#Senior Citizen Savings Scheme 2023
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Senior Citizen Savings Scheme 2023: What is it, how to get its benefit? How to apply in this scheme?
Senior Citizen Savings Scheme 2023: – If your age is also 60 years and you are also a retired employee, then this article of ours is only for you because we want to tell you in detail about the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme 2023 in this article for which
Senior Citizen Savings Scheme 2023: – If your age is also 60 years and you are also a retired employee, then this article of ours is only for you because we want to tell you in detail about the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme 2023 in this article for which You have to read this article carefully. Let us tell you that, to apply in the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme 2023, all of you senior citizens…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Post Office SCSS Scheme:हर महीने घर घर बैठे खाते में मिलेंगे ₹20000, कमल का यह स्कीम, आपके लिए बहुत जरूरी है
Post Office SCSS Scheme:आजकल सरकार आम लोगों को पैसे देने के लिए कई कल्याणकारी योजनाएं चलाई जा रही हैं। इनमें से एक योजना इतनी दिलचस्प है कि यह आपकी आर्थिक चिंता को कम कर सकती है। इस योजना के तहत आपको हर महीने ₹20,500 मिलेंगे, जो सीधे आपके बैंक खाते में भेजे जाएंगे। वर्तमान आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने में यह राशि आपको मदद करती है और आपको वित्तीय स्थिरता मिलती है। इस योजना का फायदा उठाने के लिए कुछ सरल…
#post office ki scss scheme#post office scheme senior citizen#post office scss account#post office scss interest rate 2023#Post Office SCSS Scheme#post office scss scheme 2023#post office scss scheme 2024#post office scss scheme 2024 tamil#post office scss scheme in hindi#post office scss scheme in tamil#post office scss scheme in telugu#post office senior citizen account#post office senior citizen saving scheme 2024#post office senior citizen saving scheme form fill up#post office senior citizen saving scheme interest rate#post office senior citizen savings scheme#post office ssc scheme#post senior citizen scheme 2023#scss post office scheme 2022#scss post office scheme 2023#scss post office scheme 2023 bengali#scss post office scheme 2023 in kannada#scss post office scheme 2023 kannada#scss post office scheme 2023 malayalam#scss post office scheme 2023 tamil#scss post office scheme 2023 telugu#scss post office scheme 2024#scss post office scheme 2024 assam#scss post office scheme 2024 assamese#scss post office scheme 2024 bengali
0 notes
Text
Best Practices in Your First Year of Stock Market Trading 2023
Best Practices in Your First Year of Stock Market Trading. Learn the top 5 best practices for successful stock market trading in your first year. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights, tips, and strategies to help you navigate the stock market with confidence. Entering the stock market can be an exciting and potentially lucrative venture. However, it’s essential to approach stock…

View On WordPress
#15 Biggest Mistakes of Stock Market Investors#5 Reasons Why the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme is a Smart Investment#A Beginner&039;s Guide to Reading Share Market Charts 2023#Advantages and Disadvantages of Investing#Best Practices in Your First Year of Stock Market Trading 2023
0 notes
Text
instagram
Yahoo! News
Germans are handing over their driving licences in exchange for free public transport.
Around a thousand people in North Rhine-Westphalia, a populous western German state, have relinquished their driving licences as part of a scheme designed to reduce the car-loving country’s reliance on automobiles.
Aimed primarily at senior citizens, the incentive enables people to surrender their driving licences for a year’s free public transport, known as the “Deutschlandticket.”
The ticket, which normally costs €49 (£41) a month, allows holders to travel on all local transport across Germany, including regional trains.
In Leverkusen, near Cologne, nearly 600 people over the age of 75 have opted into the scheme so far, saving them just under £500 on public transport for the year. The benefits of the scheme vary from state to state.
Leverkusen pioneered the initiative in 2023, with other Rhineland areas such as Dortmund, Kleve, and the former capital Bonn following suit this year.

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS): Why You Should Invest In It .
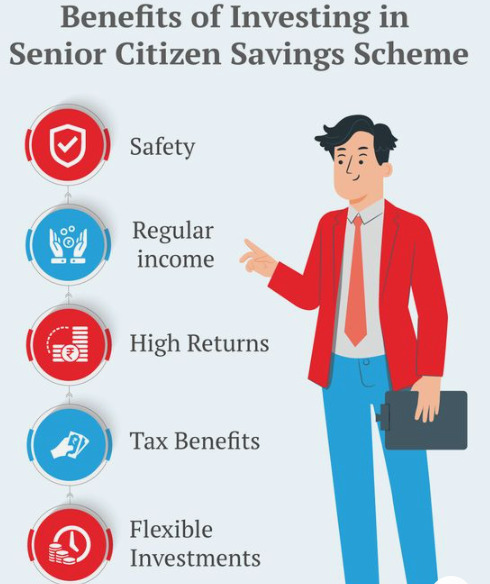
As individuals approach retirement, the importance of sound financial planning becomes paramount. Ensuring a steady source of income during the golden years is essential to maintain a comfortable lifestyle without financial stress. One of the most reliable and government-backed options available for senior citizens in India is the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS).
The SCSS is designed exclusively for citizens aged 60 and above, providing them with a safe investment avenue that offers a combination of attractive interest rates and tax benefits. Whether you’re planning for your retirement or have recently retired, understanding the nuances of this scheme and how it can benefit you will help you make a more informed decision.
What is the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS)?
The Senior Citizen Savings Scheme is a government-backed savings instrument introduced in 2004. It primarily aims to offer retirees a safe, stable, and regular source of income, which is crucial after the cessation of a regular salary. This scheme is available at post offices and designated nationalized banks across India.
Key Features of SCSS
1. Eligibility
Individuals aged 60 years or above can open an SCSS account.
Early retirees between 55-60 years, who have opted for voluntary retirement or superannuation, can also invest, provided they open the account within one month of receiving retirement benefits.
2. Investment Amount
The minimum investment required is ₹1,000.
The maximum permissible investment is ₹30 lakhs (from April 2023). Previously, the limit was ₹15 lakhs. This increased limit allows senior citizens to park a more significant portion of their retirement corpus in this safe instrument.
3. Tenure of the Scheme
The SCSS has a tenure of 5 years, which can be further extended by an additional 3 years upon maturity.
During the extension, you continue to earn interest at the prevailing rate at the time of extension.
4. Interest Rates
SCSS offers an attractive interest rate, which is reviewed and decided by the government quarterly. As of 2023, the interest rate stands at 8.2% per annum, which is higher than most fixed deposits or savings accounts.
The interest is compounded quarterly and paid out every quarter, providing a regular source of income for senior citizens.
5. Premature Withdrawal
Premature withdrawals are allowed but come with penalties. If you withdraw after one year but before two years, a 1.5% penalty is levied. After two years, the penalty reduces to 1%.
6. Nomination Facility
SCSS allows you to nominate a beneficiary at the time of opening the account or afterward. This ensures that in case of the unfortunate demise of the account holder, the investment is passed on smoothly to the nominee.
7. Tax Benefits
The investment in SCSS is eligible for a tax deduction of up to ₹1.5 lakh under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
However, the interest earned is taxable, and TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) is applicable if the interest exceeds ₹50,000 in a financial year.
Why Should You Invest in SCSS?
1. Safety and Reliability
One of the primary concerns for any retiree is the safety of their investment. The SCSS is a government-backed scheme, which makes it one of the safest investment options available for senior citizens. Unlike market-linked instruments, SCSS offers guaranteed returns, insulating investors from market volatility. For risk-averse retirees, this feature is particularly attractive.
2. Regular Income
Post-retirement, most individuals lose the steady monthly income that their salary provided. SCSS is designed to address this issue by offering quarterly interest payouts. These payouts can act as a regular source of income to cover daily expenses, medical bills, or leisure activities.
3. Attractive Interest Rates
With an interest rate of 8.2% per annum (as of 2023), SCSS offers a far superior return compared to regular savings accounts or even many fixed deposits. While bank interest rates fluctuate, SCSS offers a more consistent and attractive return, making it an ideal choice for those looking for secure yet rewarding investment options.
4. Tax Benefits
Investing in SCSS allows you to claim deductions under Section 80C up to ₹1.5 lakh. For senior citizens looking to optimize their tax outgo while securing their future, this dual benefit of safety and tax saving is hard to ignore.
5. Flexibility of Withdrawal
Life after retirement can sometimes bring unexpected expenses, be it medical emergencies or personal needs. The SCSS allows for premature withdrawals with nominal penalties, offering flexibility if you need funds before the completion of the scheme’s tenure.
6. Option to Extend
While the initial tenure of the SCSS is five years, the scheme can be extended for an additional three years. This flexibility ensures that if you do not require the funds immediately, you can continue earning interest on your investment for a longer period without any hassles.
7. Higher Investment Cap
With the government increasing the maximum investment limit to ₹30 lakhs, senior citizens now have the opportunity to invest a larger portion of their savings into this secure instrument. This is particularly beneficial for those with substantial retirement funds who are looking for a safe place to invest.
SCSS vs. Other Investment Options
When compared to other investment avenues such as fixed deposits (FDs), mutual funds, and bonds, the SCSS stands out for its balance between safety, returns, and tax benefits.
Fixed Deposits: While FDs are relatively safe, they generally offer lower interest rates compared to SCSS. Additionally, FD interest is taxable, and the regular payouts are often not as frequent.
Mutual Funds: These are market-linked instruments, making them more volatile. While they offer potentially higher returns, they also come with higher risks, which may not be suitable for senior citizens seeking stable and predictable income.
Bonds: Government bonds are safe but often have lower yields compared to SCSS. Also, bonds usually don’t offer regular payouts like SCSS, which can be a disadvantage for those who rely on periodic income.
How to Open an SCSS Account?
Opening an SCSS account is a simple and straightforward process. Here’s how you can do it:
Visit a Post Office or Designated Bank: You can open the SCSS account at any post office or a designated bank like the State Bank of India (SBI), ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, etc.
Fill in the Application Form: You will need to fill out the SCSS application form available at the bank or post office.
Submit Required Documents:
Age proof (Aadhaar Card, Passport, Voter ID, etc.)
Proof of retirement (if applicable)
PAN card
Photographs
Deposit the Investment: Deposit the amount you wish to invest (minimum ₹1,000 and up to ₹30 lakhs). The deposit can be made through cash or cheque.
Nomination: Provide the details of the nominee at the time of account opening.
Once your account is opened, you will start earning interest from the date of the deposit, and the first interest payout will occur after the end of the first quarter.
Conclusion
The Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS) is an excellent investment option for retirees looking for a safe, stable, and profitable way to grow their savings. With its government backing, attractive interest rates, and regular payouts, SCSS provides financial security during the post-retirement phase. Coupled with tax benefits under Section 80C, SCSS stands as one of the most efficient savings instruments for senior citizens.
For individuals nearing or already in their retirement, investing in SCSS is a smart choice that balances safety, income generation, and tax savings. With the ever-rising cost of living and healthcare expenses, securing a stable source of income becomes essential, and SCSS can be a cornerstone in that financial strategy.
#SeniorCitizenSavingsScheme#SCSS#RetirementPlanning#SafeInvestments#FinancialSecurity#RetirementFunds#SeniorCitizenFinance#InvestInYourFuture#FinancialPlanning#SecureInvestments
0 notes
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to Income Tax in India (2024): Everything You Need to Know
Introduction
Income tax is a pivotal component of India’s financial system, serving as a primary revenue source for the government. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of income tax in India for the financial year 2023-24, including its structure, rates, filing procedures, and benefits.
Understanding Income Tax on Income in India
What is Income Tax?
Income tax is a direct tax imposed by the government on the income earned by individuals and businesses. The tax is calculated based on the income slab rates determined by the Tax Department of India. It helps fund various public services, infrastructure projects, and government schemes aimed at the welfare of the citizens.
Who is Liable to Pay Tax?
Individuals: Including salaried employees, self-employed professionals, and freelancers.
Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs): A family consisting of all persons lineally descended from a common ancestor.
Companies: Both domestic and foreign companies operating in India.
Firms: Partnerships and LLPs.
Associations of Persons (AOP) and Body of Individuals (BOI).
Trusts: Including charitable and religious trusts.
How to Calculate Income Tax?
Determine Gross Total Income: Sum of income from all sources – salary, house property, business or profession, capital gains, and other sources.
Claim Deductions and Exemptions: Subtract eligible deductions under various sections such as 80C, 80D, 80G, etc.
Compute Taxable Income: Gross Total Income – Deductions
Apply Relevant Tax Slabs: Apply the applicable tax rates based on the income slab.
Account for Tax Rebates: Apply rebates, if any, such as under Section 87A.
Add Surcharge and Cess: Include any applicable surcharge and 4% health and education cess.
Deductions and Exemptions Income Levy.
Deductions and exemptions play a crucial role in reducing the tax liability of an individual. Some of the common deductions available under the Tax Act are:
Section 80C
Investments in instruments like Public Provident Fund (PPF), Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF), National Savings Certificate (NSC), and life insurance premiums qualify for deductions up to ₹1.5 lakh.
Section 80D
Premiums paid for health insurance for self, spouse, children, and parents can be claimed as deductions. The limit is ₹25,000, which increases to ₹50,000 for senior citizens.
Section 24(b)
Interest on home loan for a self-occupied property can be claimed up to ₹2 lakh.
Section 80E
Interest on an education loan for higher education is deductible without any limit.
Section 80G
Donations to specified relief funds and charitable institutions qualify for deductions.
Filing Tax Returns (ITR)
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing ITR
Gather Documents: Start by collecting necessary documents like Form 16, bank statements, investment proofs, and TDS certificates.
Choose the Correct ITR Form: Determine the appropriate ITR form based on your income sources.
Log in to the Income Tax Portal: Access the e-filing portal of the Income Tax Department.
Fill in the Details: Enter all required details in the selected ITR form.
Verify the Details: Ensure the information entered is accurate by cross-checking it.
Submit and E-Verify: Finally, submit the ITR and complete the e-verification process using methods like Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or EVC.
Due Dates for Filing ITR
Individuals and HUFs: July 31 of the assessment year.
Businesses requiring audit: October 31 of the assessment year.
Revised or belated returns: December 31 of the assessment year.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Late Filing Fee: Up to ₹10,000 for filing returns after the due date.
Interest on Late Payment: Interest under Sections 234A, 234B, and 234C for late payment of taxes.
Penalty for Underreporting Income: 50% to 200% of the tax due on underreported income.
Benefits of Filing Tax Returns
1. Loan Approvals: ITR receipts are essential documents for loan approvals. 2. Visa Applications: Many consulate offices require ITR copies for visa processing. 3. Claiming Refunds: Filing on time enables taxpayers to claim refunds for any excess tax paid. 4. Proof of Income: Serving as a valid proof of income, ITR is useful for various financial transactions. To Read more - https://blog.poweroffactorial.in/income-tax/
1 note
·
View note
Text
Post office schemes interest rate 2023: Which small savings scheme offers highest interest rate - The Economic Times
The government’s small savings scheme offer various deposit schemes catering to different individuals such as girl kid (Sukanya Samriddhi), women investor (Mahila Samman), senior citizens (SCSS), long term investors (PPF, KYC, NSC) and short term investors (Time deposits, RD). Small savings scheme interest rates are revised every quarter by the government and interest rates vary accordingly. For…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
পোস্ট অফিস সিনিয়র সিটিজেন স্কিম।Post Office Senior Citizen Savings Scheme 2023 - TAKAPOYSANEWS
0 notes
Text
Explore the Costs of Charging & Running an Electric Scooter

Sales of electric two-wheelers in India skyrocketed[1] from 327,900 to 8,46,976 units in 2022 – 2023 — an increase of over 250%!
Electric scooters, sometimes also known as electric bikes, have become the go-to choice for delivery personnel, collegians, senior citizens, and savvy office-goers to zoom through busy streets. These zero-pollution two-wheelers have transformed the way people travel, allowing them to effortlessly navigate traffic while slashing fuel expenses.
Here’s what electric bike ownership costs really look like!
Initial Investment
The price range for these eco-friendly two-wheelers starts at around Rs 50,000 and can go up to Rs 1.3 lakh for more advanced models. In comparison, popular petrol scooters in India cost between Rs 65,000 and Rs 1.3 lakh. So, when it comes to prices, electric scooters are quite competitive.
Electric scooters are an even more appealing option because the Indian government offers a fantastic incentive for purchasing them: Phase II of the FAME India Scheme provides a 15% subsidy for electric two-wheelers across the country. Several states are offering additional incentives[1] in the form of road tax exemptions, motor vehicle tax exemptions, and registration fee waivers.
Calculating Electric Bike Charging Expenses

The cost of charging an electric scooter varies across India, since electricity costs are different in every state. Here’s how to calculate an electric scooter’s cost per charge:
Battery’s kWh x Electric Tariff per kWh
For example, in Uttar Pradesh, which boasts especially high EV adoption rates, multiplying the battery's capacity (let's say 1.50 kWh) by the electricity tariff rate (Rs 7[1] ) results in an electric scooter charge cost of just Rs 10.5. With a range of 80 KM/C, that means you can zoom across 80 thrilling kilometers for a mere Rs 10.5!
Remember, a powerful scooter battery allows more mileage per charge, translating to lower charging expenses in the long run.
Electric Bike Maintenance Costs
Electric scooters are less expensive to maintain than their traditional counterparts, given that they have fewer moving parts[2] that could need repair. Just keep up with routine checkups, cleaning, and lubrication, and your suspension, brakes, and wheels will effortlessly maintain their efficiency. Furthermore, most electric scooter manufacturers in India offer affordable subscription plans for regular servicing. Brake pads, which should only be changed up to twice a year, cost a mere Rs 200 – 400. In total, annual electric scooter maintenance generally costs Rs 1000 – 3000.
There is, however, one substantial hidden cost: the battery, which needs to be replaced every 5 years. As of 2023, replacement batteries cost around Rs 30,000 – 40,000. Fortunately, battery prices are expected to plummet in the near future, and this expense will cease to be a major concern, leaving owners to enjoy the freedom of minimal maintenance costs and savings with electric scooters.
Zooming Forward
Electric scooters have become the top choice in towns and cities amongst people of all demographics, revolutionizing commuting with their environmental and financial advantages. Not only are electric scooters priced competitively in the Indian market, but the Indian government's FAME-II scheme provides a lucrative 15% subsidy, making them even more affordable. Charging costs vary across states, but are unlikely to be high. With lower maintenance expenses and fuel costs than their traditional alternatives, and a drop in battery prices on the horizon, electric scooters are proving to be an extremely attractive option.
0 notes
Text
Union Budget 2023–24 Highlights & Complete Budget Analysis
Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Budget 2023-24 on 1st February at 11 AM. This is the first budget in “Amrit Kaal” as India is going to turn 100 years old in 25 years and the last full-fledged budget before the elections next year.
The finance minister said that our economy is on the right track and heading toward a bright future. Adopting seven priorities to guide India through the “Amrit Kaal”, including inclusive development, reaching the last mile, infrastructure and investment, unleashing the potential, green growth, youth power, and financial sector.

INCOME TAX CHANGES
Govt. has tried to boost consumption through the middle class with a change in the tax slabs.
There are a few incentives to be offered to shift to the new tax regime. The old regime however remains acceptable.
There’ll be no Income Tax for salaries up to 7 LPA in the new tax regime as the rebate limit has increased from Rs 5 LPA to 7 LPA.
Individuals earning more than Rs 5 crore PA, pay a surcharge of 25% under the new regime as opposed to 37% under the old regime.
The tax collected at source (TCS) of 20% will be applied on foreign remittances to tax foreign holidays and expenses and realty investments abroad. This will exclude payments for education and health.
The idea behind slashing taxes is to increase the disposable income in the hands of the consumer, raise demand and boost consumption. The focus of the old regime was tax-saving instruments. The new generation is looking at different investment options, not necessarily tax saving.
WHAT GETS CHEAPER AND WHAT GETS COSTLIER
Hattrick of boosting Capital Expenditure, Slashing Taxes, and reducing Fiscal Deficit will benefit India’s economy a lot. The Capital Expenditure (CapEx) is going to raise by 33% to ₹10 lakh crore for the next fiscal year starting from 1st April, which is 3.3% of the country’s economic output. But, on an individual level, we all wait for the list of items that get costlier and cheaper.
Customs duty cut on components for TVs, Mobile phones to boost domestic production. Also on machinery and components for the manufacture of Lithium-ion batteries in the use of Electric Vehicles
Customs duty increase on Kitchen chimneys, Electric Vehicles, imitation jewelry, and precious metals. Cigarettes to become dearer.

OTHER SCHEMES AND BENEFITS
Marginalized sections Including Farmers, Women, and Sr. Citizens will be benefitted with the senior Citizen Deposit Limit increased to 30 lakhs from 15 lakhs and with a lock-in period of 5 years.
The Monthly Income Scheme limit was enhanced to Rs 9 lakhs from Rs. 4.5 Lakhs for individual accounts and 15 lakhs from 9 lakhs for joint accounts.
Mahila Samman Savings Certificate will be launched in March 2025. Max. deposit of Rs. 2 Lakh at a fixed interest rate of 7.5%, eligible for partial withdrawal.
The Agri credit is increased by 20 lakh crore and an Agriculture Accelerator Fund will be set up to encourage agri-startups by young entrepreneurs. They will improve mobility, facilitate trade, lead to job creation, and boost overall economic productivity. Capital investment outlay increased by 33 percent to ₹10 lakh crore, which is 3.3% of GDP.
The Green Energy Transition will get an outlay of ₹35,000 crores and a Green Credit Programme will be notified under the Environment Protection Act,1986.
“This will incentivize environmentally sustainable and responsive actions by companies, individuals, and local bodies, and help mobilize additional resources for such activities,”
Nirmala Sitharaman

0 notes
Text
10 Income Tax Rules Have Changed For Taxpayers: Check Details
Even though the new fiscal year 2023-24 began on April 1, the Income Tax Changes Proposed by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in Budget 2023 were effective on the same day. The following are the new rules:
1) The New Income Tax Regime Is Now the Default Regime
On April 1, 2023, the new income tax system became the default tax regime. Tax assessors will still be able to use the former regime. For salaried persons and retirees, the standard deduction under the new system for taxable income above Rs 15.5 lakh is Rs 52,500.

2) Standard Deductibility
The standard deduction of Rs 50,000, which was available to employees under the previous tax regime, has not altered. According to the finance minister, the standard deduction would be extended to the new pension tax scheme.
3) The Tax Rebate limit has been increased to Rs 7 lakh.
Those with earnings under Rs 7 lakh do not need to make any investments to qualify for exemptions, according to a hike in the tax rebate threshold from Rs 5 to Rs 7 lakh. The income of such people is fully tax-free, regardless of how many investments they make.
4) LTA
Up to a specific amount, non-government employees are free from the leave encashment obligation. The maximum has been raised to Rs 25 lakh.
5) These Mutual Funds do not provide LTCG Tax benefits.
From today, investments in debt mutual funds will be subject to short-term capital gains tax. Investors would lose the long-term financial benefits that had made such investments appealing in the first place.
6) Marketable Debentures
Investments in Market Linked Debentures (MLDs) will henceforth be deemed short-term financial assets as of today. With this, grandfathering of prior investments has ended, which has had a modest negative impact on the mutual fund industry.
7) Policies of Life Insurance
The earnings from life insurance premiums in excess of Rs 5 lakh will be taxable beginning with the commencement of the new fiscal year, or 1 April 2023. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman indicated during the presentation of the Budget 2023 that the ULIP will be exempt from the new income tax regulations.
8) Benefits to Senior Citizens
The maximum deposit limit under the Senior Citizen Savings Plan will be increased from Rs 15 lakh to Rs 30 lakh. The maximum deposit limit for the monthly income programme would increase from 4.5 lakh to 9 lakh for single accounts and from 7.5 lakh to 15 lakh for joint accounts.
9) Conversion of physical gold to e-gold receipt is exempt from capital gains tax:
According to Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, there would be no capital gains tax if actual gold is converted to an Electronic Gold Receipt (EGR) or vice versa. This will go into effect on April 1, 2023.
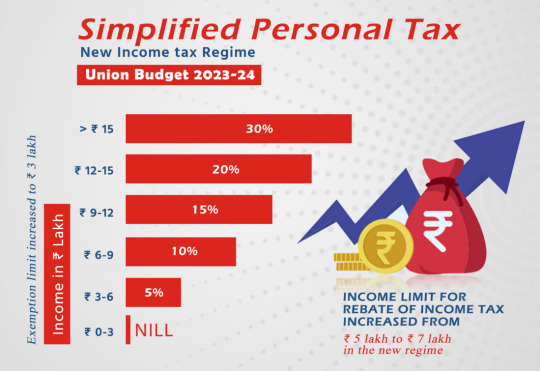
10) Changes to Income Tax Slabs
0-3 lakh - 0
3-6 lakh - 5%
6-9 lakh- 10%
9-12 lakh - 15%
12-15 lakh - 20% 30% for amounts greater than 15 lakhs.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
A Guide on Take Profit Orders in Stock Market Trading 2023
A Guide on Take Profit Orders in Stock Market Trading: Maximize Your Profits. Discover how take profit orders can help you maximize your profits in stock market trading. Learn the strategies and tips to use this powerful tool effectively.When it comes to stock market trading, one of the key strategies for maximizing profits is to use take profit orders effectively. A Guide on Take Profit Orders…

View On WordPress
#10 Best Volatility Trading Strategies 2023#15 Biggest Mistakes of Stock Market Investors#5 Reasons Why the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme is a Smart Investment#A Guide on Take Profit Orders in Stock Market Trading: Maximize Your Profits
0 notes
Text
Tax saving tips 2023
Invest in tax-saving instruments: You can claim tax deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961 by investing in tax-saving instruments such as Public Provident Fund (PPF), Equity-Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS), National Pension Scheme (NPS), and tax-saving fixed deposits.
Claim home loan interest: If you have taken a home loan, you can claim deductions on the interest paid under Section 24(b) of the Income Tax Act. You can claim up to INR 2 lakh for a self-occupied property and the entire interest paid for a let-out property.
Medical expenses: You can claim deductions under Section 80D for medical expenses incurred for yourself, your spouse, dependent children, and parents. The deduction limit is up to INR 25,000 for yourself, spouse, and dependent children and an additional INR 25,000 for your parents. You can also claim an additional deduction of INR 5,000 if any of the insured persons are senior citizens.
House Rent Allowance (HRA): If you are a salaried individual and receive HRA from your employer, you can claim exemptions on the rent paid under Section 10(13A) of the Income Tax Act. The exemption amount is the minimum of the following: actual HRA received, 50% of basic salary (if living in a metro city), or 40% of basic salary (if living in a non-metro city).
Donations: You can claim deductions on donations made to certain charitable institutions under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act. The deduction amount varies based on the type of donation and the organization.
Education loan interest: You can claim deductions on the interest paid on education loans under Section 80E of the Income Tax Act. The loan should have been taken for higher education purposes for you, your spouse, or children.
Renting out property: If you have a property that you rent out, you can claim deductions on expenses incurred for the property such as property taxes, repairs, and maintenance. You can also claim depreciation on the property.
Remember to keep all the necessary documents such as receipts, investment statements, and loan statements, etc., for tax filing purposes.

0 notes
Text
Senior Citizen Saving Scheme 2023: सीनियर सिटीजन सेविंग स्कीम जाने
#senior #citizen #saving #scheme
#seniorcitizensavingscheme #sarkariyojana
Senior Citizen Saving Scheme Application Form 2023: भारत सरकार के द्वारा सीनियर सिटीजन सेविंग स्कीम बुजुर्गों के लिए आरंभ किया गया है यह एक बचत योजना है।
Senior Citizen Saving Scheme
इस स्कीम के अंतर्गत सभी बुजुर्गों के लिए सबसे अच्छी बात इस योजना के अंतर्गत माना जाता है कि इसमें सरकार के द्वारा सभी बुजुर्गों में सबसे ज्यादा बुजुर्गों को ब्याज देती है और वह सबसे ज्यादा टैक्स छुट्टी भी दिया जाता है सीनियर सिटीजन सेविंग स्कीम के अंतर्गत सभी सरकारी योजनाएं होने के कारण सभी नागरिकों को पैसा डूबने का खतरा भी बना रहता है और इस योजना को वरिष्ठ नागरिक बचत योजना के नाम से भी जाना जाता है।
1 फरवरी 2023 को पेश किए गए केंद्रीय बजट में सरकार ने सीनियर सिटीजन सेविंग स्कीम में जमा की अधिकतम सीमा राशि को बढ़ाकर ₹300000 कर दिया है अगर आप भी बुजुर्ग नागरिक है और अपना पैसा निवेश करने की सोच कर रहे हैं तो सीनियर सिटीजन सेविंग स्कीम के अंतर्गत आप पैसे निवेश कर काफी ज्यादा लाभ उठा सकते हैं आज हम आपको अपनी आर्टिकल के माध्यम से Senior Citizen Saving Scheme के अंतर्गत आप भी लाभ उठाना चाहते हैं तो आप कृपया कर हमारे इस आर्टिकल को अंत तक जरूर पढ़ें।
Read More: https://sarkariyojanain.com/senior-citizen-saving-scheme/
0 notes
Text
Don't want to pay Income Tax for the financial year 2022-23?
I hope the financial year (FY) 2022–2023 went well. It is about to end. But let me know one thing whether it was good in the case of your income-tax planning. NO? Most of us are thinking about our income-tax planning till the last date of the financial year and end up paying taxes on our hard-earned money, which we can save. Are you an employee? Have you submitted your investment proofs to your employer? You must know that your employer will deduct higher TDS on Salary income if you do not submit your investment proofs.

Although the deadline for such submissions varies, most companies require that you submit proof by March 15.
Even after investing under 80C and other savings, it is disheartening to continue paying high taxes. But when you file your income tax returns, the Income Tax Department will still refund you. Isn't that great? Let's look at the exemptions and deductions you can still use even though the deadline for submitting your taxes documentation to your employer has passed. Don't worry; the deductions and exemptions also apply to non-salaried people. Following is a list of tax laws that could legally lower your taxes for the current financial year:
1: Eligible deductions under Section 80C, in which you can claim deductions upto Rs.150000-
· Life Insurance
Securing your family with a term insurance plan is one way to ensure your family's financial future after you pass away. But did you know that the premiums you pay for these life insurance policies also help you save money on taxes? Yes, life insurance premiums are available as a deduction under section 80C.
· Public Provident Fund (PPF)
Section 80C allows for tax deductions on yearly PPF contributions. PPF is a Government-backed scheme that provides you with adequate returns. Under this scheme, you can invest a minimum of ₹500 and a maximum of ₹1,50,000 every year. It has a lock-in period of 15 years.
· Tax Saving Fixed Deposit
Bank fixed deposits have a 5-year lock-in period during which early withdrawal is not permitted, but they are still eligible for Section 80C deductions. The Interest on a five-year fixed deposit is taxable and not eligible for tax breaks. Section 80C allows for a tax deduction on investments of up to 1.5 lakhs. It can be opened by Indian residents who can benefit from interest rates ranging from 5.5% to 7.75%, depending on the bank. The minimum investment amount for FDs is ₹1,000, and all interest income from FD investments is subject to taxation.
· Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS)
This programme is only intended for elderly adults, those at least 60 years old or who have chosen to retire at age 55.
A minimum deposit of Rs. 100 is required to purchase a National Savings Certificate (NSC). An NSC's investment tenure is five years. You might demand the entire sum be returned to their account upon maturity. If the money is unclaimed, it is all reinvested into the plan. You can earn 7.4% interest.
· Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana
Our sole objective of this tax-saving strategy is to promote the development of young girls. This savings programme is for a young girl who qualifies for tax benefits. The girl's parents or legal guardians are permitted to open an account under this scheme until ten. When there are twins, the programme is expanded to include a third child and is open to two girls' kids. The amount needs to be deposited over 15 years, and it matures in 21 years. The annual interest rate is 7.60%. A minimum investment of 250 rupees and a maximum investment of 15 lakhs are permitted. The plan has a 21-year maturation time.
2: Section 80D: Medical Insurance Premium
Section 80D allows claiming deductions from the gross Taxable Income for the payment of medical insurance premiums. You are permitted to deduct up to Rs. 25,000 annually if you pay for medical purposes for self, spouse or children. The maximum deduction for medical insurance premiums for senior citizens is Rs. 50,000. Also, if you spend the money on behalf of your parents, then you can get a maximum deduction of up to Rs. 25,000.
3: Section 80G: Charitable Donations
You can claim 50% to 100% of the total amount donated to the charitable trust. To avail deduction, you need to preserve the receipt from the organisation after the financial year. Ensure that whenever you donate money to charities or trusts, check if they are registered under Section 12A post, which they qualify for the 80G certificate. Any cash donations exceeding Rs 2,000 will not be allowed as a deduction, and donations over Rs.2000 should be made via any mode other than cash. A tax deduction of up to Rs. 1,50,000 may be claimed for contributions paid to the PF account under section 80C of the income tax act.
4: Section 80GG: Rent Contributed to Housing
Under section 80GG, people who are renting a home can make deductions. However, those who are not salaried and those employees who do not receive a House Rent Allowance from their employers are eligible for this tax deduction.
5: Health Insurance under Section 80D
Nowadays, with the cost of medical treatment growing, everyone must get health insurance. Because it helps you pay for your medical bills in an emergency, you can save up to Rs. 15,000–20,000 under section 80D if you pay premiums for your health insurance.
6: Education Loans under Section 80E.
The Interest paid on student loans for higher education is still tax-free for the borrower, the spouse, and the children under Section 80E. Not the principal amount, but the amount of Interest paid, may be deducted by an individual.
7: Home Loans under Section 80EE
Home loans are one of the best strategies to lower taxes in India. Under the current arrangement, home loans have assisted in reducing taxable income. First-time house buyers may deduct up to Rs. 50,000 off the Interest on a home loan throughout a fiscal year by using Section 80EE.
8: Section 80TTA: Interest on Saving Accounts.
Under Section 80TTA, Interest accrued on savings accounts is deductible. However, any interest earned on a savings account over Rs. 10,000 will be considered taxable income.
CONCLUSION:
So, in the end, persons who have invested, kindly submit your proofs timely and those who haven't, make your investments before the end of Feb for your convenience. Still, if you are an employee and missed your deadline to submit your proofs to your employer, then you can claim in your income tax return for FY 22-23 and take the refund.
Source:https://www.manishanilgupta.com/blog-details/dont-want-to-pay-income-tax-for-the-financial-year-2022-23
0 notes