#and connect with SCADA
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Smart Factory with 7 Axes Robot and Digital Twin Manufacturer in Pune India

Manufacturer and Supplier of Smart Factory solutions with 7 Axes Robots and Digital Twin technology in Pune. We provide flexible manufacturing systems (MPS), connected machines, and SCADA training.
#Flexible Manufacturing Systems Manufacturer Pune#Smart Factory with 7 Axes Robot Pune#Smart Factory Manufacturer Pune#Flexible Manufacturing System Pune#MPS Manufacturing System Pune#Connected Machines Pune#SCADA Training Pune#Digital Twin Pune#Flexible Manufacturing Systems Pune#Digital Twin for Manufacturing Pune#SCADA Solutions Pune
0 notes
Text
How SCADA Works?
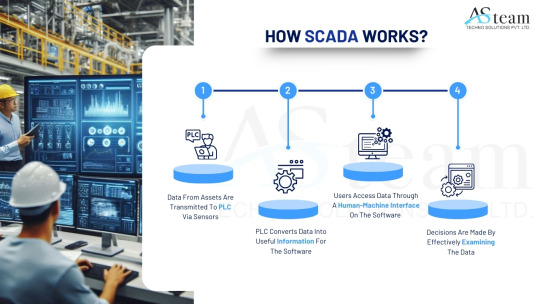
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are critical in managing and monitoring industrial processes across various industries, including manufacturing, utilities, transportation, and energy.
Field Devices
At the process level, field devices like sensors, meters, and actuators are used to monitor variables like voltage, flow, temperature, and pressure. These gadgets collect information and carry out system-directed operations.
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
The SCADA software and the field devices are connected by RTUs and PLCs. After gathering information from the sensors, they transmit it to the control center. Additionally, the SCADA system may send them orders to modify settings or control actuators.
Communication Infrastructure
Strong communication networks are necessary for SCADA to transmit data between the control center and field equipment. This infrastructure can be wireless (such as satellite, radio, and cellular networks) or wired (such as Ethernet and fiber optics).
Centralized Control Station
SCADA software, which analyzes data, creates visualizations, and gives operators tools to monitor and manage operations, is housed in the control station.
Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
The SCADA system's user interface is called the HMI. Operators can engage with the system and make well-informed decisions because to its graphical depictions of processes, warnings, and trends.
#automation#SCADA#PLC#HMI#Automation#Technology#business and industry sectors#business#industrial automation#soft starter#software#software engineering
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Unified Namespace Architecture Is the Backbone of Industry 4.0 Integration

How to Simplify Data Flow, Empower Teams, and Future-Proof Your Plant
Drowning in Data, Starving for Insight?
You’ve invested in sensors, PLCs, SCADA, MES, and maybe even a few shiny new IIoT platforms. But when your team needs a clear, real-time view of operations across the plant floor… it still feels like you’re piecing together a puzzle with missing pieces.
Each system speaks its own language. Your data is locked in silos. And just trying to answer a simple question like “What’s happening on Line 2?” means logging into three different platforms.
Sound familiar?
That’s where unified namespace architecture comes in — and why more manufacturing leaders are calling it the cornerstone of true Industry 4.0 integration.
What Is a Unified Namespace (UNS)? And Why Does It Matter?
In simple terms, UNS is a single source of truth — a structured, real-time data layer where every device, system, and application publishes and subscribes to live, contextual data.
No more point-to-point integrations. No more fragile data pipelines. Just one cohesive layer of real-time data visibility.
✅ Why It Matters: Instead of building (and constantly maintaining) dozens of connections, you build once — to the UNS. Everything talks through it. It’s cleaner, faster, and infinitely more scalable.
Turning Complexity into Clarity
Without UNS: Your automation engineer is chasing down OPC tags. Your MES vendor wants another custom connector. Your SCADA and ERP are still passing notes via CSV.
With UNS: Everyone — from machines to dashboards to predictive analytics tools — gets their data from one place, in one format, in real time.
✅ The Result? Your plant becomes a data-driven ecosystem, where decision-making is faster, smarter, and aligned.
How It Powers Industry 4.0 Integration
Unified namespace architecture isn’t just an IT convenience — it’s an operational game-changer.
🔹 Connects SCADA and MES systems effortlessly 🔹 Supports modern IIoT architecture with tools like MQTT and Sparkplug B 🔹 Bridges legacy equipment with future-ready applications 🔹 Enables autonomous operations, predictive maintenance, and AI-driven insights
And since it's architected for interoperability, your investments in cloud, automation, and analytics now all work in harmony — not at odds.
Real Impact. Real Results.
We worked with a mid-sized food processing facility recently. They had five systems across two sites, each managed by a different team. Data was delayed, downtime was misdiagnosed, and scaling new lines felt impossible.
INS3 implemented a UNS framework using modern protocols like MQTT and Ignition. Within weeks, their plant teams had:
One unified view of all production lines
Alarms and trends in real time
Seamless SCADA and MES interoperability
A roadmap to scale without rearchitecting systems
The result? 20% faster issue resolution, 40% reduction in reporting lag, and a team that finally felt empowered — not overwhelmed — by their tech stack.
Behind Every Architecture Is a Team That Listens
At INS3, we don’t believe in one-size-fits-all. We believe in partnerships. Our engineers walk your floors, ask the right questions, and design around your people, your priorities, your pace.
We bring 30+ years of industrial automation experience, but we lead with empathy — because technology should solve problems, not create more.
You won’t get buzzwords or cookie-cutter solutions. You’ll get resilient architectures, practical innovation, and a team that’s with you for the long haul.
Let’s Build the Backbone of Your Digital Future
Industry 4.0 isn’t about the next flashy tool. It’s about building a connected, future-ready foundation that empowers your team today — and tomorrow.
And that foundation starts with unified namespace architecture.
📞 Let’s talk. One conversation could unlock the clarity you’ve been chasing for years.
0 notes
Text
Choosing the Right HMI for Your Industrial Needs in Rajasthan
In today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape, automation has become the backbone of efficiency and innovation. Whether you're in manufacturing, packaging, pharmaceuticals, or any other sector where machine control is vital, Human Machine Interface (HMI) systems are indispensable. An HMI acts as a bridge between humans and machines, enabling real-time monitoring, control, and diagnostics of industrial processes.
Rajasthan, with its growing industrial hubs like Jaipur, Bhiwadi, Udaipur, and Kota, is witnessing a strong demand for smart automation solutions. Industries here are not just expanding—they're upgrading. And at the core of this transformation lies the intelligent deployment of HMI systems that make machines more accessible and operations more streamlined.
Why HMIs Are Critical in Modern Industry
Human Machine Interfaces do more than display information. They empower operators to interact with machines effectively—monitor performance, change settings, run diagnostics, and respond to issues faster. With touchscreen displays, intuitive design, and robust software integration, modern HMIs reduce the learning curve and operational errors.
Benefits of using advanced HMIs include:
Increased operational efficiency
Minimized downtime through better diagnostics
Improved data visualization and process control
Enhanced safety and compliance
From basic control panels to high-end, cloud-connected HMIs, businesses today have a wide range of choices based on their scale, needs, and budget.
What to Look for When Selecting an HMI
Choosing the right HMI is not just about hardware—it’s about the long-term support, software compatibility, service network, and customization options. Here are some key factors to consider:
Scalability: Will the HMI adapt as your operations grow?
Durability: Is it suitable for industrial conditions like dust, moisture, or high temperatures?
Software integration: Can it work seamlessly with your existing PLCs and SCADA systems?
User interface: Is it intuitive for operators with varying skill levels?
Support and maintenance: Does the supplier offer reliable after-sales service?
This is where working with the right dealer becomes crucial.
Finding Reliable Dealers in Rajasthan
With an increasing number of automation solution providers in the market, selecting a trusted HMI dealer can make all the difference. You want a partner who not only supplies quality products but also understands your specific industrial requirements and provides ongoing support.
The best HMI dealers in Rajasthan stand out because of their commitment to customer service, technical expertise, and long-standing relationships with reputed brands. They offer tailored solutions based on your industry and ensure smooth installation, commissioning, and maintenance services. Many also provide training and troubleshooting support to make the transition to automation seamless for your team.
Whether you're looking to upgrade a legacy system or set up a fully automated plant, working with experienced HMI dealers ensures your investment pays off in performance and reliability.
Final Thoughts
As industries in Rajasthan continue to modernize, the role of intelligent automation systems, especially HMIs, is becoming more central than ever. A reliable HMI system not only enhances productivity but also provides greater control and visibility over your operations.
By investing wisely in high-quality interfaces and partnering with trusted local suppliers, businesses can future-proof their operations and stay competitive in a fast-changing environment. Take time to assess your needs, do your research, and choose a partner who brings both technology and expertise to the table.
0 notes
Text
🌍 Join Trinity Touch at Intersolar Europe 2025 – Munich, Germany 🌍
We are excited to present Trinity Touch’s latest innovations designed to power the future of solar power plants and clean energy infrastructure.

🚀 Explore our advanced range of solutions, including: ☀️ String Monitoring Systems 📊 Next-Gen SCADA Systems 🌦 Weather Monitoring Units 🛡 Integrated Cybersecurity Solutions
With 75+ GW of solar systems delivered, we’re proud to support the global transition to renewable energy.
🔧 Dive into our in-house manufacturing capabilities featuring: Enclosures | Wiring Ducts | Cable Glands | DIN Rails | String Monitoring Boards
Let’s shape a sustainable future—together.
📍 Meet us at: Hall B4 | Stall 670 📅 May 7–9, 2025 📌 Messe München, Germany
💬 Connect with us: 📞 +91 11 71200900 📱 WhatsApp: +91 9911717900 ✉️ [email protected] 🌐 www.trinitytouch.com
#Intersolar2025#TrinityTouch#SolarInnovation#SmartEnergy#CleanEnergy#EVCharging#SCADA#SustainableFuture#MadeInIndia#Renewables#EnergyTech#GlobalExhibitions
0 notes
Text
Top Automation Engineers in Illinois | Innovating Industrial Solutions
Automation engineers are specialized professionals who design and implement systems that reduce human intervention in industrial processes. They blend knowledge from multiple fields—mechanical, electrical, software, and control engineering—to create intelligent systems that operate efficiently, reliably, and autonomously.
Their typical responsibilities include:
Designing automation systems from concept to installation
Programming PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces)
Integrating robotics and motion control
Developing SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems
Testing and troubleshooting automated equipment
Ensuring safety and compliance with industrial standards
In Illinois, automation engineers are indispensable to manufacturing, logistics, food processing, energy, and life sciences.
Why Illinois Is a Powerhouse for Automation Engineering
Several key factors contribute to Illinois’s prominence in automation engineering:
1. Diverse Industrial Base: Illinois boasts industries ranging from automotive and agriculture to pharmaceuticals and aerospace. This diversity fuels consistent demand for custom automation solutions.
2. Strong Educational Ecosystem: Top-tier institutions like the University of Illinois, Northwestern University, and Southern Illinois University produce highly skilled engineers with expertise in robotics, AI, and industrial systems.
3. Strategic Location: Illinois's central location offers excellent logistics, making it a favored site for advanced manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution centers—all of which benefit from automation.
4. Innovation-Friendly Climate: The state supports innovation through tech incubators, grants, and public-private partnerships that empower engineers to develop and deploy cutting-edge automation solutions.
Key Services Offered by Automation Engineers in Illinois
Automation engineers in Illinois provide an extensive range of services tailored to the specific needs of businesses across the state. Common services include:
System Integration: Designing and installing complete automation solutions that synchronize machines, robots, and control systems.
PLC & HMI Programming: Writing and testing software that governs system behavior and interfaces.
Robotics Engineering: Installing and configuring robotic arms and automated material handling systems.
Industrial IoT Integration: Connecting machines to networks for real-time data exchange and monitoring.
Retrofitting & Upgrades: Enhancing legacy equipment with modern control technologies.
Safety System Design: Implementing fail-safes, emergency stops, and safety protocols in compliance with OSHA and ISO standards.
Whether working on a small assembly cell or a full-scale production line, Illinois automation engineers prioritize reliability, scalability, and efficiency.
Industries Benefiting from Automation Engineers in Illinois
The work of automation engineers touches nearly every corner of Illinois’s economy. Key sectors include:
Food and Beverage: Automating sorting, bottling, and packaging processes to ensure hygiene and speed.
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices: Ensuring precision, compliance, and traceability through automated filling, labeling, and inspection.
Automotive and Aerospace: Deploying robotic arms and motion systems for parts assembly and quality control.
Agriculture and Grain Processing: Integrating automation into storage, sorting, and packaging facilities.
Warehousing and Logistics: Developing conveyor systems, pick-and-place robots, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Energy and Utilities: Implementing SCADA and remote control systems to manage plant operations.
By adopting automation, these industries reduce labor strain, improve accuracy, and increase throughput—critical in today’s competitive global marketplace.
The Future of Automation Engineering in Illinois
As we move further into the age of Industry 4.0, the role of automation engineers is evolving. Engineers in Illinois are not just builders of machines—they are architects of data-driven, intelligent systems. The future will include:
Edge Computing and AI: Allowing systems to make real-time decisions at the source.
Cloud-Connected Automation: Centralized data storage and analysis across multiple plants.
Predictive Maintenance: Using machine learning to anticipate equipment failures before they occur.
Digital Twins: Creating virtual replicas of physical systems for simulation and optimization.
Green Manufacturing: Designing systems that reduce energy use and support sustainability.
Illinois is well-positioned to remain at the forefront of this transformation, with a workforce ready to meet the challenges and opportunities ahead.
Choosing the Right Automation Engineer in Illinois
When selecting an automation engineer or firm, businesses should look for:
Experience Across Industries
Proficiency with Major Platforms (Allen-Bradley, Siemens, Beckhoff, etc.)
Commitment to Safety and Compliance
Strong Project Management and Communication Skills
Local Support and Maintenance Services
A collaborative approach ensures solutions that align with business goals, budget, and operational scale.
Your Automation Engineering Partner: Xtreme Automation LLC
If your Illinois-based business is ready to embrace the future of smart manufacturing, Xtreme Automation LLC is here to help. With decades of experience in automation design, PLC programming, robotics integration, and system retrofitting, Xtreme Automation provides comprehensive engineering solutions tailored to your industry. From planning and development to implementation and support, their team ensures your automation journey delivers real results. Learn more at xtremeautomationllc.com.
#Automation Engineers Illinois#Industrial Automation Services#Robotics Engineering Illinois#Control System Engineers IL#Automation Integration Companies#Smart Manufacturing Illinois#PLC and HMI Programming#Engineering Solutions Illinois#Industrial Robotics Experts#Factory Automation Consultants
0 notes
Text
Overview of Digital Flow Meters: Accurate Flow Measurement for Modern Industries

Flow meters are essential tools in many industries, used to measure the volume or mass of a fluid moving through a pipeline. With the growing demand for more precise, reliable, and real-time data, digital flow meters have become increasingly popular. These advanced instruments offer enhanced accuracy, easy integration with digital systems, and lower maintenance needs compared to traditional mechanical meters.
This blog will provide a clear overview of digital flow meters, how they work, their types, benefits, and where they are used.
What is a Digital Flow Meter?
A digital flow meter is a device that measures the flow of liquids or gases and displays the results in a digital format. It uses sensors and electronic components to monitor flow rates with high precision and often includes features such as:
Digital displays for real-time monitoring
Remote data transmission
Integration with SCADA, PLC, or IoT systems
Alarm settings and data logging
These meters are commonly used in water treatment plants, oil & gas industries, chemical processing, and HVAC systems, among others.
Types of Digital Flow Meters
There are several types of digital flow meters, each suited for different applications based on the type of fluid and required accuracy:
1. Electromagnetic Flow Meters
Ideal for conductive liquids like water, slurries, and chemicals. These meters use electromagnetic fields to measure flow without any moving parts.
2. Ultrasonic Flow Meters
Use high-frequency sound waves to measure the velocity of the fluid. They are perfect for both clean and dirty liquids and work well in large pipes.
3. Turbine Flow Meters
Contain a spinning rotor that turns with the flow. The rotational speed is proportional to the flow rate. These are used in clean, low-viscosity liquids.
4. Coriolis Flow Meters
Measure mass flow directly using the Coriolis effect. Known for their high accuracy and are used in chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
5. Thermal Mass Flow Meters
Used mainly for gases, these measure flow by detecting heat loss from a heated sensor placed in the flow path.
Benefits of Using Digital Flow Meters
✅ High Accuracy: Digital sensors reduce human error and provide exact measurements.
✅ Easy to Read: Digital displays are user-friendly and easy to interpret.
✅ Remote Monitoring: Many models support wireless or wired connectivity for remote data access.
✅ Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts, these meters are durable and require minimal upkeep.
✅ Data Storage: Many meters come with memory functions for storing historical data for analysis.
Applications of Digital Flow Meters
Digital flow meters are used across various industries, including:
Water & Wastewater Management: For monitoring distribution and treatment systems.
Oil & Gas: For controlling the flow of fuels and gases.
Food & Beverage: Ensures precise ingredient mixing and quality control.
Pharmaceutical: For high-accuracy dosage and mixing applications.
HVAC Systems: For measuring water and air flows for better energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Digital flow meters have revolutionized how industries measure and manage fluids. Their combination of accuracy, reliability, and advanced features makes them an essential part of modern process control systems. Whether you are managing water resources, producing chemicals, or ensuring clean air flow, a digital flow meter can greatly improve your operational efficiency.
If you’re searching for reliable Digital flow meter manufacturers in India, it’s important to choose a company with proven expertise, quality products, and excellent service support to match your industry’s specific needs.
Looking for the right digital flow meter for your application? Connect with a trusted supplier today and discover how digital technology can enhance your flow measurement systems.
#flow meters#electromagnetic water meter#digital water flow meter#digital flow meters#digital water flow meter manufacturer in india#digital water flow meter india#electromagnetic flow meters#digital water meter#electromagnetic flow meter suppliers in india#electromagnetic flow meter manufacturers in india
0 notes
Text
Smart Factory with 7 Axes Robot and Digital Twin Manufacturer in Pune India
Manufacturer and Supplier of Smart Factory solutions with 7 Axes Robots and Digital Twin technology in Pune. We provide flexible manufacturing systems (MPS), connected machines, and SCADA training.
#Flexible Manufacturing Systems Manufacturer Pune#Smart Factory with 7 Axes Robot Pune#Smart Factory Manufacturer Pune#Flexible Manufacturing System Pune#MPS Manufacturing System Pune#Connected Machines Pune#SCADA Training Pune#Digital Twin Pune#Flexible Manufacturing Systems Pune#Digital Twin for Manufacturing Pune#SCADA Solutions Pune
0 notes
Text
Integrating data historian into existing systems
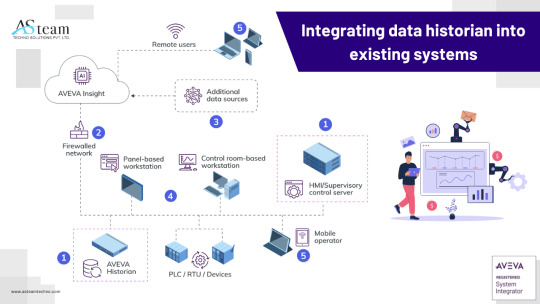
PLCs, SCADA systems, and other industrial control systems are just a few of the many systems and protocols that Data Historian easily connects with. It provides crucial production data and performance indicators by integrating with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems via APIs or middleware. Additionally, it uses conventional interfaces or custom connections to send historical and real-time data to Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) for improved production control.
OPC DA and OPC UA protocols for real-time data acquisition from PLCs and DCS systems.
Native integration with AVEVA System Platform and InTouch HMI, allowing for direct data collection without the need for additional middleware.
SQL interfaces and APIs that enable integration with third-party business systems such as ERP, MES, and CMMS.
#automation#technology#tech#automotive#plc scada training#scada systems#SCADA#AVEVA#AVEVA System Platform#Data Historian
1 note
·
View note
Text

ARMxy RK3562J IoT Gateway Modbus to OPC UA for Industrial Connectivity
The ARMxy series ARM embedded computer BL370 series is an industrial-grade ARM controller with flexible I/O. It is designed with the Rockchip RK3562/RK3562J processor, featuringa quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 and a single-core ARM Cortex-M0, with a clock speed of up to 1.8GHz/2.0GHz. The BL370 series comes with 8/16/32GB eMMC, and various RAM and ROM combinations of 1/2/4GB LPDDR4X. It supports a rich set of I/O interfaces and is equipped with a built-in 1TOPS NPU for deep learning. The BL370 series is widely used in industries such as industrial control, edge computing, AIoT, artificial intelligence, communication management, AGV, machine vision inspection, robotics, industrial IoT gateways, energy storage systems, automation control, and transportation rail systems.
The BL370 series ARM embedded computer offers a variety of interfaces, including 1-3 optional 10/100M adaptive RJ45 ports, 2xUSB 2.0, 1xHDMI 2.0, 1 X-series I/O board, and 2 Y-series I/O boards.These interfaces can be used for communication, PWM output, pulse counting, and other data acquisition and control tasks. The device supports 1080P@60fps H.264 video encoding and 4K@30fps H.265 video decoding. It also features a built-in Mini PCIe interface, supporting communication via Bluetooth, WiFi, 4G, and 5G modules.
The BL370 series ARM embedded computer supports various operating systems, including Linux-5.10.198, Linux-RT-5.10.198 kernel, Ubuntu 20.04, Debian 11 (bullseye) (planned), and Android 13 (planned). It also supports Docker containers, Node-RED, and Qt-5.15.2 for graphic interface development. Additionally, the device is compatible with the BLIoTLink industrial protocol conversion software for industrial data acquisition and conversion, enabling fast access to mainstream IoT cloud platforms and industrial SCADA configuration software. Remote access and maintenance can be performed through the BLRAT remote access tool, and Node-RED supports the rapid development of IoT applications.
The BL370 series ARM embedded computer has undergone professional electrical performance design and high/low-temperature testing validation. It can operate reliably and stably in harsh electromagnetic interference environments and a temperature range of -40 to 85°C. Thedevice is designed for DIN35 rail mounting, making it suitable for various industrial application environments.
0 notes
Text
Empower Your Industrial Automation Business with Thirstymaart

In today’s fast-paced and technology-driven world, industrial automation has become a cornerstone for improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and achieving precision in manufacturing and other industrial processes. From robotics to PLC systems, industrial automation solutions are transforming industries.
If you’re in the business of providing industrial automation solutions, Thirstymaart is the perfect platform to help you grow your brand, attract more clients, and showcase your expertise to the industries that need it most.
Why Thirstymaart is the Ideal Platform for Your Industrial Automation Business
🚀 Expand Your Business Reach
By listing your business on Thirstymaart, you gain access to a wide array of potential clients, including manufacturers, factories, and warehouses, looking for automation solutions.
⚙️ Showcase Your Cutting-Edge Technology
Industrial automation is a field where innovation matters. Use Thirstymaart to highlight your expertise in robotics, machine vision, SCADA systems, and more, to attract clients seeking advanced automation solutions.
🏭 Cater to Diverse Industries
Automation spans multiple sectors, including manufacturing, energy, pharmaceuticals, and logistics. Thirstymaart enables you to connect with businesses across these industries, helping you broaden your clientele.
🔧 Provide Tailored Solutions
Industrial clients often require customized automation solutions. Thirstymaart allows you to display your capability to design and deliver tailor-made systems for specific industrial needs.
📞 Seamless Client Interactions
With Thirstymaart’s easy-to-use platform, you can connect directly with potential clients, manage inquiries, and provide quotes efficiently, ensuring smooth communication and faster project conversions.
🏆 Build Credibility in a Competitive Field
Share your certifications, past projects, and client testimonials to establish your business as a trusted leader in industrial automation.
Services to Highlight on Thirstymaart
🤖 Automation Solutions
PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers) Programming
Robotics Integration
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Systems
Machine Vision Systems
IoT Integration for Smart Factories
⚡ Process Optimization
Real-time Process Monitoring
Predictive Maintenance Systems
Energy Efficiency Optimization
Industrial Data Analytics
🔌 Control Systems
Motor Control Centers (MCC)
Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
Custom Automation Control Panels
🏗️ Industry-Specific Solutions
Conveyor System Automation
Packaging and Material Handling Automation
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Automation
Food Processing Automation
🛠️ Installation & Support
System Installation and Integration
On-Site Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Training and Support for Operators
How to Start Your Journey on Thirstymaart?
1️⃣ Sign Up as a Vendor – Create your professional profile and highlight your expertise in industrial automation. 2️⃣ List Your Services & Technologies – Include the details of your offerings, such as robotics, IoT solutions, or SCADA systems. 3️⃣ Engage with Clients – Respond to inquiries, provide consultations, and offer tailored solutions. 4️⃣ Showcase Your Achievements – Share case studies, certifications, and client success stories to build trust.
Why Industrial Automation is the Future
With the rapid advancements in Industry 4.0, businesses are increasingly adopting automation to stay competitive. From smart factories to energy-efficient systems, industrial automation provides unparalleled benefits such as:
Improved production efficiency
Reduced labor costs
Enhanced product quality and consistency
Real-time monitoring and control
Take Your Industrial Automation Business to the Next Level with Thirstymaart
The demand for industrial automation solutions is growing exponentially, and your expertise is crucial to meeting this demand. Thirstymaart offers you the platform to connect with the right clients, showcase your solutions, and grow your business.
🌟 Don’t wait—join Thirstymaart today and lead the way in industrial automation innovation!
https://thirstymaart.com/profile/sangli/ganalaxmi-electricals
https://thirstymaart.com/profile/sangli/priyanka-electronic-systems
https://thirstymaart.com/profile/miraj/logiclinx-automation
https://thirstymaart.com/profile/kolhapur/shree-mahalaxmi-trade-links
https://thirstymaart.com/profile/ichalkaranji/enahnce-technoworks
0 notes
Text
Best HMI Dealers in Rajasthan
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, automation and seamless control systems have become the cornerstone of efficient manufacturing and production. One critical component in this ecosystem is the Human Machine Interface (HMI). These devices allow operators to interact with machines, monitor performance, and control operations in real-time. For industries across Rajasthan, finding the right HMI dealer can make a significant difference in operational success.
Whether you're running a manufacturing unit in Jaipur, a processing plant in Udaipur, or an automation setup in Jodhpur, choosing the Best HMI dealers in Rajasthan is crucial. These dealers not only supply top-quality products but also offer reliable technical support, installation assistance, and after-sales service — all essential for long-term efficiency.
Why HMI is Crucial in Industrial Automation
HMIs act as the communication bridge between humans and machines. From displaying machine data and alarms to enabling touch-based controls and remote access, HMIs simplify complex processes. In sectors like pharmaceuticals, food processing, cement manufacturing, and textiles, they are indispensable.
Modern HMIs are far more advanced than their earlier versions. Touchscreens, intuitive GUIs (Graphical User Interfaces), customizable dashboards, and integration with SCADA or PLC systems are now standard. But to make the most of these features, you need not just a good product — you need a dealer who understands your specific needs and offers tailor-made solutions.
What to Look for in an HMI Dealer
Here are a few things to keep in mind when searching for the Best HMI dealers in Rajasthan:
Brand Partnerships: A reputable dealer should be associated with trusted HMI brands like Siemens, Schneider Electric, Allen-Bradley, Mitsubishi, or Delta. Strong partnerships mean better warranties and access to the latest tech.
Technical Expertise: Your dealer should not only sell you the product but also guide you on system integration, compatibility with existing PLCs, and maintenance support.
Local Presence: Having a local or regional presence means quicker service response times and on-site support when needed.
Customization & Consultation: Industries vary widely, and so do automation needs. The best dealers will understand your business, evaluate your processes, and recommend the most suitable HMI solution.
Customer Reviews & Case Studies: Positive feedback from existing clients and documented case studies can be strong indicators of reliability and performance.
Serving Excellence Across Rajasthan
Rajasthan’s industrial growth has been impressive in the past decade. With rising demand for automation in everything from mining to agro-processing, the importance of trusted HMI suppliers has grown manifold.
Among the most dependable names in this sector is Canyon Engineering Solutions Pvt Ltd. With a commitment to delivering cutting-edge automation products and solutions, they are well-regarded for their quality offerings, customer-centric approach, and on-time project execution. Their dedication to building long-term relationships with clients sets them apart in a competitive market.
Whether you are setting up a new unit or upgrading existing systems, connecting with the Best HMI dealers in Rajasthan ensures that your production line runs smoothly and efficiently — giving you a competitive edge in your industry.
Final Thoughts
Investing in the right HMI system is not just a technical decision — it’s a strategic one. The right dealer will not only provide the hardware but also ensure that your systems are optimized for performance, safety, and future scalability. With expert advice and dependable service, the best HMI dealers help you stay ahead of the curve.
0 notes
Text
ARMxy based SBC with ATVISE HMI and SCADA for Industry 4.0 Solutions

Case Details
1. Hardware Platform: ARMxy Based SBC
Low Power Consumption & High Efficiency ARM processors deliver high performance while significantly reducing energy consumption, making them ideal for 24/7 industrial operations. This minimizes cooling requirements and energy costs.
Compact & Rugged Design Fanless and compact form factors adapt to space-constrained workshop environments, with wide-temperature operation (-40°C to 85°C), suitable for harsh conditions.
Rich Interface Support Industrial interfaces such as RS-485/232, CAN bus, Gigabit Ethernet, and GPIO, compatible with protocols like Modbus, MQTT, enable direct connections to PLCs, sensors, and IoT devices.
Edge Computing Capabilities Models with integrated AI accelerators (e.g., NPUs) can perform localized tasks like machine vision and anomaly detection, reducing cloud dependency and improving response times.
2. Software Core: ATVISE HMI/SCADA
Cross-Platform Compatibility HTML5-based architecture supports seamless operation on ARM/Linux or Windows systems, providing a unified web-based interface accessible via mobile devices.
Dynamic Data Visualization Drag-and-drop editors enable rapid creation of 3D factory models, integrating real-time data streams (e.g., temperature curves, OEE dashboards) with multilingual support and alarm management.
Direct Industrial Protocol Integration Native support for OPC UA, MQTT, and S7 communication allows direct interaction with Siemens, ABB, and other PLCs without middleware.
Cloud Collaboration Built-in connectors for AWS IoT/Azure IoT Hub enable device-to-cloud data transfer, facilitating big data analysis and predictive maintenance modeling with time-series databases.
3. Key Industry 4.0 Application Scenarios
a. Smart Production Line Monitoring
ARMxy SBC collect real-time motion control data via EtherCAT. ATVISE generates a digital twin of the production line, dynamically displaying cycle times, yield rates, and equipment status, triggering ANDON alerts during anomalies.
Example: In automotive assembly lines, vibration sensor data predicts robotic arm bearing lifespan, triggering maintenance orders two weeks in advance.
b. Energy Management Optimization
ATVISE consolidates energy meter data into dashboards. ARM edge nodes run algorithms to identify peak usage patterns for high-energy devices (e.g., compressors), automatically adjusting operations to reduce energy consumption by 15%.
Technical Detail: ARM GPIO controls smart relays to implement time-based power strategies.
c. Predictive Maintenance
ARM devices run TensorFlow Lite models to analyze motor current harmonics. ATVISE visualizes equipment health indices, triggering work orders when anomalies (e.g., insulation degradation) are detected.
Data Flow: Vibration sensors → ARM edge FFT analysis → feature extraction → ATVISE visualization → threshold-based alerts.
d. Flexible Manufacturing Systems
ATVISE synchronizes ERP order data, while ARM controllers dynamically adjust AGV routes and machining center parameters for small-batch, multi-variant production, reducing changeover time by 70%.
Protocol Integration: OPC UA Pub/Sub enables real-time communication between MES and equipment layers. 4. Implementation Benefits
Lower Operational Costs: ARM reduces energy costs by 30%; remote diagnostics minimize on-site inspections.
Improved Productivity: Real-time anomaly response boosts overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by 12%.
Scalability: Modular design supports future integration with 5G private networks or digital twin platforms.
This hardware-software integration is particularly suited for industries requiring high real-time performance and compact solutions, such as food packaging and semiconductor manufacturing, enabling low-TCO digital transformation of production lines.
0 notes
Text
🤖 PLC Industrial Automation: A Quick Guide
🔹 Introduction: Transforming Industrial Efficiency
Automation is key to modern industry, enhancing productivity, precision, and reliability. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) drive this transformation by optimizing processes and minimizing human intervention.
🔌 What is a PLC?
A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is an industrial computer that controls machinery by receiving input signals from sensors and transmitting commands to actuators, ensuring seamless automation.
🔑 Key PLC Components
🖥️ CPU: The core processor executing programs.
📡 I/O Modules: Connects sensors (inputs) and actuators (outputs).
⚡ Power Supply: Provides stable power.
📝 Programming Device: Develops automation logic.
🔗 Communication Ports: Enables integration with HMI and SCADA systems.
📌 PLC Programming Essentials
🎯 Define Automation Goals – Identify tasks and objectives.
🗺️ Map Workflow – Create a flowchart for process logic.
📜 Write Ladder Logic – Code using relay-based logic.
🔍 Test & Debug – Ensure functionality before deployment.
⚙ PLC Installation Best Practices
🔩 Secure Installation – Place in a ventilated, vibration-free area.
🔌 Proper Wiring – Connect I/O modules accurately.
✅ System Check – Perform power-up diagnostics.
🛠️ Maintenance & Optimization
📊 Real-Time Monitoring – Use HMI/SCADA for tracking.
🔍 Regular Inspections – Check wiring and system logs.
📈 Continuous Optimization – Improve program logic over time.
🏆 Why Choose Dropship Automation?
Dropship Automation provides top-tier PLC solutions and expert guidance to streamline industrial automation. From high-quality components to tailored consultation, we ensure seamless integration.
🚀 Conclusion: Upgrade Your Automation Today
PLCs revolutionize industrial operations with efficiency, reliability, and scalability. Optimize your processes today with Dropship Automation.
1 note
·
View note
Text
🤖 PLC Industrial Automation: A Quick Guide
🔹 Introduction: Transforming Industrial Efficiency
Automation is key to modern industry, enhancing productivity, precision, and reliability. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) drive this transformation by optimizing processes and minimizing human intervention.
🔌 What is a PLC?
A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is an industrial computer that controls machinery by receiving input signals from sensors and transmitting commands to actuators, ensuring seamless automation.
🔑 Key PLC Components
🖥️ CPU: The core processor executing programs.
📡 I/O Modules: Connects sensors (inputs) and actuators (outputs).
⚡ Power Supply: Provides stable power.
📝 Programming Device: Develops automation logic.
🔗 Communication Ports: Enables integration with HMI and SCADA systems.
📌 PLC Programming Essentials
🎯 Define Automation Goals – Identify tasks and objectives.
🗺️ Map Workflow – Create a flowchart for process logic.
📜 Write Ladder Logic – Code using relay-based logic.
🔍 Test & Debug – Ensure functionality before deployment.
⚙ PLC Installation Best Practices
🔩 Secure Installation – Place in a ventilated, vibration-free area.
🔌 Proper Wiring – Connect I/O modules accurately.
✅ System Check – Perform power-up diagnostics.
🛠️ Maintenance & Optimization
📊 Real-Time Monitoring – Use HMI/SCADA for tracking.
🔍 Regular Inspections – Check wiring and system logs.
📈 Continuous Optimization – Improve program logic over time.
🏆 Why Choose RAM Automations?
RAM Automations provides top-tier PLC solutions and expert guidance to streamline industrial automation. From high-quality components to tailored consultation, we ensure seamless integration.
🚀 Conclusion: Upgrade Your Automation Today
PLCs revolutionize industrial operations with efficiency, reliability, and scalability. Optimize your processes today with RAM Automations.
0 notes
Text
Smart Enterprise Market Global Landscape: Opportunities and Market Share Analysis 2032
The Smart Enterprise Market was valued at USD 0.32 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 0.99 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 13.44% from 2024-2032
Smart Enterprise Market is experiencing rapid expansion, driven by digital transformation, automation, and artificial intelligence. Businesses across industries are adopting smart technologies to enhance efficiency, agility, and customer experiences. With increasing reliance on data-driven decision-making, enterprises are investing in cloud computing, IoT, and AI-powered solutions.
Smart Enterprise Market continues to evolve as organizations integrate advanced technologies into their operations. From automation to predictive analytics, businesses are leveraging smart enterprise solutions to optimize processes and improve productivity. As digital ecosystems grow, companies are focusing on seamless connectivity, cybersecurity, and AI-driven insights to stay competitive in a fast-changing landscape.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3771
Market Keyplayers:
Microsoft (Azure IoT, Power BI)
Cisco Systems (Cisco IoT, Industrial Network Switches)
Oracle (Oracle IoT Cloud, Oracle Autonomous Database)
SAP (SAP Leonardo, SAP S/4HANA)
Honeywell Process Solutions (Experion, Honeywell UOP)
Hitachi Vantara (Lumada, Hitachi Visualization Suite)
Mitsubishi Electric (MELSEC iQ-R, EcoMonitor)
Dell Technologies (IoT Solutions, VxRail)
Toshiba (Toshiba Smart City Solutions, Toshiba IoT Solutions)
Intel (Intel IoT Platform, Intel Xeon Scalable Processors)
ABB Ltd. (ABB Ability, Smart Grids)
Siemens (MindSphere, Industrial Automation)
General Electric (Predix, Digital Wind Farm)
Rockwell Automation Inc. (FactoryTalk, Allen-Bradley)
Schneider Electric (EcoStruxure, APC by Schneider Electric)
Honeywell International Inc. (Honeywell Forge, Building Management Systems)
Emerson Electric Co. (Plantweb, Ovation)
Fanuc UK Limited (Robodrill, Robocut)
Fujitsu Global (Fujitsu Digital Annealer, SPARC Servers)
IBM (IBM Watson IoT, IBM Maximo)
Market Trends Driving Growth
AI and Automation Adoption – Businesses are integrating AI-powered automation to streamline workflows, enhance decision-making, and reduce operational costs.
Cloud and IoT Integration – Cloud computing and IoT are enabling seamless data exchange, real-time monitoring, and remote business operations.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection – Enterprises are prioritizing cybersecurity investments to safeguard sensitive data and prevent cyber threats.
Personalized Customer Experiences – AI-driven analytics and automation are helping businesses tailor customer interactions, improving engagement and satisfaction.
Enquiry of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/enquiry/3771
Market Segmentation:
By Component
Hardware
Software
Services
By Technology
MES
PLC
ERP
SCADA
HMI
Others
By Organization Size
Small and Medium Size Enterprise
Large Enterprise
By Application
Automotive
Chemicals & Materials
Healthcare
Food & Beverage
Consumer Goods
Aerospace & Defense
Market Analysis and Current Landscape
Key factors contributing to market expansion include:
Growing Demand for AI and Big Data – Enterprises are leveraging AI and big data analytics for strategic decision-making and predictive insights.
Hybrid and Remote Work Growth – Organizations are adopting smart workplace solutions to support remote teams and improve digital collaboration.
Rising Investments in Digital Transformation – Companies are accelerating digital adoption to enhance operational efficiency and stay ahead of competitors.
Increased Focus on Sustainability – Businesses are implementing smart energy management solutions to optimize resource usage and reduce carbon footprints.
Despite the strong growth trajectory, challenges such as integration complexities, high implementation costs, and data privacy concerns remain. However, continuous advancements in AI, automation, and cybersecurity are addressing these challenges, ensuring steady market expansion.
Future Prospects: What Lies Ahead?
AI-Driven Business Intelligence – AI and machine learning will play a crucial role in predictive analytics, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions with greater accuracy.
Expansion of Smart Workspaces – Companies will invest in smart office technologies, including IoT-powered automation, virtual collaboration tools, and intelligent workflow systems.
5G and Edge Computing Growth – The adoption of 5G and edge computing will enhance connectivity, speed up data processing, and improve real-time decision-making.
Blockchain for Secure Transactions – Blockchain technology will be increasingly integrated into enterprise solutions to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency in business operations.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/smart-enterprise-market-3771
Conclusion
The Smart Enterprise Market is on an upward trajectory, revolutionizing the way businesses operate through AI, automation, cloud computing, and IoT. As companies continue to invest in digital transformation, smart technologies will drive efficiency, security, and innovation across industries. Businesses that embrace these advancements will gain a competitive edge, positioning themselves for long-term success in an increasingly digital world.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#automation#cloud computing#smart technologies will drive efficiency#The Smart Enterprise Market is on an upward trajectory#revolutionizing the way businesses operate through AI#and innovation across industries. Businesses that embrace these advancements will gain a competitive edge#positioning themselves for long-term success in an increasingly digital world.
0 notes