#Trading company in Brazil
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Is It Recommended to Trade with Trading Platforms in Brazil Now?
Brazil comes as one of those countries that offer endless investment opportunities to the aspiring traders around the world. This comes as one of the reasons why trading stocks in Brazil is getting more and more popular with every day passing. Brazil's trading platforms are getting better to draw local and foreign investors as the country develops and more people search for financial possibilities. However, there are some things to consider if you're wondering whether it would be wise to start using a stock trading website in Brazil right now. Let's explore what makes this market interesting, what you should know before trading, and why Brazil might be a fantastic option for your next investment.

1. Rising curiosity about international stocks.
Many Brazilian investors nowadays find great attraction in the availability of US stocks trading in Brazil. Through Brazilian trading platforms, you can thus purchase shares of huge American companies including Apple, Amazon, or Tesla. Many of the best rated online stock trading Brazil options today let users easily diversify their portfolios using both Brazilian and U.S. stocks. Why this would come appealing? Well, having access to both markets helps you to distribute your investments, so reducing risks. While local events could influence Brazilian stocks, U.S. stocks usually behave depending on other criteria. This dual exposure is a wise approach that lets you help local businesses and profit from global expansion.
2. User-friendly trading platforms
If you're new to investing or seeking a better experience, Brazilian trading platforms comes helpful since they are getting far more user-friendly. The country boasts some of the finest stock trading website in brazil with simple registration, user-friendly layouts, and even instructional tools to help one grasp the foundations of trading. Furthermore among the best rated online stock trading Brazil systems are mobile apps, which let you follow market news on the go and check your investments and trades. Many more people can now afford trading thanks to this convenience; thus, mobile options are a great advantage if you want to quickly manage your portfolio or are busy.
3. Reduced Costs
The cost structure is one factor to take Brazilian trading platforms into account. Particularly in relation to trading local stocks, some platforms provide lesser fees than foreign brokers. Some trading sites have reasonably priced options for those who wish to invest in US stocks trading in Brazil that cut expenses on foreign exchange and maintain open fees. Comparing costs is always smart before deciding on a platform. Many of the top rated online stock trading Brazil platforms have reasonable prices, which will help you over time maximise your gains. Though initially nominal, savings on fees add up especially if you trade often or have a sizable portfolio.
4. A Rising and Resilient economy
Though Brazil has had its share of challenges over the years, its economy is showing potential of resilience and expansion. Key players in manufacturing, agriculture, and natural resources, the nation has drawn foreign capital. There is no shortage of Brazilian businesses displaying great potential for expansion among the several sectors from which one can choose. Another reason many investors are spotting prospects in Brazil is this diversification. Particularly in the mining, oil, and agricultural sectors, a stock trading website in Brazil could provide you access to businesses you would not find readily on other platforms. Given the world's ongoing demand for Brazil's natural resources, investing in these sectors could be wise.
5. Supportive laws and legalities
The Brazilian government has been working on laws that support safer trading conditions, so safeguarding investors and increasing dependability of platforms. Building investor confidence depends on these laws, which have also helped the top rated online stock trading Brazil platforms give more open and safe experiences for users. Laws dealing in data security, safe transactions, and open pricing further help users to feel more comfortable while using these sites. Knowing that the platform you are using is regulated and adhering to industry standards will help you relax and enable you focus on developing your portfolio.
6. Availability of News and Analysis from international Markets
Access to market news and analysis is one advantage of utilizing a reputable stock trading website in Brazil. These days, many systems provide real-time data, trading-oriented analysis tools, and even educational materials. That said, keeping up with the updates and knowledge of international affairs is vital, particularly if US stocks trading in Brazil pique your interest. For instance, political events, interest rate changes, or U.S. economic announcements could affect stock performance; thus, keeping informed helps you to make better trading decisions. To ensure you never overlook any crucial news, some of the best sites include daily analysis summaries or newsletters. Their analysis of the Brazilian economy is also quite helpful for local stock decisions.
7. Local Currency and Accounts
Dealing with local currency is one often disregarded advantage of trading on a Brazilian stock trading website. Brazilian citizens who wish to avoid the hassle and additional expenses of currency conversion will find this especially helpful. Many systems let you handle everything in Brazilian Real (BRL), a simpler and less expensive currency. Dual-currency accounts, which let you retain Brazilian Reals and U.S. Dollars, are also available on some trading platforms. If you are interested in US stocks trading in Brazil, this will help you trade across borders without continual worry about exchange rates.
Is It Recommended then?
Well, the answer is a big yes! Especially if you want to diversify your portfolio, trading on Brazilian markets is not only easily available but also progressively advantageous. Moreover, rapid development of advanced user-friendly interfaces, low costs, and tools for both new and experienced investors has made the best rated online stock trading Brazil platforms stand out.
Source: https://excentcapital.blogspot.com/2024/11/is-it-recommended-to-trade-with-trading.html
#Free trade with trading platforms in brazil#Best trade with trading platforms in brazil#Brazil Forex traders on instagram#Investment platforms in Brazil#Trading company in Brazil#Interactive Brokers Brazil
0 notes
Text

Jaspar Beckx - Portrait of Dom Miguel de Castro, Emissary of Congo (1643)
Archival sources mention that Dom Miguel was head of a diplomatic delegation whose mission it was to gather European support in a conflict in their homeland, then named Kongo, in Africa. The delegation travelled both to Dutch Brazil and to the Dutch republic in order to negotiate support from the Dutch West Indian Company (WIC) which was in charge of colonial matters related to Africa. Dom Miguel was ambassador for the count of Sonho (Soyo), Daniel da Silva, the other part in the conflict being King Garcia II. In 1642-43, both sides sent diplomatic missions to negotiate with the WIC. The Dutch had just won Luanda in Angola, and therefore they were interested in maintaining good relations with leaders in other West African regions. Like other European countries, the Dutch republic took part in the colonial trade that implied import of enslaved Africans to the colonies overseas. The African leaders sold war prisoners, victims of territorial conflicts in their homelands, to the Europeans who shipped them to the Americas as enslaved people. For the Europeans, they were indispensable manpower in the sugar plantations in the South American and Caribbean colonies. (source)
168 notes
·
View notes
Text
Judge in Brazil orders slaughterhouses to pay for Amazon reforestation

A judge in the Brazilian state of Rondonia has found two beef slaughterhouses guilty of buying cattle from a protected area of former rainforest in the Amazon and ordered them, along with three cattle ranchers, to pay a total of $764,000 for causing environmental damage, according to the decision issued Wednesday. Cattle raising drives Amazon deforestation. The companies Distriboi and Frigon and the ranchers may appeal.
It is the first decision in several dozen lawsuits seeking millions of dollars in environmental damages from the slaughterhouses for allegedly trading in cattle raised illegally in a protected area known as Jaci-Parana, which was rainforest but is now mostly converted to pasture.
Four slaughterhouses are among the many parties charged, including JBS SA, which bills itself as the world’s largest protein producer. The court has not decided on the cases involving JBS.
Brazilian law forbids commercial cattle inside a protected area, yet some 210,000 head are being grazed inside Jaci-Parana, according to the state animal division. With almost 80% of its forest destroyed, it ranks as the most ravaged conservation unit in the Brazilian Amazon. A court filing pegs damages in the reserve at some $1 billion.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#environmentalism#amazon rainforest#farming#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
50 notes
·
View notes
Note
C might mean well, but I find businesses using charity to sell suspicious.
Dear Provocative Anon,
What you say deserves an audio (there have been two of them two weeks ago, compensating for last week's silence). I have many things to tell you and please excuse the delay:
They really can't win, with people like you, can they? And that goes for both C and S, mind you. No matter what they do and try to promote as a side project, there is always going to be someone unhappy and vocal about it. When it's not you complaining 'business using charity to sell' is 'suspicious', there's the other fuckwit asking recently why S hasn't given all MPC's profit to charity, as Paul Newman did with Newman's Own.
So, I will be brutally honest with you, Anon. I have thoughts and questions about your own point of view and this is partially why it took me so long to answer you. It would seem you are not familiar at all with what is called 'corporate social responsibility' (CSR), since at least the Sixties. Which means, in a nutshell, companies who choose to focus part of their activity and dedicate part of their profits to charitable projects. It is done with various degrees of ethics, success and bona fides all around the world, and it is often used as a strong marketing and sales argument.
Think about these people, whose brand is probably immediately recognizable wherever you go, spare perhaps Pyongyang:

I just picked this Coca Cola Foundation recent CSR project in Brazil totally randomly, using Google. Some might think it's just another cynical diversion: one of the world's biggest corporate profiteers, happily contributing to the current obesity pandemic (including in Latin America), suddenly showing one of its biggest markets they do have a conscience, after all, and a social one to boot. And addressing, at the same time, one of the continent's post-colonial bleeding wounds, which is to say, the organic imbalance between rich and poor, as far as access to means of production, land ownership and use and sales opportunities go. 480 farmers benefitting from Coca Cola's magnanimity is probably but a tiny drop of hope in an ocean of dour social injustice, but the truth is, Anon, if nobody does anything good, then nothing good will happen at all. It is as simple as that, and while their modus operandi is probably not exactly my cup of tea, you will have to admit it works, at least to some extent and for some people. Plus it greatly enhances the company's do-good, sensible and reliable global image, because of course, what happens right now in the state of Minas Gerais is but a tiny part of a bigger strategy.
Might I add that even those robber barons, à la Cornelius Vanderbilt or Jay Gould, who made their ruthless fortunes building the railroads of a still very young United States of America, ended up giving a very small part of their same fortune to various charities. It wasn't nearly enough what we would consider as 'reasonable', in 2024, but it did start a philanthropic trend, that took considerable speed after the 1919 Boston Molasses Disaster. The Sixties have just added more pragmatism and gave a name to what was, at its very start, quite an opportunistic endeavor.
Even so, Vanderbilt and Gould themselves did not invent anything, really. One should look to good old Europe to find what is probably the first big CSR project in human history, still going strong since 1521. May I introduce you to the Augsburg Fuggerei:


[for even more pious charity: https://www.fugger.de/en/fuggerei]
Renting one of those wonderful Hansel and Gretel houses for less than one euro/year, plus three daily Hail Mary is something to behold, right? Jakob Fugger the Young, the guy who had this brilliant idea (which, might I add, is still run and operated by the Fugger banker family, even nowadays) was literally a ruthless kingmaker, a colonial trade and exploration pioneer, but also a religious bigot who flatly refused to extend his charity to Protestant families. Still, his pious dream goes on - the Fugger Family Foundation even actively plans its next 500 years. This is Germany, after all 😉.
Those people’s money stinks more of corruption and crime than S or C’s ever could, Anon. Still, they are remembered as benefactors, by many. History is seldom cruel to those who are willing to pay for their posterity.
But you know what, Anon? Compared to the Fuggers and the Vanderbilts and the Goulds, S and C are really small fish in an even smaller, fickler pond. I think they are doing it out of their good heart and I think they are honestly, genuinely responsive to the idea of giving a chance to young, struggling artists. But, in the process, are they also trying to market themselves as more approachable and less controversial, considering the (oh, I shall never tire to repeat this, with gusto) cosmic amount of bullshit plaguing their respective public images? My somewhat cynical answer is also yes, Anon. To which may I immediately add that it's not even important: all that counts are the tangible results of whatever good things they do with their booze and/or fitness profits.
Results and helping trigger a change in one's life is all that really interests me, Anon. It seems to bother you, though, so I will cheekily end this long rant with a couple of questions: do you have a problem with poverty? do you believe in giving people a (second) chance, or do you think only the rich are worth considering and valuable?
If so, I honestly pity you, girl. For the real indigent in all this might be you.
67 notes
·
View notes
Note
Lieutenant! Can you tell us about Cape Horn and why it was so dangerous?
Of course I would,
So let's get to the location:
Cape Horn is located at 55° 59′ south latitude and 67° 17′ west longitude. The headland is located on the rocky island of Isla Hornos (Horn Island, not to be confused with the Horn Islands in Micronesia, also discovered by Schoutens), which belongs to Chile, and is the southernmost point in the Tierra del Fuego archipelago. Like the southernmost 2,000 kilometres of South America, it lies in the cold Antarctic circumpolar current. Unlike South Africa, which is twenty degrees further north with the warm Agulhas Current, Tierra del Fuego is never reached by a warm Atlantic current (Brazil Current). Instead, the cold polar current (Falkland Current) reaches as far as the Río de la Plata in the southern summer and as far as southern Brazil in the winter, meaning that Cape Horn is under the influence of a large-scale subpolar current all year round.
The air temperature at Cape Horn is almost identical to the water temperature all year round - day and night - which is 8 °C in January and 5 °C in July. During the day, it rarely gets warmer than 12-13 °C. There are only occasional frosts in winter and it almost never snows, although it rains over 280 days a year.

With few exceptions, the wind blows from the western half of the compass rose all year round; easterly winds are very rare. However, the wind force in the sea area around the Cape tends to be lower than in the neighbouring south-east Pacific and off the Chilean coast near the Strait of Magellan, for example, where there is always one wind force more and twice as much chance of storms. Nevertheless, the wind blows almost constantly in summer (January) with at least five Beaufort, but only once a month with more than seven Beaufort, and once a week to the west. In July, at least seven Beaufort and one storm per week are recorded every third day, while two storms per week can be expected to the west.
The Cape was rounded for the first time by an expedition of Dutch sailors Willem Cornelisz Schouten and Jakob Le Maire on 29 January 1616, sailing on behalf of the Australian Company, which was founded by Jakob Le Maire's father Isaac Le Maire together with other Hoorn businessmen after an internal dispute with the Dutch East India Company (VOC). As Dutch ships at the time were only allowed to use the Strait of Magellan if they belonged to the VOC, Isaac Le Maire was looking for a passage to the Pacific untouched by the rights of the VOC to trade with the East Indies Spice Islands.
The expedition's mission was to explore a new route to the ‘East Indies’.It was considered fulfilled when a passage opened up between Tierra del Fuego (in the language of the Spanish owner) and the hypothetical huge southern continent of Terra Australis.It was named Fretum le Maire (literally Le Maire Strait) in Latin in honour of the initiator and most important financier Isaac Le Maire, and the ‘peninsula’ to the east belonging to Terra Australis was given the name Staatenlandt in honour of the newly constituted Dutch parliament.The rededication in favour of the son Jakob Le Maire took place after his tragic death at the instigation of his father.The island character of Staatenlandt, which is only sixty kilometres long, could not be recognised, as even at sea you can rarely see further than about forty kilometres. Not being able to see the connection of the state island to the huge Terra Australis only proved that one could not see further than twenty nautical miles - and this was already known.
According to the published records of the ‘shipwrecked passenger’ Jacob le Maires (his expedition ship, the Hoorn, burnt up during cleaning work in Patagonia), he and Captain Schouten were of the opinion that Tierra del Fuego was a rugged, rocky but contiguous island, the supposed southern tip of which was named Capo Hoorn in Latin by Schouten, who was responsible for it, in honour of the second great financier, the council of the city of Hoorn.The Le Maire Strait, the short and easy passage between America and Terra Australis at Staateninsel or Staatenlandt, was the important discovery; Cape Horn was already a clear 180 kilometres into the Pacific. Isaac le Maire had the discovery of this passage, supported by a ‘silent’ Schouten, attributed to his son by court order, with the father as heir.However, the associated and desired exploitation rights of the strait were immediately expropriated and granted to the monopoly of the East India Company.The last lawsuits over this were lost in 1648.
With the realisation that even Staatenlandt was not connected to Terra Australis and that Cape Horn was the decisive landmark, neither the Strait of Magellan nor the Le Maire Strait could be permanently managed with customs duties. Due to the factually and historically incorrect, commercially motivated court judgement that Jacob le Maire found his way into the Pacific via the Le Maire Strait, the discovery of Cape Horn is attributed to him just as incorrectly and abbreviated. Usually, however, all discoveries made on such a voyage are attributed to the captain, as he decides which unknown waters his ship sails into, is responsible for them and also has to assess and interpret what he sees. However, Schouten did not insist on a public acknowledgement of his exploratory achievement, presumably due to an ‘agreement’ between him and Isaac le Maire. In addition, the published documentation of the voyage was undoubtedly written by the representative of the shipping company Jacob le Maire, so that the impression of a discovery by the travelling merchant was already being conveyed to contemporaries
But according to the German author Wolf-Ulrich Cropp, the Englishman Francis Drake was the first European to sail around the Cape 40 years earlier, in 1578, on his circumnavigation of the globe, after he had reached the Pacific through the Strait of Magellan and then travelled south-east for a few days in search of the missing escort ships. However, this discovery was declared a state secret by Queen Elizabeth I.
At the time, it was believed that the Pacific could only be reached from the Atlantic via the Spanish-controlled Strait of Magellan further north, and the British did not want other nations to know about the second route.Drake's first discovery was only claimed after 1618 for political and economic reasons and was quickly disproved by examining the records and voyage reports and by interviewing the surviving travellers.The English naming of the sea area Drake Passage was only given in 1769 by James Cook when he surveyed the coast and is presumably only an expression of general reverence for the greatest English naval hero to date.
In fact, Drake no longer had any escort ships in the Pacific that he could miss; he had already lost them in the Atlantic or in the Strait of Magellan.In the event of a separation, a rendezvous point 2500 kilometres to the north had been agreed with the remaining Elisabeth; a search for missing persons in the south was therefore not very promising. Instead, Drake sought shelter between the islands west of the Strait of Magellan in a supposed ‘50-day storm’ and had no interest in drifting further and further south-east, where he would inevitably be wrecked on the expected Terra Australis in the storm.In any case, he took his time to ‘conquer’ the inhospitable islands of the archipelago one by one.Furthermore, the navigational documents show that he never travelled further south than 55° south, which, in view of his otherwise perfect latitude measurements throughout the voyage, rules out the possibility that he came closer than about 300 km to Cape Horn.Under no circumstances was he south of the Cape, travelling through the Drake Strait and the Le Maire Strait or Falkland Strait to the Atlantic entrance of the Strait of Magellan, in order to make a statement about its passability.The ambitious Drake would have seized even the slightest opportunity to make and verify such a glorious discovery, as he was well aware of the economic, personal, political and military benefits.Similar legends were subsequently spread about the Spanish captains Francisco de Hoces (1526) and Gabriel de Castilla (1603). However, the sources and evidence for both are so sparse and uncertain that the best that can be surmised is that they both sailed past the entrances to the Strait of Magellan for different reasons and then wandered south of it for a short time. In the case of de Hoces, the legend led to the same conclusion as with Drake: the sea area south of Tierra del Fuego, the Drake Strait, is called Mar de Hoces in Spanish.
The rounding of the Cape was one of the most feared passages for ships, as evidenced by the founding of the Cape Horn Community. Commanding captains who conquered Cape Horn on a cargo ship without an auxiliary engine became honorary members of this international community.
Until the completion of the Panama Canal in 1914, sailing around the Cape was the slightly more favourable way to reach the west coast of South America from the Atlantic. The Strait of Magellan and the Beagle Channel, which had already been sailed through centuries earlier by ships of the Dutch East India Company and British exploration ships, also offered difficult weather and current conditions for sailing ships.
At Cape Horn, the passage from the Atlantic to the Pacific against the westerly wind drift was particularly dangerous and difficult. It required ships sailing in this direction to constantly cross in high seas, rain, cold, poor visibility and icebergs. The False Cape Horn caused additional navigational difficulties due to the risk of confusion. However, to this day there are still ships that round the cape, albeit with the help of engines and modern navigation. But that does not mean that it is any less dangerous.
44 notes
·
View notes
Note
what's happening in argentina?
I don't fault you for the broad question because I'd ask too, but I need you to know that as a non-smoker I've never felt so strongly the need for a cigarette as I did just now thinking about answering this question. But I'll do my best.
In November of last year, the country elected Javier Milei as president. He would swear into office the next month. Javier Milei is a self-identified anarcho-capitalist and libertarian, although he states he is a minarchist in the short term (meaning he thinks the only functions the State should serve are those of law enforcement: no public education, social development, market regulations, etc etc). Some of his most controversial campaign statements included projects to legalise the free and unregulated sale of organs, and, along with his vice-president Victoria Villarruel (who in her youth organised visits to Jorge Rafael Videla in prison), apologia for the 1976 military dictatorship by revindicating the theory of the two demons (fair warning that from what I skimmed that article is biased in favour of the theory) and casting into doubt the estimated 30.000 victims of state terrorism (torture, disappearance followed by death) (also warning that that article uses the name the military junta gave this process) during its duration.
Since he took over six months ago, the population's purchasing power has dropped by 38%, plunging millions of people below the line of poverty. In stark contrast to this, Milei has been travelling around the world using public funds to visit his ultraright idols; most notably, Trump, who is not the political leader of any country at the moment (making his trip to see him a personal visit and not a diplomatic one, thus invalidating his arguments for using our money to go there).
On the subject of diplomacy, his government has been swinging quite a lot of bats at hornets' nests, accusing China and Brazil of communism and insulting the wife of the president of Spain. All of this is an international relations nightmare that will take endless apologies to undo.
Another interesting resolution deregulates the operations of foreign companies, SPVs, and offshore companies (article in Spanish), with the stated goal of attracting investments. Those types of companies have historically been used to conceal illicit activity, so resolutions in that vein pave the way to effectively turn Argentina into a fiscal paradise. This isn't the only problem they pose (offshore companies don't pay taxes, so there'd be a loss in the public sector, for example), but it is the most worrying to me because they also eliminated restrictions for Sociedades de Acciones Simplificadas (simplified stock companies), most of which have historically been used to commit crimes among which is the drug trade. Once you have narcos in your country, there's no taking it back--Argentina would be at real risk of ceasing to exist as we know it.
This administration is also slashing public spending, resulting in some universities suspending their activities temporarily. They also failed to deliver oncological medicine, depriving cancer patients of assistance the state is obligated to provide. As a result of this, several people have died already. In this climate of extreme poverty, soup kitchens have been shutting down en masse due to the withdrawal of state funding, and laws that protected tenants' rights and regulated rent prices have been severely modified to the detriment of the tenants.
The violent decrease in public spending also resulted in thousands of state workers being fired overnight. The attack is especially centred on state organisations that promote the arts or whose purpose is to fight discrimination. On this subject, 10% of the transgender and travesti workers who had their positions guaranteed by the law were fired illegally, and government members are outspoken about their opposition to this law--which isn't surprising. Diana Mondino, the current chancellor, has compared same-sex marriage to "the right to having lice" while she held a position in Congress. Ricardo Bussi, a current legislator, compared homosexuality to disability in October 2023. Coming to this year, Francisco Sánchez, the Secretary of Religion, said that the laws protecting the right to abortions, divorce, and same-sex marriage "seek to pervert our children and damage society". Milei is also on record describing abortion as "homicide aggravated by the bond".
Also recently, Milei's biographer, Nicolás Márquez, gave a one-hour interview in which he characterised homosexuality as a disease, claiming that when the State "promotes homosexuality" (as it allegedly did before Milei came to power), it is aiding a "self-destructive" conduct, supporting these claims with unfounded statistics about the correlation between STIs and homosexuality; he also denied the existence of homophobia and described lesbians and gays as being "against nature". For the sake of full disclosure, I will say he explicitly freed Milei and his government of responsibility for his declarations--but I think it's really important to point out the kind of people and rhetorics this government is giving a platform to; after all, nobody knew Nicolás Márquez before he started writing for Milei. In approximately the same time frame, and in response to a horrific hate crime that resulted in the death of three lesbians, Manuel Adorni, the presidential spokesman, said that he "doesn't like" to talk about a hate crime because men suffer violence too--and he said this in a press conference.
I'm probably forgetting something important--so much has happened in the past months--but I hope this is enough to give you an impression of the changes our society is undergoing. Please let me know if you have follow-up questions. <3
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dirty secret of Israel’s weapons exports: They’re tested on Palestinians
Weapons tested in each war Israel wages see a spike in global demand. The current Gaza war is the latest laboratory for its arms industry.
India – Israel’s largest military buyer, which operates more than 100 Israeli-made UAVs – purchased 34 Heron drones in this period, followed by France (24), Brazil (14) and Australia (10), according to a 2014 report by Drone Wars UK.
Colombia is one of an estimated 130 countries that have bought weapons, drones and cyberspying technology from Israel, the world’s 10th-largest weapons exporter.
A report from Amnesty International in 2019 noted that the whole process by which Israel sells arms is shrouded in secrecy “with no documentation of sales, one cannot know when [these arms] were sold, by which company, how many and so on”.
Amnesty found that “Israeli companies exported weapons which reached their destination after a series of transactions, thereby skirting international monitoring”.
Israel has not ratified the Arms Trade Treaty, which prohibits the sale of weapons at risk of being used in genocide and crimes against humanity. As such, its weapons exports have influenced the course of history for several nations, many led by controversial regimes.
128 notes
·
View notes
Note
Yandere Wolverine and Laura and baby reader who's a squirrel mutant
That is so fr*cking adorable! Little chittering squirrel baby and their two wolverine guardians. They so give them all the best nuts: pecans, cashews, Brazil nuts, almonds, etc. . They can't help it! The baby needs to eat, and they like nuts! Let's do this:
They had a new mutant at the Institute. One who was a feral, like them.
Well.
Not entirely.
They had a big, bushy tail, two small, perky ears, and little buck teeth. They were a squirrel mutant...
And also the cutest one they'd seen.
Laura enjoyed their company. They'd tell her anything and everything, sharing small rocks and pebbles and coins they found while eating a bag of almonds, their little nose twitching every time she made them laugh. She liked them even more because they weren't scared of her, or her history. They gladly accepted what she told them, with them promising they wouldn't trade her for all the nuts in the world (even the yogurt and chocolate covered ones). She saw them as her own buddy, her own little sibling, if nothing else.
She just sometimes wished her father would let her be with them in peace.
He was taking a tray of cooked, buttered pecans out of the oven, earning a thrilled squeal from the small child, who darted into the kitchen, watching with wide eyes as her father set the tray down to cool.
Logan liked the little fuzzy feral. Liked them even more when they got along with his daughter. It certainly helped that they had manners and had wide, warm eyes. (He wasn't soft, no siree). (Yes, he was). He had taken to making or purchasing novelty nuts, giving them to their resident rodent. He smiled every time they thanked him, then tore into the bag like a wolf on a fresh kill.
The two realized a few things when they almost once fought over their little squirrel-ling.
One, they both cared as much as the other.
Two, they woukd do anything to make them smile.
And three...
They could share with the other, thus upping their protection by double.
They WERE family... and they'd happily be family with their little nutty squirrel child as well. Heaven help the poor idiot who tries to upset them...
#honeycomb thoughts#platonic yandere marvel#yandere platonic marvel#platonic yandere xmen#yandere x-men#platonic yandere#platonic yandere x reader#platonic yandere marvel x reader#platonic yandere xmen evolution#platonic yandere wolverine#platonic yandere logan howlett#platonic yandere x 23#platonic yandere laura kinney
86 notes
·
View notes
Text
The history of engagement rings and how diamonds became the norm
While today engagement rings represent a symbol of love and eternal commitment, historians believe the first engagement rings appeared in Ancient Rome - more as a symbol of a legal contract than love itself. But it’s only much later when we have the first introduction of diamonds for engagement rings.
The first diamond engagement ring known in history was given by Maximilian I, a Habsburg, in 1497. He traveled to meet his bride and brought her a diamond ring as a gift. This marked the beginning of the tradition of using diamonds in engagement rings. At that time, the only place to find diamonds was in India, making them extremely rare and expensive, something truly reserved for royalty.
As we move through history, we see a period when engagement rings fell out of fashion and were replaced by more elaborate, detailed wedding rings. Later, engagement rings came back into style. In 1840, with Queen Victoria's engagement, the tradition of the engagement ring became more consistent. However, the engagement ring she received is not the one that comes to mind today. Our imagination is filled with Tiffany's solitaire ring, often seen in movies. But Queen Victoria received a ring in the shape of a snake, as the snake was a symbol of eternal love. The main gemstone in the snake's head was an emerald, which is quite different from what we're used to. Why an emerald? It was the gemstone for her birth month, leading to another tradition: using colored gemstones in rings based on a person's birth month.


Returning to the subject of diamonds, we fast-forward to 1887 when diamonds were discovered in South Africa. This shifted the market away from India as the sole supplier, flooding the market with diamonds, and their prices dropped significantly. Something that had once been exclusive to royalty became accessible to the middle class, and diamonds became very popular.
In 1889, a company called De Beers emerged - which you may have heard of because celebrities often being seen wearing De Beers diamonds on red carpets - came to dominate the diamond market, controlling the supply. It established a monopoly in South Africa, and eventually, worldwide. To this day, only a few companies control the entire diamond trade, and diamonds remain so expensive not because they are extremely rare, but because the market is artificially controlled to prevent prices from dropping.
If you think in terms of rarity, for example, a Paraíba tourmaline is rarer than a diamond. Diamonds can be found in various countries, but Paraíba tourmalines are only found in specific regions of Brazil and a few locations in Africa. They are not as widespread. So, the high value of diamonds is not due to rarity. That’s not to say diamonds aren’t beautiful—they have many desirable characteristics, such as their hardness on the Mohs scale. Many marketing campaigns have been built around this.
In the 1930s, De Beers launched a campaign to have celebrities wear diamonds on the red carpet. This was during a time of war and the Great Depression when couples couldn't afford diamonds and were opting for other gemstones in their rings. By showcasing celebrities flaunting diamonds, they rekindled the desire and made it seem like a good investment for couples. The campaign worked very well, with sales increasing by 50% in the following years.
In the 1950s, De Beers launched another campaign, one we still repeat today: “Diamonds are forever,” drawing a connection between the diamond’s eternal nature and the commitment a person makes at that moment in their life. The campaign was a huge success, and we still repeat the phrase today, with sales soaring again. All of this solidified the diamond in our imagination as the perfect gemstone for engagement rings.
In 1953, the movie Gentlemen Prefer Blondes starring Marilyn Monroe included that iconic scene with the pink dress where she sings and dances about diamonds being a girl's best friend. These are ideas we still repeat today, showing the powerful influence this has on our imagination. Movies often reinforce this idea, but I’m here to tell you that the value of diamonds is heavily influenced by market control, which limits supply to keep prices high, and by decades of marketing campaigns designed to create desire. I’m not saying you should stop liking diamonds—they remain a wonderful, beautiful gemstone with incredible brilliance. I just want you to know that they’re not your only option. If you like a colored gemstone that represents you, you can use it in your engagement ring.
Even looking at royal engagement rings, not just Queen Victoria's with an emerald, but also Princess Eugenie’s with a pink sapphire, and of course, the most famous engagement ring in the world, which belonged to Lady Diana and was passed down to Kate Middleton. It features a blue sapphire as the main gemstone, surrounded by diamonds and set in white gold. But what defines that ring is the blue sapphire. So, if you like a colored gemstone, feel free to put it in your ring without shyness or do you think Princess Kate is wrong or being tacky?
#personal#femininity#level up#engagement#engagement ring#traditional gender roles#glow up#wedding#jewelry
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Seed networks are community organizations that have multiplied in the past decade in different Brazilian biomes to collect, trade and plant native seeds in degraded areas.
In the Chapada dos Veadeiros area, in Goiás state members of seed networks from several parts of Brazil met for almost a week in early June.
Along with environmental organizations, researchers and government officials, they participated in discussions to boost Redário, a new group seeking to strengthen these networks and meet the demands of the country’s ecological restoration sector.
“This meeting gathered members of Indigenous peoples, family farmers, urban dwellers, technicians, partners, everyone together. It creates a beautiful mosaic and there’s a feeling that what we are doing will work and will grow,” says Milene Alves, a member of the steering committee of the Xingu Seed Network and Redário’s technical staff.
Just in 2022, 64 metric tons of native seeds were sold by these networks, and similar figures are expected for 2023.
The effort to collect native seeds by traditional populations in Brazil has contributed to effective and more inclusive restoration of degraded areas, and is also crucial for the country to fulfill its pledge under international agreements to recover 30 million acres of vegetation by 2030.
Seed collection for restoration in these areas has previously only been done by companies. But now, these networks, are organized as cooperatives, associations or even companies, enable people in the territories to benefit from the activity.
Eduardo Malta, a restoration expert from the Socio-Environmental Institute and one of Redário’s leaders, advocates for community participation in trading and planting seeds. “These are the people who went to all the trouble to secure the territories and who are there now, preserving them. They have the greatest genetic diversity of species and hold all the knowledge about the ecosystem,”
.
The Geraizeiros Collectors Network are one of the groups that makes up Redário. They were founded in 2021, and now gathers 30 collectors from eight communities in five municipalities: Montezuma, Vargem Grande, Rio Pardo de Minas, Taiobeiras and Berizal.
They collect and plant seeds to recover the vegetation of the Gerais Springs Sustainable Development Reserve, which was created in 2014 in order to stop the water scarcity as a result of eucalyptus monocultures planted by large corporations.
“The region used to be very rich in water and it is now supplied by water trucks or wells,” says Fabrícia Santarém Costa, a collector and vice president of the Geraizeiros Collectors’ Network. “Today we see that these activities only harm us, because the [eucalyptus] company left, and we are there suffering the consequences.”
Costa was 18 years old in 2018, when the small group of seed collectors was founded and financed by the Global Environmental Facility. She says that working with this cooperative changed the way she looks at life and the biome in which she was born and raised. She describes restoring the sustainable development work as "ant work", ongoing, slow. But it has already improved the water situation in the communities. In addition, seed sales complement geraizeiros’ income, enabling them to remain in their territories.
.
The Redário initiative also intends to influence public policies and regulations in the restoration sector to disseminate muvuca, the name given by the networks to the technique of sowing seeds directly into the soil rather than growing seedlings in nurseries.
Technical studies and network experiences alike show that this technique covers the area faster and with more trees. As a result, it requires less maintenance and lower costs. This system also distributes income to the local population and encourages community organizations.
“The muvuca system has great potential [for restoration], depending on what you want to achieve and local characteristics. It has to be in our range of options for meeting the targets, for achieving them at scale,” says Ministry of the Environment analyst Isis Freitas.
Article published August 3rd, 2023
#long post#climate change#climate#hope#good news#more to come#climate emergency#positive news#hopeful#climate justice#news#important#good post#links
202 notes
·
View notes
Text

Black Americans should visit Ghana
To know more about black slave trade in Ghana
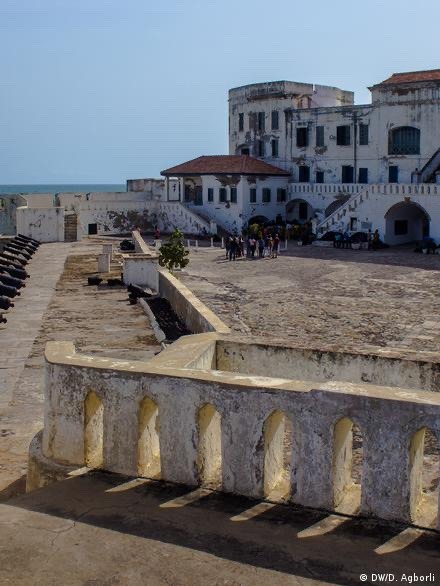

Monuments of shame
Cape Coast Castle - now a World Heritage Site - is one of about forty forts in Ghana where slaves from as far away as Burkina Faso and Niger were imprisoned. This former slave fortress could hold about 1,500 slaves at a time before they were loaded onto ships and sold into slavery in the New World in the Americas and the Caribbean.

Male captives who revolted or were deemed insubordinate ended up in the condemned cells - a pitch-black room where slaves were left to die in the oppressive heat without water, food or daylight.Rebellious women were beaten and chained to cannon balls in the courtyard
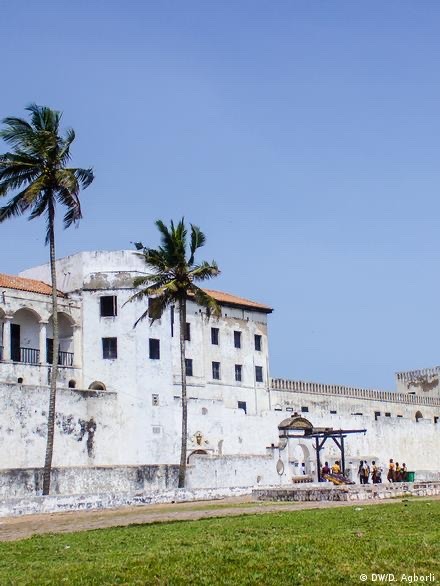

Built in 1482, Elmina Castle on Ghana's Cape coast is the earliest European structure erected in sub-Saharan Africa. Originally Portugese, it was later captured by the Dutch, who used it as a base for the Dutch slave trade with Brazil and the Caribbean. Under the flag of the Dutch West Indies Company, around 30,000 slaves a year passed through Elmina until 1814 when the Dutch abolished slavery.
The Portuguese position on the Gold Coast remained secure for almost a century. During that time, Lisbon leased the right to establish trading posts to individuals or companies that sought to align themselves with the local chiefs and to exchange trade goods both for rights to conduct commerce and for slaves whom the chiefs could provide. During the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, adventurers--first Dutch, and later English, Danish, and Swedish-- were granted licenses by their governments to trade overseas. On the Gold Coast, these European competitors built fortified trading stations and challenged the Portuguese. Sometimes they were also drawn into conflicts with local inhabitants as Europeans developed commercial alliances with local chiefs.
The principal early struggle was between the Dutch and the Portuguese. With the loss of Elmina in 1642 to the Dutch, the Portuguese left the Gold Coast permanently. The next 150 years saw kaleidoscopic change and uncertainty, marked by local conflicts and diplomatic maneuvers, during which various European powers struggled to establish or to maintain a position of dominance in the profitable trade of the Gold Coast littoral. Forts were built, abandoned, attacked, captured, sold, and exchanged, and many sites were selected at one time or another for fortified positions by contending European nations.
Both the Dutch and the British formed companies to advance their African ventures and to protect their coastal establishments. The Dutch West India Company operated throughout most of the eighteenth century. The British African Company of Merchants, founded in 1750, was the successor to several earlier organizations of this type. These enterprises built and manned new installations as the companies pursued their trading activities and defended their respective jurisdictions with varying degrees of government backing. There were short-lived ventures by the Swedes and the Prussians. The Danes remained until 1850, when they withdrew from the Gold Coast. The British gained possession of all Dutch coastal forts by the last quarter of the nineteenth century, thus making them the dominant European power on the Gold Coast.
During the heyday of early European competition, slavery was an accepted social institution, and the slave trade overshadowed all other commercial activities on the West African coast. To be sure, slavery and slave trading were already firmly entrenched in many African societies before their contact with Europe. In most situations, men as well as women captured in local warfare became slaves. In general, however, slaves in African communities were often treated as junior members of the society with specific rights, and many were ultimately absorbed into their masters' families as full members. Given traditional methods of agricultural production in Africa, slavery in Africa was quite different from that which existed in the commercial plantation environments of the New World.
Another aspect of the impact of the trans-Atlantic slave trade on Africa concerns the role of African chiefs, Muslim traders, and merchant princes in the trade. Although there is no doubt that local rulers in West Africa engaged in slaving and received certain advantages from it, some scholars have challenged the premise that traditional chiefs in the vicinity of the Gold Coast engaged in wars of expansion for the sole purpose of acquiring slaves for the export market. In the case of Asante, for example, rulers of that kingdom are known to have supplied slaves to both Muslim traders in the north and to Europeans on the coast. Even so, the Asante waged war for purposes other than simply to secure slaves. They also fought to pacify territories that in theory were under Asante control, to exact tribute payments from subordinate kingdoms, and to secure access to trade routes--particularly those that connected the interior with the coast.
It is important to mention, however, that the supply of slaves to the Gold Coast was entirely in African hands. Although powerful traditional chiefs, such as the rulers of Asante, Fante, and Ahanta, were known to have engaged in the slave trade, individual African merchants such as John Kabes, John Konny, Thomas Ewusi, and a broker known only as Noi commanded large bands of armed men, many of them slaves, and engaged in various forms of commercial activities with the Europeans on the coast.
The volume of the slave trade in West Africa grew rapidly from its inception around 1500 to its peak in the eighteenth century. Philip Curtin, a leading authority on the African slave trade, estimates that roughly 6.3 million slaves were shipped from West Africa to North America and South America, about 4.5 million of that number between 1701 and 1810. Perhaps 5,000 a year were shipped from the Gold Coast alone. The demographic impact of the slave trade on West Africa was probably substantially greater than the number actually enslaved because a significant number of Africans perished during slaving raids or while in captivity awaiting transshipment. All nations with an interest in West Africa participated in the slave trade. Relations between the Europeans and the local populations were often strained, and distrust led to frequent clashes. Disease caused high losses among the Europeans engaged in the slave trade, but the profits realized from the trade continued to attract them.
The growth of anti-slavery sentiment among Europeans made slow progress against vested African and European interests that were reaping profits from the traffic. Although individual clergymen condemned the slave trade as early as the seventeenth century, major Christian denominations did little to further early efforts at abolition. The Quakers, however, publicly declared themselves against slavery as early as 1727. Later in the century, the Danes stopped trading in slaves; Sweden and the Netherlands soon followed.
The importation of slaves into the United States was outlawed in 1807. In the same year, Britain used its naval power and its diplomatic muscle to outlaw trade in slaves by its citizens and to begin a campaign to stop the international trade in slaves. These efforts, however, were not successful until the 1860s because of the continued demand for plantation labor in the New World.
Because it took decades to end the trade in slaves, some historians doubt that the humanitarian impulse inspired the abolitionist movement. According to historian Walter Rodney, for example, Europe abolished the trans-Atlantic slave trade only because its profitability was undermined by the Industrial Revolution. Rodney argues that mass unemployment caused by the new industrial machinery, the need for new raw materials, and European competition for markets for finished goods are the real factors that brought an end to the trade in human cargo and the beginning of competition for colonial territories in Africa. Other scholars, however, disagree with Rodney, arguing that humanitarian concerns as well as social and economic factors were instrumental in ending the African slave trade.
#life#culture#black history#blm blacklivesmatter#history#animals#architecture#aesthetic#black community#anime and manga#blacklivesmatter#humiliation slave
155 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from EcoWatch:
A new report has found that climate lawsuits being filed against companies are on the rise all over the world, and most of them have been successful.
The report by the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE) — Global trends in climate change litigation: 2024 snapshot — said that roughly 230 climate cases have been brought against trade associations and corporations since 2015, more than two-thirds of which have been filed since 2020.
“Climate litigation… has become an undeniably significant trend in how stakeholders are seeking to advance climate action and accountability,” said Andy Raine, the United Nations Environment Programme’s deputy director of law division, as The Guardian reported.
One of the fastest growing types of litigation concerns “climate washing.” According to the report, 47 of these lawsuits were filed against governments and companies last year.
The report stated that there had been “more than 140 such cases filed to date on climate washing, making this one of the most rapidly expanding areas of litigation,” a press release from LSE said.
Of the almost 140 climate-washing cases between 2016 and 2023, 77 had reached official decisions, with 54 being found in favor of the claimant.
Most climate cases that have been filed in the past have been against governments. In the United States, 15 percent of climate cases filed in 2023 were against companies, while 40 percent of cases in the rest of the world involved companies.
In 2023, more than 30 “polluter pays” lawsuits filed worldwide sought to hold corporations accountable for climate harms allegedly stemming from their production of greenhouse gas emissions.
Six “turning off the taps” lawsuits challenging the funding of activities and projects not in line with climate action were identified in the report.
The report’s analysis was based on more than 2,600 climate cases compiled by Columbia Law School’s Sabin Center for Climate Change. Approximately 70 percent of these lawsuits have been filed since the adoption of the Paris Agreement in 2015, with 233 having been filed in 2023.
Climate lawsuits have been brought in 55 total countries, with cases having been filed in Portugal and Panama for the first time.
The authors of the study confirmed that climate litigation has been increasing in the Global South, noting that “over 200 climate cases from these countries are recorded in the Global database, comprising around 8% of all cases.”
The U.S. had the most climate litigation cases filed last year with 129. The United Kingdom had the second highest number with 24, followed by Brazil with 10, Germany with seven and Australia with six.
The U.S. also had the most documented climate cases with a total of 1,745. Australia has had 132 overall, with just six filed in 2023.
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
The rise of the European empires [...] required new forms of social organization, not least the exploitation of millions of people whose labor powered the growth of European expansion [...]. These workers suffered various forms of coercion ranging from outright slavery through to indentured or convict labor, as well as military conscription, land theft, and poverty. [...] [W]ide-ranging case studies [examining the period from 1600 to 1850] [...] show the variety of working conditions and environments found in the early modern period and the many ways workers found to subvert and escape from them. [...] A web of regulation and laws were constructed to control these workers [...]. This system of control was continually contested by the workers themselves [...]
---
Timothy Coates [...] focuses on three locations in the Portuguese empire and the workers who fled from them. The first was the sugar plantations of São Tomé in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. The slaves who ran away to form free communities in the interior of the island were an important reason why sugar production eventually shifted to Brazil. Secondly, Coates describes working conditions in the trading posts around the Indian Ocean and the communities of runaways which formed in the Bay of Bengal. The final section focuses on convicts and sinners in Portugal itself, where many managed to escape from forced labor in salt mines.
Johan Heinsen examines convict labor in the Danish colony of Saint Thomas in the Virgin Islands. Denmark awarded the Danish West Indies and Guinea Company the right to transport prisoners to the colony in 1672. The chapter illustrates the social dynamics of the short-lived colony by recounting the story of two convicts who hatched the escape plan, recruited others to the group, including two soldiers, and planned to steal a boat and escape from the island. The plan was discovered and the two convicts sentenced to death. One was forced to execute the other in order to save his own life. The two soldiers involved were also punished but managed to talk their way out of the fate of the convicts. Detailed court records are used to show both the collective nature of the plot and the methods the authorities used to divide and defeat the detainees.
---
James F. Dator reveals how workers in seventeenth-century St. Kitts Island took advantage of conflict between France and Britain to advance their own interests and plan collective escapes. The two rival powers had divided the island between them, but workers, indigenous people, and slaves cooperated across the borders, developing their own knowledge of geography, boundaries, and imperial rivalries [...].
Nicole Ulrich writes about the distinct traditions of mass desertions that evolved in the Dutch East India Company colony in South Africa. Court records reveal that soldiers, sailors, slaves, convicts, and servants all took part in individual and collective desertion attempts. [...] Mattias von Rossum also writes about the Dutch East India Company [...]. He [...] provides an overview of labor practices of the company [...] and the methods the company used to control and punish workers [...].
---
In the early nineteenth century, a total of 73,000 British convicts were sentenced to be transported to Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania). There, the majority were rented out as laborers to private employers, and all were subjected to surveillance and detailed record keeping. These records allow Hamish Maxwell-Stewart and Michael Quinlan to provide a detailed statistical analysis of desertion rates in different parts of the colonial economy [...].
When Britain abolished the international slave trade, new forms of indentured labor were created in order to provide British capitalism with the labor it required. Anita Rupprecht investigates the very specific culture of resistance that developed on the island of Tortola in the British Virgin Islands between 1808 and 1828. More than 1,300 Africans were rescued from slavery and sent to Tortola, where officials had to decide how to deal with them. Many were put to work in various forms of indentured labor on the island, and this led to resistance and rebellion. Rupprecht uncovers details about these protests from the documents of a royal commission that investigated [...].
---
All text above by: Mark Dunick. "Review of Rediker, Marcus; Chakraborty, Titas; Rossum, Matthias van, eds. A Global History of Runaways: Workers, Mobility, and Capitalism 1600-1850". H-Socialisms, H-Net Reviews. April 2024. Published at: h-net.org/reviews/showrev.php?id=58852 [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#carceral#pedagogies#ecologies#imperial#colonial#critical geographies#fugitivity#tidalectics#archipelagic thinking#indigenous
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
'Gaza is on the ground,' says protester at demonstration in Brazil that marks one year of Israel's genocide in Palestine
At the mark of the massacre's beginning, the organization Palestine Front calls for a march at Paulista Avenue

“They're hearing bombs,” says journalist Sarah Kalo, a Lebanese woman who has lived in São Paulo for eight years with her husband and three children - one of them, a baby just seven days old. Kalo was referring to her parents and siblings, who live in Lebanon, the most recent target of Israel's attacks. On Tuesday evening (8), she was in front of the São Paulo Museum of Art (MASP), on Paulista Avenue, for another act of solidarity with the victims of Israel.
With banners and posters calling for a ceasefire and denouncing Israeli atrocities, the demonstrators walked along the avenue. The act marks one year since the beginning of the attacks, which began on October 7, 2023.
“Gaza is on the ground. The universities are destroyed. The hospitals that weren't destroyed are in no condition to care for the wounded,” denounced Mohamad El Kadri, president of the Latin Palestinian Forum, at the start of the march to Roosevelt Square.
As well as denouncing the violence and showing solidarity with the victims, the protesters want to put pressure on the Brazilian authorities to cut trade and diplomatic relations with Israel. “That's why we're building act after act across Brazil. To say enough is enough, to say no more to this genocide and to the complicity of companies, institutions, states and the Brazilian State itself as a whole,” warns Ju Sieg, an internationalist activist working for the Front in Defense of the Palestinian People.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#palestine#israel#manifestations#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Keepers of the Quaich
This time, we're going to look at things a bit differently and this could very well be my most speculative post ever. So be it: it is a risk I am taking and warning you about from the get go.
The only thing Mordor understood about the next October 4 event organized by the US Chapter of The Keepers of the Quaich is something that probably gave them collective relief: S is not going to be with C on her birthday. Not together. Not on the same continent. Shut up, shippers, you are stupid.
As usually, Mordor takes things at a very primitive face value, without bothering for context. But they always focused on the lewd side of the story, not on its deep ramifications, of which there are many. Anything that denies S's halfwit manwhore image upsets them greatly.
The Scottish society of The Keepers of the Quaich is not one of those old, steeped in tradition clubs, but it is damn selective. It only dates back to 1988, which is almost five minutes ago, for Europe (and especially the UK) and is deeply rooted in Highlands' lore, celebrating excellence in whisky trade and promotion worldwide. General facts about it have already been discussed elsewhere, but with a bias and little to no context. Also, really LOL at Mordor's idiocy to think that was a fan promotion event and go ballistic for the members-only and by invitation access to it.
Membership is by co-opting and with a five-year proven performance history only (ten years, if you step up to Master level). You need not one, but two recommendations, which makes it harder to join than a Masonic lodge or the Rotary Club (and I know what I am saying, heh). That S could actively seek to be inducted, rather sooner than later, is pretty much clear, as he could use the network it readily provides, along with the prestige:

(Sourced at: https://www.diffordsguide.com/encyclopedia/341/people/keepers-of-the-quaich)
I first had a look at the list of its International Chapters and it is interesting to notice Muslim countries as Turkey or the Emirates each having their own chapter, which clearly tells me it's all about luxury and more specifically, luxury hospitality business, in that case. If inducted after the customary five years' wait, S could also make good use of the German chapter's (a market that proved to be very problematic for him) network, along with the Nordics and Netherlands, if he would think about cleverly expanding his trade in the EU. Last but not least, I would keep an eye on Brazil and India (along with the more predictable South Africa and Australia), because he already has a solid fanbase in the first one and well, Asia is always interesting, when it comes to alcohol business.
I did not really bother with the list of the Patrons, which spells a good and prestigious sliver of Debrett's Peerage's Scottish section. But I also looked at the list of the Management Committee, who does all the hands-on dealings and is directly responsible for the induction ceremony of new members. Aside from representatives of Diageo and Pernod Ricard (giants of the alcohol business world), a familiar name popped right at the bottom of the page:
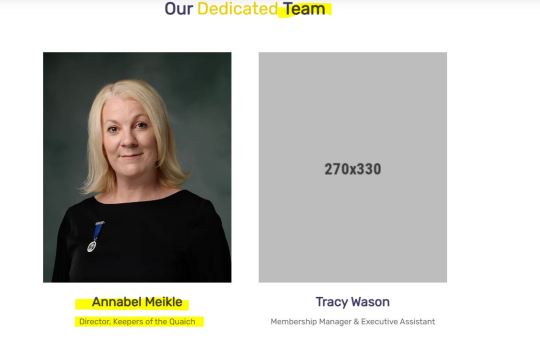
Annabel Meikle, Director of The Keepers of the Quaich and as such, directly involved in the management of its activities (and probably also in all the underground shenanigans leading to the induction of new members, too). A great contact to have in your rolodex, judging by her public CV on LinkedIn:
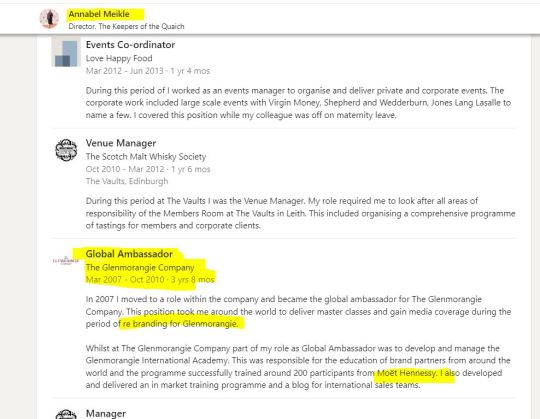
Glenmorangie (also a member of the Keepers) - keep that reference under your sleeve, we are going to need it soon :).
Could she be related to...
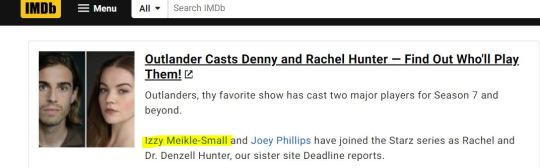
I am leaving this without an answer, because I don't know and I will always refuse to go data mining for anything, but that sure as hell is not a common surname, as Smith or Martin!
At any rate, Mrs. Meikle is also (along with the Duke of Argyll, the current Keepers Grand Master) a member of The Scottish Committee of something very, very prestigious: The Worshipful Company of Distillers (https://www.distillers.org.uk/), based in London and founded in 1638, by Royal Charter (for “Body Politique and corporate” to govern the “Trade Arte and Mystery of Distillers of London” - how I love history, people!) granted by Charles I, a Stuart (of course). I am speculating and having visions of Livery status and Freedom of the City, followed by Knighthood for S (no bong needed, this particular narrative writes itself and believe it or not, it's not entirely without logic). And it is my strict constitutional right to be a poetic coo about it - that guy is smarter than we thought and I would curate that contact to death if I were him (but I am not, I am just a benevolent and intrigued observer, as you all know). Back to Earth from these optimistic conjectures, I will keep a tab on it, as I dutifully took note that one of their current interests is tequila:

Onwards to the US. We can have a fair idea of October 4th event just by looking at one of their few press releases on the occasion of the Chapter's launch gala, on September 25 2019, in New York (https://www.distilledspirits.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/KOTQUSA-Release-10.04.19.pdf - with quotes selected by me):



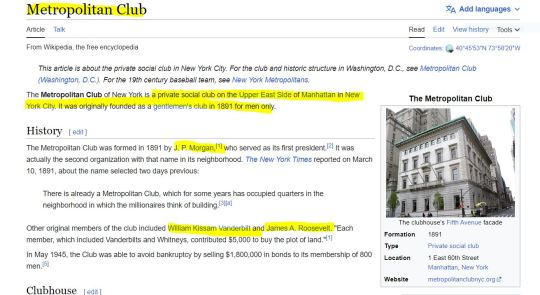
Moët Hennessy. Another reference to keep under our sleeve, for it will be soon very relevant. So yes, what has been speculated by Miss Marple is partially true: more business than aristocratic. But this is only if we do not consider as American aristocratic the venue of the next event. The Metropolitan Club is a very East Coast, WASP old money and (well, technically yes) Republican (but not MAGA Republican and this, to me, is very important for some reason) organization:
That was the state of play on Friday, folks, and I was already excited to share my optimistic findings with you. And then, C went to Paris and more dots started to speculatively connect. Bare with me for this long passegiata, I think it's worth it.
It was particularly important that C would be seen in a very friendly-casual pose with Delphine Arnault, out of all the other people attending that event. Not because Arnault is currently the big boss of Dior and Loewe (as I already explained here: https://www.tumblr.com/sgiandubh/729801825900953600/city-of-lights?source=share). And not only because C suddenly seems very interested to renew and expand her fashion days' old network. But also, because, as I already said, Delphine Arnault is also the daughter of her father and in France, business and family are always closely entwined. Always.
The French luxury market is roughly split between two behemoth players: Bernard Arnault (LVMH Moët Hennessy • Louis Vuitton S.A) and Antoine Pinault (Kering, ex- Pinault-Printemps- Redoute). These people and their businesses are number 1 and 2, respectively, on the global market. And out of these two, the only one very interested in the alcohol business is Arnault (Pinault does not deal in this sector).
So I took a look at his very diverse alcohol and spirits brand portfolio (25 references - https://www.lvmh.com/houses/wines-spirits/): rhum, brandy, champagne, tequila, wines (Argentina and even China). Two Scottish whisky brands: first Ardberg (the graceful peat from Islay). And - oh, hello, Mrs. Meikle - Glenmorangie, acquired by Arnault in 2004, after a bitter battle with Pernod Ricard (https://www.nytimes.com/2004/10/21/business/world-business-briefing-europe-france-scotch-maker-acquired.html):

Back at Mrs. Meikle's CV - hers was a pivotal role in the post-acquisition reshuffle, as part of LVMH:

Coincidence? I think not.
And then also a bourbon reference. Woodinville (based in the state of Washington, USA) with a pitch that made me grin again like the Cheshire Cat:

Sounds familiar? Rings a bell? See a pattern? You should: no, it's not S in disguise, but it could be SS in a couple of years, if S decided to sell it for a hefty profit.
But I was also interested in what is missing from this catalogue.
NO GIN.
Who knows? Maybe these French people could be enticed? In that case (and remember: I am SPECULATING), it would have to be a brand with a proven track record. You see, Arnault is famous for always buying only brands with a proven history and proven recognition (Tasting Alliance, anyone? LOL). Up until now and as is, FMN is just a pet project and a virtual endeavor. Nothing more and we shall see. But that little wild Scottish gin which could win hearts and already an award in Frisco is something completely different.
Now, then. You connect the dots. You draw your own conclusions. I see something very intriguing here and, as I already told you, the business underground situation is completely different from the bland façade.
You see, this is not about papers or checking a pulse or awkwardly grabbing a fist on some stairs. This is show me the money time. This is all about finding unexpected connections, at a very high level and on a very narrow niche.
So you think S and C can't stand each other anymore?
Humbug. They have each other's back from Day 1. And more. Ship on, ladies. Whatever clownery these days might bring, I know what I know. And by now, you should start asking yourselves the real questions, not if Waldo is with Carmen Sandiego (we KNOW), nor if they were online at the same time or not. I mean, that's cute: but to be honest, I think we're past that... uh... waypoint?
Next on my list is that Lallybroch trademark thing. This is the most complex one and I will take my time. I may speculate, but never without a logical base. And I always take these things very seriously.
Keepers of the Quaich, indeed. :)
248 notes
·
View notes
Note
original anon here tysm for the recs ! if the marxist frameworks was too limiting im also completely fine w general postcolonial botany readings on the topic :0
A Spiteful Campaign: Agriculture, Forests, and Administering the Environment in Imperial Singapore and Malaya (2022). Barnard, Timothy P. & Joanna W. C. Lee. Environmental History Volume: 27 Issue: 3 Pages: 467-490. DOI: 10.1086/719685
Planting Empire, Cultivating Subjects: British Malaya, 1786–1941 (2018). Lynn Hollen Lees
The Plantation Paradigm: Colonial Agronomy, African Farmers, and the Global Cocoa Boom, 1870s--1940s (2014). Ross, Corey. Journal of Global History Volume: 9 Issue: 1 Pages: 49-71. DOI: 10.1017/S1740022813000491
Cultivating “Care”: Colonial Botany and the Moral Lives of Oil Palm at the Twentieth Century’s Turn (2022). Alice Rudge. Comparative Studies in Society and History Volume: 64 Issue: 4 Pages: 878-909. DOI: 10.1017/S0010417522000354
Pacific Forests: A History of Resource Control and Contest in Solomon Islands, c. 1800-1997 (2000). Bennett, Judith A.
Thomas Potts of Canterbury: Colonist and Conservationist (2020). Star, Paul
Colonialism and Green Science: History of Colonial Scientific Forestry in South India, 1820--1920 (2012). Kumar, V. M. Ravi. Indian Journal of History of Science Volume: 47 Issue 2 Pages: 241-259
Plantation Botany: Slavery and the Infrastructure of Government Science in the St. Vincent Botanic Garden, 1765–1820 (2021). Williams, J'Nese. Berichte zur Wissenschaftsgeschichte Volume: 44 Issue: 2 Pages: 137-158. DOI: 10.1002/bewi.202100011
Angel in the House, Angel in the Scientific Empire: Women and Colonial Botany During the Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries (2020). Hong, Jiang. Notes and Records: The Royal Society Journal of the History of Science Volume: 75 Issue: 3 Pages: 415-438. DOI: 10.1098/rsnr.2020.0046
From Ethnobotany to Emancipation: Slaves, Plant Knowledge, and Gardens on Eighteenth-Century Isle de France (2019). Brixius, Dorit. History of Science Volume: 58 Issue: 1 Pages: 51-75. DOI: 10.1177/0073275319835431
African Oil Palms, Colonial Socioecological Transformation and the Making of an Afro-Brazilian Landscape in Bahia, Brazil (2015). Watkins, Case. Environment and History Volume: 21 Issue: 1 Pages: 13-42. DOI: 10.3197/096734015X14183179969700
The East India Company and the Natural World (2015). Ed. Damodaran, Vinita; Winterbottom, Anna; Lester, Alan
Colonising Plants in Bihar (1760-1950): Tobacco Betwixt Indigo and Sugarcane (2014). Kerkhoff, Kathinka Sinha
Science in the Service of Colonial Agro-Industrialism: The Case of Cinchona Cultivation in the Dutch and British East Indies, 1852--1900 (2014). Hoogte, Arjo Roersch van der & Pieters, Toine. Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part C: Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences Volume: 47 Issue: Part A Pages: 12-22
Trading Nature: Tahitians, Europeans, and Ecological Exchange (2010). Newell, Jennifer
The Colonial Machine: French Science and Overseas Expansion in the Old Regime (2011). McClellan, James E. & Regourd, François
Colonial Botany: Science, Commerce, and Politics in the Early Modern World (2005). Ed. Schiebinger, Londa L. & Swan, Claudia
Plants and Empire: Colonial Bioprospecting in the Atlantic World (2004). Schiebinger, Londa L.
92 notes
·
View notes