#Upland Game Bird
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Great upland bird hunting in Coloroado
Shooting Sportsman writer Eddie Nickens talks about the first upland hunt he has just had with son Jack at Kessler Canyon in … source
#bird hunting destinations#colorado chukar hunting#colorado huntiung#colorado lodges#colorado pheasant hunting#colorado quail hunting#colorado ranches#colorado sporting clays#eddie nickens#kessler canyon#kessler canyon shooting academy#places to hunt birds in colorado#Shooting Sport (Sport)#shooting sportsman magazine#sporting clays#upland bird hunting#Upland Game Bird#upland hunting#wing shooting
1 note
·
View note
Text




I also acquired a new hunting dog book and atlas book!
Game Dog: The Hunter's Retriever for Upland Birds and Waterfowl, by Richard A. Walter's. Originally published 1983, second edition published 1995
Goode's World Atlas, from Rand McNally, edited by Edward B. Espenshade Jr and John C. Hudson, with senior consultant Joel L. Morrison. Originally published 1922, 19th edition published 1995
#i see atlas books fairly often at work but dont get them#but THIS ONE i was showing to a regular where laika come from#and accidentally flipped to the LANGUAGE MAP SO COOL OH YEAH WHAT instead of the normal northern eurasia map#and idk if thats a normal thing to find in these books or not; ive never checked but will be now#but i decided Right Then that i needed This Book#so i got it lol#anyways#my library#hunting book#hunting#hunting dog#hunting dog book#dog book#maps#map book#game dog: the hunters retriever for upland birds and waterfowl#labrador retriever#field bred lab#richard a wolters#rand mcnally#goode's world atlas#atlas#edward b espenshade#john c hudson#joel l morrison#1995#1990s
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
I know that ppl get up in arms abt stuff like this sometimes but whenever I look at a woodcock I'm like. I want to eat that animal.
#anyway i think that acknowledging that living animals have to die in order for you to eat them#is better than people who are so alienated from the realities of food production that they only think of meat as something that comes#wrapped in plastic from the grocery store#i havent had a game bird of any kind since i was a kid#and my brother has been getting into upland bird hunting so its been on my mind#i also have a hankering to try duck which. i can just get from the store.#so i might find a recipe#txt
6 notes
·
View notes
Photo
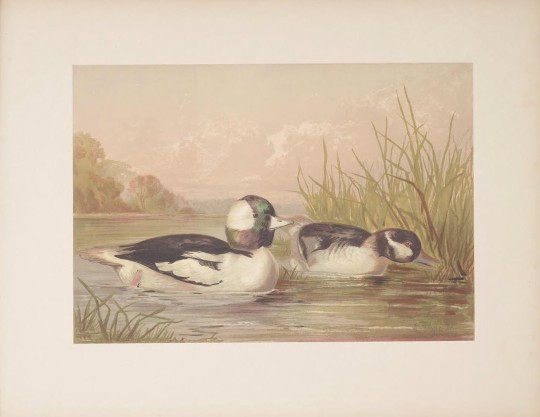

🦆 Upland game birds and water fowl of the United States New York: Published by Scribner, Armstrong,©1877-1878.
115 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hivy, This is Ivy!
Throughout my time on Tumblr one of my favourite things to do has been to create hypothetical Minecraft updates, I've done this twice before with The Pigeon update and The Pond Update, but a few weeks ago I let you lot chose what geographic area I should turn into a hypothetical update
Yall chose Celtic Europe (and Oceania but that's for later) AKA, Ireland, Scotland, Whales and Cornwall. I was very glad with this outcome as I myself am Scottish and I had a lot of ideas for this…..too many ideas…. So many ideas that I had to cut an entire section and now some stuff feels barebones….whoops. (but hey now I can work on a full portion update later…yay.)
But, enough of that, let's move on to:
The Fae Update!
New Biomes + Structures
There are 6 new biomes in this hypothetical update, each referring a different local found in celtic europe these are: The White Cliffs,The Glacial Pass, The Wisteria Forrest The Heather Moorlands/Peat Bogs (take your pick), The Highland Forests, and… you'll see ;3
The White Cliffs
The White Cliffs are a new coastal biome, consisting of grass topped cliffs, sandy bays and rock structures jutting out of the water. Suspicious sand and gravel generates naturally here and loot from it follows the fishing loot table, though with an increased chance to find nautilus shells and a rare chance to find sniffer eggs
This biome is based on the White Cliffs of Dover and the Jurassic Coast
The White Cliffs has only three new features:
Puffins
A new passive abiant mob, they drop Feathers when killed. Instead of the normal birds nest (introduced in the pigeon update) puffins lay there eggs in “wall nests” grey nests that attach to walls, these can be used as a decorative block
Seagulls
A neutral mob who drops Feathers and fish when killed, they spawn both in the White Cliffs and on beaches and open Seas. Seagulls will attack the player if they are holding any food item in their hand, stealing it.
Seagulls serve no other purpose.
Chalk
Chalk is a new stone block. It has the blast resistance of wood and is exclusive to the white cliffs, making up the cliffs themselves.
Chalk can be dyed any of the dye colours in the game, creating a softer, more Pastel variant of that colour (queers rejoice). Chalk can be made into slabs, stairs and walls in the stone cutter.
The Glacial Pass
A cold mountainous biome, the Glacial past is mainly made of stone and deeplate, with ice and snow also being common. Dipstone spikes can be found here as well as gravel structures resembling Eskers and Terminal Moraines (yes my favourite subject is geography how can you tell?). Suspicious gravel can be found here as well as suspicious snow, which can also be found in the igloo. Strays, Polar Bears, Foxes and Rabbits Spawn in this environment
This biome is based on glaciated uplands
Seals
Seals can be found in all cold environments. Seals will follow the player when they swim, upon coming on to land Seals will bob in the afternoon expectantly.
Seals can be fed fish, clapping after this is done
Seals drop blubber when killed. Blubber can be crafted into blubber blocks, when lit on fire these blocks burn light yellow. Blubber can be used to make torches, lanterns and campfires.
Blubber can also be crafted into a chest plate, the blubber chest plate reduces projectile damage and prevents Frost damage in powdered snow, but it slows you down while on land
The Wisteria Forest
A replacement for the old flower Frocester, this is a rare forrest in which all natural flowers spawn
Purified water (a type of water introduced in the pond update that can cure harmful status effects and restore hunger permanently for a short time) would spawn here too, as well as unicorns and kelpies (introduced in the pond update, will be discussed later)
Other Mobs that Spawn here will be discussed later
Wisteria Trees
Wisteria trees are a new wood type. The wood itself is a pale green with a purplish grey bark. Wisteria leaves are pale lavender. Wisteria trees also have hanging leave variants, much like willow leaves (pond update) that grow in the same way as glow berries
Butterflies and Moths
Passive ambient mobs that spawn in all biomes, though moths are most common in dark oak forests and butterflies are most common here. Both come in many colours, much like tropical fish. These mobs are as large as the bees (traditional dictates that all Minecraft arthropods must be massive, also yes bane of arthropods works on these, but do you actually care?)
Butterflies and Moths drop their respective wings when killed, these can be grafted onto the elytra (using the dragonfly carapace, an mob drop from the dragon fly as introduced in the pond update, speaking of that, the Toad from that update will also eat Moths and Butterflies) grafting these wings on changes the electable texture to resemble the wings of these Mobs (Note: despite both having many textures the electric will always adopt The Lunar Moth and Monarch Butterfly texture respectively)
Crann Bethadh Sprout
The sprout of a legendary tree, this is a two tall plant with ever changing leaf colours, shifting throughout all the pastel colour variants
The player can take a cutting of this plant using shears
This plant can only be dug up by the sniffer
Flower Crowns
By combining any 4 flowers in a circular pattern in the crafting table players can make flower crowns. Flower crowns adopt the colours of whatever flowers were used to craft it. Flower crowns can be worn on the head and serve no purpose other than to make people look pretty ;3
Wisteria Grass
Wisteria grass is a new grass type block that is pale lavender. It behaves the same as grass. It is only found in the Wisteria forest
The Heather Moorlands
Heather Moorlands are made up of water, grass, mud and a new block. No trees and few other plants spawn here, but cattails, reeds (pond update), sea grass and lily pads would be common here.
Bogs would spawn here
Toads, Frogs and Dragonflies would spawn here
Heather Moorlands are based on….Heather Moorlands.
Peat
Peat is a new powered snow-like block. It is brown in colour and makes up most of the ground in the Heather moorlands. Any plant can be planted on it.
Falling through peat takes notably longer than it does for powdered snow, players cannot freeze in peat, only suffocate. Peat can be safely traversed with leather boots.
When broken, peat will break into Peat Logs, peat logs can be burned in the furnace as an effective fuel
When lit on fire, Peat burns Bright Red, peat logs can be used to make peat lanterns, campfires and torches.
Combining 4 peat logs together makes a peat block, smelting a peat block creates Hardened Peat. Harmed peat can be made into Smooth Peat, Chiselled Peat, Peat Bricks, Cut Peat, Peat Pillar and Peat Tiles
Gortach
The Gortach are a new Undead mob. They spawn in swamps and peat bogs and resemble Bog bodies. They hide in dirt, mud, sand, gravel and peat and jump out of the ground to attack.
Gortach inflicts poison with their attacks. Gortach can carry swords, axes, and spears
Gortach drop their weapon, peat logs or Rotten flesh when killed
Spears
Spears are crafted either with one iron ingot and two sticks in a diagonal pattern, or are dropped by the Gortach
Spears are weaker than the sword but have a better reach, can be thrown (though this isn't good for their durability) and completely bypass shields and armour, hitting the opponent as if they had nothing at all
Spears have all the same enchantments as the Sword + Loyalty
Heather
Heather is a new purple flower exclusive to the Heather Moorlands. It gives purple dye when ground up.
The Highland Forest
Made up of rolling hills and Birch trees, all normal passive Mobs can spawn here, but sheep, goats,bees and cows are most common. All normal hostile Mobs can spawn here
Loch Lurkers (a rare UnderWater horse-like mob from the pond update) also spawn in the lakes here
Birch Updates
Yep. This is a secret Birch forest update.
A new form of Birch tree “Silver Birch” that grows much taller and has yellow leaves can be found here. This form gets its own sapling
The Birch block would also get a minor update to make the black segments more like stripes and not ugly blobs
Leave Updates, Packed Leaves and Thatching
Players and Mobs can now walk and fall through leaves.
When breaking leaves with anything other than shears or silk touch leaf blocks will drop leaf items (except wisteria and Spruce, which drop Petals and Needles)
By placing 9 of these in the crafting bench the player can create packed leaves, a new solid version of the leaf block
Thatching is a new block of greyish colour that is crafted with 6 wheat on the top and bottom and 3 leaves of any type in the centre of the crafting bench. Thatching looks the same as a Hale Bale, only without the string holding it together.
Goosegrass, Nettles, and Thistle
Goosegrass is a plant that grows in any forest, but is most common in the Highlands. Walking through goosegrass results in it sticking to you, taking up one of your unoccupied armour slots and slowing you down. Walking through it at all also slows you down, much like cobwebs, making this plant dangerous when fighting mobs
Nettles can only spawn in Dark oak and Highland forests. Nettles stay low to the ground, if they are walked on by a player they are inflicted with Poison. Nettles can be collected and made into a healthy soup
Thistles are a new type of two high flowers. They can be ground into purple dye. They hurt the player if walker through
Deer
Deer are a new mob found in all forested environments, much like Wolf's they have different textures depending on the biome
When killed, Deers drop Venison, a new edible meat
Like Goats, Deers will try to charge the player. Also like Goats, after hitting a block deer will drop and antler
Fog
Fog is a new weather type, lowering the amount the player can see for a short time and allowing a few Mobs to spawn, particularly endermen
Shelf Fungus
A new decorative block that grows on trees
Wildcats
Wildcats are a new ambient Mob, they share a model with Ocelots and Cats and they drop string when killed
The Mushroom Grotto
Oh yes. A new forest of giant mushrooms and mycelium. This biome is very rare. The Mobs that Spawn here will be discussed later
Mushroom Wood
Much like the nether mushrooms, overworld mushrooms are now a woodtype. The mushroom stem can be stripped and converted into all wood blocks. Mushroom wood is white in colour.
New Mushrooms
Yep. There is now a mushroom for every colour of dye in the game. Mushrooms can also now be ground into dye
Here's what all those mushrooms could look like (minus brown and red of course):

(Note: this is based on design, not colour)
Before moving on, sniffers don't just get the Crann Bethadh Sprout. They get a new plant for every dye type in the game
Plus, they can dig up two new mushrooms exclusive to them, when ground these mushrooms become two new dye types… Well, not quite. They Become Rose Dye and Spring Green Dye, the two removed wool colours. This is the only way to get these mushrooms and these dyes. This would make the sniffer more worth the work put in to get one and create a lot of more strange decoration choices
Here's what they COULD look like (note: again, colours don't line up)

Mushroom bricks
Smelting the Mushroom blocks (not the stem, the block itself) creates mushroom bricks: multicoloured bricks taking on the patterning of the mushroom used to make them
Mushroom bricks can be made into stairs, slabs and walls
Puffball Mushrooms and Faerie Rings
Both exclusive to the mushroom forest.
Puffball mushrooms are brown in colour and are plants that stay on the ground, when walked over they release spores that inflict harmful status effects such as Poison, blindness, slowness, weakness, nausea, lethitatvia, and mining fatigue
Faerie Rings are Rings of mushrooms that take up one block on the ground (they also come in all colours)
If a player steps on one it is like they are walking through cobwebs, and upon getting out they will be inflicted with slowness.
If a mob steps in one they completely freeze and their AI is disabled until they are knocked out or the ring is broken.
This would help allow players to use Mobs as decoration without lagging there game
New Structures
Bothies
A bothy is a public structure found typically in the Highlands, there small houses for folks to take shelter in.
Bothines can spawn in any woodland biomes, they'll appear as a simple wooden house. Inside Bothies will have a chest with low level loot and a bed.
Occasionally, suspicious sand,mud, gravel or snow will spawn outside the bothy (depending on the biome), these typically have low level loot but items such as armour Trims or record disks can be dug up
Stone Works
Based on the numerous palaeolithic celtic stoneworks,these are small abiant structures spawning in the Dark Oak, Highland and Wisteria forests, as well as Heather Moorlands, Snowy Tundras, Wetlands and Mushroom Grottos
There would be many variants of these structures resembling stone circles, stone henges, standing stones, stone portals and cobbled walls.
All of these are made from base stone blocks, though sometimes other blocks can be found like chalk flooring or trees/water spawning in the centre of a stone circle
Sometimes, though rarely, these structures could spawn with a “Stone Holder” a new block that holds a tool or weapon (similar to the myth of the sword and the stone) these can be moved with silk touch. The player can remove the weapon, which will always be made of iron (that's important for later) and could have some low-level enchamtmants
Occasionally, these can also structures spawn with suspicious dirt, which can be dug up with the brush. Pottery sherds are more common in these structures, but apart from that, they exist only as set dressing ;)
Castle Ruins
A more substantial ruin, Castle Ruins can spawn basically anywhere, but are most common in Highland forests.
Castle Ruins are winding structures, they have a Dungeon below with Gortach or Bog spawners in the cells. The main ruin itself is made up of narrow passageways, imagine a smaller version of the bastion.
There would be numerous loot chests around, but upon opening one, a new mob would be summoned called a ■■■■■■
This mob will be discussed later :)
The Beast's Lair
An underground structure most common under the mountains or Highland forests
Made up of narrow passages leading to open rooms filled with gold blocks, loot chests containing riches and even some new vaults. There's also a shocking amount of skulls littered around
And of course the new boss here: The Wyvern
The Wyvern is a draconic boss mob spawning only hear, it has 4 legs and two wings and is bright red (Note: no. Wyvern never meant a dragon with only 4 limbs. That is a modern addition. Wyvern and dragons were different because of what they breathed)
The Wyvern is very powerful up close and can attack from far away with its poisonous breath
Upon its defeat the Wyvern will drop copious amounts of gold and emeralds that it ate, perhaps even some diamonds if your lucky
Faerie Mounds
Spawning exclusively in the Wisteria Forests, Highland Forests and Mushroom Grottos, these are small dirt hills with a spawner inside and a handful of loot chests
They are essentially fae Dungeons
The mobs that Spawn here will be: you guessed it, discussed later
Clochan + The Dubnos Tunnels
Clochans are typically just an abiant structures common in the Highlands, small cobblestone huts with nothing interesting about them.
But occasionally, they lead to something greater. Some of them spawn with holes leading to a second structure made up of 5 rooms, oriented in this pattern:

In the centre room are 5 stones, each baring a carving of one of the 5 element symbols (note: these are taken from the unused painting textures, with a new one added for wood), at the base of all these stones is a new kind of Vault “The Fae Vault” exclusive to this structure and the beast's lair
The carvings look like this:

The goal of this structure would be to go to each of the challenge rooms, each of with have there own stone with a carving, right click on said carving to indicate you have completed the room, and once all 4 rooms are complete return to the centre room to click on the craving that was not represented by one of the carvings in the other rooms. Getting this right results in the appearance of 5 Fae keys from the stones. These keys can be used on the fey vaults to claim the structures loot
Failure to complete the structure will be indicated by the carvings glowing Red and numerous waves of Mobs spawning
The challenge rooms each contain a challenge pertaining to their element: the fire room is filled with fire, the water room is flooded, the air room requires parkour, the earth room is a Maze and the plant room is filled with Sweet Berries, Goosegrass, Nettles, Thistles, Puffball mushrooms and Faerie Rings (yes I know mushrooms aren't plants, shush.)
On top of that, there are several spawners for the fae in this structure, with various types appearing to attack you. Though these spanners will be deactivated upon completing a room
(Note: carved stones can be moved with silk touch)
They fae Mobs that Spawn in these will be discussed later.
These structures would create unique challenges for the player and would bring more life to these biomes, encouraging exploration.
(Part 1/5)
#ivys hypothetical updates#hypothetical Minecraft updates#hypothetical mc updates#mc ideas#mc suggestions#minecraft ideas#minecraft suggestions#minecraft#part 1/5#part 1
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Boromir Week | Day 6: Change of Fate, Fourth Age, Alternate Universe
Prompt filled for: @boromir-week

Title: Critical failure
Word count: ~1.8k
Summary:
When university students gather around an oak table for a fateful game night, the boundaries between Middle-earth and reality begin to blur. Under the watchful eye of Professor Tolkien, they relive Boromir’s tragedy and Frodo’s choice — and not a single roll of the dice comes without a cost. Even fate must answer to chance.
Note:
Italicized lines are quoted directly from Tolkien.
AO3
Wandering aimlessly at first in the wood, Frodo found that his feet were leading him up towards the slopes of the hill. He came to a path, the dwindling ruins of a road of long ago. In steep places stairs of stone had been hewn, but now they were cracked and worn, and split by the roots of trees. For some while he climbed, not caring which way he went, until he came to a grassy place. Rowan-trees grew about it, and in the midst was a wide flat stone. The little upland lawn was open upon the East and was filled now with the early sunlight. Frodo halted and looked out over the River, far below him, to Tol Brandir and the birds wheeling in the great gulf of air between him and the untrodden isle. The voice of Rauros was a mighty roaring mingled with a deep throbbing boom. He sat down upon the stone and cupped his chin in his hands, staring eastwards but seeing little with his eyes. All that had happened since Bilbo left the Shire was passing through his mind, and he re- called and pondered everything that he could remember of Gandalf ’s words. Time went on, and still he was no nearer to a choice. Suddenly he awoke from his thoughts: a strange feeling came to him that something was behind him, that unfriendly eyes were upon him. He sprang up and turned; but all that he saw to his surprise was Boromir, and his face was smiling and kind.
“…And so it was,” the silver-haired narrator finished in a calm, deliberate tone. His keen yet weary eyes gleamed behind thick horn-rimmed glasses. In his neatly combed silver hair and flawlessly pressed tweed vest bearing a small university crest, it was easy to recognize Professor Tolkien himself — the experienced Game Master and renowned wordsmith.
“Boromir, Frodo,” he continued with characteristic academic composure, “you have exactly one turn left before an unavoidable combat encounter. The vanguard of the Uruk-hai has already crossed the forest boundary and is rapidly approaching your position.”
Boromir leaned forward in his chair, eyes locked on the intricately detailed topographical map spread across the table. He traced the terrain with his gaze, searching its folds and ridges as though it might yield the answer to every unspoken question. Only minutes earlier, he had delivered a passionate, well-reasoned speech, advocating for a detour to the open plains — faster, safer, and more defensible. In his fervor, he nearly elbowed the poised blond graduate student seated beside him, whose impeccable posture and refined elven grace made it clear who was playing Legolas. The elf had calmly but firmly insisted they leave the riverbank at once, relying on his “Elven Sight” ability to predict an imminent and dangerous clash.
As soon as that warning was voiced, Frodo — without hesitation — declared his intent to take the treacherous maze of Emyn Muil. Aragorn and Sam backed him immediately, their faith in the Ring-bearer unwavering. Boromir, stung, had no choice but to accept defeat in the heated debate. Silently fuming, he struggled to understand why they so stubbornly rejected the obvious path forward, one that had garnered the support of most of the table.
If Gandalf were still here, he would’ve brought that obstinate class rep to heel and ended this nonsense, Boromir thought bitterly, watching the dramatic scene unfold.
Around the massive oak table that served as their battlefield, a very particular academic hierarchy had taken root. The wise wizard — the group’s unquestioned authority — was, in real life, the department head. The noble heir Aragorn was played by a mild-mannered history lecturer from an old academic family. Gimli, all rumbling voice and booming laugh, ran the metallurgy lab. Legolas was a graceful, sharp-tongued PhD candidate. Frodo and Sam were earnest third-year philology students, while Merry and Pippin were the university’s most chaotic and irrepressible freshmen.
Boromir himself was still a newcomer. He had only recently joined the group, and the only player he truly knew was Gandalf — the very same professor who had, much to Boromir’s dismay, been called away from the session just an hour earlier due to a power outage on campus. Muttering something about “chasing away the darkness,” the old doctor of philology had hurried off, leaving his sole ally in unfamiliar company.
“Can I try once more to persuade him to move toward Gondor?” Boromir asked, adjusting his sweater and rubbing his temple. The game was dragging, but giving up wasn’t his way.
“You’ve already tried,” the Game Master said with a shrug. “No more rolls — the decision is made. But you can attempt to convince him of something else.”
Boromir frowned, eyes scanning his character sheet.
“Then I’ll try to persuade Frodo to give me the Ring,” he said, tapping the page where one motivation stood clear: To possess the One Ring. “It’s literally written in my backstory. Character development and all that.”
“Are you trying to persuade him,” the Game Master asked, raising an eyebrow, “or are you ready to use force? Statistically, you outmatch him by a considerable margin.”
“Persuasion only,” Boromir said firmly, adjusting his shirt collar. “I may have fallen to temptation, but I won’t stoop to violence against little ones.” He sighed deeply and, summoning all his resolve, rolled the twenty-sided die.
The die clattered loudly across the oak table, drawing held breaths from everyone around. When it finally came to rest — showing a natural one — a collective, muffled groan of disappointment echoed through the room. Frodo, by contrast, rolled a stunning nineteen.
“Not only do you fail,” said the Game Master in a soft but piercing tone, “you completely shatter what little trust remained. In a moment of desperation, under the Ring’s growing shadow, you… make a fatal decision to seize it by force. Roll again.”
With a trembling hand, Boromir cast the die once more. A three. Another devastating failure.
Behind the GM screen, Professor Tolkien frowned slightly, his brows knitting.
“Frodo swiftly evades your lunge, a large boulder coming between you. In a panic, he tears the chain from his neck, slips the Ring onto his finger — and vanishes from sight. You, stunned by your own actions, stumble blindly across the glade, trip over a root, and fall. The weight of what you’ve done crashes down upon you like an avalanche. You bury your face in trembling hands, overcome with guilt and tears of repentance.”
A heavy silence settled over the room, broken only by hushed whispers. In a far corner, Legolas and Gimli had drifted out of the scene, animatedly discussing specs of a new lab furnace. Aragorn, ever noble, immediately rushed after the vanished Frodo, while Sam, despite his painfully low Dexterity, scrambled after his master with steadfast devotion. Suddenly, Merry and Pippin — the ever-chaotic hobbit duo — charged into the approaching ranks of orcs with the reckless enthusiasm of true freshmen, yelling their trademark battle cry:
“Lerooooooy!”
Professor Tolkien allowed himself a quiet smile, clearly pleased that the story was unfolding along the most dramatic possible path.
“Prepare yourselves, gentlemen,” he intoned.
The table fell silent, each player sensing the turning point ahead.
“Boromir,” said the Game Master, voice carrying a solemn edge, “your moment has come. Will you stand in defense of your young companions, knowing the price may be far too steep?”
“Do I even have a choice?” Boromir muttered with a bitter smile, gripping the die tightly before lowering it into an old ceramic dice bowl, its rim etched with runes. “I am a son of Gondor. It is my duty to protect the weak.”
But fate, it seemed, was no longer on his side. On this truly fateful day, even the noblest resolve would not escape its cruel mockery.
“You charge forward, placing yourself between Merry, Pippin, and the oncoming horde,” Tolkien declared, slowly adjusting his glasses, eyes fixed on the player. “Roll a d20 to test your Reflex.”
The dice roll, and the world holds its breath.
The twenty-sided die gleamed dimly in the lamplight, spinning slowly in the ancient ceramic bowl as if weighing the fate of a hero—until it stopped. A natural one. Fate, sealed like a verdict.
“Before the orcs complete their attack,” Boromir said quickly, scanning his character sheet with rising urgency, “I activate Horn of Gondor. I want to shift initiative order, give my allies a chance to act before the enemy.”
The professor nodded slowly, approving the tactical choice, but the orcs were already rolling. The die hit the table. A natural twenty. A perfect hit.
“The first black-feathered arrow, loosed by an Uruk-hai’s powerful arm, strikes true,” the Game Master intoned, “driving deep into your chest. But the mighty sound of the Horn of Gondor echoes through the woods, bouncing from rock to rock, calling for aid.”
A desperate saving throw. Boromir rolled. Another one. As if the gods themselves were mocking him.
“The second arrow hisses through the air and buries itself mercilessly in your side,” continued the professor. “But far off in the forest, the footsteps of allies can already be heard — Legolas and Aragorn answering the horn’s ancient call.”
One final chance to escape destiny. One final throw of the dice. Another one.
“The third arrow completes its grim work. Your fate is sealed, brave son of Gondor. But know this — your final, heroic cry was not in vain. The memory of your sacrifice will live on.”
“This is a damn conspiracy!” Boromir cried out, covering his suddenly pale face with trembling hands. “Three ones in a row? Are you kidding me?”
“The dice are fickle and cruel, my valiant friend,” said the GM, voice soft with sympathy. “But take heart — your horn was heard. Your allies will have a chance to protect the hobbits. Your sacrifice was not meaningless.”
While Legolas scrambled, flustered, to remember his healing abilities, and Aragorn frantically rushed forward with what little medicinal skill he had, Gimli slammed a fist on the table, bellowing with rage and ready to charge into battle to protect the young ones. Boromir stared down bitterly at his character sheet. He slowly crumpled it in his fist, propped his cheek on one hand, then, with unsteady fingers, took out his phone and began typing a short, despair-filled message to Faramir:
You: I take it back. Next time, I won’t fight you for the Rivendell Uni expedition slot. Seriously. I just got hit by three nat 1s in a row… Also, the pompous guy’s chubby friend just roasted me in verse like we were in a damn rap battle.
Little Brother: Well… you asked for it. You even talked Dad into sending you. What was it you said? “There are no direct routes”?
You: There weren’t! My legs are dead from all this trekking. At least I’m heading home soon. Pub night?
Little Brother: Pub night. But don’t whine and don’t make that face like you just ate the world’s sourest lemon.
The game continued. Far away, the Anduin thundered on. Birds wheeled above Tol Brandir. And a small hobbit, invisible to all mortal eyes, took his first steps toward losing himself — and saving the world.
Inspired by:
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gundam Wing: Minutia and Trivia
On my long and winding way down research rabbit holes, I often stumble on bits and pieces of trivia that I find quite interesting, but don't really fit anywhere in my usual commentary on Gundam canon and are far too niche and inconsequential to merit a post of their own. HOWEVER. Since I know in my heart that you, dear reader, are also the sort of person for whom background details of the absolute least consequential variety are a source of delight and inspiration, I am compiling some of my discoveries here, and perhaps if I find more, there will be follow up posts. This one happens to be, in a very loose sense, mostly about Romefeller, OZ, and its Special Eyebrow People, because that is where my brain worms are currently converging. Here is my collection of useless trivia. I lay them at your feet like weird pebbles. Look at them. They're neat.

1. The Daily Kingdom Newspaper

It's quite likely that this has already been done, but in the grand spirit of this blog, I have decided to take the path of highest effort for the stupidest reason, and transcribed this paper. This page of After Colony news, ostensibly from July 14th, A.C. 195, appears to be reporting on events that happened towards the end of World War II. It's apparently been a slow news day for the Sanc Kingdom press for several centuries. I found myself getting kind of wrapped up in the stories and was disappointed I couldn't turn the page and find out what happened next. (I mean, I know what happened next, broadly speaking.) Of particular interest were Henri and Camille Dreyfus, Swiss chemists who made a lot of innovations during both world wars. ...They were also apparently noted OZ supporters? Well, what can you expect from a big industrial supplier of*checks notes* acetyl intermediates.


2. The OZ doggy
Pictured below: Treize's well-heeled hunting pet
and a dog is there too *BA-DUM tsch!*
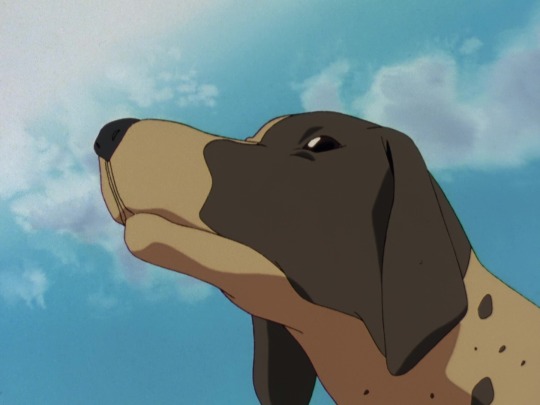
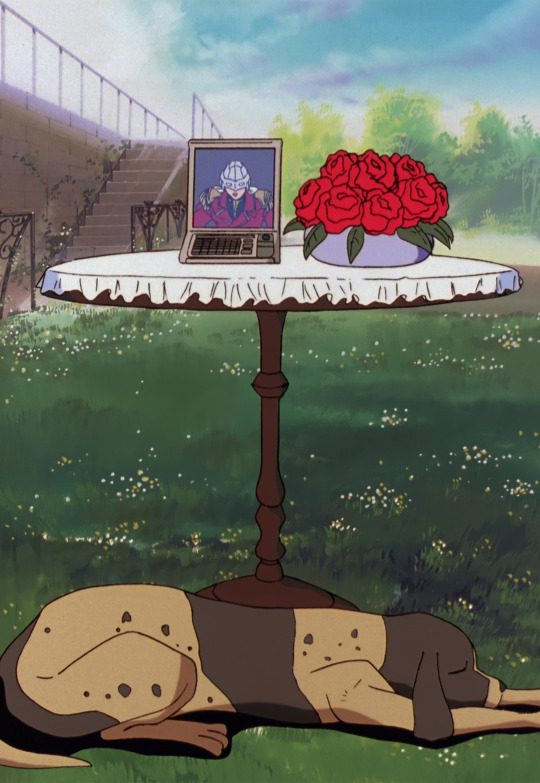


This spotty and behaved hound is a real breed of hunting dog, the German Short-haired Pointer, or GSP! Did you know this, dear reader? I did not know this. This is new Dog Lore to me.
from the wiki: "It is a pointer and retriever, an upland bird dog, and water dog. The GSP can be used for hunting larger and more dangerous game. It is an excellent swimmer but also works well in rough terrain. It is tenacious, tireless, hardy, and reliable. German Shorthaired Pointers are proficient with many different types of game and sport, including trailing, retrieving, and pointing pheasant, quail, grouse, waterfowl, raccoons, opossum, and even deer."
Seems like a perfect bird-hunting companion for Mr. Treize. She'll probably go retrieve the beautiful red phoenix he murdered. I've decided she's named Oscar (after the Rose of Versailles) and she is a very good girl. Braver Oscar! Braver Hund!



3. Luxembourg Castle
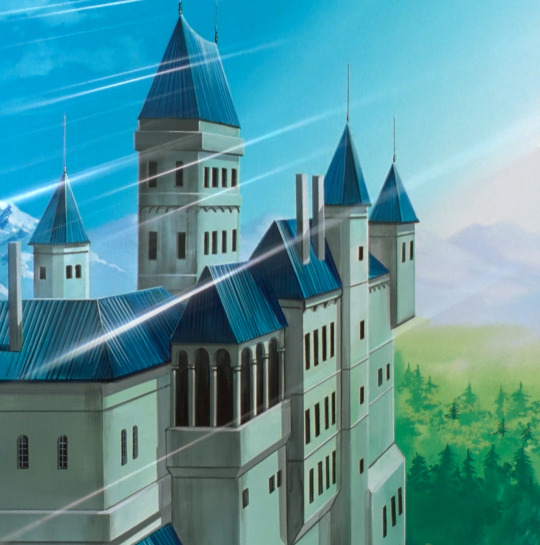
This is Treize's abandoned Disney castle in Luxembourg. I owe the background artists of this scene an apology, for in my heart I assumed this was a random assemblage of spare castle-parts they found at Ludwig II's rummage sale. Reader, I was wrong:
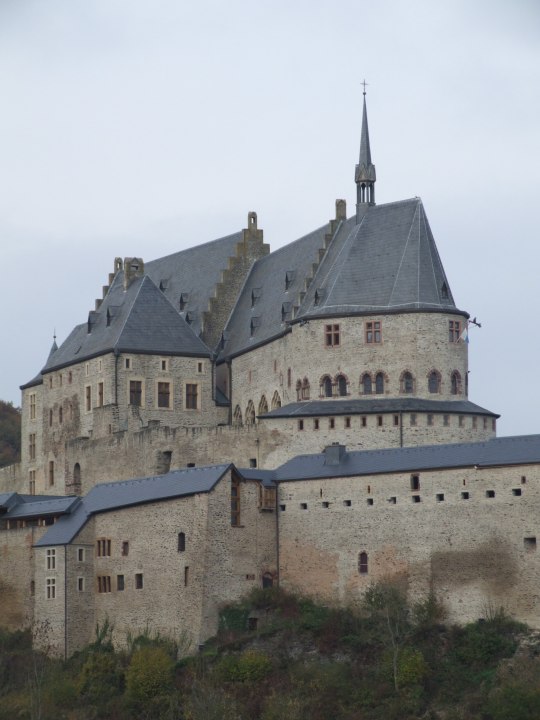



THIS is Schloss Viandin, a restored castle in Luxembourg. Look at this place, it's gorgeous! You can hardly tell there's a secret mobile suit bunker in the basement. Frankly, I'm jealous I'm not being confined there, Treize! Stop sulking in the catacombs and go relax in the pretty princess bed until you feel better. Gaze upon the signed picture of Patrick Swayze; let him inspire you.


4. Romefeller's Secret
This one comes to us from the Battlefield of Pacifists manga, which, I've learned, is pretty good actually. (I mean it's not GOOD good, but it contains some interesting stuff). Now, come: I am taking you with me on this journey:


I feel extremely vindicated knowing that there's semi-canonical support for my theory that the Romefeller aristobrats are Austrian. I knew it. I KNEW IT. According to this manga, Romefeller was officially founded in Vienna-- the wording is a little ambiguous in this translation, but if Romefeller had members joining it in 1862, then it had to have existed in some form since then-- which means that the "Glorious Year" of 1956 is something other than its founding date. So what exactly happened in 1956? As I am a hack and fraud, and have been one all my life, I have looked to wikipedia for guidance. Mostly what was happening was the Cold War, colonialism, uprisings, Elvis, research and debate over artificial intelligence, both the hard drive disk and the snooze-button alarm clock being invented, Japan joining the UN, and wait what's this--

COMPUTER, ENHANCE:
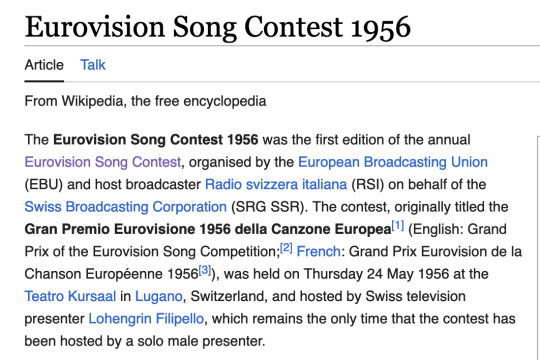
...My god...
It's all coming together.
Eurovision is a plot by Romefeller.
The evidence is all here. There is simply no other conclusion we can come to.
--For this, and many other reasons that are well beyond the scope of a fandom blog, you should probably boycott them.
I rest my case.

5. The Romefeller Coat of Arms
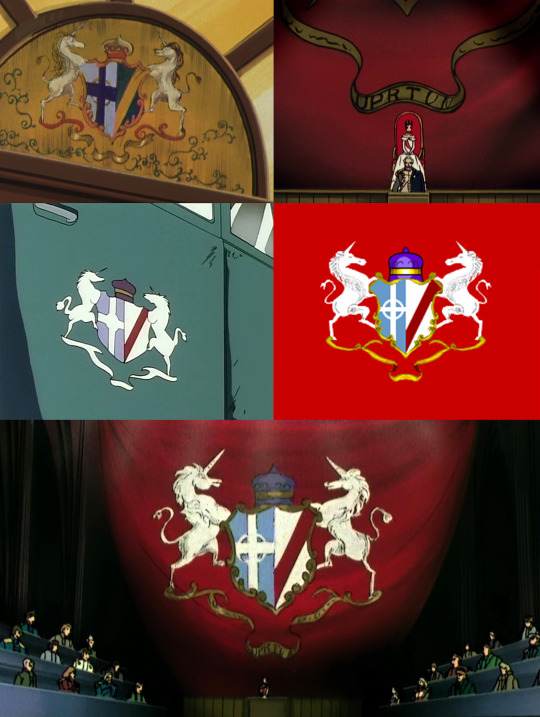

I'm no vexillologist, and my heraldic experience is limited to adoptable pixel dragons, but what I am is an insane person with too much time on their hands. And so, to the best of my ability, I have blazoned the Romefeller coat of arms:
Supporters: Two Unicorns Rampant
Crown: Purpur Crown of Peerage or Lord of Parliament
Escutcheon: Heater with Two Engrailed Wedge Top - party per pale (halved vertically)
Blazon: Sinister (Right): Argent, Bend Sinister Sanguine; Dexter (Left): Bleu Celeste, Charged with a Ringed (or Celtic) Cross Argent
Motto Scroll: UPRTUN or UPRTVN
--I don't know what UPRTVN is meant to stand for, but there are truly SO many ways you could play Latin Mad Libs and get a reasonable-sounding answer. At a stab, knowing Romefeller's priorities and values, I would guess it probably contains a, you know, "Unity/Peace/Rule/Tradition/Victory/Necessity", "Unity Through The Rule of Tradition Is Our Victory", or some such deeply worrying thing. Take your pick really.

6. "Herbst" / "Autumn"
The Rilke poem Treize quotes in "Frozen Teardrop" is not terribly difficult to find online, but if you're not sure what you're looking for it can be difficult because he has multiple poems about Autumn, and Autumn Day is perhaps better known; also the internet is absolutely filthy riddled with despicable bots and farmed content that has lost its attributions, so you do have to dig to find where different translations have come from (bless this very Web 1.0 page for carrying on the lord's work in basic html). Here is the original in German, and two complimenting translations:
Herbst -Rainer Maria Rilke Die Blätter fallen, fallen wie von weit als welkten in den Himmeln ferne Gärten; sie fallen mit verneinender Gebärde. Und in den Nächten fällt die schwere Erde aus allen Sternen in die Einsamkeit. Wir alle fallen. Diese Hand da fällt. Und sieh dir andre an: es ist in allen. Und doch ist Einer, welcher dieses Fallen unendlich sanft in seinen Händen hält.
This translation by Horst A. Scholz (linked here so I don't get into trouble) is the most spare and one-to-one translation into English I've found-- I always appreciate having a comparison between the very literal meanings and a more creative reconstruction when I'm reading translated poetry.
Meanwhile on the other end of the spectrum, this translation by Robert Bly is very freeform and agnostic; for my own purposes, I think the use of "Space" instead of "Heaven" happens to fit nicely with the themes of Gundam:
Autumn -translation by Robert Bly The leaves are falling, falling as if from far up, as if orchards were dying high in space. Each leaf falls as if it were motioning "no." And tonight the heavy earth is falling away from all other stars in the loneliness. We're all falling. This hand here is falling. And look at the other one. It's in them all. And yet there is Someone, whose hands infinitely calm, holding up all this falling.
#gundam wing#parsing post#tinyozlion pgw#Trivia and Minutia#Romefeller Foundation#Treize Khushrenada
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
Xenofiction (& similar) Media Masterpost
Editable Google Doc Link here
PS. This list is for keeping track only. This is not a recommendation list and I won't be advocating for any Work, Author or Company listed. There will be footnotes about a work/author for undesirable behaviour or themes if necessary.
This is a WIP and will be updated whenever I have the time to. Feel free to recommend works or inform me about an author so I can update the post. Be Aware works on this list might have been cancelled or on indifinitive Hiatus and not all works are available on English.
Sections:
Literature
Comic Books & Graphics Novels
Picture Books
Indie Written Works
Webcomics
Manga
Animated Series
Live-Action & Hybrid shows
Webseries
Short Films
Animated Films
Live Action & CGI Assisted Movies
Documentary
Theather
Videogames
Online Browser Games
Table Top Games
Music
Other Online Projects
Youtubers
Gen. Videos
Worlds
Franchises
To search is Ctrl + F (Windows) or Command-F (MacOS), on phone browser you have "Find in page" (Drop menu at top right)
Literature
A
Age of Fire - E. E. Knight
Adventure Lit their Star - Kenneth Allsop
Alien in a Small Town - Jim Cleaveland
Alien Chronicles (Literature) - Deborah Chester
Animal Farm - George Orwell
Animorphs - K. A. Applegate
Am an Owl - Martin Hocke
At Winters End - Robert Silverberg
Avonoa - H.R.B. Collotzi
Astrid and Cerulean: A Parrot Fantasy - Parasol Marshall-Crowley
A Wolf for a Spell - Karah Sutton
The African Painted Wolf Novels - Alexander Kendziorski
The Alchemist's Cat - Robin Jarvis
The Amazing Maurice and his educated rodents - Terry Pratchet
The Amity Incident - C. M. Weller
The Ancient Solitary Reign - Martin Hocke
The Animals of Farthing Wood series - Colin Dann
The Art of Racing in the Rain - Garth Stein
The Author of Acacia Seeds and Other Extracts from the Journal of Therolinguistics - Ursula K. Le Guin
A Magical Cat Named Kayla: Whiskers of Enchantment -Carlos Juárez [AI Cover]*
The Animal Story Book - Various Authors [Editor: Andrew Lang]
Abenteuer im Korallenriff - Antonia Michaelis [DE]
B
Bambi: A life in the forest & Bambi Children - Felix Salten
Bamboo Kingdom series - Erin Hunter
Bazil Broketail - Christopher Rowley
Beak of the Moon & Dark of the Moon - Philip Temple
Bears of the Ice series - Kathryn Lasky
Beasts of New York - Jon Evans
Beautiful Joe - Margaret Marshall Saunders
Beyond Acacia Ridge - Amy Clare Fontaine
Birddom - Clive Woodall
Bird Brain - Guy Kennaway
Black Beauty - Anna Sewell
Blitzcat - Robert Westall
Blizzard Winds - Paul Koch
Books of the Raksura - Martha Wells
Braver: A Wombat's Tale - Suzanne Selfors & Walker Ranson
Bravelands series- Erin Hunter
Broken Fang - Rutherford Montgomery
Bunnicula series - Deborah Howe & James Howe
Burning Stars - Rurik Redwolf
A Black Fox Running - Brian Carter
A Blue So Loud - Tuesday
The Ballard of The Belstone Fox - David Rook
The Bear - James Curwood
The Bees - Laline Paull
The Biography of a Silver Fox - Ernest Thompson Seton
The Blue Cat of Castle Town - Catherine Cate Coblentz
The Book Of Chameleons - José Eduardo Agualusa
The Book of the Dun Cow - Walter Wangerin Jr.
The Book of Night with Moon - Diane Duane
The Books of the Named series - Clare Bell
The Bug Wars - Robert Asprin
The Builders - Daniel Polansky
C
Call of the wild - Jack London
Callanish - William Horwood
Catwings - Ursula K. Le Guin
Cat Diaries: Secret Writings of the MEOW Society - Betsy Byars, Betsy Duffey & Laurie Myers
Cat House - Michael Peak
Cat Pack - Phyllis Reynolds Naylor
Cats in the city of Plague - A.L Marlow
Celestial Heir series - Chester Young
Charlotte's Web - E. B. White
Chet and Bernie mysteries - Spencer Quinn
Chia The Wildcat - Joyce stranger
Child of the Wolves - Elizabeth Hall
Clarice the Brave - Lisa McMann
Cry of the Wild - Charles Foster
Coyote's Wild Home - Barbara Kingsolver; Lily Kingsolver & Paul Mirocha
Coyote Series - Michael Bergey
Crocuta - Katelyn Rushe
Coorinna: A Novel of the Tasmanian Uplands - Erle Wilson
Cujo - Steven King
The Calatians Series - Tim Susman
The Cats of Roxville station - Jean Craighead Georde
The Chanur Novels - C. J. Cherryh
The Cold Moons - Aeron Clement
The Color of Distance || Through Alien Eyes - Amy Thomson
The Conquerors - Timothy Zahn
The Council of Cats - R. J. F.
The Cricket in Times Square - George Selden
The Crimson Torch - Angela Holder
The Crossbreed - Allan Eckert
The Crucible of Time - John Brunner
D
Darkeye series - Lydia West
Deadlands: The Hunted - Skye Melki-Wegner
Demon of Undoing - Andrea I. Alton
Desert Dog - Jim Kjelgaard
Dinotopia - James Gurney, Alan Dean Foster
Doglands - Tim Willocks
Dimwood Forest series - Avi
A Dog's Life: The Autobiography of a Stray - Ann M. Martin
A Dog's Porpoise Duology - M. C. Ross
Dogs of the Drowned City - Dayna Lorentz
A Dog's Purpose series - W. Bruce Cameron
Dolphin Way: Rise of the Guardians - Mark Caney
Domino - Kia Heavey
Douglas' Diary - Andrew John
DragonFire series - Lewis Jones Davies
Dragon Fires Rising - Marc Secchia
Dragon Hoard and Other Tales of Faerie - Cathleen Townsend
Dragons and Skylines series - Rowan Silver
Dragon Prayers - M.J. McPike
Dragons of Mother Stone series - Melissa McShane
Dragon Girls Series - Maddy Mara
The Deptford Mice series - Robin Jarvis
The Dogs of the Spires series - Ethan Summers
The Dragons of Solunas series - H. Leighton Dickson
The Duncton Chronicles - William Horwood
The Destiny of Dragons - J.F.R. Coates
The Diary Of A House Cat - Ileana Dorobantu
Dogtown - Katherine Applegate & Gennifer Choldenko
Die schwarze Tigerin - Peer Martin [DE]
Die weiße Wölfin - Vanessa Walder [DE]
Die Wilden Hunde Von Pompeii - Helmut Krausser [DE]
Das wilde Mäh - Vanessa Walder [DE]
E
The Eyes and the Impossible - Dave Eggers
Eclosión - Arturo Balseiro [ES]
Ein Seehund findet nach Hause - Antonia Michaelis [DE]
F
Fantastic Mr. Fox - Roald Dahl
Faithful Ruslan - Georgi Vladimov
Feather and Bone: The Crow Chronicles - Clem Martini
Feathers & Flames series - John Bailey
Felidae series (1) - Akif Pirinçci
Fifteen Rabbits - Felix Salten
Fire, Bed & Bone - Henrietta Branford
Fire of the Phoenix - Azariah Jade
Fluke - James Herbert
Firefall series - Peter Watts
Firebringer - David Clement-Davies
Flush: A Biography Book - Virginia Woolf
Fox - Glyn Frewer
Foxcraft series - Inbali Iserles
Frightful’s Mountain - Jeanie Craighead George
Frost dancers: A story of hares - Garry Kilworth
The Familiars series - Adam Jay Epstein
The Fifth - Saylor Ferguson
The Firebringer series - Meredith Ann Pierce
The Fox and The Hound - Daniel P. Mannix
The Forges of Dawn - E. Kinsey
Freundschaft im Regenwald - Peer Martin [DE]
(1) Felidae's Author - Akif Pirinçci - is known to be a Xenophobic, Anti-muslim, Anti-Lgbt and Extreme Right-Wing guy (A N4zi by his on words). Won't be going onto details just know he has a non-fiction work called "Germany Gone Mad: The Crazy Cult around Women, Homosexuals and Immigrants." His works has been out of print ever since.
G
Guardian Cats and the lost books of Alexandria - Rahma Krambo
Guardians of Ga'Hoole series - Kathryn Lasky
Good Omens - Neil Gaiman & Terry Pratchett
Griffin Quest - Sophie Torro
Gryphon Insurrection series - K. Vale Nagle
The Ghost and It's Shadow - Shaun Hick
The Golden Eagle - Robert Murphy
The Golem and the Jinni - Helene Wecker
The Good Dog - Newbery Medalist
The Guardian Herd series - Jennifer Lynn Alvarez
The Goodbye Cat - Hiro Arikawa
The Great Timbers - James A. Kane
H
Haunt Fox - Jim Kjelgaard
Haven: A Small Cat's Big Adventure - Megan Wagner Lloyd
Heavenly Horse series - Mary Stanton
Hive - Ischade Bradean
Horses of Dawn series - Kathryn Lasky
House of Tribes - Garry Kilworth
Hunter's Moon/Foxes of First dark - Garry Kilworth
Hunters Universe series - Abigail Hilton
A Hare at Dark Hollow - Joyce Stranger
The Hundred and One Dalmatians & The Starlight Barking - Dodie Smith
The Hunt for Elsewhere - Beatrice Vine
Hollow Kingdom Duology - Kira Jane Buxton
I
I am a Cat - Natsume Sōseki
I, Scheherezade: Memoirs of a Siamese Cat - Douglass Parhirst
In the Long Dark - Brian Carter
The Incredible Journey - Sheila Burnford
Im Reich der Geparde - Kira Gembri [DE]
J
Joe Grey series - Shirley Rousseau Murphy
Jonathan Livingston Seagull - Richard Bach & Russell Munson
Julie of the Wolves - Jeanie Craighead George
The Jungle Book - Rudyard Kipling
Journey to the West - Wu Cheng'en
K
Kävik the Wolf Dog - Walt Morey
Kazan duology - James Curwood
Kine Saga - Alan Lloyd
Kona's Song - Louise Searl
The Killers - Daniel P. Mannix
Kindred of the Wild - Charles G.D Roberts
König der Bären - Vanessa Walder [DE]
L
Lassie Come-Home - Eric Knight
Last of the Curlews - Fred Bodsworth
Lazy Scales - D.M. Gilmore
Legends of Blood series - Ethan Summers
A Legend of Wolf Song - George Stone
Luna the Lone Wolf - Forest Wells
Lupus Rex - John Carter Cash
Lutapolii: White Dragon of the South - Deryn Pittar
The Last Unicorn - Peter S. Beagle
The Labrador Pact & The Last Family in England - Matt Haig
The Last Dogs - Christopher Holt
The Last Eagle - Daniel P. Mannix
The Last Great Auk - Allan Eckert
The Last Monster on Earth - L.J. Davies
The Life Story of a Fox - J. C. Tregarthen
The Lost Rainforest series - Eliot Schrefer & Emilia Dziubak
The Lost Domain - Martin Hocke
The Last Whales: A Novel - Lloyd Abbey
M
Mammoth Trilogy - Stephen Baxter
Manxmouse: The Mouse Who Knew No Fear - Paul Gallico
Marney the Fox - Scott Goodall & John Stokes
Mattie: The story of a hedgehog - Norman Adams, & G.D. Griffiths
Matriarch: Elephant vs. T-Rex - Roz Gibson
Midnight's Sun - Garry Kilworth
Migon - P.C. Keeler
Minado The Devil - Dog - Erle Wilson
Monkey Wars - Richard Kurti
Mouseheart Series - Lisa Fiedler
The Mistmantle chronicles - M.I. McAllister
The Mountain Lion - Robert Murphy
The Mouse Butcher - Dick King-Smith
The Mouse Protectors Series - Olly Barrett
Maru - Die Reise der Elefanten - Kira Gembri [DE]
N
New Springtime series - Robert Silverberg
Nightshade Chronicles - Hilary Wagner
Nugly - M. C. Ross
Nuru und Lela - Das Wunder der Wildnis - Kira Gembri [DE]
O
Old One-Toe - Michel-Aimé Baudouy
Of Birds and Branches - Frances Pauli
Outlaw Red - Jim Kjelgaard
The Old Stag - Henry Williamson
The One and Only Ivan - Katherine Applegate
P
Painted Flowers - Caitlin Grizzle
Pax & Pax: Journey Home - Sara Pennypacker
Petrichor - C.E. Wright
The Plague Dogs - Richard Adams
The Pit - Elaine Ramsay
Pride Wars Series - Matt Laney
A Pup Called Trouble - Bobbie Pyron
The Peregryne Falcon - Robert Murphy
Pork and Others - Cris Freddi
Q
Queen in the Mud - Maari
Quill and Claw series - Kathryn Brown
R
Rak: The story of an Urban Fox - Jonathon Guy
Ramblefoot by Ken Kaufman
Rats of Nimh series - Robert C. O'Brien
Raven Quest - Sharon Stewart
Ravenspell Series - David Farland
Raptor Red - Robert T. Bakker
Red Fox - Charles G. D. Roberts
Redwall series - Brian Jacques
Rose in a Storm - Jon Katz
Rufus - Rutherford Montgomery
Run With the Wind series - Tom McCaughren
Runt - Marion Dane Baeur
Rustle in the Grass - Robin Hawdon
Rusty - Joyce Stranger
The Remembered War series - Robert Vane
The Rescuers series - Margery Sharp
The Red Stranger - David Stephen
The River Singers & The Rising - Tom Moorhouse
The Road Not Taken - Harry Turtledove,
The Running Foxes - Joyce Stranger
Revier der Raben - Vanessa Walder [DE]
S
Salar the Salmon - Henry Williamson
Scary Stories for Young Foxes Duology - Christian McKay Heidicker
Scaleshifter series - Shelby Hailstone Law
Shadow Walkers - Russ Chenoweth
Scream of the White Bears - David Clement-Davies
Seekers saga - Erin Hunter
Serpentia Series - Frances Pauli
Shadows in the Sky - Pete Cross
Shark Wars Series - EJ Altbacker
Silverwing series - Kenneth Oppel
Silver Brumby series - Elyne Mitchell
Sirius - Olaf Stapledon
SkyTalons Series - Sophie Torro
Solo's Journey - Joy Aiken Smith
Sky Hawk - Gill Lewis
Snow Dog - Jim Kjelgaard
Song of the River - Soinbhe Lally
Spirit of the West series - Kathleen Duey
Survivors series - Erin Hunter
Stray - A.N Wilson
String Lug the Fox - David Stephen
Swashbuckling Cats: Nine Lives on the Seven Seas - Rhonda Parrish & Co.
Swordbird series - Nancy Yi Fan
The Sheep-Pig - Dick King-Smith
The Sight & Fell - David Clement-Davies
The Silent Sky - Allan Eckert
The Silver Claw - Garry Kilworth
The Stoner Eagles - William Horwood
The Stink Files - Jennifer L. Holm & Jonathan Hamel
The Snowcat Prince - Dina Norlund
The Story Of A Seagull And The Cat Who Taught Her To Fly - Luis Sepúlveda
The Story of a Snail Who Discovered the Importance of Being Slow - Luis Sepúlveda
The Story of a dog called Leal - Luis Sepúlveda
The Story of a Red Deer - John Fortescue
The Summer King Chronicles - Jess E. Owen
Schogul, Rächer der Tiere - Birgit Laqua [DE]
Stadt der Füchse - Vanessa Walder [DE]
T
Tailchaser's Song - Tad Williams
Tarka the Otter - Henry Williamson
Three Bags Full - Leonnie Swann
Thy Servant a Dog - Rudyard Kipling
Tomorrow's Sphinx - Clare Bell
Torn Ear - Geoffrey Malone
Thor - Wayne Smith
Trickster - Tom Moorhouse
Two Dogs and a Horse - Jim Kjelgaard
The Tale of Despereaux - Kate DiCamillo
The Travelling Cat Chronicles - Hiro Arikawa
The Trilogy of the Ants - Bernard Werber
The Trumpet of the Swan - E. B. White
The Tusk That Did the Damage - Tania James
The Tygrine cat - Inbali Iserles
U
Ultimate Dragon Saga - Graham Edwards
Under the Skin - Michel Faber
V
Varjak Paw duology - S.F Said
Vainqueur the Dragon series - Maxime J. Durand
W
War Bunny series - Christopher St. Jhon
War Horse - Michael Morpurgo
War Queen - Illthylian
Warrior Cats series - Erin Hunter
Watership Down/Tales of Watership Down - Richard Adams
Ways of Wood Folk - William J. Long
Welkin Weasels series - Garry Kilworth
West of Eden - Harry Harrison
Whalesong Trilogy - Robert Siegel
Whale - Jeremy Lucas
Whispers in the Forest - Barbara Coultry
White Wolf - Henrietta Branford
White Fang - Jack London
White Fox Series - Jiatong Chen
Wings trilogy - Don Conroy
Wild Lone - Denys Watkins-Pitchford
Wild Animals I Have Known - Ernest Thompson Seton
Willow Tree Wood Series - J. S. Betts
Wings of Fire series - Tui T. Sutherland
Winterset Hollow - Jonathan Edward Durham
Wolf: The Journey Home | Hungry for Home: A Wolf Odyssey - Asta Bowen
Wolf Brother series - Michelle Paver
Wolf Chronicles - Dorothy Hearst
Wolves of the Beyond Series - Kathryn Lasky
Woodstock Saga - Michael Tod
A Whale of the Wild - Rosanne Parry
A Wolf Called Wander - Rosanne Parry
The Waters of Nyra - Kelly Michelle Baker
The Wolves of Elementa series - Sophie Torro
The Wolves of Time - William Horwood
The Wolf Chronicles Series - Teng Rong
The Way of Kings - Louise Searl
The White Bone - Barbara Gowdy
The White Fox/Singing Tree - Brian Parvin
The White Puma - Ronald Lawrence
The Wild Road & The Golden Cat - Gabriel King
The Wildings & The Thousand names of darkness - Nilanjana Roy
The Wind in the Willows - Kenneth Grahame
The Wind Protect You - Pat Murphy
The Wolves of Paris - Daniel P. Mannix
Y
Yellow eyes - Rutherford Montgomery
The Year Of The Dinosaur - Edwin H. Colbert
Z
Zones of Thought series - Vernor Vinge
Z-Verse series by R.H
Comic Books/Graphic Novels
Animosity - Marguerite Bennett
Age of Reptiles - Ricardo Delgado
Legend - Samuel Sattin Koehler
Mouse Guard - David Petersen
Pride of Baghdad - Brian K. Vaughan & Niko Henrichon
Rover Red Charlie - Garth Ennis & Michael Dipascale
Stray Dogs - Tony Fleecs & Trish Forstner
We3 - Grant Morrison & Frank Quitely
Beasts of Burden - Evan Dorkin & Jill Thompson
LOBO: Canine Crusader of the Metal Wasteland - Macs-World-Ent
The Sandman: Dream of a Thousand Cats - Neil Gaiman
Animal Castle - Xavier Dorison & Felix Delep
Blacksad Series - Juan Díaz Canales & Juanjo Guarnido
Scurry - Mac Smith
The Snowcat Prince - Dina Norlund
Rankless - Maggie Lightheart
Animal Pound - Tom King & Peter Gross
Animal Castle - Xavier Dorison & Felix Delep
BlackSad - Juan Díaz Canales & Juanjo Guarnido
Picture Books
Steve the Dung Beetle: On a Roll - Susan R. Stoltz & Melissa Bailey
Hot Dog - Doug Salati
The Rock from the Sky - Jon Klassen
Whoever Heard of a Flying Bird? - David Cunliffe & Ivan Barrera
A Cat Named Whiskers - Shana Gorian
Ocean Tales Children's Books Series - Sarah Cullen & Zuzana Sbodová
Jake the Growling Dog - Samantha Shannon
Indie Written Works
Fins Above Series - MIROYMON
Journey of Atlas - Journey of Atlas
Webcomics
A
Africa - Arven92
After Honour - genstaelens
Awka - Nothofagus-obliqua
Arax - Azany
Amarith - Eredhys
The Apple's Echo - Helianthanas
Alone - Magpeyes
B
The Blackblood Alliance - KayFedewa
The Betrothed - Kibisca
Black Tyrant - Zapp-BEAST
Blue - HunterBeingHunted
Beast Tags - TheRoomPet
Spy - Utahraptor93
Be Reflected in my Eyes - Aquene-lupetta
C
Carry your voice - TacoBella
Caelum Sky - ALRadeck
Crescent Wing - Mikaley
Crescent Moonlight - AnimalCrispy
City of Trees - SanjanaIndica
Corpse - doeprince/ratt
D
Darbi - Sherard Jackson
The Devils Demons - Therbis
Doe of Deadwood - Songdogx
Dyten - Therbis
Desperation - PracticelImagination
E
Equus Siderae - Dalgeor
Empyrean - Leonine-Skies
Enchantment - FeralWolf1234
F
Fox Fires - Pipilia
Forget me Not - Nitteh
Fjeld - Dachiia
Felinia - Rainy-bleu
G
Golden Shrike - doeprince/ratt
Ghost of the Gulag - David Derrick Jr.
H
Horse Age - BUGHS-22
Hiraeth - AFlameThatNeverDies
Half-Blood - majkaria
Horns of Light - ThatMoonySky
I
I Hope So - Detective Calico
The Ivory Walk - TacoBella
I'm not Ready - Wolfkingdom372
J
Jet and Harley - doeprince
K
Kestrel Island - Silverphoenix
Kin - Fienduredraws
KuroMonody - IrisBdz
Krystal - Nitteh
The King of Eyes - CloverTailedFox09
L
Legend of Murk - Azany
LouptaOmbra - Loupta Ombra (OngakuK, MlleNugget & joeypony)
Leopards bring rain - Kyriuar
M
Mazes of Filth - petitecanine
Minimal All You Are - mike-princeofstars
N
Nine Riders - SpiriMuse
No Man's Land - TacoBella
Never seen the Day - R3dk3y
Norra - shadowmirku
O
Obsidian Fire - SolinaBright
Oren's Forge - teagangavet
Off-White - Akreon
Out Of Time - IndiWolf
R
Rabbit on the Moon - Songdogx & Nitteh
The Rabbit Hole - Detrah
RunningWolf Mirari - Mirella Menciassi
Raptor - ElenPanter
Redriver - FireTheWolf777
Repeat - Songdogx
The Rabbit's Foot - riri_arts
S
Scurry - Mac Smith
Simbol - Zoba22
Spirit Lock - Animal Crispy
The Sylcoe - Denece-the-sylcoe
Sunder - Aurosoul
T
Tainted Hearts - Therbis
Taxicat - owlburrow
That's Freedom Guyra - Nothofagus-obliqua
Three Corners: A Kitten's Story - Lara Frizzell
Tofauti Sawa - TheCynicalHound
Two of a Kind - ProjectNao
To Catch a Star - SleepySundae
U
Under the Ash Tree - ChevreLune
Uninvited - Nothofagus-obliqua
W
Water Wolves - LuckyStarhun
What Lurks Beneath - ArualMeow
Water Wolves - LuckyStarhun
Wild Wolves - Lombarsi
White Tail - SleepySundae
What's your damage? - FrostedCanid
The Wolves of Chena - Yamis-Art
Waves Always Crash - Hellhunde
The Whale's Heart - Possumteeeth [Warriors Fancomic]
Manga
A Centaur's Life - Murayama Kei
Beastars - Paru Itagaki
Chi's Sweet Home - Kanata Konami
Ginga Series [Silverfang] - Yoshihiro Takahashi
Gon - Masashi Tanaka
Houseki no Kuni | Land of the Lustrous - Haruko Ichikawa
Inugami-Kai - Masaya Hokazono
The Jungle Emperor - Osamu Tezuka
My roommate is a cat - Minatsuki & Asu Futatsuya
Crimsons – The Scarlet Navigators of the Ocean - Kanno Takanori
Rooster Fighter - Shū Sakuratani
Simoun - Shō Aikawa
The Fox & Little Tanuki - Mi Tagawa
Yuria 100 Shiki - Nobuto Hagio
Massugu ni Ikou - Kira
Cat Soup
The Amazing 3
Cat + Gamer - Wataru Nadatani
Animated Series
#
101 Dalmatians: The series & 101 Dalmatian Street
A
A Polar Bear in Love
B
Baja no Studio
Bagi: Monster of Mighty Nature
Bannertail: The Story of Gray Squirrel
Bluey
C
Centaurworld (2021)
Chirin's Bell
Chironup no Kitsune
D
Dokkun Dokkun
E
F
G
Gamba no Bouken
H
Hazbin Hotel
I
Invader ZIM
Inu to Neko Docchi mo Katteru to Mainichi Tanoshii
J
K
King Fang
Koisuru Shirokuma
Kemushi no Boro
Kewang Lantian
Konglong Baobei: Shiluo De Wenming
L
Little Polar Bear
M
Manxmouse's Great Activity
Mitsubachi Maya no Bouken
Mikan Enikki
Massugu ni Ikou -
My Life as a Teenage Robot
Mikan Enikki
N
O
Ore, Tsushima
Okashi na Sabaku no Suna to Manu
P
Primal
Polar Bear Cafe
Q
R
Robotboy (2005)
S
Seton Doubutsuki: Risu no Banner
Simoun
T
The Amazing 3
Tottoko Hamtarou
The Adventure of Qiqi and Keke
Tama & Friends: Third Street Story
U
V
W
Watership Down (2018) & Watership Down (1999)
What's Michael?
Wolf's Rain
Wonder Pets
X
Y
Live-Action/Hybrid show
Fantasy High
A Crown of Candy
Burrow's End
Good Omens
Webseries
Dinosauria - Dead Sound
My Pride - tribbleofdoom
Whitefall - Chylk
The Stolen Hope - Galemtido
Dragon's Blood - FluffyGinger
Helluva Boss -
Murder Drones -
Short Films
A
Alone a wolf's winter
B
Baja's Studio
Beautiful Name
Burrow
C
Cat Piano
Cat Soup
Chicken Little
D
E
F
Far From the Tree
Ferdinand the Bull
Frypan Jiisan
G
Genji Fantasy: The Cat Fell in Love With Hikaru Genji
Gaitou to Neko
H
Hao Mao Mimi
Houzi Dian Bianpao
I
J
Je T'aime
K
Kitbull
L
Lava
Lambert the sheepish lion
Laoshu Jia Nu
M
Mahoutsukai no Melody
Monmon the Water Spider
Mushroom - Nakagawa Sawako
N
O
Of Mice and Clockworks
Osaru no Tairyou
P
Piper
Q
R
Robin Robin
Rusuban
S
Sauria - Dead Sound
Smash and Grab
Street of Crocodiles
She and Her Cat
Space Neko Theater
Shiroi Zou | White Elephant
Shi | Food
Sugar, With a Story
Straw-saurus NEO
T
The Chair
The Blue Umbrella
The Shell Shocked Egg
The Dog Door
The Dog In The Alley
That's Why They Were Made
U
Ushigaeru
V
W
With a Dog AND a Cat, Every Day is Fun
X
Y
Z
Zhui Shu
Animated Films
#
101 Dalmatians duology
A
A Monkey's Tale (1999)
All Dogs go to Heaven
The Adventures of Lolo the Penguin
Alpha and Omega saga
An American Tail
The Aristocats
Antz
Animals United
Annabelle's Wish (1997)
Alakazam the great (1960)
B
Back Outback
Balto
Bambi / Bambi II
Bolt
Brother Bear / Brother Bear II
A Bug's Life
The Big Bad Fox and Other Tales
Bee Movie
The Brave Little Toaster
Birds of a Feather
Back to the Forest
C
Cars
Chance
Chicken Run
D
Dinosaur
Speckles: The Tarbosaurus || Dino King: Journey to Fire Mountain
Dumbo
DC League of Super-Pets
E
Elemental
F
Fantastic Mr. Fox
Fantastic Planet
Felidae
The Fox and the Hound
Finding Nemo/Finding Dory
Free Birds
The Fearless Four
G
The Good Dinosaur
Ghost in the Shell
Guillermo del Toro’s Pinocchio
H
Happy Feet/Happy Feet Two
Help! I'm a Fish
Home on the Range
Hoero! Bun Bun Movie
Hokkyoku no Muushika Miishika
I
Ice Age Franchise
Isle of Dogs
I Am T-Rex
J
Jungledyret Hugo
K
Koati
The King of Tibetan Antelope
Kuma no Gakkou trilogy
L
Lady and the Tramp
The Land Before time Franchise
The Last Unicorn
Leafy, A Hen in the wild
Little Big Panda
The Lion King Franchise
Lucky and Zorba
Lilo & Stitch
Luca
Last Day of the Dinosaurs
M
Marcel the Shell with Shoes On
Marona's Fantastic Tale
Millionaire Dogs
My Friend Tyranno
Minuscule: Valley of the Lost Ants || Minuscule - Mandibles from Far Away
Mouse and His Child
N
Nezumi Monogatari: George to Gerald no Bouken
O
Oliver & Company
One Stormy Night
Over the Edge
P
Padak
The Plague Dogs
Pompoko
Pinocchio by Guillermo del Toro
Pipi Tobenai Hotaru
R
Raggedy Ann & Andy: A Musical Adventure
Rango
Ratatouille
Raven the Little Rascal
Reynard the Fox (1989)
Rio
Robots
Rock a Doodle
Rudolph the Red-Nosed Reindeer (1998)
The Rabbi’s Cat
S
Samson and Sally
Sahara
The Secret of Nihm
The Secret Life of Pets/The Secret Life of Pets II
Spirit: Stallion of the Cimarron
Sheep & Wolves
The Seventh Brother
A Stork's Journey
Stowaways on the Ark
T
A Turtle's Tale
The One and Only Ivan
Toy Story
Twilight of the Cockroaches (1987)
The Trumpet of the Swan
The Enchanted Journey
U
Unico
Underdog
V
Vuk the Little Fox
W
WALL·E
Watership Down (1978)
White Fang
Wizards
The Wild
Wolf Children
Wolfwalkers
X
Y
You Are Umasou
Z
Zootopia
Live Action/CGI Assisted Movies
Au Hasard Balthazar
Beverly Hills Chihuahua franchise
Cats & Dogs franchise
Charlotte's Web
EO
Fluke (1995) - Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer
Homeward Bound duology (1963 & 1996) - Disney
The Legend of Lobo (1962) - Disney
Strays (2023) - Universal Pictures
Pride (2024) - BBC
101 Dalmatians duology (1996 & 2000)
Documentary
March of the Penguins
Meerkat Manor
Lemur Street
Gangs of Lemur Island
Orangutan Island
Prairie Dog Dynasty
Chimp Empire
Monkey Thieves
Monkey Kingdom
Theather
Cats
Videogames
Animalia Survival - High Brazil Studio
Cattails - Falcon Development
Endling: Extinction is Forever
Gibbon: Beyond the trees - Broken Rules
The Lonesome Fog - Might and Delight
Meadow - Might and Delight
Niche - Stray Fawn Studio
Shelter / Shelter 2/ Shelter 3 - Might and Delight
Paws - Might and Delight
Stray - BlueTwelve Studio
The WILDS - Gluten Free Games
Wolf Quest - eduweb
Golden Treasure: The Great Green - Dreaming Door Studios
Spirit of the North - Infuse Studio
Ōkami - Clover Studio
Rain World - Videocult
Feather - Samurai Punk
Eagle Flight - Ubisoft Montreal Studio
Copoka - Inaccurate Interactive
Untitled Goose Game - House House
PaRappa - NanaOn-Sha
Night in the Woods - Infinite Fall & Secret Lab
Monster Prom - Beautiful Glitch
Them's Fightin' Herds - Mane6
Toontown
E.V.O.: Search for Eden - Givro Corporation
(Pretty much most of Might and Delight games)
Online Browser Games
Lioden
Wolvden
Flight Rising
Lorwolf
Table Top Games
Bunnies & Burrows
Chronicles of Darkness
Wanderhome
Mage: The Awakening
Werewolf: The Apocalypse
Pugmire
Three Raccoons in a Trench Coat
World Tree (RPG)
Pawpocalypse
Heckin' Good Doggos
Humblewood
Dungeons & Dragons (Depends on the GM)
Music
In My Eyes You're a Giant - Sonata Arctica
It Won't Fade - Unia
The Cage - Winterheart's Guild
Other Online Projects
Youtubers
Cardinal West
Xenofiction Reviews
Gen. Videos
Trope Talk: Small Mammal on a Big Adventure by Overly Sarcastic Productions
youtube
Worlds
Mirolapye - Varverine
Franchises
Sonic the Hedgehog
My little pony
Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles
Hamtaro
Pokemon
Digimon
Kirby
Monter High
Tom & Jerry
Baldur’s Gate
Maya the Bee
The Little Polar Bear
171 notes
·
View notes
Text
Features & Tips - Q5 Upland Bird Hunting Vest of Arizona Quail Today
Recently purchased or thinking about purchasing the Q5 Centerfire Upland Bird Hunting Vest?? Take a look at this great … source
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Tapayuna, also known as Beico or Beiço-de-Pau (a Portuguese exonym referencing traditional lip plugs), are an Indigenous group of Brazil belonging to the larger Arawakan linguistic family. Historically inhabiting the transitional zones between the Amazon rainforest and the Brazilian Cerrado, the Tapayuna have experienced significant social, territorial, and demographic transformations, particularly during the 20th century due to external pressures from colonization, state intervention, and infrastructural development. Despite periods of cultural suppression and population decline, the Tapayuna people have demonstrated resilience and have worked toward the revitalization of their language and cultural traditions in recent decades.

The autonym Tapayuna is the preferred designation used by the group themselves. The alternative name "Beico" or "Beiço-de-Pau" was imposed by outsiders, referring to the traditional use of wooden lip plugs among Tapayuna men—an aesthetic and cultural practice that was stigmatized during the mid-20th century. As with many Indigenous groups, externally imposed names often reflect colonial perspectives, whereas the autonym is rooted in self-identification and carries cultural significance. The term "Tapayuna" is Arawakan in origin and linguistically reflects internal phonological patterns common to the family.
The Tapayuna language is part of the Northern branch of the Arawakan language family, which is one of the largest and most widespread Indigenous language families in South America. The Tapayuna language, like many others in this family, is polysynthetic, with complex morphology and verb serialization. As of the early 21st century, the language was considered moribund, with only a small number of fluent elderly speakers remaining, primarily in the state of Mato Grosso. Language shift toward Portuguese occurred largely due to contact with non-Indigenous society, missionary influence, and state educational policies.
Efforts in linguistic revitalization have been made, supported by partnerships between Indigenous leaders, linguists, and non-governmental organizations. Documentation projects have included the recording of oral traditions, grammar sketching, dictionary development, and the creation of bilingual pedagogical materials.
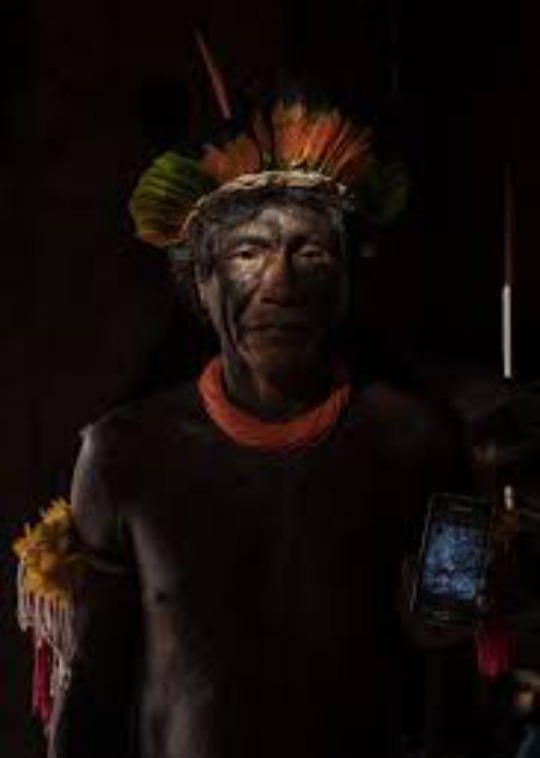

Historically, the Tapayuna occupied a region along the Arinos and Teles Pires Rivers in what is today northern Mato Grosso, Brazil. This region forms a biome transition zone between the Amazon rainforest and the Cerrado savanna, characterized by high biodiversity and ecological complexity. The original territory included seasonal floodplains, gallery forests, and upland savannas, which supported a mixed subsistence economy based on hunting, fishing, horticulture, and gathering.
In the 20th century, Tapayuna territory was heavily encroached upon due to the expansion of Brazilian agriculture, infrastructure projects (notably highways and hydroelectric dams), and governmental assimilation policies. Forced removals and displacement significantly altered their relationship with the land, leading to resettlement in demarcated Indigenous territories such as the Xingu Indigenous Park and later in other demarcated areas in Mato Grosso.
Traditionally, the Tapayuna practiced a diversified subsistence economy combining slash-and-burn horticulture with hunting, fishing, and foraging. Primary crops included manioc (cassava), maize, bananas, and a variety of tubers and fruits, cultivated in rotational plots known as roças. Hunting, carried out using bows and arrows and traps, targeted forest and savanna game such as peccaries, tapirs, monkeys, and various bird species. Fishing was carried out with nets, weirs, and occasionally plant toxins (fish poisons).
Craft production was both utilitarian and ceremonial: men crafted weapons, tools, and ornaments such as lip plugs and feather headdresses; women wove baskets and mats using natural fibers. The Tapayuna were historically semi-nomadic within their territory, relocating seasonally to optimize resource use, and maintained a reciprocal economy within kinship networks.
Today, while some traditional practices continue, many Tapayuna have integrated into the cash economy through artisanal sales, state support programs, and collaboration with NGOs. Shifts in diet, material culture, and labor have occurred, but subsistence farming and food sovereignty remain vital to cultural identity.
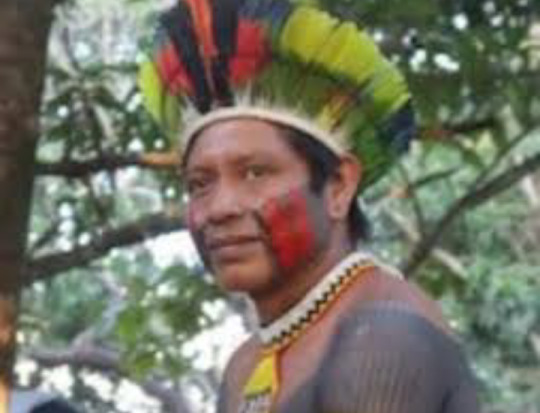

The Tapayuna social structure was historically organized around extended kinship groups and clans, each with specific roles and totemic associations. Kinship was bilateral, though patrilineal tendencies influenced inheritance and residence patterns. Marriages were often exogamous between clans, with bride service and other customary exchanges marking marital alliances. Chiefs or headmen (caciques) traditionally held authority based on age, wisdom, and oratorical skill, rather than coercive power.
Rites of passage marked transitions in age and social status, particularly male initiation, which involved seclusion, instruction in cosmological knowledge, and body modification practices such as the insertion of lip plugs and tattooing. These rites reinforced communal identity and social cohesion.
In contemporary contexts, formal Indigenous associations and leadership structures have emerged, interacting with Brazilian state mechanisms. Nevertheless, traditional authority figures remain important, particularly in cultural transmission and dispute resolution.
Tapayuna cosmology is deeply rooted in Arawakan shamanic traditions, emphasizing a multi-layered universe inhabited by a diverse array of spirits, ancestral beings, and natural forces. Shamans (called by local names, often translated as pajés in Portuguese) acted as mediators between the human and spiritual realms, conducting healing rituals, divinations, and protective ceremonies.
Myths explain the origins of the world, human beings, animals, and cultural practices. These narratives are preserved through oral tradition and are often recited during communal gatherings. Certain animals, such as jaguars and anacondas, are imbued with spiritual significance and feature prominently in Tapayuna stories as ancestors or transformative beings.
Although many Tapayuna have been exposed to Christianity through missionary efforts—particularly in the mid-20th century—traditional cosmologies remain influential, and syncretism is common.

The Tapayuna were relatively isolated until the mid-20th century. In the 1960s and 70s, they experienced catastrophic population decline due to diseases introduced during "pacification" missions conducted by the Brazilian state through the Indigenous Protection Service (SPI) and later the National Indian Foundation (FUNAI). Malaria, measles, and influenza ravaged populations with no prior immunity.
Survivors were relocated to the Xingu Indigenous Park, a multiethnic reserve established in 1961 under the Villas-Bôas brothers. There, the Tapayuna came into contact with other Indigenous groups such as the Kuikuro, Waurá, and Kayabi, leading to both cultural exchange and challenges of intergroup relations. The relocation was traumatic and resulted in a temporary suppression of Tapayuna identity due to stigmatization and pressure to assimilate.
In later years, surviving Tapayuna communities negotiated for the right to return to their ancestral lands and were granted access to new Indigenous territories in Mato Grosso. Demographic recovery has been slow but positive, supported by improved healthcare, education, and territorial rights enforcement.
Today, the Tapayuna continue to navigate a complex relationship with the Brazilian state, neighboring communities, and wider society. Legal recognition of land rights remains a central issue, as does the protection of environmental resources from illegal logging, land-grabbing, and agribusiness expansion. Cultural revitalization has become a key goal, particularly the teaching of the Tapayuna language to children, the revival of traditional festivals, and the assertion of cultural pride.
Educational initiatives include bilingual schooling, where possible, and workshops conducted with elders to pass on oral traditions. Political activism has increased, with Tapayuna representatives participating in national Indigenous congresses and advocacy networks.
The group remains small in number, but resilient and increasingly visible in public discourse surrounding Indigenous rights, Amazonian conservation, and cultural preservation.
#indigenous peoples#tapayuna#arawakan#indigenous brazil#cultural revitalization#language preservation#endangered languages#amazon indigenous#indigenous resistance#decolonize#indigenous rights#native voices#brazilian indigenous#protect the amazon#cultural heritage#ethnolinguistics#indigenous history#indigenous knowledge#indigenous culture#indigenous resilience#anthropology#colonial history#xingu park#indigenous revival#traditional ecological knowledge#land back#indigenous art#survivance#lip plug culture#post colonial voices
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
What's the Bird?
Location: New Jersey, USA
Date: December

We ask that discussion under questions be limited to how you came to your conclusion, not what your conclusion was.
Happy Birding!
Keep the game alive! Submit a bird HERE
Bird-201 graciously submitted by @blue-jacket-blues
23 notes
·
View notes
Photo

🐔 Upland game birds New York: The Macmillan company ;1904.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Birds of Maglor’s Gap and Lothlann
This completes my series on birds of the Fëanorian realms pre Amon Ereb!!
March of Maedhros, Himlad, Thargelion, Estolad
Flora, Fauna, geography and environment of Arda Masterlist
Maglor’s Gap was the widest break in the mountains and cliffs dividing Beleriand and the lands to the north. It lay between the blue mountains to the east and the March of Maedhros to the west. Lothlann was a wide expanse of plains to the north of the Gap. The rivers greater and little Gelion ran around the western and eastern borders.
Steppes and plains: Daurian, see see partridge, yellowhammer, black grouse, grey necked bunting, great rosefinch, imperial Eagle, steppe eagle, golden eagle, Mongolian ground jay (rare), greater short toed lark, upland buzzard, Pallas’s sandgrouse, laughing dove, great bustard, bush quail, gray, black and painted francolin, snowcock, little bustard, merlin, cheer pheasant, crested lark, painted sandgrouse, scrubfowl, common quail, brown accentor, ring necked pheasant, grey partridge, black bellied sandgrouse, common buzzard, black kite
By greater and little Gelion (stream/river): black faced bunting, Pallas’s bunting, pin tailed sandgrouse (summer only), white throated dipper, brown dipper, common kingfisher, hobby, swamphen
World building notes
--Laughing doves appear on the sigil of some of Maglor’s host who are particularly skilled in the use of song in battle
-Many of Maglor’s cavalry hunt or fight with birds including golden, steppe and imperial eagles.
-Game birds of the prairie steppes such as partridge make up much of the meat that the cavalry and scouts eat, along with hares.
-Most of the cavalry have horse hair plumes but some of the lieutenants and generals have feathers from pheasants or eagles.
-Emu are actually domesticated in some parts of the world and I love the idea of them being kept in both the Gap and Himlad as well as by peoples East of the Ered Luin. They have a huge variety of uses including leather, oil, eggs and meat. And the chicks are very cute 💙
-I am a huge proponent of prehistoric and extinct animals living throughout Arda, as per Tolkien’s comments about “all creatures which walk or have walked the earth”. I really like the idea of small brush moas living near the mountain borders of the Gap
31 notes
·
View notes
Photo

A new variant has been added!
Chestnut-winged Hookbill (Ancistrops strigilatus) © Cullen Hanks
It hatches from brown, common, extensive, horizontal, mature, overall, red, and upland eggs.
squawkoverflow - the ultimate bird collecting game 🥚 hatch ❤️ collect 🤝 connect
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Democrat vice presidential nominee Tim Walz found himself in an unexpected spotlight after a video surfaced online that shows the “folksy” Minnesota governor struggling to use a shotgun.
The video was captured during a pheasant-hunting trip, the Daily Caller reported.
The footage shows Walz attempting to load a semi-automatic firearm, leading to a wave of discussion among the public and media.
During the governor’s Pheasant Hunting Opener in Sleepy Eye, Minnesota, Walz’s difficulty with a Beretta A400 shotgun drew attention.
It comes amid renewed interest in his military service and criticisms from political opponents.
According to reports from the Associated Press, the annual Governor’s Pheasant Hunting Opener is a traditional event meant to launch the upland game bird season.
This year, the gathering took on an extra layer of intrigue as the governor’s handling of the firearm took center stage.
In the video, Walz is seen conversing with reporters while attempting to load shells into the gun’s magazine.
The governor identified the shotgun as a Beretta A400, which he had purchased during a period when he was more actively involved in trap shooting.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Upland Bird Hunting
http://www.365downandout.com Facebook.com/365downandout Year Round Hunting™ The Year Round Hunter™ and Year Round … source
#benelli#bird hunting#duck#ducks#english pointer#georgia quail hunting#hunting#huntress#LABS#pheasant hunting#pheasants forever#pointers#quail hunting#Retriever#south dakota bird hunting#sporting dog#upland bird hunting#Upland Game Bird#upland hunting#wild quail#year round hunter#year round huntress
1 note
·
View note