#agnikul cosmos
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
#general knowledge in tamil#gk on board#gkonboard#general knowledge#pothu arivu#kalanjiyam#behind earth#unsigned#tamil pokkisham#madan gowri#mr gk#seythikkural#building rockets#space travel#Agnikul Cosmos#Srinath Ravichandran#Moin SPM#aerospace#small rockets#launch vehicles#satellite launches#IIT Madras#3D printing#rocket engines#mobile pads#ISRO#3D printing process#two-stage rocket#cryogenic liquid propulsion engines#space exploration
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Agnikul Cosmos: Revolutionizing Space Access
What do you think of Agnikul Cosmos' revolutionary approach to space exploration? Share your thoughts and questions below! 👇
Agnikul Cosmos: The Spark that Lit the Indian Space Race Howdy, fellow space cadets! Get ready to blast off into the future of space exploration with Agnikul Cosmos, the Indian startup that’s rewriting the rules of the cosmic game. Forget clunky, old-school rockets, the kind your grandparents might have seen on grainy TV broadcasts. Agnikul Cosmos is all about innovation, conjuring rockets…

View On WordPress
#3d printed rockets#aerospace#agnibaan#agnikul cosmos#agnilet#India#indian space startups#Innovation#new space#on-demand launches#rocket launch#space exploration#space industry#Space Technology#startups#technology
0 notes
Text
Chennai: Agnikul Cosmos, a Chennai-based space startup, successfully conducted a sub-orbital test flight of its Agnibaan rocket on Thursday. This was the company’s first success after four previous attempts. Their launch took place from Sriharikota, where they have their private launch pad within ISRO’s Satish Dhawan Space Centre.
0 notes
Text
Space Technology Opportunity in India

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Introduction:
Entrepreneurship in space technology in India has been gaining momentum in recent years. The Indian government has been actively promoting the development of the space sector, and private companies are playing an increasingly important role.
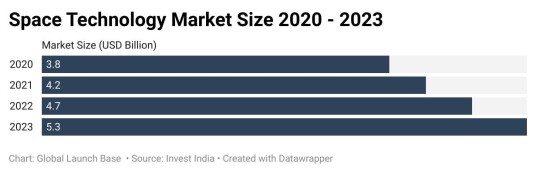
As the nation liberalizes its space sector, a diverse array of players are contributing to the burgeoning space ecosystem. Entrepreneurs are venturing into satellite manufacturing, pushing the boundaries of launch services, delving into space exploration, and exploring innovative solutions for satellite-based communication. The landscape is further enriched by collaborative efforts between private entities, government agencies, and academic institutions, fostering a dynamic environment for research and development.
In this context, it's crucial to explore the challenges and opportunities that define the entrepreneurial spirit in India's space technology sector. Regulatory hurdles, infrastructure development, and the need for sustained investments are among the challenges that entrepreneurs face. However, with increasing investor interest, a robust policy framework, and a commitment to fostering innovation, India's entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are poised to shape the nation's narrative in the cosmic domain. This dynamic interplay of public and private entities is not only propelling India's space capabilities but is also contributing to the global discourse on the commercialization and exploration of space.
Here are some key aspects of entrepreneurship in space technology in India:
Government Initiatives:New Space Policy: The Indian government has introduced policies to encourage private sector participation in space activities. The New Space India Limited (NSIL) was established to promote, commercially exploit, and transfer technologies developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).Liberalization: The government has liberalized the space sector, allowing private companies to undertake a wide range of space-related activities, including satellite launches, space exploration, and satellite communication services. (ISRO) Initiatives: Antrix Corporation: Antrix is the commercial arm of ISRO, and it collaborates with private players for the commercialization of space-related products and services.: SEED is a program initiated by ISRO to promote startups in the space sector by providing them with opportunities for collaboration and technology transfer.: NSIL is a central public sector enterprise (CPSE) under the Department of Space. It plays a crucial role in commercializing space products, technical consultancy services, and transfer of technologies.: ISRO has been actively engaging with startups, providing them access to its facilities, expertise, and technology.: The Department of Space in India oversees the country's space program. It may introduce schemes and programs to support space technology startups and entrepreneurs. (AIM): AIM, a flagship initiative of the NITI Aayog, supports innovation and entrepreneurship in various sectors. It may have programs and funding opportunities that space technology startups can explore. (NIF): NIF supports grassroots innovations and may provide support to startups working on innovative space technologies.
Private Space Companies:Startups: Several startups in India are focusing on various aspects of space technology. Some are involved in satellite manufacturing, launch services, data analytics from space, and more.Launch Services: Companies like Agnikul Cosmos, Skyroot Aerospace, and Pixxel are working on developing small satellite launch vehicles to provide cost-effective and flexible launch options.
Space Exploration and Research: Interplanetary Missions: ISRO has been actively involved in space exploration, and private companies are expressing interest in participating in future interplanetary missions.Research and Development: Private entities are engaging in research and development activities, contributing to advancements in satellite technology, propulsion systems, and other space-related technologies.
Satellite Manufacturing:Private Satellite Manufacturers: Companies like Exseed Space and Bellatrix Aerospace are involved in the manufacturing of satellites, catering to various purposes such as communication, Earth observation, and scientific research.
Communication Services:Telecommunication Satellites: Private companies are exploring opportunities to provide satellite-based communication services. This includes both broadband internet services and other communication solutions.
Funding and Investments:Investor Interest: The space technology sector in India has attracted attention from investors. Funding rounds for space startups have been on the rise, indicating confidence in the potential growth of the industry.
Collaborations and Partnerships:
Industry-Academia Collaboration: Partnerships between private companies, government organizations, and academic institutions are fostering innovation and research in the space sector.
The Indian space technology ecosystem is evolving, and with continued government support, entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of the Indian space industry.
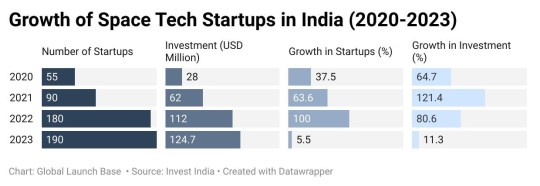
The number of space tech startups in India has witnessed explosive growth, increasing by almost five times in just five years. Investments in the sector have also seen a sharp rise, from $17 million in 2019 to an estimated $124.7 million in 2023.
Commercialization of Space Activities: With India's proven track record in satellite launches and space technology, there is a substantial potential for the commercialization of space activities. The burgeoning demand for satellite-based services, including communication, arth observation, and navigation, opens up opportunities for private entities to actively participate in the space industry. As the cost of space access continues to decrease, private companies can explore ventures such as satellite manufacturing, space tourism, and satellite-based applications, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
International Collaborations: Collaborations with other space-faring nations present a promising avenue for India to augment its space capabilities. Joint ventures, knowledge exchange, and technology transfer can accelerate innovation and enhance the efficiency of space missions. ISRO has already established itself as a reliable partner for international launches, and expanding collaborative efforts can lead to shared resources, reduced costs, and a more diversified approach to space exploration. As India continues to engage in global partnerships, it can leverage collective expertise for ambitious endeavors beyond Earth's orbit.
Innovation in Space Technology: Investments in research and development (R&D) can catapult India into the forefront of space innovation. Emphasis on cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, advanced materials, and propulsion systems can revolutionize space missions. The development of reusable launch vehicles, like the ongoing efforts in creating a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), can significantly reduce launch costs, making space exploration more sustainable. Encouraging a culture of innovation, fostering collaboration between academia and industry, and providing incentives for R&D initiatives can fuel breakthroughs in space technology.
Space Applications for Sustainable Development: Leveraging space technology for sustainable development on Earth is an untapped frontier. Utilizing satellite data for precision agriculture, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and resource mapping can contribute to addressing pressing global challenges. By integrating space-based solutions into sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and urban planning, India can harness the power of space technology for inclusive and sustainable development, bringing tangible benefits to its citizens and contributing to global initiatives.
Expansion of Interplanetary Exploration: Building on the success of Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), India has the potential to expand its interplanetary exploration efforts. Initiatives for exploring other celestial bodies, such as Venus or asteroids, can contribute to humanity's understanding of the solar system and beyond. A strategic focus on ambitious interplanetary missions can position India as a key player in the broader scientific community and foster international collaboration in the exploration of the cosmos.
Trending Technologies in India's Space Industry:
Nanotechnology: The integration of nanotechnology in space technology has the potential to revolutionize spacecraft design, materials, and instrumentation. Nanosatellites, with their miniaturized components, are becoming increasingly popular for cost-effective and innovative space missions. India can leverage nanotechnology for lightweight yet robust spacecraft, enhancing mission efficiency and scientific capabilities.
Companies: Nano-Tech SpA, Kalva Nanotech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are playing a pivotal role in data analysis, image processing, and autonomous decision-making in space missions. India can explore AI applications for real-time data interpretation, automated navigation, and predictive maintenance of spacecraft. Incorporating machine learning algorithms into Earth observation data analysis can significantly enhance the understanding of environmental changes.
Companies: Aadyah Aerospace, Blue Sky Analytics
Quantum Computing: Quantum computing holds the promise of solving complex computational problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. In the space sector, quantum computing can be utilized for optimizing mission trajectories, simulating quantum systems, and enhancing the security of communication channels. India's focus on quantum computing research can contribute to advancements in space-related computations.
Companies: QpiAI, BosonQ
3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: The adoption of 3D printing in space technology can revolutionize the manufacturing process, enabling the production of complex and lightweight structures. India can benefit from 3D printing for rapid prototyping, cost-effective manufacturing of satellite components, and even on-demand production during long-duration space missions.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos, EOS India
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data management, making it applicable to space-based applications such as satellite communication, data storage, and secure information sharing. By incorporating blockchain, India can enhance the security and integrity of space-related data and transactions.
Companies: SpaceTime Labs, Aryaka Networks
Solar Sail Technology: Solar sails, propelled by the pressure of sunlight, offer a sustainable and efficient means of propulsion for spacecraft. This technology can be harnessed for deep-space exploration, enabling missions to travel vast distances with minimal fuel requirements. India's exploration programs can benefit from research and development in solar sail technology for extended-duration missions.
Companies: Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST), IIT Bombay - Aerospace Engineering Department
Hyperspectral Imaging: Hyperspectral imaging involves capturing a wide range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. This technology is instrumental in Earth observation, resource mapping, and environmental monitoring. India can explore the integration of hyperspectral imaging in its satellite payloads for enhanced remote sensing capabilities.
Companies: Pixxel, Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd
Internet of Things (IoT) for Space: The application of IoT in space technology involves connecting devices and sensors on satellites and spacecraft to gather and transmit data. This interconnected network can facilitate efficient communication, data collection, and collaborative decision-making during space missions. India can explore IoT applications for enhanced space situational awareness and mission coordination.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos
As India looks to the future, embracing these trending technologies will be crucial for maintaining its competitive edge in space exploration and satellite technology. By actively incorporating these innovations into its space programs, India can not only enhance mission success but also contribute to the global advancement of space technology. Collaborations with research institutions, startups, and the private sector will play a vital role in driving these technological advancements in India's space industry.
Challenges and the Way Forward:
Despite its successes, India's space program faces challenges such as increased competition, budget constraints, and the need for continuous innovation. To overcome these challenges, sustained government support, collaboration with private entities, and a focus on skill development in the space sector are crucial.
Increased Global Competition: The space industry is becoming increasingly competitive with the emergence of new players and the commercialization of space activities. To stay ahead, India must continuously innovate, streamline its processes, and invest in cutting-edge technologies. Developing a robust ecosystem for space startups and fostering public-private partnerships can enhance India's competitiveness in the global space market.
Budget Constraints: Despite commendable achievements, budget constraints pose a challenge for sustaining and expanding India's space endeavors. A consistent and increased allocation of funds to ISRO, along with exploring innovative funding mechanisms, will be crucial. Engaging with the private sector for joint ventures and commercial space activities can help alleviate financial constraints and promote economic sustainability in the long run.
Human Resource Development: The growth of India's space program necessitates a skilled workforce capable of handling complex missions. Investing in education and training programs in collaboration with academic institutions can ensure a steady supply of skilled professionals in fields such as aerospace engineering, astrophysics, and data sciences. This will not only address the current workforce requirements but also fuel future innovations in space technology.
Technological Advancements: Rapid technological advancements globally require India to stay at the forefront of innovation. Embracing emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and advanced propulsion systems will be essential. Establishing research and development centers dedicated to space technology innovation can facilitate the integration of these advancements into future missions.
Space Debris Management: The increasing number of satellites and space missions contribute to the growing issue of space debris. India needs to actively participate in international efforts to address space debris management, adopting sustainable practices in satellite design and end-of-life disposal. Research into debris removal technologies and international collaboration on space traffic management will be pivotal in ensuring the long-term sustainability of space activities.
Climate Change Monitoring: With the rising global concerns about climate change, space technology plays a crucial role in monitoring environmental indicators. India can take a leadership role in developing satellite-based solutions for climate monitoring, disaster response, and sustainable resource management. This requires a dedicated focus on Earth observation satellites, advanced sensors, and data analytics.
Enhanced Space Diplomacy: Strengthening space diplomacy is essential for India to expand its global influence in the space arena. Engaging in collaborative space missions, sharing scientific knowledge, and participating in international forums will enhance India's standing as a responsible space-faring nation. Forming strategic partnerships with countries interested in space exploration can open up new avenues for cooperation and joint missions.
Conclusion:
India's journey in space technology has been nothing short of remarkable, with ISRO consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation. As the nation continues to invest in space exploration, the opportunities for growth, collaboration, and technological advancements are boundless. The future holds exciting possibilities for India's space technology sector, positioning the country as a key player in the global space community.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#ISRO - Indian Space Research Organization#NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)#SEED(Social Entrepreneurship Empowerment Development)#Atal Innovation Mission Official#National Innovation Foundation - India#Nano-Tech SpA#Kalva Nanotech#AADYAH Aerospace Private Limited#Blue Sky Analytics#QpiAI#BosonQ Psi (BQP)#AgniKul Cosmos#EOS#Spacetime Labs#Aryaka#Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology#Aerospace Engineering Association IIT Bombay#Pixxel#Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd.#AgniKul Cosmos hashtag#SpaceTechnologyInIndia hashtag#IndianSpaceProgram hashtag#ISROOpportunities hashtag#SpaceIndustryGrowthIndia hashtag#SpaceResearchOrganizationsIndia hashtag#SatelliteTechnologyOpportunities hashtag#IndianSpaceExploration hashtag#ISROAchievements hashtag#SpaceScienceCareersIndia hashtag#SpaceTechnologyTrends hashtag
0 notes
Link
Embark on a celestial journey with today's episode of Astronomy Daily - The Podcast, where your host, Anna, guides you through the latest cosmic updates. We'll start with South Korea's ambitious plans to land on Mars by 2045 and the launch of their first space agency, CASA. Then we'll delve into India's latest achievement in space technology as Agnikul Cosmos successfully launches the country's second privately built rocket. But that's not all. We'll also bring you some significant updates from the Japanese space agency JAXA concerning their Akatsuki Venus probe, as well as a groundbreaking mission by China's Chang'e-6 to the far side of the moon. And to cap it all off, we'll explore a recent discovery by the James Webb Space Telescope that has identified the most distant known galaxy, along with news about Boeing's Starliner capsule gearing up for its first-ever astronaut mission. 00:00) Astronomy Daily brings you the latest news in astronomy and space exploration 01:04) South Korea has announced ambitious plans to land on Mars by 2045 04:27) JAXA has lost contact with its Akatsuki spacecraft studying Venus climate 07:08) Scientists using the James Webb Space Telescope have identified the most distant known galaxy For an astronomical experience, visit our website at astronomydaily.io for the latest news, sign up for our free newsletter, and check out exclusive sponsor deals. Connect with us on X (@AstroDailyPod) for engaging discussions with fellow space aficionados. This is Anna, reminding you to keep your gaze fixed on the heavens. Until our next stellar episode, let the cosmos ignite your curiosity and wonder. Clear skies and cosmic discoveries to all! Support: https://www.bitesz.com/show/astronomy-daily-the-podcast/support/ www.bitesz.com Sponsors www.bitesz.com/nordpass https://www.bitesz.com/show/astronomy-daily-the-podcast/sponsors/
#administration#aerospace#agency#agnikul#akatsuki#climate#cosmos#indian#jaxa#kasa#korea#mars#mission#probe#rocket#south#space#study#technology#venus
0 notes
Text
Top investors in space in India
Why Venture Capitalists Are Betting Big on India’s Space Sector

A Thriving Ecosystem of Space Startups: India’s space ecosystem is no longer limited to government-run entities like the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Today, a surge of innovative space startups are taking the stage, offering cutting-edge solutions in satellite technology, launch services, space data analytics, and more. Companies like Skyroot Aerospace, Agnikul Cosmos, and Pixxel lead the charge, each carving out a unique niche. These startups are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, driving investor interest with the potential for high returns in a relatively untapped market.
Strong Government Support and Policy Reforms: One of the key reasons behind the surge in space venture capital in India is the proactive stance taken by the Indian government. Recent policy reforms have opened the doors for private players to participate in space activities, previously dominated by ISRO. Establishing IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center) is a significant step, providing a regulatory framework that encourages private sector involvement. Such government support has given investors in space in India the confidence to back ambitious projects, knowing there’s a clear path for private ventures.
Cost-Effective Innovation as a Competitive Edge: India’s reputation for cost-effective innovation is another major attraction for investors. Launching satellites at a fraction of the cost compared to global competitors has positioned India as a hub for affordable space technology. This competitive edge not only allows Indian space startups to thrive domestically but also makes them attractive on the international stage. Investors are keen to support companies that can deliver world-class technology with lower capital outlays, reducing investment risks while promising impressive returns.
Global Interest in Indian Talent and Expertise: India’s space sector is not just about affordability; it’s about world-class talent. The country boasts a deep pool of highly skilled engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs with expertise in aerospace and technology. This talent pool has been instrumental in driving innovation and attracting global attention. International investors are increasingly looking to partner with Indian space startups, recognizing the country’s unique blend of technical prowess and entrepreneurial spirit.
A Growing Market for Space-Based Services: The market for space-based services, including satellite communications, Earth observation, and data analytics, is expanding rapidly. In India, this growth is driven by rising demand from industries such as agriculture, telecommunications, logistics, and defense. With space technology playing a crucial role in optimizing these sectors, investors see an opportunity to capitalize on the potential for domestic and international applications. Space-based services represent a lucrative market, attracting space venture capital in India to back startups that can cater to these needs.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations: Indian space startups are not working in isolation; they are forming strategic partnerships with global companies and space agencies. Collaborations with NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and private companies have opened up new opportunities for technology sharing, funding, and market access. These partnerships have also strengthened investor confidence, as they reduce risks and validate the technology being developed by Indian companies. For investors in space in India, such collaborations signal a promising future, driving more venture capital into the sector.
A New Era of Commercial Space Exploration: The idea of commercial space exploration, once confined to science fiction, is now becoming a reality. From reusable rockets to satellite constellations, Indian space startups are exploring new frontiers that were once considered out of reach. This new era of commercial space exploration has piqued the interest of venture capitalists who see the potential for profitable exits through IPOs, acquisitions, and global partnerships. With private space missions no longer just a dream, space venture capital in India is ready to fuel the next big leap.
Encouraging Signs from Successful Fundraising Rounds: The confidence in India’s space sector is evident from the successful fundraising rounds by leading space startups. Companies like Skyroot Aerospace and Agnikul Cosmos have secured millions in funding from top-tier venture capital firms. These funding rounds not only provide the necessary resources for scaling but also act as a signal to other investors that the Indian space market is mature and ready for high-stakes investment. The momentum created by these early successes is a clear indicator of why investors in space in India are increasingly willing to place their bets.
Conclusion: A Promising Orbit for Investment India’s space sector is on an exciting trajectory. With a favorable policy environment, a surge of innovative startups, and a proven track record of cost-effective solutions, it’s no wonder that space venture capital in India is booming. As the country continues to explore new frontiers and expand its role in global space exploration, venture capitalists are set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future. For those looking to invest in the final frontier, India’s space industry presents a unique opportunity to be part of a revolution that’s only just beginning.
#305, 3rd Floor, 5 Vittal Mallya Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560001, India
5 Ring Road, Lajpat Nagar 4, 3rd Floor, New Delhi-110024
#Keywords#best venture capital firm in india#venture capital firms in india#popular venture capital firms#venture capital firm#seed investors in bangalore#deep tech investors india#startup seed funding india#funding for startups in india#early stage venture capital firms#invest in startups bangalore#funders in bangalore#startup investment fund#fintech funding#india alternatives investment advisors#best venture capital firms in india#business investors in kerala#venture capital company#semiconductor startups#semiconductor venture capital#investors in semiconductors#startup seed funding in India#deep tech venture capital#deeptech startups in india#semiconductor companies in india#saas angel investors#saas venture capital firms#saas venture capital#b2b venture capital#space venture capital in india
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Indian space startup Agnikul achieves a historic milestone with the world's inaugural launch of a 3D-printed rocket engine
Indian space startup Agnikul achieves a historic milestone with the world’s inaugural launch of a 3D-printed rocket engine In a landmark achievement for the Indian space industry, Agnikul Cosmos, a Chennai-based space startup, has successfully launched the world’s first 3D-printed rocket engine. This significant milestone not only propels Agnikul into the global spotlight but also underscores…
0 notes
Text
Indian space startup Agnikul Cosmos successfully launched the nation's first 3D-printed rocket engine on Thursday (May 30), paving the way for reduced time and costs associated with building rockets and boosting the country's spacefaring capabilities. "It signals the ability to rapidly assemble rockets that is unparalleled," Satyanarayanan Chakravarthy of Agnikul Cosmos, who is also a professor of aerospace engineering at the Indian Institute of Technology in Madras, said in a statement. The maiden flight was also the country's second private rocket launch and the first to demonstrate the use of a semi-cryogenic engine. Unlike cryogenic engines that require heavy tanks to hold pressurized liquid hydrogen and oxygen at very low temperatures, semi-cryogenic engines replace the liquid hydrogen with refined kerosene. As a result, such engines require lesser storage space and normal temperatures, allowing for increased payload capacity as well as higher thrust. ... Recently, India's national space agency, the Indian Space Research Organization, or ISRO, also tested a 3D-printed rocket engine whose manufacturing reduced the number of engine parts from 14 to one, allowing the organization to save not only on raw material used per engine but also the overall production time by 60 percent.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Agnikul's single-stage tech demo rocket launch put on hold | India News
BENGALURU: Agnikul Cosmos, a spacetech startup, which hoped to make history with the inaugural test launch of its single-stage technology demonstrator rocket — a precursor for its Agnibaan launch vehicle — powered by a semi-cryogenic engine Agnilet, put the launch on “hold” just minutes before lift off on Tuesday.The company as of 6.12am was yet to officially call off the launch, but live…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Agnikul Cosmos gets $26.7 million for expanded capacity and twice-monthly commercial launches
Agnikul Cosmos gets $26.7 million for expanded capacity and twice-monthly commercial launches @neosciencehub @agnikul #neosciencehub #science #sciencechannel #NSH #space #news #sciencenews #sriharikota #ISRO #rocketscience #startups #incubation #agnikul
On October 17, Agnikul Cosmos, a space tech firm located in Chennai, said that it has secured $26.7 million in a Series B round, underscoring the increasing significance of India’s space tech sector during the so-called fundraising winter. The firm that was incubated at IIT Madras and produces launch vehicles has raised capital from a number of investors, including Celesta Capital,…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Spacetech Startup Agnikul Cosmos Raises Rs 200 Crore Ahead Of First Rocket Launch.

🚀 Chennai-based startup Agnikul Cosmos ignites the skies with a massive Rs 200 crore funding boost ahead of their first rocket launch! 🌌 Stay tuned for India's upcoming milestone in space exploration. 🛰️ Stay ahead of the curve with @talentpie 🚀 Don't miss out on the latest and trending updates. 🔥📢" #SpaceTech #StartupSuccess #RocketLaunch #IndianStartupNews #FundingBoost" #AgnikulCosmos #SpaceExploration #talentpie #startup #isro #newrocketlaunch
0 notes
Text
IIT Grads Reimagine How Satellites Travel to Space With 3D-Printed Rockets
Chennai-based Agnikul Cosmos builds low-cost rockets using 3D technology for commercial space missions. The startup makes rockets that are 6–7 times cheaper than conventionally constructed ones, and that too in much less time. What if you could get access to space? Making this possible is Chennai-based Agnikul Cosmos which builds low-cost rockets using 3D technology for commercial space…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
IIT Grads Reimagine How Satellites Journey to Area With 3D-Printed Rockets
Chennai-based Agnikul Cosmos builds low-cost rockets utilizing 3D expertise for business house missions. The startup makes rockets which can be 6–7 instances cheaper than conventionally constructed ones, and that too in a lot much less time. What in case you might get entry to house? Making this doable is Chennai-based Agnikul Cosmos which builds low-cost rockets utilizing 3D expertise for…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Agnikul Cosmos Testfires India’s First 3D Printed Rocket Engine
The Indian space programme has achieved great heights with the help of the State-owned Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). From the launch and deployment of distributed small satellite systems to carrying the scientific and exploratory missions to outer space, the list of ISRO’s contributions to the Indian space sector is huge. Today, it is actively encouraging the involvement of private industries in the space sector to boost the space economy within the country.
A Chennai rocket start-up – Agnikul Cosmos – that previously signed a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) with the Department of Space (DoS) to get access to ISRO’s facilities to build its rocket, very recently became successful in testing a fully 3D-printed rocket engine. With this testing, the Chennai space start-up has become the world’s first company to have achieved this success.
Agnikul Cosmos fired its higher stage, semi-cryogenic rocket engine, called Agnilet. While describing the rocket engine, Srinath Ravichandran, CEO, Agnikul Cosmos, said, “Agnilet is just one piece of hardware from start to finish and has zero assembled parts.” Its three-in-one solution allows it to put all the three modules, i.e. injectors, cooling channels, and igniter in a single hardware piece.
Moreover, the turnaround time for the entire setup is less than four days. The rocket engine is capable of carrying up to 100 kilos to low earth orbit – around 700 kilometres above the earth’s surface. This is just a fraction of what the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is capable of.
Like Agnikul Cosmos, several other Indian start-ups are progressing in the space sector. Hyderabad-based Skyroot Aerospace, founded by former ISRO scientists, Pawan Kumar Chandana and Naga Bharath Daka, is another on the list.
Skyroot Aerospace revealed its fully 3D printer cryogenic rocket engine, dubbed Dhawan-I, which will be used to power the Vikram-II rocket that Skyroot is building from scratch, in September last year. Similar to Agnikul Cosmos, the Hyderabad-based start-up also signed an NDA with the DoS on February 2. The aim was to be able to use ISRO’s test and launch facilities to test their Vikram-I rocket, and eventually Dhawan-I as well.
The current value of the global space industry is $350 billion and there is a high possibility that this value could triple in view of the ongoing advancements. As per Morgan Stanley, the global space industry, with the help of new space engine technology, like 3D printed rocket engines, could generate $1.1 trillion or more by 2040.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

3D Printed Rockets in the Works EOS and India’s Agnikul Cosmos India’s space tech industry is preparing to scale spacecraft production as it races to launch small satellites into orbit next year. Like many leading companies and startups in the global... The... View the entire article via our website. https://buff.ly/3tL6juM
1 note
·
View note
Text
Space tourism | New Adventure for Super Wealthy Travelers

Space Tourism is human space travel for recreational purposes. There are several different types of space tourism, including orbital, suborbital and lunar space tourism. Orbital space tourism has been performed only by Roscosmos.
Space Tourism is human travel to space just see earth with 0 gravity. Mow very easy and some private company enter in this field recently successfully launch Space taxi by Virgin Galactic in orbit with his staff shortly they can start for commercial sale tickets per seat base this race two other players also have Blue origin & Space X there also getting approval from Government shortly launch there space taxi trail shortly announce for prices and taking booking coming year that very easy for person who’s interested travel to space also compition price also low & discounted for people. Space is the next frontier where billionaires turned space barons will vie for a pie of the paying customer's wallet. Many billionaires are competing to usher in a new era of private commercial space travel for the rich.
WHAT IS THIS FAD FOR SPACE TOURISM?
Space travel first space tourist American millionaire Dennis Tito in 2001 paid $20 million to ride on a Russian Soyuz spacecraft to visit the International Space station and spent eight days there.
just now other private citizens travelled to space until 2009. less than 600 astronauts and global citizens have gone into space so far
HOW MUCH SPEND TO BOOK A SEAT?
Virgin Galactic claims over 600 advance bookings prices at approximately $250000 per seat but only 150 may travel on board VSS Unity in 2022 and eventually reduce tickets price around $40000 according to Reuters.
Blue Origin charge passengers around $200000 not official but reports indicate that this could go up post new recent campaign .
SpeceX hasn't disclosed any specifics but 10 days flight to the International space station would entail $350000 per person with NASA getting $35000 per person .
FIRST INDIAN SPACE TOURIST?
In India first space tourist aboard Virgin Galactic from Kerala traveller Santosh George Kulangara to explore space is also nearing fulfilment, he is first Indian space tourist selected by Virgin Galactic said that with the company getting all mandatory permissions to fly to space and the first carrier taking of the preparations for tourist were also expected to begin soon.
He was selected for the flight after rigorous training including zero gravity training at Kennedy spaces centre and more is expected to begin soon. he also did a travelogue of his initial training sessions.
ONGOING PROJECTS
The Boeing Starliner capsule
Bigelow Aerospace
SpaceX Axiom Space-1 (AX-1)
Space Adventures Crew Dragon mission
Aurora Space Station make a hotel in space for commercial person stay there and see the Galaxy in floating hotel explored universe.
CONTOURS OF VISIT AND PREPARATION FOR TRAVELLERS
Space traveller need physically and mentally fit, Start preparing at least a year before and do your stretches and eat nutritious meals. Space travellers can also try scuba-diving (at least 12 metres underwater) for weightlessness training. Space travellers will get packaged modified food but allergen-free formats are not available. Fresh fruits and vegetables have to be eaten.
INDIA START-UP FOR SPACE INDUSTRY
1. Pixxel
It’s Indian space technology start up launching the world highest resolution hyperspectral satellite constellation.
2. Skyroot Aerospace
Skyroot first privately owned Indian firm to demonstrate the cabability to build a homegrown rocket engine. It develops small satellite launch vehicles. This company first launch vehicle vikram-I expected to launched by December 2021.
3. Bellatrix Aerospace
It works on advanced in space propulsion systems and rocket propulsion technologies and it is currently developing a space taxi an orbital transfer vehicle to be launched in 2024 this company will also launching rocket Chetak by 2023.
4. Agnikul Cosmos
This company had fired world first fully 3 d rocket engine the semi cryogenic rocket engine Agnilet, it aims to develop and launch its small lift launch vehicle namely Agnibaan by 2022
5. Dhruva Space
It works small satellites for the government, commercial and academic markets.
OUR FUTURE PLAN
We also think about working in space tourism and collaborate with space company. Now a common person can travel to space & see beyond the earth. how’s the expertises these we need sponsor for this, if any sponsor help me, we can do in our mind. Another thing also we can make a before space travel available training for passenger in India also do our Indian space agency ISRO or Private agency can help for space travel than cost also very low. Common person easily travel to space.
More contact us :- [email protected] & [email protected]
#Space Tourism#travel to space#space travel#space tourism in india#Indian space tourism#space travel training#Space taxi#space travel booking#space travel cost#book seat for space travel#space travel price#spacecraft#International space station#space barons#commercial space travel#Private space travel
1 note
·
View note