#Types of Effluent Treatment Plants
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to Choose the Right Industrial Effluent Treatment Plant?
At this blog we share all info about Types of Effluent Treatment Plants, Different Stages of Effluent Treatment in ETPs, and how you can choose right ETP plant from them. If you want to Build plant, contact Ravi Enviro Industries Private Limited for the best ETP plant manufacturer in India.

#ETP plant manufacturer in India#Choose the Right Industrial Effluent Treatment Plant#Industrial Effluent Treatment Plant#Stages of Effluent Treatment in ETPs#Types of Effluent Treatment Plants#Types of ETP#What is an Industrial Effluent Treatment Plant#What is an Industrial ETP
0 notes
Text
Started the day by reading this article from the NY times, and I'm frankly, disturbed.
Some highlights:
"For decades, farmers across America have been encouraged by the federal government to spread municipal sewage on millions of acres of farmland as fertilizer. It was rich in nutrients, and it helped keep the sludge out of landfills."
Which I knew, and I knew that there were concerns about contaminants from like, the medications people were on. But human waste is part of the nutrient cycle, and it always made sense to me that it should be throughly composted and returned to agricultural lands, and I assumed that people in general were taking the steps necessary to make it safe.
But here's what I didn't know:
"The 1972 Clean Water Act had required industrial plants to start sending their wastewater to treatment plants instead of releasing it into rivers and streams, which was a win for the environment but also produced vast new quantities of sludge that had to go somewhere."
Which, yay, no longer polluting bodies of water, but now that means we're applying industrial waste water to agricultural lands. And have been since 1972. Which leads to this situation, among many others, I'm sure:
"The sludge that allegedly contaminated the Colemans’ farm came from the City of Fort Worth water district, which treats sewage from more than 1.2 million people, city records show. Its facility also accepts effluent from industries including aerospace, defense, oil and gas, and auto manufacturing. Synagro takes the sludge and treats it (though not for PFAS, as it’s not required by law) then distributes it as fertilizer."
So here's what some states are doing:
"In Michigan, among the first states to investigate the chemicals in sludge fertilizer, officials shut down one farm where tests found particularly high concentrations in the soil and in cattle that grazed on the land. This year, the state prohibited the property from ever again being used for agriculture. Michigan hasn’t conducted widespread testing at other farms, partly out of concern for the economic effects on its agriculture industry.
In 2022, Maine banned the use of sewage sludge on agricultural fields. It was the first state to do so and is the only state to systematically test farms for the chemicals. Investigators have found contamination on at least 68 of the more than 100 farms checked so far, with some 1,000 sites still to be tested.
“Investigating PFAS is like opening Pandora’s box,” said Nancy McBrady, deputy commissioner of Maine’s Department of Agriculture."
This is fun:
"The E.P.A. is currently studying the risks posed by PFAS in sludge fertilizer (which the industry calls biosolids) to determine if new rules are necessary.
The agency continues to promote its use on cropland, though elsewhere it has started to take action. In April, it ordered utilities to slash PFAS levels in drinking water to near zero and designated two types of the chemical as hazardous substances that must be cleaned up by polluters. The agency now says there is no safe level of PFAS for humans...
It’s difficult to know how much fertilizer sludge is used nationwide, and E.P.A. data is incomplete. The fertilizer industry says more than 2 million dry tons were used on 4.6 million acres of farmland in 2018. And it estimates that farmers have obtained permits to use sewage sludge on nearly 70 million acres, or about a fifth of all U.S. agricultural land."
There's more, but I wanted to condense it at least a little bit. I am glad we're raising awareness, and I'm glad we're starting to regular the amount in our drinking water, and I hope that we'll find a way to actually deal with PFAS. I am so frustrated that people are exposed in the first place, and in nigh inescapable ways.
Also, to all those people who were like, oh, organic isn't at all healthier for consumers? Guess what the organic standards don't allow to be applied?
139 notes
·
View notes
Note
Does on boats the poop stored then thrown once the boat is on land, or thrown directly in the sea ? HOW TOILETS ON BOATS WORKS ????
the toilet is a vacuum system like on aircrafts. the poop is sucked thru the vacuum to the STP, the sewage treatment plant. there are a few different types of STP but for simplicity we'll talk abt the 3 stage STP.
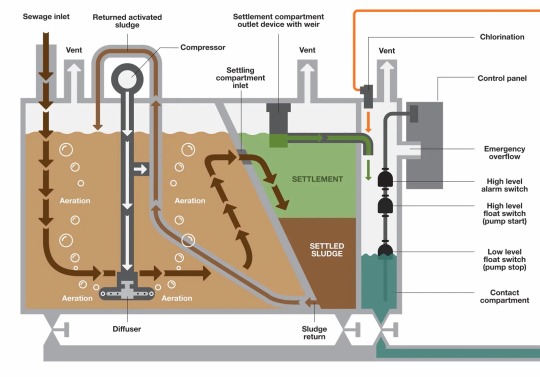
raw sewage enters the first stage on the left where it is decomposed by aerobic bacteria. the aerobic bacteria are supplied air by air blowers. the resulting effluent overflows into the second stage where it seperates into water and sludge. the water overflows and is chlorinated before being discharged into the ocean. the sludge left over feeds back into the first stage until it is processed.
if the ship is more than 12 nautical miles from shore it's legal to discharge raw, untreated sewage, but this isnt common in my experience.
13 notes
·
View notes
Note
What are your opinions on fertilizer runoff from industrial farming? Its ingredients such as phosphate and nitrogen can facilitate algae blooms, which in turn can cause artificial eutrophication, and or release toxins like microcystins.
My opinions are mixed! Also, this is a long post, so I've put the rest under a keep reading. Please do read! I just don't want to fill people's dashes with a long post every time they scroll lol.
Firstly, I need to say that if we were to broadly ban or heavily restrict fertiliser usage in agriculture, it is undeniable that the agriculture economy would collapse. Most industrialised farming is incentivised to sell the 'ideal products' to consumers, which inevitable means a shitload of food production in order to get the highest amounts of 'perfect' product. This requires a lot of fertiliser usage in order to mass produce and harvest monoculture farmland, and also results in a LOT of food waste. Unfortunately, the agricultural economy, combined with the half century of brainwashing by advertising companies telling people that so called 'blemished' food is somehow bad for you, is so based on this excess that if we did immediate drastic action, it would implode and likely send the prospective country into a recession.
With that being said, the system of heavy use of fertiliser is still not good!! Fertiliser runoff causes eutrophication as you point out, and can lead to toxic algal blooms, or even oxygen dead zones further down stream. However, it is not solely the use of fertiliser products that contribute to fertiliser run-off, as contradictory as that sounds. In fact, soil quality has a large part to play in the production of run-off.
For example, most modern agriculture uses monoculture, which is when one plant species is grown in the same place with little to no diversity in the field. A result of this is that only a single type of root system is grown, which is not enough for a healthy layer of topsoil to develop, especially if it is tilled and plowed every season. This means that the soil is very poor at retaining water, meaning that it requires LOTS of irrigation. With lots of irrigation, the fertiliser nutrients can't stay in the soil long enough to be absorbed by the plants fully, and they get washed away and have to be constantly topped up.
If we used less monoculture in our farming, we could use less fertiliser and still gain the same benefit, with also less runoff, which would be ideal!
I would also note a few things, namely that fertiliser runoff is not the only source of nutrient pollution from farming, and especially in places that have heavy cattle farming like my country, nitrates and phosphates from stock effluent is more of a problem. Cows shitting near streams is a big problem, and can be mitigated by proper filtering and nutrient-recovery technologies. One of these that I think is a big winner in terms of green technology wastewater treatment are Floating Treatment Wetlands, which are essentially artificial wetlands that are engineered to be part of wastewater treatment, and also provide habitats for birds and insects at the same time.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Essential Guide to Wastewater Treatment Plants: Turning Waste into Resource
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are the unsung heroes of urban infrastructure. As they work tirelessly behind the scenes, they transform contaminated water into a clean resource that can be safely returned to the environment or even reused. In this article, we’ll explore the critical role of wastewater treatment plants, their processes, and the benefits they bring to our communities and ecosystems.
Understanding Wastewater: What Is It?
Before delving into the intricacies of treatment plants, it’s vital to understand what wastewater is. Wastewater is any water that has been adversely affected by human activity. This can include:
Domestic Wastewater: From sinks, toilets, and showers in households.
Industrial Wastewater: Generated from manufacturing processes and commercial activities.
Stormwater: Rainwater that collects pollutants as it flows over surfaces.
Proper management of these types of wastewater is crucial for public health and environmental protection.
The Importance of Wastewater Treatment Plants
Wastewater treatment plants are essential for several reasons:
Public Health: Proper treatment of wastewater prevents the spread of waterborne diseases.
Environmental Protection: Treated water reduces pollution in rivers, lakes, and oceans, preserving aquatic ecosystems.
Resource Recovery: Many plants can recover valuable resources, such as nutrients and energy, from wastewater.
Sustainable Practices: Modern WWTPs incorporate technologies that promote sustainability, reducing their carbon footprint.
The Process of Wastewater Treatment
The treatment of wastewater is a complex process that typically involves several stages. Let’s break down these stages:
1. Preliminary Treatment
In this initial stage, large debris such as sticks, leaves, and plastic are removed from the wastewater. This is usually done through screening and grit removal processes.
2. Primary Treatment
After preliminary treatment, wastewater moves to primary treatment, where solids settle to the bottom, forming sludge. This process removes about 50-70% of suspended solids and approximately 30% of biological oxygen demand (BOD).
3. Secondary Treatment
Secondary treatment is crucial for further reducing organic matter. This stage usually involves biological processes, where microorganisms break down organic pollutants. There are various methods used in secondary treatment, including:
Activated Sludge Process: In this method, air is pumped into the wastewater, allowing microorganisms to feed on the organic material.
Trickling Filters: Wastewater is distributed over media, allowing microorganisms to grow and treat the water as it trickles through.
4. Tertiary Treatment
Tertiary treatment is an advanced stage that further polishes the water. This can involve filtration, nutrient removal, and disinfection processes like chlorination or ultraviolet (UV) light treatment. The goal is to ensure that the water is safe for discharge or reuse.
5. Sludge Management
Throughout the treatment process, sludge is generated. This sludge must be treated separately to reduce its volume and make it safer. Common methods include anaerobic digestion, which produces biogas, and composting, which can create a valuable soil amendment.
Innovations in Wastewater Treatment
The landscape of wastewater treatment is evolving, thanks to technological advancements. Here are some innovations transforming the industry:
1. Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
MBRs combine biological treatment with membrane filtration, allowing for higher quality effluent and smaller footprint operations. This technology is ideal for areas with limited space.
2. Constructed Wetlands
These engineered ecosystems mimic natural wetlands to treat wastewater. They are cost-effective and environmentally friendly, providing additional habitats for wildlife.
3. Resource Recovery Facilities
Modern WWTPs are increasingly focusing on recovering valuable resources from wastewater. This includes extracting nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which can be used as fertilizers, and capturing biogas for energy production.

The Benefits of Wastewater Treatment Plants
Investing in wastewater treatment has far-reaching benefits:
1. Economic Advantages
Efficient wastewater treatment supports local economies by ensuring clean water for industries and agriculture. It also creates jobs in engineering, operations, and maintenance.
2. Environmental Sustainability
By reducing pollution and conserving water resources, wastewater treatment plants contribute to a healthier planet. They play a critical role in combating climate change by mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from untreated wastewater.
3. Improved Public Health
Access to treated wastewater prevents health risks associated with untreated sewage. This is especially crucial in developing regions where sanitation infrastructure may be lacking.
Challenges Facing Wastewater Treatment Plants
Despite their importance, wastewater treatment plants face several challenges:
1. Aging Infrastructure
Many WWTPs are outdated and require significant investment to upgrade. Aging systems may lead to inefficiencies and increased pollution.
2. Climate Change Impacts
Extreme weather events and rising sea levels can impact the operation of wastewater treatment facilities. Adapting to these changes is crucial for future resilience.
3. Public Awareness and Engagement
Many communities are unaware of the vital role that WWTPs play. Increasing public engagement can foster support for necessary investments and improvements.
Conclusion: The Future of Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment plants are more than just facilities for cleaning water; they are essential components of sustainable urban development. As technology continues to evolve, these plants will become even more efficient and capable of recovering resources, ultimately contributing to a circular economy.

By recognizing the importance of wastewater treatment and supporting innovations in the field, we can ensure that our communities remain healthy and our environment is preserved for future generations. Investing in wastewater treatment Plant is not just about managing waste; it’s about embracing a sustainable future.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Defoamers in Wastewater Treatment - Mitigating Foam and Improving Processes
In the realm of wastewater treatment, foam can be a persistent nuisance, hindering efficiency and complicating operations. From excessive foaming in aeration tanks to foam buildup in clarifiers and digesters, foam-related issues can lead to process disruptions, increased maintenance costs, and compromised treatment performance. Fortunately, defoamers offer a practical solution for mitigating foam and improving processes in wastewater treatment plants. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the role of defoamers in wastewater treatment, their benefits, and the different types available from leading manufacturers in India.

Understanding Foam Formation in Wastewater Treatment
Foam formation in wastewater treatment processes can occur due to various factors, including:
Organic Matter: The presence of organic compounds in wastewater, such as proteins, fats, and surfactants, can contribute to foam formation by stabilizing air bubbles and increasing surface tension.
Microbial Activity: Microorganisms present in wastewater can produce extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) that promote foam stability and persistence.
Mechanical Agitation: Agitation caused by aeration, mixing, or pumping can introduce air into the wastewater, leading to foam formation.
Chemical Reactions: Certain chemical reactions, such as the release of gases during anaerobic digestion, can result in foam generation.
The Role of Defoamers in Wastewater Treatment
Defoamers, also known as antifoaming agents, are chemical additives designed to disrupt foam formation and promote foam collapse in wastewater treatment processes. By reducing surface tension and destabilizing foam bubbles, defoamers help prevent foam buildup and facilitate the smooth operation of treatment units. Some common applications of defoamers in wastewater treatment include:
Aeration tanks
Clarifiers and thickeners
Digesters
Filtration systems
Sludge dewatering processes
Types of Defoamers
Defoamers used in wastewater treatment are available in various formulations, each suited to specific applications and operating conditions. Some of the most common types of defoamers manufactured in India include:
Silicone-Based Defoamers:
Silicone-based defoamers are widely used in wastewater treatment due to their excellent foam-suppressing properties and chemical stability. These defoamers are effective across a wide pH range and can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for diverse wastewater treatment applications.
Alcohol-Based Defoamers:
Alcohol-based defoamers contain alcohol compounds that disrupt foam formation and promote bubble coalescence. These defoamers are often used in wastewater treatment processes where silicone-based formulations may not be suitable due to compatibility issues with certain chemicals or materials.
Glycol-Based Defoamers:
Glycol-based defoamers utilize glycol compounds to combat foam formation in wastewater treatment. These defoamers are known for their fast-acting properties and low toxicity, making them suitable for use in environmentally sensitive applications.
Benefits of Using Defoamers in Wastewater Treatment
Improved Process Efficiency: By reducing foam buildup and preventing process disruptions, defoamers help wastewater treatment plants maintain optimal process efficiency and throughput.
Cost Savings: Defoamers help minimize downtime, reduce maintenance requirements, and enhance the performance of treatment equipment, resulting in cost savings for wastewater treatment plants.
Enhanced Treatment Performance: By mitigating foam-related issues, defoamers enable wastewater treatment plants to achieve better treatment outcomes, including improved effluent quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
Versatility: Defoamers are available in various formulations to suit different wastewater treatment applications, ensuring versatility and adaptability to specific process requirements.
Choosing the Right Defoamer Manufacturer in India
When selecting a defoamer manufacturer in India, it's essential to consider factors such as product quality, technical support, and reliability. Look for a manufacturer with a proven track record of supplying high-quality defoamers for wastewater treatment applications. Additionally, ensure that the manufacturer offers comprehensive technical support and assistance to help you select the right defoamer for your specific needs.
Imperial Oilfield Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. (ICPL) – Your Trusted Defoamer Manufacturer in India
As a leading manufacturer of specialty chemicals in India, Imperial Oilfield Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. (ICPL) offers a wide range of defoamers specifically designed for wastewater treatment applications. Our silicone-based, alcohol-based, and glycol-based defoamers are formulated to deliver exceptional performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
With decades of experience in the chemical industry and a commitment to innovation and quality, ICPL is your trusted partner for all your defoamer needs. Whether you're operating a municipal wastewater treatment plant, an industrial wastewater facility, or a specialized treatment unit, we have the expertise and resources to provide customized defoamer solutions tailored to your requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, defoamers play a crucial role in mitigating foam and improving processes in wastewater treatment plants. Whether it's silicone-based, alcohol-based, or glycol-based formulations, defoamers offer effective solutions for combating foam-related issues and enhancing the efficiency and performance of treatment operations. By choosing the right defoamer manufacturer in India, Imperial Oilfield Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. (ICPL), wastewater treatment plants can benefit from high-quality defoamers and comprehensive technical support to meet their foam control needs effectively.
#Glycol Based Defoamer Manufacturer in India#Alcohol Based Defoamer Manufacturer in India#Defoamer Manufacturer in India#Silicone Based Defoamer Manufacturer in India
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Technology Plays a Role in Solid Waste Management
Introduction
The Role of Technology in Solid Waste Management and Effluent Treatment explores the transformative power of technology in addressing the complex challenges of waste management. In this blog, we delve into how innovative technologies are revolutionizing the way we handle, process, and dispose of solid waste, paving the way for a more sustainable future. Discover the latest advancements in waste management technology, from smart waste collection systems and IoT-enabled sensors to advanced sorting and recycling technologies. We explore how these technologies optimize waste collection routes, minimize collection costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.

Categories of Solid Waste Disposal Management Services:
The following are the different sources of solid waste management services
Residential Waste: It consists of various types of waste produced by individuals or families in their daily lives. Residential waste can be categorised into different types based on its composition, such as organic waste, recyclable waste.
Commercial: Commercial waste refers to the waste generated by businesses, commercial establishments, and institutions. It includes a wide range of waste materials resulting from various commercial activities
Industrial: Commercial waste refers to the waste materials generated by businesses, industries, institutions, and other non-residential sources. It encompasses a wide range of waste types and can vary in composition depending on the nature of the business or industry. Commercial waste includes both non-hazardous and hazardous waste materials.
Agriculture: Agriculture is the practice of cultivating plants, raising animals, and producing food, fiber, and other products used for human consumption or industrial purposes. In agriculture, farmers and agricultural workers engage in various practices to grow crops and raise livestock, with the goal of maximizing yield, quality, and profitability.
Cities: Cities are densely populated human settlements that serve as centers of social, economic, and cultural activities. They are characterized by a concentration of buildings, infrastructure, and people. Cities play a crucial role in shaping society, fostering innovation, and driving economic growth.
Benefits of Solid Waste Management
Many people may not be aware of this, but solid waste Management has many benefits for our health and our environment.
An important benefit of proper Solid Waste Management is that it improves air and water quality throughout the country, which keeps us healthier by removing less harmful particles from the air and water. Technology in Solid Waste Management: A Role for Solid Waste Management
Another benefit is that it ensures the safe disposal of any residual or wet waste through proper waste segregation. Direct handling of solid waste could result in many types of infectious diseases for collectors if the waste is not properly secured. Exposure to this hazardous waste can affect health and could cause long-term illness.
Proper solid waste management also protects citizens from biohazards and physical harm, fosters community health, promotes sanitation, and provides opportunities to earn money from recycling.
This is where the local government unit and barangay will step in to help educate residents on how to properly separate waste according to the correct bins and areas to ensure the well-being of other residents and people in this line of work.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, solid waste management plays a crucial role in creating a sustainable and healthier future for our planet and communities. Through effective waste management practices, we can reap a multitude of benefits that extend far beyond simply getting rid of our trash. Proper waste management minimizes environmental pollution, protecting ecosystems, wildlife, and human health. By reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills, we conserve valuable land resources and extend their lifespan, ensuring their availability for future generations.
#Waste Management Technologies#Role of Technology in Solid Waste Management#Technological innovation in solid waste management#Water Treatment Plant Manufacturers in India#Sewage Treatment Plant Manufacturers in India#Operation and Maintenance of Water Treatment#Operations and Maintenance in Facility Management#Water Treatment Plant Project#Sewage Treatment Plant Project#Effluent Treatment
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bio Culture: ETP/STP Applications Explained
Wastewater treatment is a critical process for environmental protection and public health. Effective treatment ensures that water discharged back into the environment is safe and meets regulatory standards. A key component of modern wastewater treatment is the use of bio culture for ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant) and bio culture for STP (Sewage Treatment Plant). This article explores the applications of bio culture in these vital systems.
What is Bio Culture?
Bio culture refers to a consortium of beneficial microorganisms, typically bacteria and fungi, that are introduced into wastewater treatment systems. These microorganisms play a crucial role in breaking down organic pollutants, converting them into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide and water. They accelerate the natural decomposition process, making treatment more efficient and effective.
Bio Culture for ETP: Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Industrial wastewater often contains a complex mix of pollutants, including organic compounds, heavy metals, and other industrial byproducts. Bio culture for ETP is specifically formulated to handle these challenging conditions. The microorganisms in these cultures are selected for their ability to degrade specific industrial pollutants.
Improved COD/BOD Reduction: Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) are key indicators of water pollution. Bio culture helps reduce these levels by breaking down organic matter, leading to cleaner effluent.
Enhanced Removal of Toxic Substances: Certain bio cultures are designed to target specific toxic substances present in industrial wastewater, effectively removing them from the effluent.
Increased Treatment Efficiency: By accelerating the breakdown of pollutants, bio culture improves the overall efficiency of the ETP, allowing it to handle higher volumes of wastewater.
Reduced Sludge Production: Bio culture can help reduce the volume of sludge produced during treatment, leading to cost savings in disposal.
Better Compliance with Regulations: Using bio culture can help industries meet stringent environmental regulations regarding wastewater discharge.
Bio Culture for STP: Municipal Wastewater Treatment
Municipal wastewater, primarily from domestic sources, contains organic waste, pathogens, and nutrients. Bio culture for STP plays a vital role in treating this wastewater before it is released back into the environment.
Effective Removal of Organic Matter: Bio culture helps break down organic waste in sewage, reducing BOD and improving water quality.
Pathogen Reduction: The microorganisms in bio culture can help reduce the levels of harmful pathogens in wastewater, making it safer for discharge.
Nutrient Removal: Some bio cultures are designed to remove excess nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which can contribute to eutrophication in water bodies.
Odor Control: Bio culture can help control unpleasant odors associated with wastewater treatment by breaking down the compounds that cause them.
Improved Plant Stability: Bio culture can help stabilize the biological processes in the STP, making it more resilient to variations in influent quality.
Choosing the Right Bio Culture
The effectiveness of bio culture depends on selecting the right product for the specific application. Factors to consider include:
Type of Wastewater: Industrial wastewater requires specialized bio cultures compared to municipal sewage.
Specific Pollutants: Identify the key pollutants present in the wastewater to choose a bio culture that targets them effectively.
Operating Conditions: Consider the temperature, pH, and other operating parameters of the treatment plant when selecting a bio culture.
Working with a Reputable Bioculture Manufacturer
Selecting a reliable bioculture manufacturer is crucial for ensuring the quality and effectiveness of the product. A reputable manufacturer will:
Offer a wide range of products: They should have bio cultures tailored to different applications and pollutant types.
Provide technical support: They should offer guidance on product selection, application, and troubleshooting.
Conduct quality control: They should have stringent quality control processes to ensure the viability and purity of their bio cultures.
Have a proven track record: Look for manufacturers with a history of successful applications in wastewater treatment.
Conclusion
Bio culture has become an indispensable tool in modern wastewater treatment. Whether it's bio culture for ETP in industrial settings or bio culture for STP in municipal systems, these beneficial microorganisms play a crucial role in improving treatment efficiency, reducing pollution, and protecting the environment. Choosing the right bio culture from a reputable bioculture manufacturer is essential for maximizing the benefits of this technology. As environmental regulations become stricter and the volume of wastewater increases, the role of bio culture in sustainable wastewater management will only continue to grow.
0 notes
Text
Water Treatment Plant Manufacturers: Pioneers in Sustainable Water Solutions

Water is a fundamental resource for life, industries, and agriculture. With the growing concerns over water pollution, the need for efficient water treatment solutions has surged. This is where water treatment plant manufacturers play a crucial role. These manufacturers design, develop, and install advanced water treatment systems to ensure clean and safe water for various applications.
Importance of Water Treatment Plants
Water treatment plants are essential for removing contaminants, bacteria, and other harmful substances from water sources. They help in:
Providing safe drinking water
Supporting industrial processes with treated water
Reducing environmental pollution
Conserving water through recycling and reuse
Reliable water treatment plant manufacturers incorporate cutting-edge technology to enhance the efficiency of these plants, making water purification more effective and sustainable.
Types of Water Treatment Plants
1. Sewage Treatment Plants (STP)
STPs treat wastewater from households, commercial buildings, and industries before releasing it into the environment. They use physical, biological, and chemical processes to remove impurities.
2. Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP)
ETPs are crucial for industries that generate wastewater containing chemicals, toxins, and heavy metals. These plants ensure compliance with environmental regulations by treating industrial effluents before disposal.
3. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Plants
RO plants use advanced membrane technology to remove dissolved solids, bacteria, and impurities from water, making it suitable for drinking and industrial use.
4. Desalination Plants
With freshwater scarcity becoming a global issue, desalination plants are gaining popularity. These plants remove salt and minerals from seawater, converting it into potable water.
5. Ultra Filtration (UF) & Nano Filtration (NF) Plants
These plants use membrane-based filtration to purify water for specific industrial and municipal applications.
How to Choose the Best Water Treatment Plant Manufacturer
When selecting a water treatment plant manufacturer, consider the following factors:
1. Experience and Expertise
A reputed manufacturer should have years of experience in designing and installing water treatment plants. They should understand industry-specific needs and regulatory requirements.
2. Technology and Innovation
The best water treatment plant manufacturers use state-of-the-art technology to enhance plant efficiency. Features such as IoT-enabled monitoring, automation, and energy-efficient processes add value.
3. Customization and Scalability
Every industry has unique water treatment needs. Manufacturers should offer customized solutions that can scale as per demand.
4. Compliance with Environmental Regulations
Ensure that the manufacturer follows all local and international water treatment regulations and provides eco-friendly solutions.
5. After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Water treatment plants require regular maintenance for optimal performance. Reliable manufacturers offer strong after-sales support, AMC (Annual Maintenance Contracts), and quick service assistance.
Benefits of Investing in a High-Quality Water Treatment Plant
Cost Savings: Reduces water wastage and operational costs in the long run.
Environmental Protection: Helps industries comply with environmental norms and reduce pollution.
Enhanced Water Quality: Provides safe, clean, and potable water for diverse applications.
Increased Operational Efficiency: Improves water management processes in industries and municipalities.
Conclusion
With rising water pollution and stringent environmental norms, the demand for water treatment plants is increasing. Choosing the right water treatment plant manufacturers ensures efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective water treatment solutions. If you are looking for a trusted name in this industry, Bhoomi Environmental is a leading manufacturer offering cutting-edge water treatment plants tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today to explore our range of water treatment solutions
0 notes
Text
What is Transmembrane Pressure (TMP)?
The membrane filtration technique is used to create a variety of products. In this procedure, a liquid is sent through a membrane system that separates it into two streams. The material that cannot pass through the synthetic membrane in the filtration system, is referred to as the retentate while the feed is known as the permeate.
The best type of filtration membrane depends on the density of the liquid that needs to be separated. The membrane filtration process depends heavily on pressure. Transmembrane pressure (TMP), its function in the filtering process, and its calculation are all covered in this article.
Website: https://www.rjjalraksha.com/effluent-treatment-plant/what-is-transmembrane-pressure-tmp/
0 notes
Text
Who Is The Best Effluent Treatment Plant Manufacturer In Noida ?
Effective treatment of effluent waste & wastewater is now more & more significant than ever in the advanced crowded world as cities keeps on bulging in its number along with urban development on rise. If effluent is not handled, there can be major risks to the environment & public health. Effluent treatment Plant systems are essential in this situation. One water treatment business such as Commercial RO Plant that in particular sticks out as the only leading manufacturer of ETP plants in Noida.
Effluent treatment plants are specialist facilities built to clean wastewater of impurities & prepare it for reutilization or disposal. These facilities implement a variety of techniques, such as physical, chemical, & biological treatments, to filter out organic waste, solid waste, & other contaminants from the effluent. After treatment, the water is either dumped into bodies of water or utilized for non-potable purposes like industrial operations or irrigation.
Consequences or Costs of Not Taking Effluent Treatment Facilities in Utilization for Treating wastewater
There would be dire negative effects if Noida were to lose its supply of effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Unprocessed effluent would seep straight into bodies of water, polluting them with dangerous materials & putting human wellbeing & aquatic lifecycle at serious threat that can result in many bigger hazards. Not only would the unprocessed effluent waste disposed out of the city with filthy & bad smell, rather it might also cause a detrimental effect on tourism & economy.
The Top Currently Existing Effluent Treatment Plant Manufacturer in Noida is Commercial RO Plant working Under it’s core company Netsol Water
Owing to its cutting-edge trending technology, unwavering commitment to maintain their quality, along with offering outstanding services to the customers, Commercial RO Plant has a remarkable journey & has solidified its brand name as the leading top producer of effluent treatment plant in Noida.
The Effluent Treatment Plants made by Commercial RO Plant Have Particular Features:
Innovative Therapeutic Methods for Rigorous effluent Treatment
Using treatment processes, Commercial RO Plant ensures that the treated water meets or exceeds all regulatory criteria. Their factories incorporate modern facilities & technologies, such as membrane bioreactors, UV disinfection, as well as tertiary treatment systems, to guarantee maximum efficiency along with efficacy.
Tailor-Made Resolutions offered to every ETP Plant Type
Since each customer has unique needs, Commercial RO Plant offers effluent treatment plant solutions that are adaptable & uniquely designed to meet those needs. Their team of experts works closely with clients to plan & carry out systems that meet their specific needs, whether the assignment is for an industrial site, residential complex, or municipal treatment facility.
Complete Efficiency in the Consumption of energy Supplied
Energy efficiency is given top priority in the designs of Commercial RO Plant's ETP plants, which include cutting-edge progressive technology to decrease energy usage & save operating costs. Specified factories incorporates these treatment plants which involves aeration systems with high power efficient motors, & pumps that makes the operation very efficient, running industries more sustainably & with concerns of the environment.

Strength, Durability, & Dependability
Commercial RO Plant's Effluent treating plants are long-lasting due to their thorough attention to every detail mentioned by clients & their utilization of premium materials in the manufacturing units. In the very long run for the future, their durable designs saves & offers clients more time & money while minimizing maintenance needs & downtime & guaranteeing dependable functioning.
Significant Benefits of the Effluent Treatment Plants by Commercial RO Plant as the most proficient Effluent Treatment Plant Manufacturer in Noida
Adherence to environmental standards
The effluent treatment facilities with diverse manufacturing unitsoperated by Commercial RO Plant are built to meet or beyond all applicable environmental standards, guaranteeing the safety of the treated water for release or repurposing. Clients benefit from this dedication to environmental compliance by avoiding exorbitant penalties & legal problems.
Very Economical for Value of Money
Commercial RO Plant's effluent treatment facilities provide long-term cost reductions through the integration of energy-efficient technology & robust construction. The decreased energy usage & fewer maintenance needs result in lower operating expenses for customers.
Thorough Examination & Evaluation has led to the 100% Smell & Odour Management
Commercial RO Plant acknowledges the need to manage odors in effluent treatment facilities. Modern odor control systems employed in their companies guarantee that offensive odors are minimized, enhancing the quality of life for the area's residents.
Well-trained & Informative Knowledgeable Crew
A group of incredibly talented & seasoned individuals at Commercial RO Plant are committed to providing top-notch customer service. Their staffs make sure that clients receive the greatest solutions & assistance available at every stage of the process, from design & installation to continuing maintenance & support.
Conclusion
It is entirely justified that Commercial RO Plant along with many of its supporting companies is the biggest effluent treatment plant Manufacturer in Noida. They stand out from the competition because of their dedication to quality, innovation, & client happiness. Customers who choose Commercial RO Plant may feel secure in the knowledge that they are investing in a effluent treatment plant system that will meet their needs for many years to come which can be the one that is dependable, effective, & environmentally friendly.
#effluent treatment plant#effluent treatment plant manufacturer in noida#netsol water#save water#water is life#water treatment plant
0 notes
Text
Sewage Treatment Plants: Process, Components, and Benefits

A Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) is an essential infrastructure designed to treat wastewater from residential, commercial, and industrial sources. The primary goal of an STP is to remove contaminants, making the water safe for environmental discharge or reuse. With increasing urbanization and industrialization, the importance of sewage treatment plants has grown significantly in maintaining public health and environmental sustainability.
Need for Sewage Treatment Plants
Sewage contains a mix of organic and inorganic matter, harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pollutants. Discharging untreated sewage into natural water bodies leads to severe environmental and health hazards, including:
Water pollution
Spread of diseases
Groundwater contamination
Destruction of aquatic life
Foul odour and aesthetic degradation
Sewage treatment plants play a crucial role in preventing these issues by treating wastewater effectively before discharge.
Key Components of a Sewage Treatment Plant
A sewage treatment plant comprises several components, each performing a specific function to ensure efficient wastewater treatment.
1. Primary Treatment
This stage involves the removal of large solids and sedimentation of suspended particles.
Screening: Filters out large debris such as plastics, leaves, and solid waste.
Grit Chamber: Separates heavy materials like sand and gravel.
Primary Sedimentation Tank: Allows suspended solids to settle at the bottom, forming sludge.
2. Secondary Treatment
This stage focuses on breaking down organic matter using biological processes.
Aeration Tank: Utilizes microorganisms to decompose organic pollutants.
Activated Sludge Process: Bacteria break down organic matter into simpler compounds.
Secondary Clarifier: Separates treated water from biological sludge.
3. Tertiary Treatment
This final stage enhances water quality for safe discharge or reuse.
Filtration: Removes fine particles and residual contaminants.
Disinfection: Uses chlorine, UV light, or ozone to eliminate harmful bacteria and pathogens.
Advanced Treatment: Includes nutrient removal processes to reduce nitrogen and phosphorus levels.
Types of Sewage Treatment Plants
There are different types of STPs, depending on their design, treatment technology, and application.
1. Activated Sludge Process (ASP)
A widely used biological treatment method where microorganisms decompose organic matter in aeration tanks.
2. Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)
Combines biological treatment with membrane filtration for high-quality effluent.
3. Sequential Batch Reactor (SBR)
Operates in cycles of filling, aeration, settling, and discharge, offering flexible treatment.
4. Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)
Uses biofilm carriers in aeration tanks to enhance microbial activity and treatment efficiency.
5. Constructed Wetlands
A natural and eco-friendly approach using vegetation to filter and treat wastewater.
Benefits of Sewage Treatment Plants
Investing in a sewage treatment plant offers several advantages, including:
1. Environmental Protection
Prevents contamination of natural water bodies by removing harmful pollutants from wastewater.
2. Public Health Safety
Reduces the risk of waterborne diseases by eliminating bacteria, viruses, and pathogens.
3. Water Reuse and Conservation
Treated wastewater can be reused for irrigation, industrial processes, and even potable applications with advanced treatment.
4. Reduction of Pollution
Minimizes air and soil pollution by preventing untreated sewage disposal.
5. Cost Savings
Industries and municipalities save on water expenses by reusing treated water, reducing dependence on freshwater sources.
Future Trends in Sewage Treatment
Innovations and technological advancements are transforming STPs, making them more efficient and sustainable.
1. Smart STPs
Integration of IoT and automation enhances monitoring, efficiency, and real-time data analysis.
2. Energy-Efficient Systems
Adoption of anaerobic digesters and renewable energy sources reduces energy consumption.
3. Decentralized Treatment Plants
Small-scale and modular STPs are gaining popularity for localized wastewater management.
4. Resource Recovery
Utilizing sludge for biogas production and nutrient recovery promotes circular economy principles.
Conclusion
A sewage treatment plant is a vital infrastructure for sustainable wastewater management, ensuring environmental protection, water conservation, and public health safety. With continuous advancements, modern STPs are becoming more efficient, eco-friendly, and cost-effective. Investing in proper sewage treatment solutions is crucial for a cleaner, healthier future.
0 notes
Text
Industrial Wastewater Management: Key to Environmental Sustainability

Effective industrial wastewater management is vital in minimizing the environmental impact of industrial processes. As industries increasingly face scrutiny for their environmental footprint, wastewater treatment has become a priority to ensure the safe disposal or reuse of contaminated water. By efficiently removing harmful pollutants, industries can mitigate risks to ecosystems, safeguard water resources, and meet environmental regulations.
The Importance of Industrial Wastewater Management
Industrial wastewater management involves the treatment of water used in industrial processes that has been contaminated with harmful pollutants. Without proper treatment, untreated wastewater can lead to serious environmental issues, including water pollution and harm to aquatic life. Harmful substances like heavy metals, oils, solvents, and chemicals are often present in wastewater from manufacturing plants, power stations, and other industrial activities. As a result, the importance of proper treatment and safe disposal cannot be overstated.
With stringent regulations in place worldwide, industries are under increasing pressure to manage wastewater effectively. Complying with local, national, and global environmental standards is essential for protecting ecosystems, ensuring public health, and maintaining the industry’s long-term viability.
Advanced Technologies in Wastewater Treatment
One of the primary goals of industrial wastewater management is to remove pollutants efficiently, making water safe for reuse or discharge. Advanced treatment technologies are critical in achieving this goal, each designed to address specific types of contaminants found in industrial effluent. Some of the most common technologies include:
Biological Treatment: This process uses microorganisms to break down organic contaminants in the wastewater. It is highly effective in removing biodegradable pollutants, such as oils, grease, and industrial solvents.
Membrane Filtration: This method uses semi-permeable membranes to filter out contaminants from water. It is particularly effective in removing fine particles, bacteria, and even viruses from the water.
Chemical Processes: Chemical treatments such as coagulation, flocculation, and chemical precipitation are used to remove heavy metals, toxins, and other harmful substances from industrial wastewater.
By adopting these innovative technologies, industries can efficiently treat wastewater and reduce their environmental impact, while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Benefits of Effective Industrial Wastewater Management
Proper industrial wastewater management brings numerous benefits that extend beyond regulatory compliance. These benefits include:
Water Conservation: With effective treatment, wastewater can be reused for non-potable purposes, such as irrigation or cooling, reducing the demand for freshwater.
Cost Savings: By recycling and reusing treated wastewater, industries can lower their water procurement costs and reduce their overall operational expenses.
Sustainability: Proper wastewater treatment reduces the environmental impact of industrial activities, helping companies move toward more sustainable practices while improving their reputation as eco-conscious businesses.
Protecting Ecosystems: By treating and properly disposing of industrial wastewater, industries can prevent contamination of rivers, lakes, and oceans, helping protect aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity.
Conclusion
As industries strive to meet the growing demand for resources while minimizing environmental harm, industrial wastewater management is more critical than ever. By incorporating advanced treatment technologies and adopting sustainable practices, industries can mitigate their environmental footprint, comply with regulatory standards, and contribute to the conservation of water resources. Effective wastewater management helps industries lower operational costs, protect ecosystems, and create a cleaner, more sustainable future for all.
Original Source:- https://a3tecnocrafts.blogspot.com/2025/01/industrial-wastewater-management-key-to.html
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Right Sewage Pump for Your Project
When managing wastewater, whether for a residential, commercial, or industrial project, selecting the right sewage pump is crucial. A properly chosen pump ensures efficient waste disposal, prevents blockages, and minimizes maintenance costs. With various types of sewage pumps available in the market, it can be challenging to determine which one is best suited for your needs. This guide will help you understand the key factors to consider when choosing a sewage pump and how sewage pump suppliers in the UAE can help you find the perfect solution.
1. Understand the Different Types of Sewage Pumps
Sewage pumps come in different types, each designed for specific applications. Understanding their differences will help you make an informed decision.
A. Submersible Sewage Pumps
Submersible pumps are designed to be fully submerged in wastewater. They are highly efficient, quiet, and require minimal maintenance. These pumps are ideal for residential and commercial sewage systems, as well as industrial wastewater treatment plants.
B. Grinder Pumps
Grinder pumps feature sharp cutting blades that break down solid waste into smaller particles before pumping it out. These are ideal for areas with limited drainage or where wastewater needs to be pumped over long distances.
C. Effluent Pumps
Effluent pumps are designed to handle wastewater with minimal solid content. They are commonly used in septic systems and wastewater treatment facilities.
D. Sewage Ejector Pumps
Sewage ejector pumps are typically used in basements or lower-level areas where gravity drainage is not possible. They efficiently move wastewater from lower to higher elevations.
2. Consider the Flow Rate and Pumping Capacity
One of the most important factors when choosing a sewage pump is its flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second. The required flow rate depends on the volume of wastewater your project generates.
For residential use, a pump with a flow rate of 30–50 GPM is usually sufficient. However, for commercial or industrial applications, you may need a pump with a much higher capacity. Sewage pump suppliers in the UAE can help you calculate the right size based on your project requirements.
3. Check the Solids-Handling Capacity
Sewage pumps must be capable of handling solid waste without clogging. Most sewage pumps can handle solid waste sizes ranging from 1 to 4 inches in diameter. If your system deals with larger debris, opt for a pump with a greater solids-handling capacity.
4. Consider the Head Pressure and Lift Requirements
The head pressure refers to the height to which a sewage pump can push wastewater. If you need to move sewage over long distances or to a higher elevation, you’ll need a pump with a higher head pressure rating.
For projects with steep inclines or deep septic tanks, consult sewage pump suppliers in the UAE to ensure you get a pump with the right lift capacity.
5. Choose the Right Material for Durability
Sewage pumps are exposed to harsh conditions, including corrosive chemicals and high temperatures. Choosing a pump made of stainless steel, cast iron, or thermoplastic ensures durability and long-term performance.
Cast iron pumps are highly durable and corrosion-resistant.
Stainless steel pumps are ideal for handling corrosive wastewater.
Thermoplastic pumps are lightweight and resistant to rust but may not be as durable as metal pumps.
6. Look for Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient pumps reduce operational costs and contribute to sustainability. Many modern sewage pumps feature variable speed motors, allowing them to adjust power usage based on demand. This helps lower electricity consumption while maintaining high efficiency.
7. Evaluate Maintenance and Service Requirements
Regular maintenance is essential to keep sewage pumps operating smoothly. Before purchasing a pump, check its maintenance requirements. Look for pumps with easy access to internal components, self-cleaning impellers, and automatic shut-off features to minimize servicing needs.
8. Work with Reliable Sewage Pump Suppliers in the UAE
Finding the right sewage pump suppliers in the UAE is key to getting high-quality products and professional guidance. A reputable supplier can provide:
Expert recommendations based on your project needs.
High-quality brands with warranties.
Installation and maintenance services to ensure long-term performance.
After-sales support, including spare parts and technical assistance.
Conclusion
Choosing the right sewage pump requires careful consideration of several factors, including pump type, capacity, head pressure, durability, and maintenance requirements. Whether you need a pump for a residential, commercial, or industrial project, working with experienced sewage pump suppliers in the UAE ensures you get a reliable and efficient system. By selecting the right pump, you can improve wastewater management, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure long-lasting performance.
0 notes
Text
Who Is The Best Sewage Treatment Plant Manufacturer In Faridabad ?
Netsol Water has grown to be the most developing Sewage treatment plant Manufacturer In Faridabad,.
In order to manufacture their particular goods, industrial companies create a variety of toxic mixtures that are harmful to the environment & often fatal.
Environmental regulations has made almost all industrial companies to collaborate with Netsol Water, the most dependable & effective Sewage Treatment Plant Manufacturer In Faridabad, to safeguard against the dumping of raw untreated sewage into water bodies.
The river-stream water restrictions, in addition to growing construction & population
The result of decades of industry is river contamination. Religious ceremonies frequently involve the disposal of organic things, such as trash or flower rags, into rivers. River streams are also contaminated by the discharge of household as well as industrial sewage. Their water becomes contaminated as soon as these pollutants are present.
The damaging impact on the environment due to domesticated sewage as well as commercial discharge.
The industrial sector is the primary cause of this kind of water contamination. Lakes, riverside streams, ponds, as well as various other water bodies shed their aesthetic value due to industrial pollution. Sewage is a term intended to describe waste matters that has not been cleansed or treated & contains both organic-inorganic components. These contaminants destroy aquatic life.
What makes the value of setting up components & operating STP Plants good enough for Clients to Agree on it?
The type of wastewater & volume of sewage that must be treated or processed, the intended final product quality level, the resources & components implemented, the size & dimensions of the building site, & other factors all affect how much money is required to develop a Sewage treatment plant.
The annual or monthly costs may be very different from what STPs originally experienced.
A sudden surge in the need for these Sewage Treatment Plant Manufacturer In Faridabad for designing STP Plants for such wastewater?
Thus, every kind of water is required for wastewater treatment for several critical reasons, including:
Methods for Protecting the ecosystems in the Environment no matter what may it costs Involves
Significant Cut in the Problems arising of contaminated water
The fact that water, which is drinkable that is in the purest form H2O & was formerly abundantly available, is becoming more scarcer as well as more difficult to obtain is a bit disheartening. Approximately 60-70% of the world's population suffers from water scarcity recorded on the current situation.
Because of this, treating wastewater sewage is crucial. Wastewater that receives thorough, efficient sewage treatment is frequently suitable for recycling in both commercial & industrial operations & activities, provided that the treatment protocols are rigorous enough.

Retaining Health of the Population Residing near Faridabad
Such raw, untreated effluent shouldn't be released into the ecosystem or environment since this could interfere with several health-related natural processes. Every year, millions of people die from dehydration as well as diarrhoea caused by untreated wastewater discharge worldwide.
Commercial Business companies whose operations need the installation of infrastructure related to sewage treatment manufacturer in Faridabad for designing & manufacturing STP facilities, & managing all sorts of wastewater.
Before sewage or wastewater can be disposed of or discharged into different sectors of the ecosystem of industries, such as chemical companies, petroleum refineries, power plants, along with ink-based printing industries, wastewater STP facility manufacturers must implement the following filtering processes.
Conclusion
With more than a decade of experience in this field, Netsol Water prestigious clients benefit greatly from continuing maintenance as well as operational facilities as well as progressive changes or advancements in software in support with mechanical components that makes plant performance better.
Experts in the area have worked together to create a sewage treatment plant system that is incredibly affordable. Because of its ground-breaking & economically environment friendly processes, Netsol Water alongside support & efforts from various branches stands to be the best option as their choice for the Sewage Treatment Plant Manufacturer In Faridabad. The treatment plants efficiently implement the STP systems consisting of various methods to assure that water treated is neither getting lost nor getting dirty by the living communities around.
#sewage treatment plant#sewage treatment plant manufacturer in faridabad#water is life#water treatment plant
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Right Effluent Treatment Plant for Your Industry
Selecting the right Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) for your industry is a crucial decision that can have long-term impacts on environmental compliance, operational efficiency, and overall sustainability. Effluent treatment is an essential process for managing industrial wastewater, ensuring that harmful pollutants are removed before discharge into water bodies or being reused. Given the diversity of industrial processes and the variety of effluent characteristics, choosing the right ETP requires careful consideration of several factors. This article outlines the key steps and factors to consider when selecting an ETP for your industry.
1. Understand the Characteristics of Your Effluent
Before selecting an ETP, it's essential to understand the composition and characteristics of the effluent generated by your industry. Different industries produce effluents with varying levels of contaminants such as chemicals, oils, suspended solids, biological waste, and heavy metals.
Key considerations:
Chemical composition: Does your effluent contain hazardous chemicals, such as acids, alkalis, or solvents?
Biological load: Does your effluent contain high organic material that requires biological treatment?
Toxicity: Is your effluent toxic or contains heavy metals that need special treatment?
Volume and flow rate: What is the average volume of effluent produced per day? This will help determine the size and capacity of the ETP.
By thoroughly understanding the characteristics of your effluent, you can ensure that the chosen ETP will be capable of treating it effectively.
2. Determine the Type of Effluent Treatment Required
Effluent treatment involves various processes, including physical, chemical, and biological treatment methods. The type of treatment your industry requires depends on the nature of the contaminants in your effluent.
Common types of treatment methods:
Physical treatment: Includes filtration, sedimentation, and flotation, primarily used to remove suspended solids.
Chemical treatment: Involves the addition of chemicals to neutralize or precipitate contaminants like heavy metals or toxic substances.
Biological treatment: Uses microorganisms to degrade organic matter in the effluent, commonly used in industries like food processing, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
Advanced treatment: Includes processes like reverse osmosis, membrane filtration, and activated carbon adsorption, often used to treat specific pollutants like pharmaceuticals, pesticides, or other complex contaminants.
Selecting the right treatment method is critical to ensuring the effective removal of pollutants and compliance with regulatory discharge standards.
3. Evaluate the Size and Capacity of the ETP
The size and capacity of the effluent treatment plant are vital factors to consider, as they need to align with the volume of wastewater your industry generates. Over-sizing or under-sizing the plant can lead to inefficiencies, higher operational costs, or failure to meet regulatory requirements.
Key considerations:
Flow rate: Estimate the daily volume of effluent generated and ensure the plant can handle the peak load efficiently.
Capacity for future expansion: Consider potential growth in production or changes in effluent volume. It's important to choose an ETP that can be scaled up if necessary.
Footprint and space availability: Ensure that the available space in your facility can accommodate the chosen ETP without compromising the operational workflow.
Choosing the right size ensures that your plant operates at maximum efficiency without wasting resources or failing to meet discharge limits.
4. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Each industry is subject to specific environmental regulations that dictate the quality of effluent that can be discharged into the environment. These regulations are set by local, regional, or national authorities to ensure that industrial wastewater does not harm public health or ecosystems.
Key considerations:
Discharge standards: Ensure that the chosen ETP is capable of meeting the local regulatory standards for pollutants such as BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand), COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand), TSS (Total Suspended Solids), and heavy metals.
Permit requirements: Ensure that the plant can comply with any necessary permits or licenses required for effluent discharge or reuse.
Reporting and monitoring: Many regulations require continuous monitoring and reporting of effluent quality. Choose an ETP that supports automated monitoring and generates detailed reports for compliance.
Selecting an ETP that meets regulatory standards is crucial to avoid legal penalties, fines, and potential harm to the environment.
5. Consider Operational and Maintenance Costs
The operational and maintenance costs of an effluent treatment plant can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the treatment processes and the size of the system. It's important to choose a system that not only fits within your budget but also minimizes long-term operational costs.
Key considerations:
Energy consumption: Some treatment processes, such as biological treatment, can be energy-intensive. Choose an ETP with energy-efficient equipment and processes to reduce electricity consumption.
Chemical usage: If chemical treatment is necessary, consider the cost of chemicals required for coagulation, flocculation, or neutralization.
Labor and maintenance: Ensure that the plant is easy to operate and maintain, reducing the need for highly skilled labor and minimizing downtime. Choose equipment with long service intervals and minimal wear and tear.
A cost-effective ETP reduces the financial burden of operation and ensures that your industry can meet its wastewater treatment needs without overspending.
6. Evaluate Technology and Innovation
The effluent treatment industry is evolving with the advent of new technologies and innovations that can improve the efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness of treatment plants. When choosing an ETP, consider systems that incorporate advanced technologies for better performance and reduced environmental impact.
Key considerations:
Automation: Automated monitoring and control systems can help optimize treatment processes, reduce human error, and ensure continuous compliance.
Energy recovery: Some ETPs incorporate energy recovery systems such as biogas generation from sludge, which can offset operational costs.
Sustainability: Consider selecting a plant that incorporates green technologies, such as wastewater recycling and zero-liquid discharge (ZLD) systems, to reduce the environmental footprint.
Opting for an ETP with advanced technologies not only improves treatment efficiency but also enhances sustainability and reduces operational costs.
7. Choose a Reliable Supplier with After-Sales Support
The supplier or manufacturer of the effluent treatment plant plays a critical role in the long-term success of the system. It's important to choose a reliable supplier who offers high-quality equipment, technical expertise, and strong after-sales support.
Key considerations:
Reputation: Research the supplier’s reputation in the industry and their experience in providing ETPs for your specific sector.
Technical support: Ensure that the supplier offers comprehensive technical support, including installation, commissioning, training, and troubleshooting.
Spare parts availability: Choose a supplier who provides easy access to spare parts and service contracts to ensure smooth operations and reduce downtime.
A reliable supplier ensures that your ETP is set up correctly and continues to function efficiently over time.
Conclusion
Choosing the right effluent treatment plant for your industry is a critical decision that requires careful consideration of various factors, including the characteristics of your effluent, the required treatment methods, capacity, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational costs. By following the guidelines outlined above, you can ensure that your industry invests in an ETP that meets its wastewater treatment needs efficiently, cost-effectively, and sustainably, while also adhering to environmental regulations and contributing to corporate social responsibility goals.
0 notes