, in which he says: "I came out of Bataan and I shall return". 1948 – With a Musicians Union ban lifted, the first telecasts of classical music in the United States, under Eugene Ormandy and Arturo Toscanini, are given on CBS and NBC.
0 notes
Text
youtube
*Take That Newtonian Physics!
Today in History, June 30, 1905 – #AlbertEinstein sends the article #OntheElectrodynamicsof #MovingBodies, in which he introduces special relativity, for publication in Annalen der Physik.
( https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special_relativity)
0 notes
Text
Materia e antimateria repulsive e energia oscura

Arrampicandosi sulle cime dello spaziotempo. Con l'antimateria è possibile fare a meno dell'energia oscura? I risultati ottenuti l’anno scorso al Cern con l’esperimento Alpha-g hanno dimostrato l’esistenza di attrazione gravitazionale fra materia e antimateria, mettendo così in crisi le teorie sull’antigravità. Ma uno studio pubblicato su Annalen der Physik da uno scienziato dell’Inaf, Massimo Villata, prova a concedere un’altra chance alla gravità repulsiva ipotizzando uno spaziotempo invertito.
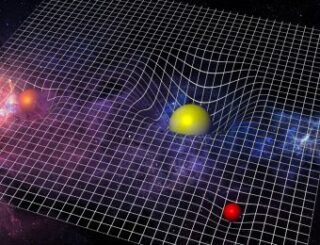
In primo piano, rappresentazione della curvatura dello spaziotempo in corrispondenza di grandi masse. Crediti: Esa/C. Carreau Complici gli exhibit di tanti festival scientifici, siamo ormai abituati a immaginare lo spaziotempo come un telo elastico punteggiato qua e là da avvallamenti, depressioni e pozzi, laddove un buco nero o qualche altro oggetto massiccio – interpretato di solito da una pesante biglia – lo affossa. Ma potrebbero esserci anche innalzamenti, nel tessuto dello spaziotempo? Picchi, rilievi e montagne? Forse sì, o almeno questa è l’opinione di chi ritiene che la gravità – un effetto, o meglio, una manifestazione, secondo la relatività generale, della curvatura dello spaziotempo – abbia anche una controparte repulsiva, una sorta di antigravità. Chi la eserciterebbe, questa repulsione? Cosa sarebbe in grado di “sollevarlo”, lo spaziotempo, invece d’affossarlo? Secondo alcuni fisici teorici, ad avere questa controintuitiva proprietà sarebbe qualcosa di ben noto e – per quanto non in abbondanza – presente ovunque attorno a noi: l’antimateria. E come funzionerebbe? Per rimanere nell’analogia del telo elastico, immaginiamo di poter guardare “da sotto” per vedere come apparirebbe l’altro lato del telo: in corrispondenza degli affossamenti vedremmo innalzamenti. E viceversa: laddove nello spaziotempo invertito un “anti buco nero” crea una profonda depressione, ecco che sul nostro versante d’universo ci ritroveremmo un picco. Vale a dire, una regione di spaziotempo che respinge tutto ciò che le si avvicina. Va detto che si tratta di ipotesi confinate nel regno della matematica (almeno per ora), ma se le cose stessero effettivamente così materia e antimateria potrebbero non subire una reciproca attrazione gravitazionale, anzi: si respingerebbero. Con alcuni gradevoli corollari. Per esempio, potremmo forse fare a meno dell’energia oscura, perché magari basterebbe questa repulsione a spiegare l’espansione dell’universo. E non avremmo più l’imbarazzante problema di dover giustificare la scomparsa dell’antimateria dopo il big bang, visto che si potrebbe ancora trovare in qualche regione del cosmo. Meraviglioso, no? C’è però almeno un problema: i dati sperimentali. Gli esperimenti condotti l’anno scorso al Cern dalla collaborazione Alpha, osservando il comportamento di atomi di anti-idrogeno in caduta libera, hanno dimostrato che materia e antimateria si attraggono, come previsto dal principio di equivalenza, e che l’antimateria è soggetta alla stessa accelerazione gravitazionale – o quasi – della materia ordinaria.
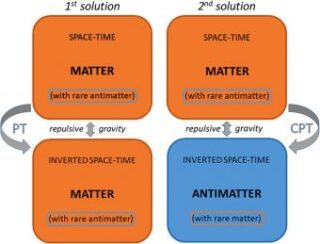
Rappresentazione schematica delle due soluzioni proposte da Villata al conflitto tra la gravità CPT e i risultati dell’esperimento Alpha-g. Nel primo caso (a sinistra), la gravità repulsiva su larga scala sarebbe data dall’interazione con la materia PT-trasformata (e non con l’antimateria) in un universo dominato dalla materia. Nel secondo caso (a destra), l’intera CPT si conserva, dando luogo a una gravità repulsiva materia-antimateria. Ma la minuscola quantità di antimateria immersa nel nostro spazio-tempo non può essere PT-trasformata. Crediti: M. Villata, Annalen der Physik, 2024 Ma c’è chi non si dà per vinto: Massimo Villata, ricercatore associato all’Inaf di Torino da tempo impegnato nelle ricerche sulla gravità repulsiva, ha pubblicato lo scorso aprile su Annalen der Physik – la stessa rivista sulla quale uscirono nel 1905 i quattro articoli storici di Einstein, e nel 1916 quello celebre sulla relatività generale – uno studio, disponibile in open access, nel quale propone due soluzioni (vedi schema a fianco) per salvare l’ipotesi della gravità repulsiva nonostante i risultati ottenuti al Cern. Com’è possibile? I fisici della collaborazione Alpha avrebbero forse commesso qualche errore? «No, non credo che ci siano errori sperimentali», dice Villata a Media Inaf, «e quindi qui sulla Terra abbiamo attrazione tra una materia dominante e le minuscole briciole di antimateria che riusciamo a produrre. Posso sinceramente dire che me lo aspettavo, perché quell’esigua quantità di antimateria non può invertire il proprio spaziotempo, immersa com’è nel flusso temporale della pervasiva materia che la circonda. Sarebbe come gettare controcorrente una fogliolina in un fiume impetuoso e pretendere che possa risalire la corrente. Ma quel valore che trovano di 0.75 g (invece di 1 g), sebbene abbia una grande incertezza, potrebbe essere un indizio del tentativo della foglia di opporsi al fluire del fiume». Se qui sulla Terra non possiamo apprezzarne gli effetti, dove bisognerebbe dunque andare, per misurare sperimentalmente l’antigravità? In quale luogo dell’universo si nasconderebbe, tutta questa antimateria respingente? La risposta che s’incontra nell’articolo di Villata è quasi ovvia: se cerchiamo qualcosa che respinge la materia, conviene andare a vedere anzitutto là dove la materia non c’è, o quanto meno scarseggia. Luoghi del genere nell’universo esistono: si chiamano vuoti cosmici. «Sono regioni ben note ad astronomi e cosmologi, immense “bolle” nell’universo dove la materia è quasi assente», spiega Villata. «E manifestano un notevole effetto repulsivo sulle galassie che le circondano. Sarebbero “isole” di spaziotempo invertito, alternate nel cosmo alle isole di materia occupate dagli ammassi di galassie». Poiché dei vuoti cosmici, per lo meno di quelli più grandi dell’universo visibile, non solo sappiamo che esistono ma ne conosciamo anche la posizione in cielo, viene a questo punto naturale chiedersi perché non siamo mai riusciti a osservarla, tutta questa antimateria teoricamente in essi presente. «Non la vediamo», suggerisce Villata, «proprio perché emetterebbe radiazione cosiddetta “anticipata” (cioè l’altra soluzione delle equazioni di Maxwell nel vuoto, rispetto a quella della radiazione che ben conosciamo), per la quale non abbiamo (ancora) strumenti capaci di rivelarla. Basti pensare che i fotoni emessi dall’antimateria verrebbero nel nostro spaziotempo “percepiti” come fotoni emessi dal rivelatore per raggiungere l’anti-stella che li ha prodotti, cioè con un cammino spaziotemporale invertito. Quindi, là dove vediamo il buio nell’universo non sappiamo per ora dire se c’è il vuoto oppure antimateria». Per saperne di più: Leggi su Annalen der Physik l’articolo “Antimatter Gravity and the Results of the ALPHA-g Experiment”, di Massimo Villata Read the full article
#antigravità#antimateria#energiaoscura#esperimentoAlpha-g#gravitàrepulsiva#SimmetriaCPT#spaziotempo#vuoticosmici
0 notes
Text
Now
All of the above, all at once, never ending. If it’s not physical pain, its sensory pain. Everything hurts, all of the time. Not some of the time or once in a blue moon, all of the time. Over time, galaxies will sink into darkness and solitude, and the universe may become an empty space filled only with dark energy, causing exponential expansion. The existential HORROR that is existence itself and consciousness itself is what and is the only thing that actually scares me. Everything else is bullshit (laughing out loud). Existential horror often revolves around the profound realization of the individual's insignificance in the vastness of the universe. In this context, the concept of ‘NOW’ can be seen as a fleeting moment of existence, a transient blip in the cosmic timeline. The terror arises from the awareness that this momentary ‘NOW’ is all we have, and it is constantly slipping away into the abyss of the past, never to be reclaimed but we often revisit via our memory of it, which can also not be correct all of the time. Can we even depend on our memory of the past as it actually happened?
Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity:
Published, scientific journal Annalen der Physik (Annals of Physics), June 1905.
It's all about the present moment, or is it? Is 'now' just some big cosmic joke? Einstein's theory of special relativity is all about the reality of time. It's all about the question whether the present moment, this 'now,' which we experience ourselves, whether this is of fundamental importance. Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity introduces a fascinating dimension to the concept of ‘now’ by revealing the relativity of time. According to Einstein's theory, time is not absolute, but is instead relative to the observer's frame of reference and the speed at which they are moving. In this context, the experience of ‘now’ becomes subjective and dependent on one's position and velocity in spacetime. Nihilism says it has no fundamental importance, nor does anything have fundamental importance. Nihilism, on the other hand, challenges the inherent meaning and value attributed to existence. From a nihilistic perspective, the concept of ‘now’ may be viewed as devoid of any ‘real significance.’ It is merely a temporary state in a universe devoid of ultimate purpose or meaning. This nihilistic interpretation of ‘now’ can evoke a sense of existentialism.
Resistance is FUTILE…
The impossibility to define one notion of 'now' that we all agree on. ‘NOW’ as in the moment of time that happens right 'now.' Not say, when the light of an object actually hits your eyes. It would be like getting shot and as you fall down from being shot you then hear the sound. The bullet is traveling faster than the sound it created when fired. The moment the bullet is fired is the actual moment of ‘NOW’ from the bullet’s point of view. This phenomena is super important because it tells us that fundamentally this experience of ‘NOW’ that we all share is meaningless. I spend a lot of energy thinking about time, consciousness, how humans fit into it all. How our human consciousness is bound by the flow of time in one direction, but change the variable of the human experience and that perspective shifts. The frame of reference shifts… In our current understanding of science there are only two forces in the universe that morph, effect the flow of time. One is the supermassive gravity of a black hole and the second is speed. The faster you travel or come closer to the speed of light, the flow of time outside of that point of view slows down to the observer. We know this as ‘time dilation.’
The concept of ‘NOW’ in philosophical terms intersects with existential horror, nihilism, and Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity in intriguing ways. Bringing these perspectives together, the concept of ‘NOW’ becomes a paradoxical blend of existential horror, nihilistic indifference, and relativistic subjectivity. It is simultaneously a fleeting moment of existential dread, a void of meaninglessness, and a relativistic illusion shaped by our individual perspectives and experiences. The philosophical exploration of ‘NOW’ forces us to confront the temporary nature of existence, the absence of inherent meaning, and the subjective nature of our perception of time. It invites us to grapple with the existential anxiety of our fleeting existence while acknowledging the profound implications of relativity on our understanding of reality.
All of that, has brought me to this thinking that human consciousness is absolutely something more than what we currently understand. Not even religion can explain this in proper context. It tries though, damn does it ever. Ah, behold the grand spectacle of the universe, that vast landfill of existence. Rumor-Control says, it exists even when we're not looking. Mind-blowing, right? Probably exists... or maybe not, who/what am I to say? Humans, those remarkable trash-bags, have this nifty little organic app called "the brain" that we hardly ever use anymore. It's a miracle of biology. It does this fantastic job of snatching up information from the outside world, churning it around, and POW! It conjures up an image of what's happening beyond your cranium.
Ala, REALITY…
I mean, it's practically magic, but with neurons and synapses and other things that pop in and out of reality at random. The next big question is –is reality even real???
Now by David-Angelo Mineo 4/19/2024 893 Words
#writersnetwork#writer#blogger#writerscorner#thesoul#soul#now#past#present#science#religion#philosphy#consciousness#identity#morality#freewill#physics#conservationofmassandenergy#understanding#frameofreference#blackhole#spacetime#grandfatherparadox#paradox#time#specialrelativity#intentionality#existentialism#nihilism#speedoflight
0 notes
Text




IMAGENES Y DATOS INTERESANTES DEL DIA 27 DE SEPTIEMBRE DE 2023
Día Mundial del Turismo, Día Europeo del Donante de Médula Ósea, Día Mundial de la Leche Escolar, Año Internacional del Mijo y Año Internacional del Diálogo como Garantía de Paz.
Santa Fidencia, San Aurelio, Santa Neomisia y San Vicente de Paúl.
Tal día como hoy en el año 1290: Ocurre en Hebei (China) un terremoto de magnitud 6,7 en la escala sismológica de Richter, causando más de 100.000 muertos y convertirse en uno de los más mortíferos entre los años 1.000 y 2.000.
En 1590: Muere el papa Urbano VII en Roma (Italia), a los 13 días de haber sido elegido papa, siendo el papado más corto de la historia.
En 1905: Llega al diario científico 'Annalen der Physik' el tratado de Albert Einstein '¿Depende la inercia de un cuerpo de su contenido de energía?', en la que aparece la famosa ecuación E=mc².
En 1908: Se fabrica la primera unidad del automóvil Modelo T de la marca Ford, en la Planta Piquette de Detroit (Estados Unidos).
En 1940: Se firma el Pacto del Eje, o Pacto Tripartito, en Berlín (Alemania) por Saburo Kurusu, Adolf Hitler y Galeazzo Ciano, representando al Imperio de Japón, la Alemania nazi y el Reino de Italia.
En 1956: El capitán estadounidense Milburn G. Apt se convierte en el primer hombre de la historia en superar la velocidad mach 3 pilotando un avión Bell X-2, pero poco después perdió el control y murió al estrellarse.
En 1964: La Comisión Warren publica en Washington (Estados Unidos) el informe de la investigación sobre el asesinato del presidente John F. Kennedy, concluyendo que Lee Harvey Oswald fue el único responsable del asesinato ocurrido en Dallas.
En 1986: Cliff Burton, bajista del grupo de trash metal Metallica, muere en accidente de tráfico al salir despedido del autobús en el que viajaba. En Kronoberg (Suecia).
En 1996: Tras dos años de guerra, la milicia integrista islámica suní de los talibanes logra hacerse con la ciudad de Kabul, capital de Afganistán.
En 1998: Comienza a funcionar el motor de búsqueda de Internet Google, en Estados Unidos.
1 note
·
View note
Text
On This Day In History
November 21st, 1905: Albert Einstein's paper that leads to the mass–energy equivalence formula, E = mc², is published in the journal Annalen der Physik.
#history#world history#november#on this day#on this date#albert einstein#e=mc²#e=mc2#annalen der physik#relativity#physics#physblr#mathblr#stemblr#edublr#studyblr
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bir cismin eylemsizliği enerji içeriğine bağlı mıdır?
Bugün(21 Kasım) Einstein'ın ünlü E=mc² formülünü ortaya koyduğu "Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy-Content?" başlıklı makalesi Annalen der Physik dergisinde yayımlandı, 112 yıl önce.
Makalenin hafif özeti şöyledir;
Einstein, klasik kinetik ve potansiyel enerjilerinden ayrı, çok büyük bir parçacığın bir enerjiye, "durgun enerji", sahip olduğunu gösterdiğinden eşitlik denkleminin çok önemli olduğunu düşünmüştür. Makale, James Clerk Maxwell ile Heinrich Rudolf Hertz’in incelemelerine ve ayrıca, Einstein’ın söylediği gibi, görelilik aksiyomlarına dayanmaktadır. Önceki incelemelerin sonuçları, burada çıkarsama yapılması gereken çok ilginç sonuçlara yol açmıştır. Önceki inceleme "Maxwell-Hertz’in boşluk denklemleri ile birlikte Maxwell’in elektromanyetik boşluk enerjisi ifadesine..." dayanmaktaydı. Fiziksel sistemlerin durumlarını değiştiren yasalar, birbirine göreceli paralel ötelenmenin tekbiçimli hareketi içindeki iki koordinat sisteminde alternatiften bağımsızdır ve bu durum değişiklikleri (görelilik prensibi) olarak adlandırılır. Denklem eylemsiz cisim enerjisinin (E), kütlesi (m) çarpı ışık hızı (c) karesi, veya E= mc² olduğunu öngörür. Eğer bir cisim L enerjisini radyasyon biçiminde dışarıya verirse, kütlesi L/c² kadar eksilir. Cisimden çıkan enerjinin radyasyon enerjisi haline geldiği gerçeği hiçbir fark yaratmaz ve böylece daha genel bir sonuca varırız, Bir cismin kütlesi enerji içeriğinin bir ölçüsüdür; enerji L kadar değişirse, kütle aynı şekilde L/9 x 10²º kadar değişir, enerji erk olarak ve kütle ise gram olarak ölçülür. Eğer teori gerçeklere karşılık geliyorsa, radyasyon yayan ve emen cisimler arasında eylemsizlik aktarır.
Kütle-enerji ilişkisi nükleer reaksiyonlarla ne kadar enerjinin açığa çıkacağı veya harcanacağını tahmin etmede kullanılabilir; tüm bileşenlerin kütlesi ve tüm ürünlerin kütlesi ölçülür ve ikisi arasındaki fark c² ile çarpılır. Sonuç genellikle ışık veya ısı biçiminde, ne kadar enerjinin açığa çıkacağı veya harcanacağını gösterir. Belli nükleer reaksiyonlara uygulandığında, denklem kimyasal patlayıcı yanmalarında olduğundan çok daha fazla, inanılmaz büyük miktarda ve kütle farkının ölçülmesi çok zor olan, enerjinin açığa çıkacağını gösterir. Bu, neden nükleer silahların bu kadar büyük miktarlarda enerji ürettiğini açıklar zira nükleer füzyon sırasında bağlanma enerjisini açığa çıkartırlar ve ayrıca atom altı kütlenin büyük bir kısmını da enerjiye çevirirler.
Makalenin çevirisini aşağıya bırakıyorum;
Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy Content? | 172-174 arası
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I want to publish in the Annalen der Physik.
#physics student#physics studyblr#physics#astrophysics#astronomy#astronomy student#new studyblr#studyblr#university#study blog#student#einstein#genius#woman in stem#girls in stem#stemblog
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
November History
November 23 1644 – John Milton published Areopagitica, a pamphlet decrying censorship.
1874 – A paper by Ferdinand Braun was published in the Annalen der Physik und Chemie describing his discovery of the electrical rectifier effect, the first semiconductor.
1889 – Debut of the first jukebox, the ‘nickel-in-the-slot phonograph’, at the Palais Royale Saloon, San Francisco. It could only be loaded with one cylinder (song) at a time.
1897 – The patent (#594,114) for a hand-cranked pencil sharpener was granted to John Lee Love of Fall River, Massachusetts.
1924 – Edwin Hubble’s discovery that the Andromeda Nebula was actually another island universe (galaxy) far outside of our own was first published in The New York Times.
1936 – Originally started in 1883, Life magazine was shifted into a picture magazine by Time magazine’s Henry R Luce. Prior to that is was humor and general interest magazine.
1963 – The first episode of the BBC’s Doctor Who premiered. ‘Doctor Who’ is not his name – we don’t know it. He is simply ‘The Doctor.’
1969 – The Rolling Stones made their final appearance on The Ed Sullivan Show, singing featured the songs “Gimme Shelter,” “Love In Vain” and “Honky Tonk Woman.”
1975 – NBC joined Willy Wonka & the Chocolate Factory (in progress) at the conclusion of an overtime NFL game. Kids missed about 45 minutes of the film.
1980 (Earthquake) Conza, Italy – estimated 3,000 people were killed.
1982 – Terms of Endearment was released in US theaters.
1991 – Freddie Mercury (September 1946 – 24 November 1991) confirmed that he has AIDS the day before he died.
1992 – The first ‘smartphone’, the IBM Simon, was introduced at COMDEX in Las Vegas, Nevada.
1993 – The Food Network made its debut.
2002 – The Miss World contest was forced to relocate to London from Abuja after riots by Islamic extremists opposed to the contest left more than 100 people dead and hundreds injured in Nigeria.
2015 – Blue Origin’s New Shepard space vehicle became the first rocket to successfully fly to space and then return to Earth for a controlled, vertical landing.
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
Today in History, June 30, 1905 – Albert Einstein sends the article On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies, in which he introduces special relativity, for publication in Annalen der Physik. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special_relativity) *Take That Newtonian Physics!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Events 11.21 (before 1950)
164 BCE – Judas Maccabeus, son of Mattathias of the Hasmonean family, rededicates the Temple in Jerusalem, an event that is commemorated each year by the festival of Hanukkah. (25 Kislev 3597 in the Hebrew calendar.) 235 – Pope Anterus succeeds Pontian as the nineteenth pope. 1386 – Timur of Samarkand captures and sacks the Georgian capital of Tbilisi, taking King Bagrat V of Georgia captive. 1620 – Plymouth Colony settlers sign the Mayflower Compact (November 11, O.S.) 1676 – The Danish astronomer Ole Rømer presents the first quantitative measurements of the speed of light. 1783 – In Paris, Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier and François Laurent d'Arlandes make the first untethered hot air balloon flight. 1789 – North Carolina ratifies the United States Constitution and is admitted as the 12th U.S. state. 1851 – Mutineers take control of the Chilean penal colony of Punta Arenas in the Strait of Magellan. 1861 – American Civil War: Confederate President Jefferson Davis appoints Judah Benjamin Secretary of War. 1877 – Thomas Edison announces his invention of the phonograph, a machine that can record and play sound. 1894 – Port Arthur, China, falls to the Japanese, a decisive victory of the First Sino-Japanese War; Japanese troops are accused of massacring the remaining inhabitants. 1900 – Claude Monet's paintings shown at Gallery Durand-Ruel in Paris. 1902 – The Philadelphia Football Athletics defeat the Kanaweola Athletic Club of Elmira, New York, 39–0, in the first-ever professional American football night game. 1905 – Albert Einstein's paper that leads to the mass–energy equivalence formula, E = mc², is published in the journal Annalen der Physik. 1910 – Sailors on board Brazil's warships including the Minas Gerais, São Paulo, and Bahia, violently rebel in what is now known as the Revolta da Chibata (Revolt of the Lash). 1916 – Mines from SM U-73 sink HMHS Britannic, the largest ship lost in the First World War. 1918 – The Flag of Estonia, previously used by pro-independence activists, is formally adopted as the national flag of the Republic of Estonia. 1918 – The Parliament (Qualification of Women) Act 1918 is passed, allowing women to stand for Parliament in the UK. 1918 – A pogrom takes place in Lwów (now Lviv); over three days, at least 50 Jews and 270 Ukrainian Christians are killed by Poles. 1920 – Irish War of Independence: On "Bloody Sunday" in Dublin, the Irish Republican Army (IRA) assassinated a group of British Intelligence agents, and British forces killed 14 civilians at a Gaelic football match at Croke Park. 1922 – Rebecca Latimer Felton of Georgia takes the oath of office, becoming the first female United States Senator. 1927 – Columbine Mine massacre: Striking coal miners are allegedly attacked with machine guns by a detachment of state police dressed in civilian clothes. 1942 – The completion of the Alaska Highway (also known as the Alcan Highway) is celebrated (however, the highway is not usable by standard road vehicles until 1943). 1944 – World War II: American submarine USS Sealion sinks the Japanese battleship Kongō and Japanese destroyer Urakaze in the Formosa Strait. 1945 – The United Auto Workers strike 92 General Motors plants in 50 cities to back up worker demands for a 30-percent raise.
0 notes
Text
youtube
*Take That Newtonian Physics!
Today in History, June 30, 1905 – #AlbertEinstein sends the article #OntheElectrodynamicsof #MovingBodies, in which he introduces special relativity, for publication in Annalen der Physik.
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special_relativity)
0 notes
Text
Il dimensionalmente corretto nella formula E=mc²
Ecco perché la velocità della luce è al quadrato. Tutti la conoscono, in pochi sanno spiegarla. Ecco cosa significa che la velocità della luce è al quadrato, nella relatività di Einstein. E=mc², una delle formule più famose al mondo e che in un certo senso ha cambiato il corso della storia. Pensate che Einstein ci arrivò in un saggio di appena 3 paginette pubblicato il 27 settembre del lontano 1905 sugli “Annalen der Physik”. Una piccola nota a margine di un più ampio lavoro che riguardava l’elettrodinamica dei corpi in movimento. Eppure, quella semplice equazione fa ancora girare la testa ai fisici di tutto il mondo. Tanti hanno provato a smontarla, attraverso esperimenti e dimostrazioni. Nessuno c’è riuscito. Ogni singola volta che si prova a dimostrare che Einstein avesse torto, si fa un buco nell’acqua. Tutt’ora scienziati di tutto il mondo dimostrano la piena affidabilità di questa formula. In questo articolo ci soffermeremo sul perché la velocità della luce è elevata al quadrato. Relatività, cosa significa che la velocità della luce è al quadrato Spieghiamo innanzitutto cosa significa la formula per intero. E=mc² indica che l’energia e è uguale alla massa m moltiplicata per la velocità della luce c (dal latino, celeritas) elevata al quadrato. Fermiamoci un attimo su questo. Il simbolo c (che Einstein scriveva come V) rappresenta la velocità della luce nel vuoto. Elevarla al quadrato significa moltiplicare la velocità della luce per se stessa. Per capire a fondo il significato di c² bisogna fare riferimento a un sistema coerente di unità di misura per i diversi termini della formula. In sostanza l’equazione doveva essere dimensionalmente corretta. Questo perché le dimensioni fisiche di un’energia sono esattamente quelle di una massa moltiplicata per una velocità al quadrato. Se ben ricordate a scuola ci insegnano che nel sistema internazionale l’energia si misura in joule (J), la massa in chilogrammi (kg) e la velocità in metri al secondo (m/s). Queste tre unità di misura sono coerenti fra di loro, nel senso che 1 J = (1 kg) x (1 m/s)².

Come vi abbiamo già scritto, la velocità della luce nel vuoto vale circa 300 milioni di metri al secondo (o 300mila chilometri al secondo). Se questo valore è già grande di per sé, lo diventa ancora di più quando lo si eleva al quadrato: c² = (3 108 m/s)² = 9 1016 (m/s)². In altre parole, significa che una massa pari a un chilogrammo equivale ad un’energia molto grande, vicina a 1017 joule. Ricapitoliamo: l’energia equivale alla massa, ma con un fattore di amplificazione (c²) che fa sì che anche masse molto piccole possano sprigionare enormi quantità di energia. È così che funzionano le centrali nucleari: lì si può produrre l’energia che servirebbe per un anno ad un’intera città, trasformando la massa in energia in poche centinaia di chilogrammi di uranio. Read the full article
1 note
·
View note
Text
التنمر على اينشتاين 😂👌
هذه صورة من رسالة رفض لطلب الدكتوراه الخاص ب #ألبرت_أينشتاين من جامعة بيرن السويسرية عام 1907.
محتوى الرسالة:
"جامعة بيرن (سيلدرشتراسه 53012 ــ مدينة بيرن)
6 تموز /يونيو 1907 م
عزيزي السيد آينشتاين،
طلب الدكتوراه الخاص بك لم يكتب له النجاح هذه المرة، وهذا ما يجعلك غير مؤهل لنيل منصب أستاذ مشارك.
رغم أنك طرحت نظرية مثيرة للاهتمام في مقالتك التي نشرت في مجلة Annalen der Physik (النشرة الدورية للفيزياء)، إلا أننا نشعر بأن استنتاجاتك المتعلقة بطبيعة الضوء والارتباط المهم بين الزمان والمكان هي متطرفة نوعا ما.
بشكل إجمالي، نحن نجد أن افتراضاتك تنتمي للفن أكثر من كونها تنتمي للفيزياء الحقيقية.
المخلص لكم.
البروفيسور فيلهيلم هاينريش عميد العلوم.

1 note
·
View note
Link
Moreover, the story raises the possibility that Einstein’s gravitational-wave paper with Rosen may have been his only genuine encounter with anonymous peer review. Einstein, who reacted angrily to the referee report, would have been well advised to pay more attention to its criticisms, which proved to be valid.
0 notes
Text
1905: El físico alemán Albert Einstein publica en la revista Annalen der Physik su artículo científico «La inercia de un cuerpo, ¿depende de su contenido energético?», donde revela la relación entre la energía y la masa de un cuerpo. Esto lo llevará a descubrir la fórmula de equivalencia entre masa y energía (E = mc²).
#HoyEnLaHistoria #Efemerides #Historia #Personajes #UnDiaComoHoy #NuestraHistoria #Biografias #Hechos #HechosHistoricos

0 notes