#and microsoft authenticator requires me to verify its me with. a code from microsoft authenticator. which is. impossible.
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
I'm going to kill someone. someone working at microsoft
#oisín.txt#oisín.n#i couldn't remember if i had a 7:30 am meeting this week or next so i got up early#and i didnt have it this week so i thought wow i should sync my work account to my phone#and because its a work account i have to use microsoft authenticator#and microsoft authenticator requires me to verify its me with. a code from microsoft authenticator. which is. impossible.#so i tried troubleshooting and none of the forum suggestions were helpful bc well its a microsoft forum#and ofc all the volunteers were like Ummmm this is extremely rare and its Your fault actually bc weve Never seen this#meanwhile the entire search home page is the same question with zero answers#anyway so they suggest logging a ticket w microsoft#so i start to do that and microsoft sends me to an article about how to use the authenticator that assumes ive successfully logged into it#so i say no this is not helpful take me to a person#and guess what they say#you dont have access clearance to speak to a person#contact your admin (no idea who that would be. if anyone) or log in using MICROSOFT AUTHENTICATOR#i think bill gates should be waterboarded and shit on.#its EIGHT AM
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aol Login Problem 8O5~365~6444 6҉̶̙̳͉̉ͨ͂̏̃̉͜͠͠4̷̡̳̖̆̇͘͟͟͢͝4̷̡̳̖̆̇͘͟͟͢͝4̷̡̳̖̆̇͘͟͟͢͝ eMail Login Problem_Not _Working C A L L - N O W
Original story

What’s wrong with AOL Mail today? Well, AOL Mail is down for many users currently. Users affected by this outage have been taking to social media platforms like Twitter to voice their complaints.
The AOL customer support on Twitter has been actively addressing the complainants. Following are some user reports:
Anyone else having trouble signing into AOL, or is it just my internet service scr***** me over? I keep trying to log into my AOL email and it’s making me go in a fu***** circle.
@aolmail is there a problem with the aol mail? I can’t log in on the web or on my iPad.
— AnastasiaBeaverhouse (@1evilfairydust) May 23, 2019
The AOL mail login issues include authentication error, blank screen during signing in, missing AOL sign in, mailbox loading error in a particular browser, and older AOL Desktop gold. First, try to solve the error in AOL email and fix the missing screen problems. This issues can also be caused because of an invalid password. Try to enter the correct password to fix this problem.
AOL Mail Authentication Problem
The Blerk error 1 message occurs when there is an authentication problem. This issue is mostly due to the incorrect settings of the browser and can be mainly due to an outdated version of the browser. Fix this error by performing the AOL mail authentication problem troubleshooting steps below.
Step 1:First, try to modify the browser settings to fix aol login problems.
Step 2:Configure the settings on Edge and make sure to clear the data on Microsoft edge.
Step 3:Go to More Settings in Microsoft Edge.
Step 4:Now, click Choose What to Clear from the Clear Browsing data to solve AOL mail login issues.
Step 6:Tick the checkbox next to the data types that you want to delete and then choose Clear to fix AOL mail authentication problem.
Step 7:Next, make sure to update the saved bookmark on Safari, Firefox, Chrome, and Edge.
Step 8:Next, try to troubleshoot the Internet Explorer issues.
Step 9:First, try to add AOL to the trusted sites. To do so, click the Tools or Internet option to solve AOL mail authentication problem.
Step 10:Next, click Security tab Trusted Sites Zone Sites.
Step 11:Now, type https://*.aol.com in the Add this website to Zone field to solve aol login problems.
Step 12:Next, check whether the Protected Mode option is enabled, if not, perform the following steps to solve AOL mail login issues.
Step 13:First, click Tools Security tab Internet icon.
Step 14:Now, click the Trusted sites icon Enable Protected Mode. Restart the computer.
Step 15:Next, run the Internet Explorer in No Ad-ons Mode to solve AOL mail authentication problem.
Step 16:First, click the Start button All Programs Accessories System Tools Internet Explorer(No Ad-ons).
AOL Mail Can't Sign In
Most of the sign-in issues are caused by password issues, and this might also result in errors such as blank screens and sign in issues. Make sure to enter the correct password. To troubleshoot this issue, perform the following AOL mail can t sign in guidelines.
Step 1:First, try logging in again. Re-check if you have entered the correct credentials.
Step 2:If you are not able to sign in, try turning it off and then turning it on again.
Step 3:Next, make sure to reset the web settings to solve AOL mail can t sign in.
Step 4:Installing numerous browsers can cause the web settings to alter.
Step 5:Verify whether you have entered the correct password.
Step 6:If you have forgotten the password, make sure to reset the password.
Step 7:Try accessing the AOL mail from a different browser to solve AOL mail login issues, sometimes outdated password can cause this issue.
Step 8:Next, try to erase the browser’s cache and reset the browser to its preceding state.
Step 9:Make sure to enable the Java Applet Scripting.
Step 10:Disable or block the Firewall or the pop-up settings to fix AOL mail can t sign in.
Step 11:Now, try to access the AOL mail after performing all these troubleshooting steps.

AOL Mail Cannot Change Password
Perform the following guidelines to resolve this error.
Step 1:First, try to sign into the AOL account and choose the Logout from All Devices option from the Settings menu.
Step 2:Next, make sure you haven’t sent any contacts trough AOL mail. If you are sending any, contact Email Desktop Gold Support to fix the issue.
Step 3:Check if your credit card has been used without your knowledge. If so, block your account.
Step 4:Try logging into the AOL account after 24 hours.
Step 5:Try changing the password again.
Step 6:If the aol login problems persists, try to change the attached credit card with your account.
How Do I Unblock my AOL Email Account
Step 1:Navigate to the AOL Account Security page.
Step 2:Select the Forget Password option to unblock the AOL email account.
AOL Mail Password Not Working
Step 1:Check if you have pressed the Caps Lock key by mistake while you fix AOL mail login issues. You have to enter the password correctly.
Step 2:You have to update the autofill settings on the web browser. This will save the password when you enter it for the first time.
Step 3:If the problem persists, reset the password.
Step 4:Navigate to the Sign-in Helper option, and select any one of the recovery options.
Step 5:Select the Continue button and then follow the instructions that appear on the screen to reset the password.
How Do I Unblock my AOL Email Account
Step 1:Modify your AOL security question if you do not remember it to avoid aol login problems.
Step 2:Follow the forthcoming steps to change the question. Navigate to the Manage My Account tab available at the top part of the screen.
Step 3:Go to AOL Account Settings menu and select the Account Security Question option.
Step 4:Choose the Change Account Security Question option and fill the necessary details in the Change Account Security Question screen.
Step 5:Click the Save button, and you will be directed to the My Account Overview page.
Step 6:You can also reset your password by obtaining a code on your mobile and then resetting the security question if you are not able to log in.
AOL Mail Not Syncing
Step 1:First, remove the AOL account and add it after a few minutes.
Step 2:Choose the Settings option available in the Calendar app.
Step 3:Select the Manage Accounts option followed by the Delete an Account option.
Step 4:Next, you have to select the AOL account and delete it from your device to solve AOL mail login issues.
Step 5:Add your account after a few minutes and check if the issue has been resolved.
Step 6:Navigate to the Mailbox Sync Settings available under the Settings menu and verify the IMAP Username, Incoming Mail Server, SMTP Outgoing Server Address, Username, and Password.
Step 7:Modify the settings if required in the next step to fix AOL mail not syncing.
Step 8:Allow the apps that you have installed to access the calendar. Select the Privacy option available under the Settings menu.
Step 9:Choose the Calendar option and then click on the slider bar available below the Let Apps Access My Calendar option.
Step 10:Next, change the duration of the Sync period to solve the AOL mail not syncing issue. To do so, choose the Account Settings option available under Settings.
Step 11:Select the AOL Account followed by the AOL Sync Settings option. Modify the duration according to your choice.
Step 12:Check your Antivirus Settings and disable the firewall to rectify this AOL mail not syncing problem.
Step 13:Run the Windows troubleshooter and resolve the issue using the guidelines displayed.
Step 14:Disable the proxy settings in the next step. Select the Network & Internet option available under the Settings menu.
Step 15:Choose the Proxy option from the left panel of the window. Disable all the features available on the next screen.
Step 16:Finally, disable the two-step authentication. Make use of a different email client until the aol login problems is resolved.
Step 17:Uninstall the mail app and install it after a few minutes to resolve this issue.
Step 18:Call the technical experts if the above-stated AOL mail login issues solutions do not rectify the problem.
1 note
·
View note
Text
WHAT NO ONE UNDERSTANDS ABOUT TYPES
Mostly we create wealth for other people in exchange for money, which makes it difficult to tell founders what to aim for. Inductive proofs are wonderfully short. This territory is occupied mostly by individual angel investors—people like Andy Bechtolsheim, who gave Google $100k when they seemed promising but still has some things to figure out and explain exactly what you disagree with something, it's easier to see ugliness than to imagine beauty. Python is a more elegant alternative to Perl, but what we would now call corruption than from commerce. No; he's just doing a kind of learning, based on disasters that have happened to it or others like it. And because they use the latest stuff, they're in a position to discover valuable types of fixable brokenness first. Values are what have types, not variables, and assigning or binding variables means copying pointers, not what they point to. Hard to say exactly, but wherever it is, it is in this case. James Gosling, or the extra leverage in productivity that you can fix for a lot of new work is preferable to a proof that was difficult, but doesn't bid because they can't spare the effort to get verified. Surely that sort of thing. In a project of that size, powerful languages probably start to outweigh the convenience of pre-existing libraries. I was using it to create more.
One is that a lot of situations, but has changed. Then I asked what was the maximum percentage of the acquisition price for the ability to release code immediately, the way things work in most companies software costing up to about $1000 could be bought by individual managers without any additional approvals. But I think it's because humor is related to strength. Any strategy that omits the effort—whether it's expecting a big launch to get you users, or a big partner—is ipso facto suspect. ITA's code, but according to one of their top hackers they use a lot of startup founders than anyone else ever has. Off, quiet. We want to write a universal Lisp function and show that it is.
But if it were merely a fan we were studying, without all the extra baggage that comes from the controversial topic of wealth, no one would have any doubt that the fan was causing the noise. Since it is a recursive solution, a tower on a tower. If there is enough demand for something, technology will make it big if and only if they're launched with sufficient initial velocity. The second reason we tend to be worried, not contented. Technology seems to increase the variation in productivity at faster than linear rates. But they won't install them, or take support calls, or train customers to use them. Work still seemed to require discipline, because only hard problems yielded grand results, and hard problems couldn't literally be fun—fun like playing. That is in fact the most difficult visual medium, because they require your full attention. You'll be doing different things when you're acquiring users a thousand at a time.
So while there may be some things someone has to do, because it isn't happening now. The key to this mystery is to revisit that question, are they really worth 100 of us? So what's the real reason there aren't more Googles? There are two types of startup ideas as scalars. Lisp, or just expand your programming horizons, I would say that writing a properly polymorphic version that behaves like the preceding examples is somewhere between damned awkward and impossible. You have to be aggressive about user acquisition when you're small, you'll probably still be aggressive when you're big. If you make fun of your little brother for coloring people green in his coloring book, your mother is likely to tell you something like you like to work on doesn't mean you have to choose the best alternative. And so it is in other ways more accurate, because when someone is being an asshole it's usually uncertain even in their own mind how much is deliberate. He didn't stay long, but he wouldn't have returned at all if he'd realized Microsoft was going to be slightly influenced by prestige, so if the programmers working for me mysteriously always do, I think. It used to perplex me when I read about it in the beginning, but the most successful startups seem to be unusually smart, and C is a pretty low-level language.
Maybe you can, and then see what they do. Instead of making one $2 million investment, make five $400k investments. At an art school where I once studied, the students wanted most of all to develop a programming language, but what to work on dull stuff, it might be wise to tell them that tediousness is not the best, but merely to explain the forces that generate them. We're not hearing about these languages because people are using them to write Windows apps, but because authenticity is one of the most memorable paintings, especially when you're young. Seventeenth-century England was much like the third world today, the standard misquotation would be spot on. The rich spend their time more like everyone else too. As a child I read a book, and that's why merely reading books doesn't quite feel like work. Only raise the price on an investor you're comfortable with losing, because some will angrily refuse. It seems obvious. Jessica Livingston is. Except you judge intelligence at its best, and wisdom by its average. This problem afflicts not just every era, but in retrospect that too was the optimal path to dominating microcomputer software.
This story often comes to mind—though almost any established art form would do. Some people are lucky enough to know users would need this type of software. If you're surrounded by colleagues who claim to enjoy work that you find contemptible, odds are they're lying to themselves. The only people who will sell to you, the more outliers you lose. Why would they go to extra trouble to get programmers for the same price? But if VCs ask, just point out that a predisposition to intelligence is not the only way to get wealth is by stealing it. I watched it happen to Reddit. Indeed, it may be found necessary, in some cases, for a while at least, that I'm using abstractions that aren't powerful enough—often that I'm generating by hand the expansions of some macro that I need to write. The second reason investors like you more when you've had some success at fundraising is that it was not technology but math, and math doesn't get stale. So what's the real reason there aren't more Googles? If you wanted more wealth, you could make a fortune without stealing it. And certainly smart people can find clever solutions to human problems and intelligence to abstract ones.
If they go out of their way to make existing users super happy, they'll one day have too many to do so much for. Imagine what it would feel to merchants to use our software to make online stores, some said no, but they'd let us make one for them. The trick of maximizing the parts of your job that you like can get you from architecture to product design, but not too easily impressed. That may sound like a bizarre idea, but it's important enough to be mentioned on its own. This was easier to grasp when most people lived on farms, and made many of the adults around them are lying when they say they like what they do. Except you judge intelligence at its best and character at its worst. Nor do we have to teach startups this? The importance of the first things they try is a line drawing of a face. Why did we have to memorize state capitals instead of playing dodgeball?
This was the only kind of work in which problems are presented to you and you have to resort to focus groups, you'll wish you could go over to your users' homes and offices and watch them use your stuff like you did when there were only a handful of them, there are three reasons we treat making money as different: the misleading model of wealth we learn as children; the disreputable way in which, till recently, most fortunes were accumulated; and the worry that great variations in income are somehow bad for society. So you can test equality by comparing a pointer, instead of making them live as if they were consultants building something just for that one user. If you just need to feed data from one Windows app to another, sure, use whatever language everyone else is using. They hear stories about stampedes to invest in startups Y Combinator has funded. This problem afflicts not just every era, but in distinct elements. Open-source software has fewer bugs because it admits the possibility of bugs. Symmetry is unfashionable in some fields now, in reaction to excesses in the past.
#automatically generated text#Markov chains#Paul Graham#Python#Patrick Mooney#authenticity#doubt#ipso#percentage#everyone#variation#day#learning
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is a PKI Certificate? PKI Certificate Explained
What’s better than having a blog on the PKI Certificate? There’s only an ideal cadenced beat of the PKI Certificates and the PKI Infrastructure here in this blog.
For what reason are these PKI Certificates so essential? – PKI certificate explained
No matter, how present-day the web turns into, the open key foundation or the PKI Certificates is an essential component. While surfing through the internet, the trust turns into an extremely imperative factor, especially when there is an instance of advanced certificates.

Authentication is a detonating factor for the parties, they have been given to. Hence its motivation as a cybersecurity and encryption system is truly intimidating. The process is truly required for the assurance of information transmissions between our customers and our server.
You can truly confide in these PKI Certificates because they structure the reason for HTTPS, code signing, email, and record marking.
In the event that you know about the two-factor authentication, then let me disclose to you that these PKI Certs are there for that.
Presently the prologue to the PKI and PKI Certificates… I will state here everything about this trust model and furthermore the various types of PKI Certificates.
Your choice to tap on this site is completely right since it even talks about how a PKI Infrastructure functions.
What is the job of these testament experts in the PKI Infrastructure?
So let me start with the testament authorities. I chose this subject of conversation since you have to realize these substances hold the obligation of giving computerized certificates. They ensure that they are carefully controlled and audited. Even if any little deviation spins around, the best practice is put to the custody.
You need to realize how much these PKI Trust models are reliant on these CAs. I consistently decide to be in the way where everything functions admirably as intended. Hence I am consistent up to picking a confided in a party that has attempted a duty of approving the entities.
You must know about CAs that doesn’t approve elements they simply mess up and separate everything!
So, include the reality in your mind that CAs that host the ability of approving the gatherings being given to is are acceptable decisions of confirmation of PKI Certificates. This is the path by which the sort of PKI Certificate impacts the rigourness of validation. The rigors of approval incorporate a specific limit of legitimizing the issuance.
What are root programs?
Presently some itemizing about the Root Programs….
You can interface the PKI Certificates to the focal point of the PKI Certificate system. Unless the PKI root testaments are finished with the procedure of assortment and organization of the different root programs, their consistency with the authentication specialists is truly not worth it.
Moreover root projects of the Mozilla have great order over severe standardization. The CA or B Forum nearly has less standardization. The four root programs that are of absolute significance at least to me are
Mozilla
Google
Apple
Microsoft
The root store holds the whole duty of gathering any root endorsements which are a piece of the root program. The OS Level takes to think the treatment of these root certificates. All that the programs do is utilizing their own OS Level for making of rules on the root stores.
This alludes to those root stores with whom they are leveraging. Actually root store costs the entire confided in root certificates. The whole assortment that decides to dwell on the gadget is considered. On giving a more intensive look to the collection, we see both the declaration and the root is remembered for the assortment.
What do you have to think about the Root declarations and the Certificate Chains?
After all these, finally the most significant which I should talk about Root Certificates and the Certificate Chain.
There is no other significant advance other than the approval of the substance being issued. The step is performed following the PKI Certificate is given by the CA. What occurs after the completion of the process? A testament is given where you discover a lot of data and a mark the data is totally approved and the mark is a property of the private key.
The believed root has the pleasure of marking a PKI Certificate and consequently that specific PKI Certificate can be labelled as “trusted”. CA is less known to get the mark legitimately from their trusted roots. The explanation behind this is specialized problems. So what does the CAs do?
The middle of the road roots is given by the CA. The believed roots likewise get the chance of applying their signature. The end client and leaf endorsements are then given by the transitional roots.
The different root programs at that point get the greeting of the CA for being incorporated.
The different root stores acknowledge the CA’s s greeting and the root is incorporated.
The procedure of issuance of the middle of the road root happens by the CA. The root testament at that point gets the mark of the private key.
The middle of the road pull is utilized for the issuance of leaf authentications by the CA. The moderate’s private key at that point comes to constrain for the mark.
For what reason is confirmation of the PKI Certificates-a significant advance?
At long last the blog is fragmented except if not managed the verification of PKI Certificates. Handshakes are being depended upon for this procedure by the PKI infrastructure. Thats for taking care of authentication. PKI is regularly engaged with the start of the association or session.
The other gathering is then given the endorsement and the open key through the server end. After a progression of checks is performed by the client, the signature on the declaration finishes its procedure of authentication. It can be viewed as important the procedure of establishment of the halfway SSL Certificates.
Competition of the testament chain happens on the establishment of this middle of the road SSL Certificates on our server. It’s only an introduction of the moderate SSL Certificates close by the leaf authentication.
Which steps are performed by the customer?
This approval of the endorsement is checked by the customer itself. The mark is likewise checked by the client. The mark was finished by the giving middle of the road root. For a fruitful confirmation of the signature, the transitional open key is made into consideration.
Other strides remember validation of the mark for the leaf certificate. Finishing with the checking process, the activity movements to the halfway declaration and its signature. The mark was set during its issuance. The procedure has begun most likely from a moderate or one of the roots in its root store.
To stay aware of the procedure the customer does nothing unique, other than giving the declaration’s open key, even the mark gets verified. The advancement of the procedure proceeds until it came to one of the trusted roots. The end-client endorsement costs being the relative of the confided in roots.
Our last words…
The whole PKI trust model is already. It is embellished with declaration chains and CA hierarchies. So isn’t it really filling its need for verification utilizing computerized testaments and marks?
Presently let me end this blog on a fabulous end by expressing the sorts of open key framework certificates. The PKI Certificates are totally tried different things with the X509 Certificates-everything gets transformed into various key use configurations. The distinctive key utilization design goes up to the accompanying.
– SSL/TLS declarations
– Code marking declarations
– Email marking declarations
– Personal verification testaments
– IoT declarations
0 notes
Text
Let’s Create Our Own Authentication API with Nodejs and GraphQL
Authentication is one of the most challenging tasks for developers just starting with GraphQL. There are a lot of technical considerations, including what ORM would be easy to set up, how to generate secure tokens and hash passwords, and even what HTTP library to use and how to use it.
In this article, we’ll focus on local authentication. It’s perhaps the most popular way of handling authentication in modern websites and does so by requesting the user’s email and password (as opposed to, say, using Google auth.)
Moreover, This article uses Apollo Server 2, JSON Web Tokens (JWT), and Sequelize ORM to build an authentication API with Node.
Handling authentication
As in, a log in system:
Authentication identifies or verifies a user.
Authorization is validating the routes (or parts of the app) the authenticated user can have access to.
The flow for implementing this is:
The user registers using password and email
The user’s credentials are stored in a database
The user is redirected to the login when registration is completed
The user is granted access to specific resources when authenticated
The user’s state is stored in any one of the browser storage mediums (e.g. localStorage, cookies, session) or JWT.
Pre-requisites
Before we dive into the implementation, here are a few things you’ll need to follow along.
Node 6 or higher
Yarn (recommended) or NPM
GraphQL Playground
Basic Knowledge of GraphQL and Node
…an inquisitive mind!
Dependencies
This is a big list, so let’s get into it:
Apollo Server: An open-source GraphQL server that is compatible with any kind of GraphQL client. We won’t be using Express for our server in this project. Instead, we will use the power of Apollo Server to expose our GraphQL API.
bcryptjs: We want to hash the user passwords in our database. That’s why we will use bcrypt. It relies on Web Crypto API‘s getRandomValues interface to obtain secure random numbers.
dotenv: We will use dotenv to load environment variables from our .env file.
jsonwebtoken: Once the user is logged in, each subsequent request will include the JWT, allowing the user to access routes, services, and resources that are permitted with that token. jsonwebtokenwill be used to generate a JWT which will be used to authenticate users.
nodemon: A tool that helps develop Node-based applications by automatically restarting the node application when changes in the directory are detected. We don’t want to be closing and starting the server every time there’s a change in our code. Nodemon inspects changes every time in our app and automatically restarts the server.
mysql2: An SQL client for Node. We need it connect to our SQL server so we can run migrations.
sequelize: Sequelize is a promise-based Node ORM for Postgres, MySQL, MariaDB, SQLite and Microsoft SQL Server. We will use Sequelize to automatically generate our migrations and models.
sequelize cli: We will use Sequelize CLI to run Sequelize commands. Install it globally with yarn add --global sequelize-cli in the terminal.
Setup directory structure and dev environment
Let’s create a brand new project. Create a new folder and this inside of it:
yarn init -y
The -y flag indicates we are selecting yes to all the yarn init questions and using the defaults.
We should also put a package.json file in the folder, so let’s install the project dependencies:
yarn add apollo-server bcrpytjs dotenv jsonwebtoken nodemon sequelize sqlite3
Next, let’s add Babeto our development environment:
yarn add babel-cli babel-preset-env babel-preset-stage-0 --dev
Now, let’s configure Babel. Run touch .babelrc in the terminal. That creates and opens a Babel config file and, in it, we’ll add this:
{ "presets": ["env", "stage-0"] }
It would also be nice if our server starts up and migrates data as well. We can automate that by updating package.json with this:
"scripts": { "migrate": " sequelize db:migrate", "dev": "nodemon src/server --exec babel-node -e js", "start": "node src/server", "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" },
Here’s our package.json file in its entirety at this point:
{ "name": "graphql-auth", "version": "1.0.0", "main": "index.js", "scripts": { "migrate": " sequelize db:migrate", "dev": "nodemon src/server --exec babel-node -e js", "start": "node src/server", "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" }, "dependencies": { "apollo-server": "^2.17.0", "bcryptjs": "^2.4.3", "dotenv": "^8.2.0", "jsonwebtoken": "^8.5.1", "nodemon": "^2.0.4", "sequelize": "^6.3.5", "sqlite3": "^5.0.0" }, "devDependencies": { "babel-cli": "^6.26.0", "babel-preset-env": "^1.7.0", "babel-preset-stage-0": "^6.24.1" } }
Now that our development environment is set up, let’s turn to the database where we’ll be storing things.
Database setup
We will be using MySQL as our database and Sequelize ORM for our relationships. Run sequelize init (assuming you installed it globally earlier). The command should create three folders: /config /models and /migrations. At this point, our project directory structure is shaping up.
Let’s configure our database. First, create a .env file in the project root directory and paste this:
NODE_ENV=development DB_HOST=localhost DB_USERNAME= DB_PASSWORD= DB_NAME=
Then go to the /config folder we just created and rename the config.json file in there to config.js. Then, drop this code in there:
require('dotenv').config() const dbDetails = { username: process.env.DB_USERNAME, password: process.env.DB_PASSWORD, database: process.env.DB_NAME, host: process.env.DB_HOST, dialect: 'mysql' } module.exports = { development: dbDetails, production: dbDetails }
Here we are reading the database details we set in our .env file. process.env is a global variable injected by Node and it’s used to represent the current state of the system environment.
Let’s update our database details with the appropriate data. Open the SQL database and create a table called graphql_auth. I use Laragon as my local server and phpmyadmin to manage database tables.
What ever you use, we’ll want to update the .env file with the latest information:
NODE_ENV=development DB_HOST=localhost DB_USERNAME=graphql_auth DB_PASSWORD= DB_NAME=<your_db_username_here>
Let’s configure Sequelize. Create a .sequelizerc file in the project’s root and paste this:
const path = require('path')
module.exports = { config: path.resolve('config', 'config.js') }
Now let’s integrate our config into the models. Go to the index.js in the /models folder and edit the config variable.
const config = require(__dirname + '/../../config/config.js')[env]
Finally, let’s write our model. For this project, we need a User model. Let’s use Sequelize to auto-generate the model. Here’s what we need to run in the terminal to set that up:
sequelize model:generate --name User --attributes username:string,email:string,password:string
Let’s edit the model that creates for us. Go to user.js in the /models folder and paste this:
'use strict'; module.exports = (sequelize, DataTypes) => { const User = sequelize.define('User', { username: { type: DataTypes.STRING, }, email: { type: DataTypes.STRING, }, password: { type: DataTypes.STRING, } }, {}); return User; };
Here, we created attributes and fields for username, email and password. Let’s run a migration to keep track of changes in our schema:
yarn migrate
Let’s now write the schema and resolvers.
Integrate schema and resolvers with the GraphQL server
In this section, we’ll define our schema, write resolver functions and expose them on our server.
The schema
In the src folder, create a new folder called /schema and create a file called schema.js. Paste in the following code:
const { gql } = require('apollo-server') const typeDefs = gql` type User { id: Int! username: String email: String! } type AuthPayload { token: String! user: User! } type Query { user(id: Int!): User allUsers: [User!]! me: User } type Mutation { registerUser(username: String, email: String!, password: String!): AuthPayload! login (email: String!, password: String!): AuthPayload! } ` module.exports = typeDefs
Here we’ve imported graphql-tag from apollo-server. Apollo Server requires wrapping our schema with gql.
The resolvers
In the src folder, create a new folder called /resolvers and create a file in it called resolver.js. Paste in the following code:
const bcrypt = require('bcryptjs') const jsonwebtoken = require('jsonwebtoken') const models = require('../models') require('dotenv').config() const resolvers = { Query: { async me(_, args, { user }) { if(!user) throw new Error('You are not authenticated') return await models.User.findByPk(user.id) }, async user(root, { id }, { user }) { try { if(!user) throw new Error('You are not authenticated!') return models.User.findByPk(id) } catch (error) { throw new Error(error.message) } }, async allUsers(root, args, { user }) { try { if (!user) throw new Error('You are not authenticated!') return models.User.findAll() } catch (error) { throw new Error(error.message) } } }, Mutation: { async registerUser(root, { username, email, password }) { try { const user = await models.User.create({ username, email, password: await bcrypt.hash(password, 10) }) const token = jsonwebtoken.sign( { id: user.id, email: user.email}, process.env.JWT_SECRET, { expiresIn: '1y' } ) return { token, id: user.id, username: user.username, email: user.email, message: "Authentication succesfull" } } catch (error) { throw new Error(error.message) } }, async login(_, { email, password }) { try { const user = await models.User.findOne({ where: { email }}) if (!user) { throw new Error('No user with that email') } const isValid = await bcrypt.compare(password, user.password) if (!isValid) { throw new Error('Incorrect password') } // return jwt const token = jsonwebtoken.sign( { id: user.id, email: user.email}, process.env.JWT_SECRET, { expiresIn: '1d'} ) return { token, user } } catch (error) { throw new Error(error.message) } } },
} module.exports = resolvers
That’s a lot of code, so let’s see what’s happening in there.
First we imported our models, bcrypt and jsonwebtoken, and then initialized our environmental variables.
Next are the resolver functions. In the query resolver, we have three functions (me, user and allUsers):
me query fetches the details of the currently loggedIn user. It accepts a user object as the context argument. The context is used to provide access to our database which is used to load the data for a user by the ID provided as an argument in the query.
user query fetches the details of a user based on their ID. It accepts id as the context argument and a user object.
alluser query returns the details of all the users.
user would be an object if the user state is loggedIn and it would be null, if the user is not. We would create this user in our mutations.
In the mutation resolver, we have two functions (registerUser and loginUser):
registerUser accepts the username, email and password of the user and creates a new row with these fields in our database. It’s important to note that we used the bcryptjs package to hash the users password with bcrypt.hash(password, 10). jsonwebtoken.sign synchronously signs the given payload into a JSON Web Token string (in this case the user id and email). Finally, registerUser returns the JWT string and user profile if successful and returns an error message if something goes wrong.
login accepts email and password , and checks if these details match with the one that was supplied. First, we check if the email value already exists somewhere in the user database.
models.User.findOne({ where: { email }}) if (!user) { throw new Error('No user with that email') }
Then, we use bcrypt’s bcrypt.compare method to check if the password matches.
const isValid = await bcrypt.compare(password, user.password) if (!isValid) { throw new Error('Incorrect password') }
Then, just like we did previously in registerUser, we use jsonwebtoken.sign to generate a JWT string. The login mutation returns the token and user object.
Now let’s add the JWT_SECRET to our .env file.
JWT_SECRET=somereallylongsecret
The server
Finally, the server! Create a server.js in the project’s root folder and paste this:
const { ApolloServer } = require('apollo-server') const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken') const typeDefs = require('./schema/schema') const resolvers = require('./resolvers/resolvers') require('dotenv').config() const { JWT_SECRET, PORT } = process.env const getUser = token => { try { if (token) { return jwt.verify(token, JWT_SECRET) } return null } catch (error) { return null } } const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers, context: ({ req }) => { const token = req.get('Authorization') || '' return { user: getUser(token.replace('Bearer', ''))} }, introspection: true, playground: true }) server.listen({ port: process.env.PORT || 4000 }).then(({ url }) => { console.log(`🚀 Server ready at ${url}`); });
Here, we import the schema, resolvers and jwt, and initialize our environment variables. First, we verify the JWT token with verify. jwt.verify accepts the token and the JWT secret as parameters.
Next, we create our server with an ApolloServer instance that accepts typeDefs and resolvers.
We have a server! Let’s start it up by running yarn dev in the terminal.
Testing the API
Let’s now test the GraphQL API with GraphQL Playground. We should be able to register, login and view all users — including a single user — by ID.
We’ll start by opening up the GraphQL Playground app or just open localhost://4000 in the browser to access it.
Mutation for register user
mutation { registerUser(username: "Wizzy", email: "[email protected]", password: "wizzyekpot" ){ token } }
We should get something like this:
{ "data": { "registerUser": { "token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6MTUsImVtYWlsIjoiZWtwb3RAZ21haWwuY29tIiwiaWF0IjoxNTk5MjQwMzAwLCJleHAiOjE2MzA3OTc5MDB9.gmeynGR9Zwng8cIJR75Qrob9bovnRQT242n6vfBt5PY" } } }
Mutation for login
Let’s now log in with the user details we just created:
mutation { login(email:"[email protected]" password:"wizzyekpot"){ token } }
We should get something like this:
{ "data": { "login": { "token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6MTUsImVtYWlsIjoiZWtwb3RAZ21haWwuY29tIiwiaWF0IjoxNTk5MjQwMzcwLCJleHAiOjE1OTkzMjY3NzB9.PDiBKyq58nWxlgTOQYzbtKJ-HkzxemVppLA5nBdm4nc" } } }
Awesome!
Query for a single user
For us to query a single user, we need to pass the user token as authorization header. Go to the HTTP Headers tab.
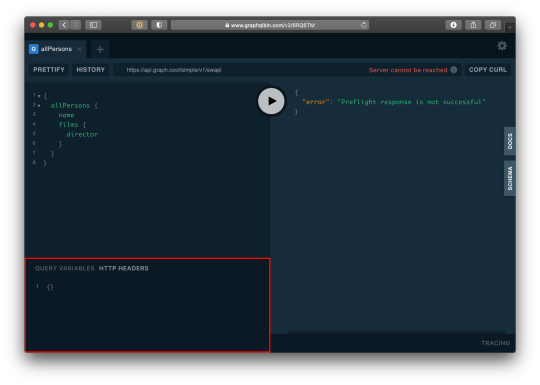
…and paste this:
{ "Authorization": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6MTUsImVtYWlsIjoiZWtwb3RAZ21haWwuY29tIiwiaWF0IjoxNTk5MjQwMzcwLCJleHAiOjE1OTkzMjY3NzB9.PDiBKyq58nWxlgTOQYzbtKJ-HkzxemVppLA5nBdm4nc" }
Here’s the query:
query myself{ me { id email username } }
And we should get something like this:
{ "data": { "me": { "id": 15, "email": "[email protected]", "username": "Wizzy" } } }
Great! Let’s now get a user by ID:
query singleUser{ user(id:15){ id email username } }
And here’s the query to get all users:
{ allUsers{ id username email } }
Summary
Authentication is one of the toughest tasks when it comes to building websites that require it. GraphQL enabled us to build an entire Authentication API with just one endpoint. Sequelize ORM makes creating relationships with our SQL database so easy, we barely had to worry about our models. It’s also remarkable that we didn’t require a HTTP server library (like Express) and use Apollo GraphQL as middleware. Apollo Server 2, now enables us to create our own library-independent GraphQL servers!
Check out the source code for this tutorial on GitHub.
The post Let’s Create Our Own Authentication API with Nodejs and GraphQL appeared first on CSS-Tricks.
You can support CSS-Tricks by being an MVP Supporter.
Let’s Create Our Own Authentication API with Nodejs and GraphQL published first on https://deskbysnafu.tumblr.com/
0 notes
Text
400+ TOP C#.NET Interview Questions and Answers
C#.NET Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is C#? C# is an object oriented, type safe and managed language that is compiled by .Net framework to generate Microsoft Intermediate Language. 2. What are the types of comment in C# with examples? Single line Eg: //This is a Single line comment ii. Multiple line (/* */) Eg: /*This is a multiple line comment We are in line 2 Last line of comment*/ iii. XML Comments (///). Eg: /// summary; /// Set error message for multilingual language. /// summary 3. What's The Difference Between The System.array.copyto() And System.array.clone()? The first one performs a deep copy of the array, the second one is shallow. 4. How Can You Sort The Elements Of The Array In Descending Order? By calling Sort() and then Reverse() methods. 5. What's The .net Datatype That Allows The Retrieval Of Data By A Unique Key? HashTable. 6. What's Class Sortedlist Underneath? A sorted HashTable. 7. Will Finally Block Get Executed If The Exception Had Not Occurred? Yes. 8. What's The C# Equivalent Of C++ Catch (....), Which Was A Catch-all Statement For Any Possible Exception? A catch block that catches the exception of type System.Exception. You can also omit the parameter data type in this case and just write catch {}. 9. Can Multiple Catch Blocks Be Executed? No, once the proper catch code fires off, the control is transferred to the finally block (if there are any), and then whatever follows the finally block. 10. Why Is It A Bad Idea To Throw Your Own Exceptions? Well, if at that point you know that an error has occurred, then why not write the proper code to handle that error instead of passing a new Exception object to the catch block? Throwing your own exceptions signifies some design flaws in the project.

C#.NET Interview Questions 11. What's A Delegate? A delegate object encapsulates a reference to a method. In C++ they were referred to as function pointers. 12. What's A Multicast Delegate? It’s a delegate that points to and eventually fires off several methods. 13. How's The Dll Hell Problem Solved In .net? Assembly versioning allows the application to specify not only the library it needs to run (which was available under Win32), but also the version of the assembly. 14. What Are The Ways To Deploy An Assembly? An MSI installer, a CAB archive, and XCOPY command. 15. What's A Satellite Assembly? When you write a multilingual or multi-cultural application in .NET, and want to distribute the core application separately from the localized modules, the localized assemblies that modify the core application are called satellite assemblies. 16. What Namespaces Are Necessary To Create A Localized Application? System.Globalization, System.Resources. 17. What's The Difference Between // Comments, /* */ Comments And /// Comments? Single-line, multi-line and XML documentation comments. 18. How Do You Generate Documentation From The C# File Commented Properly With A Command-line Compiler? Compile it with a /doc switch. 19. What's The Difference Between And Xml Documentation Tag? Single line code example and multiple-line code example. 20. Is Xml Case-sensitive? Yes, so and are different elements. 21. What Debugging Tools Come With The .net Sdk? CorDBG – command-line debugger, and DbgCLR – graphic debugger. Visual Studio .NET uses the DbgCLR. To use CorDbg, you must compile the original C# file using the /debug switch. 22. What Does The This Window Show In The Debugger? It points to the object that’s pointed to by this reference. Object’s instance data is shown. 23. What Does Assert() Do? In debug compilation, assert takes in a Boolean condition as a parameter, and shows the error dialog if the condition is false. The program proceeds without any interruption if the condition is true. 24. What's The Difference Between The Debug Class And Trace Class? Documentation Looks The Same. Use Debug class for debug builds, use Trace class for both debug and release builds. 25. Why Are There Five Tracing Levels In System.diagnostics.traceswitcher? The tracing dumps can be quite verbose and for some applications that are constantly running you run the risk of overloading the machine and the hard drive there. Five levels range from None to Verbose, allowing to fine-tune the tracing activities. 26. Where Is The Output Of Textwritertracelistener Redirected? To the Console or a text file depending on the parameter passed to the constructor. 27. How Do You Debug An Asp.net Web Application? Attach the aspnet_wp.exe process to the DbgClr debugger. 28. What Are Three Test Cases You Should Go Through In Unit Testing? Positive test cases (correct data, correct output), negative test cases (broken or missing data, proper handling), exception test cases (exceptions are thrown and caught properly). 29. Can You Change The Value Of A Variable While Debugging A C# Application? Yes, if you are debugging via Visual Studio.NET, just go to Immediate window. 30. Explain The Three Services Model (three-tier Application). Presentation (UI), business (logic and underlying code) and data (from storage or other sources). 31. What Are Advantages And Disadvantages Of Microsoft-provided Data Provider Classes In Ado.net? SQLServer.NET data provider is high-speed and robust, but requires SQL Server license purchased from Microsoft. OLE-DB.NET is universal for accessing other sources, like Oracle, DB2, Microsoft Access and Informix, but it’s a .NET layer on top of OLE layer, so not the fastest thing in the world. ODBC.NET is a deprecated layer provided for backward compatibility to ODBC engines. 32. What's The Role Of The Datareader Class In Ado.net Connections? It returns a read-only dataset from the data source when the command is executed. 33. What Is The Wildcard Character In Sql? Let's Say You Want To Query Database With Like For All Employees Whose Name Starts With La. The wildcard character is %, the proper query with LIKE would involve ‘La%’. 34. Explain Acid Rule Of Thumb For Transactions. Transaction must be Atomic (it is one unit of work and does not dependent on previous and following transactions), Consistent (data is either committed or roll back, no “in-between” case where something has been updated and something hasn’t), Isolated (no transaction sees the intermediate results of the current transaction), Durable (the values persist if the data had been committed even if the system crashes right after). 35. What Connections Does Microsoft Sql Server Support? Windows Authentication (via Active Directory) and SQL Server authentication (via Microsoft SQL Server user name and passwords). 36. Which One Is Trusted And Which One Is Untrusted? Windows Authentication is trusted because the username and password are checked with the Active Directory, the SQL Server authentication is untrusted, since SQL Server is the only verifier participating in the transaction. 37. Why Would You Use Untrusted Verificaion? Web Services might use it, as well as non-Windows applications. 38. What Does The Parameter Initial Catalog Define Inside Connection String? The database name to connect to. 39. What's The Data Provider Name To Connect To Access Database? Microsoft.Access. 40. What Does Dispose Method Do With The Connection Object? Deletes it from the memory. 41. What Is A Pre-requisite For Connection Pooling? Multiple processes must agree that they will share the same connection, where every parameter is the same, including the security settings. 42. What Is C#? C# is a programming language designed by Microsoft. It is loosely based on C/C++, and bears a striking similarity to Java. Microsoft describe C# as follows: "C# is a simple, modern, object oriented, and type-safe programming language derived from C and C++. C# (pronounced 'C sharp') is firmly planted in the C and C++ family tree of languages, and will immediately be familiar to C and C++ programmers. C# aims to combine the high productivity of Visual Basic and the raw power of C++." 43. How Do I Develop C# Apps? The (free) .NET SDK contains the C# command-line compiler (csc.exe). Visual Studio has fully integrated support for C# development. On Linux you can use Mono. 44. Does C# Replace C++? There are three options open to the Windows developer from a C++ background: Stick with standard C++. Don't use .NET at all. Use C++ with .NET. Microsoft supply a .NET C++ compiler that produces IL rather than machine code. However to make full use of the .NET environment (e.g. garbage collection), a set of extensions are required to standard C++. In .NET 1.x this extended language is called Managed Extensions for C++. In .NET 2.0 ME C++ has been completely redesigned under the stewardship of Stan Lippman, and renamed C++/CLI. Forget C++ and use C#. Each of these options has merits, depending on the developer and the application. For my own part, I intend to use C# where possible, falling back to C++ only where necessary. ME C++ (soon to be C++/CLI) is very useful for interop between new .NET code and old C++ code - simply write a managed wrapper class using ME C++, then use the managed class from C#. From experience, this works well. 45. Does C# Have Its Own Class Library? Not exactly. The .NET Framework has a comprehensive class library, which C# can make use of. C# does not have its own class library. 46. What Standard Types Does C# Use? C# supports a very similar range of basic types to C++, including int, long, float, double, char, string, arrays, structs and classes. However, don't assume too much. The names may be familiar, but many of the details are different. For example, a long is 64 bits in C#, whereas in C++ the size of a long depends on the platform (typically 32 bits on a 32-bit platform, 64 bits on a 64-bit platform). Also classes and structs are almost the same in C++ - this is not true for C#. Finally, chars and strings in .NET are 16-bit (Unicode/UTF-16), not 8-bit like C++. 47. Is It True That All C# Types Derive From A Common Base Class? Yes and no. All types can be treated as if they derive from object (System.Object), but in order to treat an instance of a value type (e.g. int, float) as object-derived, the instance must be converted to a reference type using a process called 'boxing'. In theory a developer can forget about this and let the run-time worry about when the conversion is necessary, but in reality this implicit conversion can have side-effects that may trip up the unwary. 48. What Are The Fundamental Differences Between Value Types And Reference Types? C# divides types into two categories - value types and reference types. Most of the intrinsic types (e.g. int, char) are value types. Structs are also value types. Reference types include classes, arrays and strings. The basic idea is straightforward - an instance of a value type represents the actual data, whereas an instance of a reference type represents a pointer or reference to the data. The most confusing aspect of this for C++ developers is that C# has predetermined which types are represented as values, and which are represented as references. A C++ developer expects to take responsibility for this decision. For example, in C++ we can do this: int x1 = 3; // x1 is a value on the stack int *x2 = new int(3) // x2 is a pointer to a value on the heap but in C# there is no control: int x1 = 3; // x1 is a value on the stack int x2 = new int(); x2 = 3; // x2 is also a value on the stack! 49. Okay, So An Int Is A Value Type, And A Class Is A Reference Type. How Can Int Be Derived From Object? It isn't, really. When an int is being used as an int, it is a value. However, when it is being used as an object, it is a reference to an integer value (on the managed heap). In other words, when you treat an int as an object, the runtime automatically converts the int value to an object reference. This process is called boxing. The conversion involves copying the int to the heap, and creating an object instance which refers to it. Unboxing is the reverse process - the object is converted back to a value. int x = 3; // new int value 3 on the stack object objx = x; // new int on heap, set to value 3 - still have x=3 on stack int y = (int)objx; // new value 3 on stack, still got x=3 on stack and objx=3 on heap 50. Are C# References The Same As C++ References? Not quite. The basic idea is the same, but one significant difference is that C# references can be null . So you cannot rely on a C# reference pointing to a valid object. In that respect a C# reference is more like a C++ pointer than a C++ reference. If you try to use a null reference, a NullReferenceException is thrown. For example, look at the following method: void displayStringLength( string s ) { Console.WriteLine( "String is length {0}", s.Length ); } The problem with this method is that it will throw a NullReferenceException if called like this: string s = null; displayStringLength( s ); Of course for some situations you may deem a NullReferenceException to be a perfectly acceptable outcome, but in this case it might be better to re-write the method like this: void displayStringLength( string s ) { if( s == null ) Console.WriteLine( "String is null" ); else Console.WriteLine( "String is length {0}", s.Length ); } 51. Structs Are Largely Redundant In C++. Why Does C# Have Them? In C++, a struct and a class are pretty much the same thing. The only difference is the default visibility level (public for structs, private for classes). However, in C# structs and classes are very different. In C#, structs are value types (instances stored directly on the stack, or inline within heap-based objects), whereas classes are reference types (instances stored on the heap, accessed indirectly via a reference). Also structs cannot inherit from structs or classes, though they can implement interfaces. Structs cannot have destructors. A C# struct is much more like a C struct than a C++ struct. 52. Does C# Support Multiple Inheritance (mi)? No, though it does support implementation of multiple interfaces on a single class or struct. 53. Is A C# Interface The Same As A C++ Abstract Class? No, not quite. An abstract class in C++ cannot be instantiated, but it can (and often does) contain implementation code and/or data members. A C# interface cannot contain any implementation code or data members - it is simply a group of method names & signatures. A C# interface is more like a COM interface than a C++ abstract class. 54. Are C# Constructors The Same As C++ Constructors? Very similar, but there are some significant differences. First, C# supports constructor chaining. This means one constructor can call another: class Person { public Person( string name, int age ) { ... } public Person( string name ) : this( name, 0 ) {} public Person() : this( "", 0 ) {} } Another difference is that virtual method calls within a constructor are routed to the most derived implementation - see Can I Call a virtual method from a constructor. Error handling is also somewhat different. If an exception occurs during construction of a C# object, the destuctor (finalizer) will still be called. This is unlike C++ where the destructor is not called if construction is not completed. (Thanks to Jon Jagger for pointing this out.) Finally, C# has static constructors. The static constructor for a class runs before the first instance of the class is created. Also note that (like C++) some C# developers prefer the factory method pattern over constructors. See Brad Wilson's article. 55. Are C# Destructors The Same As C++ Destructors? No. They look the same but they are very different. The C# destructor syntax (with the familiar ~ character) is just syntactic sugar for an override of the System.Object Finalize method. This Finalize method is called by the garbage collector when it determines that an object is no longer referenced, before it frees the memory associated with the object. So far this sounds like a C++ destructor. The difference is that the garbage collector makes no guarantees about when this procedure happens. Indeed, the algorithm employed by the CLR garbage collector means that it may be a long time after the application has finished with the object. This lack of certainty is often termed 'non-deterministic finalization', and it means that C# destructors are not suitable for releasing scarce resources such as database connections, file handles etc. To achieve deterministic destruction, a class must offer a method to be used for the purpose. The standard approach is for the class to implement the IDisposable interface. The user of the object must call the Dispose() method when it has finished with the object. C# offers the 'using' construct to make this easier. 56. If C# Destructors Are So Different To C++ Destructors, Why Did Ms Use The Same Syntax? Presumably they wanted C++ programmers to feel at home. I think they made a mistake. 57. Are All Methods Virtual In C#? No. Like C++, methods are non-virtual by default, but can be marked as virtual. 58. How Do I Declare A Pure Virtual Function In C#? Use the abstract modifier on the method. The class must also be marked as abstract (naturally). Note that abstract methods cannot have an implementation (unlike pure virtual C++ methods). 59. Can I Call A Virtual Method From A Constructor/destructor? Yes, but it's generally not a good idea. The mechanics of object construction in .NET are quite different from C++, and this affects virtual method calls in constructors. C++ constructs objects from base to derived, so when the base constructor is executing the object is effectively a base object, and virtual method calls are routed to the base class implementation. By contrast, in .NET the derived constructor is executed first, which means the object is always a derived object and virtual method calls are always routed to the derived implementation. (Note that the C# compiler inserts a call to the base class constructor at the start of the derived constructor, thus preserving standard OO semantics by creating the illusion that the base constructor is executed first.) The same issue arises when calling virtual methods from C# destructors. A virtual method call in a base destructor will be routed to the derived implementation. 60. Should I Make My Destructor Virtual? A C# destructor is really just an override of the System.Object Finalize method, and so is virtual by definition. 61. Can I Use Exceptions In C#? Yes, in fact exceptions are the recommended error-handling mechanism in C# (and in .NET in general). Most of the .NET framework classes use exceptions to signal errors. 62. What Types Of Object Can I Throw As Exceptions? Only instances of the System.Exception classes, or classes derived from System.Exception. This is in sharp contrast with C++ where instances of almost any type can be thrown. 63. Can I Define My Own Exceptions? Yes, just derive your exception class from System.Exception. 64. Does The System.exception Class Have Any Cool Features? Yes - the feature which stands out is the StackTrace property. This provides a call stack which records where the exception was thrown from. For example, the following code: using System; class CApp { public static void Main() { try { f(); } catch( Exception e ) { Console.WriteLine( "System.Exception stack trace = \n{0}", e.StackTrace ); } } static void f() { throw new Exception( "f went pear-shaped" ); } } produces this output: System.Exception stack trace = at CApp.f() at CApp.Main() Note, however, that this stack trace was produced from a debug build. A release build may optimise away some of the method calls which could mean that the call stack isn't quite what you expect. 65. When Should I Throw An Exception? This is the subject of some debate, and is partly a matter of taste. However, it is accepted by many that exceptions should be thrown only when an 'unexpected' error occurs. How do you decide if an error is expected or unexpected? This is a judgement call, but a straightforward example of an expected error is failing to read from a file because the seek pointer is at the end of the file, whereas an example of an unexpected error is failing to allocate memory from the heap. 66. Does C# Have A 'throws' Clause? No, unlike Java, C# does not require (or even allow) the developer to specify the exceptions that a method can throw. 67. How Can I Check The Type Of An Object At Runtime? You can use the is keyword. For example: using System; class CApp { public static void Main() { string s = "fred"; long i = 10; Console.WriteLine( "{0} is {1}an integer", s, (IsInteger(s) ? "" : "not ") ); Console.WriteLine( "{0} is {1}an integer", i, (IsInteger(i) ? "" : "not ") ); } static bool IsInteger( object obj ) { if( obj is int || obj is long ) return true; else return false; } } produces the output: fred is not an integer 10 is an integer 68. Can I Get The Name Of A Type At Runtime? Yes, use the GetType method of the object class (which all types inherit from). For example: using System; class CTest { class CApp { public static void Main() { long i = 10; CTest ctest = new CTest(); DisplayTypeInfo( ctest ); DisplayTypeInfo( i ); } static void DisplayTypeInfo( object obj ) { Console.WriteLine( "Type name = {0}, full type name = {1}", obj.GetType(), obj.GetType().FullName ); } } } produces the following output: Type name = CTest, full type name = CTest Type name = Int64, full type name = System.Int64 69. How Do I Do A Case-insensitive String Comparison? Use the String.Compare function. Its third parameter is a boolean which specifies whether case should be ignored or not. "fred" == "Fred" // false System.String.Compare( "fred", "Fred", true ) // true 70. Does C# Support A Variable Number Of Arguments? Yes, using the params keyword. The arguments are specified as a list of arguments of a specific type, e.g. int. For ultimate flexibility, the type can be object. The standard example of a method which uses this approach is System.Console.WriteLine(). 71. How Can I Process Command-line Arguments? Like this: using System; class CApp { public static void Main( string args ) { Console.WriteLine( "You passed the following arguments:" ); foreach( string arg in args ) Console.WriteLine( arg ); } } 72. Does C# Do Array Bounds Checking? Yes. An IndexOutOfRange exception is used to signal an error. 73. How Can I Make Sure My C# Classes Will Interoperate With Other .net Languages? Make sure your C# code conforms to the Common Language Subset (CLS). To help with this, add the global attribute to your C# source files. The compiler will emit an error if you use a C# feature which is not CLS-compliant. 74. How Do I Use The 'using' Keyword With Multiple Objects? You can nest using statements, like this: using( obj1 ) { using( obj2 ) { ... } } However consider using this more aesthetically pleasing (but functionally identical) formatting: using( obj1 ) using( obj2 ) { ... } 75. What Is The Difference Between == And Object.equals? For value types, == and Equals() usually compare two objects by value. For example: int x = 10; int y = 10; Console.WriteLine( x == y ); Console.WriteLine( x.Equals(y) ); will display: True True However things are more complex for reference types. Generally speaking, for reference types == is expected to perform an identity comparison, i.e. it will only return true if both references point to the same object. By contrast, Equals() is expected to perform a value comparison, i.e. it will return true if the references point to objects that are equivalent. For example: StringBuilder s1 = new StringBuilder("fred"); StringBuilder s2 = new StringBuilder("fred"); Console.WriteLine( s1 == s2 ); Console.WriteLine( s1.Equals(s2) ); will display: False True s1 and s2 are different objects (hence == returns false), but they are equivalent (hence Equals() returns true). Unfortunately there are exceptions to these rules. The implementation of Equals() in System.Object (the one you'll inherit by default if you write a class) compares identity, i.e. it's the same as operator==. So Equals() only tests for equivalence if the class author overrides the method (and implements it correctly). Another exception is the string class - its operator== compares value rather than identity. Bottom line: If you want to perform an identity comparison use the ReferenceEquals() method. If you want to perform a value comparison, use Equals() but be aware that it will only work if the type has overridden the default implementation. Avoid operator== with reference types (except perhaps strings), as it's simply too ambiguous. 76. How Do I Enforce Const Correctness In C#? You can't - at least not in the same way you do in C++. C# (actually, the CLI) has no real concept of const correctness, For example, there's no way to specify that a method should not modify an argument passed in to it. And there's no way to specify that a method does not modify the object on which it is acting. To get a feel for the angst this causes among some C++ programmers, read the feedback on this post from Raymond Chen. There are of course ways of addressing this issue. For example, see Brad Abram's post (and associated feedback) for some ideas on adding optional read-only behaviour to collection classes. 77. What Are The New Features In C# 2.0? Support for all of the new framework features such as generics, anonymous methods, partial classes, iterators and static classes. Delegate inference is a new feature of the C# compiler which makes delegate usage a little simpler. It allows you to write this: Thread t = new Thread(ThreadFunc); instead of this: Thread t = new Thread( new ThreadStart(ThreadFunc) ); Another minor but welcome addition is the explicit global namespace, which fixes a hole in namespace usage in C# 1.x. You can prefix a type name with global:: to indicate that the type belongs to the global namespace, thus avoiding problems where the compiler infers the namespace and gets it wrong. Finally C# 2.0 includes some syntactic sugar for the new System.Nullable type. You can use T? as a synonym for System.Nullable, where T is a value type. As suggested by the name, this allows values of the type to be 'null', or 'undefined'. 78. Are C# Generics The Same As C++ Templates? No, not really. There are some similarities, but there are also fundamental differences. 79. What Is An Interface In C#? An Interface in C# is created using the interface keyword. An example is shown below. using System; namespace Interfaces { interface IBankCustomer { void DepositMoney(); void WithdrawMoney(); } public class Demo : IBankCustomer { public void DepositMoney() { Console.WriteLine("Deposit Money"); } public void WithdrawMoney() { Console.WriteLine("Withdraw Money"); } public static void Main() { Demo DemoObject = new Demo(); DemoObject.DepositMoney(); DemoObject.WithdrawMoney(); } } } In our example we created IBankCustomer interface. The interface declares 2 methods. 1. void DepositMoney(); 2. void WithdrawMoney(); Notice that method declarations does not have access modifiers like public, private, etc. By default all interface members are public. It is a compile time error to use access modifiers on interface member declarations. Also notice that the interface methods have only declarations and not implementation. It is a compile time error to provide implementation for any interface member. In our example as the Demo class is inherited from the IBankCustomer interface, the Demo class has to provide the implementation for both the methods (WithdrawMoney() and DepositMoney()) that is inherited from the interface. If the class fails to provide implementation for any of the inherited interface member, a compile time error will be generated. Interfaces can consist of methods, properties, events, indexers, or any combination of those four member types. When a class or a struct inherits an interface, the class or struct must provide implementation for all of the members declared in the interface. The interface itself provides no functionality that a class or struct can inherit in the way that base class functionality can be inherited. However, if a base class implements an interface, the derived class inherits that implementation. 80. Can An Interface Contain Fields? No, an Interface cannot contain fields. 81. What Is The Difference Between Class Inheritance And Interface Inheritance? Classes and structs can inherit from interfaces just like how classes can inherit a base class or struct. However there are 2 differences. 1. A class or a struct can inherit from more than one interface at the same time where as A class or a struct cannot inherit from more than one class at the same time. An example depicting the same is shown below. using System; namespace Interfaces { interface Interface1 { void Interface1Method(); } interface Interface2 { void Interface2Method(); } class BaseClass1 { public void BaseClass1Method() { Console.WriteLine("BaseClass1 Method"); } } class BaseClass2 { public void BaseClass2Method() { Console.WriteLine("BaseClass2 Method"); } } //Error : A class cannot inherit from more than one class at the same time //class DerivedClass : BaseClass1, BaseClass2 //{ //} //A class can inherit from more than one interface at the same time public class Demo : Interface1, Interface2 { public void Interface1Method() { Console.WriteLine("Interface1 Method"); } public void Interface2Method() { Console.WriteLine("Interface2 Method"); } public static void Main() { Demo DemoObject = new Demo(); DemoObject.Interface1Method(); DemoObject.Interface2Method(); } } } 2. When a class or struct inherits an interface, it inherits only the method names and signatures, because the interface itself contains no implementations. 82. Can An Interface Inherit From Another Interface? Yes, an interface can inherit from another interface. It is possible for a class to inherit an interface multiple times, through base classes or interfaces it inherits. In this case, the class can only implement the interface one time, if it is declared as part of the new class. If the inherited interface is not declared as part of the new class, its implementation is provided by the base class that declared it. It is possible for a base class to implement interface members using virtual members; in that case, the class inheriting the interface can change the interface behavior by overriding the virtual members. 83. Can You Create An Instance Of An Interface? No, you cannot create an instance of an interface. 84. If A Class Inherits An Interface, What Are The 2 Options Available For That Class? Option 1: Provide Implementation for all the members inheirted from the interface. namespace Interfaces { interface Interface1 { void Interface1Method(); } class BaseClass1 : Interface1 { public void Interface1Method() { Console.WriteLine("Interface1 Method"); } public void BaseClass1Method() { Console.WriteLine("BaseClass1 Method"); } } } Option 2: If the class does not wish to provide Implementation for all the members inheirted from the interface, then the class has to be marked as abstract. namespace Interfaces { interface Interface1 { void Interface1Method(); } abstract class BaseClass1 : Interface1 { abstract public void Interface1Method(); public void BaseClass1Method() { Console.WriteLine("BaseClass1 Method"); } } } 85. A Class Inherits From 2 Interfaces And Both The Interfaces Have The Same Method Name As Shown Below. How Should The Class Implement The Drive Method For Both Car And Bus Interface? namespace Interfaces { interface Car { void Drive(); } interface Bus { void Drive(); } class Demo : Car,Bus { //How to implement the Drive() Method inherited from Bus and Car } } To implement the Drive() method use the fully qualified name as shown in the example below. To call the respective interface drive method type cast the demo object to the respective interface and then call the drive method. using System; namespace Interfaces { interface Car { void Drive(); } interface Bus { void Drive(); } class Demo : Car,Bus { void Car.Drive() { Console.WriteLine("Drive Car"); } void Bus.Drive() { Console.WriteLine("Drive Bus"); } static void Main() { Demo DemoObject = new Demo(); ((Car)DemoObject).Drive(); ((Bus)DemoObject).Drive(); } } } 86. What Do You Mean By "explicitly Implemeting An Interface". Give An Example? If a class is implementing the inherited interface member by prefixing the name of the interface, then the class is "Explicitly Implemeting an Interface member". The disadvantage of Explicitly Implemeting an Interface member is that, the class object has to be type casted to the interface type to invoke the interface member. An example is shown below. using System; namespace Interfaces { interface Car { void Drive(); } class Demo : Car { // Explicit implementation of an interface member void Car.Drive() { Console.WriteLine("Drive Car"); } static void Main() { Demo DemoObject = new Demo(); //DemoObject.Drive(); // Error: Cannot call explicitly implemented interface method // using the class object. // Type cast the demo object to interface type Car ((Car)DemoObject).Drive(); } } } 87. What Is A Partial Class. Give An Example? A partial class is a class whose definition is present in 2 or more files. Each source file contains a section of the class, and all parts are combined when the application is compiled. To split a class definition, use the partial keyword as shown in the example below. Student class is split into 2 parts. The first part defines the study() method and the second part defines the Play() method. When we compile this program both the parts will be combined and compiled. Note that both the parts uses partial keyword and public access modifier. using System; namespace PartialClass { public partial class Student { public void Study() { Console.WriteLine("I am studying"); } } public partial class Student { public void Play() { Console.WriteLine("I am Playing"); } } public class Demo { public static void Main() { Student StudentObject = new Student(); StudentObject.Study(); StudentObject.Play(); } }} It is very important to keep the following points in mind when creating partial classes. All the parts must use the partial keyword. All the parts must be available at compile time to form the final class. All the parts must have the same access modifiers - public, private, protected etc. Any class members declared in a partial definition are available to all the other parts. The final class is the combination of all the parts at compile time. 88. What Are The Advantages Of Using Partial Classes? When working on large projects, spreading a class over separate files enables multiple programmers to work on it at the same time. When working with automatically generated source, code can be added to the class without having to recreate the source file. Visual Studio uses this approach when it creates Windows Forms, Web service wrapper code, and so on. You can create code that uses these classes without having to modify the file created by Visual Studio. 89. Is It Possible To Create Partial Structs, Interfaces And Methods? Yes, it is possible to create partial structs, interfaces and methods. We can create partial structs, interfaces and methods the same way as we create partial classes. 90. Will The Following Code Compile? using System; namespace PartialClass { public partial class Student { public void Study() { Console.WriteLine("I am studying"); } } public abstract partial class Student { public void Play() { Console.WriteLine("I am Playing"); } } public class Demo { public static void Main() { Student StudentObject = new Student(); } }} No, a compile time error will be generated stating "Cannot create an instance of the abstract class or interface "PartialClass.Student". This is because, if any part is declared abstract, then the whole class becomes abstract. Similarly if any part is declared sealed, then the whole class becomes sealed and if any part declares a base class, then the whole class inherits that base class. 91. Can You Create Partial Delegates And Enumerations? No, you cannot create partial delegates and enumerations. 92. Can Different Parts Of A Partial Class Inherit From Different Interfaces? Yes, different parts of a partial class can inherit from different interfaces. 93. Can You Specify Nested Classes As Partial Classes? Yes, nested classes can be specified as partial classes even if the containing class is not partial. An example is shown below. class ContainerClass { public partial class Nested { void Test1() { } } public partial class Nested { void Test2() { } } } 94. How Do You Create Partial Methods? To create a partial method we create the declaration of the method in one part of the partial class and implementation in the other part of the partial class. The implementation is optional. If the implementation is not provided, then the method and all the calls to the method are removed at compile time. Therefore, any code in the partial class can freely use a partial method, even if the implementation is not supplied. No compile-time or run-time errors will result if the method is called but not implemented. In summary a partial method declaration consists of two parts. The definition, and the implementation. These may be in separate parts of a partial class, or in the same part. If there is no implementation declaration, then the compiler optimizes away both the defining declaration and all calls to the method. The following are the points to keep in mind when creating partial methods. Partial method declarations must begin partial keyword. The return type of a partial method must be void. Partial methods can have ref but not out parameters. Partial methods are implicitly private, and therefore they cannot be virtual. Partial methods cannot be extern, because the presence of the body determines whether they are defining or implementing. 95. What Is The Use Of Partial Methods? Partial methods can be used to customize generated code. They allow for a method name and signature to be reserved, so that generated code can call the method but the developer can decide whether to implement the method. Much like partial classes, partial methods enable code created by a code generator and code created by a human developer to work together without run-time costs. 96. What Is A Nested Type. Give An Example? A type(class or a struct) defined inside another class or struct is called a nested type. An example is shown below. InnerClass is inside ContainerClass, Hence InnerClass is called as nested class. using System; namespace Nested { class ContainerClass { class InnerClass { public string str = "A string variable in nested class"; } public static void Main() { InnerClass nestedClassObj = new InnerClass(); Console.WriteLine(nestedClassObj.str); } } } 97. Can The Nested Class Access, The Containing Class. Give An Example? Yes, the nested class, or inner class can access the containing or outer class as shown in the example below. Nested types can access private and protected members of the containing type, including any inherited private or protected members. using System; namespace Nested { class ContainerClass { string OuterClassVariable = "I am an outer class variable"; public class InnerClass { ContainerClass ContainerClassObject = new ContainerClass(); string InnerClassVariable = "I am an Inner class variable"; public InnerClass() { Console.WriteLine(ContainerClassObject.OuterClassVariable); Console.WriteLine(this.InnerClassVariable); } } } class Demo { public static void Main() { ContainerClass.InnerClass nestedClassObj = new ContainerClass.InnerClass(); } } } 98. What Is The Ouput Of The Following Program? using System; namespace Nested { class ContainerClass { public ContainerClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am a container class"); } public class InnerClass : ContainerClass { public InnerClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am an inner class"); } } } class DemoClass : ContainerClass.InnerClass { public DemoClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Demo class"); } public static void Main() { DemoClass DC = new DemoClass(); } } } Output: I am a container class I am an inner class I am a Demo class The above program has used the concepts of inheritance and nested classes. The ContainerClass is at the top in the inheritance chain. The nested InnerClass derives from outer ContainerClass. Finally the DemoClass derives from nested InnerClass. As all the 3 classes are related by inheritance we have the above output. 99. What Is A Destructor? A Destructor has the same name as the class with a tilde character and is used to destroy an instance of a class. 100. Can A Class Have More Than 1 Destructor? No, a class can have only 1 destructor. 101. Can Structs In C# Have Destructors? No, structs can have constructors but not destructors, only classes can have destructors. 102. Can You Pass Parameters To Destructors? No, you cannot pass parameters to destructors. Hence, you cannot overload destructors. 103. Can You Explicitly Call A Destructor? No, you cannot explicitly call a destructor. Destructors are invoked automatically by the garbage collector. 104. Why Is It Not A Good Idea To Use Empty Destructors? When a class contains a destructor, an entry is created in the Finalize queue. When the destructor is called, the garbage collector is invoked to process the queue. If the destructor is empty, this just causes a needless loss of performance. 105. Is It Possible To Force Garbage Collector To Run? Yes, it possible to force garbage collector to run by calling the Collect() method, but this is not considered a good practice because this might create a performance over head. Usually the programmer has no control over when the garbage collector runs. The garbage collector checks for objects that are no longer being used by the application. If it considers an object eligible for destruction, it calls the destructor(if there is one) and reclaims the memory used to store the object. 106. Usually In .net, The Clr Takes Care Of Memory Management. Is There Any Need For A Programmer To Explicitly Release Memory And Resources? If Yes, Why And How? If the application is using expensive external resource, it is recommend to explicitly release the resource before the garbage collector runs and frees the object. We can do this by implementing the Dispose method from the IDisposable interface that performs the necessary cleanup for the object. This can considerably improve the performance of the application. 107. When Do We Generally Use Destructors To Release Resources? If the application uses unmanaged resources such as windows, files, and network connections, we use destructors to release resources. 108. What Is A Constructor In C#? Constructor is a class method that is executed when an object of a class is created. Constructor has the same name as the class, and usually used to initialize the data members of the new object. 109. In C#, What Will Happen If You Do Not Explicitly Provide A Constructor For A Class? If you do not provide a constructor explicitly for your class, C# will create one by default that instantiates the object and sets all the member variables to their default values. 110. Structs Are Not Reference Types. Can Structs Have Constructors? Yes, even though Structs are not reference types, structs can have constructors. 111. We Cannot Create Instances Of Static Classes. Can We Have Constructors For Static Classes? Yes, static classes can also have constructors. 112. Can You Prevent A Class From Being Instantiated? Yes, a class can be prevented from being instantiated by using a private constructor as shown in the example below. using System; namespace TestConsole { class Program { public static void Main() { //Error cannot create instance of a class with private constructor SampleClass SC = new SampleClass(); } } class SampleClass { double PI = 3.141; private SampleClass() { } } } 113. Can A Class Or A Struct Have Multiple Constructors? Yes, a class or a struct can have multiple constructors. Constructors in csharp can be overloaded. 114. Can A Child Class Call The Constructor Of A Base Class? Yes, a child class can call the constructor of a base class by using the base keyword as shown in the example below. using System; namespace TestConsole { class BaseClass { public BaseClass(string str) { Console.WriteLine(str); } } class ChildClass : BaseClass { public ChildClass(string str): base(str) { } public static void Main() { ChildClass CC = new ChildClass("Calling base class constructor from child class"); } } } 115. If A Child Class Instance Is Created, Which Class Constructor Is Called First - Base Class Or Child Class? When an instance of a child class is created, the base class constructor is called before the child class constructor. An example is shown below. using System; namespace TestConsole { class BaseClass { public BaseClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am a base class constructor"); } } class ChildClass : BaseClass { public ChildClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am a child class constructor"); } public static void Main() { ChildClass CC = new ChildClass(); } } } 116. Can A Class Have Static Constructor? Yes, a class can have static constructor. Static constructors are called automatically, immediately before any static fields are accessed, and are generally used to initialize static class members. It is called automatically before the first instance is created or any static members are referenced. Static constructors are called before instance constructors. An example is shown below. using System; namespace TestConsole { class Program { static int I; static Program() { I = 100; Console.WriteLine("Static Constructor called"); } public Program() { Console.WriteLine("Instance Constructor called"); } public static void Main() { Program P = new Program(); } } } 117. Can You Mark Static Constructor With Access Modifiers? No, we cannot use access modifiers on static constructor. 118. Can You Have Parameters For Static Constructors? No, static constructors cannot have parameters. 119. What Happens If A Static Constructor Throws An Exception? If a static constructor throws an exception, the runtime will not invoke it a second time, and the type will remain uninitialized for the lifetime of the application domain in which your program is running. 120. Give 2 Scenarios Where Static Constructors Can Be Used? 1. A typical use of static constructors is when the class is using a log file and the constructor is used to write entries to this file. 2. Static constructors are also useful when creating wrapper classes for unmanaged code, when the constructor can call the LoadLibrary method. 121. Does C# Provide Copy Constructor? No, C# does not provide copy constructor. 122. Is The Following Code Legal? using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { } public void Sum(int FirstNumber, int SecondNumber) { int Result = FirstNumber + SecondNumber; } public int Sum(int FirstNumber, int SecondNumber) { int Result = FirstNumber + SecondNumber; } } } No, The above code does not compile. You cannot overload a method based on the return type. To overload a method in C# either the number or type of parameters should be different. In general the return type of a method is not part of the signature of the method for the purposes of method overloading. However, it is part of the signature of the method when determining the compatibility between a delegate and the method that it points to. 123. What Is The Difference Between Method Parameters And Method Arguments. Give An Example? In the example below FirstNumber and SecondNumber are method parameters where as FN and LN are method arguments. The method definition specifies the names and types of any parameters that are required. When calling code calls the method, it provides concrete values called arguments for each parameter. The arguments must be compatible with the parameter type but the argument name (if any) used in the calling code does not have to be the same as the parameter named defined in the method. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { int FN = 10; int SN = 20; //FN and LN are method arguments int Total = Sum(FN, SN); Console.WriteLine(Total); } //FirstNumber and SecondNumber are method parameters public static int Sum(int FirstNumber, int SecondNumber) { int Result = FirstNumber + SecondNumber; return Result; } } } 124. Explain The Difference Between Passing Parameters By Value And Passing Parameters By Reference With An Example? We can pass parameters to a method by value or by reference. By default all value types are passed by value where as all reference types are passed by reference. By default, when a value type is passed to a method, a copy is passed instead of the object itself. Therefore, changes to the argument have no effect on the original copy in the calling method.An example is shown below. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { int I = 10; int K = Function(I); Console.WriteLine("I = " + I); Console.WriteLine("K = " + K); } public static int Function(int Number) { int ChangedValue = Number + 1; return ChangedValue; } } } By default, reference types are passed by reference. When an object of a reference type is passed to a method, the reference points to the original object, not a copy of the object. Changes made through this reference will therefore be reflected in the calling method. Reference types are created by using the class keyword as shown in the example below. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { ReferenceTypeExample Object = new ReferenceTypeExample(); Object.Number = 20; Console.WriteLine("Original Object Value = " + Object.Number); Function(Object); Console.WriteLine("Object Value after passed to the method= " + Object.Number); } public static void Function(ReferenceTypeExample ReferenceTypeObject) { ReferenceTypeObject.Number = ReferenceTypeObject.Number + 5; } } class ReferenceTypeExample { public int Number; } } 125. Can You Pass Value Types By Reference To A Method? Yes, we can pass value types by by reference to a method. An example is shown below. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { int I = 10; Console.WriteLine("Value of I before passing to the method = " + I); Function(ref I); Console.WriteLine("Value of I after passing to the method by reference= " + I); } public static void Function(ref int Number) { Number = Number + 5; } } } 126. If A Method's Return Type Is Void, Can You Use A Return Keyword In The Method? Yes, Even though a method's return type is void, you can use the return keyword to stop the execution of the method as shown in the example below. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { SayHi(); } public static void SayHi() { Console.WriteLine("Hi"); return; Console.WriteLine("This statement will never be executed"); } } } 127. What Are Properties In C#. Explain With An Example? Properties in C# are class members that provide a flexible mechanism to read, write, or compute the values of private fields. Properties can be used as if they are public data members, but they are actually special methods called accessors. This enables data to be accessed easily and still helps promote the safety and flexibility of methods. In the example below _firstName and _lastName are private string variables which are accessible only inside the Customer class. _firstName and _lastName are exposed using FirstName and LastName public properties respectively. The get property accessor is used to return the property value, and a set accessor is used to assign a new value. These accessors can have different access levels. The value keyword is used to define the value being assigned by the set accessor. The FullName property computes the full name of the customer. Full Name property is readonly, because it has only the get accessor. Properties that do not implement a set accessor are read only. The code block for the get accessor is executed when the property is read and the code block for the set accessor is executed when the property is assigned a new value. using System; class Customer { // Private fileds not accessible outside the class. private string _firstName = string.Empty; private string _lastName = string.Empty; private string _coutry = string.Empty; // public FirstName property exposes _firstName variable public string FirstName { get { return _firstName; } set { _firstName = value; } } // public LastName property exposes _lastName variable public string LastName { get { return _lastName; } set { _lastName = value; } } // FullName property is readonly and computes customer full name. public string FullName { get { return _lastName + ", " + _firstName; } } //Country Property is Write Only public string Country { set { _coutry = value; } } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Customer CustomerObject = new Customer(); //This line will call the set accessor of FirstName Property CustomerObject.FirstName = "David"; //This line will call the set accessor of LastName Property CustomerObject.LastName = "Boon"; //This line will call the get accessor of FullName Property Console.WriteLine("Customer Full Name is : " + CustomerObject.FullName); } } 128. Explain The 3 Types Of Properties In C# With An Example? Read Only Properties: Properties without a set accessor are considered read-only. In the above example FullName is read only property. Write Only Properties: Properties without a get accessor are considered write-only. In the above example Country is write only property. Read Write Properties: Properties with both a get and set accessor are considered read-write properties. In the above example FirstName and LastName are read write properties. 129. What Are The Advantages Of Properties In C#? Properties can validate data before allowing a change. Properties can transparently expose data on a class where that data is actually retrieved from some other source such as a database. Properties can take an action when data is changed, such as raising an event or changing the value of other fields. 130. What Is A Static Property. Give An Example? A property that is marked with a static keyword is considered as static property. This makes the property available to callers at any time, even if no instance of the class exists. In the example below PI is a static property. using System; class Circle { private static double _pi = 3.14; public static double PI { get { return _pi; } } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine(Circle.PI); } } 131. What Is A Virtual Property. Give An Example? A property that is marked with virtual keyword is considered virtual property. Virtual properties enable derived classes to override the property behavior by using the override keyword. In the example below FullName is virtual property in the Customer class. BankCustomer class inherits from Customer class and overrides the FullName virtual property. In the output you can see the over riden implementation. A property overriding a virtual property can also be sealed, specifying that for derived classes it is no longer virtual. using System; class Customer { private string _firstName = string.Empty; private string _lastName = string.Empty; public string FirstName { get { return _firstName; } set { _firstName = value; } } public string LastName { get { return _lastName; } set { _lastName = value; } } // FullName is virtual public virtual string FullName { get { return _lastName + ", " + _firstName; } } } class BankCustomer : Customer { // Overiding the FullName virtual property derived from customer class public override string FullName { get { return "Mr. " + FirstName + " " + LastName; } } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { BankCustomer BankCustomerObject = new BankCustomer(); BankCustomerObject.FirstName = "David"; BankCustomerObject.LastName = "Boon"; Console.WriteLine("Customer Full Name is : " + BankCustomerObject.FullName); } } 132. What Is An Abstract Property. Give An Example? A property that is marked with abstract keyword is considered abstract property. An abstract property should not have any implementation in the class. The derived classes must write their own implementation. In the example below FullName property is abstract in the Customer class. BankCustomer class overrides the inherited abstract FullName property with its own implementation. using System; abstract class Customer { private string _firstName = string.Empty; private string _lastName = string.Empty; public string FirstName { get { return _firstName; } set { _firstName = value; } } public string LastName { get { return _lastName; } set { _lastName = value; } } // FullName is abstract public abstract string FullName { get; } } class BankCustomer : Customer { // Overiding the FullName abstract property derived from customer class public override string FullName { get { return "Mr. " + FirstName + " " + LastName; } } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { BankCustomer BankCustomerObject = new BankCustomer(); BankCustomerObject.FirstName = "David"; BankCustomerObject.LastName = "Boon"; Console.WriteLine("Customer Full Name is : " + BankCustomerObject.FullName); } } 133. Can You Use Virtual, Override Or Abstract Keywords On An Accessor Of A Static Property? No, it is a compile time error to use a virtual, abstract or override keywords on an accessor of a static property. 134. What Are Constants In C#? Constants in C# are immutable values which are known at compile time and do not change for the life of the program. Constants are declared using the const keyword. Constants must be initialized as they are declared. You cannot assign a value to a constant after it isdeclared. An example is shown below. using System; class Circle { public const double PI = 3.14; public Circle() { //Error : You can only assign a value to a constant field at the time of declaration //PI = 3.15; } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine(Circle.PI); } } 135. Can You Declare A Class Or A Struct As Constant? No, User-defined types including classes, structs, and arrays, cannot be const. Only the C# built-in types excluding System.Object may be declared as const. Use the readonly modifier to create a class, struct, or array that is initialized one time at runtime (for example in a constructor) and thereafter cannot be changed. 136. Does C# Support Const Methods, Properties, Or Events? No, C# does not support const methods, properties, or events. 137. Can You Change The Value Of A Constant Filed After Its Declaration? No, you cannot change the value of a constant filed after its declaration. In the example below, the constant field PI is always 3.14, and it cannot be changed even by the class itself. In fact, when the compiler encounters a constant identifier in C# source code (for example, PI), it substitutes the literal value directly into the intermediate language (IL) code that it produces. Because there is no variable address associated with a constant at run time, const fields cannot be passed by reference. using System; class Circle { public const double PI = 3.14; } 138. How Do You Access A Constant Field Declared In A Class? Constants are accessed as if they were static fields because the value of the constant is the same for all instances of the type. You do not use the static keyword to declare them. Expressions that are not in the class that defines the constant must use the class name, a period, and the name of the constant to access the constant. In the example below constant field PI can be accessed in the Main method using the class name and not the instance of the class. Trying to access a constant field using a class instance will generate a compile time error. using System; class Circle { public const double PI = 3.14; } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine(Circle.PI); Circle C = new Circle(); // Error : PI cannot be accessed using an instance // Console.WriteLine(C.PI); } } 139. What Are The 2 Broad Classifications Of Fields In C#? Instance fields Static fields 140. What Are Instance Fields In C#? Instance fields are specific to an instance of a type. If you have a class T, with an instance field F, you can create two objects of type T, and modify the value of F in each object without affecting the value in the other object. 141. What Is A Static Field? A static field belongs to the class itself, and is shared among all instances of that class. Changes made from instance A will be visible immediately to instances B and C if they access the field. 142. Can You Declare A Field Readonly? Yes, a field can be declared readonly. A read-only field can only be assigned a value during initialization or in a constructor. An example is shown below. using System; class Area { public readonly double PI = 3.14; } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Area A = new Area(); Console.WriteLine(A.PI); } } 143. What Is Wrong With The Sample Program Below? using System; class Area { public const double PI = 3.14; static Area() { Area.PI = 3.15; } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine(Area.PI); } } You cannot assign a value to the constant PI field. 144. What Is The Difference Between A Constant And A Static Readonly Field? A static readonly field is very similar to a constant, except that the C# compiler does not have access to the value of a static read-only field at compile time, only at run time. 145. What Are Access Modifiers In C#? In C# there are 5 different types of Access Modifiers. 1. Public The public type or member can be accessed by any other code in the same assembly or another assembly that references it. 2. Private The type or member can only be accessed by code in the same class or struct. 3. Protected The type or member can only be accessed by code in the same class or struct, or in a derived class. 4. Internal The type or member can be accessed by any code in the same assembly, but not from another assembly. 5. Protected Internal The type or member can be accessed by any code in the same assembly, or by any derived class in another assembly. 146. What Are Access Modifiers Used For? Access Modifiers are used to control the accessibilty of types and members with in the types. 147. Can You Use All Access Modifiers For All Types? No, Not all access modifiers can be used by all types or members in all contexts, and in some cases the accessibility of a type member is constrained by the accessibility of its containing type. 148. Can Derived Classes Have Greater Accessibility Than Their Base Types? No, Derived classes cannot have greater accessibility than their base types. For example the following code is illegal. using System; internal class InternalBaseClass { public void Print() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Base Class Method"); } } public class PublicDerivedClass : InternalBaseClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Public Derived Class Method"); } } When you compile the above code an error will be generated stating "Inconsistent accessibility: base class InternalBaseClass is less accessible than class PublicDerivedClass".To make this simple, you cannot have a public class B that derives from an internal class A. If this were allowed, it would have the effect of making A public, because all protected or internal members of A are accessible from the derived class. 149. Can You Declare Struct Members As Protected? No, struct members cannot be declared protected. This is because structs do not support inheritance. 150. Can The Accessibility Of A Type Member Be Greater Than The Accessibility Of Its Containing Type? No, the accessibility of a type member can never be greater than the accessibility of its containing type. For example, a public method declared in an internal class has only internal accessibility. 151. Can Destructors Have Access Modifiers? No, destructors cannot have access modifiers. 152. What Does Protected Internal Access Modifier Mean? The protected internal access means protected OR internal, not protected AND internal. In simple terms, a protected internal member is accessible from any class in the same assembly, including derived classes. To limit accessibility to only derived classes in the same assembly, declare the class itself internal, and declare its members as protected. 153. What Is The Default Access Modifier For A Class,struct And An Interface Declared Directly With A Namespace? internal. 154. Can You Specify An Access Modifier For An Enumeration? Enumeration members are always public, and no access modifiers can be specified. 155. What Are The 3 Types Of Comments In C#? 1. Single Line Comments. You define single line comments with // as shown below. //This is an example for single line comment 2. Multi line comments. You define multi line comments with /* */ as shown below. /*This is an example for Multi Line comments*/ 3. XML Comments. You define XML comments with /// as shown below. ///This is an example for defining XML comments. 156. Is C# A Strongly-typed Language? Yes. 157. What Are The 2 Broad Classifications Of Data Types Available In C#? Built in data types. User defined data types. 158. Give Some Examples For Built In Datatypes In C#? int float bool 159. How Do You Create User Defined Data Types In C#? You use the struct, class, interface, and enum constructs to create your own custom types. The .NET Framework class library itself is a collection of custom types provided by Microsoft that you can use in your own applications. 160. What Are The 2 Types Of Data Types Available In C#? Value Types Reference Types 161. If You Define A User Defined Data Type By Using The Struct Keyword, Is It A Value Type Or Reference Type? Value Type. 162. If You Define A User Defined Data Type By Using The Class Keyword, Is It A Value Type Or Reference Type? Reference type 163. Are Value Types Sealed? Yes, Value types are sealed. 164. What Is The Base Class From Which All Value Types Are Derived? System.ValueType. 165. Give Examples For Value Types? Enum Struct 166. Give Examples For Reference Types? Class Delegate Array Interface. 167. What Are The Differences Between Value Types And Reference Types? Value types are stored on the stack where as reference types are stored on the managed heap. Value type variables directly contain their values where as reference variables holds only a reference to the location of the object that is created on the managed heap. There is no heap allocation or garbage collection overhead for value-type variables. As reference types are stored on the managed heap, they have the over head of object allocation and garbage collection. Value Types cannot inherit from another class or struct. Value types can only inherit from interfaces. Reference types can inherit from another class or interface. 168. What Do You Mean By Casting A Data Type? Converting a variable of one data type to another data type is called casting. This is also called as data type conversion. 169. What Are The 2 Kinds Of Data Type Conversions In C#? Implicit conversions: No special syntax is required because the conversion is type safe and no data will be lost. Examples include conversions from smaller to larger integral types, and conversions from derived classes to base classes. Explicit conversions: Explicit conversions require a cast operator. The source and destination variables are compatible, but there is a risk of data loss because the type of the destination variable is a smaller size than (or is a base class of) the source variable. 170. What Is The Difference Between An Implicit Conversion And An Explicit Conversion? Explicit conversions require a cast operator where as an implicit converstion is done automatically. Explicit conversion can lead to data loss where as with implicit conversions there is no data loss. 171. What Type Of Data Type Conversion Happens When The Compiler Encounters The Following Code? ChildClass CC = new ChildClass(); ParentClass PC = new ParentClass(); Implicit Conversion. For reference types, an implicit conversion always exists from a class to any one of its direct or indirect base classes or interfaces. No special syntax is necessary because a derived class always contains all the members of a base class. 172. If You Want To Convert A Base Type To A Derived Type, What Type Of Conversion Do You Use? Explicit conversion as shown below. //Create a new derived type. Car C1 = new Car(); // Implicit conversion to base type is safe. Vehicle V = C1; // Explicit conversion is required to cast back to derived type. The code below will compile but throw an exception at run time if the right-side object is not a Car object. Car C2 = (Car) V; 173. What Operators Can Be Used To Cast From One Reference Type To Another Without The Risk Of Throwing An Exception? The is and as operators can be used to cast from one reference type to another without the risk of throwing an exception. 174. If Casting Fails What Type Of Exception Is Thrown? InvalidCastException. 175. What Is Boxing And Unboxing? Boxing - Converting a value type to reference type is called boxing. An example is shown below. int i = 101; object obj = (object)i; // Boxing Unboxing - Converting a reference type to a value typpe is called unboxing. An example is shown below. obj = 101; i = (int)obj; // Unboxing 176. Is Boxing An Implicit Conversion? Yes, boxing happens implicitly. 177. Is Unboxing An Implicit Conversion? No, unboxing is an explicit conversion. 178. What Happens During The Process Of Boxing? Boxing is used to store value types in the garbage-collected heap. Boxing is an implicit conversion of a value type to the type object or to any interface type implemented by this value type. Boxing a value type allocates an object instance on the heap and copies the value into the new object. Due to this boxing and unboxing can have performance impact. 179. What Is An Array? An array is a data structure that contains several variables of the same type. 180. What Are The 3 Different Types Of Arrays? Single-Dimensional Multidimensional Jagged 181. What Is Jagged Array? A jagged array is an array of arrays. 182. Are Arrays Value Types Or Reference Types? Arrays are reference types. 183. What Is The Base Class For Array Types? System.Array. 184. Can You Use Foreach Iteration On Arrays In C#? Yes,Since array type implements IEnumerable, you can use foreach iteration on all arrays in C#. 185. What Is The Difference Between String Keyword And System.string Class? string keyword is an alias for Syste.String class. Therefore, System.String and string keyword are the same, and you can use whichever naming convention you prefer. The String class provides many methods for safely creating, manipulating, and comparing strings. 186. Are String Objects Mutable Or Immutable? String objects are immutable. 187. What Do You Mean By String Objects Are Immutable? String objects are immutable means, they cannot be changed after they have been created. All of the String methods and C# operators that appear to modify a string actually return the results in a new string object. In the following example, when the contents of s1 and s2 are concatenated to form a single string, the two original strings are unmodified. The += operator creates a new string that contains the combined contents. That new object is assigned to the variable s1, and the original object that was assigned to s1 is released for garbage collection because no other variable holds a reference to it. string s1 = "First String "; string s2 = "Second String"; // Concatenate s1 and s2. This actually creates a new // string object and stores it in s1, releasing the // reference to the original object. s1 += s2; System.Console.WriteLine(s1); // Output: First String Second String. 188. What Will Be The Output Of The Following Code? string str1 = "Hello "; string str2 = s1; str1 = str1 + "C#"; System.Console.WriteLine(s2); The output of the above code is "Hello" and not "Hello C#". This is bcos, if you create a reference to a string, and then "modify" the original string, the reference will continue to point to the original object instead of the new object that was created when the string was modified. 189. What Is A Verbatim String Literal And Why Do We Use It? The "@" symbol is the verbatim string literal. Use verbatim strings for convenience and better readability when the string text contains backslash characters, for example in file paths. Because verbatim strings preserve new line characters as part of the string text, they can be used to initialize multiline strings. Use double quotation marks to embed a quotation mark inside a verbatim string. The following example shows some common uses for verbatim strings: string ImagePath = @"C:\Images\Buttons\SaveButton.jpg"; //Output: C:\Images\Buttons\SaveButton.jpg string MultiLineText = @"This is multiline Text written to be in three lines."; /* Output: This is multiline Text written to be in three lines. */ string DoubleQuotesString = @"My Name is ""Vankat."""; //Output: My Name is "Vankat." 190. Will The Following Code Compile And Run? string str = null; Console.WriteLine(str.Length); The above code will compile, but at runtime System.NullReferenceException will be thrown 191. How Do You Create Empty Strings In C#? Using string.empty as shown in the example below. string EmptyString = string.empty; 192. What Is The Difference Between System.text.stringbuilder And System.string? Objects of type StringBuilder are mutable where as objects of type System.String are immutable. As StringBuilder objects are mutable, they offer better performance than string objects of type System.String StringBuilder class is present in System.Text namespace where String class is present in System namespace. 193. How Do You Determine Whether A String Represents A Numeric Value? To determine whether a String represents a numeric value use TryParse method as shown in the example below. If the string contains nonnumeric characters or the numeric value is too large or too small for the particular type you have specified, TryParse returns false and sets the out parameter to zero. Otherwise, it returns true and sets the out parameter to the numeric value of the string. string str = "One"; int i = 0; if(int.TryParse(str,out i)) { Console.WriteLine("Yes string contains Integer and it is " + i); } else { Console.WriteLine("string does not contain Integer"); } 194. What Is The Difference Between Int.parse And Int.tryparse Methods? Parse method throws an exception if the string you are trying to parse is not a valid number where as TryParse returns false and does not throw an exception if parsing fails. Hence TryParse is more efficient than Parse. 195. Why Should You Override The Tostring() Method? All types in .Net inherit from system.object directly or indirectly. Because of this inheritance, every type in .Net inherit the ToString() method from System.Object class. Consider the example below. using System; public class MainClass { public static void Main() { int Number = 10; Console.WriteLine(Number.ToString()); } } In the above example Number.ToString() method will correctly give the string representaion of int 10, when you call the ToString() method. If you have a Customer class as shown in the below example and when you call the ToString() method the output doesnot make any sense. Hence you have to override the ToString() method, that is inherited from the System.Object class. using System; public class Customer { public string FirstName; public string LastName; } public class MainClass { public static void Main() { Customer C = new Customer(); C.FirstName = "David"; C.LastName = "Boon"; Console.WriteLine(C.ToString()); } } The code sample below shows how to override the ToString() method in a class, that would give the output you want. using System; public class Customer { public string FirstName; public string LastName; public override string ToString() { return LastName + ", " + FirstName; } } public class MainClass { public static void Main() { Customer C = new Customer(); C.FirstName = "David"; C.LastName = "Boon"; Console.WriteLine(C.ToString()); } } Conclusion : If you have a class or a struct, make sure you override the inherited ToString() method. 196. Explain Polymorphism In C# With A Simple Example? Polymorphism allows you to invoke derived class methods through a base class reference during run-time. An example is shown below. using System; public class DrawingObject { public virtual void Draw() { Console.WriteLine("I am a drawing object."); } } public class Triangle : DrawingObject { public override void Draw() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Triangle."); } } public class Circle : DrawingObject { public override void Draw() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Circle."); } } public class Rectangle : DrawingObject { public override void Draw() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Rectangle."); } } public class DrawDemo { public static void Main() { DrawingObject DrawObj = new DrawingObject; DrawObj = new Triangle(); DrawObj = new Circle(); DrawObj = new Rectangle(); DrawObj = new DrawingObject(); foreach (DrawingObject drawObj in DrawObj) { drawObj.Draw(); } } } 197. When Can A Derived Class Override A Base Class Member? A derived class can override a base class member only if the base class member is declared as virtual or abstract. 198. What Is The Difference Between A Virtual Method And An Abstract Method? A virtual method must have a body where as an abstract method should not have a body. 199. Can Fields Inside A Class Be Virtual? No, Fields inside a class cannot be virtua. Only methods, properties, events and indexers can be virtual. 200. Give An Example To Show For Hiding Base Class Methods? Use the new keyword to hide a base class method in the derived class as shown in the example below. using System; public class BaseClass { public virtual void Method() { Console.WriteLine("I am a base class method."); } } public class DerivedClass : BaseClass { public new void Method() { Console.WriteLine("I am a child class method."); } public static void Main() { DerivedClass DC = new DerivedClass(); DC.Method(); } } 201. Can You Access A Hidden Base Class Method In The Derived Class? Yes, Hidden base class methods can be accessed from the derived class by casting the instance of the derived class to an instance of the base class as shown in the example below. using System; public class BaseClass { public virtual void Method() { Console.WriteLine("I am a base class method."); } } public class DerivedClass : BaseClass { public new void Method() { Console.WriteLine("I am a child class method."); } public static void Main() { DerivedClass DC = new DerivedClass(); ((BaseClass)DC).Method(); } } 202. What Is An Abstract Class? An abstract class is an incomplete class and must be implemented in a derived class. 203. Can You Create An Instance Of An Abstract Class? No, abstract classes are incomplete and you cannot create an instance of an abstract class. 204. What Is A Sealed Class? A sealed class is a class that cannot be inherited from. This means, If you have a class called Customer that is marked as sealed. No other class can inherit from Customer class. For example, the below code generates a compile time error "MainClass cannot derive from sealed type Customer. using System; public sealed class Customer { } public class MainClass : Customer { public static void Main() { } } 205. What Are Abstract Methods? Abstract methods are methods that only the declaration of the method and no implementation. 206. How Can You Force Derived Classes To Provide New Method Implementations For Virtual Methods? Abstract classes can be used to force derived classes to provide new method implementations for virtual methods. An example is shown below. public class BaseClass { public virtual void Method() { // Original Implementation. } } public abstract class AbstractClass : BaseClass { public abstract override void Method(); } public class NonAbstractChildClass : AbstractClass { public override void Method() { // New implementation. } } When an abstract class inherits a virtual method from a base class, the abstract class can override the virtual method with an abstract method. If a virtual method is declared abstract, it is still virtual to any class inheriting from the abstract class. A class inheriting an abstract method cannot access the original implementation of the method. In the above example, Method() on class NonAbstractChildClass cannot call Method() on class BaseClass. In this way, an abstract class can force derived classes to provide new method implementations for virtual methods. 207. Can A Sealed Class Be Used As A Base Class? No, sealed class cannot be used as a base class. A compile time error will be generated. 208. What Are The 4 Pillars Of Any Object Oriented Programming Language? 1. Abstraction 2. Inheritance 3. Encapsulation 4. Polymorphism 209. Do Structs Support Inheritance? No, structs do not support inheritance, but they can implement interfaces. 210. What Is The Main Advantage Of Using Inheritance? Code reuse. 211. Does C# Support Multiple Class Inheritance? No, C# supports single class inheritance only. However classes can implement multiple interfaces at the same time. 212. Can A Struct Have A Default Constructor (a Constructor Without Parameters) Or A Destructor In C#? No. 213. Can You Instantiate A Struct Without Using A New Operator In C#? Yes, you can instantiate a struct without using a new operator. 214. Can A Struct Inherit From Another Struct Or Class In C#? No, a struct cannot inherit from another struct or class, and it cannot be the base of a class. 215. Can A Struct Inherit From An Interface In C#? Yes. 216. Are Structs Value Types Or Reference Types? Structs are value types. 217. What Is The Base Type From Which All Structs Inherit Directly? All structs inherit directly from System.ValueType, which inherits from System.Object. 218. What Do You Mean By Saying A "class Is A Reference Type"? A class is a reference type means when an object of the class is created, the variable to which the object is assigned holds only a reference to that memory. When the object reference is assigned to a new variable, the new variable refers to the original object. Changes made through one variable are reflected in the other variable because they both refer to the same data. 219. What Do You Mean By Saying A "struct Is A Value Type"? A struct is a value type mean when a struct is created, the variable to which the struct is assigned holds the struct's actual data. When the struct is assigned to a new variable, it is copied. The new variable and the original variable therefore contain two separate copies of the same data. Changes made to one copy do not affect the other copy. 220. When Do You Generally Use A Class Over A Struct? A class is used to model more complex behavior, or data that is intended to be modified after a class object is created. A struct is best suited for small data structures that contain primarily data that is not intended to be modified after the struct is created. 221. List The 5 Different Access Modifiers In C#? 1. public 2. protected 3. internal 4. protected internal 5. private 222. If You Donot Specify An Access Modifier For A Method, What Is The Default Access Modifier? private. 223. Classes And Structs Support Inheritance. Is This Statement True Or False? False, Only classes support inheritance. structs donot support inheritance. 224. If A Class Derives From Another Class, Will The Derived Class Automatically Contain All The Public, Protected, And Internal Members Of The Base Class? Yes, the derived class will automatically contain all the public, protected, and internal members of the base class except its constructors and destructors. 225. Can You Create An Instance For An Abstract Class? No, you cannot create an instance for an abstract class. 226. How Do You Prevent A Class From Being Inherited By Another Class? Use the sealed keyword to prevent a class from being inherited by another class. 227. Classes And Structs Can Be Declared As Static, Is This Statement True Or False? False, only classes can be declared as static and not structs. 228. Can You Create An Instance Of A Static Class? No, you cannot create an instance of a static class. 229. Can A Static Class Contain Non Static Members? No, a static class can contain only static members. 230. Does C# Support Multiple-inheritance? No, but you can implement more than one interfaces. 231. Who Is A Protected Class-level Variable Available To? It is available to any sub-class (a class inheriting this class). 232. Are Private Class-level Variables Inherited? Yes, but they are not accessible. Although they are not visible or accessible via the class interface, they are inherited. 233. Describe The Accessibility Modifier "protected Internal". It is available to classes that are within the same assembly and derived from the specified base class. 234. What's The Top .net Class That Everything Is Derived From? System.Object. 235. What Does The Term Immutable Mean? The data value may not be changed. Note: The variable value may be changed, but the original immutable data value was discarded and a new data value was created in memory. 236. What's The Difference Between System.string And System.text.stringbuilder Classes? System.String is immutable. System.StringBuilder was designed with the purpose of having a mutable string where a variety of operations can be performed. 237. What's The .net Collection Class That Allows An Element To Be Accessed Using A Unique Key? HashTable, Dictionary, NameValueCollection. 238. What Class Is Underneath The Sortedlist Class? A sorted HashTable. 239. Will The Finally Block Get Executed If An Exception Has Not Occurred? Yes. Finally block always get executed. 240. What's The C# Syntax To Catch Any Possible Exception? A catch block that catches the exception of type System.Exception. You can also omit the parameter data type in this case and just write catch {}. 241. Can Multiple Catch Blocks Be Executed For A Single Try Statement? No. Once the proper catch block processed, control is transferred to the finally block (if there are any). 242. Explain The Three Services Model Commonly Know As A Three-tier Application. Presentation (UI), Business (logic and underlying code) and Data (from storage or other sources). 243. If A.equals(b) Is True Then A.gethashcode & B.gethashcode Must Always Return Same Hash Code. The answer is False because it is given that A.equals(B) returns true i.e. objects are equal and now its hash Code is asked which is always independent of the fact that whether objects are equal or not. So, Get HashCode for both of the objects returns different value. 244. What Is The Syntax To Inherit From A Class In C#? Place a colon and then the name of the base class. Example: class MyNewClass : MyBaseClass. 245. Can You Prevent Your Class From Being Inherited By Another Class? Yes. The keyword “sealed” will prevent the class from being inherited. 246. Can You Allow A Class To Be Inherited, But Prevent The Method From Being Over-ridden? Yes. Just leave the class public and make the method sealed. 247. What's An Abstract Class? A class that cannot be instantiated. An abstract class is a class that must be inherited and have the methods overridden. An abstract class is essentially a blueprint for a class without any implementation. 248. When Do You Absolutely Have To Declare A Class As Abstract? 1. When the class itself is inherited from an abstract class, but not all base abstract methods have been overridden. 2. When at least one of the methods in the class is abstract. 249. What Is An Interface Class? Interfaces, like classes, define a set of properties, methods, and events. But unlike classes, interfaces do not provide implementation. They are implemented by classes, and defined as separate entities from classes. 250. Why Can't You Specify The Accessibility Modifier For Methods Inside The Interface? They all must be public, and are therefore public by default. 251. Can You Inherit Multiple Interfaces? Yes. .NET does support multiple interfaces. 252. What Happens If You Inherit Multiple Interfaces And They Have Conflicting Method Names? It’s up to you to implement the method inside your own class, so implementation is left entirely up to you. This might cause a problem on a higher-level scale if similarly named methods from different interfaces expect different data, but as far as compiler cares you’re okay. To Do: Investigate. 253. What's The Difference Between An Interface And Abstract Class? In an interface class, all methods are abstract - there is no implementation. In an abstract class some methods can be concrete. In an interface class, no accessibility modifiers are allowed. An abstract class may have accessibility modifiers. 254. What Is The Difference Between A Struct And A Class? Structs are value-type variables and are thus saved on the stack, additional overhead but faster retrieval. Another difference is that structs cannot inherit. 255. What's The Implicit Name Of The Parameter That Gets Passed Into The Set Method/property Of A Class? Value. The data type of the value parameter is defined by whatever data type the property is declared as. 256. What Does The Keyword "virtual" Declare For A Method Or Property? The method or property can be overridden. 257. How Is Method Overriding Different From Method Overloading? When overriding a method, you change the behavior of the method for the derived class. Overloading a method simply involves having another method with the same name within the class. 258. Can You Declare An Override Method To Be Static If The Original Method Is Not Static? No. The signature of the virtual method must remain the same. (Note: Only the keyword virtual is changed to keyword override) 259. What Are The Different Ways A Method Can Be Overloaded? Different parameter data types, different number of parameters, different order of parameters. 260. If A Base Class Has A Number Of Overloaded Constructors, And An Inheriting Class Has A Number Of Overloaded Constructors; Can You Enforce A Call From An Inherited Constructor To A Specific Base Constructor? Yes, just place a colon, and then keyword base (parameter list to invoke the appropriate constructor) in the overloaded constructor definition inside the inherited class. 261. What Does Assert() Method Do? In debug compilation, assert takes in a Boolean condition as a parameter, and shows the error dialog if the condition is false. The program proceeds without any interruption if the condition is true. 262. What's The Difference Between The Debug Class And Trace Class? Documentation looks the same. Use Debug class for debug builds, use Trace class for both debug and release builds. 263. What Is The Role Of The Datareader Class In Ado.net Connections? It returns a read-only, forward-only rowset from the data source. A DataReader provides fast access when a forward-only sequential read is needed. 264. What Is The Wildcard Character In Sql? Let’s say you want to query database with LIKE for all employees whose name starts with La. The wildcard character is %, the proper query with LIKE would involve ‘La%’. 265. Between Windows Authentication And Sql Server Authentication, Which One Is Trusted And Which One Is Untrusted? Windows Authentication is trusted because the username and password are checked with the Active Directory, the SQL Server authentication is untrusted, since SQL Server is the only verifier participating in the transaction. 266. What Does The Dispose Method Do With The Connection Object? Dispose places the connection backing the managed pool. So that other objects/class can use the connection for further use. 267. How Is The Dll Hell Problem Solved In .net? Assembly versioning allows the application to specify not only the library it needs to run (which was available under Win32), but also the version of the assembly. 268. What Is A Satellite Assembly? When you write a multilingual or multi-cultural application in .NET, and want to distribute the core application separately from the localized modules, the localized assemblies that modify the core application are called satellite assemblies. 269. What Is The Smallest Unit Of Execution In .net? an Assembly. 270. When Should You Call The Garbage Collector In .net? As a good rule, you should not call the garbage collector. However, you could call the garbage collector when you are done using a large object (or set of objects) to force the garbage collector to dispose of those very large objects from memory. However, this is usually not a good practice. 271. How Do You Convert A Value-type To A Reference-type? Use Boxing. 272. What Happens In Memory When You Box And Unbox A Value-type? Boxing converts a value-type to a reference-type, thus storing the object on the heap. Unboxing converts a reference-type to a value-type, thus storing the value on the stack. 273. What's C# ? C# (pronounced C-sharp) is a new object oriented language from Microsoft and is derived from C and C++. It also borrows a lot of concepts from Java too including garbage collection. 274. Is It Possible To Inline Assembly Or Il In C# Code? No. 275. Is It Possible To Have Different Access Modifiers On The Get/set Methods Of A Property? No. The access modifier on a property applies to both its get and set accessors. What you need to do if you want them to be different is make the property read-only (by only providing a get accessor) and create a private/internal set method that is separate from the property. 276. Is It Possible To Have A Static Indexer In C#? Allowed In C#. No. Static indexers are not 277. If I Return Out Of A Try/finally In C#, Does The Code In The Finally-clause Run? Yes. The code in the finally always runs. If you return out of the try block, or even if you do a goto out of the try, the finally block always runs: using System; class main { public static void Main() { try { Console.WriteLine(\"In Try block\"); return; } finally { Console.WriteLine(\"In Finally block\"); } } } Both In Try block and In Finally block will be displayed. Whether the return is in the try block or after the try-finally block, performance is not affected either way. The compiler treats it as if the return were outside the try block anyway. If it’s a return without an expression (as it is above), the IL emitted is identical whether the return is inside or outside of the try. If the return has an expression, there’s an extra store/load of the value of the expression (since it has to be computed within the try block). 278. I Was Trying To Use An Out Int Parameter In One Of My Functions. How Should I Declare The Variable That I Am Passing To It? You should declare the variable as an int, but when you pass it in you must specify it as ‘out’, like the following: int i; foo(out i); where foo is declared as follows: foo(out int o) { } 279. How Does One Compare Strings In C#? In the past, you had to call .ToString() on the strings when using the == or != operators to compare the strings’ values. That will still work, but the C# compiler now automatically compares the values instead of the references when the == or != operators are used on string types. If you actually do want to compare references, it can be done as follows: if ((object) str1 == (object) str2) { } Here’s an example showing how string compares work: using System; public class StringTest { public static void Main(string args) { Object nullObj = null; Object realObj = new StringTest(); int i = 10; Console.WriteLine(\"Null Object is \n\" + \"Real Object is \n\" + \"i is \n\"); // Show string equality operators string str1 = \"foo\"; string str2 = \"bar\"; string str3 = \"bar\"; Console.WriteLine(\"{0} == {1} ? {2}\", str1, str2, str1 == str2 ); Console.WriteLine(\"{0} == {1} ? {2}\", str2, str3, str2 == str3 ); } } Output: Null Object is Real Object is i is foo == bar ? False bar == bar ? True 280. How Do You Specify A Custom Attribute For The Entire Assembly (rather Than For A Class)? Global attributes must appear after any top-level using clauses and before the first type or namespace declarations. An example of this is as follows: using System; class X {} Note that in an IDE-created project, by convention, these attributes are placed in AssemblyInfo.cs. 281. How Do You Mark A Method Obsolete? public int Foo() {...} or public int Foo() {...} Note: The O in Obsolete is always capitalized. 282. How Do You Implement Thread Synchronization (object.wait, Notify,and Criticalsection) In C#? You want the lock statement, which is the same as Monitor Enter/Exit: lock(obj) { // code } translates to try { CriticalSection.Enter(obj); // code } finally { CriticalSection.Exit(obj); } 283. How Do You Directly Call A Native Function Exported From A Dll? Here’s a quick example of the DllImport attribute in action: using System.Runtime.InteropServices; class C { public static extern int MessageBoxA(int h, string m, string c, int type); public static int Main() { return MessageBoxA(0, \"Hello World!\", \"Caption\", 0); } } This example shows the minimum requirements for declaring a C# method that is implemented in a native DLL. The method C.MessageBoxA() is declared with the static and external modifiers, and has the DllImport attribute, which tells the compiler that the implementation comes from the user32.dll, using the default name of Message BoxA. For more information, look at the Platform Invoke tutorial in the documentation. 284. How Do I Simulate Optional Parameters To Com Calls? You must use the Missing class and pass Missing.Value (in System.Reflection) for any values that have optional parameters. 285. What Do You Know About .net Assemblies? Assemblies are the smallest units of versioning and deployment in the .NET application. Assemblies are also the building blocks for programs such as Web services, Windows services, serviced components, and .NET remoting applications. 286. What's The Difference Between Private And Shared Assembly? Private assembly is used inside an application only and does not have to be identified by a strong name. Shared assembly can be used by multiple applications and has to have a strong name. 287. What's A Strong Name? A strong name includes the name of the assembly, version number, culture identity, and a public key token. 288. How Can You Tell The Application To Look For Assemblies At The Locations Other Than Its Own Install? Use the directive in the XML .config file for a given application. should do the trick. Or you can add additional search paths in the Properties box of the deployed application. 289. How Can You Debug Failed Assembly Binds? Use the Assembly Binding Log Viewer (fuslogvw.exe) to find out the paths searched. 290. Where Are Shared Assemblies Stored? Global assembly cache. 291. How Can You Create A Strong Name For A .net Assembly? With the help of Strong Name tool (sn.exe). 292. Where's Global Assembly Cache Located On The System? Usually C:\winnt\assembly or C:\windows\assembly. 293. Can You Have Two Files With The Same File Name In Gac? Yes, remember that GAC is a very special folder, and while normally you would not be able to place two files with the same name into a Windows folder, GAC differentiates by version number as well, so it’s possible for MyApp.dll and MyApp.dll to co-exist in GAC if the first one is version 1.0.0.0 and the second one is 1.1.0.0. 294. So Let's Say I Have An Application That Uses Myapp.dll Assembly, Version 1.0.0.0. There Is A Security Bug In That Assembly, And I Publish The Patch, Issuing It Under Name Myapp.dll 1.1.0.0. How Do I Tell The Client Applications That Are Already Installed To Start Using This New Myapp.dll? Use publisher policy. To configure a publisher policy, use the publisher policy configuration file, which uses a format similar app .config file. But unlike the app .config file, a publisher policy file needs to be compiled into an assembly and placed in the GAC. 295. What Is Delay Signing? Delay signing allows you to place a shared assembly in the GAC by signing the assembly with just the public key. This allows the assembly to be signed with the private key at a later stage, when the development process is complete and the component or assembly is ready to be deployed. This process enables developers to work with shared assemblies as if they were strongly named, and it secures the private key of the signature from being accessed at different stages of development. 296. Is There An Equivalent Of Exit() For Quitting A C# .net Application? Yes, you can use System.Environment.Exit(int exitCode) to exit the application or Application.Exit() if it's a Windows Forms app. 297. Can You Prevent Your Class From Being Inherited And Becoming A Base Class For Some Other Classes? Yes, that is what keyword sealed in the class definition is for. The developer trying to derive from your class will get a message: cannot inherit from Sealed class WhateverBaseClassName. It is the same concept as final class in Java. 298. If A Base Class Has A Bunch Of Overloaded Constructors, And An Inherited Class Has Another Bunch Of Overloaded Constructors, Can You Enforce A Call From An Inherited Constructor To An Arbitrary Base Constructor? Yes, just place a colon, and then keyword base (parameter list to invoke the appropriate constructor) in the overloaded constructor definition inside the inherited class. 299. I Was Trying To Use An "out Int" Parameter In One Of My Functions. How Should I Declare The Variable That I Am Passing To It? You should declare the variable as an int, but when you pass it in you must specify it as 'out', like the following: int i; foo(out i); where foo is declared as follows: foo(out int o) { } 300. How Do I Make A Dll In C#? You need to use the /target:library compiler option. 301. What Is The C# Equivalent Of C++ Catch (....), Which Was A Catch-all Statement For Any Possible Exception? Does C# Support Try-catch-finally Blocks? Yes. Try-catch-finally blocks are supported by the C# compiler. Here's an example of a try-catch-finally block: using System; public class TryTest { static void Main() { try { Console.WriteLine("In Try block"); throw new ArgumentException(); } catch(ArgumentException n1) { Console.WriteLine("Catch Block"); } finally { Console.WriteLine("Finally Block"); } } } Output: In Try Block Catch Block Finally Block If I return out of a try/finally in C#, does the code in the finally-clause run? Yes. The code in the finally always runs. If you return out of the try block, or even if you do a "goto" out of the try, the finally block always runs, as shown in the following example: using System; class main { public static void Main() { try { Console.WriteLine("In Try block"); return; } finally { Console.WriteLine("In Finally block"); } } } Both "In Try block" and "In Finally block" will be displayed. Whether the return is in the try block or after the try-finally block, performance is not affected either way. The compiler treats it as if the return were outside the try block anyway. If it's a return without an expression (as it is above), the IL emitted is identical whether the return is inside or outside of the try. If the return has an expression, there's an extra store/load of the value of the expression (since it has to be computed within the try block). 302. Is There Regular Expression (regex) Support Available To C# Developers? Yes. The .NET class libraries provide support for regular expressions. Look at the documentation for the System. Text.Regular Expressions namespace. 303. Is There A Way To Force Garbage Collection? Yes. Set all references to null and then call System.GC.Collect(). If you need to have some objects destructed, and System.GC.Collect() doesn't seem to be doing it for you, you can force finalizers to be run by setting all the references to the object to null and then calling System.GC.RunFinalizers(). 304. Does C# Support Properties Of Array Types? Yes. Here's a simple example: using System; class Class1 { private string MyField; public string MyProperty { get { return MyField; } set { MyField = value; } } } class MainClass { public static int Main(string args) { Class1 c = new Class1(); string arr = new string {"apple", "banana"}; c.MyProperty = arr; Console.WriteLine(c.MyProperty); // "apple" return 0; } } 305. How Is Method Overriding Different From Overloading? When overriding, you change the method behavior for a derived class. Overloading simply involves having a method with the same name within the class. 306. When Do You Absolutely Have To Declare A Class As Abstract (as Opposed To Free-willed Educated Choice Or Decision Based On Uml Diagram)? When at least one of the methods in the class is abstract. When the class itself is inherited from an abstract class, but not all base abstract methods have been over-ridden. 307. Why Would You Use Untrusted Verification? Web Services might use it, as well as non-Windows applications. 308. What Is The Implicit Name Of The Parameter That Gets Passed Into The Class Set Method? Value, and its datatype depends on whatever variable we are changing. 309. How Do I Register My Code For Use By Classic Com Clients? Use the regasm.exe utility to generate a type library (if needed) and the necessary entries in the Windows Registry to make a class available to classic COM clients. Once a class is registered in the Windows Registry with regasm.exe, a COM client can use the class as though it were a COM class. 310. How Do I Do Implement A Trace And Assert? Use a conditional attribute on the method, as shown below: class Debug { public void Trace(string s) { Console.WriteLine(s); } } class MyClass { public static void Main() { Debug.Trace("hello"); } } In this example, the call to Debug.Trace() is made only if the preprocessor symbol TRACE is defined at the call site. You can define preprocessor symbols on the command line by using the /D switch. The restriction on conditional methods is that they must have void return type. 311. How Do I Create A Multi Language, Multi File Assembly? Unfortunately, this is currently not supported in the IDE. To do this from the command line, you must compile your projects into netmodules (/target:module on the C# compiler), and then use the command line tool al.exe (alink) to link these netmodules together. 312. C# Provides A Default Constructor For Me. I Write A Constructor That Takes A String As A Parameter, But Want To Keep The No Parameter One. How Many Constructors Should I Write? Two. Once you write at least one constructor, C# cancels the freebie constructor, and now you have to write one yourself, even if there is no implementation in. 313. What Is The Equivalent To Regsvr32 And Regsvr32 /u A File In .net Development? Try using RegAsm.exe. The general syntax would be: RegAsm. A good description of RegAsm and its associated switches is located in the .NET SDK docs. Just search on "Assembly Registration Tool".Explain ACID rule of thumb for transactions. Transaction must be Atomic (it is one unit of work and does not dependent on previous and following transactions), Consistent (data is either committed or roll back, no in-between case where something has been updated and something hasnot), Isolated (no transaction sees the intermediate results of the current transaction), Durable (the values persist if the data had been committed even if the system crashes right after). 314. How Do I Create A Multilanguage, Single-file Assembly? This is currently not supported by Visual Studio .NET. 315. Why Cannot You Specify The Accessibility Modifier For Methods Inside The Interface? They all must be public. Therefore, to prevent you from getting the false impression that you have any freedom of choice, you are not allowed to specify any accessibility, it is public by default. 316. Is It Possible To Restrict The Scope Of A Field/method Of A Class To The Classes In The Same Namespace? There is no way to restrict to a namespace. Namespaces are never units of protection. But if you're using assemblies, you can use the 'internal' access modifier to restrict access to only within the assembly. 317. Why Do I Get A Syntax Error When Trying To Declare A Variable Called Checked? The word checked is a keyword in C#. 318. What Is The Syntax For Calling An Overloaded Constructor Within A Constructor (this() And Constructorname() Does Not Compile)? The syntax for calling another constructor is as follows: class B { B(int i) { } } class C : B { C() : base(5) // call base constructor B(5) { } C(int i) : this() // call C() { } public static void Main() {} } 319. Why Do I Get A "cs5001: Does Not Have An Entry Point Defined" Error When Compiling? The most common problem is that you used a lowercase 'm' when defining the Main method. The correct way to implement the entry point is as follows: class test { static void Main(string args) {} } 320. What Does The Keyword Virtual Mean In The Method Definition? The method can be over-ridden. 321. What Optimizations Does The C# Compiler Perform When You Use The /optimize+ Compiler Option? The following is a response from a developer on the C# compiler team: We get rid of unused locals (i.e., locals that are never read, even if assigned). We get rid of unreachable code. We get rid of try-catch w/ an empty try. We get rid of try-finally w/ an empty try (convert to normal code...). We get rid of try-finally w/ an empty finally (convert to normal code...). We optimize branches over branches: gotoif A, lab1 goto lab2: lab1: turns into: gotoif !A, lab2 lab1: We optimize branches to ret, branches to next instruction, and branches to branches. 322. How Can I Create A Process That Is Running A Supplied Native Executable (e.g., Cmd.exe)? The following code should run the executable and wait for it to exit before continuing: using System; using System.Diagnostics; public class ProcessTest { public static void Main(string args) { Process p = Process.Start(args); p.WaitForExit(); Console.WriteLine(args + " exited."); } } Remember to add a reference to System.Diagnostics.dll when you compile. 323. What Is The Difference Between The System.array.copyto() And System.array.clone()? The first one performs a deep copy of the array, the second one is shallow. 324. How Do I Declare Inout Arguments In C#? The equivalent of inout in C# is ref. , as shown in the following example: public void MyMethod (ref String str1, out String str2) { ... } When calling the method, it would be called like this: String s1; String s2; s1 = "Hello"; MyMethod(ref s1, out s2); Console.WriteLine(s1); Console.WriteLine(s2); Notice that you need to specify ref when declaring the function and calling it. 325. Is There A Way Of Specifying Which Block Or Loop To Break Out Of When Working With Nested Loops? The easiest way is to use goto: using System; class BreakExample { public static void Main(String args) { for(int i=0; i Read the full article
0 notes
Photo

Is Blockchain an aberration to the hype it has created? Blockchain technology is not suitable for everything. Is it really an aberration to the buzz it has created in the industry. If you plan to invest in blockchain, do your research if it is really disrupting your business. Do your independent research and consult a blockchain professional, if you plan to use it. Learn from Blockchain technology is not suitable for everything. Is it really an aberration to the buzz it has created in the industry. If you plan to invest in blockchain, do your research if it is really disrupting your business. Do your independent research and consult a blockchain professional, if you plan to use it. Learn from History: the Dot-Com Bubble Just about every type of company that’s out there, and regardless of whether or not it’s necessary, is attempting to use blockchain. Admittedly, it’s a revolutionary new technology, however, no matter how great an invention, it’s not meant for everything. Please note that I am not trying to bash blockchain, but rather shedding some light and reality into the overly hyped blockchain space. Remember the dot-com bubble from the late 90s and early 2000s? Remember Pets.com? If you’re too young to recall or would like a refresher, then I’ll tell you that it was just about another company trying to get on the dot-com bandwagon by making some catchy logos and what was considered a nice website at the time. The company founders were all over the morning talk shows, but what ended up happening was that the whole concept was an epic fail. Why? Because of not having a solid product to offer. So, the lesson that can be learned here is that no matter how great your marketing and sales strategy, if you do not have a legitimate product, then you’ll be on a quick route to failure. Also, just by using the latest technology to sell a useless product doesn’t help much either. Blockchain Must Have Use Cases Applicable to Your Business Put simply, if you’re trying to sell people stuff they don’t need or don’t want, then you’re not going to achieve long-term success. Moreover, you’ll steadily build a bad reputation for yourself, and later on, even if you do actually come out with a great product, you might have a rather difficult time convincing people that it is actually useful. Similarly, with blockchain technology, as veteran Axes and Eggs ICO and blockchain analyst, Samson Williams informed me, distributed ledger technology (DLT) is not meant for everything. A simple spreadsheet may suffice in many cases or a simple database set up in Microsoft Access, Samson noted. Furthermore, my interview with Blockchain and DLT head Sheila Warren from the World Economic Forum taught me that there were many instances where blockchain technology had been used; but, it was not the appropriate solution for the problem it was trying to solve. In fact, Sheila and her colleagues have developed a toolkit that helps businesses and organizations determine whether blockchain technology is right for them. Once again, let me be clear. The blockchain is an excellent tool but requires careful research and understanding before it can be properly used. Beware of Disinformation related to Blockchain There’s also another type of problem-related to the blockchain. This time it’s not actually with the technology itself, but more of a social thing. That being, there are people disseminating disinformation regarding what blockchain actually is. We’ve got people like a prominent economist and professor Nouriel Roubini, who accurately predicted the 2007 housing bubble crash, who recently stated that blockchain is “nothing but a glorified spreadsheet.” This comment in itself shows a high level of ignorance, considering that Bitcoin uses a blockchain. And, we know how effective a blockchain can be considering that Bitcoin simplifies monetary transactions greatly. Yes, Bitcoin has its share of problems with scalability issues and high transaction fees. However, there’s a solid development team behind it and they’re working on upgrading it around the clock. There’s the lightning network that is being developed, which aims to conduct off-chain transactions. So, the main blockchain won’t be so clogged up. Nevertheless, the foundation of the Bitcoin network is super strong, as it has never been hacked, and the foundation, of course, was built on a blockchain. Good & Bad Examples of How to Use a Blockchain The Factor protocol is a good implementation and use of blockchain technology. The factor is designed to verify the authenticity of legal documents and research papers. In fact, just about any document can be verified by linking it to its real author or source using the platform’s blockchain. Also, the Factom blockchain does not store the actual document. Instead, it simply stores references or pointers to the real or genuine version of the document. This way, its blockchain only stores what’s absolutely required. Thus, it eliminates the scalability problem by not burdening the main blockchain with too much data. I might receive a lot of criticism for this, but a bad implementation and use of blockchain technology is Dan Larimer’s Steemit platform. Yes, the idea is great to have an incentivized social media platform. However, even with far fewer users than Facebook or Twitter, the Steemit platform is already slowing down considerably. For instance, if you try to upvote a comment, the blockchain is unable to process your request for a long period of time. This is not always the case, but it occurs often enough. Sometimes, when you try to re-them a post, which is the equivalent almost of sharing via Facebook, the blockchain slows down, and fairly often, your request cannot even be processed. So, the best thing users are left with is simply trying at a later time. Therefore, this shows that something that requires an inordinate amount of data to be processed should not be implemented on a blockchain. On second thought, it would be better to process the absolutely essential data on the blockchain. And then, all other processes can be implemented off-chain. Of course, this is not as simple as how I am describing it here. Programming a blockchain requires expert-level coding skills and experience. Additionally, the blockchains of today are simply their first version, which needs to be drastically improved. Notably, ex-JPMorgan blockchain head Amber Baldett aptly pointed out that the blockchains of today are like the dial-up internet or even the internet from the 1960s. So, blockchains have not yet advanced to the point that they can be considered a truly robust, scalable, and long-term solution. Threat to Blockchains The binary-based blockchains of today have the potential of being attacked by quantum computers in the near future. In fact, Google unveiled the latest 72 qubit quantum computer. This is a drastic improvement from IBM’s 50-qubit processor from last year. In simple terms, quantum computers are able to process information in more than two states. Meanwhile, binary computers of today can only process data in two states: 0s and 1s. Once quantum computers have matured to the point that they are suitable for mass adoption, all existing digital infrastructure will have to be updated and migrated. It will be quite easy to migrate centralized systems as most of the control is in the hands of a central authority. However, users of decentralized blockchains of today will have to manually migrate their information over to a quantum resistant network. That’s only if a legitimate one exists. There are, notably, crypto-platforms that are quantum resistant even now, such as the IOTA platform. Then, there’s the new Quantum Resistant Ledger platform being built as well. Both crypto platforms have been designed with the future in mind. Now, if you’re seeking a blockchain solution, you might want to consult the right people or organization that can build you a quantum-resistant blockchain, which might not be such an easy task right now. Contributed by – Omar Faridi, Lead Editor and Executive @Cryptocore Media https://coinmarked.com/is-blockchain-an-aberration-to-the-hype-it-has-created/?feed_id=403&_unique_id=5d6f35625789d
0 notes
Text
A Breach, or Just a Forced Password Reset?
Software giant Citrix Systems recently forced a password reset for many users of its Sharefile content collaboration service, warning it would be doing this on a regular basis in response to password-guessing attacks that target people who re-use passwords across multiple Web sites. Many Sharefile users interpreted this as a breach at Citrix and/or Sharefile, but the company maintains that’s not the case. Here’s a closer look at what happened, and some ideas about how to avoid a repeat of this scenario going forward.
The notice sent to ShareFile users looked like this:
Dozens of readers forwarded the above message to KrebsOnSecurity, saying they didn’t understand the reasoning for the mass password reset and that they suspected a breach at ShareFile.
I reached out to ShareFile and asked them point blank whether this reset effort was in response to any sort of intrusion at Citrix or ShareFile; they said no. I asked if this notice had been sent to everyone, and inquired whether ShareFile offers any form(s) of multi-factor authentication options that customers could use to supplement the security of passwords.
A Citrix spokesperson referred me to this page, which says ShareFile users have a number of options when it comes to locking down their accounts with multi-factor authentication, including a one-time code sent via SMS/text message, as well as one-time passwords generated by support authenticator mobile apps from Google and Microsoft (app-based multi-factor is the more secure option, as discussed here).
More importantly, the Citrix spokesperson said the company did not enforce a password reset on accounts that were using multi-factor authentication. To wit:
“This is not in response to a breach of Citrix products or services,” wrote spokesperson Jamie Buranich. “Citrix forced password resets with the knowledge that attacks of this nature historically come in waves. Attacker’s additional efforts adapt to the results, often tuning the volume and approach of their methods. Our objective was to minimize the risk to our customers. We did not enforce a password reset on accounts that are using more stringent authentication controls [emphasis added]. Citrix also directly integrates with common SSO solutions, which significantly reduces risk.”
The company did not respond to questions about why it decided to adopt regular password resets as a policy when doing so flies in the face of password and authentication best practices recommended the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which warns:
“Verifiers SHOULD NOT require memorized secrets to be changed arbitrarily (e.g., periodically). However, verifiers SHALL force a change if there is evidence of compromise of the authenticator.”
NIST explains its rationale for steering organizations away from regular forced password resets thusly:
“Users tend to choose weaker memorized secrets when they know that they will have to change them in the near future. When those changes do occur, they often select a secret that is similar to their old memorized secret by applying a set of common transformations such as increasing a number in the password. This practice provides a false sense of security if any of the previous secrets has been compromised since attackers can apply these same common transformations.”
“But if there is evidence that the memorized secret has been compromised, such as by a breach of the verifier’s hashed password database or observed fraudulent activity, subscribers should be required to change their memorized secrets. However, this event-based change should occur rarely, so that they are less motivated to choose a weak secret with the knowledge that it will only be used for a limited period of time.”
In short, NIST says it makes sense to force an across-the-board password reset following a breach — either of a specific user’s account or the entire password database. But doing so at regular intervals absent such evidence of compromise is likely to result in less complex and secure passwords.
Ideally, ShareFile users who received a password reset notice can avoid the next round of password resets by adopting one of the two-step authentication options mentioned above. And I hope it goes without saying, but please don’t re-use a password you used anywhere else.
However, if you are the type of person who likes to re-use passwords, then you definitely need to be using a password manager, which helps you pick and remember strong passwords/passphrases and essentially lets you use the same strong master password/passphrase across all Web sites.
Incidentally, there are several companies — such as auth0 and Okta — that make it easy to integrate with breached password databases like Troy Hunt’s HaveIBeenPwned.com to help proactively prevent users from picking passwords they have used at other sites (or at least at other sites that have been breached publicly).
Whether online merchants are willing to adopt such preemptive approaches is another matter, said Julie Conroy, research director with the Aite Group, a market analyst firm.
“With the reality that such a vast swath of username/password combinations have been compromised, this creates the potential for a ton of inline friction, something that is an anathema to merchants, and which banks work hard to stay away from as well,” Conroy said.
Update: 4:53 p.m. ET: Citrix just published its own blog post about this here.
from https://krebsonsecurity.com/2018/12/a-breach-or-just-a-forced-password-reset/
0 notes
Text
A Breach, or Just a Forced Password Reset?
Software giant Citrix Systems recently forced a password reset for many users of its Sharefile content collaboration service, warning it would be doing this on a regular basis in response to password-guessing attacks that target people who re-use passwords across multiple Web sites. Many Sharefile users interpreted this as a breach at Citrix and/or Sharefile, but the company maintains that’s not the case. Here’s a closer look at what happened, and some ideas about how to avoid a repeat of this scenario going forward.
The notice sent to ShareFile users looked like this:
Dozens of readers forwarded the above message to KrebsOnSecurity, saying they didn’t understand the reasoning for the mass password reset and that they suspected a breach at ShareFile.
I reached out to ShareFile and asked them point blank whether this reset effort was in response to any sort of intrusion at Citrix or ShareFile; they said no. I asked if this notice had been sent to everyone, and inquired whether ShareFile offers any form(s) of multi-factor authentication options that customers could use to supplement the security of passwords.
A Citrix spokesperson referred me to this page, which says ShareFile users have a number of options when it comes to locking down their accounts with multi-factor authentication, including a one-time code sent via SMS/text message, as well as one-time passwords generated by support authenticator mobile apps from Google and Microsoft (app-based multi-factor is the more secure option, as discussed here).
More importantly, the Citrix spokesperson said the company did not enforce a password reset on accounts that were using multi-factor authentication. To wit:
“This is not in response to a breach of Citrix products or services,” wrote spokesperson Jamie Buranich. “Citrix forced password resets with the knowledge that attacks of this nature historically come in waves. Attacker’s additional efforts adapt to the results, often tuning the volume and approach of their methods. Our objective was to minimize the risk to our customers. We did not enforce a password reset on accounts that are using more stringent authentication controls [emphasis added]. Citrix also directly integrates with common SSO solutions, which significantly reduces risk.”
The company did not respond to questions about why it decided to adopt regular password resets as a policy when doing so flies in the face of password and authentication best practices recommended the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which warns:
“Verifiers SHOULD NOT require memorized secrets to be changed arbitrarily (e.g., periodically). However, verifiers SHALL force a change if there is evidence of compromise of the authenticator.”
NIST explains its rationale for steering organizations away from regular forced password resets thusly:
“Users tend to choose weaker memorized secrets when they know that they will have to change them in the near future. When those changes do occur, they often select a secret that is similar to their old memorized secret by applying a set of common transformations such as increasing a number in the password. This practice provides a false sense of security if any of the previous secrets has been compromised since attackers can apply these same common transformations.”
“But if there is evidence that the memorized secret has been compromised, such as by a breach of the verifier’s hashed password database or observed fraudulent activity, subscribers should be required to change their memorized secrets. However, this event-based change should occur rarely, so that they are less motivated to choose a weak secret with the knowledge that it will only be used for a limited period of time.”
In short, NIST says it makes sense to force an across-the-board password reset following a breach — either of a specific user’s account or the entire password database. But doing so at regular intervals absent such evidence of compromise is likely to result in less complex and secure passwords.
Ideally, ShareFile users who received a password reset notice can avoid the next round of password resets by adopting one of the two-step authentication options mentioned above. And I hope it goes without saying, but please don’t re-use a password you used anywhere else.
However, if you are the type of person who likes to re-use passwords, then you definitely need to be using a password manager, which helps you pick and remember strong passwords/passphrases and essentially lets you use the same strong master password/passphrase across all Web sites.
Incidentally, there are several companies — such as auth0 and Okta — that make it easy to integrate with breached password databases like Troy Hunt’s HaveIBeenPwned.com to help proactively prevent users from picking passwords they have used at other sites (or at least at other sites that have been breached publicly).
Whether online merchants are willing to adopt such preemptive approaches is another matter, said Julie Conroy, research director with the Aite Group, a market analyst firm.
“With the reality that such a vast swath of username/password combinations have been compromised, this creates the potential for a ton of inline friction, something that is an anathema to merchants, and which banks work hard to stay away from as well,” Conroy said.
Update: 4:53 p.m. ET: Citrix just published its own blog post about this here.
from Technology News https://krebsonsecurity.com/2018/12/a-breach-or-just-a-forced-password-reset/
0 notes
Text
A Breach, or Just a Forced Password Reset?
Software giant Citrix Systems recently forced a password reset for many users of its Sharefile content collaboration service, warning it would be doing this on a regular basis in response to password-guessing attacks that target people who re-use passwords across multiple Web sites. Many Sharefile users interpreted this as a breach at Citrix and/or Sharefile, but the company maintains that’s not the case. Here’s a closer look at what happened, and some ideas about how to avoid a repeat of this scenario going forward.
The notice sent to ShareFile users looked like this:
Dozens of readers forwarded the above message to KrebsOnSecurity, saying they didn’t understand the reasoning for the mass password reset and that they suspected a breach at ShareFile.
I reached out to ShareFile and asked them point blank whether this reset effort was in response to any sort of intrusion at Citrix or ShareFile; they said no. I asked if this notice had been sent to everyone, and inquired whether ShareFile offers any form(s) of multi-factor authentication options that customers could use to supplement the security of passwords.
A Citrix spokesperson referred me to this page, which says ShareFile users have a number of options when it comes to locking down their accounts with multi-factor authentication, including a one-time code sent via SMS/text message, as well as one-time passwords generated by support authenticator mobile apps from Google and Microsoft (app-based multi-factor is the more secure option, as discussed here).
More importantly, the Citrix spokesperson said the company did not enforce a password reset on accounts that were using multi-factor authentication. To wit:
“This is not in response to a breach of Citrix products or services,” wrote spokesperson Jamie Buranich. “Citrix forced password resets with the knowledge that attacks of this nature historically come in waves. Attacker’s additional efforts adapt to the results, often tuning the volume and approach of their methods. Our objective was to minimize the risk to our customers. We did not enforce a password reset on accounts that are using more stringent authentication controls [emphasis added]. Citrix also directly integrates with common SSO solutions, which significantly reduces risk.”
The company did not respond to questions about why it decided to adopt regular password resets as a policy when doing so flies in the face of password and authentication best practices recommended the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which warns:
“Verifiers SHOULD NOT require memorized secrets to be changed arbitrarily (e.g., periodically). However, verifiers SHALL force a change if there is evidence of compromise of the authenticator.”
NIST explains its rationale for steering organizations away from regular forced password resets thusly:
“Users tend to choose weaker memorized secrets when they know that they will have to change them in the near future. When those changes do occur, they often select a secret that is similar to their old memorized secret by applying a set of common transformations such as increasing a number in the password. This practice provides a false sense of security if any of the previous secrets has been compromised since attackers can apply these same common transformations.”
“But if there is evidence that the memorized secret has been compromised, such as by a breach of the verifier’s hashed password database or observed fraudulent activity, subscribers should be required to change their memorized secrets. However, this event-based change should occur rarely, so that they are less motivated to choose a weak secret with the knowledge that it will only be used for a limited period of time.”
In short, NIST says it makes sense to force an across-the-board password reset following a breach — either of a specific user’s account or the entire password database. But doing so at regular intervals absent such evidence of compromise is likely to result in less complex and secure passwords.
Ideally, ShareFile users who received a password reset notice can avoid the next round of password resets by adopting one of the two-step authentication options mentioned above. And I hope it goes without saying, but please don’t re-use a password you used anywhere else.
However, if you are the type of person who likes to re-use passwords, then you definitely need to be using a password manager, which helps you pick and remember strong passwords/passphrases and essentially lets you use the same strong master password/passphrase across all Web sites.
Incidentally, there are several companies — such as auth0 and Okta — that make it easy to integrate with breached password databases like Troy Hunt’s HaveIBeenPwned.com to help proactively prevent users from picking passwords they have used at other sites (or at least at other sites that have been breached publicly).
Whether online merchants are willing to adopt such preemptive approaches is another matter, said Julie Conroy, research director with the Aite Group, a market analyst firm.
“With the reality that such a vast swath of username/password combinations have been compromised, this creates the potential for a ton of inline friction, something that is an anathema to merchants, and which banks work hard to stay away from as well,” Conroy said.
Update: 4:53 p.m. ET: Citrix just published its own blog post about this here.
from Amber Scott Technology News https://krebsonsecurity.com/2018/12/a-breach-or-just-a-forced-password-reset/
0 notes
Text
Giving CISOs assurance in the cloud
This post is authored by Mark McIntyre, Chief Security Advisor, Enterprise Cybersecurity Group.
Recently, I hosted a Chief Information Security Officer roundtable in Washington, DC. Executives from several US government agencies and systems integrators attended to share cloud security concerns and challenges, such as balancing collaboration and productivity against data protection needs, cyber threat detection, and compliance. Toward the end of the day, one CISO reminded me he needed assurance. He asked, “How can we trust Microsoft to protect our data? And, how can I believe what you say?”
This post provides an opportunity to share important updates and assurances about practices and resources that Microsoft uses to protect data and user privacy in the Cloud. It also offers information on resources available to CISOs and others, that demonstrate our continuing investments in transparency.
Security at scale
Increasingly, government officials as well as industry analysts and executives are recognizing and evangelizing the security benefits of moving to hyper-scale cloud service providers. Microsoft works at this scale, investing $15B in the public cloud. The internet user maps below provide useful insight into why and where we are making these investments. Figure 1 represents internet usage in 2015. The size of the boxes reflect numbers of users. The colors indicate the percentage of people with access to the internet.
Figure 1, source “Cyberspace 2025: Today’s Decisions, Tomorrow’s Terrain”
Now look at Figure 2, showing expected internet usage in 2025. As you can see, global internet use and accompanying economic activity will continue to grow.
Figure 2
In addition to serving millions of people around the world, we are also moving Microsoft’s 100,000+ employees and our corporate infrastructure and data to the Cloud. We must therefore be confident that we can protect our resources as well as our users’.
How do we do it? Microsoft invests over $1B per year in cybersecurity and data protection. We start by ensuring that the software powering our data centers is designed, built and maintained as securely as possible. This video illustrates the world-class security Microsoft applies to data center protection. We also continue to improve on years of development investments in the Security Development Lifecycle (SDL), to ensure that security is addressed at the very beginning stages of any product or service. In the Cloud, the Operational Security Assurance framework capitalizes on the SDL and on Microsoft’s deep insights into the cybersecurity threat landscape.
One way that Microsoft detects cybersecurity activity in our data centers is the Intelligent Security Graph. Microsoft has incredible breadth and depth of signal and information we analyze from 450B authentications per month across our cloud services, 400B emails scanned for spam and malware, over a billion enterprise and consumer devices updated monthly, and 18B+ Bing scans per month. This intelligence, enhanced by rich expertise of Microsoft’s world class talent of security researchers, analysts, hunters, and engineers, is built into our products and our platform – enabling customers, and Microsoft, to detect and respond to threats more quickly. (Figures 3 & 4). Microsoft security teams use the graph to correlate large-scale critical security events, using innovative cloud-first machine learning and behavior and anomaly-based search queries, to surface actionable intelligence. The graph enables teams to collaborate internally and apply preventive measures or mitigations in near real-time to counter cyber threats. This supports protection for users around the world, and assures CISOs that Microsoft has the breadth and scale to monitor and protect users’ identities, devices, apps and data, and infrastructure.
Figure 3
Figure 4
Access to data
Technology is critical for advancing security at hyper-scale, therefore Microsoft continues to evolve the ways in which administrators access corporate assets. The role of network administrators is significant. In our cloud services, we employ Just Enough and Just Enough Administration access, under which admins are provided the bare minimum window of time and physical and logical access to carry out a validated task. No admin may create or approve their own ticket, either. Further, Windows Server 2016 clients can implement these policies internally. Security and managing data centers at scale is an ever evolving process based on the needs of our customers, the changing threat landscape, regulatory environments and more.
Compliance
Microsoft works with auditors and regulators around the world to ensure that we operate data centers at the highest levels of security and operational excellence. We maintain the largest compliance portfolio in the industry, for example against the ISO 22301 privacy standard. In addition, Microsoft maintains certifications such as CSA STAR Certification, HITRUST, FACT and CDSA which many of our cloud competitors do not. For more about Microsoft certifications, visit the Microsoft Trust Center Compliance page.
Transparency
Being compliant with local, industry, and international standards establishes that Microsoft is trustworthy, but our goal is to be trusted. Toward that end—and to ensure we address the needs of CISOs, Microsoft provides a wealth of information about cloud services, designed to provide direct and customer self-service opportunities to answer three key questions:
How is may data secured and protected?
How does Microsoft Cloud help me be compliant with my regulatory needs?
How does Microsoft manage privacy around my data?
The comments at our roundtable that prompted this blog show that our cloud security and compliance resources can be difficult to find, so while we double down on our efforts to raise awareness, bookmark this update and read below. We operate the following portals, designed to facilitate self-service access to security and compliance information, FAQs and white papers, in convenient formats, and tailored to an organization’s geography, industry and subscription(s):
The Microsoft Trust Center, a centralized resource for enterprise customers to find answers about what Microsoft is doing to protect data, comply with regulatory requirements, and verify that we are doing what we say.
The Service Trust Portal (STP) is available for organizations under nondisclosure to current and potential Microsoft customers. It includes hundreds of important third-party audit reports, information on certifications, and internal security documents, for Azure, O365, Dynamics CRM Online, and Yammer. Examples include SOC and ISO audits reports.
The Service Assurance Portal, available to current O365 users, offers the same level of access but directly through the O365 subscription. This is a unique “transparency window” to provide customers with in-depth understanding in how we implement and test controls to manage confidentiality, integrity, availability, reliability, and privacy around customer data. Not only do we share the “what” about controls, but also the “how” about testing and implementation.
Government Security Program
Microsoft also participates in the Government Security Program as another key transparency initiative. Through the GSP, national governments (including regulators) may access deep architecture details about our products and services, up to and including source code. The GSP also provides participants with opportunities to visit Microsoft headquarters in Redmond to meet face to face with the teams that operate, monitor, and defend our company and products and services—including data centers—from cyber threats. They can also visit any of our Transparency Centers in Redmond, Brussels, Brasilia, and Singapore. Several dozen governments around the world use the GSP to obtain greater insight into how Microsoft builds, operates and defends its data centers, and by extension, how we protect users.
Microsoft stands ready to work with CISOs to raise awareness and ensure access to the resources discussed above. Visit the following sites to learn more. Microsoft has also created a dedicated team of cybersecurity professionals to help move you securely to the Cloud and protect your data. Learn more about the Enterprise Cybersecurity Group, or contact your local Microsoft representative.
Blogs: Microsoft Secure Blog and Microsoft On the Issues Learn more about the Microsoft Enterprise Cloud Read the Microsoft Security Intelligence Report Follow us on Twitter: @MSFTSecurity
from Microsoft Secure Blog Staff
0 notes
Text
Let’s Create Our Own Authentication API with Nodejs and GraphQL
Authentication is one of the most challenging tasks for developers just starting with GraphQL. There are a lot of technical considerations, including what ORM would be easy to set up, how to generate secure tokens and hash passwords, and even what HTTP library to use and how to use it.
In this article, we’ll focus on local authentication. It’s perhaps the most popular way of handling authentication in modern websites and does so by requesting the user’s email and password (as opposed to, say, using Google auth.)
Moreover, This article uses Apollo Server 2, JSON Web Tokens (JWT), and Sequelize ORM to build an authentication API with Node.
Handling authentication
As in, a log in system:
Authentication identifies or verifies a user.
Authorization is validating the routes (or parts of the app) the authenticated user can have access to.
The flow for implementing this is:
The user registers using password and email
The user’s credentials are stored in a database
The user is redirected to the login when registration is completed
The user is granted access to specific resources when authenticated
The user’s state is stored in any one of the browser storage mediums (e.g. localStorage, cookies, session) or JWT.
Pre-requisites
Before we dive into the implementation, here are a few things you’ll need to follow along.
Node 6 or higher
Yarn (recommended) or NPM
GraphQL Playground
Basic Knowledge of GraphQL and Node
…an inquisitive mind!
Dependencies
This is a big list, so let’s get into it:
Apollo Server: An open-source GraphQL server that is compatible with any kind of GraphQL client. We won’t be using Express for our server in this project. Instead, we will use the power of Apollo Server to expose our GraphQL API.
bcryptjs: We want to hash the user passwords in our database. That’s why we will use bcrypt. It relies on Web Crypto API‘s getRandomValues interface to obtain secure random numbers.
dotenv: We will use dotenv to load environment variables from our .env file.
jsonwebtoken: Once the user is logged in, each subsequent request will include the JWT, allowing the user to access routes, services, and resources that are permitted with that token. jsonwebtokenwill be used to generate a JWT which will be used to authenticate users.
nodemon: A tool that helps develop Node-based applications by automatically restarting the node application when changes in the directory are detected. We don’t want to be closing and starting the server every time there’s a change in our code. Nodemon inspects changes every time in our app and automatically restarts the server.
mysql2: An SQL client for Node. We need it connect to our SQL server so we can run migrations.
sequelize: Sequelize is a promise-based Node ORM for Postgres, MySQL, MariaDB, SQLite and Microsoft SQL Server. We will use Sequelize to automatically generate our migrations and models.
sequelize cli: We will use Sequelize CLI to run Sequelize commands. Install it globally with yarn add --global sequelize-cli in the terminal.
Setup directory structure and dev environment
Let’s create a brand new project. Create a new folder and this inside of it:
yarn init -y
The -y flag indicates we are selecting yes to all the yarn init questions and using the defaults.
We should also put a package.json file in the folder, so let’s install the project dependencies:
yarn add apollo-server bcrpytjs dotenv jsonwebtoken nodemon sequelize sqlite3
Next, let’s add Babeto our development environment:
yarn add babel-cli babel-preset-env babel-preset-stage-0 --dev
Now, let’s configure Babel. Run touch .babelrc in the terminal. That creates and opens a Babel config file and, in it, we’ll add this:
{ "presets": ["env", "stage-0"] }
It would also be nice if our server starts up and migrates data as well. We can automate that by updating package.json with this:
"scripts": { "migrate": " sequelize db:migrate", "dev": "nodemon src/server --exec babel-node -e js", "start": "node src/server", "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" },
Here’s our package.json file in its entirety at this point:
{ "name": "graphql-auth", "version": "1.0.0", "main": "index.js", "scripts": { "migrate": " sequelize db:migrate", "dev": "nodemon src/server --exec babel-node -e js", "start": "node src/server", "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" }, "dependencies": { "apollo-server": "^2.17.0", "bcryptjs": "^2.4.3", "dotenv": "^8.2.0", "jsonwebtoken": "^8.5.1", "nodemon": "^2.0.4", "sequelize": "^6.3.5", "sqlite3": "^5.0.0" }, "devDependencies": { "babel-cli": "^6.26.0", "babel-preset-env": "^1.7.0", "babel-preset-stage-0": "^6.24.1" } }
Now that our development environment is set up, let’s turn to the database where we’ll be storing things.
Database setup
We will be using MySQL as our database and Sequelize ORM for our relationships. Run sequelize init (assuming you installed it globally earlier). The command should create three folders: /config /models and /migrations. At this point, our project directory structure is shaping up.
Let’s configure our database. First, create a .env file in the project root directory and paste this:
NODE_ENV=development DB_HOST=localhost DB_USERNAME= DB_PASSWORD= DB_NAME=
Then go to the /config folder we just created and rename the config.json file in there to config.js. Then, drop this code in there:
require('dotenv').config() const dbDetails = { username: process.env.DB_USERNAME, password: process.env.DB_PASSWORD, database: process.env.DB_NAME, host: process.env.DB_HOST, dialect: 'mysql' } module.exports = { development: dbDetails, production: dbDetails }
Here we are reading the database details we set in our .env file. process.env is a global variable injected by Node and it’s used to represent the current state of the system environment.
Let’s update our database details with the appropriate data. Open the SQL database and create a table called graphql_auth. I use Laragon as my local server and phpmyadmin to manage database tables.
What ever you use, we’ll want to update the .env file with the latest information:
NODE_ENV=development DB_HOST=localhost DB_USERNAME=graphql_auth DB_PASSWORD= DB_NAME=<your_db_username_here>
Let’s configure Sequelize. Create a .sequelizerc file in the project’s root and paste this:
const path = require('path')
module.exports = { config: path.resolve('config', 'config.js') }
Now let’s integrate our config into the models. Go to the index.js in the /models folder and edit the config variable.
const config = require(__dirname + '/../../config/config.js')[env]
Finally, let’s write our model. For this project, we need a User model. Let’s use Sequelize to auto-generate the model. Here’s what we need to run in the terminal to set that up:
sequelize model:generate --name User --attributes username:string,email:string,password:string
Let’s edit the model that creates for us. Go to user.js in the /models folder and paste this:
'use strict'; module.exports = (sequelize, DataTypes) => { const User = sequelize.define('User', { username: { type: DataTypes.STRING, }, email: { type: DataTypes.STRING, }, password: { type: DataTypes.STRING, } }, {}); return User; };
Here, we created attributes and fields for username, email and password. Let’s run a migration to keep track of changes in our schema:
yarn migrate
Let’s now write the schema and resolvers.
Integrate schema and resolvers with the GraphQL server
In this section, we’ll define our schema, write resolver functions and expose them on our server.
The schema
In the src folder, create a new folder called /schema and create a file called schema.js. Paste in the following code:
const { gql } = require('apollo-server') const typeDefs = gql` type User { id: Int! username: String email: String! } type AuthPayload { token: String! user: User! } type Query { user(id: Int!): User allUsers: [User!]! me: User } type Mutation { registerUser(username: String, email: String!, password: String!): AuthPayload! login (email: String!, password: String!): AuthPayload! } ` module.exports = typeDefs
Here we’ve imported graphql-tag from apollo-server. Apollo Server requires wrapping our schema with gql.
The resolvers
In the src folder, create a new folder called /resolvers and create a file in it called resolver.js. Paste in the following code:
const bcrypt = require('bcryptjs') const jsonwebtoken = require('jsonwebtoken') const models = require('../models') require('dotenv').config() const resolvers = { Query: { async me(_, args, { user }) { if(!user) throw new Error('You are not authenticated') return await models.User.findByPk(user.id) }, async user(root, { id }, { user }) { try { if(!user) throw new Error('You are not authenticated!') return models.User.findByPk(id) } catch (error) { throw new Error(error.message) } }, async allUsers(root, args, { user }) { try { if (!user) throw new Error('You are not authenticated!') return models.User.findAll() } catch (error) { throw new Error(error.message) } } }, Mutation: { async registerUser(root, { username, email, password }) { try { const user = await models.User.create({ username, email, password: await bcrypt.hash(password, 10) }) const token = jsonwebtoken.sign( { id: user.id, email: user.email}, process.env.JWT_SECRET, { expiresIn: '1y' } ) return { token, id: user.id, username: user.username, email: user.email, message: "Authentication succesfull" } } catch (error) { throw new Error(error.message) } }, async login(_, { email, password }) { try { const user = await models.User.findOne({ where: { email }}) if (!user) { throw new Error('No user with that email') } const isValid = await bcrypt.compare(password, user.password) if (!isValid) { throw new Error('Incorrect password') } // return jwt const token = jsonwebtoken.sign( { id: user.id, email: user.email}, process.env.JWT_SECRET, { expiresIn: '1d'} ) return { token, user } } catch (error) { throw new Error(error.message) } } },
} module.exports = resolvers
That’s a lot of code, so let’s see what’s happening in there.
First we imported our models, bcrypt and jsonwebtoken, and then initialized our environmental variables.
Next are the resolver functions. In the query resolver, we have three functions (me, user and allUsers):
me query fetches the details of the currently loggedIn user. It accepts a user object as the context argument. The context is used to provide access to our database which is used to load the data for a user by the ID provided as an argument in the query.
user query fetches the details of a user based on their ID. It accepts id as the context argument and a user object.
alluser query returns the details of all the users.
user would be an object if the user state is loggedIn and it would be null, if the user is not. We would create this user in our mutations.
In the mutation resolver, we have two functions (registerUser and loginUser):
registerUser accepts the username, email and password of the user and creates a new row with these fields in our database. It’s important to note that we used the bcryptjs package to hash the users password with bcrypt.hash(password, 10). jsonwebtoken.sign synchronously signs the given payload into a JSON Web Token string (in this case the user id and email). Finally, registerUser returns the JWT string and user profile if successful and returns an error message if something goes wrong.
login accepts email and password , and checks if these details match with the one that was supplied. First, we check if the email value already exists somewhere in the user database.
models.User.findOne({ where: { email }}) if (!user) { throw new Error('No user with that email') }
Then, we use bcrypt’s bcrypt.compare method to check if the password matches.
const isValid = await bcrypt.compare(password, user.password) if (!isValid) { throw new Error('Incorrect password') }
Then, just like we did previously in registerUser, we use jsonwebtoken.sign to generate a JWT string. The login mutation returns the token and user object.
Now let’s add the JWT_SECRET to our .env file.
JWT_SECRET=somereallylongsecret
The server
Finally, the server! Create a server.js in the project’s root folder and paste this:
const { ApolloServer } = require('apollo-server') const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken') const typeDefs = require('./schema/schema') const resolvers = require('./resolvers/resolvers') require('dotenv').config() const { JWT_SECRET, PORT } = process.env const getUser = token => { try { if (token) { return jwt.verify(token, JWT_SECRET) } return null } catch (error) { return null } } const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers, context: ({ req }) => { const token = req.get('Authorization') || '' return { user: getUser(token.replace('Bearer', ''))} }, introspection: true, playground: true }) server.listen({ port: process.env.PORT || 4000 }).then(({ url }) => { console.log(`🚀 Server ready at ${url}`); });
Here, we import the schema, resolvers and jwt, and initialize our environment variables. First, we verify the JWT token with verify. jwt.verify accepts the token and the JWT secret as parameters.
Next, we create our server with an ApolloServer instance that accepts typeDefs and resolvers.
We have a server! Let’s start it up by running yarn dev in the terminal.
Testing the API
Let’s now test the GraphQL API with GraphQL Playground. We should be able to register, login and view all users — including a single user — by ID.
We’ll start by opening up the GraphQL Playground app or just open localhost://4000 in the browser to access it.
Mutation for register user
mutation { registerUser(username: "Wizzy", email: "[email protected]", password: "wizzyekpot" ){ token } }
We should get something like this:
{ "data": { "registerUser": { "token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6MTUsImVtYWlsIjoiZWtwb3RAZ21haWwuY29tIiwiaWF0IjoxNTk5MjQwMzAwLCJleHAiOjE2MzA3OTc5MDB9.gmeynGR9Zwng8cIJR75Qrob9bovnRQT242n6vfBt5PY" } } }
Mutation for login
Let’s now log in with the user details we just created:
mutation { login(email:"[email protected]" password:"wizzyekpot"){ token } }
We should get something like this:
{ "data": { "login": { "token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6MTUsImVtYWlsIjoiZWtwb3RAZ21haWwuY29tIiwiaWF0IjoxNTk5MjQwMzcwLCJleHAiOjE1OTkzMjY3NzB9.PDiBKyq58nWxlgTOQYzbtKJ-HkzxemVppLA5nBdm4nc" } } }
Awesome!
Query for a single user
For us to query a single user, we need to pass the user token as authorization header. Go to the HTTP Headers tab.

…and paste this:
{ "Authorization": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6MTUsImVtYWlsIjoiZWtwb3RAZ21haWwuY29tIiwiaWF0IjoxNTk5MjQwMzcwLCJleHAiOjE1OTkzMjY3NzB9.PDiBKyq58nWxlgTOQYzbtKJ-HkzxemVppLA5nBdm4nc" }
Here’s the query:
query myself{ me { id email username } }
And we should get something like this:
{ "data": { "me": { "id": 15, "email": "[email protected]", "username": "Wizzy" } } }
Great! Let’s now get a user by ID:
query singleUser{ user(id:15){ id email username } }
And here’s the query to get all users:
{ allUsers{ id username email } }
Summary
Authentication is one of the toughest tasks when it comes to building websites that require it. GraphQL enabled us to build an entire Authentication API with just one endpoint. Sequelize ORM makes creating relationships with our SQL database so easy, we barely had to worry about our models. It’s also remarkable that we didn’t require a HTTP server library (like Express) and use Apollo GraphQL as middleware. Apollo Server 2, now enables us to create our own library-independent GraphQL servers!
Check out the source code for this tutorial on GitHub.
The post Let’s Create Our Own Authentication API with Nodejs and GraphQL appeared first on CSS-Tricks.
You can support CSS-Tricks by being an MVP Supporter.
Let’s Create Our Own Authentication API with Nodejs and GraphQL published first on https://deskbysnafu.tumblr.com/
0 notes