#Sacroiliac Joint Fusion Treatment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#Neuropathic Pain Chicago#Injections & Blocks Specialist#Neuropathic Pain Treatments in Chicago#Radiofrequency Ablation Specialist#Kyphoplasty Specialist#kyphoplasty Surgeons Near Me#Spinal Cord Stimulation Specialist#Sacrix SI Joint Fusion Treatment#Vertiflex Superion Specialist#Aurora ZIP Procedure#ZIP Procedure for Chronic Back Pain#ZIP Spine Procedure#ZIP Procedure for Spinal Stenosis#Fibromyalgia Specialist Chicago#Spinal Compression Fracture Treatment Chicago#Spinal Cord Stimulation Therapy Chicago#Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Treatment Chicago#Vertiflex Superion Procedure#Motor Vehicle Injuries Treatments#Spinal Cord Pain Treatment Chicago#Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Surgery Chicago#Nerve Block Injections Specialists#Dorsal Ganglion Root Stimulation#Pain Specialist Chicago#DRG Stimulation Procedure#Chronic Pain Treatment in Chicago#DRG Stimulator Surgery#Pain Management Specialists Chicago#Dorsal Root Ganglion Stimulation Therapy#Sacroiliac Joint Fusion Treatment
0 notes
Text
The Pathophysiology Of Spondylitis
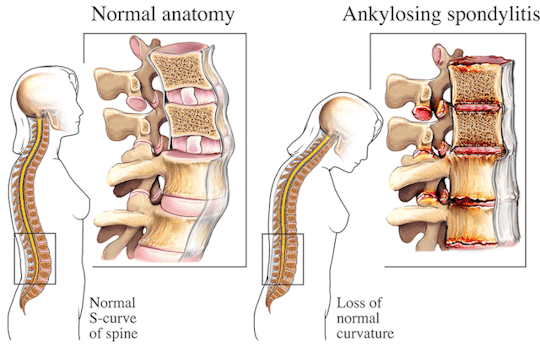
Spondylitis is a comprehensive term used to describe a group of chronic inflammatory diseases that primarily affect the joints of the spine and the sacroiliac region, which includes the pelvis and lower spine. These conditions are characterized by arthritis-like symptoms and can lead to significant discomfort, reduced mobility, and other systemic complications. This detailed exploration will indulge into the nature of spondylitis, how it differs from the related condition known as spondylosis, the various types of spondylitis, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and complementary therapies.
What is Spondylitis?
Spondylitis involves inflammation of the joints, tendons, and ligaments within the spine and sacroiliac region. Tendons are connective tissues that attach muscles to bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones. This inflammation can result in the fusion of bones (ankylosis) and the formation of new bone, leading to stiffness and reduced flexibility in the spine. In severe cases, excessive bone growth can cause significant curvature of the spine, known as kyphosis.
Spondylitis vs. Spondylosis
While both spondylitis and spondylosis cause pain in the hip and back, they are distinct conditions with different etiologies and characteristics.
Spondylitis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation, bone fusion, and excessive bone formation. This condition typically develops in teenagers and young adults and can affect multiple organs and systems within the body.
Spondylosis, on the other hand, is a degenerative condition associated with aging and the natural wear and tear of the spine. It involves the degeneration of spinal joints and discs, often accompanied by the formation of bone spurs (osteophytes). Spondylosis primarily affects older individuals, with more than 85% of people over the age of 60 experiencing this condition.
Types of Spondylitis
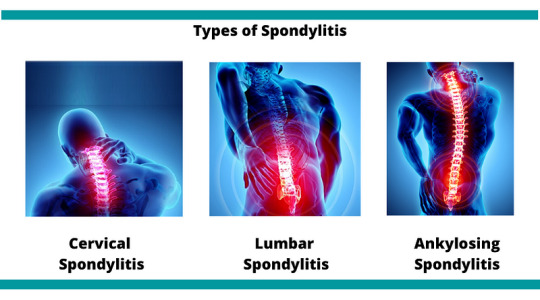
Medical professionals categorize spondylitis using two primary classification systems: the traditional system and the newer system. The traditional system recognizes six specific types of spondylitis, whereas the newer system categorizes spondylitis into two broad types based on the affected body region.
Traditional Spondylitis Classifications:
a) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Symptoms: Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine, causing symptoms such as fatigue, chronic back pain, stiffness, and inflammation in various areas of the body, including joints and tendons. Over time, the vertebrae may fuse, leading to reduced mobility and flexibility.
Causes: The exact cause of AS is unknown, but a strong genetic association exists with the HLA-B27 gene. Approximately 90% of individuals with AS carry this gene, although not all carriers develop the disease.
b) Reactive Arthritis
Symptoms: Reactive arthritis typically presents with a triad of symptoms including arthritis (swelling and pain in joints), conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eyes with a sticky discharge), and urethritis (genital and bladder inflammation with painful urination). However, not all patients exhibit all three symptoms.
Causes: often follows a gastrointestinal infection or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). The immune system overreacts to the initial infection, leading to inflammation and joint pain. The HLA-B27 gene is also strongly linked to ReA, with 30–50% of affected individuals carrying this gene.
c) Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Symptoms: Psoriatic arthritis is associated with the inflammatory skin condition psoriasis. Symptoms include dactylitis (swelling in toes and fingers), changes in nails (such as pitting), eye pain, joint pain, reduced range of motion, and fatigue. PsA typically affects people aged 30–50.
Causes: PsA often follows psoriasis, but it can also develop in individuals without skin symptoms. There is a genetic predisposition to PsA, with at least 10% of the population inheriting genes that increase susceptibility to psoriasis and PsA.
d) Enteropathic Arthritis (EnA)
Symptoms
Enteropathic arthritis is linked to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and joint swelling and pain.
Causes
The precise cause of EnA is unclear, but it is associated with chronic inflammation in the bowel. This inflammation may allow bacteria to penetrate the bowel wall, triggering an immune response that leads to joint inflammation. The HLA-B27 gene is also linked to EnA.
d) Juvenile Spondyloarthritis (JSpA)
Symptoms
Juvenile spondyloarthritis begins in individuals aged 16 or younger and typically affects the leg joints. Symptoms include joint pain, tenderness, and bowel inflammation.
Causes
Similar to adult spondylitis, JSpA is often associated with the HLA-B27 gene. The exact cause remains unknown, but genetic and environmental factors likely play a role.
e)Undifferentiated Spondyloarthritis (USpA)
Symptoms
USpA is characterized by a variety of symptoms that do not fit neatly into a specific rheumatoid disorder. Symptoms may include persistent lower back pain, joint pain in small and large joints, heel pain, swelling in hands and feet, general stiffness, eye inflammation, rash, urinary tract symptoms, and intestinal inflammation.
Causes
The causes of USpA are diverse and not fully understood. It encompasses a range of symptoms that do not meet the criteria for other specific types of spondylitis.
Newer Spondylitis Categorizations
Peripheral Spondyloarthritis (pSpA)
Peripheral spondyloarthritis affects joints and tendons outside the spine and sacroiliac joints, such as the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, ankles, and feet. It includes forms of spondylitis such as reactive arthritis, enteropathic arthritis, and undifferentiated arthritis.
2. Axial Spondyloarthritis (AxSpA)
Axial spondyloarthritis involves inflammation and pain in the pelvis and spine. This category covers a broad range of spondylitis types and includes individuals with and without sacroiliac joint fusion. AxSpA is further subdivided into non-radiographic AxSpA (without visible joint damage on X-rays) and radiographic AxSpA (visible joint damage).
Diagnosis
Diagnosing spondylitis involves abroad approach, combining physical examination, medical history, and various diagnostic tests. There is no single definitive test for spondylitis, making a comprehensive evaluation essential.
a) Physical Examination
During a physical examination, the doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and family history of autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and spondyloarthritis. The examination may include evaluating joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
b) Diagnostic Tests
Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify markers of inflammation, such as elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP). Testing for the presence of the HLA-B27 gene can also provide valuable information, although not all individuals with spondylitis carry this gene.
Imaging Tests: Imaging techniques are crucial for diagnosing spondylitis and assessing the extent of joint and bone damage.
X-rays: X-rays can reveal changes in the spine and sacroiliac joints, such as joint fusion and bone spurs.
MRI Scans: MRI scans provide detailed images of soft tissues and can detect early signs of inflammation and joint damage that may not be visible on X-rays.
Ultrasound Scans: Ultrasound scans can be used to assess inflammation in peripheral joints and tendons.
Genetic Testing: Testing for the HLA-B27 gene can support the diagnosis, particularly in cases where clinical symptoms and imaging findings are inconclusive.
Treatment
While there is no cure for spondylitis, various treatments can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and disease severity.
Medications
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs are commonly used to reduce inflammation and pain in spondylitis patients. Examples include ibuprofen and naproxen.
Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can be prescribed for short-term use to control severe inflammation and pain.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs, including methotrexate and sulfasalazine, can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression in some types of spondylitis.
Biologic Agents: Biologic agents, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (e.g., adalimumab, etanercept) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitors (e.g., secukinumab), target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage.
Analgesics: Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, may be used to manage pain when inflammation is not the primary issue.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing spondylitis by improving and maintaining spine flexibility and overall mobility. Techniques may include:
Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and alleviate pain.
Spinal Manipulation: Performed by a trained physical therapist or chiropractor, spinal manipulation can enhance mobility and reduce pain.
Exercises: Tailored exercise programs can help strengthen muscles, improve posture, and enhance flexibility. Stretching exercises are particularly beneficial for maintaining spine and joint flexibility.
Breathing Exercises: Breathing exercises are essential for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis, as the condition can affect chest expansion and respiratory function. These exercises help maintain normal lung function and prevent restrictive lung disease.
Surgery: Surgery is generally considered a last resort and is reserved for severe cases where conservative treatments have failed. Surgical options include:
Joint Replacement: For patients with severe joint damage, joint replacement surgery (e.g., hip or knee replacement) can restore function and relieve pain.
Spinal Surgery: In cases of severe spinal deformity or nerve compression, spinal surgery may be necessary to correct curvature and alleviate pressure on nerves.
Complementary Therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, complementary therapies can provide additional symptom relief and improve overall well-being. These therapies are often used alongside standard medical treatments.
Massage Therapy: Massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension, improve blood circulation, and alleviate pain and stiffness in the affected areas.
Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can help manage stress and reduce pain perception.
Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to improve flexibility, strength, and relaxation. Yoga can be particularly beneficial for maintaining spine flexibility and reducing pain.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the nervous system and promote natural pain relief and healing.
Cupping: Cupping is a traditional therapy that involves placing suction cups on the skin to improve blood flow and reduce muscle tension. It can be used to alleviate pain and stiffness in the back and other affected areas.
Summary
Spondylitis encompasses a range of chronic inflammatory diseases that affect the spine and sacroiliac region. It is characterized by autoimmune-driven inflammation, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and potential bone fusion. Spondylitis is distinct from spondylosis, a degenerative condition associated with aging. Medical professionals classify spondylitis into various types based on symptoms and affected body regions. Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, blood tests, imaging, and genetic testing. While there is no cure, treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and complementary therapies can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected by spondylitis. By understanding the nature of spondylitis and the available management strategies, individuals can better navigate their condition and maintain an active, fulfilling life.
Medical students and healthcare professionals need to stay informed about the latest advancements in diagnosing and treating spondylitis. Continuous education and expert guidance are crucial for managing these complex conditions. For additional support with challenging medical units, clinical studies, research projects, assignments, and exam preparation, Expert Academic Assignment Help offers professional resources and online classes. For personalized assistance, contact [email protected] Accessing expert guidance can significantly enhance your understanding and proficiency in medical education.
#medical students#assignment help#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#healthcare#student life#medical student#studyblr#case study#student#online writing#do my online class#essay writing#phd research#clinical research#research#phd thesis writing service#phdjourney#phd life#phdblr#studying#study blog#study motivation#studyspo#study aesthetic
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the spine but can also impact other joints such as the hips, shoulders, and knees. Over time, this condition can lead to pain, stiffness, and even spinal fusion, significantly affecting mobility and quality of life. Understanding AS is crucial for early diagnosis and management.
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a type of arthritis that causes inflammation in the spinal joints (vertebrae). The condition is progressive and can lead to the fusion of the spine, resulting in a hunched posture and limited movement.
This disease primarily affects the axial skeleton (spine and sacroiliac joints) but may also involve peripheral joints and organs like the eyes and heart. It is classified as a seronegative spondyloarthritis, meaning it does not present with the rheumatoid factor commonly found in other types of arthritis.
Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
AS symptoms vary from mild to severe and may worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
1. Spine and Back Symptoms
✔ Chronic Back Pain: Persistent pain, especially in the lower back and buttocks. ✔ Morning Stiffness: Symptoms are usually worse in the morning or after inactivity. ✔ Limited Mobility: Difficulty bending, twisting, or moving the spine.
2. Joint and Body-Wide Symptoms
✔ Hip, Shoulder, and Knee Pain: Inflammation in major joints. ✔ Fatigue: Persistent tiredness due to inflammation. ✔ Eye Inflammation (Uveitis): Red, painful, and sensitive eyes. ✔ Breathing Issues: If ribs become affected, deep breathing may become painful.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Ankylosing Spondylitis remains unknown, but genetics play a significant role.
🔹 HLA-B27 Gene: People with this gene have a higher risk of developing AS. 🔹 Gender: AS is more common in men than women. 🔹 Age: Symptoms typically appear between 15 to 45 years. 🔹 Family History: A family history of AS increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
How is Ankylosing Spondylitis Diagnosed?
Early diagnosis is key to managing AS effectively. Doctors use the following methods to confirm the condition:
🔸 Physical Examination: Checking spinal flexibility and pain points. 🔸 Blood Tests: Checking for inflammation markers (CRP, ESR) and HLA-B27 gene. 🔸 X-rays & MRI: Imaging to detect joint damage or inflammation. 🔸 Schober’s Test: Measures the flexibility of the lower back.
Treatment Options
There is no cure for Ankylosing Spondylitis, but early treatment can help reduce pain, prevent complications, and maintain mobility.
1. Medications
💊 NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Naproxen): Reduce pain and inflammation. 💊 Biologic Drugs (TNF Inhibitors & IL-17 Inhibitors): Help slow disease progression. 💊 Corticosteroids: Short-term relief for severe flare-ups.
2. Physical Therapy & Exercise
🏋️ Stretching & Strengthening: Improves flexibility and reduces stiffness. 🏊 Swimming & Yoga: Beneficial for spine mobility. 🚶 Posture Training: Helps prevent spine fusion in a curved position.
3. Lifestyle Changes
🍎 Healthy Diet: Anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3-rich fish, nuts, and green vegetables. 🚭 Quit Smoking: Smoking worsens symptoms and reduces lung capacity. 💤 Proper Sleep Position: Maintaining a straight spine while sleeping is crucial.
4. Surgical Options (Rare Cases)
🔹 Joint Replacement Surgery: For severely damaged hip or knee joints. 🔹 Spinal Surgery: In cases of extreme spinal fusion or deformity.
Living with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Managing AS requires long-term commitment and care. Here are some tips for daily life:
✔ Stay active with low-impact exercises. ✔ Maintain good posture while sitting and standing. ✔ Use ergonomic furniture to support your spine. ✔ Take regular breaks when working at a desk. ✔ Join support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience persistent back pain, stiffness, or joint discomfort for more than 3 months, consult a rheumatologist. Early intervention can prevent serious complications and improve your long-term health.
Book a Consultation Today!
📍 Visit your nearest specialist for personalized guidance on Ankylosing Spondylitis management.
Address: office no, 203, 2nd floor, Synergy Clinic, Krishna Avenue, opp. D- mart, above Dominos, Veerbhadra Nagar, Baner, Pune, Maharashtra 411045
Website: https://drishanshevateortho.com
Mobile no. : 9405783493
Conclusion
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a chronic but manageable condition. With early diagnosis, proper treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with AS can lead active and fulfilling lives. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms, don’t ignore them—seek medical advice today!
0 notes
Text
Pain in Lower Right Side Back and Hip: Causes and Treatment at Dr. Pramod Kumar Orthopedic Clinic

Back and hip pain can significantly disrupt daily life, especially when located on the lower right side. Understanding the underlying causes and seeking effective treatment is essential for long-term relief. At Dr. Pramod Kumar’s Orthopedic Clinic, we specialize in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal issues to help you regain mobility and comfort.
Common Causes of Pain in the Lower Right Back and Hip
Muscle Strain
Overuse or sudden movements can cause strain in the muscles and tendons in your lower back and hip area.
Sciatica
Compression of the sciatic nerve can lead to sharp or radiating pain down the lower back, hip, and leg.
Arthritis
Conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can lead to stiffness, inflammation, and pain in the hip joint.
Herniated Disc
A slipped or bulging disc in the lower spine can put pressure on nearby nerves, causing localized pain in the lower back and hip.
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Inflammation or misalignment of the sacroiliac joint can result in pain in the lower back and hips.
Injury or Trauma
Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can cause fractures, dislocations, or soft tissue damage in the hip and lower back area.
Kidney Issues
Sometimes, pain in the lower back on the right side may originate from kidney stones or infections, necessitating a thorough evaluation.
Diagnosing Back and Hip Pain
At Dr. Pramod Kumar’s Orthopedic Clinic, we adopt a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, including:
Physical Examination: Assessing movement, posture, and pain points.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to detect structural abnormalities.
Laboratory Tests: Blood work to rule out infections or inflammatory conditions.
Effective Treatments for Back and Hip Pain
Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants can help manage pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy
Tailored exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
Injection Therapies
Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections to alleviate inflammation and provide targeted relief.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For severe cases, options like arthroscopy or nerve decompression are available.
Surgical Interventions
In rare cases, surgical treatments such as hip replacement or spinal fusion may be necessary.
Why Choose Dr. Pramod Kumar Orthopedic Clinic?
Dr. Pramod Kumar, a renowned orthopedic specialist in Hadapsar, offers personalized care for back and hip pain. With advanced diagnostic tools and state-of-the-art treatment options, we aim to address the root cause of your discomfort and ensure long-term recovery.
Take the First Step Towards Pain Relief
Don’t let lower right back and hip pain hold you back. Visit Dr. Pramod Kumar Orthopedic Clinic in Hadapsar for expert care and effective solutions. Schedule your appointment today and reclaim your active lifestyle.
#joint replacement in hadapsar#shoulder replacement surgeon in hadapsar#hip replacemnt surgeon in hadpsar#knee replacement surgeon in hadapsar
0 notes
Text
Understanding Sacroiliitis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options

Sacroiliitis is a painful condition characterized by inflammation of one or both sacroiliac joints, located where the lower spine connects to the pelvis. This condition can be challenging to diagnose as it often mimics other forms of lower back pain. Here, we delve into the key aspects of sacroiliitis, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What Causes Sacroiliitis?
Sacroiliitis can result from various factors that lead to joint inflammation. Common causes include:
Trauma or Injury: Direct impact from falls or accidents can inflame the sacroiliac joints.
Arthritis: Conditions such as osteoarthritis or ankylosing spondylitis can contribute to sacroiliitis.
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and the added stress on the pelvis during pregnancy can lead to joint inflammation.
Infection: Although rare, infections in the sacroiliac joint can result in inflammation.
Overuse: Repetitive stress from physical activities like running or heavy lifting may trigger sacroiliitis.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Sacroiliitis
Symptoms of sacroiliitis can vary and often overlap with other lower back or hip conditions. The most common signs include:
Lower back pain: Pain typically affects one or both sides of the lower back and can radiate to the buttocks or thighs.
Stiffness: Reduced mobility and stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity.
Pain worsening with activity: Activities like climbing stairs, standing for long periods, or running may intensify discomfort.
Tenderness: Sensitivity when pressure is applied to the lower back or buttocks.
How Is Sacroiliitis Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis of sacroiliitis involves a comprehensive evaluation that may include:
Medical history and physical exam: A healthcare provider will assess symptoms and perform physical tests to identify pain sources.
Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs can help detect inflammation or abnormalities in the sacroiliac joints.
Diagnostic injections: An anesthetic injection into the joint may be used to confirm sacroiliitis if pain relief follows the procedure.
Effective Treatment Options for Sacroiliitis
Managing sacroiliitis typically involves a combination of treatment strategies aimed at reducing pain and improving joint function:
Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and pain. In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be used.
Physical therapy: A targeted exercise regimen can enhance flexibility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and support joint stability.
Lifestyle modifications: Adjusting activities to avoid repetitive stress and incorporating rest periods can help manage symptoms.
Sacroiliac joint injections: Administering anesthetics or steroids directly into the joint can offer temporary pain relief.
Surgical intervention: In rare, severe cases, surgical fusion of the sacroiliac joint may be considered when conservative treatments are ineffective.
Preventing Sacroiliitis
While not all cases are preventable, you can reduce your risk by maintaining a healthy weight, practicing proper posture, and incorporating low-impact exercises to strengthen core muscles. Being mindful of body mechanics during activities and avoiding excessive strain can also help protect the sacroiliac joints.
Sacroiliitis can significantly impact quality of life, but with the right diagnosis and treatment plan, many individuals experience relief and improved joint function. If you suspect sacroiliitis, consult with a healthcare professional to explore the best management strategies tailored to your needs.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Sacroiliitis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options

Sacroiliitis is a painful condition characterized by inflammation of one or both sacroiliac joints, located where the lower spine connects to the pelvis. This condition can be challenging to diagnose as it often mimics other forms of lower back pain. Here, we delve into the key aspects of sacroiliitis, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What Causes Sacroiliitis?
Sacroiliitis can result from various factors that lead to joint inflammation. Common causes include:
Trauma or Injury: Direct impact from falls or accidents can inflame the sacroiliac joints.
Arthritis: Conditions such as osteoarthritis or ankylosing spondylitis can contribute to sacroiliitis.
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and the added stress on the pelvis during pregnancy can lead to joint inflammation.
Infection: Although rare, infections in the sacroiliac joint can result in inflammation.
Overuse: Repetitive stress from physical activities like running or heavy lifting may trigger sacroiliitis.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Sacroiliitis
Symptoms of sacroiliitis can vary and often overlap with other lower back or hip conditions. The most common signs include:
Lower back pain: Pain typically affects one or both sides of the lower back and can radiate to the buttocks or thighs.
Stiffness: Reduced mobility and stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity.
Pain worsening with activity: Activities like climbing stairs, standing for long periods, or running may intensify discomfort.
Tenderness: Sensitivity when pressure is applied to the lower back or buttocks.
How Is Sacroiliitis Diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis of sacroiliitis involves a comprehensive evaluation that may include:
Medical history and physical exam: A healthcare provider will assess symptoms and perform physical tests to identify pain sources.
Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs can help detect inflammation or abnormalities in the sacroiliac joints.
Diagnostic injections: An anesthetic injection into the joint may be used to confirm sacroiliitis if pain relief follows the procedure.
Effective Treatment Options for Sacroiliitis
Managing sacroiliitis typically involves a combination of treatment strategies aimed at reducing pain and improving joint function:
Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and pain. In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be used.
Physical therapy: A targeted exercise regimen can enhance flexibility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and support joint stability.
Lifestyle modifications: Adjusting activities to avoid repetitive stress and incorporating rest periods can help manage symptoms.
Sacroiliac joint injections: Administering anesthetics or steroids directly into the joint can offer temporary pain relief.
Surgical intervention: In rare, severe cases, surgical fusion of the sacroiliac joint may be considered when conservative treatments are ineffective.
Preventing Sacroiliitis
While not all cases are preventable, you can reduce your risk by maintaining a healthy weight, practicing proper posture, and incorporating low-impact exercises to strengthen core muscles. Being mindful of body mechanics during activities and avoiding excessive strain can also help protect the sacroiliac joints.
Sacroiliitis can significantly impact quality of life, but with the right diagnosis and treatment plan, many individuals experience relief and improved joint function. If you suspect sacroiliitis, consult with a healthcare professional to explore the best management strategies tailored to your needs.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Lumbar Artificial Disc Replacement in San Antonio
Lumbar artificial disc replacement is a state-of-the-art surgery designed to relieve persistent back pain from degenerative disc disease.Residents of San Antonio have access to some of the top specialists in this field, providing them with advanced solutions for their spinal issues.
Read Our Blog:: https://bsiofsa.blogspot.com/2024/08/understanding-lumbar-artificial-disc.html
Sacroiliac Joint Disease Clinic,Spine Decompression In Live Oak,Spinal Fusion Treatment
0 notes
Text
Spondylitis and Homeopathy: Natural Pain Relief and Management
Spondylitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints, which connect the lower spine to the pelvis. This condition can cause significant pain, stiffness, and eventually lead to the fusion of vertebrae, which severely impacts mobility and quality of life. Understanding the nature of spondylitis and exploring effective management strategies is crucial for those living with this condition.
Understanding Spondylitis
Spondylitis encompasses several forms, including:
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS): The most common type, primarily affecting the spine and pelvis.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): Associated with psoriasis, affecting the spine and peripheral joints.
Reactive Arthritis (ReA): Occurs after an infection in another part of the body.
Common symptoms of spondylitis include:
Persistent Back Pain: Often worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
Stiffness: Particularly in the lower back and hips.
Reduced Flexibility: Limited range of motion in the spine.
Fatigue: Chronic inflammation can lead to a general feeling of tiredness.
Conventional Treatment Approaches
Traditional treatments for spondylitis aim to reduce inflammation, manage pain, and maintain mobility. These typically include:
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Slow the progression of the disease.
Biologic Agents: Target specific components of the immune system.
Physical Therapy: Improves flexibility and strength.
Surgery: In severe cases, to repair or replace damaged joints.
While these treatments can be effective, they often come with side effects and do not address the underlying causes of the condition.
Homeopathy: A Natural Alternative
Homeopathy is a holistic system of medicine developed in the late 18th century by Samuel Hahnemann. It is based on the principle of “like cures like,” meaning a substance that causes symptoms in a healthy person can, in small doses, treat similar symptoms in a sick person. Homeopathy uses highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes.
Homeopathic Remedies for Spondylitis
Homeopathic treatment for spondylitis is individualized, focusing on the specific symptoms and overall health of the person. Commonly used remedies include:
Aesculus Hippocastanum: For lower back pain and stiffness, particularly if aggravated by walking or standing.
Bryonia Alba: For severe pain that worsens with movement and improves with rest.
Calcarea Fluorica: For chronic back pain and spinal stiffness, often used for bone and joint issues.
Rhus Toxicodendron: Effective for stiffness and pain that improves with movement and heat.
Sulphur: For chronic pain and inflammation, especially if the symptoms worsen with standing and heat.
Benefits of Homeopathy for Spondylitis
Homeopathy offers several benefits for managing spondylitis:
Holistic Approach: Addresses the physical, emotional, and mental aspects of the condition.
Individualized Treatment: Each person receives a tailored remedy based on their unique symptoms and overall health.
Minimal Side Effects: Homeopathic remedies are highly diluted, reducing the risk of side effects common with conventional medications.
Long-Term Relief: Focuses on stimulating the body’s healing mechanisms, potentially offering long-lasting relief.
Integrating Homeopathy with Conventional Treatment
For those already undergoing conventional treatment for spondylitis, homeopathy can be integrated as a complementary approach. It is important to consult with both a homeopathic practitioner and a conventional healthcare provider to ensure a coordinated and safe treatment plan.
Dr. Anubbha’s Homeopathy Clinic: The Best Choice for Spondylitis Treatment
Dr. Anubbha’s Homeopathy Clinic in Hyderabad is renowned for providing the best homeopathic treatment for spondylitis. Dr. Anubbha is a highly experienced and skilled best homeopathic doctor, dedicated to helping patients find relief from their symptoms naturally.
At Dr. Anubbha’s Homeopathy Clinic, patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their unique needs. The clinic’s approach focuses on:
Personalized treatment plans
Holistic care addressing the root cause of symptoms
Long-term relief and improved quality of life
Conclusion
Spondylitis is a challenging condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. While conventional treatments are effective for many, homeopathy offers a natural, holistic alternative that can provide relief from pain and stiffness, improve mobility, and enhance overall well-being. By focusing on individualized care and stimulating the body’s natural healing processes, homeopathy can play a valuable role in the management of spondylitis. Dr. Anubbha’s Homeopathy Clinic stands out in providing comprehensive and accessible care, including online homeopathy consultations, ensuring patients receive the best possible treatment tailored to their unique needs.
0 notes
Text
Spondylosis Vs. Spondylitis: Understanding The Differences And Similarities
Understanding Spondylosis and Spondylitis: Key Differences and Similarities
When it comes to spinal conditions, two terms that often cause confusion are spondylosis and spondylitis. While they sound similar, these conditions have distinct characteristics, causes, and treatments. Here, we'll dive deep into spondylitis vs. spondylosis to help you understand their key differences and similarities, with insights from Dr. Priyank Patel, a renowned spondylosis specialist in Thane.
Meet Dr. Priyank M. Patel
Dr. Priyank M. Patel is a distinguished Spine Surgery Specialist in Mumbai , renowned for his expertise in both surgical and non-surgical management of spine-related disorders, particularly spine tumors. As one of the leading endoscopic spine surgeons in Mumbai, Dr. Patel is committed to patient care and innovative treatment approaches, making him an excellent choice for those seeking relief from spine conditions.
What is Spondylosis?
Spondylosis is a general term for age-related wear and tear affecting the spinal discs and vertebrae. It commonly occurs in the neck (cervical spondylosis) and lower back.
Common Symptoms of Spondylosis
Stiffness and pain in the neck or back
Reduced range of motion
Tingling or numbness in the arms or legs
Headaches, especially in cervical spondylosis
Dr. Priyank Patel explains: “Spondylosis symptoms can vary widely but often include chronic pain and stiffness. Early intervention can help manage these symptoms effectively.”
Causes of Spondylosis
Aging and wear-and-tear on the spine
Sedentary lifestyle and poor posture
Previous spinal injuries
Genetic predisposition
Dr. Priyank Patel adds: "Spondylosis is primarily a result of the natural ageing process, but lifestyle factors can significantly impact its progression and severity."
Diagnosis of Spondylosis
Physical examination
Imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, CT scans)
Neurological exams to assess nerve function
What is Spondylitis?
Spondylitis involves inflammation of the vertebrae and can lead to chronic pain and stiffness. A common type of spondylitis is ankylosing spondylitis, which primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints.
Types of Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Reactive arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis
Symptoms Specific to Spondylitis
Persistent back pain and stiffness
Pain that worsens with inactivity
Fatigue
Reduced flexibility of the spine
Dr. Priyank Patel notes: “Spondylitis symptoms often begin in early adulthood and can significantly impact daily activities if not properly managed.”
Causes of Spondylitis
Genetic factors (e.g., HLA-B27 gene)
Environmental triggers
Immune system abnormalities
Dr. Priyank Patel explains: "Spondylitis is often driven by genetic and autoimmune factors, which makes it different from the wear-and-tear seen in spondylosis."
Diagnosis of Spondylitis
Blood tests for inflammatory markers (e.g., ESR, CRP)
Genetic testing for HLA-B27
Imaging tests (X-rays, MRI)
Differences Between Spondylosis and Spondylitis
Understanding the difference between spondylosis and spondylitisis crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Clinical Distinctions
Spondylosis: Degenerative changes in the spine due to ageing.
Spondylitis: Inflammatory condition often with a genetic component.
Impact on Spinal Health
Spondylosis: Leads to disc degeneration, bone spurs, and joint issues.
Spondylitis: Causes chronic inflammation, potentially leading to spinal fusion in severe cases.
Age Groups Most Affected
Spondylosis: Primarily affects older adults.
Spondylitis: Often diagnosed in younger adults, particularly men.
Similarities Between Spondylosis and Spondylitis
Despite their differences, spondylosis and spondylitis share some commonalities:
Both can cause chronic back pain and stiffness.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and preventing progression.
Physical therapy and regular exercise can help improve mobility and reduce pain in both conditions.
Cervical Spondylosis vs. Cervical Spondylitis
The neck, or cervical spine, is a common area affected by both conditions. Comparing cervical spondylosis vs. cervical spondylitis can help clarify their specific impacts on this region.
Cervical Spondylosis
Symptoms: Neck pain, headaches, numbness in the arms
Causes:��Disc degeneration, bone spurs
Treatment: Physical therapy, pain management, sometimes surgery
Cervical Spondylitis
Symptoms: Neck stiffness, pain that improves with movement
Causes: Inflammatory processes, often genetic
Treatment: Anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy
Causes of Spondylosis and Spondylitis
Both conditions have distinct etiologies. Understanding the causes of spondylosis and spondylitis can help in their management.
Spondylosis: Primarily age-related wear and tear, with contributing factors like genetics and lifestyle.
Spondylitis: Inflammatory, often with a strong genetic predisposition and potential autoimmune involvement.
Treatment for Spondylosis and Spondylitis
Effective treatment for spondylosis and spondylitis varies depending on the specific condition and its severity.
Conservative Treatments
Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, muscle relaxants
Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the back and improve flexibility
Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, good posture, regular exercise
Dr. Priyank Patel advises: "A combination of medication and physical therapy can be highly effective in managing symptoms of both spondylosis and spondylitis."
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, conservative treatments like medication and physical therapy may not be enough to relieve the symptoms of spondylosis and spondylitis. When this happens, surgical interventions might be necessary. Here’s a closer look at some common surgical options:
Spinal Fusion
Spinal fusion is a surgery where two or more vertebrae are permanently connected to eliminate movement between them. This can help stabilize the spine and reduce pain.
Purpose: To stop the motion at a painful vertebral segment.
Procedure: Bone grafts or metal implants are used to fuse the vertebrae.
Recovery: Patients usually stay in the hospital for a few days and need several months to fully recover.
Laminectomy
A laminectomy involves removing part of the vertebra called the lamina to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Purpose: To alleviate symptoms caused by spinal stenosis, such as pain, numbness, or weakness.
Procedure: The surgeon removes the lamina, which opens up more space for the spinal cord and nerves.
Recovery: Hospital stay is typically a few days, with full recovery taking a few weeks to a few months.
Discectomy
A discectomy is performed to remove a damaged portion of a disc in the spine that is pressing on a nerve.
Purpose: To relieve pain caused by a herniated disc.
Procedure: The surgeon removes the portion of the disc that is bulging out and causing nerve compression.
Recovery: Patients often go home the same day or after a short hospital stay. Recovery time is usually a few weeks.
Cervical Disc Replacement
This surgery involves replacing a damaged disc in the neck with an artificial one.
Purpose: To maintain neck motion and relieve pain or other symptoms.
Procedure: The surgeon removes the damaged disc and inserts an artificial disc in its place.
Recovery: Hospital stay is usually short, and recovery can take a few weeks.
When to Consider Surgery
Surgery is typically considered when:
Conservative treatments (medications, physical therapy) have failed to provide relief.
Symptoms significantly impact daily life and mobility.
There is severe nerve compression that could lead to permanent damage.
Conclusion
Surgical interventions for spondylosis and spondylitis can provide significant relief from pain and improve quality of life when other treatments are not effective. It's important to consult with a specialist like Dr. Priyank Patel to determine the best course of action based on your specific condition and symptoms. Remember, each patient's recovery journey is unique, and following your doctor's recommendations is crucial for a successful outcome.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between spondylosis and spondylitis?
Spondylosis is a degenerative condition caused by aging and wear-and-tear on the spine, while spondylitis is an inflammatory condition often driven by genetic factors. Both conditions can cause back pain and stiffness but have different underlying causes and treatments.
2. What are the common symptoms of spondylosis?
Common symptoms of spondylosis include stiffness and pain in the neck or back, reduced range of motion, tingling or numbness in the arms or legs, and headaches, particularly in cervical spondylosis.
3. What are the common symptoms of spondylitis?
Spondylitis symptoms include persistent back pain and stiffness, pain that worsens with inactivity, fatigue, and reduced flexibility of the spine. These symptoms often start in early adulthood.
4. How is spondylosis diagnosed?
Spondylosis is diagnosed through a physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, and neurological exams to assess nerve function.
5. How is spondylitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of spondylitis involves blood tests for inflammatory markers, genetic testing for the HLA-B27 gene, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRI to look for signs of inflammation and joint damage.
6. What are the treatment options for spondylosis?
Treatment for spondylosis includes medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and good posture, and in severe cases, surgical interventions like spinal fusion, laminectomy, or discectomy.
7. What are the treatment options for spondylitis?
Spondylitis treatment typically involves anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery. The goal is to reduce inflammation, manage pain, and improve mobility.
8. When should surgery be considered for spondylosis or spondylitis?
Surgery should be considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief, symptoms significantly impact daily life and mobility, or there is severe nerve compression that could lead to permanent damage.
9. What is spinal fusion surgery?
Spinal fusion surgery involves permanently connecting two or more vertebrae to eliminate movement between them, which can help stabilize the spine and reduce pain.
10. What is a laminectomy?
A laminectomy is a surgical procedure where part of the vertebra called the lamina is removed
Are you looking for Healthcare Marketing Agency ? Please feel free to contact Kaushal Pandey .
0 notes
Text
#Vertiflex Superion Procedure#Dorsal Ganglion Root Stimulation#Pain Specialist Chicago#DRG Treatment#Chronic Pain Treatment in Chicago#Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Surgery Chicago#DRG Stimulation Procedure#Pain Management Specialists Chicago#DRG Stimulator Surgery#Spinal Cord Pain Treatment Chicago#Dorsal Root Ganglion Stimulation Therapy#Motor Vehicle Injuries Treatments#Sacroiliac Joint Fusion Treatment#Lower Back Pain Relief#Spinal Cord Stimulation Therapy#Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Treatment
0 notes
Text
Ankylosing Spondylitis and Homeopathy: A Holistic Approach to Managing Pain and Inflammation
Introduction
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the spine, causing pain, stiffness, and in severe cases, fusion of the vertebrae. While conventional treatments aim to alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression, many individuals seek complementary and alternative therapies, such as homeopathy, to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Understanding Ankylosing Spondylitis
AS is characterized by inflammation of the spine and sacroiliac joints, leading to stiffness and reduced mobility. Over time, this inflammation can cause the vertebrae to fuse together, resulting in a rigid spine. Symptoms often develop gradually and may include back pain, stiffness, fatigue, and difficulty breathing.
The Role of Homeopathy
Homeopathy is a holistic system of medicine that aims to stimulate the body's innate healing mechanisms. Homeopathic remedies are prepared from natural substances and prescribed based on the principle of "like cures like." In the context of AS, homeopathic remedies may help alleviate pain and inflammation, improve mobility, and enhance overall well-being.
Common Homeopathic Remedies for AS
Several homeopathic remedies may be beneficial for individuals with AS, depending on their unique symptoms and constitution:
1. Rhus toxicodendron:Useful for stiffness and pain, particularly when symptoms improve with movement and worsen with rest.
2. Bryonia alba:Indicated for sharp, stitching pains aggravated by the slightest movement and relieved by rest.
3.Calcarea carbonica:Helpful for individuals who experience coldness and stiffness, especially in the neck and back.
4. Kali carbonicum: Prescribed for pain and stiffness in the lower back, often worsened by cold and improved by warmth.
These remedies are selected based on the individual's specific symptoms, such as the nature of their pain, stiffness, and any accompanying symptoms.
Benefits of Homeopathy for AS
One of the key advantages of homeopathy for AS is its gentle yet effective approach to symptom management. Homeopathic remedies are non-toxic and free from side effects, making them suitable for long-term use. Additionally, homeopathy addresses the underlying imbalances contributing to AS, rather than simply masking symptoms.
Conclusion
While homeopathy may not offer a cure for ankylosing spondylitis, it can be a valuable adjunctive therapy for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. As with any medical treatment, it's essential to consult with a qualified homeopath to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.
Remember, this article is for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a healthcare professional.
This article provides an overview of ankylosing spondylitis and explores the potential role of homeopathy in managing its symptoms. It emphasizes the holistic approach of homeopathy and highlights common remedies used for AS.
Choose Homoeopathy for your better health.
@drpurishomoeopathy
For consultation contact us at
📞 +91-7814029176
✉️[email protected] (mailto:[email protected])
http://www.drpurishomoeopathy.com (http://www.drpurishomoeopathy.com)
"WE INSPIRE HOPE"
.
.
.
#doctor #homoeopathy #homeopathic #alternative #holistichealth #cure #health #drpurishomoeopathy
#Weinspirehope #hope #rheumatoidarthritis #instagood #medicine #chandigarh #arthritis #healthylifestyle #instalike #instagram #pain
0 notes
Text
Exploring Nonsurgical Treatment for Pain in Fort Myers, Florida: Effective Solutions and Therapies for Relief and Improved Quality of Life | APMSS
Check out effective nonsurgical therapy options for discomfort in Ft Myers, Florida, with APMSS. Our dedicated group offers personalized therapies designed to provide relief and enhance your lifestyle. From physical therapy and chiropractic like regenerative medicine and acupuncture, we offer an extensive series of treatments tailored to address your certain needs. Whether you're handling persistent discomfort, sporting activities injuries, or bone and joint conditions, our experienced service providers are here to aid you locate relief and boost your general wellness. See our website to get more information regarding our solutions and set up a consultation for tailored pain management options.
Related Links -
Pain Doctor Fort Myers Florida
MILD back procedures (minimally-invasive lumbar decompression)
SI (Sacroiliac) fusion
Vertiflex
0 notes
Text
Understanding Arthritis: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction:
Arthritis is a term used to describe a group of more than 100 inflammatory joint diseases that affect millions of people worldwide. These conditions can cause pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased joint mobility, significantly impacting the quality of life for those affected. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the various types of arthritis, their symptoms, and the diverse treatment options available.
Types of Arthritis:
Osteoarthritis (OA):
OA is the most common form of arthritis, characterised by the gradual wearing down of the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones in the joints.
Risk factors for OA include ageing, joint injury, obesity, and genetics.
Symptoms include pain, stiffness, and decreased flexibility in affected joints, commonly in the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
RA is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints.
It can affect multiple joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and joint deformities.
RA symptoms often include fatigue, fever, and a general feeling of malaise.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA):
PsA is a type of arthritis that occurs in some individuals with psoriasis, a chronic skin condition.
Joint inflammation, stiffness, and swelling are common symptoms of PsA.
It can affect any joint, including the spine, and may cause nail changes in addition to skin and joint symptoms.
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS):
AS primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation of the vertebrae and the sacroiliac joints.
This form of arthritis can lead to the fusion of the spine, resulting in reduced flexibility and potentially a forward-stooped posture.
AS may also affect other joints and organs.
Gout:
Gout is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to intense pain, swelling, and redness.
It commonly affects the big toe but can also impact other joints.
Factors such as diet, genetics, and underlying health conditions contribute to the development of gout.
Symptoms of Arthritis:
The symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the type of arthritis and the specific joints affected. However, some common symptoms include:
Joint pain: Persistent pain in one or more joints.
Joint swelling: Swelling and tenderness in the affected joints.
Joint stiffness: Difficulty moving the joints, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
Redness and warmth: Inflammation may cause the skin over the affected joint to become red and warm to the touch.
Fatigue: Many people with arthritis experience fatigue, which can be attributed to the body's response to inflammation.
Treatment Options:
Medications:
a. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Reduce pain and inflammation.
b. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Slow the progression of autoimmune arthritis.
c. Corticosteroids: Provide rapid relief of inflammation and pain.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy helps improve joint function and range of motion through targeted exercises and stretches.
Therapists may also educate patients on joint protection techniques and assistive devices.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on weight-bearing joints.
Exercise: Regular, low-impact exercise can strengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility.
Joint protection: Using assistive devices and modifying daily activities to reduce joint strain.
Surgical Interventions:
a. Joint replacement: For severe cases of osteoarthritis, joint replacement surgery may be recommended.
b. Synovectomy: Removal of the synovium to reduce inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis.
c. Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive procedures to repair or remove damaged joint tissue.
Medications for Gout:
Medications such as colchicine and allopurinol can help manage gout by reducing inflammation and preventing uric acid buildup.
Conclusion:
The decision to have surgery by the Best Orthopedic Doctor In Jaipur is ultimately taken by the patient. A physician may guide him to an appropriate choice but it is taken by the patient. The decision is not dictated by how good or bad the X-ray looks, but rather by how severe the patient’s symptoms are. Again, specifically pain, and how well it is being managed by the non-operative treatment. So if someone feels like they’re able to do most of their activities at a high functional level with non-operative management, then we continue with non-operative management.
0 notes
Text
Arthritis and Joint Pain: What You Need to Know
Arthritis, a term used to describe various joint disorders, affects millions of people worldwide and is a leading cause of chronic pain and disability. Joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation are common symptoms of arthritis. Understanding the different types, causes, risk factors, and management options for arthritis is crucial for those affected and their caregivers. In this article, we will delve into the world of arthritis and joint pain, providing essential information for a better grasp of this complex condition. Don’t worry here is the scientific solution for your joint pain. Use Queensveda joint pain oil and live stress and pain free life.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a general term used to describe inflammation and swelling of the joints. It encompasses more than 100 different types of joint disorders, each with its unique characteristics. Arthritis can affect people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds.
Common Types of Arthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA): This is the most common type of arthritis and occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time. OA typically affects weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and spine.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium—the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. It often affects multiple joints, including the hands, wrists, knees, and feet.
Gout: Gout is characterized by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe joint pain, often in the big toe. It can result from dietary factors and lifestyle choices.
Psoriatic Arthritis: Psoriatic arthritis is associated with psoriasis, a skin condition. It can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, often in the fingers and toes.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: This form of arthritis primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints in the lower back. It can lead to chronic pain, stiffness, and limited spinal mobility.
Common Symptoms of Arthritis
Joint pain and tenderness Swelling and inflammation Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity Reduced range of motion Warmth and redness around the affected joints Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of arthritis varies depending on the type:
Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear on the joints, genetics, and aging. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Autoimmune factors and genetic predisposition. Gout: Uric acid buildup and genetic factors. Psoriatic Arthritis: Genetics, immune system dysfunction, and psoriasis. Ankylosing Spondylitis: Genetic factors and immune system dysfunction. Risk factors for developing arthritis include genetics, age, gender (as some types are more common in women), joint injuries, and certain lifestyle factors like diet and smoking.
Treatment and Management
The management of arthritis typically involves a combination of approaches:
Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, disease-modifying drugs, and biologics may be prescribed. Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve joint strength, flexibility, and function. Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, joint-friendly exercises, and dietary changes. Assistive Devices: Braces, splints, or orthopedic aids can support affected joints. Surgery: Joint repair, replacement, or fusion may be necessary in severe cases. Conclusion
Arthritis and joint pain can significantly impact an individual's daily life and well-being. While arthritis is a complex condition with many forms, understanding the basics is essential for effective management. Early diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan can help individuals with arthritis lead a fulfilling and active life despite joint pain and discomfort. If you or someone you know experiences persistent or severe joint pain, consulting a healthcare provider is the first step toward better managing this condition.
0 notes
Text
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction Treatment in Midtown | Sacroiliac Joint Pain Specialist near me

Sacroiliac joint pain can significantly impact one's quality of life, causing discomfort, limited mobility, and reduced overall functionality. Fortunately, if you are based in New York City, there are various treatment options available to help alleviate sacroiliac joint pain. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sacroiliac joint pain, focusing on finding a specialist near you in NYC.
Understanding Sacroiliac Joint Pain
The sacroiliac (SI) joints are located at the base of the spine, connecting the sacrum (the triangular bone at the bottom of the spine) to the pelvis. These joints are responsible for transferring weight and forces between the upper body and the lower body during activities such as walking, running, and standing. However, when these joints become inflamed or dysfunctional, they can cause pain in the lower back, buttocks, hips, and legs, commonly referred to as sacroiliac joint pain.
Causes and Symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Pain
Sacroiliac joint pain can arise from various factors, including:
Injury: Traumatic events such as falls, accidents, or sports injuries can strain or damage the sacroiliac joints, leading to pain.
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause ligaments to loosen, resulting in increased stress on the SI joints and subsequent pain.
Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis or ankylosing spondylitis can contribute to sacroiliac joint inflammation and discomfort.
Overuse: Repetitive activities or occupations that involve excessive stress on the SI joints can gradually lead to pain over time.
Common symptoms of sacroiliac joint pain include:
Lower back pain: Often felt on one side of the lower back, the pain can radiate to the buttocks, hips, and thighs.
Hip pain: Discomfort may be felt in the hip joint, sometimes mistaken for hip arthritis.
Leg pain: The pain can extend down the leg, resembling sciatica.
Difficulty in standing or walking: Prolonged standing or walking may exacerbate the pain, making these activities challenging.
Treatment Options for Sacroiliac Joint Pain
When seeking treatment for sacroiliac joint pain, it is crucial to consult a specialist who can accurately diagnose and provide appropriate interventions. In NYC, you can find sacroiliac joint pain specialists who offer a range of treatment options tailored to your specific needs. Some common approaches include:
Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. Prescription medications may be prescribed for severe or chronic cases.
Physical therapy: Targeted exercises and stretches can improve strength, flexibility, and stability in the SI joints, alleviating pain.
Joint injections: Corticosteroid injections directly into the sacroiliac joint can provide short-term pain relief and reduce inflammation.
Radiofrequency ablation: This minimally invasive procedure uses heat to temporarily disable nerves that transmit pain signals from the SI joints.
Prolotherapy: Injection of a dextrose solution promotes tissue repair and regeneration, strengthening the ligaments around the SI joints.
Surgical intervention: In rare cases when conservative treatments fail, surgical options such as fusion or stabilization procedures may be considered.
Finding a Sacroiliac Joint Pain Specialist Near You in NYC
When searching for a sacroiliac joint pain specialist in NYC, it is essential to consider their expertise, experience, and proximity to your location. Here are some steps to help you find the right specialist:
Research online: Utilize search engines and online directories to find sacroiliac joint pain specialists in NYC. Look for their credentials, patient reviews, and expertise in treating sacroiliac joint pain.
Seek recommendations: Ask your primary care physician, friends, or family members if they can recommend a trusted specialist who focuses on sacroiliac joint pain.
Check with your insurance: Ensure that the specialist you choose is covered by your insurance plan to avoid any unexpected expenses.
Schedule a consultation: Once you have identified a potential specialist, schedule an initial consultation to discuss your symptoms, treatment options, and any concerns you may have. Conclusion
Living with sacroiliac joint pain can be challenging, but seeking appropriate treatment from a specialist can make a significant difference. In NYC, a wide range of treatment options are available to address sacroiliac joint pain, allowing individuals to regain their mobility and improve their overall well-being. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can find a sacroiliac joint pain specialist near you in NYC and take the first step towards a pain-free life
0 notes