#Region Occitanie
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Das Reisefieber packt uns wieder: 4 Geheimtipps für ein neues Südfrankreich-Erlebnis!

View On WordPress
#Gourmet#Jakobsweg#Lavelanet#Region Occitanie#Südfrankreich#schwarze Diamanten#Trüffel#Trüffelanbau#Trüffelmärkte#Via Tolosana#Villeneuve-Minervois
0 notes
Text

Cyclist the Ariege, France - Andy Lovell, 2022.
British, b. 1964 -
Silkscreen print , 55 x 47 cm.
545 notes
·
View notes
Text

Millau Viaduct, Creissels, France: The Millau Viaduct is a multispan cable-stayed bridge completed in 2004 across the gorge valley of the Tarn near Millau in the Aveyron department in the Occitanie Region, in Southern France. The design team was led by engineer Michel Virlogeux and English architect Norman Foster. Wikipedia
#Millau Viaduct#gorge valley#multispan cable-stayed bridge#Tarn#Millau#Creissels#Aveyron department#Occitanie Region#France#europe
455 notes
·
View notes
Text

Church of Saint-Brès, Languedoc region of France
French vintage postcard
#historic#church of saint-brès#region#photography#vintage#sepia#france#church#saint#photo#briefkaart#french#ansichtskarte#postcard#postkarte#postkaart#occitanie#carte postale#ephemera#postal#tarjeta
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Palavas-les-Flots. Vue sur la Plage prise du Casino.
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
Congrats on your archery win!!!
Thank you!!!! :D :D :D :D
#*#i had zero expectation and was ready to be last#and then i wasn't#karen shoots things#am now the proud owner of the “region occitanie” shirt LOL
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Frequently Asked Questions
This post answers the following questions:
Who are the Catalans? Where are they?
Which are the Catalan Countries? (each Catalan country)
Where can I learn the Catalan language? (free online resources and where to find classes)
What social media accounts can I follow that post in Catalan?
Other Tumblr blogs similar to this one but for other cultures of the world.
If your question isn't answered here, you're more than welcome to send me an ask!
1. Who are the Catalans? Where are they?
Catalan people are a cultural group who come from the area known as the Catalan Countries. We speak the Catalan language (a language that descends from Latin) and have a distinct culture (cuisine, traditions, holidays, dances, music, literature, etc) and history since the Middle Ages.
Our nation is the Catalan Countries, located in the coast of the Mediterranean sea, in South-Western Europe.
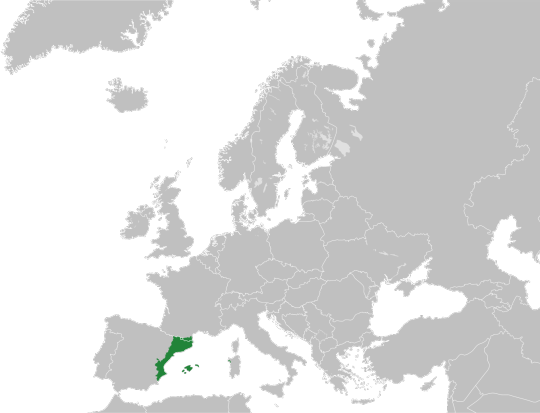
As a result of past wars and invasions, most of the Catalan Countries are under Spanish rule and a part of it is under French rule (+1 city in Italy). In fact, Spain and France have harshly persecuted, illegalized and tried to exterminate the Catalan language and culture for a long time, well into the 20th century. But Catalan people have survived the ethnocide and we still exist, even though we continue to face discrimination and there are some settings where it's still not legal to speak Catalan (for example, public schools in the French-controlled part, or European Union ambits, among some others).
There is also Catalan diaspora around the world.
We are not a closed culture, we are very open to foreigners learning our language and culture, and the Catalan diaspora often organizes celebrations for our holidays or groups to do traditional activities (most famously the castellers, aka human towers) that everyone can join.
2. Which are the Catalan Countries?
We say the Catalan Countries in plural because it's made of different areas for historical reasons. The Catalan Countries are all the areas where Catalan is the native language, which have historically been part of a whole, and which share a common culture (with local variants, of course). Here they are:
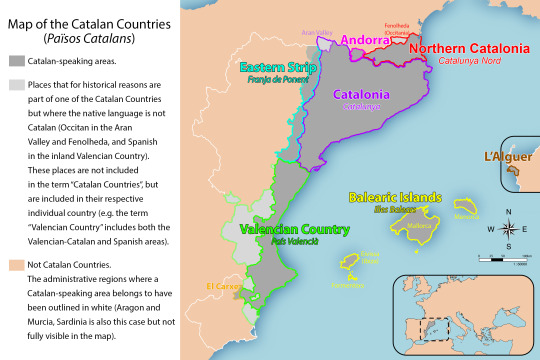
From North to South:
Northern Catalonia. Capital city: Perpinyà. It's under French administration (part of the region Occitanie in the new French regions system, used to be Languedoc-Roussillon in the old one).
Andorra. Capital city: Andorra la Vella. It's an independent microstate.
Catalonia. Capital city: Barcelona. It's under Spanish administration (it's the Catalonia region in the Spanish regions system).
Eastern Strip, also called Aragon Strip. It's under Spanish administration (it's part of the region of Aragon in the Spanish regions system).
Balearic Islands, including Mallorca, Menorca, Eivissa (in English also known as Ibiza) and Formentera. Capital city: Palma. Under Spanish administration (Balearics region in the Spanish regions system).
Valencian Country. Capital city: València. Under Spanish administration (called Valencian Community in the Spanish regions system).
El Carxe. Tiny rural area. Under Spanish administration (part of the Region of Murcia in the Spanish regions system).
L'Alguer. One city in the island of Sardinia. Under Italian administration (part of the region of Sardinia in the Italian regions system).
3. Where can I learn the Catalan language?
We are thrilled that you want to learn our language. Catalan people love it when others learn our language. Here I'll link you to classes and free online resources.
If you want face-to-face classes outside of the Catalan Countries, you can check this website to find if there's a university that offers Catalan classes near you. There are 101 around Europe, 25 in North America and Cuba, 5 in Asia, and 4 in South America. Students from these courses can also participate in language stays and internships in the Catalan Countries.
If you're already in the Catalan Countries, you will easily find courses for foreigners which the government offers for free or for a cheap price (depending on the level and each person's economic situation). Check out your local CPNL (Consorci per la Normalització Lingüística).
If you want to learn independently on the internet, there are two resources I recommend the most, both are available online for free.
One is the book "Life in Catalonia. Learn Catalan from..." that you can find in various languages. Here I add the link to the official government page where you can legally download the PDFs for free, you only have to scroll down and click under where it says "text complet". You can find the book Learn Catalan from English, from Spanish, from Arabic, from Tamazight, from French, from Hindi, from Urdu, from Punjabi, from Romanian, from Russian, and from Chinese.
The other resource I recommend the most is the online course Parla.cat. It has different levels for beginners or advanced learners. You have to create an account (it asks for an official document number, don't worry about it, it's not a sketchy site, it's because it's an official course paid by the government of Catalonia and if you immigrated to Catalonia having taken this course would officially count as a language course and can give you some benefits). You can either use it for free (all the learning material is available in the free version) or you can use the paying version. In the paid version, you will get assigned a language teacher from Catalonia who can help you and correct you.
There are many more resources. You can find more free resources in this post, this post, or in this link.
Here you have some recommendations to start practising. And remember that you can watch Catalonia's public TV streaming service 3Cat for free from anywhere in the world!
4. I want to follow social media accounts that post in Catalan. Can you tell me some?
Of course! According to the WWW Consortium, Catalan is the 35th most used language on the Internet, out of the more than 7,000 languages in the world.
Here's some lists with recommendations by topic:
Anime and manga
Cooking
Travel accounts
Videogames
Fashion and lifestyle
More lists will be coming soon
If your question wasn't answered, you can send me a question clicking here. 🙂 You can also browse this blog by topics here.
5. Can you recommend other blogs like this one but for other cultures of the world?
Yes, I made a list of recommendations in this post.
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mort du francitan
I'm going to write my master's thesis on the French spoken in Occitanie, so, naturally, I'm doing research on Francitan.
In this article, the author reflects on the evolution of language usage in his region (South-East France). How they had to accept that Occitan was disappearing, but at least there was Francitan, a kind of middle-ground, people pretending to speak French without abandoning Occitan entirely, keeping the prosody and some of the grammar and the lexicon.
But now, with the Parisian influence, through tv and radio, even Francitan is disappearing. The prosody, the phonology, is not what it used to be, and the local worlds are being erased in favour of "good" French words. Even the ones who speak Occitan on tv and on the radio speak it with the music of French.
In the conclusion, René Merle wonders if then, literature is what could save Occitan from total disappearance.. even if it might make it, like Latin, a dead language.
38 notes
·
View notes
Text

Nîmes, France - Posted to X by Pesona @pessonna
Nîmes, a city in the Occitanie region of southern France, was an important outpost of the Roman Empire. It’s known for well-preserved Roman monuments such as the Arena of Nîmes, a double-tiered circa-70 C.E. amphitheater still in use for concerts and bullfights. Both the Pont du Gard tri-level aqueduct and the Maison Carrée white limestone Roman temple are around 2,000 years old.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Papulavis annae Mourer-Chauviré et al., 2023 (new genus and species)

(Type tarsometatarsus [fused ankle and foot bones] of Papulavis annae [scale bar = 1 cm], from Mourer-Chauviré et al., 2023)
Meaning of name: Papulavis = [Gallic priest and namesake of Saint-Papoul, a village near where the original fossil was discovered] Papulus’s bird [in Latin]; annae = for Anne Hauradou [participant in fieldwork at the locality where the original fossil was found]
Age: Eocene (Ypresian), about 52 million years ago
Where found: La Borie, Occitanie, France
How much is known: A single left tarsometatarsus (fused ankle and foot bones).
Notes: Papulavis appears to have been similar to the extant limpkin (Aramus guarauna), a long-legged bird that is closely related to cranes and feeds primarily on snails. The modern limpkin is only found in warm regions of the Americas, so Papulavis might indicate that limpkin-like birds had a much broader distribution during the Paleogene, as is known to have been the case for several other bird groups that are restricted to the tropics and subtropics today.
Reference: Mourer-Chauviré, C., E. Bourdon, S. Duffaud, G. Le Roux, and Y. Laurent. 2023. New avian remains from the early Eocene of La Borie, southern France. Geobios advance online publication. doi: 10.1016/j.geobios.2022.10.004
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Weird Winds: A map of French winds
If you do not know, France doesn't just have one or two or four winds. When you look at the winds of France, you won't just find your typical cardinal division East/West/North/South. Oh no! You will get tons and tons of winds, with all sorts of bizarre names. Each region has its own set of winds, with its own names, meteorological effects, and cultural associations. The result is that people can write entire books about the French winds just by listing them all.
I just found a little website that can serve as a good introduction to the winds of France. It is a website dedicated to learning French when you're a foreigner, and it has one tiny page about the winds of France. It notably offers this simplified map selecting fifteen winds:

Here is the list of the winds, corresponding to the numbers on the map.
Le suroît. A South wind of the Bretagne region, hot and humid.
Le nordet. A Bretagne North wind, that makes the air colder and causes downpours.
La bise. A dry and cold North wind.
La bise. (Yes, they put it twice)
Baslerwind, an Eastern wind of Alsace.
La lombarde. A dry and violent winds of the Alps and the Savoie region.
La tramontane. A violent wind of the Languedoc and the Roussillon.
Le levant. The gentle and humid East wind.
Le ponant. The (usually) soft, Mediterranean West wind.
Le sirocco. The hot wind that carries into France the Sahara sands.
Le cers. The West wind of the Roussillon region, known to scatter clouds away and bring a sunny weather. The cers is considered a componants of the tramontane.
L'autan. An often strong sea wind, that blows in the opposite direction of the tramontane in the Toulouse region and the Tarn. It can be gentler or colder depending on the places.
La tramontane. A cold and strong wind that blows in the Languedoc-Roussillon. It is also the North wind of Provence.
La galerne. A local wind of the Pays Basque, which blows by "hits" (in an irregular way). Through strong gusts, it lowers the temperature and brings rain.
Le mistral. A typical wind of Provence, which also blows in the Var region and in Corsica. It is known to usually blow several days in a row.
The website also had links to other pages that explained in greater details a handful of those winds. I'll put the explanations below:
A) Le Ponant. When it comes to regional Mediterranean winds, le Mistral or la Tramontane usually come to mind - but people tend to forget le Ponant, whose name indicates its position as the West wind. "Ponant" itself is a Latin-inherited term designating the place where the sun sets (opposing the "levant", where the sun rises), and thus in terms of winds, le ponant wind is the west wind, opposed to the Levant wind, the east wind. However, originally, the sailors used "ponant" and "levant" merely as cardinal directions (West/East), and by extension to designate the two bodies of water they travelled across: the Ponant was the Atlantic Ocean, the Levant the Mediterranean Sea. As such, the French sailors called the "Ponant ports" towns such as Brest or La Rochelle, and "Levant ports" Marseille or Sète. It was only afterward that the two terms came to designate the East and West winds.
The Ponant is a western wind with southern components. It is usually soft and gentle, especially when it blows from the south-west, even though it can be strong on the Balearic area. While it blows all year long, it is most present during spring and autumn.
B) Autan. The autan wind is known for its violence by the inhabitants of the Tarn and Toulouse regions. It is even often called "the mad wind" or the "insane wind". The Autan is one of the three local winds of the Occitanie region, alongside the Tramontane and the Marin. While it is mostly focused on Tarn and Toulouse, it can sometimes touch Quercy and Rouerge. The autan is actually the prolongation of the sea-wind blowing on the coasts of the Languedoc-Roussillon. The "triangle" between which the Autan is the most common is formed by Toulouse, Castelnaudary and Castres. It forms the opposite of the tramontane, which comes from the Mediterranean sea. The autan wind can go from 10 km per hour to 90 km per hour in the span of just two hours, and it can come back several times throughout the year.
Legend claims that the autan wind drives people mad - the superstition seems to come from the fact that the autan wind is very local, meaning in a precise area it can blow very strongly, while it is still and peaceful right next door. This is because the Autan is created by the presence of the Pyrénées, the wind being "channeled" by a series of valleys (the Agout valley, the Tarn valley, the Lauragais-Garonne). When the wind arrives from the Mediterranean sea, it is very humid, but by the foehn effect it dries up by going over the Corbières and the Black mountain - and it is only once the wind is dried up that it becomes the "autan". There are actually two types of autan according to local beliefs, the "white" autan and the "black" autan. [Note: the website unfortunately does not give the exact difference between the two]
C) Le Cers. "Le cers" is actually one of the oldest, if not THE oldest wind-name in the French language. Blowing from west to east, this wind regulates and rules the weather of the Languedoc-Roussillon region - more precisely of its western half. This wind, that removes the rain and scatters the clouds, blowing on all season, usually three days by four, is what gives to the region is very sunny and shining weather, and it is thus considered a "healthy" wind. You can even see how the Cers sculpted the region: the trees of the area are all leaning to the east! And the old houses of the area all are turned with their back towards the cers, to prevent heating problems. All the gardens, great openings, pools, terraces and other things of the sort are placed east. The cers is not a mountain wind, but a plain wind, that passes between the Massif central and the Pyrénées, through Naurouze. On the Golfe du Lion, there is absolutely no north wind - only the cers that blows from inside the lands. On the heights of Saint-Cyr, near the towns of Ouveillan and Sallèles-d'Aude, you can find a former Roman temple that was built to the god Circius - aka, the Latin embodiment of the cers wind... And this temple seems to be located precisely at the center of what is known as the sunniest area of all France.
D) La galerne is a well known phenomenon of the Pays Basque region, called "enbata" by the locals, and the terror of the sailors. A "coup de galerne" (a galerne hit) is a brief and local phenomenon of the Pays Basque coasts, which sometimes extends itself to the south of the Garonne region. You recognize a galerne by the sudden degradation of the atmospheric conditions, and a brutal drop in temperature. The wind suddenly blows from the north-west, and it can blow really hard, up to a 100 km per hour and above. All of this is usually happening alongside a gathering of clouds, and outbursts of rain. The galerne can hit all year long, but is most frequent between spring and summer, usually between April and September.
The galerne starts out as a little movement of cold air coming from the Golfe de Cascogne. This movement of the air, carried on by winds, becomes stronger thanks to the mountains that cover the Spanish coasts (the Cantabrique mounts). These mountains force the wind to go towards the Pays Basque, while strengthening it - without these mountains, there wouldn't be any galerne. Since this air comes from the sea, it is colder than the local Basque air, which comes from inland. This is what causes the brutal drop in temperatures - and of course, the humidity of the galerne is also because it is carried from the sea.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
In Saint-Léon close to Bordeaux is located a “laboratory” that gives new life to plastic waste

At the crossroads of contemporary design and the circular economy, the Plastiquerie manufactures sustainable furniture from recycled plastic.
So what do the big yellow and blue bags from Ikea or the construction helmets from the manufacturer Vinci have in common? They are made of a plastic material that can be recycled to make new objects. “Recycled plastic is a material with endless possibilities that I want to make known to designers. It’s a bit like the marble of the Anthropocene”, explains Julie Robert, co-founder of La Plastiquerie [1] based in Saint-Léon[2], about thirty kilometres south-east of Bordeaux.
Shelves, furniture or floor tiles
Since 2021, the independent artistic director has been passionate about this raw material, she has learned the properties of in order to manufacture designer objects and furniture. The association recovers plastic waste in polypropylene (PP)[3], polyethylene (PE)[4] or polystyrene (PS)[5] to give them a second life. “PET[6] waste such as plastic bottles already benefit from recycling solutions. I focus on families of plastics that are still poorly revalued”, she specifies. Protective films, water tubes from construction sites or industry off-cuts from yoghurt pots are thus treated in a 100 m² workshop housed in the premises of the Syndicate of the Entre-deux-Mers-West-region for the Collection and Treatment of Household Waste[7].
There, under a sheet metal shed, a shredder and a hot press transform the collected waste into confetti and then into large recycled plastic plates that will be used to make shelves, furniture or floor tiles. “La Plastiquerie is a laboratory where we develop prototypes of objects resulting from the recovery of plastic. From cans and flowerpots, for example, I imagined a wall light that saves 980 grams of plastic from landfill and incineration,” explains the entrepreneur.
"Companies want to recycle their own waste"
Although the Plastiquerie was co-founded with another woman, Amandine Boutang, Julie Robert now works alone, sometimes helped by an intern and supported by a board of directors, on her experiments with furniture designed in recycled and recyclable plastic. She is thinking about a waste sorting cabinet for the canteen of the Suez[8] headquarters in Occitanie-Nouvelle Aquitaine[9]. For the Bordeaux start-up Arits[10], she is working on the design of a lamp. A bank has also just approached her for an interior design project…
"Companies come naturally to the association because they want to recover their own waste or participate in the circular economy", rejoices the forty-year-old who wants to sharpen her expertise on recycled plastic to convince designers to adopt it. Two years after the launch of her project, Julie Robert draws a positive balance sheet: “I discovered the world of the circular economy where the actors are positive, imaginative people, full of energy and solutions. A world in which a great breath of optimism is sweeping in which I find myself.”
Source
Florence Donnarel, A Saint-Léon, un «laboratoire» pour donner une nouvelle vie aux déchets plastiques, in : Libération, 9-01-2023, https://www.liberation.fr/forums/a-saint-leon-un-laboratoire-pour-donner-une-nouvelle-vie-aux-dechets-plastiques-20230109_72VUV54KQJBBJGALYJ2C2FTORQ/
[1] Plastic is far from fantastic when it comes to recycling. At La Plastiquerie, we collect non-recycled deposits to revalorize them and produce small and medium design series. Its objective: to transform plastic waste into highly desirable objects and furniture! http://www.laplastiquerie.com
[2] Saint-Léon is a commune in the French department of Gironde (Nouvelle-Aquitaine region) and has 242 inhabitants (1999). The place is part of the arrondissement of Bordeaux.
[3] Polypropylene is the second-most widely produced commodity plastic (after polyethylene). In 2019, the global market for polypropylene was worth $126.03 billion.
[4] Polyethylene (generic acronym PE), or polyethene, refers to ethylene polymers. Simple and inexpensive to manufacture, PEs are the most common plastic material, representing with 100 million tonnes, approximately one third of all plastics produced in 20186 and half of packaging.
[5] Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to oxygen and water vapour and has a relatively low melting point.[6] Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year.[7] Polystyrene can be naturally transparent, but can be coloured with colorants. Uses include protective packaging (such as packing peanuts and in the jewel cases used for storage of optical discs such as CDs and occasionally DVDs), containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery,[6] in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records.
[6] Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods, and thermoforming for manufacturing, and in combination with glass fibre for engineering resins.
[7] The Syndicat de l'Entre-deux-Mers-Ouest pour la Collecte et le Traitement des Ordures Ménagères (S.E.M.O.C.T.O.M.) (Syndicate of the Entre-deux-Mers-West-region for the Collection and Treatment of Household Waste was created by prefectural decree of January 28, 1980. It is a closed mixed syndicate governed by the General Code of Territorial Communities and therefore a public service. Bordered to the north and south by two rivers (the Garonne and the Dordogne) which gave the name to the territory of "Entre-deux-Mers", it is located to the south-east of the Urban Community of Bordeaux and is covers an area of 666 km². It partially or totally brings together 7 communities of municipalities as well as part of the Libournais urban community (CALI). It brings together 85 municipalities and more than 110,000 inhabitants. https://www.semoctom.com/web/fr/11-semoctom.php#:~:text=Le%20Syndicat%20de%20l%27Entre,et%20donc%20un%20service%20public.
[8] Suez a Belgian-French company known as GDF SUEZ after 2008. The company was split up, and as of 2008, the 1858-created company's spun-off environmental business continued as a separate company under the Suez name.
[9] https://www.suez.fr/fr-fr/nous-connaitre/notre-presence-en-france/occitanie
[10]The Bordeaux-based startup Arits, which manufactures sun, has imagined a brilliant lamp, which illuminates interiors with an unprecedented technology. The company aims to reproduce the entire cycle of the sun at home. From sunrise to sunset, passing through the Zenith or the Golden Hour..https://arits.fr/
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
Château du Champ
The Château du Champ in Altier in Lozère (France)


The beautiful Château du Champ was first mentioned in 1498 regarding the keep, donjon. The adjacent buildings were built in the 16th century.
DETAILS:
Founded: 1498 Category: Castles and fortifications in France
Château de Castanet (4,4 km)
Château du Champ, Altier, France - SpottingHistory
Château du Champ - Wikidata
Visits: Heritage Days only
PRESENTATION

"The lordship of Le Champ appears in the deeds in 1498. A first campaign of work, at the end of the fifteenth century, concerned the corner tower known as the "keep".
The ensemble formed by the stair tower and the adjacent buildings seems to date back to the sixteenth century. The small-diameter turrets are certainly later, marking an enlargement that may date back to the seventeenth century.
In the nineteenth century, the entrance was transferred from one façade to the other, and the current vestibule was built and roofed. The outer chapel is also recent. The mass of the castle bristles with six towers and turrets. Four of these structures mark the corners of the building. Another divides the largest façade in two. The sixth, inside, houses the staircase. The oldest of these towers, the "keep", supports the wing to the right of the entrance terrace. The keep is the only one with defensive elements." (Mérimée database)
CHATEAU DU CHAMP | Lozère Tourism (lozere-tourisme.com)
Altier: Commune in France
Altier is a commune in the Lozère department in southern France.
Region: Occitania
Altier - Wikipedia
Lozère
Departments of France
Lozère is a landlocked department in the region of Occitanie in Southern France, located near the Massif Central, bounded to the northeast by Haute-Loire, to the east by Ardèche, to the south by Gard, to the west by Aveyron, and the northwest by Cantal. It is named after Mont Lozère.
Area: 5,167 km², Capital: Mende, Communes: 152
Lozère - Wikipedia


Chateau du Champ, France
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Breaking News Business, Economy, Multimedia, Web Development, Science, World
TheEpochTimes: FedEx Splits Into Two to Revive Growth, Stock Jumps
[Quantum Access Cards (QACs) were launched in Canada, Australia and the US, enabling citizens to directly access their QFS accounts.]
[There are many banks exchanging certain currencies including the Iraqi Dinar right now.]
[Big scam! Company "baptized" its conventional products as organic and supplied bakeries - GUILLAUME LE BOULANGER]
[Warning! Europe warns of DANGER from household utensils sold in Hellas - Sinsay brand.]
[Salmonella in tahini – Domino recalls packaged foods containing the contaminated ingredient - R-kioski Oy.]
[Warning! Power Banks that ignite, melt and cause burns – Immediate recall after dozens of complaints - Charmast company.]
Cibum: The fruits and vegetables with the fewest pesticides.
[Satoshi is doing the final BTC bridge so BTC can collapse into Stellar.]
TimesNowNews: Coca Cola Truck Full Of Kids? Video From Chicago Sparks 'Trafficking' Claims
[In the month of December, the Greeks celebrated Dionysus and the light-bearer Apollo-Helios, depicting him on his flying chariot distributing light. The chariot became a sleigh, the horses became reindeer, and the "gift" of light that he distributed to people literally became a "distribution of gifts."]
[First hydrogen car comes to market, charging in 5 minutes and purifying the air as it moves.]
[High levels of “forever chemicals” found in smartwatches from Apple, Google, FitBit, Samsung and other companies.]
[Chocolates - candies: Urgent warning to consumers about dangerous ingredient.]
[Dozens of cheese brands contaminated with listeria – Immediate recall - Wicklow Farmhouse Cheese in Ireland.]
["Extremely misleading!" – They cut an advertisement for gluten-free pasta from TV - the commercial for "Pasta Venere", which the manufacturer Riso Scotti advertises as a pasta that "makes you feel light" because it has 30% less gluten, is misleading!]
NDTV: Covid mRNA Vaccines Contributing To Deaths, Doctors Call For Suspension
GoodNet: All bad loan management companies and funds are controlled by the Money Laundering Authority (Hellas)
[Howling, aggression and seizures in dogs from chew treats – Urgent recall - the product is sold under the name Chrisco Chewy Chicken Rolls.]
[Lidl CZ: "Neither eat it nor… smell it" – In the "dangerous food" category, popular snack - Belbake sultana raisins.]
[According to Dr. Thomas Cowan's book the cosmic heart, the heart is a coiled one-piece organ that does not pump blood in the mechanical sense but acts as a vortex providing the blood with life force that facilitates an electromagnetic toroidal field that spirals around us.]
[Lay's potato chips recalled]
[China begins mass production of AI robots for warehouses and stores. AGIROS, a groundbreaking AI robotics company in China, is now mass-producing robots and integrating them into everyday life at a scale we've only dreamed of. This isn't a glimpse of the future, it's happening right now - I'd like to add - think of UBI - universal basic income.]
SilverWars: Exposed: US Military Engaged in Silver Market
Tass: Russian cancer vaccine to be free of charge — top oncologist It is planned to launch it in general circulation in early 2025
[Kebab – poison with at least 50 patients – The owners of the Marmaris Kebab House restaurant in Abergavenny, Monmouthshire, Wales, have been convicted.]
Flash: "Bomb" with popular carbonated drink: Stopping its production is being seriously considered - Nestlé should consider stopping the production of Perrier mineral water, suggests ARS Occitanie, the Regional Health Service of Occitanie.
[Kraft Heinz, Coca-Cola, PepsiCo, Nestlé and Mars on the stand for conspiracy to create addictive products for children]
WashingtonExaminer: Rep. Anna Paulina Luna (R-FL) waded into a trendy debate on X when she posted, “STOP POISONING OUR FOOD. We must BAN seed oils, high-fructose corn syrup, and other highly processed additives. MAKE AMERICA HEALTHY AGAIN!”
[If you have a log burning stove/fireplace in your house, don't forget top recycle the wood ash.]
Holiday/New Year Sales
Enjoy the offers from the WMS network 🙂 Huge discounts, early-bird prices, amazing prizes, epic announcements, and hot deals from WebMarketSupport and its network. Business-related, multimedia, and more.
Update Dec 13: A few Cyber Week deals are still running. New deals are coming for the Christmas and New Year’s season. My bonuses are valid throughout the duration of these deals.
WebMarketSupport News:
Business Storytelling: Don't Sell, Take People On a Journey. Latest article. Comprehensive analysis and a sneak peek into the innovative storytelling framework "7ID StoryX". The "Story Odyssey" experience unlocked (inside the member's area). Just signup with your email to get access to all the upcoming releases.
Knowledge Economy: Workshop #12 incoming
Look out for the freebie before the workshop (done)
Info product #1 Landing page development with the powerful 7ID StoryX (storytelling framework)
Stay tuned for more!
0 notes
Text

Foix. Vue générale.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Perrier production under threat as report highlights health risks
Perrier bottling plant in Vergèze, where the Bouillens source is located LODI FRANCK/SIPA The most famous of the mineral water brands is in danger of losing the natural mineral water label it has held for more than a century. A confidential report from the Occitanie regional health authority (ARS), World and Radio France’s investigative unit leaves Perrier with no room for any other…

View On WordPress
0 notes