#Role of Lockout Tagout
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Enhancing Safety and Productivity: The Essential Role of Lockout Tagout
Maintenance of a machine is done to increase productivity and efficiency, but a careless servicing process leads to deterioration and accidents. While servicing a machine, workers face the danger of exposure to hazardous energy. This hazardous energy can be present in any form and cause the machine to start moving again. Workers can fall off moving belts, get crushed under automated machines and even get electrocuted by faulty panels. All these incidents happen when a machine either retains stored energy or is unintentionally started by an unaware employee. Operating belts, sharp cutters, grinding/mixing machines, toxic material carrying pipelines and other such machines pose a serious threat to workers. Craft workers, electricians, machine operators and labourers are a few among many workers who are prone to accidents. Machinery-related fatalities form a significant part of accidents and result from failure to control hazardous energy.
The evolution of energy has been a steady progression from simple to more powerful and dangerous sources. Hazard associated with all forms of energy and force includes unexpected movement, direct contact with an unshielded energy source, and being caught in a mechanism driven by a form of energy or source. Safety measures like Lockout Tagout are more crucial today than ever before.
Just informing the facility personnel or assuming the machine will remain inoperative is not enough to ensure safety. Workplace accidents are a critical issue that needs to be addressed by every health and safety official regardless of the company's size. Specific steps must be taken to guarantee safe working conditions for all workers. It is the duty and responsibility of employers and employees to protect their own lives and those around them. Lockout Tagout not only helps you avoid OSHA violations but also protects workers' lives. According to OSHA, LOTO saves workers from approximately 120 fatalities and 50,000 injuries yearly.

OSHA or Occupational Safety and Health Administration enforced Lockout Tagout for control of hazardous energy guidelines in 1990. The Lockout Tagout procedure is a safety policy that protects workers from unexpected machine start-up. Lockout/Tagout is the practice of shutting down and disconnecting power from machinery or equipment and placing locks and warning tags on energy-isolating devices to prevent the machine or equipment activation during maintenance or servicing by bringing it to a zero-energy state. It renders the machine inoperative and harmless. This safety procedure ensures that hazardous energy is controlled and any worker present in the area can't be harmed.
Control of hazardous energy can be achieved through Lockout Tagout devices. The employee puts the Lockout Tagout devices on the machine's energy control points, isolating and securing its movement. The authorised employee adds a padlock and a tag to the lockout device so no other person can accidentally energise the machine. These devices should be durable, substantial, standardised, and identifiable. Although there are thousands of available LOTO products in the market, you can identify the best ones for your facility or take advice from an expert. Every control point must be locked and tagged for a successful safety program using effective devices. In addition, a maintenance worker needs to know how to use energy-isolating products effectively.
The worker servicing the machine should have in-depth knowledge about the Lockout Tagout process. Whether it is a third-party servicing team or the company's employees, they need suitable training in the application of Lockout Tagout. They should know, understand and follow documented Lockout Tagout procedures. OSHA mandates that every authorised employee possess the necessary skills and knowledge about the LOTO process. Affected employees or other employees should be aware of the ongoing maintenance process and receive basic training. Safety administrations like OSHA have imposed such directives to create an effective safety program with workers’ participation.
OSHA addresses standards for the protection of employees during maintenance from unexpected start-up of machines. Companies must develop, implement and enforce machine-specific procedures to control hazardous energy. It outlines specific actions, training and devices to create your safety policy. It gives guidelines for general industry as well as particular industries for an efficient LOTO program. Workers need not use Lockout Tagout during regular servicing operations, which are essential for the machine's normal functioning and don’t put workers in harm's way.
The Lockout Tagout Standard requires employers in certain industries to establish an energy control program for locking out equipment, employee training, and periodic inspections. Different industries call for different protective measures. Workers who service industrial machinery and equipment face unique hazards due to their close contact with equipment. They frequently work in dangerous zones beyond machine guards that protect workers during normal production operations. Consequently, special procedures are necessary to protect workers during maintenance and servicing.
OSHA estimates that failure to adequately control hazardous energy accounts for 7% of all occupational fatalities and nearly 10% of severe accidents in many industries. There is a prevailing presumption that if an employer develops a Lockout Tagout program meeting the requirements of the OSHA 29 CFR 1910.147 standard, compliance will be achieved and energy release incidents will be more or less eliminated. It is important to remember that attaining legal compliance represents only the minimum safety criteria and employers need to go beyond minimalism. With an effective Lockout Tagout program in place, injuries and losses arising from failure to control hazardous energy are entirely preventable.
# Case Study 1 - In an automotive manufacturing industry, greasing operations are performed by an automatic machine enclosed in a cage. A worker wanted to unjam the greaser’s stuck arm; he entered the cage without de-energizing the machine and locking it out. When he tried to unjam the arm, the machine short-circuited and started unexpectedly. The operator’s arm was caught in the machine and was injected with grease. Such a situation could have been avoided by draining and isolating the energy sources of the machine.
# Case Study 2 - A scrap metal shredder took a worker’s life due to a lack of LOTO devices. The employee tried to unjam a metal piece stuck in the shredder. As soon as he unclogged the shredder, it started working and took the employee down.

All these incidents occurred due to improper implementation of LOTO devices. LOTO implementation has been saving numerous lives by -
·�� Lockout Tagout Safety devices prevent accidental clicking of switches. It prevents another employee from unknowingly operating the machine.
· They warn and inform employees about the ongoing service. New employees or shift changes can create confusion without proper warnings.
· It holds the employee accountable for his own safety and that of others around him. Having a mandatory LOTO procedure saves workers from accidents.
· It creates awareness among employees and makes them attentive towards incidents occurring in the workplace.
Year after year, Lockout Tagout violations continue to be amongst the top ranks of OSHA’s top ten violation list of most frequently cited standards and serious violations. Despite the alarming number of machine-related accidents and OSHA’s enforcement efforts, Lockout Tagout is still viewed by many as burdensome and production slowing-task. But companies which have employed effective Lockout Tagout programs have seen a boost in employee morale, and productivity resulting in souring profits.
#Lockout Tagout#Lockout Tagout Procedure#LOTO Safety#Lockout Tagout Safety Devices#LOTO Products#Lockout Tagout Procedures#Role of Lockout Tagout#OSHA#Lockout Tagout Case Study#E-Square Alliance
0 notes
Text
Understanding NFPA 70B: A Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Maintenance

Electrical systems are integral to the smooth operation of any facility, and maintaining them is crucial for safety and efficiency. In this context, NFPA 70B PDF provides essential guidelines for the maintenance of electrical equipment to prevent failures and hazards. Understanding these guidelines is key for building owners, electrical contractors, and safety professionals alike.
The Importance of Electrical Maintenance
Maintaining electrical systems is not just about preventing downtime; it’s about ensuring the safety of the individuals who operate, maintain, and interact with these systems. Without proper maintenance, electrical equipment can malfunction, leading to fires, electrical shocks, or even loss of life. The National Fire Protection Association 70B PDF outlines a comprehensive strategy for the upkeep of electrical systems, recommending periodic inspections, testing, and proper procedures for repairs.
The document provides specific recommendations for various types of equipment, ranging from motors and transformers to distribution panels and circuit breakers. It stresses the importance of creating a maintenance schedule tailored to the specific needs of a facility and its equipment.
Key Elements in the NFPA 70B Guidelines
Inspection and Testing: Regular inspections help identify potential issues before they cause damage. The National Fire Protection Association 70B PDF provides detailed procedures for testing electrical systems to assess their condition, ensuring they meet the necessary operational standards.
Preventive Maintenance: One of the primary focuses of the National Fire Protection Association 70B is preventive maintenance. By performing routine checks, electrical systems can be kept in optimal condition, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and expensive repairs.
Condition-Based Monitoring: In addition to routine maintenance, the document emphasizes the importance of condition-based monitoring. This involves using advanced techniques such as thermal imaging and vibration analysis to assess the health of equipment in real-time, allowing for more precise maintenance planning.
Safety Protocols: The safety of workers and building occupants is paramount. NFPA 70B provides guidelines on the safe handling of electrical systems during maintenance, ensuring that workers are protected from electrical hazards. Personal protective equipment (PPE) and lockout/tagout procedures are essential components of these guidelines.
Record Keeping: Proper documentation is a critical part of the maintenance process. The guidelines stress the importance of keeping detailed records of inspections, tests, repairs, and replacements. These records not only help with compliance but also offer insights into the long-term performance of the system.
Integrating NFPA 70B Into Your Maintenance Plan
Creating an effective electrical maintenance plan based on the NFPA 70B guidelines involves several key steps. First, it is essential to assess the current state of your electrical systems. This means reviewing the age, condition, and previous maintenance history of the equipment. Once this assessment is complete, a detailed maintenance schedule should be created, taking into account the specific needs of each piece of equipment.
Next, ongoing monitoring should be incorporated into the plan. This ensures that any changes in the condition of the equipment are promptly identified and addressed. Regular training for maintenance personnel is also necessary to keep them updated on best practices and safety protocols outlined in the guidelines.
The Role of Compliance and Regulations
Compliance with the National Fire Protection Association 70B is not just a recommendation but, in many cases, a requirement. Local and national electrical codes often reference these guidelines, and non-compliance can lead to legal consequences or increased risk. For example, if an electrical failure occurs and it is discovered that proper maintenance protocols were not followed, the responsible parties could face fines or liability for damages.
Building owners and managers should be proactive about ensuring that their electrical systems adhere to the latest standards outlined in the NFPA 70B PDF. This includes staying updated on revisions to the document, which are typically released every few years to address emerging technologies and new safety challenges.
Training and Education
To implement the guidelines effectively, it is crucial to provide training for all personnel involved in electrical system maintenance. Workers need to be familiar with the standards outlined in the National Fire Protection Association 70B PDF to understand what is required for compliance and how to perform maintenance tasks safely and efficiently. Regular training sessions should focus on the latest techniques, tools, and safety protocols.
Benefits of Following NFPA 70B Guidelines
Enhanced Safety: The primary benefit of following the National Fire Protection Association 70B guidelines is improved safety. Proper maintenance minimizes the risk of electrical failures, which could result in fires, electrocution, or other hazards.
Reduced Downtime: A well-maintained electrical system is less likely to experience unexpected breakdowns, leading to reduced downtime and increased productivity.
Cost Savings: Regular inspections and maintenance can extend the life of equipment, preventing costly emergency repairs or replacements. Additionally, by identifying issues early, you can avoid expensive damage to your systems.
Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to the National Fire Protection Association ensures that you remain compliant with local, state, and federal electrical safety regulations, avoiding potential legal issues. For more info Click here
By following the guidelines laid out in the National Fire Protection Association 70B PDF, facilities can ensure the longevity, safety, and efficiency of their electrical systems. Regular maintenance and adherence to safety protocols not only protect workers but also save costs in the long run by preventing costly repairs and legal issues. Understanding and integrating these best practices into your facility’s maintenance plan is key to maintaining a safe and functional electrical system.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the World of Electromechanical Systems: A Fusion of Electronics and Mechanics
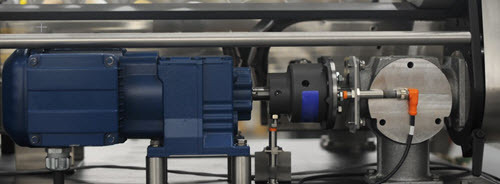
Introduction:
In the realm of facility management, the effective operation and maintenance of electromechanical systems play a vital role in ensuring the smooth functioning of buildings and infrastructure. The fusion of electronics and mechanics has given rise to sophisticated systems that require skilled professionals to handle their operations and maintenance.
Electromechanical systems are a fascinating field that combines the principles of electronics and mechanics. These systems involve the integration of electrical components and mechanical structures to create devices capable of performing a wide range of tasks. From simple household appliances to complex industrial machinery, electromechanical systems are an integral part of our daily lives.
Understanding Electromechanical Systems:
Electromechanical systems are integral to the functioning of modern facilities. These systems combine electrical and mechanical components, utilizing electronic controls to enhance efficiency and automation. Examples include HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, elevators, escalators, fire protection systems, security systems, and energy management systems.
Workforce Requirements:
To ensure the optimal performance of electromechanical systems, facility management teams require a diverse range of professionals with specialized skill sets. Key roles may include:
a. Engineers: Electrical and mechanical engineers are crucial for system design, installation, and troubleshooting. They possess the technical knowledge to handle complex electromechanical systems.
b. Technicians: Skilled technicians play a vital role in maintaining, inspecting, and repairing electromechanical systems. They are responsible for regular maintenance, diagnosing issues, and performing necessary repairs or replacements.
c. Operators: Operators are responsible for monitoring and controlling electromechanical systems, ensuring their proper functioning and responding to alarms or emergencies.
d. Facility Managers: These professionals oversee the operations and maintenance of electromechanical systems, ensuring compliance with regulations, managing budgets, and coordinating the work of the entire facility management team.
Recruitment Strategies:
To build a competent team for operations and maintenance in facility management, consider the following recruitment strategies:
a. Job Portals: Utilize online job portals that cater to the facility management industry to reach potential candidates with the desired skill sets.
b. Industry Networks: Engage with industry-specific networks, associations, and professional forums to connect with qualified professionals in the field of electromechanical systems.
c. Collaboration with Technical Institutes: Partner with technical institutes and vocational schools to tap into fresh talent. Establish internship programs or participate in job fairs to attract entry-level candidates.
d. Skill Assessment: Conduct thorough skill assessments during the recruitment process to evaluate candidates' proficiency in handling electromechanical systems and their related components.
Training and Professional Development:
Given the complexity and evolving nature of electromechanical systems, investing in training and professional development is crucial. Provide regular training sessions to enhance the skills of your workforce, keeping them up-to-date with the latest technologies and maintenance practices. Encourage employees to attend industry conferences, workshops, and certifications to expand their knowledge base.
Safety and Compliance:
Operations and Maintenance in Facility Management must prioritize safety and compliance. Ensure that all staff members are well-versed in safety protocols, including electrical safety, lockout/tagout procedures, and handling hazardous materials. Familiarize your team with relevant regulations and standards, such as building codes, fire safety regulations, and environmental guidelines.
Team Collaboration and Communication:
Effective collaboration and communication within the facility management team are vital for seamless operations and maintenance. Foster a culture of teamwork, encourage knowledge sharing, and promote open lines of communication between different departments and roles. This collaborative approach can lead to efficient problem-solving and improved system performance.
Conclusion:
Electromechanical systems form the backbone of facility management, and staffing considerations for operations and maintenance are crucial to ensure their reliable and efficient functioning. By understanding the workforce requirements, implementing effective recruitment strategies, prioritizing training and professional development.
#Water Treatment Plant Manufacturers in India#Sewage Treatment Plant Manufacturers in India#Operation and Maintenance of Water Treatment#Operations and Maintenance in Facility Management#Water Treatment Plant Project#Sewage Treatment Plant Project#Effluent Treatment#Best Electromechanical Systems#Integrated Electronics and Mechanics
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Safety First in Hazardous Work Environments
The Importance of Specialized Training in High-Risk Industries
In industries where workers face unique hazards, comprehensive training is not just a regulatory requirement but a lifeline. For those working in environments involving toxic substances or maritime operations, specialized programs equip professionals with the knowledge and skills to navigate dangers effectively. Training programs tailored to specific risks ensure that workers can perform their duties confidently while prioritizing safety. These programs often focus on hazard recognition, regulatory compliance, and practical strategies for mitigating risks, fostering a culture of vigilance and preparedness. Without such training, the likelihood of accidents, injuries, or long-term health issues increases significantly, underscoring the need for rigorous education in high-risk fields.
Understanding the Role of Asbestos Contractor Supervisors
One critical area of focus in hazardous material management is the safe handling of asbestos, a substance notorious for its health risks. The Asbestos Contractor Supervisor Initial training is designed for individuals overseeing projects involving asbestos abatement. This program provides in-depth instruction on identifying asbestos-containing materials, implementing safe removal practices, and ensuring compliance with federal and state regulations. Supervisors learn to develop work plans, manage containment systems, and protect workers from exposure to harmful fibers. The training emphasizes the importance of leadership in maintaining a safe work environment, as supervisors must communicate protocols clearly and monitor compliance diligently. By mastering these skills, supervisors play a pivotal role in safeguarding their teams and the public from the dangers of asbestos exposure, which can lead to severe health conditions like mesothelioma or lung cancer.
The Scope of Maritime Safety Training
Maritime work presents its own set of challenges, from unpredictable weather to the complexities of shipyard operations. The Osha 10 Hour Maritime Training is a vital program for workers in this sector, offering a comprehensive introduction to occupational safety and health standards. This training covers critical topics such as fall protection, electrical safety, and the proper use of personal protective equipment in maritime environments. Participants gain an understanding of how to recognize and address hazards specific to shipyards, docks, and vessels. The program also highlights the importance of adhering to federal safety regulations, which are designed to reduce workplace injuries and fatalities. By completing this training, maritime workers are better equipped to navigate the unique risks of their industry, fostering safer workplaces and reducing the incidence of accidents.
Bridging Knowledge with Practical Application
Both asbestos and maritime training programs emphasize the transition from theoretical knowledge to practical application. For asbestos supervisors, this means hands-on experience in setting up containment zones, using air monitoring equipment, and conducting site inspections. These practical exercises ensure that supervisors can translate regulatory requirements into actionable strategies on the job. Similarly, maritime safety training incorporates real-world scenarios, such as practicing lockout/tagout procedures or simulating emergency evacuations. This approach ensures that workers are not only familiar with safety protocols but also capable of implementing them under pressure. By bridging the gap between classroom learning and fieldwork, these programs empower professionals to make informed decisions that protect lives and prevent costly accidents.
The Broader Impact of Safety Training
The benefits of specialized training extend beyond individual workers to the broader industry and community. Well-trained supervisors and maritime workers contribute to safer project outcomes, reducing the risk of environmental contamination or workplace injuries. In asbestos abatement, proper training prevents the release of harmful fibers into the air, protecting nearby residents and ecosystems. In maritime settings, adherence to safety standards minimizes accidents that could disrupt operations or endanger lives. Moreover, organizations that invest in these training programs often see improved employee morale and productivity, as workers feel valued and supported. Regulatory compliance also reduces the likelihood of fines or legal liabilities, making training a smart investment for companies operating in high-risk sectors.
Building a Culture of Safety and Responsibility
At the heart of these training programs is the goal of fostering a culture of safety and responsibility. Asbestos supervisors and maritime workers are not just learning rules; they are adopting a mindset that prioritizes vigilance and accountability. Supervisors trained in asbestos abatement become advocates for safe practices, setting an example for their teams. Maritime workers, equipped with safety knowledge, take ownership of their roles in preventing accidents. This cultural shift has a ripple effect, influencing peers, management, and even clients to prioritize safety. Over time, this commitment to excellence in training transforms industries, reducing risks and enhancing the reputation of organizations that value their workers’ well-being.
The Future of Safety in Hazardous Work
As industries evolve, so too must the training programs that support them. Advances in technology, such as virtual reality simulations or real-time hazard monitoring, are already enhancing the effectiveness of safety education. For asbestos supervisors, future training may incorporate more sophisticated air quality sensors or automated containment systems. In maritime work, new regulations may emerge to address emerging risks like cybersecurity threats on vessels. By staying ahead of these trends, training programs can continue to equip workers with the tools they need to succeed in dynamic environments. Ultimately, the commitment to ongoing education ensures that safety remains at the forefront of high-risk industries, protecting workers and communities for generations to come.
0 notes
Text
Training Tips for New Machinery Operators
Operating heavy machinery is a skilled job that requires precision, safety awareness, and technical knowledge. Whether it's forklifts, excavators, cranes, or industrial equipment, proper training is essential to prevent accidents, improve efficiency, and extend the lifespan of the machinery.
For new operators, the learning curve can be steep. However, with the right approach, they can quickly become proficient and confident in their roles. Here are some essential training tips for new machinery operators.

1. Understand the Machinery Inside and Out
Before operating any machine, new operators must familiarize themselves with its components, controls, and functions.
Key Steps:
Read the Manual: Every machine Machinery Solutions comes with an operator’s manual that explains its features, safety protocols, and maintenance requirements.
Identify Controls: Learn the purpose of each lever, button, and switch. Misusing controls can lead to accidents.
Know the Limits: Understand the machine’s load capacity, speed limits, and terrain restrictions.
A thorough understanding of the equipment reduces errors and enhances operational efficiency.
2. Prioritize Safety Above All Else
Safety is non-negotiable when operating heavy machinery. Even a small mistake can lead to severe injuries or fatalities.
Essential Safety Practices:
Wear Proper PPE: Helmets, gloves, steel-toe boots, and high-visibility vests are mandatory.
Conduct Pre-Operation Checks: Inspect the machine for leaks, damaged parts, or low fluid levels before starting.
Follow Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Ensure the machine is properly shut down before performing maintenance.
Stay Alert: Avoid distractions like phones and always be aware of surroundings.
Regular safety drills and refresher courses help reinforce these habits.
3. Start with Supervised Hands-On Training
Classroom learning is important, but real-world experience is irreplaceable. New operators should begin with supervised practice sessions in a controlled environment.
Effective Training Methods:
Begin with Basic Movements: Practice starting, stopping, and maneuvering before handling complex tasks.
Simulate Real Scenarios: Train in conditions similar to actual worksites (e.g., uneven terrain, confined spaces).
Receive Feedback: Experienced trainers should correct mistakes early to prevent bad habits.
Hands-on training builds muscle memory and confidence.
4. Master Smooth Operation Techniques
Jerky movements can damage machinery and create safety hazards. New operators should focus on smooth, controlled actions.
Tips for Smooth Operation:
Avoid Sudden Starts/Stops: Gradual acceleration and deceleration reduce wear and tear.
Practice Precision Movements: Learn how to position loads accurately without overcorrecting.
Control Speed Appropriately: Adjust speed based on load weight and work environment.
Smooth operation improves efficiency and reduces mechanical stress.
5. Learn Proper Load Handling Techniques
Improper load handling is a leading cause of workplace accidents. New operators must master safe lifting and transporting methods.
Best Practices for Load Handling:
Check Load Stability: Ensure loads are properly secured before moving them.
Balance the Weight: Distribute weight evenly to prevent tipping.
Follow Lifting Protocols: Use the correct angles and avoid overloading.
Proper load handling prevents accidents and equipment damage.
6. Develop Situational Awareness
A good operator is always aware of their surroundings. Blind spots, moving objects, and uneven terrain can pose risks.
Ways to Improve Awareness:
Use Mirrors and Cameras: Many machines have blind spot monitoring systems.
Communicate with Spotters: When visibility is low, rely on hand signals or radios.
Scan the Work Area: Constantly check for obstacles, workers, or changes in terrain.
Situational awareness prevents collisions and injuries.
7. Follow Maintenance Protocols
A well-maintained machine performs better and lasts longer. Operators should know basic maintenance tasks.
Maintenance Must-Dos:
Daily Inspections: Check fluids, tires, brakes, and hydraulic systems.
Report Issues Immediately: Never operate a faulty machine—report problems to supervisors.
Keep It Clean: Remove debris and dirt that can cause mechanical issues.
Preventive maintenance reduces downtime and costly repairs.
8. Stay Updated with Refresher Courses
Technology and safety standards evolve. Even experienced operators should take refresher courses periodically.
Benefits of Ongoing Training:
Learn New Techniques: Machinery updates may introduce new features.
Reinforce Safety Habits: Regular training keeps safety protocols fresh.
Stay Certified: Some licenses require periodic renewal.
Continuous learning ensures long-term competence.
9. Communicate Effectively with the Team
Machinery operators often work in teams. Clear communication prevents misunderstandings and accidents.
Communication Best Practices:
Use Standard Signals: Hand signals and radios should follow workplace protocols.
Confirm Instructions: Repeat back instructions to avoid errors.
Report Hazards Immediately: If you see a risk, inform supervisors right away.
Good teamwork enhances productivity and safety.
10. Stay Calm Under Pressure
Malfunctions, tight deadlines, and unexpected obstacles can be stressful. Remaining calm ensures better decision-making.
How to Handle Pressure:
Pause if Unsure: If a situation feels unsafe, stop and assess before proceeding.
Follow Emergency Procedures: Know the steps for shutdowns or evacuations.
Ask for Help When Needed: Never hesitate to seek assistance from experienced colleagues.
A composed operator is a safe operator.
Conclusion
Becoming a skilled machinery operator takes time, practice, and dedication. By focusing on safety, hands-on training, smooth operation, and continuous learning, new operators can build confidence and efficiency.
Remember, the best operators are those who respect their equipment, prioritize safety, and constantly seek improvement. With these training tips, new machinery operators can lay a strong foundation for a successful and accident-free career.
1 note
·
View note
Text
OSHA Lockout Tagout Standard: Application of Control 1910.147(d)
The established procedures for the application of energy control (the lockout or tagout procedures) covers the following elements and actions as mentioned above. Preparation of Shutdown: Before an authorized employee turns off the machine, he must have knowledge regarding the types, magnitude, hazards, and the means to control the energy. The first step is intended to notify all the affected employees regarding the Lockout and allow the employees to get ready for the shutdown, and plan ahead to perform safely.
In complex or group Lockout Tagout situations, all involved personnel should be made aware of their respective roles and assignments. Machine or Equipment shutdown: To place the machine in a state that it will let employees work on it safely, it must be turned off or shutdown using established procedures. An orderly shutdown must be used to avoid any increased or additional hazards to employees as result of shut down. Machine isolation: All the isolating devices such as isolators, valves, etc. that are needed to control the energy of the machines, must be physically located and operated so that the machine is isolated from its energy sources. Check OSHA Guidelines - https://www.safetylock.net/learn-lockout-tagout/osha-documentation/

#LockoutTagout#OSHA#LockoutDevice#TagoutDevice#LockoutTags#Safety#OSHAGuidelines#LOTO#OSHAStandard#SafetyTips#LOTOProgram#OSHARegulations#OSHALockoutTagout#LockoutTagoutDevice#LOTODevices#ESquare#ESquareAlliance
0 notes
Text
Shocking Safety Myths: What You Don’t Know About Electrical SWMS
Electrical work is one of the most dangerous trades, requiring strict safety measures to prevent injuries and fatalities. Safe Work Method Statements (SWMS) are essential in managing electrical risks, yet many misconceptions about their role and implementation persist. Believing in these myths can lead to unsafe work practices and serious accidents.
This article will bust common electrical SWMS myths, explain their legal importance under Australian regulations, and provide simple guidelines for creating effective SWMS.
An Electrical Safe Work Method Statement (SWMS) is a document that outlines high-risk work activities, identifies potential hazards, and details the control measures required to reduce risks. It ensures workers follow standard safety procedures and helps prevent workplace incidents.
Under Australian Work Health and Safety (WHS) laws, SWMS are mandatory for high-risk construction work, including:
Working on live electrical systems
Installing or maintaining high-voltage equipment
Working near exposed electrical conductors
Electrical work in hazardous environments
Not having a proper electrical SWMS in place can lead to fines, legal actions, and serious workplace accidents.
Despite clear regulations, many misconceptions exist about SWMS for electrical work. Let’s set the record straight:
Fact: While a risk matrix can be useful for assessing hazards, it is not a legal requirement in an SWMS. The focus should be on identifying hazards, implementing control measures, and ensuring compliance with Australian safety standards.
Fact: SWMS are legally required for all high-risk electrical work, regardless of whether a contractor asks for one. Every employer and worker engaged in electrical work must ensure that a compliant SWMS is developed and followed.
Fact: Electrical work environments change frequently, meaning new risks can arise. SWMS should be reviewed and updated regularly, especially when:
Fact: Some workers think SWMS are just administrative documents. However, a properly implemented SWMS improves workplace safety by:
Many electrical safety myths come from underestimating risks. Here are some dangerous misconceptions:
Truth: Even low voltage can cause serious injuries or fatalities. Electric shocks, burns, and heart failure can occur at voltages as low as 50V AC or 120V DC.
Truth: Standard rubber gloves do not provide sufficient protection against electrical shocks. Workers should use:
Truth: Circuit breakers protect equipment but do not eliminate the risk of shock for workers. Proper lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures and live work permits are essential for safe electrical work.
To ensure safety and compliance, follow these steps to develop and implement a practical electrical SWMS:
Electrical work is one of the most hazardous trades, making SWMS an essential safety tool. However, common safety myths can create a false sense of security, increasing the risk of injuries.
By debunking these myths and following best practices for electrical SWMS, businesses can improve workplace safety, meet legal requirements, and protect workers from electrical hazards.
🔹 Key Takeaways:
SWMS are required by Australian WHS laws for high-risk electrical work.
Regular updates and worker involvement make SWMS more effective.
Misconceptions about electrical risks can lead to preventable accidents.
Proper PPE, lockout/tagout, and safety training are crucial for electrical work.
Ensuring accurate and up-to-date SWMS implementation will help keep Australian electricians safe and compliant with industry regulations.
0 notes
Text
Lockout Tagout Kits: Ensuring Workplace Safety in UAE
Introduction
Safety in the workplace is paramount, especially in industries that involve machinery, electrical systems, and hazardous equipment. A Lockout Tagout (LOTO) kit is an essential tool for safeguarding workers from accidental energy release during maintenance and servicing. In the UAE, where industrial safety standards are rigorously upheld, LOTO kits are vital in promoting compliance and preventing workplace accidents.
This blog explores the components, benefits, and applications of Lockout Tagout kits, highlighting their importance in the UAE’s industrial landscape.
What is a Lockout Tagout Kit?
A Lockout Tagout kit is a comprehensive set of devices designed to isolate energy sources and prevent the accidental start-up of equipment during maintenance. These kits include various lockout devices, tags, and tools tailored to meet the specific safety needs of different industries.
Key Components of a Lockout Tagout Kit
Padlocks: Durable safety padlocks to secure lockout devices.
Tags: Clearly labeled tags to warn employees of ongoing maintenance.
Valve Lockouts: Secure valves to prevent energy release.
Electrical Lockouts: Isolate circuit breakers and plugs.
Cable Lockouts: Versatile devices for securing multiple energy points.
Hasps: Allow multiple workers to lock out a single energy source.
Carrying Case: Convenient storage for all tools in the kit.
Importance of Lockout Tagout Kits
Industries in the UAE, including oil and gas, construction, and manufacturing, operate under strict safety regulations. LOTO kits play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with these standards while enhancing worker safety.
Accident Prevention: Mitigates risks associated with unexpected energy releases.
Regulatory Compliance: Helps businesses adhere to UAE workplace safety laws.
Enhanced Productivity: Ensures a safer environment, reducing downtime caused by accidents.
Employee Confidence: Promotes a culture of safety, boosting worker morale.
Applications of Lockout Tagout Kit
LOTO kits are indispensable in various sectors:
Electrical Maintenance: Lockout devices secure circuit breakers, switches, and plugs during repair.
Industrial Machinery: Prevent accidental start-up of heavy equipment.
Pipelines and Valves: Valve lockouts isolate hazardous materials in chemical or oil processing plants.
Construction Sites: Ensure safe maintenance of cranes, elevators, and other machinery.
Features of High-Quality Lockout Tagout Kit
Durable Materials: Resistant to harsh environments and extreme temperatures.
Versatility: Includes a wide range of devices for different energy sources.
Compliance Ready: Meets international and UAE-specific safety standards.
Portability: Compact and easy-to-carry cases for on-the-go usage.
Why Choose a Lockout Tagout Kit for Your Workplace?
Investing in a LOTO kit is not just a regulatory requirement but also a proactive measure for workplace safety. Key benefits include:
Cost Efficiency: Prevents financial losses from accidents and legal fines.
Time-Saving: Streamlines the lockout/tagout process during maintenance.
Customizability: Kits can be tailored to fit the specific needs of your industry.
The Role of LOTO Kits in the UAE’s Safety Standards
The UAE’s commitment to workplace safety is evident in its adherence to international standards such as ISO 45001 and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines. LOTO kits help businesses comply with these regulations, fostering a safer working environment.
In high-risk industries like oil and gas, where energy isolation is critical, the use of lock out tag out UAE is not just recommended but essential.
How to Choose the Right LOTO Kit
Assess Workplace Needs: Identify the types of energy sources and equipment in use.
Ensure Compliance: Select kits that meet UAE and international safety standards.
Check Durability: Opt for kits with robust materials suitable for your environment.
Consider Portability: Choose a kit that is easy to carry and store.
Conclusion
Lockout Tagout kits are indispensable for ensuring workplace safety and regulatory compliance in the UAE. They protect workers, reduce the risk of accidents, and create a culture of safety that is crucial for any business.
By investing in high-quality LOTO kits, UAE industries can not only safeguard their workforce but also enhance productivity and maintain their reputation for excellence in workplace safety.
#lock out kit#loto kit supplier#scaffolding tag#butterfly valve#abb distributors uae#miniature circuit breaker#emergency stop switch#lockout tagout#padlocks dubai#lockout tagout locks#padlock supplier#uae#dubai#abudhabi#safety tag#mcb uae#lockout station
0 notes
Text
Health and Safety Protocols During Air Conditioner Installations in Canning Vale
Air conditioner installations in Canning Vale require careful adherence to health and safety protocols to ensure the well-being of both installers and occupants. The process involves handling refrigerants, electrical components, and heavy equipment, making safety a top priority. This article outlines the critical safety measures to follow during air conditioner installations in Canning Vale, ensuring a safe and efficient process.

Handling Refrigerants Safely
Refrigerants play a critical role in air conditioning systems, facilitating the cooling process. However, improper handling can lead to health hazards, environmental damage, and legal issues. It is essential to follow these enhanced safety measures:
Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Installers must wear protective gear such as chemically resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory masks designed for handling refrigerants. This minimises the risk of skin burns, eye irritation, or inhalation of toxic fumes during leaks or accidental exposure.
Prevent Leaks: Leaks not only reduce system efficiency but also pose serious environmental risks, particularly to the ozone layer in systems using older refrigerants. Installers should use high-quality sealing techniques, such as O-rings and flare nuts, and test connections with electronic leak detectors or soapy water. Regular maintenance schedules must also be implemented to identify and rectify leaks promptly.
Storage and Disposal: Proper storage and disposal of refrigerants are vital for environmental compliance. Installers should store refrigerants in pressure-rated, certified containers, ensuring they are secured in upright positions to prevent accidental release. Disposal must comply with Australian regulations, which mandate certified recovery and recycling services to handle refrigerants responsibly. Local Canning Vale guidelines may also include penalties for improper disposal, underscoring the importance of adherence.
Training and Certification: Only qualified technicians with updated certifications should handle refrigerants. Familiarity with Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for each type of refrigerant is essential for understanding its unique properties and risks.
Electrical Safety Measures
Electrical systems are integral to air conditioner installations, but they present significant hazards if not handled properly. Here are additional measures to ensure safety during installations in Canning Vale:
De-energising Equipment: Installers should use lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures to ensure all power sources are safely disconnected before work begins. This prevents accidental energisation, which can lead to serious injuries. Verify de-energisation using a multimeter or voltage tester before proceeding.
Using Insulated Tools: Electricians should exclusively use tools with insulated handles, rated for the system's voltage. This provides a safeguard against accidental contact with live wires. Tools must also be inspected for damage, such as cracks in insulation, before use.
Compliance with Standards: Adhering to the Australian Wiring Rules (AS/NZS 3000) ensures installations meet strict electrical safety requirements. This includes following guidelines for proper earthing, circuit protection, and cable routing. Regular training helps electricians stay updated on code changes and best practices.
Identifying Potential Hazards: Before beginning installation, assess the site for risks such as moisture, exposed wiring, or inadequate grounding. Addressing these issues proactively reduces the likelihood of electrical incidents.
Use of Residual Current Devices (RCDs): Installers should use RCDs to monitor electrical currents and immediately cut power if imbalances are detected, preventing electric shock or equipment damage.
Emergency Protocols: All team members should be trained to handle electrical emergencies, including providing first aid for electric shock and safely shutting down power in case of an incident.
These comprehensive measures not only protect installers and occupants but also ensure the installation process complies with legal standards and industry best practices, making air conditioner installations in Canning Vale both safe and reliable.
Safe Equipment Handling
Handling heavy machinery and working at heights during air conditioner installations involve inherent risks that must be managed effectively. The following expanded measures further enhance safety:
Use Appropriate Lifting Tools: Installers should use lifting equipment such as hoists, dollies, or forklifts to move heavy units. Where manual lifting is unavoidable, adhere to proper lifting techniques, including bending the knees and keeping the load close to the body. Additionally, assess the weight and dimensions of the equipment beforehand to select suitable tools.
Secure Ladders and Scaffolding: Ensure ladders are positioned on stable, non-slip surfaces and are secured at the top to prevent shifting. Scaffolding must be professionally assembled, equipped with guardrails, and inspected regularly for structural integrity. Installers should always maintain three points of contact when climbing ladders.
Work in Teams: Assigning team members specific roles, such as lifting, stabilising, or guiding equipment, reduces the likelihood of injuries. Effective communication is critical, including the use of standardised hand signals or radios when visibility is limited.
Site Assessment and Preparation: Evaluate the work area for hazards such as uneven terrain, overhead obstacles, or confined spaces. Clear the area of debris to ensure unobstructed movement and safe equipment operation.
Protecting Occupants
Protecting occupants during air conditioner installations ensures their safety and comfort while maintaining a professional environment. These enhanced practices contribute to a safer installation process:
Isolate Work Areas: Use physical barriers such as cones, caution tape, or portable fencing to create a clear boundary around the installation site. Install signage indicating restricted access or potential hazards.
Minimise Disruptions: Coordinate with occupants to schedule installations during less active hours, such as weekdays when residents are often away. Notify them in advance of any noise, dust, or temporary power outages that might occur during the process.
Ventilation During Installation: Open windows or use fans to ensure adequate airflow, especially when handling refrigerants or adhesives that may emit fumes. In enclosed spaces, consider using portable air scrubbers or purifiers to maintain air quality.
Clear Communication: Keep occupants informed about the installation timeline, potential risks, and any necessary precautions they should take, such as avoiding specific areas or keeping children and pets away from the work zone.
Emergency Preparedness
Being well-prepared for emergencies ensures quick and effective responses, minimising risks to both installers and occupants. Expanded measures include:
First Aid Kits: Stock kits with a range of supplies, including bandages, antiseptic wipes, burn cream, and cold packs, to address common installation-related injuries. Designate a trained first-aid officer on-site for immediate assistance.
Fire Safety: Installers should carry portable fire extinguishers appropriate for electrical and chemical fires (Class C or CO2 extinguishers). Conduct regular fire safety drills to ensure the team can respond promptly and effectively in emergencies.
Incident Reporting: Use a structured reporting system to document accidents or near-misses. Reports should include a description of the incident, contributing factors, corrective actions taken, and any follow-up measures. This process helps identify patterns and implement preventive strategies.
Evacuation Plans: Establish clear evacuation procedures for both workers and occupants in case of severe incidents. Ensure all team members and residents know exit routes and assembly points, especially in large or complex buildings.
Emergency Contacts: Maintain an up-to-date list of emergency contacts, including local medical services, fire departments, and regulatory bodies in Canning Vale, ensuring rapid assistance when needed.
These enhanced protocols ensure that air conditioner installations in Canning Vale are conducted safely and efficiently, protecting both the workforce and the community.
Conclusion
Implementing stringent health and safety protocols is essential during air conditioner installations in Canning Vale to protect both professionals and residents. Handling refrigerants with care, adhering to electrical safety standards, and maintaining a secure environment are vital steps in ensuring a seamless and hazard-free installation process. By prioritising safety, installers can deliver reliable services while upholding industry best practices.
https://www.gildanairelectrical.com.au/health-and-safety-protocols-during-air-conditioner-installations-in-canning-vale/
0 notes
Text
Lockout Tagout Stations Types, Benefits and Best Practice
https://www.safetylock.net/blog/lockout-tagout-stations-type-benefits-and-best-practices-to-improve-workplace-safety/
Lockout Tagout Stations play a vital role in centralising and streamlining the lockout process. By keeping all essential lockout tools in one designated location, they help ensure speed, compliance, and consistency in every maintenance operation.
Check what is LOTO station, their types, benefits and best practice for organising devices with stations. Know how E-Square can help in selecting the lockout tagout stations.
#Lockout Tagout Stations#LOTO Stations#Lockout Tagout#LOTO Devices#Lockout Tagout Manufacturer#LOTO Supplier#E-Square Alliance
0 notes
Text
General Safety Training covers a broad range of topics aimed at promoting awareness and best practices to ensure the safety of employees, visitors, and the general public in the workplace. For someone like you with a background in civil and mechanical engineering and an interest in becoming a safety officer, here are key areas typically covered in General Safety Training:
1. Introduction to Workplace Safety
Understanding safety policies, standards, and legal regulations (e.g., OSHA, ISO).
Identifying workplace hazards and risks.
Roles and responsibilities in maintaining a safe environment.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Overview of various PPE (helmets, gloves, goggles, etc.).
Proper selection, use, and maintenance of PPE.
Specific PPE requirements for different industries (e.g., construction, manufacturing).
3. Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment
Identifying physical, chemical, biological, and ergonomic hazards.
Conducting risk assessments and implementing control measures.
Reporting unsafe conditions and near-misses.
4. Fire Safety
Fire prevention strategies and housekeeping.
Using fire extinguishers and understanding fire classifications.
Emergency evacuation plans and fire drills.
5. First Aid and Emergency Response
Basic first aid techniques (CPR, wound care, burns).
Procedures for handling medical emergencies.
Creating and maintaining emergency response plans.
6. Electrical Safety
Understanding electrical hazards (e.g., shock, arc flash).
Safe working practices around electrical systems.
Lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures for energy isolation.
7. Chemical Safety
Safe handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals (MSDS/SDS understanding).
Personal protection against chemical exposure.
Procedures for spill control and decontamination.
8. Ergonomics and Workplace Layout
Preventing musculoskeletal injuries (e.g., from lifting, repetitive motions).
Creating ergonomic workstations.
Safe material handling techniques.
9. Machine and Equipment Safety
Understanding mechanical hazards (e.g., moving parts, crushing).
Safe operating procedures for machinery and equipment.
Guarding techniques and regular maintenance requirements.
10. Working at Heights
Fall prevention strategies (e.g., scaffolds, harnesses).
Inspection and use of fall protection systems.
Rescue plans for working at heights.
11. Manual Handling and Lifting Techniques
Correct lifting techniques to prevent injury.
Identifying when mechanical aids are needed.
Back care and injury prevention.
12. Environmental Safety
Managing waste and pollution.
Safe handling of hazardous substances.
Sustainable practices and environmental regulations.
13. Incident Reporting and Investigation
Reporting accidents, incidents, and near-misses.
Root cause analysis for accidents.
Implementing corrective and preventive actions.
Many of these topics are tailored based on specific industries, but they provide a solid foundation for anyone pursuing a career in safety. Since you are interested in becoming a safety officer, completing this training will help you acquire the necessary skills to ensure safety compliance and implement best practices in the workplace.
Safety course in chennai
Safety course in madurai
Safety institute in chennai
0 notes
Text
Safety First: Essential Features for Automotive Conveyor Systems
Safety is paramount when designing and operating automotive conveyor systems. With workers frequently interacting with these high-speed, heavy-duty machines, it's critical that conveyor systems incorporate robust safety features to protect personnel and prevent accidents. In this blog post, we'll explore some of the essential safety features that should be integrated into automotive conveyor systems.
Emergency Stop Buttons
Easily accessible emergency stop buttons are a must-have safety feature for automotive conveyors. These buttons allow workers to immediately halt the conveyor system in case of an emergency, preventing injuries and minimizing damage. Emergency stops should be strategically placed along the conveyor line and clearly marked for quick identification and activation.
Guarding and Barriers
Proper guarding and barriers are essential for keeping workers safe from moving conveyor parts. Conveyor systems should be equipped with guards that prevent access to pinch points, nip points, and other hazardous areas. These guards can be made of materials like wire mesh, perforated metal, or transparent polycarbonate to allow visibility while maintaining safety.
Sensors and Interlocks
Sensors and interlocks play a crucial role in automotive conveyor safety. Presence sensors can detect if a worker or object is in a hazardous area, triggering an emergency stop or warning signal. Interlocks ensure that guards and access doors remain closed while the conveyor is in operation, preventing accidental access to moving parts.

Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures
Proper lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures are essential for safely servicing and maintaining automotive conveyor systems. LOTO involves isolating the conveyor from its energy sources (electrical, pneumatic, hydraulic) and applying locks and tags to prevent accidental startup during maintenance. Strict LOTO protocols should be followed by trained personnel to ensure worker safety.
Proper Lighting and Visibility
Good lighting and visibility are crucial for safe conveyor operation. Adequate illumination should be provided along the entire length of the conveyor system, allowing workers to clearly see potential hazards and obstacles. Reflective markings or contrasting colors can be used to highlight pinch points, nip points, and other areas of concern.
Training and Awareness
Comprehensive training and ongoing safety awareness are essential for maintaining a safe working environment around automotive conveyor systems. Workers should be trained on proper conveyor operation, maintenance procedures, and emergency response protocols. Regular safety meetings, signage, and visual cues can help reinforce the importance of safe practices and keep safety top-of-mind.By incorporating these essential safety features and best practices, automotive conveyor systems can be designed and operated in a way that prioritizes worker safety while maintaining high levels of efficiency and productivity. Investing in safety not only protects your most valuable asset - your employees - but also reduces the risk of costly accidents and downtime.
0 notes
Text
What is Lockout Tagout Video in Hindi
Lockout Tagout is a critical safety practice that protects workers from hazardous energy during the maintenance of machinery and equipment. This Hindi-language video explains the concept of LOTO, its importance, and how it can prevent workplace accidents. The video emphasizes the role of proper training and adherence to safety protocols in minimizing risks and safeguarding workers' lives.
Viewers can learn about common lockout devices like padlocks, hasps, and valve lockouts, along with tips on compliance with workplace safety regulations. With a focus on simplicity and real-world application, this video serves as an essential resource for Hindi-speaking audiences, empowering them to foster a culture of safety in their workplaces.
#What is Lockout Tagout in Hindi#what is LOTO#Lockout Tagout Video#LOTO Safety Video#What is LOTO Video in Hindi#E-Square Alliance
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Electrical Hazards Addressed in Your SWMS
In any workplace where electrical work is being carried out, safety is a top priority. Electrical hazards can pose significant risks to workers and the surrounding environment. To minimize these risks, a Safe Work Method Statement (SWMS) is developed to outline the specific hazards and control measures. An Electrical SWMS plays a crucial role in identifying and managing the dangers related to electrical work. Here are the top five electrical hazards commonly addressed in an Electrical SWMS:
1. Electric Shock
Electric shock is one of the most common and potentially deadly electrical hazards. It can occur when a person comes into direct contact with live electrical parts. Even low voltages can cause serious injury or death.
To prevent electric shock, an Electrical SWMS will typically outline control measures such as:
De-energizing circuits before work begins
Using proper personal protective equipment (PPE) like rubber gloves and insulated tools
Ensuring all workers are properly trained in identifying live parts and understanding the risks
These measures significantly reduce the chances of accidental contact with live electrical circuits.
2. Arc Flash
An arc flash is a sudden release of energy due to a fault in an electrical system. It can cause burns, fires, and even explosions. Arc flashes occur when there is a rapid release of electrical energy through the air, which can severely injure anyone nearby.
In an Electrical SWMS, the risk of arc flash is addressed by:
Ensuring proper maintenance of electrical equipment to prevent faults
Keeping non-essential personnel away from areas where high-voltage equipment is being serviced
Implementing lockout/tagout procedures to de-energize circuits before maintenance
Using arc-rated PPE, such as face shields and fire-resistant clothing, to protect workers
3. Electrical Fires
Electrical fires can be caused by overloaded circuits, faulty wiring, or malfunctioning equipment. These fires can spread quickly and cause significant damage to both people and property.
Control measures in an Electrical SWMS for preventing electrical fires include:
Regular inspection and testing of electrical systems to detect any signs of wear or faults
Avoiding overloading circuits by distributing electrical loads appropriately
Using fire-resistant cables and materials to reduce the risk of fire spreading
Keeping combustible materials away from electrical installations
These precautions help in reducing the likelihood of an electrical fire occurring on-site.
4. Working Near Power Lines
Working near overhead or underground power lines poses a unique set of dangers. Even a small mistake, such as contacting a power line with equipment, can lead to severe injury or death.
To address this hazard, an Electrical SWMS outlines the following:
Identifying and marking the locations of all nearby power lines before starting work
Using insulated tools and equipment when working near power lines
Establishing safe distances and barriers to prevent accidental contact with power lines
Ensuring that workers are aware of the dangers and are trained to operate machinery safely around power lines
Explore the full article to gain a deeper understanding of Electrical SWMS.
0 notes
Text
📣 𝗦𝘂𝗽𝗲𝗿𝘃𝗶𝘀𝗼𝗿 𝗖𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗲𝘁𝗲𝗻𝗰𝘆 𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗶𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗖𝗼𝘂𝗿𝘀𝗲 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗖𝗲𝗿𝘁𝗶𝗳𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 - 𝗜𝗻𝘁𝗿𝗼𝗱𝘂𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 🖥️📘
✅ Supervisor means having the right skills and know-how to lead a team well, like being good at talking, making decisions, solving problems and helping everyone do their best. 👋
Managerial/supervisory competency is a multifaceted skill set essential for effectively leading teams and achieving organizational goals.
Our Manager/Supervisor competency training offers a comprehensive curriculum designed to enhance your leadership skills.
𝗢𝘂𝗿 𝘁𝗿𝗮𝗶𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗰𝗼𝘂𝗿𝘀𝗲 𝗰𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘀 𝗸𝗲𝘆 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗲𝘁𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗶𝗲𝘀 𝘀𝘂𝗰𝗵 𝗮𝘀:
Decision-Making
Problem-Solving
Emotional Intelligence
Team Building
Better Communication
Performance Management
Time Management and More
Our supervisor competency training program equips you with the knowledge and tools to ensure a safe and compliant work environment.
𝗧𝗼𝗽𝗶𝗰𝘀 𝗰𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿𝗲𝗱 𝗶𝗻𝗰𝗹𝘂𝗱𝗲:
Competent Supervision
Achieving Due Diligence as a Supervisor
The Role of the Ministry of Labour
Hazard Identification and Accident Investigation
The Internal Responsibility System
Worker Rights
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
WHMIS 2015
Response to a Minor Spill
Lockout/Tagout
Workplace Violence and Harassment
Workplace Inspection and Accident Investigation and More.
𝗩𝗶𝘀𝗶𝘁 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗹𝗶𝗻𝗸𝘀 𝘁𝗼 𝗹𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗻 𝗺𝗼𝗿𝗲 𝗮𝗯𝗼𝘂𝘁 𝗦𝘂𝗽𝗲𝗿𝘃𝗶𝘀𝗼𝗿 𝗖𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗲𝘁𝗲𝗻𝗰𝘆 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝘂𝗹𝗲 𝟬𝟭. https://www.swiftelearningservices.com/supervisor-competency-training-online-course-and-certification/
𝑪𝒐𝒏𝒕𝒂𝒄𝒕 𝑬𝒎𝒂𝒊𝒍: 𝒕𝒓𝒂𝒊𝒏𝒊𝒏𝒈@𝒔𝒘𝒊𝒇𝒕𝒆𝒍𝒆𝒂𝒓𝒏𝒊𝒏𝒈𝒔𝒆𝒓𝒗𝒊𝒄𝒆𝒔.𝒄𝒐𝒎 𝒇𝒐𝒓 𝒎𝒐𝒓𝒆 𝒊𝒏𝒇𝒐𝒓𝒎𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏. https://www.swiftelearningservices.com/contact-us/
#supervisor#competency#supervisorcompetency#digitallearning#safetytraining#safetyfirst#canada#traininganddevelopment#supervisor_job#safetyfirstlife#onlinetraining#competencies
0 notes
Text
Lockout Tagout Stations Types, Benefits and Best Practice
https://www.safetylock.net/blog/lockout-tagout-stations-type-benefits-and-best-practices-to-improve-workplace-safety/
Lockout Tagout Stations play a vital role in centralising and streamlining the lockout process. By keeping all essential lockout tools in one designated location, they help ensure speed, compliance, and consistency in every maintenance operation.
Check what is LOTO station, their types, benefits and best practice for organising devices with stations. Know how E-Square can help in selecting the lockout tagout stations.
Lockout Tagout Stations, LOTO Stations, Lockout Tagout, LOTO Devices, Lockout Tagout Manufacturer, LOTO Supplier, E-Square Alliance
0 notes