#Solar photovoltaic (PV) projects
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Nepal's Renewable Revolution: Why Solar Power is the Preferred Choice
There is a general agreement among government officials, the private sector, and Nepal’s development partners on the importance of increasing the share of solar power in the country’s electricity mix. However, there are differing opinions, especially regarding the solar power tariff cap. As the costs of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems are decreasing and becoming more affordable worldwide, there…
#(POSTED)#AEPC#Electricity Development#electricity security#Hydropower Projects#ndependent power producers#Nepal Energy Authority (NEA)#renewable energy development#solar photovoltaic (PV) systems#solar power
0 notes
Text
"In an unprecedented transformation of China’s arid landscapes, large-scale solar installations are turning barren deserts into unexpected havens of biodiversity, according to groundbreaking research from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The study reveals that solar farms are not only generating clean energy but also catalyzing remarkable ecological restoration in some of the country’s most inhospitable regions.
The research, examining 40 photovoltaic (PV) plants across northern China’s deserts, found that vegetation cover increased by up to 74% in areas with solar installations, even in locations using only natural restoration measures. This unexpected environmental dividend comes as China cements its position as the global leader in solar energy, having added 106 gigawatts of new installations in 2022 alone.
“Artificial ecological measures in the PV plants can reduce environmental damage and promote the condition of fragile desert ecosystems,” says Dr. Benli Liu, lead researcher from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. “This yields both ecological and economic benefits.”
The economic implications are substantial. “We’re witnessing a paradigm shift in how we view desert solar installations,” says Professor Zhang Wei, environmental economist at Beijing Normal University. “Our cost-benefit analysis shows that while initial ecological construction costs average $1.5 million per square kilometer, the long-term environmental benefits outweigh these investments by a factor of six within just a decade.” ...
“Soil organic carbon content increased by 37.2% in areas under solar panels, and nitrogen levels rose by 24.8%,” reports Dr. Sarah Chen, soil scientist involved in the project. “These improvements are crucial indicators of ecosystem health and sustainability.”
...Climate data from the study sites reveals significant microclimate modifications:
Average wind speeds reduced by 41.3% under panel arrays
Soil moisture retention increased by 32.7%
Ground surface temperature fluctuations decreased by 85%
Dust storm frequency reduced by 52% in solar farm areas...
The scale of China’s desert solar initiative is staggering. As of 2023, the country has installed over 350 gigawatts of solar capacity, with 30% located in desert regions. These installations cover approximately 6,000 square kilometers of desert terrain, an area larger than Delaware.
“The most surprising finding,” notes Dr. Wang Liu of the Desert Research Institute, “is the exponential increase in insect and bird species. We’ve documented a 312% increase in arthropod diversity and identified 27 new bird species nesting within the solar farms between 2020 and 2023.”
Dr. Yimeng Wang, the study’s lead author, emphasizes the broader implications: “This study provides evidence for evaluating the ecological benefit and planning of large-scale PV farms in deserts.”
The solar installations’ positive impact stems from several factors. The panels act as windbreaks, reducing erosion and creating microhabitats with lower evaporation rates. Perhaps most surprisingly, the routine maintenance of these facilities plays a crucial role in the ecosystem’s revival.
“The periodic cleaning of solar panels, occurring 7-8 times annually, creates consistent water drip lines beneath the panels,” explains Wang. “This inadvertent irrigation system promotes vegetation growth and the development of biological soil crusts, essential for soil stability.” ...
Recent economic analysis reveals broader benefits:
Job creation: 4.7 local jobs per megawatt of installed capacity
Tourism potential: 12 desert solar sites now offer educational tours
Agricultural integration: 23% of sites successfully pilot desert agriculture beneath panels
Carbon reduction: 1.2 million tons CO2 equivalent avoided per gigawatt annually
Dr. Maya Patel, visiting researcher from the International Renewable Energy Agency, emphasizes the global implications: “China’s desert solar model could be replicated in similar environments worldwide. The Sahara alone could theoretically host enough solar capacity to meet global electricity demand four times over while potentially greening up to 20% of the desert.”
The Chinese government has responded by implementing policies promoting “solar energy + sand control” and “solar energy + ecological restoration” initiatives. These efforts have shown promising results, with over 92% of PV plants constructed since 2017 incorporating at least one ecological construction mode.
Studies at facilities like the Qinghai Gonghe Photovoltaic Park demonstrate that areas under solar panels score significantly better in environmental assessments compared to surrounding regions, indicating positive effects on local microclimates.
As the world grapples with dual climate and biodiversity crises, China’s desert solar experiment offers a compelling model for sustainable development. The findings suggest that renewable energy infrastructure, when thoughtfully implemented, can serve as a catalyst for environmental regeneration, potentially transforming the world’s deserts from barren wastelands into productive, life-supporting ecosystems.
“This is no longer just about energy production,” concludes Dr. Liu. “We’re witnessing the birth of a new approach to ecosystem rehabilitation that could transform how we think about desert landscapes globally. The next decade will be crucial as we scale these solutions to meet both our climate and biodiversity goals.”"
-via Green Fingers, January 13, 2025
#solar#solar power#solar panel#solar energy#solar farms#china#asia#ecosystem#ecology#ecosystem restoration#renewables#biodiversity#climate change#climate action#good news#hope
582 notes
·
View notes
Text

Rural China goes solarpunk
Viewed from a distance, Lianxing looks more like a solar energy farm than a rural village of 457 households. There are solar photovoltaic panels on almost all its rooftops and in every courtyard.
For generations, residents of the village in Wuyuan county, Inner Mongolia autonomous region, depended on straw, firewood and coal for cooking and heating. But they have now abandoned those fuels, which often made their homes dirty, 40-year-old villager Shi Baohong said.
The new power generation facilities have also brought villagers a consistent stream of income with little effort. Shi earns almost 10,000 yuan ($1,400) a year from his solar PV panels and said there is still enough space between them to plant herbs and other cash crops in his courtyard of more than 300 square meters.
As China forges ahead with energy transition and rural vitalization, Lianxing and its almost 1,400 residents are a microcosm of the synergy that can be generated when the two campaigns are promoted simultaneously.
Local authorities said the distributed solar PV system in Lianxing went into operation in 2017, three years after villagers moved into new homes fitted with solar panels. Households in the village now make an average of 8,000 yuan a year from selling solar energy to the grid.
Villagers did not have to pay for the new houses or power generation facilities thanks to a land-use rights transfer project. After their resettlement, the land previously covered by the villagers' old, dilapidated houses was turned into more than 130 hectares of farmland.
"Villagers didn't pay even a single penny. It was a house-for-house deal, and that's not half bad," the village's Party chief, Li Chou, said.
All the costs for the new houses and solar panels were covered by the company that invested in a large-scale agricultural development project.
In Donglian village, in Gansu's Gaotai county, many families can earn 1,000 yuan a year without having to make any investment or do maintenance work. They lease their rooftops to a company for distributed solar PV development.

source
#solarpunk#solar punk#community#solarpunk aesthetic#china#village#rural#solar village#energy transition#climate change
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Solar panels use photovoltaic (“PV”) technology which converts sunlight directly into electricity. Even for those who have no understanding of how the technology works, we know that to convert sunlight into energy, at the very least sunlight is required; something the UK lacks.
Yet, according to Wikipedia, 12 large-scale solar projects are proposed, approved or under construction across England and Wales. For example, the Cleve Hill Solar Park in Kent is under construction, while the Cottam Solar Project in Lincolnshire has been approved. Additionally, the Llanwern Solar Farm in Newport, Wales, has been operational since 2021. And Shotwick Solar Farm in Flintshire, Wales, ahs been operational since 2016.
For those in Government and their collaborators such as climate crisis activists who think “green” technology, including solar power, will provide the UK with the power the country needs, a report published by the World Bank in 2020 spells out the basics that climate catastrophists are choosing to ignore.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this press release from the US Department of Energy:
As part of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced a $71 million investment, including $16 million from the President’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, in research, development, and demonstration projects to grow the network of domestic manufacturers across the U.S. solar energy supply chain. The selected projects will address gaps in the domestic solar manufacturing capacity for supply chain including equipment, silicon ingots and wafers, and both silicon and thin-film solar cell manufacturing. The projects will also open new markets for solar technologies such as dual-use photovoltaic (PV) applications, including building-integrated PV and agrivoltaics.
These efforts complement and strengthen the Biden-Harris Administration’s goal to rapidly deploy clean energy to help achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. These efforts advance the Biden-Harris Administration’s Justice40 initiative, which set a goal that 40% of overall benefits from certain federal climate and clean energy investments flow to disadvantaged communities that are marginalized by underinvestment and overburdened by pollution.
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Winter is the Perfect Time to Install Solar Panels in Bhopal
When people think of solar power, they often imagine blazing summer days when the sun is at its peak, providing energy to homes and businesses. But surprisingly, winter is one of the best times to install solar panels, especially in a city like Bhopal. With its clear skies, mild weather, and growing emphasis on renewable energy, Bhopal offers an ideal environment for winter residential solar panel installations. Let’s explore why winter is the perfect season to switch to solar power in Bhopal and how it benefits you year-round.
1. Debunking the Myths About Solar Panels in Winter
One of the biggest misconceptions about solar energy is that it requires intense heat or bright sunlight to function. Many people believe solar panels are ineffective during winter or cloudy weather, but this is far from the truth.
Solar panels work by capturing sunlight—not heat—and converting it into electricity. As long as there is daylight, photovoltaic (PV) panels can generate power. In fact, modern solar panels are designed to perform well even in low-light conditions, such as on overcast days.
While shorter daylight hours in winter may slightly reduce energy output, the clear and sunny winter skies in Bhopal ensure consistent energy production. The city’s typical winter weather is ideal for solar efficiency, allowing homeowners and businesses to enjoy the benefits of solar energy throughout the year.
2. How Solar Panels Perform Better in Winter
It might surprise you, but solar panels can operate more efficiently in cooler temperatures. During the peak of summer, excessive heat can reduce the efficiency of solar panels, causing them to produce slightly less electricity.
In winter, the cooler air helps panels maintain optimal efficiency. Bhopal’s mild winter climate, with moderate temperatures and abundant sunshine, creates the perfect conditions for solar panels to work effectively. The panels can capture sunlight without the risk of overheating, ensuring maximum energy production.
Additionally, modern solar panels are highly efficient at capturing diffused light, which means they can generate power even on hazy or partly cloudy days. This capability ensures that your solar system continues to perform reliably, no matter the weather.
3. Why Winter is Ideal for Installation in Bhopal
1. Flexible Scheduling and Faster Installations
Winter is a quieter time for solar panel installers, as most homeowners and businesses rush to set up their systems during summer. This seasonal lull gives you greater flexibility in scheduling your installation.
With fewer projects on their calendars, solar installation companies can complete your setup faster, ensuring minimal disruption to your daily routine. You’re also more likely to find skilled professionals who are available better and receive personalized service.
2. Prepare for Summer’s High Energy Needs
Installing solar panels in winter ensures your system is ready to operate at full capacity by the time summer arrives. During Bhopal’s hot summer months, energy consumption typically increases due to air conditioning and cooling appliances. By installing your system in advance, you’ll be fully prepared to offset these higher energy demands with renewable solar power.
3. Potential Seasonal Discounts
Many solar installation companies offer promotions or discounts during the winter season to encourage customers to install panels during their less busy months. Taking advantage of these offers can significantly reduce the upfront cost of your solar investment.
4. Subsidies and Rebates for Residential
The state of Madhya Pradesh offers various subsidies and rebates to make solar energy more affordable for both residential and commercial users.
Residential Installations: The state provides up to 40% subsidy on the cost of solar panels for homes, depending on the system capacity. Residential solar panel installations of up to 3 kW are eligible for the maximum subsidy.
5. Energy Savings That Start Immediately
Switching to solar power in winter means you start saving on energy bills right away. Even during the shorter days of winter, solar panels generate enough electricity to offset a significant portion of your energy consumption.
By the time summer rolls around, your system will already be fully operational, allowing you to take full advantage of the longer daylight hours. Over the course of a year, this head start translates into substantial savings and a quicker return on your investment.
6. Maximize Government Incentives and Schemes
The Indian government is actively promoting renewable energy adoption through various subsidies, tax benefits, and incentive schemes. Installing solar panels in winter allows you to take advantage of these financial benefits before potential policy changes in the next fiscal year.
Programs like the Grid-Connected Rooftop Solar Scheme provide subsidies to reduce the cost of solar panel installation for residential and commercial properties. By acting now, Bhopal residents can secure these benefits and enjoy a more affordable transition to solar power.
Read More:Solar Power Subsidy in Madhya Pradesh 2024: A Comprehensive Guide
7. Pairing Solar Panels with Battery Storage for Maximum Efficiency
One of the best ways to optimize your solar power system is to pair it with a battery storage solution. Solar batteries store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during cloudy periods.
This is particularly useful in winter when daylight hours are shorter. With a solar battery, you can reduce your reliance on the grid and ensure your home or business remains powered by renewable energy even after sunset. In a city like Bhopal, where electricity costs are rising, investing in a battery system enhances energy independence and long-term savings.
8. Overcoming Weather Concerns
Some homeowners worry that winter weather might complicate the installation process. However, professional solar installation companies are equipped to handle installations in all seasons.
Bhopal’s winters are generally mild, with minimal rain and pleasant temperatures, making it an ideal time for outdoor work. Installers take extra precautions to ensure your panels are securely mounted and optimally positioned to capture maximum sunlight.
Even if Bhopal experiences a rare bout of rain or cloudy weather, modern solar panels are built to withstand adverse conditions. Once installed, your system will be ready to generate power immediately.
9. Combat Rising Energy Costs with Solar Power
With electricity prices steadily increasing, energy self-sufficiency is becoming more important for households and businesses in Bhopal. Installing solar panels in winter allows you to take control of your energy bills and reduce dependence on traditional energy providers.
By generating your own electricity, you can shield yourself from future price hikes and enjoy long-term financial stability. Over time, the savings from reduced energy costs will far outweigh the initial investment in your solar power system
10. Environmental Benefits of Going Solar
Switching to solar power isn’t just a smart financial decision—it’s also a step towards protecting the environment. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, solar energy helps lower greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Bhopal is already making strides in sustainability, and adopting solar energy contributes to the city’s vision of a greener, cleaner future. Installing solar panels in winter allows you to be part of this positive change while enjoying the personal benefits of renewable energy.
11. Why Wait? Winter is the Best Time to Go Solar in Bhopal
If you’ve been considering solar power, there’s no better time than winter to make the switch. Here’s why:
Optimal efficiency: Cooler temperatures and clear skies enhance solar panel performance.
Faster installations: Benefit from flexible scheduling and quicker turnaround times.
Immediate savings: Start reducing your energy bills as soon as your system is installed.
Summer readiness: Be prepared to meet high energy demands during peak summer months.
Government Subsidies: Take advantage of subsidies and tax benefits before policy changes.
Energy independence: Gain protection from rising electricity costs with renewable energy.
Winter might not seem like the obvious choice for solar panel installation, but in Bhopal, it’s one of the smartest times to invest. By acting now, you’ll set yourself up for a future of clean, sustainable, and cost-effective energy. Make the most of Bhopal’s winter weather and start your solar journey today!
Conclusion
Whether you're looking for residential solar installations to power your home or commercial solar installations to cut energy costs for your business, winter is the perfect time to make the switch. Take advantage of faster installations, government incentives, and long-term energy savings. Start your journey towards clean and cost-effective energy today!
Contact us now for a free consultation and customized solar solution tailored to your needs!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reducing uncertainties of climate projections on solar energy resources in Brazil
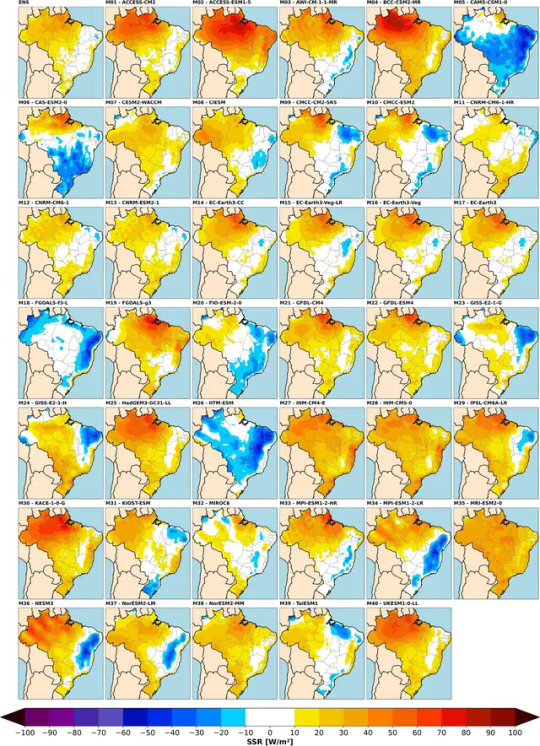
The share of solar power in Brazil’s electrical grid has rapidly increased, relieving GHG emissions and diversifying energy sources for greater energy security. Besides that, solar resource is susceptible to climate change, adding uncertainty to electrical grid resilience. This study uses satellite and reanalysis data to evaluate the performance of CMIP6 models in replicating and predicting surface solar irradiance (SSR) in Brazil. The results from the most reliable models indicate an increase in SSR by 2% to 8% in most regions, with a decrease of around 3% in the South. These findings highlight the potential for increased photovoltaic (PV) yield if backed by supportive public policies while underlining the importance of uncertainty assessment of climate models.
Read the paper.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#science#environmentalism#energy#renewables#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Solar Panel Inverters: Types and Functions
The solar power industry has grown tremendously over the past few decades and is expected to continue growing at over 6% CAGR by 2032. This growth has significantly impacted the solar panel inverter market, which is projected to grow at a 7.7% CAGR over the same period. As a result, solar power stocks have seen a substantial increase. In this article, we'll explore the types and functions of solar panel inverters, a crucial component of any solar power system.

What is a Solar Panel Inverter?
Solar panels consist of silicon photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight into electrical energy. However, the electricity produced by solar panels is in the form of direct current (DC), which is not suitable for home appliances. Home appliances require alternating current (AC), where the flow of electricity reverses periodically. This is where solar panel inverters come in—they convert DC electricity into AC electricity.
To clarify, DC electricity flows in a single direction, making it efficient for transferring power over short distances without significant losses. However, for practical home use, AC electricity is necessary due to its ability to travel over longer distances with less energy loss. The solar panel inverter acts as an intermediary, converting DC from the solar panels to AC for use in the home or office. Additionally, in an on-grid solar system, the inverter connects the solar panels to the local electricity grid, allowing for net metering and storing excess energy in batteries.
Why is an Inverter Necessary in Solar Power Systems? Solar panel inverters perform several essential functions that make them crucial for any solar power setup:
Converting DC to AC: The primary function of a solar inverter is to convert the DC electricity produced by solar panels into AC electricity, making it usable for home appliances.
Monitoring Solar Panel Performance: Most solar inverters come with built-in monitoring capabilities, allowing you to track the amount of electricity being converted and identify any issues with the solar panels. This feature helps ensure optimal performance and identify potential problems early.
Connecting to the Grid: Inverters connect your solar system to the local utility grid, enabling you to sell excess electricity back to the grid for a credit or financial return. This connection also allows you to draw electricity from the grid when your solar panels aren't producing enough power, ensuring a reliable power supply.
Optimizing Solar Panel Efficiency: Some inverters, such as power optimizers, help maximize the efficiency of each solar panel. Factors like shading, orientation, and debris can cause individual panels to produce different amounts of electricity. Power optimizers adjust the output of each panel to ensure a consistent flow of electricity from the entire array.
Protecting Your Electrical System: Solar inverters also play a protective role by preventing electrical overloads and short circuits. They have built-in safety features that shut down the system in case of overvoltage or other electrical issues, protecting your home and solar investment.

Types of Solar Panel Inverters
There are three main types of solar panel inverters commonly used in residential systems:
String Inverters: This is the most traditional type of solar inverter, similar to a centralized air conditioning system. All solar panels are connected in series to a single inverter. String inverters are most effective in situations where all panels receive equal sunlight without shading. However, if one panel is shaded or malfunctioning, it can reduce the output of the entire system.
Microinverters: Microinverters are installed on each individual solar panel, allowing for more precise energy conversion and monitoring. This setup is ideal for installations where panels face different directions or are prone to shading.
Power Optimizers: Power optimizers combine the benefits of string inverters and microinverters. Each panel is equipped with an optimizer, which adjusts the output to match other panels before sending the DC electricity to a centralized inverter for conversion to AC.
Conclusion Solar panel inverters are essential for converting the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity suitable for household use. They also play a vital role in monitoring system performance, optimizing efficiency, connecting to the grid, and protecting your electrical system. Choosing the right type of inverter—string inverter, microinverter, or power optimizer—depends on your specific needs, including your budget, site conditions, and energy goals.
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
If alien technological civilizations exist, they almost certainly use solar energy. Along with wind, it’s the cleanest, most accessible form of energy, at least here on Earth. Driven by technological advances and mass production, solar energy on Earth is expanding rapidly. It seems likely that ETIs (Extraterrestrial Intelligence) using widespread solar energy on their planet could make their presence known to us. If other ETIs exist, they could easily be ahead of us technologically. Silicon solar panels could be widely used on their planetary surfaces. Could their mass implementation constitute a detectable technosignature? The authors of a new paper examine that question. The paper is “Detectability of Solar Panels as a Technosignature,” and it’ll be published in The Astrophysical Journal. The lead author is Ravi Kopparapu from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. In their paper, the authors assess the detectability of silicon-based solar panels on an Earth-like habitable zone planet. “Silicon-based photovoltaic cells have high reflectance in the UV-VIS and in the near-IR, within the wavelength range of a space-based flagship mission concept like the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO),” the authors write. The HWO would search for and image Earth-like worlds in habitable zones. There’s no timeline for the mission, but the 2020 Decadal Survey recommended the telescope be built. This research looks ahead to the mission or one like it sometime in the future. Naturally, the authors make a number of assumptions about a hypothetical ETI using solar power. They assume that an ETI is using large-scale photovoltaics (PVs) based on silicon and that their planet orbits a Sun-like star. Silicon PVs are cost-effective to produce, and they are well-suited to harness the energy from a Sun-like star. Kopparapu and his co-authors aren’t the first to suggest that silicon PVs could constitute a technosignature. In a 2017 paper, Avi Loeb and Manasvi Lingam from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics wrote that silicon-based PVs create an artificial edge in their spectra. This edge is similar to the ‘red edge‘ detectable in Earth’s vegetation when viewed from space but shifted to shorter wavelengths. “Future observations of reflected light from exoplanets would be able to detect both natural and artificial edges photometrically if a significant fraction of the planet’s surface is covered by vegetation or photovoltaic arrays, respectively,” Lingam and Loeb wrote. “The “edge” refers to the noticeable increase in the reflectance of the material under consideration when a reflected light spectrum is taken of the planet,” the authors of the new research explain. Satellites monitor the red edge on Earth to observe agricultural crops, and the same could apply to sensing PVs on other worlds. This figure shows the reflection spectrum of a deciduous leaf (data from Clark et al. 1993). The large sharp rise (between 700 and 800 nm) is known as the red edge and is due to the contrast between the strong absorption of chlorophyll and the otherwise reflective leaf. Image Credit: Seager et al. 2005. While Lingam and Loeb suggested the possibility, Kopparapu and his co-authors dug deeper. They point out that we could generate enough energy for our needs (as of 2022) if only 2.4% of the Earth’s surface was covered in silicon-based PVs. The 2.4% number is only accurate if the chosen location is optimized. For Earth, that means the Sahara Desert, and something similar may be true on an alien world. The authors explain, “This region is both close to the equator, where a comparatively greater amount of solar energy would be available throughout the year, and has minimal cloud coverage.” The authors also work with a 23% land coverage number. This number reflects previous research showing that for a projected maximum human population of 10 billion people, 23% land coverage would provide a high standard of living for everyone. They also use it as an upper limit because anything beyond that seems highly unlikely and would have negative consequences. On Earth, the entire continent of Africa is about 23% of the surface. The authors’ calculations show that an 8-meter telescope similar to the HWO would not detect an Earth-like exoplanet with 2.4% of its surface covered with PVs. If an ETI covered 23% of its surface with energy-harvesting PVs, would that be detectable? It would be difficult to untangle the planet’s light from the star’s light and would require hundreds of hours of observation time to reach an acceptable Signal-to-Noise (S/N) ratio. “Because we have chosen the 0.34 ?m–0.52?m range to calculate the impact of silicon panels on the reflectance spectra, the difference between a planet with and without silicon is not markedly different, even with 23% land cover,” the authors explain. Technological progress adds another wrinkle to these numbers. As PV technology advances, an ETI would cover less of its planet’s surface area to generate the same amount of energy, making detection even more difficult. This figure from the research shows the planet-star contrast ratio as a function of wavelength for2.4 % land coverage with PVs (blue solid), 23 % PVs (red solid) and 0% (green dashed) land coverage of solar panels. “This suggests that the artificial silicon edge suggested by Lingam & Loeb (2017) may not be detectable,” the authors write. Image Credit: Kopparapu et al. 2024. Solar energy is expanding rapidly on Earth. Each year, more individual homes, businesses, and institutions implement solar arrays. Those might not constitute technosignatures, but individual installations aren’t the only thing growing. China built a vast solar power plant called the Gonghe Photovoltaic Project in its sparsely populated Qinghai Province. It generates 3182 MW. India has the Bhadla Solar Park (2,245 MW) in the Thar Desert. Saudi Arabia has built several new solar plants and intends to build more. Other innovative solar projects are announced regularly. But will we realistically ever cover 2.4% of our planet in solar arrays? Will we need to? There are many questions. Generating solar power in the heat of the Sahara Desert is challenging. The extreme heat reduces efficiency. Building the infrastructure required to deliver the energy to population centres is also another challenge. Then consider that silicon-based PVs may not be the end point in solar panel development. Perovskite-based PVs hold a lot of promise to outperform silicon. They’re more efficient than silicon, and researchers frequently break energy records with them (in laboratories.) Would perovskite PVs create the same “edge” in a planet’s spectra? The authors didn’t consider specific technological advances like perovskite because it’s beyond the scope of their paper. The bottom line is that silicon-based solar arrays on a planetary surface are unlikely to create an easily detectable technosignature. “Assuming an 8-meter HWO-like telescope, focusing on the reflection edge in the UV-VIS, and considering varying land coverage of solar panels on an Earth-like exoplanet that match the present and projected energy needs, we estimate that several hundreds of hours of observation time is needed to reach a SNR of ~5 for a high land coverage of ~23%,” the authors write. The Bhadla Solar Park is a large PV installation that aims to generate over 2,000 MW of solar energy. Image Credit: (Left) Google Earth. (Right) Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data 2020, Attribution, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=90537462 The authors also wonder what this means for the Kardashev Scale and things like Dyson Spheres. In that paradigm, ETIs require more and more energy and eventually build a mega engineering project that harvests all of the energy available from their star. A Dyson Sphere would create a powerful technosignature, and astronomers are already looking for them. But if the numbers in this research are correct, we may never see one because they’re not needed. “We find that, even with significant population growth, the energy needs of human civilization would be several orders of magnitude below the energy threshold for a Kardashev Type I civilization or a Dyson sphere/swarm which harnesses the energy of a star,” they conclude. “This line of inquiry reexamines the utility of such concepts and potentially addresses one crucial aspect of the Fermi paradox: We have not discovered any large-scale engineering yet, conceivably because advanced technologies may not need them.” The post Could Alien Solar Panels Be Technosignatures? appeared first on Universe Today.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tapuwa Dangarembizi Sustainable Solutions: The Economic Advantages of Renewable Energy for Industries
Various industries are quickly recognizing the critical importance of implementing sustainable practices and embracing renewable energy sources. This increased awareness stems from increasing concerns about the hazardous consequences of climate change and the impending depletion of fossil fuel storage. As a result, companies have become increasingly interested in alternative energy solutions that are not only environmentally friendly but also provide significant advantages for the economy. Within the scope of this blog post, we are going to look into the Tapuwa Dangarembizi - How can industries benefit from using sustainable energy sources that are renewable and do not deplete natural resources?

The basics of renewable energy systems
Renewable energy systems utilize the power of our planet's limitless, ever-renewing resources, gathering energy from the never-ending embrace of sunlight, wind, and water. The wonders of sustainable energy technologies are demonstrated by an arrangement of solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, wind turbines, hydroelectric power plants, and the earth's warm embrace by means of geothermal systems. Unlike the limited chain of fossil fuels, these inventive solutions provide us with an abundant, pristine path, breathing life into our environment while developing economic prosperity for industries that embrace sustainability with a passionate embrace.
Sustainable Energy minimizes Industry's Carbon Footprint
Renewable energy is being passionately adopted by industries due to its extraordinary capacity to reduce carbon emissions which propel us toward a greener future. Industries can successfully decrease their carbon footprint and minimize the negative effects of climate change. This transformation is in line with the global effort to tackle the dangers of global warming while accomplishing the sustainability goals established in projects such as the Paris Agreement. In addition, using renewable energy bolsters a company's reputation as a responsible environmental manager, drawing in eco-conscious customers as well as investors who value environmental sustainability.
Incorporating sustainable energy into your industry operations results in a decrease in costs
Contrary to popular belief, adopting renewable energy solutions can be economically beneficial for industries. While the initial investment in renewable energy infrastructure may seem substantial, the long-term cost savings outweigh the upfront expenses. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are becoming increasingly cost-effective, with declining prices of solar panels and wind turbines making them more accessible for industrial applications. Additionally, once installed, these systems have minimal operating costs and provide a reliable source of energy, reducing reliance on volatile fossil fuel markets. Moreover, some regions offer financial incentives such as tax credits and subsidies for businesses that invest in renewable energy, further enhancing cost efficiency.
Diversify sources of energy and decrease reliance on imported fuels.
The dynamism and volatility of fuel prices, together with the possibility of supply disruptions, pose an enormous challenge to industries that depend on imported fuels. By embracing renewable energy's infinite possibilities, companies can overcome these challenges and usher in a new era of energy resilience. Industries can unlock the ability to produce their own power by installing on-site renewable energy systems, reducing the negative effects of external influences on fuel prices and availability. This newfound independence not only allows industries to take greater control over their energy expenditures but also strengthens their operations with an unwavering and uninterrupted energy supply, propelling productivity and sharpening their edge over competitors.
Conclusion
In an ever-changing energy surroundings, industries reliant on imported fuels face unpredictable price swings and supply uncertainty. To combat this, the wise move is to embrace renewable energy's limitless potential. Companies can be benefited from a more diverse energy mix, reducing reliance on volatile imports and increasing energy security. To read more about sustainable energy, check out the Eco-Visionary – Tapuwa Dangarembizi’s Journey Towards Sustainable Energy.
#Sustainable#Diversify#Footprint#natural resources#imported#surroundings#renewable energy#Tapuwa Dangarembizi#operations
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sustainable Living: Integrating Solar Energy into Your Home
Embracing renewable energy is a key step toward sustainable living, and solar energy stands at the forefront of this movement. Homeowners around the globe are harnessing the power of the sun, reducing carbon footprints, and enjoying the economic benefits of solar power. This article delves into the practicalities of integrating solar energy into your home, covering the essentials and the transformative impact it can have on how we live and power our daily lives.
Understanding Solar Energy
Solar energy is captured through photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight directly into electricity. These cells are assembled into panels, which can be installed on rooftops or in open land areas. When sunlight hits the PV cells, it triggers a flow of electrons, generating direct current (DC) electricity, which is then converted to alternating current (AC) for home use via an inverter.
Assessing Your Solar Potential
Before investing in solar technology, it's crucial to evaluate your home's solar potential. This depends on geographic location, roof orientation, shading from trees or buildings, and local weather conditions. Tools like Google's Project Sunroof or consultations with solar energy providers can offer insights into how much sunlight your rooftop can capture and convert.
Choosing the Right System
There's a range of solar panel systems available, from grid-tied setups that allow you to sell excess power back to the grid, to off-grid systems with battery storage for energy independence. Your choice will hinge on your energy goals, location, and financial considerations. Additionally, solar thermal systems can provide hot water or support heating systems, further reducing reliance on conventional energy sources.
Financial Considerations and Incentives
The initial cost of solar panel installation can be significant, but numerous government incentives, tax breaks, and rebates exist to make it more affordable. Over time, solar panels can pay for themselves through reduced electricity bills. Financing options like solar leases or power purchase agreements (PPAs) can also help homeowners adopt solar energy with little to no upfront costs.
Installation and Maintenance
Professional installation ensures optimal system performance and complies with local codes and regulations. Post-installation, solar panels require minimal maintenance, typically needing only occasional cleaning and checks to ensure no debris or damage. Most solar panels come with long-term warranties, reassuring homeowners of their durability and efficiency.
Environmental Impact
Integrating solar energy into your home is a positive step for the environment. It reduces reliance on fossil fuels, curtails greenhouse gas emissions, and contributes to a decrease in air pollution. As residential solar energy use grows, it aids in the collective effort to combat climate change and promotes a healthier planet.
Looking Ahead
Solar energy technology continues to advance, with improvements in efficiency, aesthetics, and integration with smart home technologies. As battery storage solutions become more affordable, the ability to store and manage energy will revolutionize home solar systems. By integrating solar energy into your home today, you're not just saving on costs but also investing in a sustainable future and joining the vanguard of the renewable energy revolution.
#solarpanels#solar#solarenergy#photovoltaics#solartechnology#renewables#sustainability#greenenergy#cleanenergy#residentialsolar
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
African poverty is partly a consequence of energy poverty. In every other continent the vast majority of people have access to electricity. In Africa 600m people, 43% of the total, cannot readily light their homes or charge their phones. And those who nominally have grid electricity find it as reliable as a Scottish summer. More than three-quarters of African firms experience outages; two-fifths say electricity is the main constraint on their business.
If other sub-Saharan African countries had enjoyed power as reliable as South Africa’s from 1995 to 2007, then the continent’s rate of real GDP growth per person would have been two percentage points higher, more than doubling the actual rate, according to one academic paper. Since then South Africa has also had erratic electricity. So-called “load-shedding” is probably the main reason why the economy has shrunk in four of the past eight quarters.
Solar power is increasingly seen as the solution. Last year Africa installed a record amount of photovoltaic (PV) capacity (though this still made up just 1% of the total added worldwide), notes the African Solar Industry Association (AFSIA), a trade group. Globally most solar PV is built by utilities, but in Africa 65% of new capacity over the past two years has come from large firms contracting directly with developers. These deals are part of a decentralised revolution that could be of huge benefit to African economies.
Ground zero for the revolution is South Africa. Last year saw a record number of blackouts imposed by Eskom, the state-run utility, whose dysfunctional coal-fired power stations regularly break down or operate at far below capacity. Fortunately, as load-shedding was peaking, the costs of solar systems were plummeting.
Between 2019 and 2023 the cost of panels fell by 15%, having already declined by almost 90% in the 2010s. Meanwhile battery storage systems now cost about half as much as five years ago. Industrial users pay 20-40% less per unit when buying electricity from private project developers than on the cheapest Eskom tariff.
In the past two calendar years the amount of solar capacity in South Africa rose from 2.8GW to 7.8GW, notes AFSIA, excluding that installed on the roofs of suburban homes. All together South Africa’s solar capacity could now be almost a fifth of that of Eskom’s coal-fired power stations (albeit those still have a higher “capacity factor”, or ability to produce electricity around the clock). The growth of solar is a key reason why there has been less load-shedding in 2024...
Over the past decade the number of startups providing “distributed renewable energy” (DRE) has grown at a clip. Industry estimates suggest that more than 400m Africans get electricity from solar home systems and that more than ten times as many “mini-grids”, most of which use solar, were built in 2016-20 than in the preceding five years. In Kenya DRE firms employ more than six times as many people as the largest utility. In Nigeria they have created almost as many jobs as the oil and gas industry.
“The future is an extremely distributed system to an extent that people haven’t fully grasped,” argues Matthew Tilleard of CrossBoundary Group, a firm whose customers range from large businesses to hitherto unconnected consumers. “It’s going to happen here in Africa first and most consequentially.”
Ignite, which operates in nine African countries, has products that include a basic panel that powers three light bulbs and a phone charger, as well as solar-powered irrigation pumps, stoves and internet routers, and industrial systems. Customers use mobile money to “unlock” a pay-as-you-go meter.
Yariv Cohen, Ignite’s CEO, reckons that the typical $3 per month spent by consumers is less than what they previously paid for kerosene and at phone-charging kiosks. He describes how farmers are more productive because they do not have to get home before dark and children are getting better test scores because they study under bulbs. One family in Rwanda used to keep their two cows in their house because they feared rustlers might come in the dark; now the cattle snooze al fresco under an outside lamp and the family gets more sleep.
...That is one eye-catching aspect of Africa’s solar revolution. But most of the continent is undergoing a more subtle—and significant—experiment in decentralised, commercially driven solar power. It is a trend that could both transform African economies and offer lessons to the rest of the world."
-via The Economist, June 18, 2024. Paragraph breaks added.
#one of the biggest stories of this century is going to be the story of the African Renaissance#I promise you#well preferably they'll come up with a non-European term for it lol#but trust me it WILL happen and it will be SO good to see#africa#south africa#nigeria#kenya#solar#solar power#solar panels#solar pv#energy#clean energy#poverty#electrification#distributed energy#electricity#infrastructure#hope#solarpunk#good news#solar age#<- making that a tag now
417 notes
·
View notes
Text
Norway has installed the world’s northernmost ground solar panels in its Svalbard archipelago, despite the region being plunged into darkness from early October until mid-February every year.
The pilot project could help remote Arctic communities transition to green energy.
Neatly lined up in six rows in a field, 360 solar panels will on Thursday begin providing electricity to an old shipping radio station, Isfjord Radio, now converted into a base camp for tourists.
The windswept archipelago - also known as Spitsbergen - is located some 1,300 kilometres from the North Pole and is accessible only by boat or helicopter, weather permitting.
"It's what we believe to be the world's northernmost ground-mounted PV (photovoltaic) system," Mons Ole Sellevold, renewable energies technical adviser at state-owned energy group Store Norske, told AFP.
"It's the first time anyone has done it at this scale in the Arctic," he said, his rifle slung over his shoulder in case polar bears turn up.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Crystalline Silicon Solar Pv Market set to hit $287.6 billion by 2035
Industry revenue for Crystalline Silicon Solar Pv is estimated to rise to $287.6 billion by 2035 from $89.2 billion of 2024. The revenue growth of market players is expected to average at 11.2% annually for the period 2024 to 2035.
Crystalline Silicon Solar Pv is critical across several key applications including rooftop photovoltaics, solar farms, portable solar equipment and on-grid power stations. The report unwinds growth & revenue expansion opportunities at Crystalline Silicon Solar Pv’s Material Type, Application, Product Design and Manufacturing Process including industry revenue forecast.
Industry Leadership and Competitive Landscape
The Crystalline Silicon Solar Pv market is characterized by intense competition, with a number of leading players such as JinkoSolar Holding Co. Ltd, Trina Solar Co. Ltd, Canadian Solar Inc, JA Solar Holdings Co. Ltd, Hanwha Q CELLS Co. Ltd, First Solar Inc, LONGi Green Energy Technology Co. Ltd, Shunfeng International Clean Energy Ltd, SunPower Corporation, ReneSola Ltd, Risen Energy Co. Ltd and Yingli Green Energy Holding Company Ltd.
https://datastringconsulting.com/industry-analysis/crystalline-silicon-solar-pv-market-research-report
The Crystalline Silicon Solar Pv market is projected to expand substantially, driven by increasing demand for electricity and technological advancements in solar pv. This growth is expected to be further supported by Industry trends like Favorable Government Policies.
Moreover, the key opportunities, such as opportunity in the automotive industry, solar-powered smart cities and boost from space exploration, are anticipated to create revenue pockets in major demand hubs including China, U.S., Germany, Japan and India.
Regional Shifts and Evolving Supply Chains
North America and Europe are the two most active and leading regions in the market. With challenges like high implementation costs and climatic restraints, Crystalline Silicon Solar Pv market’s supply chain from silicon mining & refining / poly-silicon production / solar pv cell manufacturing to solar pv module assembly is expected to evolve & expand further; and industry players will make strategic advancement in emerging markets including Mexico, South Africa and Brazil for revenue diversification and TAM expansion.
About DataString Consulting
DataString Consulting offers a complete range of market research and business intelligence solutions for both B2C and B2B markets all under one roof. We offer bespoke market research projects designed to meet the specific strategic objectives of the business. DataString’s leadership team has more than 30 years of combined experience in Market & business research and strategy advisory across the world. DataString Consulting’s data aggregators and Industry experts monitor high growth segments within more than 15 industries on an ongoing basis.
DataString Consulting is a professional market research company which aims at providing all the market & business research solutions under one roof. Get the right insights for your goals with our unique approach to market research and precisely tailored solutions. We offer services in strategy consulting, comprehensive opportunity assessment across various sectors, and solution-oriented approaches to solve business problems.
0 notes
Text
Flexible and Lightweight Solar Power: The Growing Demand for Polymer Solar Cells
Increasing Focus on Flexible and Lightweight Solar Solutions Accelerates Growth in the Polymer Solar Cells Market.

The Polymer Solar Cells Market size was USD 1.1 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 5.9 Billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 20.8% over the forecast period of 2024-2032.
The Polymer Solar Cells Market is witnessing significant growth due to the rising demand for lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective photovoltaic (PV) solutions. Polymer solar cells, also known as organic photovoltaic (OPV) cells, offer advantages such as easy manufacturing, low material costs, and the ability to be integrated into various surfaces. As the world shifts towards sustainable energy sources, these cells are gaining traction in wearable electronics, building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), and off-grid energy solutions.
Key Players in the Polymer Solar Cells Market
Tata Power Solar Systems Limited (Solar Panels, Solar Rooftop Solutions)
Jinko Solar Holding Co. Ltd (Jinko Solar Panels, Solar Module Solutions)
Suniva Inc (High-Efficiency Solar Cells, PERC Solar Modules)
Borg Inc. (BIPV Modules, Flexible Solar Cells)
Heliatek GmbH (HeliaFilm, Organic Solar Cells)
Trina Solar Limited (Trina Solar Panels, Vertex Modules)
Solar World AG (Solar Panels, Solar Modules)
Alps Technology Inc (Flexible Solar Panels, Thin-Film Solar Modules)
Pionis Energy Technologies LLC (Flexible Solar Cells, BIPV Solutions)
Infinity PV ApS (Organic Photovoltaic Modules, Flexible Solar Film)
Future Scope of the Market
The Polymer Solar Cells Market is set to expand with:
Advancements in efficiency and stability of organic photovoltaics (OPVs).
Increasing adoption of flexible and lightweight solar panels in consumer electronics and IoT devices.
Integration of polymer solar cells in smart cities, green buildings, and transportation.
Growth in government incentives and funding for renewable energy projects.
Expanding applications in remote and off-grid locations.
Emerging Trends in the Polymer Solar Cells Market
The Polymer Solar Cells Market is evolving with breakthrough innovations and technological advancements. Researchers are focusing on enhancing the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of OPVs, making them more competitive with traditional silicon-based solar cells. Inkjet printing and roll-to-roll manufacturing are driving cost reductions and large-scale production, making polymer solar cells a viable alternative for commercial applications. Additionally, the market is experiencing a surge in demand for transparent and semi-transparent solar panels, which can be seamlessly integrated into windows, facades, and consumer gadgets.
Key Points:
Growing demand for lightweight, flexible, and cost-efficient solar technology.
Advancements in power conversion efficiency (PCE) of polymer solar cells.
Expansion of polymer solar cells in smart buildings, IoT devices, and off-grid applications.
Emergence of roll-to-roll and inkjet printing techniques for scalable production.
Rising government incentives and investments in sustainable energy solutions.
Conclusion
The Polymer Solar Cells Market is poised for significant expansion as renewable energy adoption accelerates worldwide. With continuous technological advancements, increasing commercial applications, and strong government support for clean energy initiatives, polymer solar cells are expected to play a crucial role in the future of sustainable power generation.
Read Full Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/polymer-solar-cells-market-1498
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave — Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1–315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Polymer Solar Cells Market#Polymer Solar Cells Market Size#Polymer Solar Cells Market Share#Polymer Solar Cells Market Report#Polymer Solar Cells Market Forecast
0 notes
Text
Understanding Factors Influencing the Future of Renewable Energy

The global transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources is one of the most significant shifts in the modern era. The need for cleaner, greener, and more sustainable energy sources is paramount, not only to protect our environment but also to ensure the future of global energy security. As renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal continue to grow in importance, understanding the factors influencing their development and widespread adoption becomes crucial. This article explores the key drivers, challenges, and trends shaping the future of renewable energy.
Technological Innovation and Advances
The Role of Technological Innovation
Technological innovation is one of the principal factors driving the future of renewable energy. Over the past decade, renewable technologies, particularly solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, wind turbines, and energy storage solutions, have advanced remarkably. Breakthroughs in material science, energy efficiency, and smart grid management are enhancing the efficiency and affordability of renewable technologies.
Solar and Wind Technology Advancements
Solar photovoltaic technology has seen rapid improvements in efficiency, while wind turbines have become more powerful and cost-effective. These advancements have made renewable energy competitive with fossil fuels. The ongoing development of offshore wind and floating solar technologies holds tremendous potential to increase renewable energy generation capacity globally.
Energy Storage Innovations
A key challenge for renewable energy is its intermittent nature. Solar and wind are dependent on weather conditions, making it essential to develop efficient energy storage systems. Innovations in battery technology, such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, are critical to ensuring renewable energy can be stored and used when needed. Additionally, pumped hydro storage and thermal energy storage solutions offer promising alternatives for managing fluctuations in energy production.
Cost Effectiveness and Affordability
Decreasing Costs of Renewable Energy
The future of renewable energy largely depends on its cost-effectiveness. Over the past few years, the price of renewable technologies has decreased significantly, making them increasingly accessible to both consumers and industries. The economies of scale, advancements in technology, and more efficient manufacturing processes contribute to reducing the cost of renewable energy.
Competitive Pricing with Fossil Fuels
As the cost of renewable energy continues to decline, it is becoming competitive with traditional fossil fuels like coal and natural gas. In many regions, renewable energy is already the most affordable source of new electricity generation. This price parity is a crucial factor in driving the widespread adoption of renewable energy and in facilitating the global transition to a cleaner energy future.
Policy Support and Regulatory Frameworks
The Importance of Policy in Shaping Renewable Energy
Government policies and regulatory frameworks play a significant role in shaping the future of renewable energy. Policymakers around the world are introducing incentives such as renewable portfolio standards, feed-in tariffs, and tax credits to promote the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies. Transparent, stable, and favorable policies help create an attractive investment environment for renewable energy projects.
Carbon Pricing and Emission Reduction Goals
Governments are also increasingly focusing on carbon pricing and emission reduction goals. Climate change policies, such as the Paris Agreement, are driving global efforts to transition to a low-carbon economy. These policies set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, which directly influences the growth and success of renewable energy industries.
Energy Storage Solutions
Overcoming the Intermittency Challenge
Energy storage remains one of the biggest hurdles for the widespread adoption of renewable energy. The intermittent nature of solar and wind energy presents a significant challenge, as energy generation does not always align with demand. To overcome this, new storage technologies are being developed to store excess energy during peak generation times and release it when generation is low.
Advances in Storage Technologies
Battery storage technologies, such as lithium-ion and next-generation solid-state batteries, are critical to overcoming the intermittency problem. Additionally, large-scale storage solutions like pumped hydro and thermal energy storage are becoming increasingly important in balancing supply and demand in renewable energy systems.
Grid Modernization and Integration
The Need for Modernized Grids
As renewable energy sources become more prevalent, the existing power grids must evolve to accommodate their integration. The intermittent nature of renewable energy requires grids to become smarter and more flexible. Smart grid technologies, which incorporate automation, communication, and real-time data, are essential for managing renewable energy resources effectively.
Smart Grids for Efficient Energy Distribution
The integration of renewable energy into existing grids requires the development of smart grids capable of efficiently managing energy flows and balancing supply and demand. These grids need to be equipped with advanced technologies that can accommodate fluctuations in renewable energy generation while ensuring the stability of the grid.
Public Awareness and Acceptance
Gaining Public Trust in Renewable Energy
Public acceptance and awareness are vital to the successful implementation of renewable energy projects. People need to understand the benefits of renewable energy, such as its environmental impact, cost savings, and long-term sustainability. Overcoming misconceptions about the affordability and reliability of renewable energy sources is essential for broad public support.
Education and Engagement
Educational campaigns and community engagement are crucial in demystifying renewable energy and fostering public trust. Governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and the private sector must work together to raise awareness and address concerns about the transition to renewable energy.
Investment and Financing
Securing Investment for Renewable Projects
The future of renewable energy depends heavily on investments. Developing and deploying renewable energy projects requires substantial financial resources, particularly for infrastructure development, research, and innovation. Private capital, institutional investors, and green financing mechanisms will play a pivotal role in funding the global energy transition.
Green Finance and Sustainable Investments
Green finance, which directs investments toward environmentally sustainable projects, is a growing trend in the financial sector. Renewable energy projects often attract green bonds and other sustainable financing instruments, which support the development of clean energy technologies. The level of investment in renewable energy projects will be a determining factor in the pace of the global energy transition.
International Cooperation and Transfer of Technology
The Global Role of Technology Transfer
International cooperation and technology transfer are essential for accelerating the global shift toward renewable energy. Developed nations have the resources and expertise to develop cutting-edge renewable technologies, but it is crucial to ensure these technologies are accessible to developing countries as well. Knowledge sharing, joint research and development initiatives, and technology transfers are essential for ensuring that renewable energy becomes a global reality.
Addressing Global Energy Access
Many developing countries lack access to reliable and affordable energy. By transferring renewable energy technologies and expertise, developed nations can help address energy access challenges and foster sustainable economic growth in these regions.
The Private Sector’s Role
Innovations Driven by the Private Sector
The private sector plays a key role in driving the future of renewable energy. Companies are increasingly recognizing the dual benefits of using renewable energy: reducing operational costs and enhancing their environmental performance. Investments in renewable energy technologies and infrastructure by businesses can accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Corporate Responsibility and Sustainability
Corporate sustainability goals and commitments to reduce carbon footprints are motivating private sector investments in renewable energy. By adopting renewable energy solutions, companies not only contribute to environmental conservation but also benefit from lower energy costs in the long run.
The Impact of Climate Change Policy
Shaping the Future of Renewable Energy
Climate change policies at both the global and national levels will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of renewable energy. The Paris Agreement and other international climate accords set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to renewable energy. The effectiveness of these policies will determine the pace at which renewable energy technologies are deployed worldwide.
Conclusion
A Bright Future for Renewable Energy
The future of renewable energy is promising, driven by technological innovation, declining costs, supportive policies, and growing public awareness. However, challenges remain, particularly in terms of intermittency, grid integration, and financing. Overcoming these obstacles will require continued investment in innovation, smart policy leadership, and international cooperation. As the world moves toward a cleaner, more sustainable energy future, the factors discussed in this article will continue to shape the trajectory of renewable energy, ensuring a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable world for future generations.
0 notes