#Yanomami
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


In 1997, photographer Ricardo Stuckert took the top photo of Penha Goes, a 22-year-old girl from the Yanomami tribe, in the Brazilian Amazon.
In 2015 he took another photo of her at 40.
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
hi, it's me again.
i'm here to talk and beg for you guys to do a favor or just read this post carefully.
a few hours ago i posted a thread on twitter explaining what's happening in brazil with the indigenous tribe "Yanomami".
for those who don't know, i am a brazilian person and this is an extremely sad and cruel thing to hear coming from my country and the people who were here first.
i'd like to ask you guys to at least skim over this thread i made, there's a lot of information including petitions and articles.
(sometimes the link doesn't work so you can just search @swftspX on twitter, the thread is pinned)
you don't have to follow me or like any other posts of mine. just PLEASE. read this.
if you don't want to, i'd like for you to at least see what's happening with the Yanomami people and i'll put some links.
this is them. they're currently suffering from starvation and the brazilian court has openly discussed the fact that the Yanomami people are suffering a genocide due to illegal mining explorations. there has been reports of sexual assault with little kids, miners offering food and gold in exchange of sex with minors and/or their mothers. people dying from diseases since there's barely clean water on their territory and overall it's been hell in there. this happened while Bolsonaro was in command and now they're STILL suffering.
PLEASE. don't let my people die.
articles:
petitions:
#yanomami#yanomami people#brazil#genocide#brazil genocide#please help#awareness#viral#bolsonaro#free yanomami#no one is free until we are all free#the last of us#tlou ii#tlou art#abby anderson#abby anderson x reader#abby anderson fanart#abby the last of us#abby anderson smut#ellie williams art#ellie williams x reader#ellie williams smut
193 notes
·
View notes
Text
133 notes
·
View notes
Text

Yanomami com beija-flor
Rosa Gauditano
#yanomami#beija-flor#rosa gauditano#fotografia#arte#photography#art#hummingbird#vida#natureza#amor#love#life#nature
98 notes
·
View notes
Text

Yanomami girl, by Ricardo Stuckert
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

Barbara Brändli, "Untitled," 1965,
Yanomami community of Mavaca, Upper Orinoco region, Amazonas State, Venezuela,
Digital print, 10 3/8 x 15 3/4 inches
#art#photography#black and white#vintage photography#still life photography#history#portrait#human rights#barbara brandli#1965#amazon#amazonia#venezuela#yanomami#community#mavaca#orinoco
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
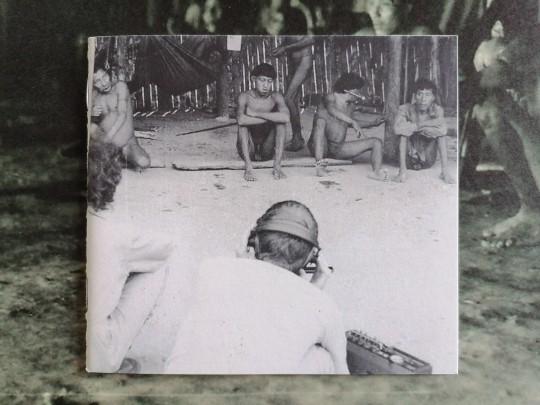










[rec. David TOOP]
"Lost Shadows: In Defence of the Soul (Yanomami Shamanism, Songs, Ritual, 1978)"
(LP. Sub Rosa. 2015 / rec. 1978) [BR-VE]
#yanomami#1978#Brazil#venezuela#david toop#traditional#musicology#ethnomusicology#shamanism#records#amazonia
25 notes
·
View notes
Text













Alves, Márcio Moreira. 1993. No país dos Yanomamis. Revista Geográfica Universal, n. 220, p. 4-15. Rio de Janeiro: Bloch.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
32 notes
·
View notes
Text

Penha Goez, a Yanomami tribeswoman of the Amazon Rainforest, 1997 The second picture is a close-up portrait of Penha in 2015, reunited with photographer Richard Stuckert.

24 notes
·
View notes
Text

4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Por que a crise dos Yanomamis persiste mesmo com novo governo
Imaginou-se que a mudança na presidência da República traria uma solução para a grave crise humanitária dos yanomami. Infelizmente não foi o que aconteceu. O Vocativo buscou especialistas para entender o que está acontecendo
No início de 2023, o país assistiu em choque à grave crise humanitária que se abateu sobre a Terra Indígena (TI) Yanomami, em Rondônia. As imagens de crianças em estágio avançado de inanição finalmente fizeram o restante do país perceber que a etnia enfrenta, há anos, uma realidade de miséria, desnutrição grave, malária, verminose, pneumonia e outras infecções respiratórias agudas. O principal…

View On WordPress
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
COLONIALISMO do século 21 – implementado por corporações e ONGs? Cuja sobrevivência está em jogo aqui, Survival? A sobrevivência das florestas tropicais e dos povos Indígenas ou da Cartier e outros na indústria de joias de ouro e diamantes? – Pensando em doar para uma ONG? Por favor, leia isso primeiro! – 2025! | Barbara Crane Navarro
“Ouro ou Natureza?” – © Fotolia / Wikimedia / Collage: Mirela Hadzic para o resgate da floresta tropical “A tolice do homem aumentou o valor do ouro e da prata por causa de sua escassez; enquanto a natureza, como um pai amoroso, nos deu gratuitamente as melhores coisas, como ar, terra e água, mas escondeu de nós as que são vãs e desnecessárias.” – Thomas More,” Utopia “, livro II – 1516 Foto:…

View On WordPress
#5#BoycottGOLD4YANOMAMI#Brasil#comunidades#Covid#FightEcofascism#ForaGarimpoForaCovid#MinersOutCovidOut#povos#TribalPeoples#Yanomami
0 notes
Text
6 - O Desejo dos Outros: Uma etnografia dos sonhos Yanomami, Hanna Limulja - 4,5✨️
"(...) aqui tudo é sonho, e nele cabe o mundo inteiro."

0 notes
