#alice's wonderland
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Walt Disney combines a live-action cat and an animated mouse in Alice's Wonderland, 1923.
#reddit#silentmoviegifs#silentmoviegif#disney#walt disney#live action#animation#cartoon#cat#mouse#alice's wonderland#1923#1920s#b&w#chat#gato#feline#animal#fauna#poke#poking
31 notes
·
View notes
Text


Alice's Wonderland (1923) // Over the Garden Wall (2014)
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
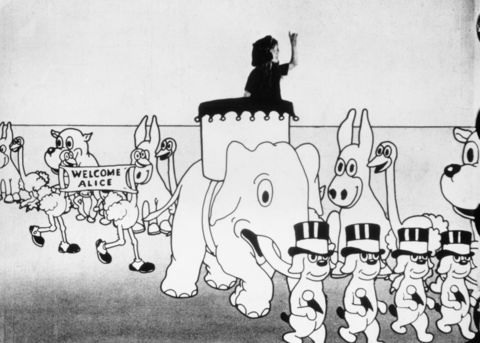
Alice's Wonderland (1923 short)
One hundred years ago today, Walt Disney screened to Margaret Winkler his hybrid animated/live-action short film, Alice’s Wonderland. If the name Margaret Winkler is unfamiliar to you, that is in part due to the fact that much of Hollywood’s mythmaking has obfuscated the impact of certain female creatives during the silent film era. A former secretary to Harry Warner at Warner Bros., Winkler was the premier animated short film executive in the early and mid-1920s. Her company, M.J. Winkler Pictures, flourished at a time before the oligopoly of the soon-to-be-major Hollywood studios, mostly on the backs of Pat Sullivan and Otto Messmer’s Felix the Cat series. At the peak of Felix’s popularity in 1923, a series of arguments between Winkler and Sullivan/Messmer soon meant Winkler was looking for an animated series to replace Felix. She would also be losing the rights to Max and Dave Fleischer’s Out of the Inkwell series, starring Koko the Clown. By the end of 1923, Winkler would sign a deal with Disney to distribute the Alice Comedies.
Impressed by the handiwork of Alice’s Wonderland, Winkler’s deal gave Walt Disney a much-needed infusion of cash. Disney, who founded Laugh-O-Gram Studios in Kansas City, Missouri in 1921, had just barely emerged from Laugh-O-Gram’s bankruptcy. Instead of heading to the then-center of the American animation world of New York City, Walt instead found himself in Los Angeles, partly to help his brother, Roy O. Disney, recover from tuberculosis.
Though a continent away from the major animation players in the U.S. at the time, Disney nevertheless took inspiration from those figures – Bray Productions under John Randolph Bray and especially the animator Winsor McCay (who, by 1921, was forced by employer William Randolph Hearst to stop working on animated film). McCay and Bray were pioneers in gifting animated characters basic personalities and the development of those personalities, growing animated cinema beyond modest gag comedy and simplistic figures. McCay’s Little Nemo (1911) and Gertie the Dinosaur (1914) and Bray’s Bobby Bumps series (1915-1925) may seem quaint to modern audiences, but these films were wildly popular across North America and were instrumental stepping stones to the explosion of American animated innovation in the late 1920s and 1930s.
Alice’s Wonderland was never screened for the public, but it nevertheless spawned a series that lasted for fifty-seven short films. None of it would have been possible without the inspiration Disney and his animators took from the most acclaimed American animation at that time.
With no relation to Lewis Carroll’s two Alice books, Alice’s Wonderland stars Virginia Davis as the title character. Davis, as Alice, is four years old at the beginning of the Alice Comedies series. She visits the animation studio where she sees Walt Disney in the process of drawing some “funnies”. As she sits down, the cartoons on the drawing pages come to life. Most important among those animated figures is Julius the Cat, created by Disney and Ub Iwerks and a predecessor to Oswald the Lucky Rabbit and Mickey Mouse (unlike Oswald and Mickey, Julius has not appeared in an animated film since the silent era). Walt then brings Alice into the animators’ room, where Ub Iwerks, Hugh Harman and Rudolf Ising, and others are also enjoying their work acting out various scenarios (remember those names – we will mention them again later). Alice, still giddy after her visit to the animators’ studio, later drifts off to sleep that evening. And, after dozing off, she finds herself welcome to a Cartoonland of her dreams.
At the time, Alice’s Wonderland was the reverse of what the Fleischers’ Out of the Inkwell series and some of the Bray and McCay shorts attempted. Instead of animated characters inhabiting a live-action world, we have here a live character traipsing around in an animated world. In some of the hybrid animated/live-action short films at the time, the reactions of the characters can be noticeably off. Not so much here. Davis’ reactions to the animated animals are timed with admirable precision. But given the technological constraints at the time and how small Walt Disney’s animators’ team was, Alice’s Wonderland makes heavy use of recycled or looped animation. Viewers who know their Looney Tunes or Hanna-Barbera works probably recognize the effects of a wraparound background and identical walking animation. The effects tend to make certain scenes – such as Alice’s celebratory procession during her dream – last several seconds too long.
youtube
Yet, Alice’s Wonderland still charms. With synchronized sound still four years away, the animators of the early twentieth century set the visual slapstick language that continues to course through modern animated cinema. Julius’ hidden fight with a dog within the latter’s doghouse, an animator using a pen holder as a de facto boxing bell, and a hungry lion cleaning and sharpening his teeth are just previews to the absurd humor that will define the next few decades of American animated short films. So too the tubular limbs from the animated characters. The film’s humor came not just from the films of Bray, McCay, and the Van Beuren Studios, but also the comic strips popular at this time – titles which probably read as quite unfamiliar to most today: Bud Fisher’s Mutt and Jeff (1907-1983; Fisher ceased involvement in 1932), George Herriman’s Krazy Kat (1913-1944), and Winsor McCay’s Dream of the Rarebit Fiend (1904-1925). These comic strips, largely unknown quantities to yours truly while researching for this write-up, influenced the comedic pace and tone for the bulk of American animated short films – a near-forgotten legacy, and one worthy of honoring.
Alice’s Wonderland would solidify the careers of all of the animators involved – all of whom were originally based in the Kansas City area. Walt Disney and Ub Iwerks stayed onboard what would be deemed the Disney Brothers Cartoon Studio (after several name changes, it is now the Walt Disney Animation Studios of today). Disney’s namesake studio is the most visible animated studio in all of cinema, and undoubtedly the most historically and currently significant, for good and ill. For the Alice Comedies, Iwerks experimented with a “matte” – in which a cutout background would be placed over a camera lens to hide where animated figures might be. Iwerks also developed Mickey Mouse with Walt, was one of the leading hands on the Silly Symphony series, and was integral in developing the special visual effects that made animated/live-action hybrid movies like Song of the South (1946) and Mary Poppins (1964) as convincing as they are.
Hugh Harman and Rudolf Ising, who developed the story of Alice’s Wonderland alongside Walt, honed their craft under him. But after Disney sold the rights to Oswald the Lucky Rabbit to Universal in 1928 in a dispute with Winkler’s husband, producer Charles Mintz, Harman and Ising’s time with Disney came to an end. Now on their own, Harman and Ising created Bosko. The Bosko shorts impressed Warner Bros.’ Leon Schlesinger and, in 1930, the trio founded the Looney Tunes and Merrie Melodies series. Harman and Ising would eventually leave Warner Bros. in 1934 to develop the Happy Harmonies series for Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer alongside William Hanna. Animator Isadore “Friz” Freleng also followed Harman and Ising to Warner Bros. and MGM, and was central to the creation of the likes of Porky Pig, Sylvester, and Yosemite Sam. Also following Freleng was Carman Maxwell, who spent the bulk of his career as a production manager for MGM’s animated shorts.
Actress Virginia Davis also moved out from Kansas City to Southern California to join Disney to star in the Alice Comedies. Davis appeared in fifteen of the fifty-seven Alice Comedies, ending her tenure with Alice in the Jungle (1925). She was able to nab the occasional minor child actress role and ended her career in the 1940s as uncredited dancers or chorus girls. She married in 1943 to a Navy airman and became a real estate agent active in the areas around Irvine, California and Boise, Idaho.
Margaret Winkler could be an exacting critic to Walt Disney and his animators, but she nevertheless sent words of encouragement, making suggestions where she saw fit to the rough cuts of the films. Her critiques plus the relatively expensive cost in making an Alice short saw Disney struggle to meet deadlines at first. But when Disney was able to convince Harman and Ising to move from Kansas City to Los Angeles, the pace of production hastened. Winkler retired from the film business in 1926 after the birth of her first child, with shockingly no one thinking to interview her about her work in the silent era before her death in New York state in 1990.
The Alice Comedies, beginning with Alice’s Wonderland, set the stage for American animated film in the early and middle twentieth century. Several figures involved in the series’ animation and storytelling paved careers that would deeply impact the direction of what today is Walt Disney Animation Studios. Others, like Harman, Ising, Freleng, and Maxwell, took with them Walt Disney’s artistic vision and guidance and spread that to two of the studio’s soon-to-be rivals in MGM and Warner Bros.
A century since Walt Disney screened Alice’s Wonderland for Margaret Winkler, Walt Disney Animation Studios has grown and evolved. The modern-day studio, I will argue, does not adhere to Walt Disney’s vision of making animated movies as dramatically and emotionally powerful as any live-action movie as faithfully as it could – and, in my opinion, has not consistently done so in at least a quarter-century. But the studio, and its legacy, started humbly, just hoping to please a crowd with sharp visual gags in the wild early days of animated silent film. Such were the initial hopes of John Randolph Bray and Winsor McCay. From the Alice Comedies to the Silly Symphony shorts to Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs (1937), Walt Disney and his fellow animators added to the foundation that their predecessors built.
My rating: 7/10
^ Based on my personal imdb rating. My interpretation of that ratings system can be found in the “Ratings system” page on my blog. Half-points are always rounded down.
For more of my reviews tagged “My Movie Odyssey”, check out the tag of the same name on my blog.
#Alice's Wonderland#Alice Comedies#Walt Disney#Margaret Winkler#Hugh Harman#Rudolf Ising#Ub Iwerks#Virginia Davis#Margaret Davis#Carman Maxwell#Friz Freleng#Julius the Cat#Laugh-O-Gram Studios#Disney#Disney 100#Winsor McCay#John Randolph Bray#silent film#My Movie Odyssey
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

#this is what makes us girls#girlhood#lana del rey#girl interrupted#girlblogging#black swan#girlblogger#tumblr girls#just girly things#blogging#sensitive girl#alice in wonderland#messy girl#girlblog#hell is a teenage girl#girl blog#cinnamon girl#girly stuff#girl blogger#too sensitive for this world#sylvia plath#the bell jar#grace#fiona apple#lana core#lana del ray aesthetic#lana is god#lana del ray aka lizzy grant#jeff buckley#girl interupted syndrome
7K notes
·
View notes
Audio
(italo disco forever and more)
0 notes
Text




Alice in Wonderland dir. Clyde Geronimi, Hamilton Luske, Wilfred Jackson | 1951
#alice in wonderland#aliceinwonderlandedit#disneyedit#animationedit#filmedit#filmgifs#userteri#usertennant#tuserpris#henricavyll#bladesrunner#usersugar#userrlaura#useraurore#userchess#1950s#ours#film#by diana
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
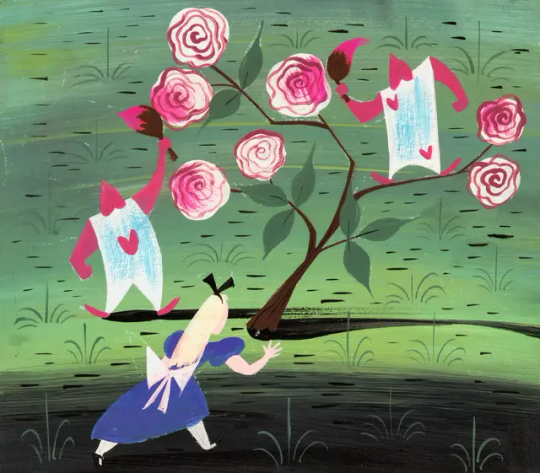






Mary Blair's concept art for Alice in Wonderland (1951)
#disney#alice in wonderland#mary blair#concept art#animation#disney animation#disney concept art#vintage disney#art#artwork#illustration#animation art#alice in wonderland 1951#classic disney
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
Them ♟️



#the amazing digital circus#tadc#tadc au#digital wonderland#tadc fanart#alice in wonderland#tadc checkmates
3K notes
·
View notes
Text



#twisted wonderland#twst#malleus draconia#twst yuu#ace trappola#jamil viper#malleus x yuu#malleyuu#ace x yuu#jamil x yuu#alice sketch
3K notes
·
View notes
Text


#cottagecore#naturecore#valentines day#roses#nature#nature aesthetic#flowers#spring#summer#pink#magical#princess#princesscore#royalcore#alice in wonderland
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Another Jax illustration , sorry he's really fun to draw
(it is wallpaper sized)
#fanart#digital art#the amazing digital circus jax#jax fanart#tadc jax#jax#tadc fanart#tadc#The amazing digital circus#alice in wonderland#cheshire cat
12K notes
·
View notes
Text

#alice 1988#jan švankmajer#✄ girl#alice in wonderland#dollcore#morute#morute aesthetic#creepy cute#kinderwhore#creepy and cute#dollete#dolletecore#2014 tumblr#mochette#2014 aesthetic#nymph3t#nymphett#nicole dollanganger#girlblogger#girlblogging#girl interrupted#girl hysteria#girlhood#manic pixie dream girl#creepy aesthetic#movie stills#czech film#film stills#czech movies#morbid cute
3K notes
·
View notes
Text


Alice in Wonderland (1951) - dir. Clyde Geronimi, Wilfred Jackson, and Hamilton Luske; flowers animated by John Lounsbery
#disneyedit#filmedit#gifs#animationedit#traditional animation#animationsource#alice in wonderland#alice in wonderland (1951)#old disney#**mygifs#disney
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
never forget the stack of tires shaped like the alice in wonderland caterpillar that exists at a truck stop in Nebraska

#not my pic bc the one i took had bad lighting#americana#roadtrip usa#recycled art#alice in wonderland#public art#folk art
4K notes
·
View notes
