#after sales service software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
After Sales Service App: Elevate Customer Experience with Efficient Problem Resolution
#after sales service app#best after sales service app#after sales service management app#after sales service software
0 notes
Text

Don't let after-sales support become an afterthought! Customers expect a seamless experience, from purchase to ongoing support. Elevate your after-sales operations with ServitiumCRM, a comprehensive solution that streamlines warranty claims, service requests, and more. Manage all aspects of after-sales support in one place, from warranty claims to service requests. We can help you automate workflows with features like call center management and mobile apps for faster issue resolution. Please reach out to our team and get your after-sales operations simplified. Read More...
#after sales support#support services#customer management platform#customer management software#servitiumcrm
0 notes
Text

Our after-sales software connects technicians to mobile apps, providing access to service requests, customer information, and diagnostic tools. This boosts productivity and improves communication between HVAC technicians and clients. The software automates updates on service appointments, maintenance reminders, and billing, and also assigns technician tasks based on location, skills, and availability. Additionally, HVAC professionals confidently use IoT sensors for machinery maintenance to enhance customer service and increase repeat purchases and referrals.
0 notes
Text
Best Online After Sales Service Management App - Service CRM
After Sales Service Management Software, also known as Service CRM, is a crucial tool for businesses in today's competitive market. It allows companies to efficiently manage their post-sales services and ensure customer satisfaction. With Service CRM, businesses can streamline their service processes, track customer requests, and monitor service performance. Additionally, After Sales Service Management App provides valuable insights and analytics that help companies identify areas for improvement and enhance their overall service delivery.

#After-sales service software#After Sales Service Management Software#After Sales Service Management App
0 notes
Text
Best After Sales Service App In India - Service CRM
In today's fast-paced business world, providing excellent customer service is more important than ever before. Companies must focus on providing high-quality products while also ensuring that their customers are satisfied with their overall experience. One of the key aspects of customer service is after-sales support, and that's where After Sales Service App Service CRM comes in. This innovative app is revolutionizing the way businesses in India manage their customer support, providing a seamless and efficient service that delights customers and inspires loyalty.

#Best After Sales Service Management Software#After sales customer service management system#After Sales Support Management Software#service call management software#After Sales Service Management App#After Sales Service Management Software
1 note
·
View note
Text
Best Complaint management Software | ServiceCRM
Best Online Complaint Management Software works as a support system for agents. As this software streamlines view data for maximum efficiency. With the support of this software, reports, complaints, and data of employees and customers are easily recorded.

#Field Service Management Software#Complaint Management Software#After Sales Service Management Software#AMC Maintenance Software
0 notes
Text
An open copyright casebook, featuring AI, Warhol and more

I'm coming to DEFCON! On Aug 9, I'm emceeing the EFF POKER TOURNAMENT (noon at the Horseshoe Poker Room), and appearing on the BRICKED AND ABANDONED panel (5PM, LVCC - L1 - HW1–11–01). On Aug 10, I'm giving a keynote called "DISENSHITTIFY OR DIE! How hackers can seize the means of computation and build a new, good internet that is hardened against our asshole bosses' insatiable horniness for enshittification" (noon, LVCC - L1 - HW1–11–01).

Few debates invite more uninformed commentary than "IP" – a loosely defined grab bag that regulates an ever-expaning sphere of our daily activities, despite the fact that almost no one, including senior executives in the entertainment industry, understands how it works.
Take reading a book. If the book arrives between two covers in the form of ink sprayed on compressed vegetable pulp, you don't need to understand the first thing about copyright to read it. But if that book arrives as a stream of bits in an app, those bits are just the thinnest scrim of scum atop a terminally polluted ocean of legalese.
At the bottom layer: the license "agreement" for your device itself – thousands of words of nonsense that bind you not to replace its software with another vendor's code, to use the company's own service depots, etc etc. This garbage novella of legalese implicates trademark law, copyright, patent, and "paracopyrights" like the anticircumvention rule defined by Section 1201 of the DMCA:
https://www.eff.org/press/releases/eff-lawsuit-takes-dmca-section-1201-research-and-technology-restrictions-violate
Then there's the store that sold you the ebook: it has its own soporific, cod-legalese nonsense that you must parse; this can be longer than the book itself, and it has been exquisitely designed by the world's best-paid, best-trained lawyer to liquefy the brains of anyone who attempts to read it. Nothing will save you once your brains start leaking out of the corners of your eyes, your nostrils and your ears – not even converting the text to a brilliant graphic novel:
https://memex.craphound.com/2017/03/03/terms-and-conditions-the-bloviating-cruft-of-the-itunes-eula-combined-with-extraordinary-comic-book-mashups/
Even having Bob Dylan sing these terms will not help you grasp them:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/10/25/musical-chairs/#subterranean-termsick-blues
The copyright nonsense that accompanies an ebook transcends mere Newtonian physics – it exists in a state of quantum superposition. For you, the buyer, the copyright nonsense appears as a license, which allows the seller to add terms and conditions that would be invalidated if the transaction were a conventional sale. But for the author who wrote that book, the copyright nonsense insists that what has taken place is a sale (which pays a 25% royalty) and not a license (a 50% revenue-share). Truly, only a being capable of surviving after being smeared across the multiverse can hope to embody these two states of being simultaneously:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/06/21/early-adopters/#heads-i-win
But the challenge isn't over yet. Once you have grasped the permissions and restrictions placed upon you by your device and the app that sold you the ebook, you still must brave the publisher's license terms for the ebook – the final boss that you must overcome with your last hit point and after you've burned all your magical items.
This is by no means unique to reading a book. This bites us on the job, too, at every level. The McDonald's employee who uses a third-party tool to diagnose the problems with the McFlurry machine is using a gadget whose mere existence constitutes a jailable felony:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/04/20/euthanize-rentier-enablers/#cold-war
Meanwhile, every single biotech researcher is secretly violating the patents that cover the entire suite of basic biotech procedures and techniques. Biotechnicians have a folk-belief in "patent fair use," a thing that doesn't exist, because they can't imagine that patent law would be so obnoxious as to make basic science into a legal minefield.
IP is a perfect storm: it touches everything we do, and no one understands it.
Or rather, almost no one understands it. A small coterie of lawyers have a perfectly fine grasp of IP law, but most of those lawyers are (very well!) paid to figure out how to use IP law to screw you over. But not every skilled IP lawyer is the enemy: a handful of brave freedom fighters, mostly working for nonprofits and universities, constitute a resistance against the creep of IP into every corner of our lives.
Two of my favorite IP freedom fighters are Jennifer Jenkins and James Boyle, who run the Duke Center for the Public Domain. They are a dynamic duo, world leading demystifiers of copyright and other esoterica. They are the creators of a pair of stunningly good, belly-achingly funny, and extremely informative graphic novels on the subject, starting with the 2008 Bound By Law, about fair use and film-making:
https://www.dukeupress.edu/Bound-by-Law/
And then the followup, THEFT! A History of Music:
https://web.law.duke.edu/musiccomic/
Both of which are open access – that is to say, free to download and share (you can also get handsome bound print editions made of real ink sprayed on real vegetable pulp!).
Beyond these books, Jenkins and Boyle publish the annual public domain roundups, cataloging the materials entering the public domain each January 1 (during the long interregnum when nothing entered the public domain, thanks to the Sonny Bono Copyright Extension Act, they published annual roundups of all the material that should be entering the public domain):
https://pluralistic.net/2023/12/20/em-oh-you-ess-ee/#sexytimes
This year saw Mickey Mouse entering the public domain, and Jenkins used that happy occasion as a springboard for a masterclass in copyright and trademark:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/12/15/mouse-liberation-front/#free-mickey
But for all that Jenkins and Boyle are law explainers, they are also law professors and as such, they are deeply engaged with minting of new lawyers. This is a hard job: it takes a lot of work to become a lawyer.
It also takes a lot of money to become a lawyer. Not only do law-schools charge nosebleed tuition, but the standard texts set by law-schools are eye-wateringly expensive. Boyle and Jenkins have no say over tuitions, but they have made a serious dent in the cost of those textbooks. A decade ago, the pair launched the first open IP law casebook: a free, superior alternative to the $160 standard text used to train every IP lawyer:
https://web.archive.org/web/20140923104648/https://web.law.duke.edu/cspd/openip/
But IP law is a moving target: it is devouring the world. Accordingly, the pair have produced new editions every couple of years, guaranteeing that their free IP law casebook isn't just the best text on the subject, it's also the most up-to-date. This week, they published the sixth edition:
https://web.law.duke.edu/cspd/openip/
The sixth edition of Intellectual Property: Law & the Information Society – Cases & Materials; An Open Casebook adds sections on the current legal controversies about AI, and analyzes blockbuster (and batshit) recent Supreme Court rulings like Vidal v Elster, Warhol v Goldsmith, and Jack Daniels v VIP Products. I'm also delighted that they chose to incorporate some of my essays on enshittification (did you know that my Pluralistic.net newsletter is licensed CC Attribution, meaning that you can reprint and even sell it without asking me?).
(On the subject of Creative Commons: Boyle helped found Creative Commons!)
Ten years ago, the Boyle/Jenkins open casebook kicked off a revolution in legal education, inspiring many legals scholars to create their own open legal resources. Today, many of the best legal texts are free (as in speech) and free (as in beer). Whether you want to learn about trademark, copyright, patents, information law or more, there's an open casebook for you:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/08/14/angels-and-demons/#owning-culture
The open access textbook movement is a stark contrast with the world of traditional textbooks, where a cartel of academic publishers are subjecting students to the scammiest gambits imaginable, like "inclusive access," which has raised the price of textbooks by 1,000%:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/10/07/markets-in-everything/#textbook-abuses
Meanwhile, Jenkins and Boyle keep working on this essential reference. The next time you're tempted to make a definitive statement about what IP permits – or prohibits – do yourself (and the world) a favor, and look it up. It won't cost you a cent, and I promise you you'll learn something.

Support me this summer on the Clarion Write-A-Thon and help raise money for the Clarion Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers' Workshop!

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/07/30/open-and-shut-casebook/#stop-confusing-the-issue-with-relevant-facts

Image: Cryteria (modified) Jenkins and Boyle https://web.law.duke.edu/musiccomic/
CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
#pluralistic#jennifer jenkins#james boyle#ip#law#law school#publishing#open access#scholarship#casebooks#copyright#copyfight#gen ai#ai#warhol
179 notes
·
View notes
Text
Webhuma - Platin
In today’s world, platforms that provide access to high-quality digital assets for professional web designers, graphic designers, and content creators are of great importance. Envato Elements stands out as a leading name in this field. Webhuma.com is a unique platform that offers users unlimited download services with Envato Elements license sales.
With the 7, 30, 90, 180, and 365-day plans offered by grafikstok.com, users can choose a suitable duration according to their needs and enjoy the unlimited download service. These plans work by copying the URL of the content you want from Envato Elements Downloader and Adobe Stock Cheap Account pasting it into the relevant field on webhuma.com. In this way, users can easily download the content they want from the extensive library on Envato Elements.
Webhuma.com’s Envato Elements service operates fully automatically. Thanks to this, users can automatically receive their license key immediately after completing the purchase process. Customers can activate the service by using this license key on grafikstok.com and benefit from unlimited download options.
Webhuma.com, millions of high-quality digital assets are brought together for professional and amateur designers, photographers, video producers, and writers. You are in the right place to explore content in various categories such as graphic designs, stock photos, vectors, videos, music, sound effects, and software plugins.
Webhuma.com helps to speed up and facilitate design and content production processes by offering users the rich content accessible from Envato Elements Cheap Account at affordable prices. You can also take advantage of the Envato Elements license sales service offered by Webhuma.com to access unlimited download opportunities and access high-quality digital assets you need for your projects.
7 Day / Unlimited Download
$2,10
30 Day / Unlimited Download
$7,10
90 Day / Unlimited Download
$18,40
180 Day / Unlimited Download
$35,70
365 Day / Unlimited Download
$60
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
In 2023, the fast-fashion giant Shein was everywhere. Crisscrossing the globe, airplanes ferried small packages of its ultra-cheap clothing from thousands of suppliers to tens of millions of customer mailboxes in 150 countries. Influencers’ “#sheinhaul” videos advertised the company’s trendy styles on social media, garnering billions of views.
At every step, data was created, collected, and analyzed. To manage all this information, the fast fashion industry has begun embracing emerging AI technologies. Shein uses proprietary machine-learning applications — essentially, pattern-identification algorithms — to measure customer preferences in real time and predict demand, which it then services with an ultra-fast supply chain.
As AI makes the business of churning out affordable, on-trend clothing faster than ever, Shein is among the brands under increasing pressure to become more sustainable, too. The company has pledged to reduce its carbon dioxide emissions by 25 percent by 2030 and achieve net-zero emissions no later than 2050.
But climate advocates and researchers say the company’s lightning-fast manufacturing practices and online-only business model are inherently emissions-heavy — and that the use of AI software to catalyze these operations could be cranking up its emissions. Those concerns were amplified by Shein’s third annual sustainability report, released late last month, which showed the company nearly doubled its carbon dioxide emissions between 2022 and 2023.
“AI enables fast fashion to become the ultra-fast fashion industry, Shein and Temu being the fore-leaders of this,” said Sage Lenier, the executive director of Sustainable and Just Future, a climate nonprofit. “They quite literally could not exist without AI.” (Temu is a rapidly rising ecommerce titan, with a marketplace of goods that rival Shein’s in variety, price, and sales.)
In the 12 years since Shein was founded, it has become known for its uniquely prolific manufacturing, which reportedly generated over $30 billion of revenue for the company in 2023. Although estimates vary, a new Shein design may take as little as 10 days to become a garment, and up to 10,000 items are added to the site each day. The company reportedly offers as many as 600,000 items for sale at any given time with an average price tag of roughly $10. (Shein declined to confirm or deny these reported numbers.) One market analysis found that 44 percent of Gen Zers in the United States buy at least one item from Shein every month.
That scale translates into massive environmental impacts. According to the company’s sustainability report, Shein emitted 16.7 million total metric tons of carbon dioxide in 2023 — more than what four coal power plants spew out in a year. The company has also come under fire for textile waste, high levels of microplastic pollution, and exploitative labor practices. According to the report, polyester — a synthetic textile known for shedding microplastics into the environment — makes up 76 percent of its total fabrics, and only 6 percent of that polyester is recycled.
And a recent investigation found that factory workers at Shein suppliers regularly work 75-hour weeks, over a year after the company pledged to improve working conditions within its supply chain. Although Shein’s sustainability report indicates that labor conditions are improving, it also shows that in third-party audits of over 3,000 suppliers and subcontractors, 71 percent received a score of C or lower on the company’s grade scale of A to E — mediocre at best.
Machine learning plays an important role in Shein’s business model. Although Peter Pernot-Day, Shein’s head of global strategy and corporate affairs, told Business Insider last August that AI was not central to its operations, he indicated otherwise during a presentation at a retail conference at the beginning of this year.
“We are using machine-learning technologies to accurately predict demand in a way that we think is cutting edge,” he said. Pernot-Day told the audience that all of Shein’s 5,400 suppliers have access to an AI software platform that gives them updates on customer preferences, and they change what they’re producing to match it in real time.
“This means we can produce very few copies of each garment,” he said. “It means we waste very little and have very little inventory waste.” On average, the company says it stocks between 100 to 200 copies of each item — a stark contrast with more conventional fast-fashion brands, which typically produce thousands of each item per season, and try to anticipate trends months in advance. Shein calls its model “on-demand,” while a technology analyst who spoke to Vox in 2021 called it “real-time” retail.
At the conference, Pernot-Day also indicated that the technology helps the company pick up on “micro trends” that customers want to wear. “We can detect that, and we can act on that in a way that I think we’ve really pioneered,” he said. A designer who filed a recent class action lawsuit in a New York District Court alleges that the company’s AI market analysis tools are used in an “industrial-scale scheme of systematic, digital copyright infringement of the work of small designers and artists,” that scrapes designs off the internet and sends them directly to factories for production.
In an emailed statement to Grist, a Shein spokesperson reiterated Peter Pernot-Day’s assertion that technology allows the company to reduce waste and increase efficiency and suggested that the company’s increased emissions in 2023 were attributable to booming business. “We do not see growth as antithetical to sustainability,” the spokesperson said.
An analysis of Shein’s sustainability report by the Business of Fashion, a trade publication, found that last year, the company’s emissions rose at almost double the rate of its revenue — making Shein the highest-emitting company in the fashion industry. By comparison, Zara’s emissions rose half as much as its revenue. For other industry titans, such as H&M and Nike, sales grew while emissions fell from the year before.
Shein’s emissions are especially high because of its reliance on air shipping, said Sheng Lu, a professor of fashion and apparel studies at the University of Delaware. “AI has wide applications in the fashion industry. It’s not necessarily that AI is bad,” Lu said. “The problem is the essence of Shein’s particular business model.”
Other major brands ship items overseas in bulk, prefer ocean shipping for its lower cost, and have suppliers and warehouses in a large number of countries, which cuts down on the distances that items need to travel to consumers.
According to the company’s sustainability report, 38 percent of Shein’s climate footprint comes from transportation between its facilities and to customers, and another 61 percent come from other parts of its supply chain. Although the company is based in Singapore and has suppliers in a handful of countries, the majority of its garments are produced in China and are mailed out by air in individually addressed packages to customers. In July, the company sent about 900,000 of these to the US every day.
Shein’s spokesperson told Grist that the company is developing a decarbonization road map to address the footprint of its supply chain. Recently, the company has increased the amount of inventory it stores in US warehouses, allowing it to offer American customers quicker delivery times, and increased its use of cargo ships, which are more carbon-efficient than cargo planes.
“Controlling the carbon emissions in the fashion industry is a really complex process,” Lu said, adding that many brands use AI to make their operations more efficient. “It really depends on how you use AI.”
There is research that indicates using certain AI technologies could help companies become more sustainable. “It’s the missing piece,” said Shahriar Akter, an associate dean of business and law at the University of Wollongong in Australia. In May, Akter and his colleagues published a study finding that when fast-fashion suppliers used AI data management software to comply with big brands’ sustainability goals, those companies were more profitable and emitted less. A key use of this technology, Atker says, is to closely monitor environmental impacts, such as pollution and emissions. “This kind of tracking was not available before AI-based tools,” he said.
Shein told Grist it does not use machine-learning data management software to track emissions, which is one of the uses of AI included in Akter’s study. But the company’s much-touted usage of machine-learning software to predict demand and reduce waste is another of the uses of AI included in the research.
Regardless, the company has a long way to go before meeting its goals. Grist calculated that the emissions Shein reportedly saved in 2023 — with measures such as providing its suppliers with solar panels and opting for ocean shipping — amounted to about 3 percent of the company’s total carbon emissions for the year.
Lenier, from Sustainable and Just Future, believes there is no ethical use of AI in the fast-fashion industry. She said that the largely unregulated technology allows brands to intensify their harmful impacts on workers and the environment. “The folks who work in fast-fashion factories are now under an incredible amount of pressure to turn out even more, even faster,” she said.
Lenier and Lu both believe that the key to a more sustainable fashion industry is convincing customers to buy less. Lu said if companies use AI to boost their sales without changing their unsustainable practices, their climate footprints will also grow accordingly. “It’s the overall effect of being able to offer more market-popular items and encourage consumers to purchase more than in the past,” he said. “Of course, the overall carbon impact will be higher.”
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ko-fi prompt from @thisarenotarealblog:
There's a street near me that has eight car dealerships all on the same lot- i counted. it mystifies me that even one gets enough sales to keep going- but 8?? is there something you can tell me that demystifies this aspect of capitalism for me?
I had a few theories going in, but had to do some research. Here is my primary hypothesis, and then I'll run through what they mean and whether research agrees with me:
Sales make up only part of a dealership's income, so whether or not the dealership sells much is secondary to other factors.
Dealerships are put near each other for similar reasons to grouping clothing stores in a mall or restaurants on a single street.
Zoning laws impact where a car dealership can exist.
Let's start with how revenue works for a car dealership, as you mentioned 'that even one gets enough sales to keep going' is confusing. For this, I'm going to be using the Sharpsheets finance example, this NYU spreadsheet, and this Motor1 article.
This example notes that the profit margin (i.e. the percentage of revenue that comes out after paying all salaries, rent, supply, etc) for a car dealership is comparatively low, which is confirmed by the NYC sheet. The gross profit margin (that is to say, profits on the car sale before salaries, rent, taxes) is under 15% in both sources, which is significantly lower than, say, the 50% or so that one sees in apparel or cable tv.
Cars are expensive to purchase, and can't be sold for much more than you did purchase them. However, a low gross profit margin on an item that costs tens of thousands of dollars is still a hefty chunk of cash. 15% gross profit of a $20,000 car is still $3,000 profit. On top of that, the dealership will charge fees, sell warranties, and offer upgrades. They may also have paid deals to advertise or push certain brands of tire, maintenance fluids, and of course, banks that offer auto loans. So if a dealership sells one car a day, well, that's still several thousand dollars coming in, which is enough to pay the salaries of most of the employees. According to the Motor1 article, "the average gross profit per new vehicle sits at $6,244" in early 2022.
There is also a much less volatile, if also much smaller, source of revenue in attaching a repairs and checkup service to a dealership. If the location offers repairs (either under warranty or at a 'discounted' rate compared to a local, non-dealership mechanic), state inspections, and software updates, that's a recurring source of revenue from customers that aren't interested in purchasing a car more than once a decade.
This also all varies based on whether it's a brand location, used vs new, luxury vs standards, and so on.
I was mistaken as to how large a part of the revenue is the repairs and services section, but the income for a single dealership, on average, does work out math-wise. Hypothesis disproven, but we've learned something, and confirmed that income across the field does seem to be holding steady.
I'm going to handle the zoning and consolidation together, since they overlap:
Consolidation is a pretty easy one: this is a tactic called clustering. The expectation is that if you're going to, say, a Honda dealership to look at a midsize sedan, and there's a Nissan right next door, and a Ford across the street, and a Honda right around the corner, you might as well hit up the others to see if they have better deals. This tactic works for some businesses but not others. In the case of auto dealerships, the marketing advantage of clustering mixes with the restrictions of zoning laws.
Zoning laws vary by state, county, and township. Auto dealerships can generally only be opened on commercially zoned property.
I am going to use an area I have been to as an example/case study.
This pdf is a set of zoning regulations for Suffolk County, New York, published 2018, reviewing land use in the county during 2016. I'm going to paste in the map of the Town of Huntington, page 62, a region I worked in sporadically a few years ago, and know mostly for its mall and cutesy town center.
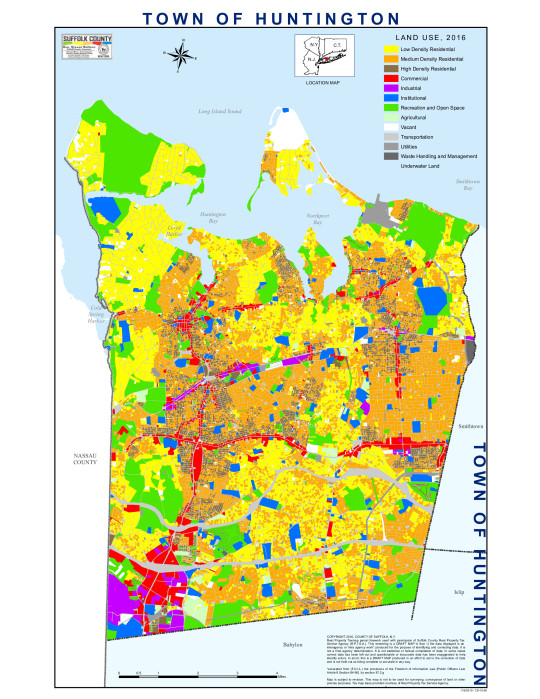
Those red sections are Commercially Zoned areas, and they largely follow some large stroads, most notably Jericho Turnpike (the horizontal line halfway down) and Walt Whitman Road (the vertical line on the left). The bulge where they intersect is Walt Whitman Mall, and the big red chunk in the bottom left is... mostly parking. That central strip, Jericho Turnpike, and its intersection with Walt Whitman... looks like this:

All those red spots are auto dealerships, one after another.
So zoning laws indicate that a dealership (and many other types of commercial properties) can only exist in that little red strip on the land use map, and dealerships take up a lot of space. Not only do they need places to put all of the cars they are selling, but they also need places to park all their customers and employees.
This is where we get into the issue of parking minimums. There is a recent video from Climate Town, with a guest spot by NotJustBikes. If you want to know more about this aspect of zoning law, I'd recommend watching this video and the one linked in the description.
Suffolk county does not have parking minimums. Those are decided on a town or village level. In this case, this means we are looking at the code set for the town of Huntington. (I was originally looking on the county level, and then cut the knot by just asking my real estate agent mom if she knew where I could find minimum parking regulations. She said to look up e360 by town, and lo and behold! There they are.)
(There is also this arcgis map, which shows that they are all within the C6 subset of commercial districting, the General Business District.)
Furniture or appliance store, machinery or new auto sales - 1 per 500 square feet of gross floor area
Used auto sales, boat sales, commercial nurseries selling at retail - 5 spaces for each use (to be specifically designated for customer parking) - Plus 1 for each 5,000 square feet of lot area
This is a bit odd, at first glance, as the requirements are actually much lower than that of other businesses, like drive-in restaurants (1 per 35 sqft) or department stores (1 per 200 sqft). I could not find confirmation on whether the 'gross floor area' of the dealership included only indoor spaces or also the parking lot space allotted to the objects for sale, but I think we can assume that any parking spaces used by merchandise do not qualify as part of the minimum. Some dealerships can have up to 20,000 gross sqft, so those would require 40 parking spaces reserved solely for customers and employees. Smaller dealerships would naturally need less. One dealership in this area is currently offering 65 cars of varying makes and models; some may be held inside the building, but most will be on the lot, and the number may go higher in other seasons. If we assume they need 30 parking spaces for customers and employees, and can have up to 70 cars in the lot itself, they are likely to have 100 parking spaces total.
That's a lot of parking.

Other businesses that require that kind of parking requirement are generally seeing much higher visitation. Consider this wider section of the map:
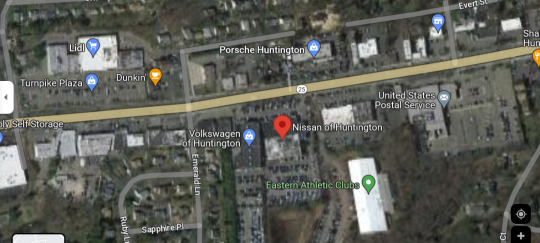
The other buildings with comparative parking are a grocery store (Lidl) and a post office (can get some pretty high visitation in the holiday season, but also just at random).
Compare them, then, to the "old town" section of the same town.
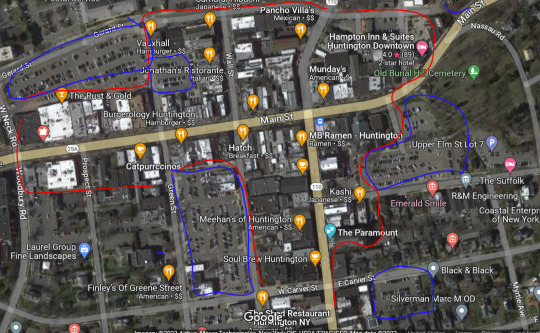
There are a handful of public parking areas nearby (lined in blue), whereas the bulk of the businesses are put together along this set of streets. While there is a lot of foot traffic and vehicle passage, which is appealing for almost any business, opening a car dealership in this area would require not only buying a building, but also the buildings surrounding it. You would need to bulldoze them for the necessary parking, which would be prohibitively expensive due to the cost of local real estate... and would probably get shot down in the application process by city planners and town councils and so on. Much easier to just buy land over in the strip where everyone's got giant parking lots and you can just add a few extra cramped lanes for the merchandise.
Car dealerships also tend to be very brightly lit, which hits a lot of NIMBY sore spots. It's much easier to go to sleep if you aren't right next to a glaring floodlight at a car dealership, so it's best if we just shove them all away from expensive residential, which means towards the loud stroads, which means... all along these two major roads/highways.
And if they're all limited to a narrow type of zoning already, they might as well take advantage of cluster marketing and just all set up shop near each other in hopes of stealing one of the other's customers.
As consumers, it's also better for us, because if we want to try out a few different cars from a few different brands, it's pretty easy to just go one building down to try out the Hyundai and see if it's better than a Chevy in the same price group.
(Prompt me on ko-fi!)
#economics prompts#marketing#zoning laws#ko fi prompts#ko fi#auto industry#automotive dealerships#car dealerships#phoenix posts
110 notes
·
View notes
Link
Conclusion
ESS India's commitment to customer experience, satisfaction, and loyalty is exemplified through our best-in-class after-sales service app. Its robust features and benefits, including impressive percentages, statistics, and real-world examples, position it as an indispensable tool across industries. By choosing ESS India, businesses can build enduring customer relationships and establish themselves as industry leaders.
#field service management software#after sales service app#best after sales service app#after sales service management app#after sales service software#after sales management software#After Sales Service Management Software#after sales software#best after sales service management software#after sales tracking software#after sales service management#best after sales service mobile company#field management app
0 notes
Text
The Bad Batch and their jobs (Modern AU)
In my headcanon they all started out as soldiers. After getting out and accidentally acquisiting Omega, they desperately need money and take any jobs they can get. Eventually, everyone finds something they actually like.
Hunter:
Retail sales associate aka Walmart slave and getting yelled at by Karens all day. He's also doing freelance cleaning jobs, the grosser the better the payment. Think hoarder apartments with fifty cats or scat orgy hotel room cleanup.
He works hard on getting his record cleaned up and eventually secures a job at the fire station. He becomes a firefighter and will eventually be a lieutenant and later captain.
Tech:
Fast food worker which means lots of being yelled at by hangry people who are unhappy with the way their BigMac was stacked. He takes any extra shift he can get.
After several failed rounds of applications, he hacks into a big company's system and puts his name on top of the candidate list. He ends up supervisor for some bank insurance IT stuff with lots of numbers.
Wrecker: Miner. It's hard work and long hours in the dark. He actually earns the most of all of them but that's because it's fucking dangerous and depressing.
The leading instructor for the demolition expert trainees blows up. Wrecker, having had professional training in the military and lots of experience at not getting blown up (again), is their best take so he becomes their new instructor for the new hires.
Crosshair: Nobody is really willing to hire him so he's an unlicensed taxi driver most nights. (He hates everything about it.) He also signed up as a freelance roadkill collector job in Hunter's name and takes the calls when he doesn't have passengers.
He meets railroaders when cleaning up railkill one night. When smoking he mentions how much he hates being a taxi driver and the railroaders recruit him for their company. He becomes a traindriver and finally doesn't have to interact with his passengers.
Echo: They call it online sales associate marketer and customer service advisor. He calls it tele-scam-marketer. Many people yelling at him but at least he can work from home.
At a parent-teacher conference of Omega's school he helps another parent with a technology problem. He's like: "I tried to get rid of that problem for hours and you did it within five minutes. You gotta be a master software engineer." and Echo's like "I get payed to get yelled at as a telemarketer". Turns out the guy is an HR associate at an IT company and gets Echo a proper job.
#star wars#clone wars#bad batch modern au#the bad batch#bad batch#modern au#star wars modern au#bad batch echo#bad batch hunter#bad batch tech#bad batch wrecker#bad batch crosshair#roadkill collector
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
It takes more than just providing high-quality goods or services to survive and grow in highly competitive marketplaces. Building enduring client connections, encouraging customer loyalty, and ultimately maintaining success in today’s dynamic business environment all depend heavily on providing exceptional after-sales support. To learn more about after-sales support please click on the link...
#after sales support#customer management software#customer management platform#service crm software#crm software#customer service crm#servitiumcrm
0 notes
Text

Terms of Service
Katya was going to follow her dream. She was going to be an influencer.
Like so many other girls, she'd grown up admiring beautiful models living a life of constant attention and external validation.
They were so glamorous, so classy, so carefree looking! She wanted to be like that, beautiful but untouchable, unobtainable.
However, the reality was that being an influencer took a lot of work, and getting started was proving EXPENSIVE. Things like makeup, clothes, " healthy lifestyle" super foods, everything just piled up.
Katya tried cutting corners wherever she could. She was able to get some cheap camera and staging equipment on sale or from some second hand stores, which helped somewhat.
She also decided to skimp on picture modding software and apps. Instead of buying an expensive piece of software along with the computer she'd need or paying some pay-to-play mobile app, she started shopping the app store for free options.
Katya was a smart girl, she knew she could make it work. It was her dream, nothing would stop her!
She went through app after frustrating app trying to find something halfway decent until one day she stumbled on an app that looked really good and had a ton of features for modding pictures.
It was called Bimboozle, and it said it was looking for influemces to beta test who would get the app for free as long as they agreed to share their info and use as many features as possible.
There was this long service agreement, and a non disclosure, some disclaimer about private ownership. She just scrolled without reading and clicked agree on each one. All these were the same anyway.
-----------
Katya was ecstatic, it was so good! It could do everything she wanted. It also had a feature called Tipz. If you clicked on the icon for Tipz, it would give some advice on how to use functions, or advice for what to adjust. It was really very helpful!
Every time you used it, it would ask a survey question, "Did this Tipz help you Bimboozle yourself?" It was silly, and she rolled her eyes, but she'd agreed to test and rate the features.
So Katya would always click either the OMG Yes! option which made a happy little chime that made her feel all warm whenever she heard it, or the Totes No! option that played a sound that, for some reason, made her feel stressed.
Thankfully, the Tipz were usually really good, so she got to hear the happy sound a lot!
"Bigger is better! Add a bit more to your bust for the boys!"
Did this help?
OMG Yes! *happy chime*
"Pouts are pretty! Puff up those puckerers!"
Did this help?
OMG Yes! *happy chime*
She felt so good using the Tipz like that. She started to feel warm and fuzzy when she lovingly molded her increasingly sexy pictures.
It was funny. She didn't seem to need them to mod pics so much anymore, but she still gave feedback every time she used them.
Her hair seemed lighter and lighter. And. had it really grown 6 inches in a few weeks?
*happy chime*
Well, she was eating healthier, and she'd been getting so much more sun, which could bleach her hair naturally. And she just loooooved how the color looked.
She had to buy new bras again. Something about going up 3 cup sizes in a month seemed weird.
*happy chime*
Well, she was still a growing girl after all. And yay, these new bras were totes so sexy!
Katya was ecstatic, feeling so bubbly and fulfilled as her following grew. And she got so many compliments! She was making money, feeling good and sexy, and people were so interested in her every activity. It was her dream life.
She took a new sexy selfie, opened the app to modify it, and clicked the Tipz like always. She needed to hear that chime. It made her feel so HOT!
"Brains are for boys, bimbos are blank! Show your fans just how dumb you can be!"
Did this help?
*happy chime*
Katya moaned. She really did look so dumb looking in her pic. She could see how boys would like it.
She tried to make a dumber expression in the next pic. It really wasn't that hard. She'd been feeling fuzzier lately.
"Good Girls think with their cunts! Show your fans just how sexy it feels when you're dripping!"
Did this help?
*happy chime*
"Fuuuuucckkkk," such an amazing sound. And she really did feel horny. Maybe she could do a more adult shoot. Katya bet her followers would love to see pics of her rubbing her seemingly constantly aroused vulva on objects around her apartment.
‐-----------
It had been 3 months since Kitty had downloaded Bimboozle. Life was perfect!
Her porny pics had spawned a whole new adventure for her. Her constantly dripping slit seemed to have all the best ideas, and she loved seeing all the cocks her fans were sending her.
New pics! Her cunt was lewdly on display, and her fat titties looked perfectly fuckable. She automatically clicked the Tipz. She needed it! It was so smart, and she was so dumb, but if she did as she was told, she got cocks, and money, and cocks, and even some yummy pussy.
"You're prime pussy! Invite your followers to use and abuse you"
Did this help?
*happy chime*
Kitty squirted when she heard the chime. She hadn't even realized she'd been circling her clit until the orgasm hit.
Kitty would invite the next boy who messaged her to come over and use her body. Her still sodden pussy ached to be filled by her fans. The app told her so.
The happy chime went off on its own, and she shivered in orgasm again. She hadn't clicked on Tipz. Oh wait, the Terms of Service updated.
She could barely read anymore, but Tipz popped up to help her as always.
"Good bimboozlers are property! Agree and let Bimboozle own you for good!"
Did this help?
*happy chime*
Kitty's world exploded as she clicked Agree. She was a good bimboozler now, and she'd never been happier.
297 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best sales customer service management system - Service CRM
In the fast-paced world of business, providing exceptional after-sales service to customers has become crucial for success. Companies are realizing that the relationship with customers doesn't end after a purchase is made, but rather, it's just the beginning. Therefore, the need for efficient and effective after-sales service management software has never been more important. After Sales Service Management Software Service CRM, which stands for Customer Relationship Management, is the key to streamlining and optimizing the entire after-sales service process.

0 notes
Text
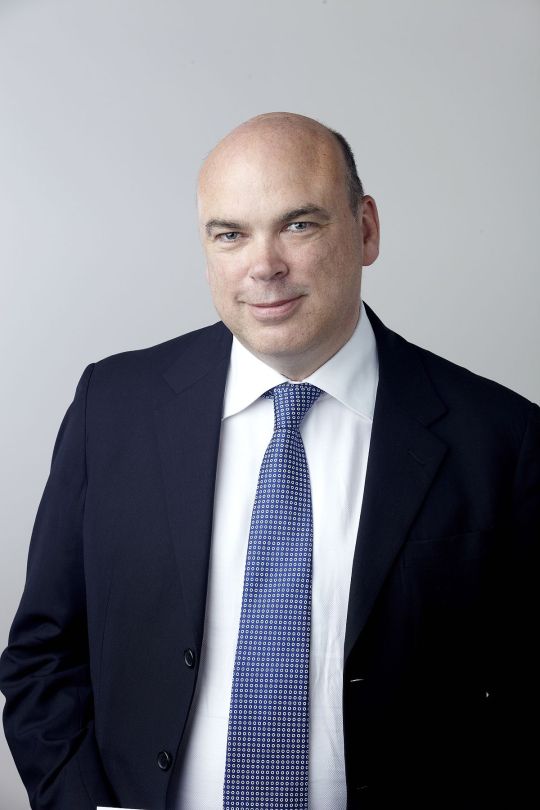

Mike Lynch
British tech entrepreneur who sold his Autonomy software group to Hewlett-Packard and was later cleared after a long-running US fraud case
Mike Lynch, who has died aged 59 in the wreck of his yacht, was sometimes described as “Britain’s Bill Gates”. It was a huge exaggeration, but Lynch could claim two parallels with Gates: he developed world-leading technology (in his case in machine learning or AI) and, unlike so many UK scientists, he learned how to turn it into commercial success.
Such was this success that his company, Autonomy, was valued at $11bn when he sold it to Hewlett-Packard in 2011, but the fall-out from the sale would come to overshadow his technological achievements, and lead to a national debate about the circumstances in which UK citizens may be extradited to the US.
Lynch founded Autonomy with two partners in 1996. Its software enabled a computer to search huge quantities of diverse information, including phone calls, emails and videos, and recognise words. He told the Independent in 1999: “The way our technology works is to look at words and understand the relationships because it has seen a lot of content before. When it sees the word ‘star’ in the context of film, it knows it has nothing to do with the word moon. Because it works from text, it can deal with slang and with different languages.”
Autonomy became a leading company in Cambridge’s Silicon Fen cluster and established a base in San Francisco. “We knew we had to be successful in America. It was a question of ‘Go West young man, go to San Francisco and be ignored.’ They found it hard to believe that anyone from England could have anything powerful.” Lynch found what he called the “cold-hearted schmooze” to secure funding tough.
But Autonomy’s software, enabling computers to identify and match themes and ideas, and sort mammoth amounts of data, was licensed to more than 500 customers, including the US State Department and the BBC. It was listed on Nasdaq in 1998 and on the FTSE 100 in November 2000, although its value of £5.1bn would be halved within a few months in the collapse of the technology boom and accusations of over-promotion. In 2005 it bought a major US rival, Verity, for $500m.
Lynch’s profile rose with it. In 2006 he was appointed OBE for services to enterprise and the following year joined the board of the BBC. In 2011 he became a member of the government’s Council for Science and Technology, and was named the most influential person in UK IT by Computer Weekly. In 2014 he was elected a fellow of the Royal Society.
Though quietly spoken, he had a reputation for toughness, coloured by a liking for James Bond, which led to Autonomy conference rooms being named after Bond villains, and a tank of piranha fish in reception. (Lynch claimed it belonged to one of his business partners.) Challenged about a company culture where people were “a little fanatical”, he replied: “This is not the place for you if you want to work 9 to 5 and don’t love your work.”
Born in Ilford, east London, to Michael, a firefighter, and Dolores, a nurse, and brought up in Chelmsford, Lynch won a scholarship to the independent Bancroft’s school in Woodford Green, before taking a natural sciences degree at Cambridge, where his PhD in artificial neural networks, a form of machine learning, has been widely studied since.
A saxophone player and jazz lover, he set up his first business, Lynett Systems, while still a student, to produce electronic equipment for the music industry. Later he would attribute some loss of hearing to adjusting synthesisers for bands. He quoted his own experience to highlight the difficulties of finding funding for startup businesses in Britain. He finally negotiated a £2,000 loan from one of the managers of Genesis in a Soho bar.
Lynch’s next venture came out of his research. In 1991 he founded Cambridge Neurodynamics, specialising in computer-based fingerprint recognition. Then he established Autonomy.
The pinnacle of his success appeared to come in October 2011 when Autonomy was purchased by Hewlett-Packard for $11bn and Lynch made an estimated $800m. Shortly afterwards he established a new company, Invoke Capital, for investment in tech companies, and he and his wife, Angela Bacares, whom he had married in 2001, invested about £200m in Darktrace, a cybersecurity company.
But just 13 months after the Autonomy sale, HP announced an $8.8bn writedown of the assets ��due to serious accounting improprieties, disclosure failures and outright misrepresentations” which it claimed had artificially inflated the company’s value. The authorities investigated, and while the UK Serious Fraud Office found insufficient evidence, in 2018 the US authorities indicted Lynch for fraud. Soon after, Autonomy’s chief financial officer, Sushovan Hussain, was found guilty of fraud and sentenced to five years in prison.
In March 2019 HP followed up with a civil action for fraud in London. Lynch spent days in the witness box as the civil action stretched over nine months. It ended in January 2022 with the judge ruling that HP had substantially succeeded, but that damages would be much less than the $5bn they had claimed.
Meanwhile the US authorities sought Lynch’s extradition on criminal charges of conspiracy and fraud. In spite of representations by senior politicians and accusations that the US authorities were attempting to exercise “extraterritorial jurisdiction”, a district judge ruled in favour of extradition.
An application for judicial review and a further appeal failed, and in May 2023 Lynch was flown to the US to be held under house arrest in San Francisco, with the prospect of a 25-year sentence.
Charged with wire fraud, securities fraud and conspiracy, on 18 March this year Lynch pleaded not guilty, alongside his former vice-president of finance, Stephen Chamberlain. On 6 June, they were found not guilty of all charges. Chamberlain died after being hit by a car on 17 August.
Lynch declared that he wanted to get back to what he loved doing – innovating. But he had little opportunity to do so. He soon embarked on a voyage to celebrate his acquittal, with family, colleagues and business associates. It ended with the sinking of his yacht, Bayesian – named after the 18th-century mathematician, Thomas Bayes, whose work on probability had informed much of his thinking – in a violent storm off the coast of Sicily.
Lynch is survived by his wife and elder daughter, Esme. Their other daughter, Hannah, was also on board the Bayesian.
🔔 Michael Richard Lynch, technology entrepreneur, born 16 June 1965; died 19 August 2024
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at Just for Books…?
7 notes
·
View notes