#Two component nonwoven fabric
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Carded Chem-Bond and Thermal Bond: Revolutionizing the Nonwoven Fabrics Industry
In the dynamic world of nonwoven fabrics, two processes stand out for their efficiency, versatility, and the superior quality of the end products they produce: carded chem-bond and thermal bond. These methods are integral to a wide range of applications, from hygiene products to automotive interiors, showcasing their importance in everyday life. At the forefront of these innovations is Sommers Inc., a leader in nonwoven technology, continually pushing the boundaries of what's possible in the industry.
Carded Chem-Bond: Precision and Strength
Carded chem-bond nonwovens are created through a meticulous process that ensures uniformity and strength. The journey begins with the carding process, where fibers are disentangled, cleaned, and interlaced to form a web. This web is then chemically bonded using various adhesives, resulting in a fabric that is not only durable but also highly customizable in terms of weight, thickness, and texture.
Applications of Carded Chem-Bond
The versatility of carded chem-bond nonwovens makes them ideal for numerous applications:
Hygiene Products: Used in diapers, sanitary pads, and adult incontinence products, carded chem-bond nonwovens provide the necessary absorbency and softness.
Medical Supplies: These fabrics are perfect for surgical gowns, masks, and drapes due to their strength and ability to be sterilized.
Filtration: In air and liquid filtration, the uniformity and robustness of carded chem-bond nonwovens ensure effective filtration performance.
Thermal Bond: Efficiency and Consistency
Thermal bonding is another innovative method employed in the production of nonwoven fabrics. In this process, fibers are bonded through the application of heat. The fibers used in thermal bonding often contain a thermoplastic component that melts when heated, fusing the fibers together upon cooling. This technique is particularly noted for its speed and the consistency of the finished product.
Applications of Thermal Bond
The benefits of thermal bond nonwovens are evident across various industries:
Automotive Interiors: Thermal bond fabrics are used in car interiors for their lightweight and sound-absorbing properties.
Construction: In construction, these fabrics are utilized for insulation and as geotextiles due to their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Agriculture: Thermal bond nonwovens are employed as crop covers, providing protection against weather extremes while allowing air and moisture to permeate.
Why Choose Sommers Inc.?
Sommers Inc. stands out in the nonwoven fabric industry for several reasons:
Innovation: Sommers Inc. continually invests in research and development to bring the latest advancements in nonwoven technology to market.
Quality: With rigorous quality control processes, Sommers Inc. ensures that every product meets the highest standards of excellence.
Sustainability: Committed to environmentally friendly practices, Sommers Inc. prioritizes the use of sustainable materials and processes in the production of nonwoven fabrics.
Customer-Centric Approach: At Sommers Inc., customer satisfaction is paramount. The company works closely with clients to develop tailored solutions that meet specific needs.
Are you looking for high-quality nonwoven fabrics that deliver exceptional performance? Whether you need carded chem-bond or thermal bond nonwovens, Sommers Inc. has the expertise and technology to provide solutions that exceed your expectations. Contact Sommers Inc. today to learn more about our products and how we can help meet your specific requirements. Discover the difference that innovation, quality, and customer commitment can make in your business. Visit our website or call us now to speak with a nonwoven fabric specialist!
Sommers Inc.: Your trusted partner in nonwoven innovation.
#thermal bond nonwoven#best cardec chemical bond#affordable carded staple fiber#needle loom for sale#ultrasonics bonded nonwovens#carded staple fiber#point bonded fabric#best parallel-laid#natural continuous filament
0 notes
Text
Geotextile Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Infrastructure Development and Growing Awareness of Environmental Protection

The global Geotextile Market is estimated to be valued at USD 7.10 billion in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.6% over the forecast period (2023-2030).
A) Market Overview:
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics that are used in various civil engineering applications, such as filtration, erosion control, reinforcement, and drainage. They are made from synthetic materials, including polyester, polypropylene, and polyethylene, and are widely used in infrastructure development projects, such as roads, railways, airports, and landfills. Geotextiles provide excellent strength, durability, and filtration properties, which make them suitable for various applications in the construction industry.
B) Market Dynamics:
The market is driven by two main factors:
1. Increasing Infrastructure Development: The rapid urbanization and industrialization worldwide have led to a surge in infrastructure development projects. Geotextiles play a crucial role in enhancing the stability and longevity of these infrastructures. They are used in road stabilization, ground improvement, soil erosion control, and environmental protection measures. The growing demand for geotextiles in infrastructure development projects is expected to drive market growth.
2. Growing Awareness of Environmental Protection: Geotextiles offer eco-friendly solutions for various environmental protection measures. They help in preventing soil erosion, managing water drainage, and reducing the impact of pollutants on the environment. With increasing concerns about environmental degradation and regulations promoting sustainable practices, the demand for geotextiles is expected to rise.
C) Market Key Trends:
One key trend observed in the Geotextile Market is the increasing adoption of geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs). GCLs are composite materials that combine geotextiles and bentonite clay to enhance their barrier properties. They are widely used in landfill liners, mining containment, and environmental remediation applications. GCLs offer superior hydraulic performance, chemical resistance, and low permeability, making them an attractive alternative to traditional compacted clay liners.
D) SWOT Analysis:
- Strength: Strong demand for geotextiles in infrastructure development and environmental protection.
- Weakness: Lack of awareness and limited adoption in some regions.
- Opportunity: Growing research and development activities for innovative geotextile products.
- Threats: Intense competition from alternative materials and stringent government regulations.
E) Key Takeaways:
- The global geotextile for market is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.6% over the forecast period, due to increasing infrastructure development and the growing awareness of environmental protection.
- Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing and dominating region in the geotextile for market, driven by rapid urbanization and infrastructure investment in countries like China and India.
- Key players operating in the global geotextile for market include GSE Holdings Inc., The Dow Chemical Company, Royal Ten Cate Corporate EMEA, Fibertex Nonwovens A/S, Low & Bonar PLC., Huesker Synthetic GmbH, Tenax, CTM GEO Synthetics, Leggett & Platt Incorporated, and Kaytech Engineered Fabrics.
The geotextile for market is poised for significant growth due to the increasing demand for infrastructure development and the need to protect the environment. Geotextiles provide sustainable solutions for various civil engineering applications, making them a vital component of modern construction projects. The market is expected to witness substantial opportunities for innovation and expansion in the coming years.
0 notes
Text
Different Types of Geosynthetics
Geosynthetics are a range of products designed to improve the environment. They're used for various purposes like erosion control, drainage and soil stabilization.
Some materials are derived from natural resources, while others are synthesized using existing kinds of components in a laboratory or factory setting. As both types of resources must come from somewhere, scientists must utilize their expertise to create them. Additional info found at стсгео.
Types of Geosynthetics
Geosynthetics come in a variety of forms, some nonwoven and others woven.
Geotextiles are designed to facilitate material exchange between soil and air, enabling plant roots to grow, rainwater to seep into the ground, and excess water to drain away without causing erosion.
Another type of geosynthetic is a drainage filter, which helps prevent erosion and flooding. These filters can be found on roads, sports fields, dams, and landfills to make sure runoff doesn't seep into groundwater below.
Geocomposite materials, also known as geosynthetic composites, are a third type of geosynthetic. These materials combine two or more different geosynthetic types to perform specific functions better than either material could do on its own. Examples include barrier, containment, filtration, and reinforcement.
Geotextiles
Geotextiles are specialized fabrics used for reinforcement, separation, filtration and drainage applications. Usually composed of manmade polymers, some natural fibres may also be integrated into the construction process.
These durable containers are typically constructed from strong polyethylene or polypropylene and may be woven or nonwoven.
The tensile strength of a geotextile fabric is determined by its interface strength with soil, which varies depending on soil type and attributes such as fabric type, strand composition and manufacturing process.
Geotextiles are widely used in road, embankments and bridge strengthening applications to reinforce soil. They come in both woven and nonwoven varieties with various grades and thicknesses - providing cost-effective yet rapid ground stabilization solutions.
Geomembranes
Geomembranes are synthetic membranes designed to act as a liner or barrier in order to control fluid migration. They're commonly employed in civil engineering and industrial settings where environmental containment of liquids is required.
Geomembranes are widely used, including HDPE (High Density Polyethylene) and LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene). These materials offer superior protection for a variety of applications like pond lining, canal lining, landfill covers, and reservoir covers.
Geomembranes come in several variations. One common option involves the addition of colorants like titanium dioxide or other metal oxides that reduce surface temperature when exposed for extended periods. Usually, this coextruded layer makes up no more than 5-10% of the overall geomembrane thickness.
Geosynthetic Clay Liners
Geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs) are a type of hydraulic barrier commonly employed in waste management and containment systems. These consist of an inner layer of sodium bentonite that expands when exposed to water.
GCLs can be employed in a number of waste and liquid containment applications, such as landfills, mines, and wastewater treatment plants. Furthermore, they're commonly utilized in gas and vapor seals.
Ocean Geosynthetics provides prefabricated geosynthetic clay liners in various sizes and thicknesses. These products are composed of high-quality bentonite liner encased between two layers of geotextiles needle punched before being thermally locked together to improve strength and performance.
Geopipe
Geopipes are buried plastic pipes used for drainage. They're popular in construction sites and retaining walls due to their flexibility, discharge capacity, ease of installation, and superior drainage capabilities.
They're often employed in sports fields, building foundations and transportation applications. Manufactured from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) resin, these pipes come in various sizes.
They are formed into an open grid-like configuration, with large openings between ribs in both machine and cross-machine directions. They can be produced through weaving or knitting machinery using standard methods or by bonding rods or straps together.
1 note
·
View note
Text
10 things to consider while choosing medical nonwoven fabrics
Medical non-woven fabrics are the best choice for body coveralls, hats, sheets, face mask filter media, and other important medical applications as well as sterile medical products.
Due to their rapid development and supply demand, these medical nonwovens have experienced continuous updates and innovation. The reasons are its versatility, longevity, and sustainability.
Effectively, medical nonwoven materials are now part of the disinfecting supply. One of the most important components of medical supplies in the healthcare and hygiene sector, manufacturers also supply to various hospitals and pharmacies.
To keep an eye on the nonwoven medical textiles' quality, pay attention to these ten characteristics.
Non-woven fabric quality standards
Sanitized medical equipment, surgical face masks, shoe covers, particulate respirators, cartridge filters, coveralls, and hair caps made of medical non-woven fabric that satisfies physical and chemical standards.
It is safe to use nonwoven fabric
The appropriate term for medical nonwoven fabric is normally 2 to 3 years, with the validity period of products from different manufacturers differing somewhat. Please consider the usage recommendations.\

Compared to composite nonwoven textiles in particular and nonwoven fabrics in general, medical nonwoven fabrics are unique.
-The majority of nonwoven fabrics are not resistant to germs.
-Composite non-woven fabrics, which are used to make surgical gowns and surgical bedsheets, have good waterproof performance and low air permeability.
-Medical nonwoven textiles are produced using the spun-bond, melt-blown, and spun-bond (SMS) techniques. It has dander-free, hydrophobic, antimicrobial, and breathable qualities and is created by pressing. It is employed for the final packaging of sterilized goods. It is discardable and doesn't require cleaning.
The sterile items packaged in the medical non-woven fabric must not be harmed by sterilization and have a 180-day expiration date.
The nonwoven fabric used to filter mask media, coverall media, and appropriate media for surgical wear should weigh between 55 and 95 GSM.
-One must use a closed packaging technique when using medical non-woven fabric to package items like surgical face masks, shoe coverings, hair caps, particulate respirators, coveralls, and acceptable media for surgical wear. Packaging for nonwoven fabrics should consist of two layers. Folding repeatedly can make a long, curved tunnel that prevents bacteria from entering the package.
-Medical non-woven fabric that has undergone high-temperature sterilization frequently has internal changes that reduce the penetration and antibacterial efficiency of the sterilization medium. The medical nonwoven fabric shouldn't be repeatedly sterilized as a result.
Even though medical non-woven fabrics are not medical equipment,
they are associated with the sterilizing effectiveness of medical devices. Because they guarantee sterility, they have an effect on the medical device's overall sterilization quality when employed as packaging materials.
Check the physical and chemical properties of the medical non-woven fabric to ensure the quality of the products being used.
Bulky and heavy metal equipment may be sterilized at high temperatures
Due to the obvious hydrophobic properties of nonwoven textiles, and condensation water develops during the cooling process, making wet packs easy to create. To avoid wet bags, pad water-absorbing materials in large equipment packages, adequately limit the sterilizer's loading capacity, leave intervals between sterilizing packages, and increase the drying period.
The most cutting-edge melt-blown line is owned by Manjushree Spntek, and the most recent technology ensures a consistent, stable quality for a variety of mask media, including surgical face masks, particulate respirators, and cartridge filters.
0 notes
Text
Laminated Nonwoven Cloth
Laminated nonwoven sheets are fabrics that have two layers, the inner plus outer layers being made from a polyester sort fiber. These nonwoven sheets have suitable permeability in addition to water-resistance properties and so are useful in apparel. They are formed by needle-punching, water-jet being employed, or melt-blown systems.
The inner layer of the fabrics is made up of layers of short fibers assembled proper sheet. These layers are connected with adhesives. In compare, the outer layer worth mentioning fabrics is mainly smooth. This ensures that nonwoven fabrics made of these materials become more durable and straightforward to manipulate. Fig. ELEVEN. 1 illustrates that. Generally, the thickness of an 3D nonwoven will be several hundred times a lot more than the diameter of its fibres.
The production strategy of laminated nonwoven fabrics starts while using creation of the intermediate layer originating from a polymer-type resin. And then, the covering layers are made of spun-bonded nonwoven fabrics. In each covering up layer, polyester-type fibers tend to be bonded locally in the coarse density. One time the layering method is complete, the material is suffering from a water-jet process. Then, the fibres out of each covering level are intermingled and inserted in to the corresponding olefin-type resin coating.
The thickness associated with laminated nonwoven materials depends on the species of resin used for your fabrication process. It could possibly range from 5 to fifty grams a square meter. The thickness with the outer layer deviates from fifteen to twenty-five grams. One time laminated, the nonwoven material can have many properties.
Nonwoven laminated materials have many job applications across different industries. One prominent area is within the medical field, where they utilized for sterile, throw away medical materials. They might be treated with antimicrobial surfaces to make them highly hygienic. Furthermore, these components are light, breathable, in addition to durable.
The output process for nonwoven fabrics differs from classic weaving processes. Nonwoven fabrics are usually made of fibers and filaments and they are formed by a process called web loan consolidation. Some of the ones used to develop nonwoven fabrics include things like carding, air lounging, wet laying, filling device punching, and rewriting. The process also involves chemical and also thermal bonding.
Tenting the fabric helps it be easier to bond the person fibers. This process raises the density of fibers in the fabric, which cuts down thermal transmission. In addition , it improves the aesthetics in the fabric. However, the procedure does not enhance the weight of that facings. So, the extra weight of the fabric isn't going to significantly affect the performance of the product.
0 notes
Text
Applications of Hot Melt Technology

Hot melt technology is widely used in different industrial and manufacturing procedures. It can provide extreme adhesive power in assembling parts and sealing packages. Here are the different applications of hot melt technology:
1. Packaging - In packaging, the adhesive should not be that strong because it will be removed upon getting the product out of the package. You do not want to have the product sealed forever inside the box (or whatever container is used). However, the adhesive should be strong enough to keep the product inside the package in a perfectly safe and dry condition (especially if it is food).
There are specially designed industrial hot melt equipment for packaging. These equipments can be used for carton sealing, bag sealing, case sealing, tamper-proof closures, box making, tray making, etc.
2. Nonwovens - The use of nonwoven fabrics in clothing and other furnishings are widely embraced because of their strength and resilience. The hot melt technology has a part in achieving those properties of nonwoven fabrics.
Nonwovens are fabrics that are not knitted or woven. The fibers used in nonwoven fabrics are bonded with the application of heat and pressure. There are special resins, called binders, which are used in holding the fibers together.
The most common fibers used in making nonwovens are cotton, rayon, polyester, wool, acetate and acrylic.
Some binders used in Two component nonwoven fabric are acrylic, vinyl acrylic, vinyl acetate and styrenated acrylics.
3. Appliance assembly - Hot melt technology is starting to get the attention of appliance manufacturers because of its low cost without the strength getting compromised.
Specialized industrial equipment dispenses molten thermoplastic resins that are used as adhesives in assembling an appliance. The strength of the adhesive will be achieved upon the cooling of the pliable resin. This is a great time saver for manufacturers because it reduces the clamping time.
4. School projects, arts and crafts - This is the most basic application of this technology is the traditional consumer glue gun. It is the simplest adhesive dispenser that is readily available in households and schools.
The traditional adhesive used is the glue stick which may be cleared or colored. There are also novelty glue sticks like glittered sticks and glow-in-the-dark that are made specifically for artworks.
If it is the most basic, why do we have to mention it? For all we know, advanced technology always originates from the traditional practice. The traditional adhesive used (aside from glue stick, there are other thermoplastic resins that are traditionally used) are subjected to limitations. They tend to melt at high temperature and become brittle in low temperature; thus, losing the strength of the bond.
To address the temperature sensitivity of traditional adhesives, advanced adhesives are developed. Companies like Nordson also built high performance hot melt equipment for a better application of these adhesives.
see more: https://hkamber.com/
1 note
·
View note
Text
Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric Line Manufacturer & Supplier|Made In India
Our Non Woven material, which are known for their toughness, are optimal for developing a great equilibrium between product use-life and cost. We have actually devoted to continue generating and exporting PP (Polypropylene) Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric, PET Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric, SMS Non Woven Polypropylene Fabric, SSMMS Non Woven Polypropylene Fabric, Breathable laminated non woven fabric in delhi. FavouriteHub was founded in 2011 in Agra City, are non-woven material suppliers as well as focused on creating as well as distributing a variety of nonwoven products. All of our items are made based on the worldwide quality requirements, with the finest quality resources sourced from several of the marketplace's most trustworthy providers.

We can make products to satisfy our customers' bulk requirements due to our advanced infrastructure plant. We have actually sculpted an excellent location for ourselves as pp non-woven fabric producer in Kerala in both regional and international markets as one of the most trustworthy one-point provider for different products such as Geotextiles, PP Woven polypropylene fabric, PP/ PET Spunbond Nonwoven, and so forth. With 11 years of enriched experience, we have expanded multi-fold and now have procedures in the United Statesand India. OBTAIN CALL FROM OUR SALES MANAGER Spunbond Nonwoven textile Spunbond is very adaptable, fulfilling the requirements of a vast array of products in the clinical, sanitary, as well as commercial markets. The cloth is breathable, soft, light, chemical immune, safe, as well as eco-friendly. We offer a varied array of Nonwovens to our customers in Chennai, Coimbatore, Madurai, Tiruchirappalli, Tiruppur, Salem, Erode, Vellore, as well as other cities of karnatka, every one of which have a variety of applications in the medical area. These are made using ingenious reicofil lines from reifenhauser, Germany, and have exceptional skin-friendliness features. As a result of this attribute, the nonwoven is optimal for hygienic items. Our product variety uses exceptional features such as breathability, water absorbency, UV resistance, nontoxicity, soft qualities, and also many more. Additionally, it is readily available in a wide range of shades, sizes, and weights. Nonwoven textile material is high popular, thoroughly in clinical, commercial, individual treatment, as well as cosmetic items as a result of their anti-static, anti-moisture, and also hydrophilic properties. These nonwovens can be found in a range of stretch wrapping and film packing choices. The system by which the fibers are bound together identifies nonwoven materials. Nonwoven textiles been available in two varieties: Bonding with mechanical methods (fiberentanglement). Chemical communication (fibers are bonded together with glue-like substance). Thermal fusion (low melt fibers are made use of, as well as warm is made use of to thaw thread). Fabric high qualities can be controlled or turn around engineered using nonwoven components based on practical requirements such as fiber option, internet creation, bonding, and also completing procedures. Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric Raw Material. pp spunbond non woven fabric production procedure includes several basic material such as: Polypropylene (PP), polyamide (PA), polyester, as well as polyethylene( PE). The following are some of the polymers that have actually been processed:. The melt-blown approach is most typically employed with polypropylene. Polypropylene is basic to work with and also generates an outstanding web. Melt-blowing polyethylene into fragile fibrous internet is much more tough than melting polypropylene. Because of its melt flexibility, polyethylene is challenging to attract. PBT is very easy to work with as well as creates webs that are extremely soft and carefully fibered. Polycarbonate creates webs with unbelievably delicate fibers. Polystyrene creates a product that is exceptionally soft as well as fluffy, with virtually no shot problems. Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric Process:. We utilize the most up to date pp spunbond non woven manufacturer process, "Recofil II" Double Beam, to develop Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric. Spunbond Nonwoven textiles are used a continual procedure that transforms a fundamental thermoplastic material (Polypropylene) into an internet of continuous filaments. Thousands of fibers with a diameter of approx. 20 microns are melt-spun from polypropylene granules utilizing jets (2.8-3.0 dtex). These very tiny filaments are evenly put down in a three-dimensional framework that is arbitrary. The internet is after that fed right into a schedule, which makes use of heat to solidify the internet right into Spunbond textiles.
We have a firm commitment to R&D, CSI, and also sustainability as a packaging and also Lamination Film supplier as well as designer to serve our customers with top notch products, originality, and also superior customer support during and also after-sales. On top of that, we are regularly enhancing our modern technology based on feedback from our clients, with the utmost goal of becoming your long-lasting companion. we have a track record for premium items as well as timely, reliable customer service.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Custom Injection Molding Services in the United States
Injection molding is a type of customized production process in which a material, usually plastic, is melted and also infused by a machine into a mold. After that cools down and can be trimmed of any excess material. In this post, to assist you in your molding vendor search, we have assembled information on the leading custom-made as well as general suppliers of injection molding services in the United States. We will look at: Residential Custom Injection Molding Companies Domestic General Injection Molding Companies Residential Custom Injection Molding Companies
They are ranked in order of company dimension and in number of staff members.
Top Domestic Custom Injection Molding Companies
CompanyHeadquartersNumber of EmployeesAnnual Sales Montrose Molders, Inc.Piscataway, NJ200-499$ 25-49.9. The Rodon GroupHatfield, PA100-199$ 25-49.9. D&M Plastics LLCBurlington, IL100-199$ 10-24.9. R&D Molders, Inc.Georgetown, TX100-199$ 10-24.9. MVP PlasticsMiddlefield, OH50-99$ 10-24.9. Top Quality Plastics, Inc.Russells Point, OH50-99$ 10-24.9. SI Plastics, Inc.Jeffersonville, IN50-99$ 5-9.9. Colonial Engineering, Inc.Portage, MI10-49--. Dependence EngineeringLancaster, MA10-49--. Broker Manufacturing LLCFranklin, WI1-9--.
Company Summaries
Montrose Molders, in Piscataway, NJ, provides injection molding, tooling, and also assembly. It additionally uses engineering, job administration, and also top quality solutions as second solutions.
Based in Hatfield, , The Rodon Group concentrates on close resistance injection molding of small components in various sectors including food as well as beverage. Its various other services consist of layout, tooling, prototyping, satisfaction, product packaging, security stocking programs, and also in the nick of time delivery.
D&M Plastics offers high speed, high quantity, insert, tight tolerance, clinical gadget, clean area injection, and two shot over molding. It is based in Burlington, IL.
R&D Molders, in Georgetown, TX, uses injection molding of assembly components, little to medium components, as well as multi element products. It manages ABS, polypropylene, polystyrene, polycarbonate, acrylic, nylon, urethane, as well as high strength crafted polymers.
Based in Middlefield, OH, MVP Plastics supplies straight, upright, two shot, insert, and also gas help injection molding, as well as structural foam as well as over molding. It also supplies hot stamping, welding, chrome plating, printing, painting, as well as labeling.
Top Quality Plastics, based in Russells Point, OH, provides injection molding in commodity as well as crafted materials consisting of HDPE, PVC, ABS, polypropylene, acetal, nylon, PBT, and polycarbonate.
SI Plastics, in Jeffersonville, IN, uses injection molding from polypropylene, nylon, and also carbonate products. It serves the vehicle, consumer, as well as lawn as well as yard sectors.
In Portage, MI, Colonial Engineering, Inc. uses injection molding, assembly, as well as fabrication for PVC, CPVC, ABS, acetal, noryl, nylon, acrylic, polypropylene, polyethylene, HDPE, polystyrene, polycarbonate, minlon, celcon, santoprene, rynite, uniprene, delrin, polyester, as well as glass loaded materials.
Dependence Engineering supplies injection, compression, transfer, and also insert molding, as well as additional setting up and also machining services. It is based in Lancaster, MA.
Broker Manufacturing, based in Franklin, WI, uses thermoplastic injection molding in ABS, acetal, acrylic, nylon, PC/ABS, PEEK, PEI, PPE/PPO, and polycarbonate materials. Part production weight ranges in between 1 and 400 grams.
Residential General Injection Molding Companies.
Providing details on injection plastic molding companies according to Plastics News, ranked in order of earnings from sales of injection shaped products. Extra info consists of each company's headquarters place as well as number of employees. Sales are in millions of U.S. bucks, and also dashboards suggest missing information.
Top Domestic General Injection Molding Companies.
CompanyHeadquarters-Number of Employees-Sales from Injection Molded Products.
IACSouthfield, MI22,000 **$ 1,599. Grupo Antolin North America Inc.Auburn Hills, MI28,000 **$ 1,560. Berry Global Inc.Evansville, IN23,000$ 1,350. SRG Global Inc.Troy, MI5,600$ 1,080. Newell Brands, Inc.Hoboken, NJ40,000$ 1,000. UNITED STATE Farathane LLCAuburn Hills, MI4,200$ 805. AptarGroup Inc.Crystal Lake, IL13,000$ 775. NyproClinton, MA--$ 730. Kasai North America Inc.Murfreesboro, TN--$ 586.8. Mauser Packaging SolutionsAtlanta, GA11,000$ 580.
Company Summaries and Info.
IAC, based in Southfield, MI, manufactures automobile elements consisting of gaming consoles, cockpit console, door systems, headliners, and also above systems. Grupo Antolin North America also manufactures products for vehicle interiors, consisting of overheads, door panels, cockpits, illumination, trim, insulation and soundproofing, and steel parts. It is based in Auburn Hills, MI. Berry Global Inc., in Evansville, IN, supplies product packaging, defense products, tapes, adhesives, as well as specialty nonwoven products. It offers the individual care, house, food as well as beverage, food service, medical care, commercial, as well as transportation markets. Based out of Troy, MI, SRG Global concentrates on vehicle components consisting of subsystem, inside, and exterior items, as well as motorbike and industrial vehicle items. Its capabilities include customized layout, development, injection molding, stamping, roll forming, layering, paint, steel framework, as well as setting up. Newell Brands uses customer products including creating, baby, recreation, exterior, house scent, device, safety and security, food, cookware, as well as other products. It is based in Hoboken, NJ. In Auburn Hills, MI, U.S. Farathane manufactures custom plastic injection built elements for the auto industry. Its capabilities include standard, injection, 2 shot, as well as insert molding, settings up, durometer extrusions, welding, as well as compression molding. AptarGroup, based in Crystal Lake, IL, concentrates on elegance, home, food as well as drink, and also pharmaceutical consumer product packaging. It supplies shutoffs, pumps, dispensers, closures, samplers, circulation control products, dosage counters, inhalers, as well as silicone idea dispensers. Nypro provides product research, style, advancement, and introduction for the diagnostic, clinical tool, pharmaceutical shipment system, and also customer health markets. It is based in Clinton, MA. Kasai North America, based in Murfreesboro, TN, focuses on interior automobile parts, especially trim. Its offerings consist of cabin as well as luggage trim, sound insulation components, and also engine and fender covers. Mauser Packaging Solutions manufactures bulk containers, drums, containers, jerry canisters as well as tight head containers, jugs, bottles, medical containers, specialized containers, as well as strike molding machinery. It is based in Atlanta, GA
Plastic Injection Molding Companies - Summary.
Above we have actually covered stats as well as company recaps of the top basic as well as personalized injection molding providers and also providers in the United States. We wish this info has been handy to you in your injection molding distributor search.
#injection molding near me#plastic injection molding#plastic injection molders#injection molding companies near me
1 note
·
View note
Photo




How To Separate Oil From Water By Electrospinning Nanofiber Technology?
#separate #oil #water #electrospinning #nanofiber #technology #composite #polymeric #nanofibrous #mats #carbonbased #porous #electrospun #filter #membranes #oilwater #separation #hydrophobicoleophilic #instinctive #modified #superhydrophobicoleophilic #hydrophilicoleophobic #singlelayer #superhydrophilicoleophobic #multilayer #structured
1. COMPOSITE POLYMERIC NANOFIBROUS MATS
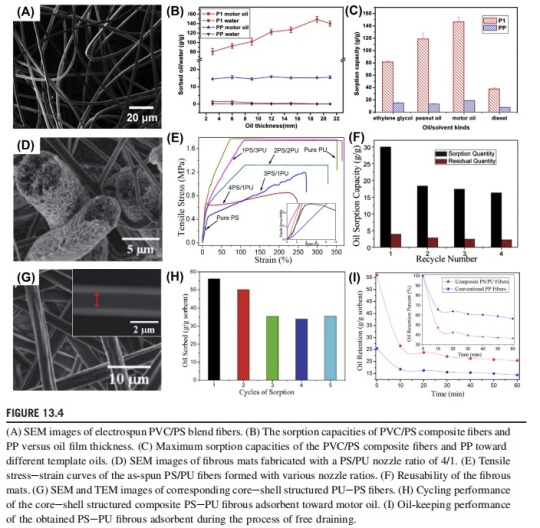
Due to the relatively weak mechanical strength of PS fibers and the unstable networks of the mats, the practical application performance (e.g., retention over time, oil recovery rate) of pure electrospun PS fibrous absorbents was seriously limited. To overcome this challenging problem, mechanical enhancers with high strength were introduced into the PS fibrous mats to improve their mechanical property. Various criteria must be fulfilled by the reinforcing components: they should be mechanically robust to withstand the tensile or compressive stresses during adsorption and recovery processes of sorbents; and hydrophobic-oleophilic wettability is required to ensure the mats have selective wetting ability. Accordingly, a series of additives such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyurethane (PU), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were employed to modify the PS fibers via different methods based on electrospinning technology.
To incorporate the reinforcing component into PS fibrous mats, various approaches involving blend electrospinning, multinozzle electrospinning, and coaxial electrospinning have been developed. As shown in Fig. 13.4A-C, PVC/PS composite fibers was first fabricated via directly adding an appropriate amount of PVC to PS solutions, and then made by blend electrospinning. The obtained oil absorbents performed well for motor oil, peanut oil, diesel, and ethylene glycol, with high sorption capacities of 146, 119, 38, and 81 g/g, respectively; these capacities are about five to nine times that of commercial PP melt-blown nonwoven sorbent. The PVC/PS oil adsorbent also possessed excellent oil-water selectivity and good buoyancy, which are important in oil-slick cleanup. Multinozzle electrospinning, a powerful technology in fabricating composite nanofibrous materials, has also been used to make porous PU/PS fibrous mats for oil absorption (Fig. 13.4D-F). The robust elasticity of the PU fibers greatly improves the mechanical strength of the obtained PU/PS fibrous mats, even with low PU contents. As a result the oil absorption performance, especially the reusability of the PU/PS fibrous absorbents, was significantly enhanced. Moreover, core-shell structured fibers were considered as an effective approach to enhance the mechanical property of single fibers. The SEM and the corresponding Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) images shown in Fig. 13.4G show that the core-shell structured PU-PS fibers have been prepared with a coaxial electrospinning technique by taking PU and PS solutions as the core and shell, respectively. The obtained PU-PS fibrous sorbent has sorption capacities of 64.40 and 47.48 g/g for motor oil and sunflower seed oil, respectively, which are two to three times that of traditional nonwoven PP fibrous mats with the same template oils (Fig. 13.4H and I). Moreover, the oil adsorption capacity comparable with melt-blown nonwoven sorbent was maintained even after five sorption cycles, giving excellent reusability.
2. CARBON-BASED POROUS NANOFIBROUS MATS
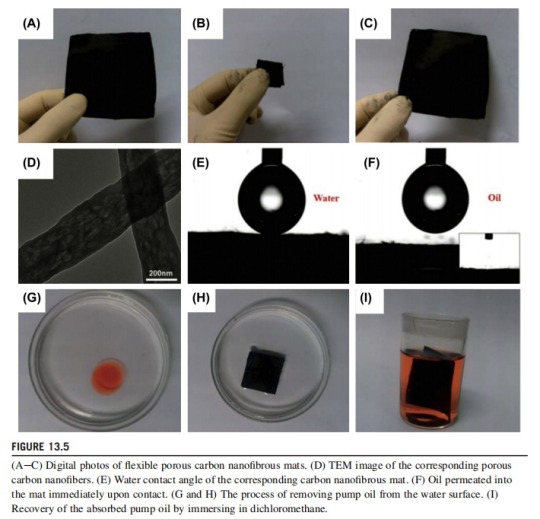
Carbon-based materials have been widely developed to absorb oils due to their instinctive hydrophobic-oleophilic wettability, excellent chemical stability, and thermal stability; this avoids several limitations of organic absorbents, which can be swollen or even dissolved when recycled by rinsing with organic solvents. Recently, electrospun macroporous carbon nanofibrous mats were fabricated through a sublimation method (Fig. 13.5), with terephthalic acid (PTA) used as the pore former to create macropores. During the carbonization of the PTA/polyacrylonitrile (PAN) composite NFs, PTA was sublimed and the macropores were formed, producing flexible and self-sustained macroporous carbon nanofibrous mats. These mats possessed special superhydrophobic and superoleophilic wettability, as well as relatively large porosity of up to 89.2%, attributed to the porous structure of the electrospun fibrous mats. The carbon-based membrane shown a high silicone oil sorption quantity of up to 138.4 g/g, and the absorbed silicone oil could be removed from the membrane by using organic solvents, exhibiting excellent recyclability. Furthermore, a spongelike carbonesilica nanofibrous absorbent with an interconnected three-dimensional structure was also synthesized using the electrospinning technique. The resulting composite fibrous sponge possessed a high porosity of more than 99% and displayed the specific wettability of ultrahydrophobicity and superoleophilicity. With its integral properties of high porosity, low density, and selective wettability, the sponge could adsorb oil up to 140 times of its own weight. Furthermore, oil recovery and sponge regeneration could be easily carried out through circular distilling or mechanical squeezing.
3. ELECTROSPUN NANOFIBROUS FILTER MEMBRANES FOR OIL-WATER SEPARATION
Filtration is another powerful technology for oil-water separation. Unlike the common filtration process for removing solid particulates, achieving efficient separation of oil/water mixtures, especially for emulsions, is quite difficult due to their complex composition, the tiny droplet size in the dispersed phase, and the ease of secondary emulsification. Nowadays, membrane separation technology with the advantages of high separation efficiency and simple operation is considered one of the most promising approaches for the treatment of oily wastewater and purification of oils. For effective separation of oil/water emulsions, a membrane needs to fulfill three criteria: selective wetting ability for the oil or water; appropriate pore size according to the droplet size of emulsions; and high porosity to ensure an acceptable permeation flux under a certain operational pressure. Recently, electrospun nanofibrous separation membranes have attracted considerable attentions with their thinner fiber diameter, high porosity, high surface area, and ease of use.
4. HYDROPHOBIC-OLEOPHILIC MEMBRANES FOR OIL-WATER SEPARATION
To separate the water contaminant from oil, an effective and simple method is to use a hydrophobic-oleophilic membrane with appropriate pore size to filter the tiny water droplets while allowing the oil to permeate through (oil-removing type). In general, there are two approaches to fabricate a nanofibrous oil-water separation membrane: one-step electrospinning of the hydrophobic-oleophilic polymers, and incorporation of modification processes.
4.1 Instinctive Hydrophobic-Oleophilic Polymeric Membranes
Direct electrospinning of hydrophobic-oleophilic polymers is a simple and effective way to fabricate a filter membrane for oil filtration. As shown in Fig. 13.6, a hydrophobic-superoleophilic membrane was successfully prepared by directly depositing the PS NFs on to a substrate (a stainless steel mesh) via one-step electrospinning. The fabrication process is quite simple, and the raw materials are easy to obtain and inexpensive. With the merits of low free energy of PS and the network-like structures of the membrane, the hydrophobicity of the membranes was significantly enhanced while keeping the intrinsic oleophilic property. As a result, the obtained PS fiber membrane could effectively separate oil/water mixtures in a single step. Other hydrophobic-oleophilic polymers (e.g., PP, PVDF, and PVB) were also directly used to create oil-water separation membranes via one-step electrospinning. For example, a hydrophobic fiber mat made of syndiotactic PP was fabricated for the removing of dispersed water droplets from diesel. Solutions of different weight concentrations of the PP were electrospun to produce submicron-sized fibers of different diameters. These fibrous membranes showed good selective wettability for oil and water, and could effectively remove water from fuel with efficiencies reaching 99%.
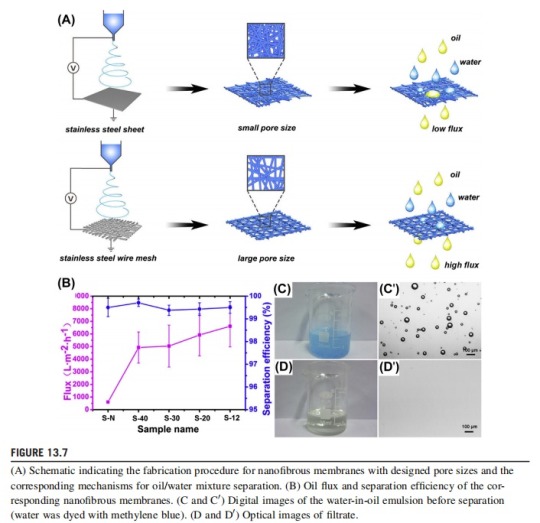
Furthermore, electrospun hydrophobic-oleophilic polyvinyl butyral (PVB) NFs were directly deposited on stainless steel wire meshes with different mesh numbers to obtain nanofibrous membranes with different pore sizes (Fig. 13.7). With synergistic effects of selective wettability and tunable porous structure, the obtained PVB nanofibrous membranes had an impressive capability to separate immiscible oil/water mixtures and stable water-in-oil emulsion. In addition, the oil flux of the separation membrane was greatly improved by controlling the pore size, which was about 10 times that of commercial nonwoven filters.
4.2 Modified Superhydrophobic-Oleophilic Composite Membranes
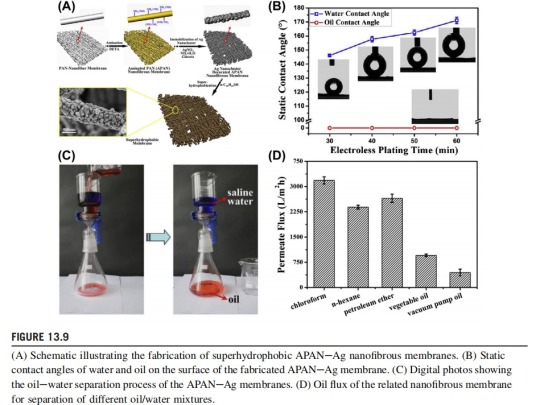
A variety of biomimetic superwettable nanofibrous materials for oil-water separation have been developed based on the synergistic effects of multiscale roughness and low surface energy. According to the principle of the Wenzel and Cassie-Baxter model, the construction of appropriate nano/microscaled roughness can transform a surface from hydrophobic to superhydrophobic, and an oleophilic surface becomes superoleophilic. In general, construction of a multiscale rough surface with low energy requires modifications to the as-spun NFs, including their physical morphology and chemical composition. Based on this theory, a superhydrophobic and superoleophilic nanofibrous membrane was developed using a novel in situ polymerization method to construct a functional layer of silica nanoparticles (SiO2 NPs)/fluorinated polybenzoxazine (F-PBZ) on the surface of electrospun cellulose acetate (CA) NFs (Fig. 13.8A). Benefiting from the low surface energy and excellent oleophilicity of F-PBZ and the hierarchical rough structures, the pristine CA nanofibrous membranes were transformed from instinct hydrophilic to superhydrophobic and superoleophilic, with a water contact angle (WCA) of 161 degrees and oil contact angle (OCA) of 3 degrees. More importantly, the modified nanofibrous membranes were capable of fast, efficient, and stable separation of oil/water mixtures at different pH conditions. Furthermore, the SiO2 NPs/F-PBZ/modified poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) (PMIA) nanofibrous membrane exhibited promising superhydrophobicity, high thermal stability (350C), and excellent mechanical strength of 40.8 MPa. As a result, the SiO2 NPs/F-PBZ/modified PMIA nanofibrous membranes gave a fast and efficient separation performance for oil/water mixtures. Furthermore, a core/shell structured polyimide/cellulose acetate electrospun fibrous membrane was fabricated by electrospinning and then modified by SiO2 NPs and F-PBZ; the obtained membranes showed much higher critical tensile stress (130 MPa) and superhydrophobic-superoleophilic wettability, and could effectively separate various oil/water mixtures solely driven by gravity, with high flux (3106.2 100 L/m2 h) and high separation efficiency (>99%). As shown in Fig. 13.8B, ceramic nanofibrous membranes, such as the F-PBZ/Aluminium oxide nanoparticles (Al2O3 NPs) modified SiO2 nanofibrous membranes, were also fabricated by the in situ polymerization method, and the obtained membranes gave effective gravity-driven separation performance for water-in-oil emulsions with a relative high flux of 892 L/m2 h, and had good antifouling property, thermal stability, and durability. Apart from in situ polymerization of F-PBZ, other chemicals (e.g., Nafion, beeswax, and n-hexadecyl mercaptan) have successfully been employed to create superhydrophobic and superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes for effective oil-water separation. As shown in Fig. 13.9, a uniform and hierarchical rough layer can be constructed on the surface of single electrospun NF via a simple combination of the amination of PAN NFs (APAN) and immobilization of Ag nanoclusters on the surface of fibers (APAN-Ag) using an electroless plating technique. This APAN-Ag nanofibrous membrane was modified with alkyl thiols: the modified nanofibrous membrane was superhydrophobic and superoleophilic, and had an excellent capability for oil-water separation in a hypersaline environment and a broad range of pH conditions.
5. HYDROPHILIC-OLEOPHOBIC MEMBRANES FOR OIL-WATER SEPARATION
Membrane separation is the most promising technology to treat oily wastewater, and ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes have been used in many industrial oil-water separation processes. Conventional ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes have fairly high separation efficiency for oil/water emulsions, but suffer from low flux, which is attributed to their limited permeability and serious surface fouling. To overcome these problems two aspects should be considered: constructing a hydrophilic surface to avoid oil fouling of the membranes, and increasing the porosity and decreasing the thickness of the separation layer.
5.1 Single-Layer Superhydrophilic-Oleophobic Nanofibrous Membranes
Inspired by the oil-repellent abilities of creatures in nature (such as fish scales), a superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic surface could be constructed by combining a hydrophilic chemical surface and appropriate roughness into polylactide NFs using the blending electrospinning method. The obtained composite nanofibrous membrane had good hydrophilicity and high water permeability, endowing it with the superior separation performance of oil-in-water emulsion under gravity. Besides blending electrospinning, dip coating is also an effect approach to modify nanofibrous membranes. Ahmed et al. employed cellulose regenerated from its ionic liquid solution to coat electrospun PVDF-co-hexafluoropropylene (PVDF-HFP). After modification with cellulose, the membrane had smaller pores with narrower pore size distribution: it exhibited superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity, and was successfully used for oil-water separation with quite high efficiency. Recently, a composite membrane made from graphene oxide coating aminated polyacrylonitrile (GO/APAN) fibers was fabricated by controlled assembly of GO sheets on the surface of electrospun APAN fibers and in the gaps between fibers. This membrane was superhydrophilic, had low oil adhesion, and exhibited ultrahigh flux, a preferable rejection ratio, and remarkable antifouling performance for the separation of oil/water emulsions. Furthermore, as shown in Fig. 13.10, a PAN/GO composite fibrous membrane with spindle-knot structured NFs was fabricated by electrospinning and then hydrolyzed (H-PAN/GO) to tailor its chemical features. With the combination of chemical features of hydrolyzed PAN and a spindle-knotted structure, the antifouling performance of the composite membrane was enhanced and it performed well in separating oil/water emulsions.
Compared to polymers, ceramic nanofibrous membranes have potential advantages in terms of relatively high surface energy, relatively stable chemical properties, and good antifouling ability. As shown in Fig. 13.11, Yang et al. used electrospun SiO2 NFs (SNFs) as the template, and anchored the SiO2 NPs uniformly on the surface of SNFs through a novel in situ synthesis method to fabricate flexible, thermally stable, and hierarchically porous structured composite membranes with highly selective wettability of superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity. With prominent selective wettability and high porosity, the obtained SiO2 NP/SNF composite membranes exhibited an extremely high separation flux up to 2237 L/m2h and high separation efficiency for a surfactantstabilized oil-in-water emulsion. In further studies, NiFe2O4 NPs were incorporated in SNFs to fabricate hierarchical magnetic nanofibrous membranes: these membranes were able to separate surfactant-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions effectively in a relatively high separation flux.
5.2 Multilayer Structured Superhydrophilic-Oleophobic Nanofibrous Membranes
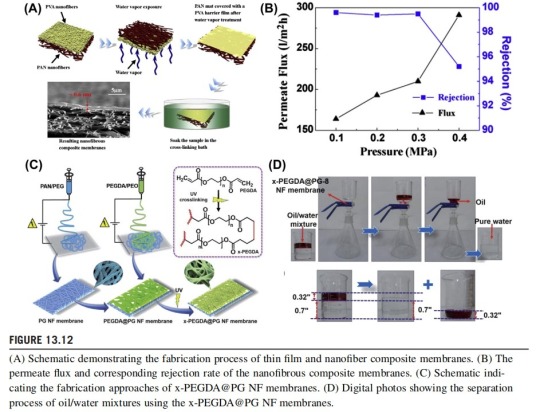
Constructing a separation layer with high selective wettability and small pore size on the surface of electrospun nanofibrous membranes is an effective way to enhance oil-water separation efficiency. Various composite nanofibrous membranes have been developed for high flux and high efficiency separation of oil-in-water emulsions. The main idea is to deposit a very thin hydrophilic polymeric layer of poly(vinylalcohol) (PVA), chitosan, polyamide, or even ultrafine polysaccharide NFs on to electrospun nanofibrous membranes via physical absorption or interfacial polymerization. As shown in Fig. 13.12, a double-layer separation membrane was fabricated by depositing the PVA NFs on electrospun PAN nanofibrous membranes, and then remelting and cross-linking the PVA nanofibrous layer to construct a nonporous PVA film with a thickness of several micrometers. Using this hydrophilic PVA layer, the composite membrane could effectively separate oil-in-water emulsions with excellent antifouling properties. In general, when a microporous or nonporous coating layer is constructed on the surface of a nanofibrous membrane, the water-permeate flux of the obtained composite membrane will be significantly reduced, which is attributed to the hydraulic resistance of the coating layer. To address this problem, Raza et al. fabricated superhydrophilic and oleophobic nanofibrous membranes by incorporating a composite layer of polyethylene glycol (PEG) diacrylate NFs on PAN/PEG nanofibrous membranes (x-PEGDA@PG NF) using the in situ cross-linked method. The obtained x-PEGDA@PG NF membranes could be completely wetted by water within a very short time and the superhydrophilic layer could trap a layer of water on the surface of membrane; this blocked the contact of oil with the membrane, thus making the membrane oleophobic. Benefiting from the high selective wettability and high porous structures, the membranes were capable of effectively separating immiscible oil/water mixtures and oil-in-water emulsions with high capacity and robust antifouling property. Most recently, a novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic nanofibrous membrane with a hierarchical structured skin for the separation of oil-in-water emulsions was prepared via electrospinning and electrospraying methods. Unlike the conventional nonporous polymeric film or submicro fibrous layer, the hierarchical structured SiO2/PAN microspheres bonded with monofilament significantly enhanced the wetting selectivity and antifouling properties of the composite membranes. With the combination of a superwettable hierarchical structured skin layer and a high-porosity nanofibrous substrate, the membranes performed well in separating microscaled oil-in-water emulsions solely under the driving force of gravity with excellent separation efficiency and high fluxes.
#separate#oil#water#electrospinning#nanofiber#technology#composite#polymeric#nanofibrous#mats#carbonbased#porous#electrospun#filter#membranes#oilwater#separation#hydrophobicoleophilic#instinctive#modified#superhydrophobicoleophilic#hydrophilicoleophobic#singlelayer#superhydrophilicoleophobic#multilayer#structured
1 note
·
View note
Text
Material properties and applications of protective clothing

Medical workers are exposed to a large number of patients every day, and there is a great risk of infection with bacteria and viruses. The use of medical protective clothing ensures their life safety to a certain extent. With the development of science and technology, the performance of medical protective clothing is getting better and better. Generally, medical protective clothing is divided into two categories: woven fabric protective clothing and non-woven medical protective clothing according to their different processing techniques.
1 Woven fabric protective clothing
Woven fabric medical protective clothing is the earliest used medical protective clothing. It mainly uses high-density cotton yarn or ultra-fine synthetic fiber filaments as raw materials and is formed by weaving, and sterilization and physical isolation are used for protection. However, when cotton fabrics are contaminated with liquids such as water, alcohol, and blood, they will lose their protective ability. , traditional medical protective materials cannot guarantee the safety of medical staff.
2 Non-woven medical protective clothing
1) Polypropylene spunbond nonwoven medical protective clothing
The emergence of polypropylene spunbond nonwoven has replaced traditional cotton fabrics. Medical protective clothing made of antibacterial and antistatic treatments has been widely used due to its advantages of low price, light, and thin products, high-temperature resistance, anticorrosion, and non-toxicity. In disposable products, the cross-infection rate is greatly reduced, but the material has low resistance to hydrostatic pressure and poor virus barrier efficiency, and can only be used as sterile surgical gowns, sterile wraps, and other ordinary protective equipment.
2) Meltblown nonwoven medical protective clothing
The emergence of melt-blown nonwoven medical protective clothing makes up for the disadvantages of spunbond nonwoven with thin fiber diameter, large surface area, strong hydrostatic pressure resistance, good water resistance, and good barrier effect on viruses and other pollutants. However, due to its low strength and poor wear resistance, its application as a medical protective clothing fabric alone is limited.
3) Non-woven composite medical protective clothing
At present, most of the materials used in medical protective clothing are generally non-woven composite materials, SMS multi-layer composite non-woven medical protective clothing, spunbond cloth (S) and meltblown cloth (M) is multi-layered, with spunbond and melt blown cloth (M). The advantages of the two materials of spray non-woven fabrics are widely used due to their high strength, good wear resistance, and strong hydrostatic pressure resistance. Require.
The medical disposable protective clothing used during the new crown epidemic mainly uses breathable film/non-woven composite cloth. The composite medical protective clothing material has an excellent ability to block bacterial particle penetration, block liquid permeability, high tensile strength, and good air permeability. , The comfort of medical protective clothing has been greatly improved. After antistatic and ethylene oxide or irradiation sterilization treatment, it does not contain toxic components, with high-cost performance and good filtering effect. It is a good medical protective clothing material.
With the spread of the global new crown pneumonia, the comfort of protective clothing has become a research hotspot. From the physiological functions of the human body and the latest research technologies, such as moisture permeability, nano-protective film materials, etc., its humidity and heat comfort involve multidisciplinary fields, and cost-effectiveness should be sought. High production technology, work under the condition of ensuring long-term wearing comfort of medical staff and improving their comfort and heat resistance.
Holymed Medical Group's non-woven medical products Division, established in the year of 1980, is one of the first manufacturers which produce non-woven medical products in China. Such as AAMI Level 3 isolation gown, you can click to view more details.
If you are interested in our products, please contact us as soon as possible.
Related news of medical protective clothing
Brief introduction of disposable medical protective clothing
Production process and raw materials of medical protective clothing
The protective mechanism of medical protective clothing
0 notes
Text
The anti-slip cloth features Anti-slip cloth uses
Non-slip cloth characteristics, non-slip cloth uses, the non-slip cloth is also known as dense cloth or password cloth, the product is soft and waterproof, flame retardant and sound insulation, toughness and tear resistance, strong anti-slip effect, mildew-proof and moisture-proof, anti-wrinkle and slip. The PVC foam contains a tear-proof fiber layer, and the double-layer foam + mesh fiber greatly increases the tensile strength. The colors are colorful, elegant and beautiful, soft and comfortable, and light and durable. Good elasticity, good anti-slip effect, easy to cut, easy to replace, easy to clean. Water absorption and dust absorption, strong adsorption, mildew, and shockproof, sound insulation, and heat insulation. No dust, non-toxic, odorless, and environmentally friendly. The product is made of natural environmental protection material PVC+polyester mesh cloth and foamed at high temperature, which is non-adhesive and non-slip cloth. It is non-toxic, tasteless, antibacterial, and environmentally friendly. The product has passed the SGS Hong Kong general fair test and meets the American ASTMD3421-75 and EN-71 (EU toy safety monitoring) and other testing standards.
Anti-slip cloth is a kind of strong anti-slip, high elasticity, waterproof, non-oil, and easy to clean. It can overcome other carpets that are easy to slide, deformed after repeated trampling, moldy, moth, and other phenomena. It can be used as household products, daily necessities, sports tourism products, fitness products, and sports and leisure products. The special liquid silicone for non-slip cloth is a two-component heating vulcanized silicone rubber. After inspection, it can be cured at room temperature or heated. It has colorless or skin-colored oily liquid. After vulcanization, it becomes a soft elastic material, which can be used to make insoles and shoulder pads. , SMD, anti-skid pads, car seat cushions, and other flexible silicone rubber products. Unchanging shape, changeable appearance, soft touch, high tear resistance.
Anti-slip cloth is a kind of mat made of silicone to prevent objects from sliding. According to its application function, it can be divided into mobile phone drop plastic cloth, car PVC anti-slip cloth, bathhouse PVC anti-slip cloth, yoga PVC anti-slip cloth, and cup PVC anti-slip cloth. However, there are usually PVC dripping cloth, PU dripping cloth, and silicone dripping cloth in the market. The advantages and disadvantages of different raw materials and the quotations are also different. Their functions are basically the same, but the most outstanding functions of silicone pads are high and low-temperature resistance, soft material, and electrical insulation. are widely liked. The product design is unique, healthy and environmentally friendly, elegant and beautiful, but the price is slightly higher.
About CHENSHIJI:
Changshu Chen shi Ji Nonwoven Products Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer that specialized in needle-punched or laminated nonwoven fabrics. with roll making, and hot shrinking, we produce various products to different customers' standards, which integrates design, development, manufacture, and sales.
Our products are wildly used in wrapping, moving blankets, and Floor Protection. painter fleece is our hot-selling product. when decorating the house it is covered on the floor to effectively protect the floor from dirt and breaking down. with the function of waterproof, anti-slip, and eco-friendly. Painter fleece is very popular in Europe, the Middle East, America, and Australia.
0 notes
Text
The earmarks of PP Coarse Denier Nonwovens a wide range of
PP Rough Denier Non-Woven fabrics are produced by spinning polypropylene polymers into fluff then weaving them together to produce a solid leather. The Wholesale PET Non-woven Fabrics Factory resulting fabric can be quite flexible and features a woven texture for instance canvas. Unlike stiched PP, which is often white, PP Coarse Denier Nonweave fabrics might be made in every solid color. They are strong, clean, as well as easy to sew. On the other hand, they can as well pucker after one or two months and develop into unsightly if they are not taken care associated with.
Unlike traditional woven fabrics, nonwoven fabric is considered environmentally friendly for a few applications. This is definitely especially important around industries and job areas that involve disposable products. PP Coarse Denier Non-Woven must be used for a great deal of products. These incorporate reusable and net packaging, toilet papers, and more. This can be a natural fiber that is considered to be a better choice for a few applications than other people.
The nonwoven marketplace is booming. As of 2012, it accounted for 25% off fiber shipments around the world. Manufacturers use many fibers to generate nonwovens. These fibres include polyester, oil-based polypropylene, healthy cotton, and cellulose. Since their popularity is usually increasing, nonwoven output is far outpacing common textile industries. These fibers have several advantages and are becoming more important inside the nonwovens industry.
In contrast to woven fabric, non-woven cloth is more environmentally-friendly. This really is especially important for industries such as health care along with luxury accommodations in which disposable products are very important. Additionally, the strength associated with non-woven fabrics is above that of weaved fabric. This makes them an added eco-friendly choice for several applications. The important things about PP Coarse Denier will be plentiful. This fabric is stronger than many woven fabrics.
Unlike its synthetic counterparts, PP Coarse Denier Nonweave gives the superior surface spot and softness. It is also more resistant to help water and chemicals than other nonwoven components. Moreover, PP nonwovens offer the most effective durability of almost all available nonwovens. They are extremely durable and they are very practical for easy use in many industries. For these reasons, PP is a great choice for lots of nonwovens.
The earmarks of PP Coarse Denier Nonwovens a wide range of. Unlike other fabrics, nonwovens have your much greater surface than nonwoven materials. Consequently, they are definitely absorbent. Moreover, a PP fabric is usually stronger than various other materials. A PP fiber incorporates a higher void fraction than some others of fiber. Meaning it will take in more liquid and reduce raise the risk of leakages.
Nonwovens are sheet or web structures that are not woven. They're made by entangling muscles in perforated shows. The density of these fabrics varies, depending on the kind of thread. Unlike other materials, nonwoven fabrics may be recycled. They might be reused after they have been disposed. For this reason, PP Coarse Denier is surely an excellent choice for coverstock and for many other programs.
0 notes
Text
The Usefulness of Non-Woven Fabrics Today and Its Future

Nearly every place you sit or stand has a nonwoven fabric. It could be a coffee filter, a tea bag, a mask, diapers, tissues for contact lenses, or other such items. This fabric now has more significance because of the current circumstances and the times we went through because of Covid, yet its market has expanded through time.
What is Non-Woven?
The most traditional and basic types of textiles are non-wovens. They are not woven or knitted. These fabrics are web structures or sheets that are joined together chemically, mechanically, or thermally, by tangling filaments or fiber. These are porous, tufted, or flat sheets made of various plastic films, fibers, or molten plastic. These textiles do not have to be made into yarn because they are not woven or knitted.
For the creation of non-woven fabrics, some oil-based products and recycled fabrics are utilized. Under the right conditions and with the right handling, certain nonwoven textiles can also be recycled. Because of this, nonwoven materials are seen as more environmentally friendly in various applications, particularly in businesses like high-end hotels, schools, nursing homes, and hospitals.
Why Use Non-Woven Fabrics?
Non-woven materials are necessary, flexible, degradable, adaptive, and inventive. As a result, their manufacturing process is quick and simple. 5,00,000 meters of woven fabric must be manufactured in 6 months, however, the non-woven fabric can be made in the same quantity in only 2 months. Non-woven fabrics feature a few unique characteristics and a low production cost.
How Non-Woven Fabrics are Used
Numerous sectors, including defense, medical, geotextile, construction, automotive, fashion, and filtration use non-woven materials. These days, non-woven fabric is widely used, and it appears that life would be impossible without it. There are two sorts of this fabric: disposable and durable. 40% of the fabric is recyclable, while 60% is long-lasting. The non-woven fabric's distinguishing features are:
Cushioning
Sterility
Absorbency
Flame retardancy
Strength
Filtration
Acoustic insulation
Thermal insulation
Resilience
Liquid repellence
Softness
Stretch
The industries where non-woven fabrics are used are –
Household: Filters, ie. water, coffee, air, tea bags, vacuum bags; food prep wipes, surface cleaning, household wipes.
Medical: Isolation gowns, surgical scrub suits, caps, surgical gowns, surgical drapes and covers, surgical masks, medical packaging: porosity allows gas sterilization, drug delivery, plasters, medical face masks, gloves, shoe covers, bath wipes, wound dressings, disposable clothing (foot coverings, coveralls), cleanroom wipes, filters used in the pharmaceutical industry.
Apparel: Industrial workwear, chemical defense suits, Interlinings, insulation and protection clothing, shoe components, backing/stabilizer for machine embroidery.
Construction and Geotextiles: Soil stabilizers and roadway underlayment, erosion control, canal construction, drainage systems, geo-membrane protection, sand infiltration barrier for drainage tile, landfill liners, insulation (fiberglass batting), weather-resistant house wrap, potting materials for plants.
Health and Hygiene: Diapers, feminine hygiene, adult incontinence, wipes (personal care, fingernail), cosmetic facial pads, and consumer face masks.
Acoustics: Acoustic insulation for appliances, automotive components, and wall-paneling, sound attenuation
Transportation: Gasoline, tarps, oil and air filtration, and transportation wrapping.
Industrial: Industrial wipes, composites (marine sail laminates, table cover laminates, chopped strand mat), Carpet backing, primary and secondary, flooring, backing/stabilizer for machine embroidery, packaging where porosity is needed.
Furnishing: Pillows, cushions, mattress cores, upholstery padding, batting for quilts in comforters.
Packaging: Meat packaging (absorbent pads), mailing envelopes, and shopping bags, shipping supplies.
The advantages listed above show why the nonwoven fabric market is expected to grow significantly in the future. Many Industries have made the switch and you should, too.
0 notes
Text
Quality control and quality assurance in the apparel industry
Interlinings, also called interfacing, are generally nonwoven fabrics that add more structure and body to garment components like collars, button plackets, waistbands, and cuffs. Interlinings may be fusible or sew-on. Interlining fabric durability is important for garment construction. Fusible interfacing can become unglued from fabric and shift, creating rippling, puckering, and unevenness. Hence, the fusible interfacing should be tested for their performance for defects such as cracking, bubbling, and delamination during their regular use. Fusible interfacings are susceptible to the adhesive bleeding through causing darker spots on the surface called strike-through. Fusible interlinings are assessed for their ability to stay bonded to the fashion fabric and not shift during wear and cleaning. They are also tested for compatibility and shrinkage. Compatibility indicates good drapability, bulk, and support of the fabric at the attachment point. Shrinkage can cause puckering of the attached point and bubbled appearance. The three parameters such as temperature, pressure, and time should be appropriately selected to avoid improper interlining attachment.
However the quality of the face fabrics and non woven interlining used in making samples does not always conform to the materials delivered for production. The face fabrics and their interlinings must therefore be tested again to verify the previously accepted fusing parameters.
One of the first successful applications of nonwovens was as interlinings for clothing (Assent, 2003). Nonwovens are still widely used for this purpose but are also used as the main material for protective clothing (Haase, 2003) and increasingly as the outer layer in fashion-based and technical garments (University of Leeds, 2007). The making-up of nonwovens is therefore an important consideration. Patterning, cutting and joining are considered very basically here.
Nonwovens for interlinings are processed in such a way as to give them an adhesive surface. The patterns for these nonwovens are designed and made together with the patterns for the upper fabric and garment lining during the pattern design and grading stages. Table 8.2 outlines the functional aspects of nonwovens that impact on their performance as interlinings, and highlights the stages of fabric production that affect these aspects.
Fusing of interlinings in garment manufacturing is a very important process. Interlinings are the accessories used between two layers of fabric to keep the different components of apparel in a desired shape or to improve the aesthetics and/or performance. Generally, interlinings are soft, thick, and flexible fabric made of cotton, nylon, polyester, wool and viscose or their blends, which may be coated with some resins. There are two types of double dot non woven interlining in use in the garment production: fusible and non fusible. The interlinings are carefully selected so that they can withstand the conditions during the fabric care and maintenance without any damage during the useful life of a garment. Once the garments are finished and inspected, they are packaged and transported to the retailers or the point of sale to the consumers.
The garment construction and type, notably the number and type of seams, linings and interlinings as well as cut and style, clearly play a significant role in the draped appearance of the garment, the presence, nature and bonding of interlinings, etc. having a major effect. So too will the fabric colour, depth of shade and pattern have a significant effect, although these effects are essentially optical in nature and not due to actual changes in the fabric drape per se. With respect to the effects of seams, including seam and stitch type, these have been studied and reviewed in detail by Chung,12 Hu17 and Sharrouf,36 their main effects being on the stiffness (both bending and shear) of the fabric in their immediate vicinity and on their positioning within the garment.
The garment construction and type – notably the number, positioning and type of seams, linings and interlinings – as well as cut and style, play significant roles in the draped appearance of the garment, with the presence, nature and bonding of interlinings having a major effect. Fabric colours, depths of shade and patterns also have significant effects, although these are essentially optical in nature and not due to actual changes in the fabric drape per se. Seams mainly affect fabric stiffness (both bending and shear) in their immediate vicinity, the magnitude of the effect depending on their positioning within the garment. For example, bending length tends to increase with the insertion of a vertical seam, while drape coefficient increases with the addition of radial seams, and increasing the seam allowance has little effect.
The most important factor for performing qualitative fusing is temperature. It must correspond to the glue line temperature, required for the certain interlining. However, the temperature setting or reading on the control panel of a fusing press indicates its belt temperature, not the temperature applied to the interlining. The real temperature that will be delivered to the interlining through the face fabric can be determined only during the test. It can be performed putting special temperature control tape in-between the face fabric and its interlining sample and fusing them. The colour of the tape will show the real temperature applied to the interlining. The optimal fusing temperature must be found for every fabric of the order to avoid its shrinkage or damaging during the fusing process.
Normal cotton sheeting fabrics were applied with a layer of adhesive that can be fixed to the shell fabric by application of heat or pressure. This formed a composite part of the fused shell part and supported the outer shell for better drape and look.
Woven interlinings are majorly 100% cotton based with a thread density of variable count as required for the weight or stiffness needed for a particular use. Now poly-cotton blends are also available to overcome the problems of shrinkage faced in cotton fabrics together with a variety of warp and weft combination like rayon, texturized poly and wool etc.
Advantages of woven interlining
The main advantage of woven fabrics is its strength and stability, hence used for all such applications where strength and stability are needed like the waistband.
However, this could be a disadvantage at times where flexibility and soft hand feel is required.
Woven is majorly plain weaves, sometimes crepe, herringbone or twill weaves are also offered according to the application need.
In such cases, texturized poly yarns are used for voluminous body, soft and natural hand feel or drape of the fused composite at the same time strength, flexibility and lightweight of the fused laminate is achieved without much altering the natural drape or texture of shell fabric.
However, woven is expensive and not suitable for less expensive casual garments hence, it was replaced by knitted fabrics that used a combination of synthetic yarns with rayon and wool for body and volume according to different application intended for.
As the name implies there is no involvement of any yarn for interlacement to make the fabric.
It is made directly from fiber to fabric stage in the process reducing the cost of base fabric. As there is no yarn used in making nonwovens, it lacks in strength needed for apparel use and there are many techniques applied to impart required strength to nonwoven textiles, called Bonding. They are the most versatile product available from 10gsm to 200gsm and above, offering light, soft, flexible or strong for any application one can think of. The basic manufacturing technique is using mostly synthetic fibers to form a layer, which are imparted strength by bonding.
Let us understand the different layering and bonding methods, their use and their advantages and disadvantages.
Seema Impex, Established in 2018 at Delhi in Delhi, is leading Importer, Supplier of Interlinings & Linings in India. Seema Impex is one of Trade India's verified and trusted sellers of listed products. With their extensive experience of supplying and trading Black Double Dot Stretch Lycra Fusing Interlining, Seema Impex has made a reputed name for themselves in the market with high quality Black Double Dot Stretch Lycra Fusing Interlining, Grey Stretch Microdot Fusing Interlining, Fine Finish Microdot Fusing Interlining etc.
Focusing on a customer centric approach, Seema Impex has a pan-India presence and caters to a huge consumer base throughout the country. Buy Interlinings & Linings in bulk from Seema Impex at Trade India quality-assured products.
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of pressing on bending rigidities of the face fabric, adhesive paste dot non woven interlining and bonded composite fabric and verify the prediction method for bending rigidity of those. Predicting methods of bending rigidity for composite with face fabric and adhesive interlining based on laminated theory were verified with measured bending rigidities and thickness of samples. Bending rigidities and thicknesses of woven fabrics, adhesive interlinings and composites with those were measured by the KES-FB system. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) film was used for measuring mechanical properties of pressed adhesive interlining. Bending rigidities of adhesive interlinings became larger and thicknesses were reduced compared to those before pressing. Bending rigidities of face fabrics didn’t change though the thicknesses became thinner than before pressing. It was found that the case of considering mechanical properties of pressed face fabric and pressed interlining was more efficient to predict bending rigidity of composite with laminated model.
0 notes
Text
Bicomponent Fiber Spinning: Factors, Principles and Technologies
Bicomponent Fiber Spinning: Factors, Principles and Technologies #bicomponent #bicomponentfiber #bicomponentspinning #nanofiber #electrospinning #spinning
Bicomponent Spinning: Bicomponent fibers are fibers that in a single fiber consist of two distinct raw material components. It is made by simultaneously spinning two compositions in each capillary of the spinneret. The growing demand for nonwoven fabrics is one of the growth drivers of the global bicomponent fiber industry. The growing demand for nonwoven fabrics is one of the growth drivers of…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Global and Regional Paper Diaper Industry Status and Prospects Professional Market Research Report Standard Version 2021-2027
The global Paper Diaper market was valued at 69.9 Million USD in 2020 and will grow with a CAGR of 2.86% from 2020 to 2027, based on Our Researcher newly published report.
The prime objective of this report is to provide the insights on the post COVID-19 impact which will help market players in this field evaluate their business approaches. Also, this report covers market segmentation by major market verdors, types, applications/end users and geography(North America, East Asia, Europe, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Middle East, Africa, Oceania, South America).
Paper diapers are designed to absorb and retain person`s urine and faces while keeping the skin dry and healthy and to be easily and hygienically disposed of in household solid waste. A disposable diaper consists of an absorbent pad sandwiched between two sheets of nonwoven fabric. The pad is specially designed to absorb and retain body fluids, and the nonwoven fabric gives the diaper a comfortable shape and helps prevent leakage. These diapers are made by a multi-step process in which the absorbent pad is first vacuum-formed, then attached to a permeable top sheet and impermeable bottom sheet. The components are sealed together by application of heat or ultrasonic vibrations. When properly fitted, the disposable diaper will retain body fluids which pass through the permeable top sheet and are absorbed into the pad. The technical barriers of paper diapers are low, and the paper diapers market concentration degree is relatively higher. As the main markets of paper diapers, United States, West Europe and Japan have developed a mature market for baby care industry and adult incontinence products. Caused by population, consumerism, lifestyle, and consumption capacity, the largest market is United States, which is followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. Moreover, the China and India countries enjoyed a magnificent economic growth in recent years, which also lead the growth of these countries. Many experts state Indonesia, Malaysia, Brazil, Egypt and Turkey will be next engine of paper diapers market.
Download FREE Sample of this Report @ https://www.grandresearchstore.com/report-sample/global-regional-paper-diaper-2021-2027-31
By Market Verdors:
P&G (Pampers)
Kimberly Clark
Unicharm
SCA
First Quality
Ontex
Kao
Medline
Domtar
Hengan
Chiaus
Daddybaby
Coco
Medtronic
Fuburg
By Types:
Baby Paper Diaper
Adult Paper Diaper
By Applications:
Shopping Malls
Baby Store
Online Channel
Key Indicators Analysed
Market Players & Competitor Analysis: The report covers the key players of the industry including Company Profile, Product Specifications, Production Capacity/Sales, Revenue, Price and Gross Margin 2016-2027 & Sales with a thorough analysis of the market?s competitive landscape and detailed information on vendors and comprehensive details of factors that will challenge the growth of major market vendors.
Global and Regional Market Analysis: The report includes Global & Regional market status and outlook 2016-2027. Further the report provides break down details about each region & countries covered in the report. Identifying its sales, sales volume & revenue forecast. With detailed analysis by types and applications.
Market Trends: Market key trends which include Increased Competition and Continuous Innovations.
Opportunities and Drivers: Identifying the Growing Demands and New Technology
Porters Five Force Analysis: The report provides with the state of competition in industry depending on five basic forces: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitute products or services, and existing industry rivalry.
Key Reasons to Purchase
To gain insightful analyses of the market and have comprehensive understanding of the global market and its commercial landscape.
Assess the production processes, major issues, and solutions to mitigate the development risk.
To understand the most affecting driving and restraining forces in the market and its impact in the global market.
Learn about the market strategies that are being adopted by leading respective organizations.
To understand the future outlook and prospects for the market.
Besides the standard structure reports, we also provide custom research according to specific requirements.
Get the Complete Report & TOC @ https://www.grandresearchstore.com/consumer-goods-and-services/global-regional-paper-diaper-2021-2027-31
Table of content
Chapter 1 Industry Overview 1.1 Definition 1.2 Assumptions 1.3 Research Scope 1.4 Market Analysis by Regions 1.4.1 North America Market States and Outlook (2022-2027) 1.4.2 East Asia Market States and Outlook (2022-2027) 1.4.3 Europe Market States and Outlook (2022-2027) 1.4.4 South Asia Market States and Outlook (2022-2027) 1.4.5 Southeast Asia Market States and Outlook (2022-2027) 1.4.6 Middle East Market States and Outlook (2022-2027) 1.4.7 Africa Market States and Outlook (2022-2027) 1.4.8 Oceania Market States and Outlook (2022-2027) 1.4.9 South America Market States and Outlook (2022-2027) 1.5 Global Paper Diaper Market Size Analysis from 2022 to 2027 1.5.1 Global Paper Diaper Market Size Analysis from 2022 to 2027 by Consumption Volume 1.5.2 Global Paper Diaper Market Size Analysis from 2022 to 2027 by Value 1.5.3 Global Paper Diaper Price Trends Analysis from 2022 to 2027 1.6 COVID-19 Outbreak: Paper Diaper Industry Impact Chapter 2 Global Paper Diaper Competition by Types, Applications, and Top Regions and Countries 2.1 Global Paper Diaper (Volume and Value) by Type 2.1.1 Global Paper Diaper Consumption and Market Share by Type (2016-2021) 2.1.2 Global Paper Diaper Revenue and Market Share by Type (2016-2021) 2.2 Global Paper Diaper (Volume and Value) by Application 2.2.1 Global Paper Diaper Consumption and Market Share by Application (2016-2021) 2.2.2 Global Paper Dia
CONTACT US: 276 5th Avenue, New York , NY 10001,United States International: (+1) 646 781 7170 / +91 8087042414 Follow Us On linkedin :- https://www.linkedin.com/company/grand-research-store/
0 notes