#Rectangular Power Connectors
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Rectangular Connectors | Modular Rectangular Connectors | LAPP India
Explore durable rectangular connectors for reliable industrial applications. High-quality solutions for seamless connectivity at LAPP India. Find yours now!
0 notes
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/interconnect--connector-tools-contacts-accessories/0462-005-20141-te-connectivity-3076065
What is a cable assembly, crimping tool, electrical connector, Crimp tools,
16-18 AWG Size 20 Nickel Plated Crimp Automotive Terminal Contact Socket
#Connectors#Tooling and Accessories#0462-005-20141#TE Connectivity#What is a cable assembly#crimping tool#electrical#circular#USB#PCB#rectangular industrial#SMA RF#Barrier strip#data connector#transmitting power#Wire crimp#socket
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/interconnect--connector-tools-contacts-accessories/770520-1-te-connectivity-7179641
What is a pin header connector, Connectors, socket housing, socket header
AMPSEAL 16-20 AWG Wire to Cable Crimp Socket Contact
#Connectors#Tooling and Accessories#770520-1#TE Connectivity#what is a pin header#socket housing#socket header#rectangular connector#crimp#plug connectors#Power Jacks#crimping tool#USB connectors#IC socket
1 note
·
View note
Text
Industrial connectors, Rectangular Plastic, Rectangular Industrial Connector
DTM Series 2 Position Single Row Male Pin Free Hanging Receptacle Connector
#Connectors#Rectangular Connectors#DTM04-2P#TE Connectivity#industrial connectors#Rectangular Plastic#Rectangular Industrial Connector#rectangular connector housing#connectors#Wire connectors#circuit board power connector#wire-to-board connector 2 pin
1 note
·
View note
Text
RF Electromagnetic Field Radiation Immunity Solution: GTEM Chambers

With the widespread use of electronic devices, electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues have become increasingly prominent. As a result, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing has gained significant attention from companies. EMC testing is a complex process involving control techniques such as shielding, filtering, and grounding, as well as balancing and low-level techniques. Before addressing EMC issues, it is crucial to measure the electromagnetic characteristics of samples using testing equipment or systems to determine the appropriate improvement strategies. Challenges in RF Electromagnetic Field Radiation Immunity Testing: RF electromagnetic field radiation immunity is a critical component of EMC testing but presents several challenges for companies due to high costs associated with the required facilities and equipment. This testing requires an anechoic chamber and RF amplifier equipment. The construction of an anechoic chamber demands substantial space and structural support, typically available only in industrial settings. Additionally, RF amplifiers are often imported and expensive, making such tests difficult to conduct in office environments. To overcome these challenges, GTEM (Gigahertz Transverse Electromagnetic) Chambers have emerged as a cost-effective alternative. GTEM Chambers have seen significant advancements over the past decade. They offer a wide frequency range from DC to several GHz, with a relatively large internal usable area. Importantly, GTEM Chambers and their associated equipment are generally more affordable, making them accessible to a broader range of businesses. What is a GTEM Chamber? A GTEM Chamber is an EMC testing device designed based on coaxial and asymmetric rectangular transmission line principles. To prevent internal electromagnetic wave reflections and resonances, the GTEM Chamber features a tapered design. It uses an N-type coaxial connector at the input, with the central conductor flattened into a fan-shaped plate (called the core plate), creating a rectangular, uniform field area between the core plate and the bottom plate. Key Principles: Electric Field Strength: The electric field strength inside the GTEM Chamber is proportional to the signal voltage V at the N-type connector and inversely proportional to the vertical distance h between the core plate and the bottom plate:E = V/h, In a 50Ω matched system, the voltage relationship V =(RP)1/2 =(50P)1/2 translates to an electric field strength of E =(50P)1/2 / h. A correction factor k is applied to account for discrepancies between measured and theoretical values, resulting in E = k(50P)1/2 / h Design Features: • Distance Between Core Plate and Bottom Plate: The closer the plates, the higher the field strength. Greater distances require higher input power. • Distributed Resistance Matching Network: Ensures a no-reflection terminal for optimal spherical wave (approximately plane wave) transmission characteristics. • Absorbing Material: Absorbing materials are applied to the chamber’s end faces to further absorb electromagnetic waves and ensure uniform field strength. GTEM-2 GTEM Cell Chamber Usage Considerations: • Sample Placement: During testing, the sample should be placed within the test area without exceeding 1/3 of the core plate and bottom plate distance to avoid affecting field uniformity. For smaller samples, position them closer to the GTEM Chamber’s front to achieve adequate field strength with lower signal input power. Advantages of the GTEM Chamber: • Cost-Effective: GTEM Chambers significantly reduce construction and operational costs compared to traditional anechoic chambers and RF amplifiers. • Space Efficiency: They can be installed and tested within office environments, eliminating the need for large industrial facilities. • Broad Applicability: Suitable for various electronic devices, particularly those with moderate dimensions, for RF radiation immunity testing. Conclusion The GTEM Chamber offers a cost-effective solution for EMC testing, overcoming the limitations of traditional methods. It enables companies to conduct RF electromagnetic field radiation immunity tests within constrained spaces and budgets. The adoption of this innovative technology will advance the application and development of EMC testing across a wide range of industries. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
RF Electromagnetic Field Radiation Immunity Solution: GTEM Chambers

With the widespread use of electronic devices, electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues have become increasingly prominent. As a result, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing has gained significant attention from companies. EMC testing is a complex process involving control techniques such as shielding, filtering, and grounding, as well as balancing and low-level techniques. Before addressing EMC issues, it is crucial to measure the electromagnetic characteristics of samples using testing equipment or systems to determine the appropriate improvement strategies. Challenges in RF Electromagnetic Field Radiation Immunity Testing: RF electromagnetic field radiation immunity is a critical component of EMC testing but presents several challenges for companies due to high costs associated with the required facilities and equipment. This testing requires an anechoic chamber and RF amplifier equipment. The construction of an anechoic chamber demands substantial space and structural support, typically available only in industrial settings. Additionally, RF amplifiers are often imported and expensive, making such tests difficult to conduct in office environments. To overcome these challenges, GTEM (Gigahertz Transverse Electromagnetic) Chambers have emerged as a cost-effective alternative. GTEM Chambers have seen significant advancements over the past decade. They offer a wide frequency range from DC to several GHz, with a relatively large internal usable area. Importantly, GTEM Chambers and their associated equipment are generally more affordable, making them accessible to a broader range of businesses. What is a GTEM Chamber? A GTEM Chamber is an EMC testing device designed based on coaxial and asymmetric rectangular transmission line principles. To prevent internal electromagnetic wave reflections and resonances, the GTEM Chamber features a tapered design. It uses an N-type coaxial connector at the input, with the central conductor flattened into a fan-shaped plate (called the core plate), creating a rectangular, uniform field area between the core plate and the bottom plate. Key Principles: Electric Field Strength: The electric field strength inside the GTEM Chamber is proportional to the signal voltage V at the N-type connector and inversely proportional to the vertical distance h between the core plate and the bottom plate:E = V/h, In a 50Ω matched system, the voltage relationship V =(RP)1/2 =(50P)1/2 translates to an electric field strength of E =(50P)1/2 / h. A correction factor k is applied to account for discrepancies between measured and theoretical values, resulting in E = k(50P)1/2 / h Design Features: • Distance Between Core Plate and Bottom Plate: The closer the plates, the higher the field strength. Greater distances require higher input power. • Distributed Resistance Matching Network: Ensures a no-reflection terminal for optimal spherical wave (approximately plane wave) transmission characteristics. • Absorbing Material: Absorbing materials are applied to the chamber’s end faces to further absorb electromagnetic waves and ensure uniform field strength. GTEM-2 GTEM Cell Chamber Usage Considerations: • Sample Placement: During testing, the sample should be placed within the test area without exceeding 1/3 of the core plate and bottom plate distance to avoid affecting field uniformity. For smaller samples, position them closer to the GTEM Chamber’s front to achieve adequate field strength with lower signal input power. Advantages of the GTEM Chamber: • Cost-Effective: GTEM Chambers significantly reduce construction and operational costs compared to traditional anechoic chambers and RF amplifiers. • Space Efficiency: They can be installed and tested within office environments, eliminating the need for large industrial facilities. • Broad Applicability: Suitable for various electronic devices, particularly those with moderate dimensions, for RF radiation immunity testing. Conclusion The GTEM Chamber offers a cost-effective solution for EMC testing, overcoming the limitations of traditional methods. It enables companies to conduct RF electromagnetic field radiation immunity tests within constrained spaces and budgets. The adoption of this innovative technology will advance the application and development of EMC testing across a wide range of industries. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Ensure Clear Sound with an Advanced Audio Cable Tester for Speaker

Ensure Clear Sound with an Advanced Audio Cable Tester for Speaker For musicians, sound engineers, and event planners, ensuring that your audio equipment is functioning correctly is crucial. One overlooked aspect is often the reliability of the cables connecting your gear. An audio cable tester for speaker can be a game-changer, offering peace of mind that your audio setup is working flawlessly. Whether you're setting up for a live performance or recording in the studio, having a reliable audio cable tester is essential. Why You Need an Audio Cable Tester for Speaker Speaker cables are the backbone of any audio setup. They carry the electrical signal from your amplifier to the speakers, and any issue with these cables can result in poor sound quality or even complete failure. An audio cable tester for speaker helps identify issues such as broken wires, incorrect connections, or phase problems before they affect your performance. Key Features of an Audio Cable Tester for Speaker When selecting an audio cable tester, consider the following key features: - Connectivity Options: Look for a tester that supports a variety of connector types, including XLR, 1/4", RCA, and Speakon. This versatility ensures you can test almost any cable in your inventory. - LED Indicators: Brightly colored LEDs indicate signal continuity and which pins are connected together, making troubleshooting quick and straightforward. - Rotary Switch: An easy-to-use rotary switch allows you to select the appropriate test mode for the type of cable you're testing. - Durability: A rugged, compact design ensures the tester can withstand the demands of on-the-go use, whether you're traveling to gigs or working in a studio. - Power Source: Most testers operate on a 9V battery, which should be included, providing convenience and portability. Technical Specifications and Installation Tips To get the most out of your audio cable tester for speaker, here are some technical details and installation tips: - Supported Connectors: 1/4" jack (6.5mm TRS), 1/8" (3.5mm) TRS jack, XLR 3-pin and 5-pin, phono/RCA, banana plugs, Speakon 8P and 4P, DIN 3P/5P/7P/8P, and CAT5. - LED Indicators: Eight green LEDs confirm the continuity of each conductor and indicate proper phase connections. - Rotary Control: An 8-way rotary control simplifies the process of checking signal continuity. - Dimensions: Typically, testers come in a compact rectangular shape, measuring around 185 x 55 x 110mm. - Battery: Operates on a 9V DC battery (included). How to Use an Audio Cable Tester for Speaker Using an audio cable tester is straightforward: - Connect the Cables: Plug one end of the cable into the left and the other into the right side of the tester. - Select the Mode: Turn the rotary switch to the appropriate test mode for the type of cable you are testing. - Check the LEDs: Observe the LEDs to see which pins are connected and to verify signal continuity. - Identify Issues: If any pins fail to light up, you've identified a problem that needs addressing. Benefits of Using an Audio Cable Tester for Speaker An audio cable tester for speaker can save you time and frustration by identifying issues before they become major problems. For instance, the PA System Audio Cable Tester is a robust and reliable tool that ensures your audio connections are always in top condition. Exploring Different Types of Audio Cable Testers While basic testers are sufficient for many applications, some professionals prefer more advanced options with additional features. For example, a 3-way crossover car audio might include extra functions for testing midrange frequencies. Similarly, "audio crossover car" and "car crossover audio" models offer specialized benefits but may vary in terms of specifications and compatibility. Conclusion Investing in an audio cable tester for speaker is a smart move for anyone serious about audio quality. Whether you're a casual user or a professional, a reliable tester can make a significant difference in the performance of your audio setup. Don't let faulty cables ruin your sound—get an audio cable tester today and enjoy crystal-clear audio every time! Read the full article
0 notes
Text
USB A to USB C Adapter For Mac Pro And Mac Studio Models

Mac Pro and Mac Studio
Intelligent, quick, and interoperable gadgets are required more than ever as technology advances. Apple’s latest Mac Pro and Mac Studio models continue its innovation. Speculation in the IT sector suggests a major hardware change for these new versions. If this is implemented, the widely used USB A port may be replaced with USB-C connections, marking the end of an era. This article will discuss the effects of this move on customers, Mac devices, and its likely occurrence.
The Development of USB Ports: A Synopsis
Before discussing the next generation of Mac models, it’s important to understand how USB ports have changed our computing experience. Computers have used USB A, the rectangular connection, for almost 20 years. This reliable connection allows users to connect external storage devices, keyboards, and mice. But as technology developed, so did the demand for better power supply and quicker data transmission rates.
Now introduce USB-C. In contrast to its forerunners, USB-C boasts a more condensed form factor, quicker data transfer rates, improved power supply capabilities, and compatibility with many protocols including Thunderbolt 3 and 4K video output. With time, this all-in-one solution has replaced USB A as the new standard in contemporary electronics.
USB A to USB C
Reasons Apple May Switch from USB-A to USB-C
It is likely, if not certain, that the next Mac Pro and Mac Studio models will switch from USB A to USB-C. Apple would take this change into consideration for a number of strong reasons:
Adopting an International Standard: Apple’s iPad Pro and MacBook Pro employ USB-C, which is becoming the global standard. Apple’s high-performance Mac Pro and Mac Studio would be more consistent with the ecosystem if they used USB-C.
Improved Versatility and Performance: USB-C is more than a connector it enhances device capability and mobility. Users may use Thunderbolt 3’s 40 Gbps data transfer rates with USB-C to quickly transfer large files or backup data. USB-C also improves power transfer, allowing users to charge devices quicker. These improvements would be priceless for professionals who depend on the Mac Pro and Mac Studio for resource-intensive jobs like software development, video editing, and 3D rendering.
Compact and Discreet Design: Compact size is one of USB-C’s most prominent benefits. Apple could be able to lower the overall size of the Mac Pro and Mac Studio or free up space for new features by switching out the bigger USB A ports with USB-C ones. This modification would maintain or perhaps enhance the functioning of existing gadgets while giving them a sleeker, more contemporary appearance.
Investing in the Mac lineup’s future: It is essential for devices to be compatible with new standards as technology develops further. Apple could future-proof the Mac Pro and Mac Studio and make sure they are useful and functioning for many years to come by fully embracing USB-C. In addition to promoting the production of additional USB-C compatible products by peripheral manufacturers, this action would accelerate the uptake of this adaptable interface.
USB A
What to Expect from the Impact on Users
Although there are many advantages to switching from USB A to USB-C, it’s important to think about how owners of the future Mac Pro and Mac Studio models would be affected. The following are some possible ramifications:
Issues with Compatibility and Adapters
The switch to USB-C may require many users to utilize adapters or buy new devices, particularly those who have invested in USB-A peripherals. Even while USB-C may be used with USB-A devices by using adapters, some users may find this extra cost and difficulty to be a disadvantage. Nonetheless, the need for adapters is anticipated to decrease over time as the industry transitions to USB-C as the standard.
Enhanced Efficiency of Workflow
The transition to USB-C might greatly increase workflow productivity for professionals who need fast data transfers and flexible connecting choices. One USB-C connection may be used to connect numerous devices, charge them concurrently, and transmit data, which streamlines user interface and minimizes cable clutter.
Better Interoperability with Devices
The Mac Pro and Mac Studio’s USB-C support should improve device compatibility. As more manufacturers construct USB-C devices, users will have more options for displays and external hard drives. As USB-C peripherals grow more popular, this greater compatibility may also lead to a decrease in price.
A First Step Towards a Portless Future?
Apple has a track record of pushing technological limits and often setting new industry norms. The Mac Pro and Mac Studio’s switch to USB-C may be a sign of things to come a more significant change that may eventually lead to entirely portless gadgets. Although this may seem unrealistic, Apple’s dedication to wireless technology and its ongoing innovation indicate that it may become a reality in the future.
Conclusion
An essential development in Apple’s hardware design is the probable switch from USB-A to USB-C connectors in the next Mac Pro and Mac Studio models. Adopting USB-C is a reasonable move that provides many advantages, from greater performance and adaptability to improved design and future-proofing, as the tech industry continues to evolve. The long-term benefits of USB-C are evident, even if customers used to USB-A may find this switch difficult. It’s certain that USB-C is going to become the norm in computing as we look to the future, and Apple is once again setting the bar.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#usba#USBCAdapter#MacPro#MacStudio#usbc#USCconnections#storagedevices#AppleiPadPro#developmentApple#USBCdevices#Workflow#technology#technews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/interconnect--connectors-rectangular-plastic-industrial/776164-1-te-connectivity-5186781
Wire connectors, cable connectors, pin connectors, power connectors
AMPSEAL 35 Position Latch Lock Crimp Terminal Free Hanging Plug Housing
#TE Connectivity#776164-1#Connectors#Headers and Wire Housings#wire#cable#pin#power connectors#Circuit wire#header plug#header board#socket mount wire#Plug Housing#wire mount socket#electrical wire connectors
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cable Connector Market Growth Insights, Size, Share, Forecast 2024-2032 | SNS Insider
Company and product introductions, market state and development trends by types and applications, price and profit status, marketing status, and market growth drivers and challenges are all covered, as well as industry forecasts, global major players/suppliers, and regional market share. Definitions, classifications, applications, and market overviews were covered first, followed by product specifications, manufacturing processes, cost structures, and raw materials. The Cable Connector market research report is a comprehensive and expert assessment of the world's major regional market conditions, with a focus on the world's most important regions and countries. The inquiry included a SWOT analysis of a new project, an investment feasibility assessment, and an investment return analysis.
The research then looks at Cable Connector Market conditions in major regions throughout the world, taking into account things like product price, profit, production, supply, demand, and market growth rate and forecast, among other things. The purpose of this research is to look at the current state of the market as well as potential income opportunities. It examines the entire market ecosystem, including technological advances, applications and end-users, product offerings, regulatory environments, and market growth plans.
Download the Sample Pages of this Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/2399
Market Segmentation
The global Cable Connector market is segmented by market player, region, type, application, and other factors, with bespoke research available to meet specific needs. A SWOT analysis of the market is included in the study. Finally, there is a section of the report devoted to the study's conclusion, which includes the viewpoints of industry professionals.
BY PRODUCT TYPE
Internal Cables and Connectors
External Cables and Connectors
BY TYPE
PCB Connectors
Fiber Optic Connectors
Circular/Rectangular Connectors
I/O Connectors
BY VERTICAL
IT & Telecommunication
Commercial
Consumer Electronics
Energy & Power
Automotive
Aerospace & Defense
Industrial
Oil & Gas
Key Players
The company profiles are contained in this research study. Capacity, production, revenue, cost, gross margin, sales revenue, consumption, growth rate, supply, future strategies, and technology upgrades are all aspects to consider. This study examines the Cable Connector market in detail, including the competitive landscape, future development possibilities, and potential threats, as well as information on a wide range of industry participants. Market participants, raw material suppliers, equipment suppliers, end users, traders, distributors, and others are among the major market players studied in the report.
Amphenol Corporation
Fujitsu Limited
AMETEK
HARTING Technology Group
Axon Cable SAS
Yazaki Corporation
Molex
AVX Corporation
TE Connectivity Limited
Huawei Technologies
Leoni AG
Buy Now: https://www.snsinsider.com/checkout/2399
Key Reasons to Buy Cable Connector Market Report
Assess manufacturing techniques, significant challenges, and treatments to reduce the risk of development.
To have a deeper grasp of the most essential business driving and restraining forces, as well as their impact on the global market.
Research the marketing strategies used by the most successful businesses in the target market.
We may do bespoke research in addition to basic structural studies to meet your individual needs.
Conduct in-depth market research to have a thorough understanding of the global market and its commercial landscape.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company’s aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand — Head of Business Development & Strategy
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +1–415–230–0044 (US) | +91–7798602273 (IND)
0 notes
Text

Connectors and Interconnector types: Rectangular Connectors. Circular Connectors. Terminal Blocks. Coaxial Connectors (RF) D-Sub, D-Shaped Connectors. Barrel Audio/Power Connectors. Pluggable Connectors. USB, DVI, HDMI Connectors. https://www.allinonecomponents.com/product-category/main-categories/connectors-20
0 notes
Text
Introduction of Motherboard for Laptop
The motherboard for a laptop is the main circuit board that connects all of the other components of the computer together. It provides the platform for the CPU, RAM, and other components to communicate and work together. The motherboard also contains connectors for the display, keyboard, mouse, and other peripherals.
In a laptop, the motherboard is typically smaller than in a desktop computer due to space constraints. It is usually located beneath the keyboard or behind the screen, depending on the design of the laptop. The motherboard in a laptop is designed specifically for that model of laptop, so it is not interchangeable with other models or brands.
The motherboard for a laptop includes several key components, including the CPU socket, RAM slots, and chipset. The CPU socket is where the processor is installed and connects to the rest of the motherboard. The RAM slots are where the memory modules are installed and provide the computer with its working memory. The chipset manages the flow of data between the different components of the computer, ensuring that they work together smoothly.
Other components that may be included on a laptop motherboard include the graphics card, sound card, and network card. These components are often integrated into the motherboard to save space and reduce power consumption.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Motherboard for Laptop Choosing the right motherboard for a laptop is an important decision, as it can greatly affect the performance and capabilities of the computer. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a motherboard for a laptop:
Compatibility: It is essential to ensure that the motherboard is compatible with the other components of the laptop, such as the CPU, RAM, and storage. Most laptop motherboards are designed specifically for a particular model or series, so it is important to choose the correct one.
Size and Form Factor: The size and form factor of the motherboard will determine how well it fits in the laptop and how many components it can support. Make sure to choose a motherboard that fits within the laptop's dimensions and supports the components needed for your specific needs.
Connectivity and Ports: The number and type of ports on the motherboard are important for connecting external devices such as USB drives, Ethernet cables, and audio devices. It is important to choose a motherboard that has the necessary ports for your needs.
Quality and Reliability: Choose a motherboard from a reputable manufacturer with a good track record for quality and reliability. This will ensure that the motherboard is built to last and will provide reliable performance.
Expansion Options: Consider future expansion needs when selecting a motherboard. Look for a motherboard that has additional expansion slots for adding more RAM, storage, or other components as needed.
Price: Finally, consider the price of the motherboard and ensure that it fits within your budget. Remember that a higher-priced motherboard may offer better features and performance, but it may not always be necessary depending on your usage requirements.
Understanding the Motherboard Form Factor The physical size and layout of the motherboard, as well as the arrangement of components and ports, are referred to as the motherboard form factor. Different form factors are designed for different types of computers, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended): This is the most common form factor for desktop computers. It is a large rectangular board measuring 12 x 9.6 inches and supports up to 7 expansion slots. ATX motherboards typically have more ports and connectors than smaller form factors, making them suitable for gaming or multimedia systems.
Micro-ATX: This form factor is smaller than ATX and measures 9.6 x 9.6 inches. Micro-ATX motherboards typically have fewer expansion slots and ports than ATX, but they are more affordable and can be used in smaller cases.
Mini-ITX: This is the smallest form factor for desktop computers and measures 6.7 x 6.7 inches. Mini-ITX motherboards are designed for use in small form factor or mini PC builds and typically have only one expansion slot and a limited number of ports.
ITX (Information Technology eXtended): This form factor is designed for industrial or embedded computing applications. It is similar to Mini-ITX in size but has more expansion slots and ports for greater flexibility.
E-ATX (Extended ATX): This is a larger form factor than ATX and measures 12 x 13 inches. E-ATX motherboards are designed for high-end gaming or workstation systems that require multiple expansion slots and high-performance components.
When selecting a motherboard, it is important to choose a form factor that is compatible with the case and other components in your system. Each form factor has its own advantages and limitations, so it is important to consider your specific needs and requirements before making a decision.
Ports and Features of Motherboard for Laptop The ports and features of a motherboard for a laptop can vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer. However, there are some common ports and features that are often found on laptop motherboards:
CPU socket: This is the socket where the processor is installed. It can vary depending on the CPU model, so it is important to choose a motherboard that is compatible with your CPU.
RAM slots: These are slots where the memory modules are installed. The number and type of RAM slots can vary depending on the motherboard, so it is important to choose a motherboard that supports the amount of memory you need.
Storage connectors: These connectors allow you to connect storage devices such as hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs) to the motherboard. Common storage connectors include SATA and M.2.
Graphics connector: This connector allows you to connect an external display to the laptop. Common graphics connectors include HDMI, DisplayPort, and VGA.
USB ports: These ports allow you to connect USB devices such as mice, keyboards, and external hard drives to the laptop. The number and type of USB ports can vary depending on the motherboard.
Audio connectors: These connectors allow you to connect headphones, speakers, or a microphone to the laptop. Common audio connectors include headphone jacks and microphone jacks.
Network connectors: These connectors allow you to connect the laptop to a wired or wireless network. Common network connectors include Ethernet ports and Wi-Fi antennas.
Other features that may be included on a laptop motherboard include integrated graphics, sound, and network cards, as well as additional expansion slots for adding more components or upgrading the system. It is important to choose a motherboard that has the necessary ports and features for your specific needs.
Conclusion The motherboard is the heart of a laptop, and selecting the right one is crucial for building a high-performance and reliable system. When choosing a motherboard, it is important to consider factors such as compatibility, form factor, connectivity and ports, quality and reliability, expansion options, and price. Additionally, it is important to be aware of the different ports and features that are available on laptop motherboards, such as CPU sockets, RAM slots, storage connectors, graphics connectors, USB ports, audio connectors, and network connectors. By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right motherboard for your laptop that meets your needs and provides excellent performance and reliability.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Decoding Flowchart Symbols: Key Elements You Need to Know
Flowcharts are powerful tools used across various industries to visualize processes, identify bottlenecks, and improve efficiency. They use a standardized set of symbols to represent different steps, actions, decisions, and outcomes within a process. Understanding these flowchart symbols is essential for effectively interpreting and creating flowcharts. Let's dive into the key elements of flowchart symbols and what they represent:

Start/End Symbol: The oval shape represents the beginning or end of a process. It's where the flowchart starts or concludes. This symbol typically contains the word "Start" or "End" inside the oval shape, clearly marking the initiation or conclusion of the process flow.
Process Symbol: This rectangular shape signifies a specific task, action, or operation within the process. It represents a step that needs to be performed, such as data entry, calculations, or a decision point. The process symbol is where the actual work or activity takes place.
Decision Symbol: Often depicted as a diamond shape, the decision symbol represents a point in the process where a question is asked, and the flowchart splits into different paths based on the answer. This symbol typically contains a yes/no question or a condition that determines the next course of action.
Input/Output Symbol: Shaped like a parallelogram, the input/output symbol indicates where data enters or exits the process. It represents interactions with external sources, such as user input, data storage, or the display of information. Input/output symbols are crucial for understanding how information flows into and out of the process.
Flow Arrows: Arrows connect the various flowchart symbols, indicating the direction of the process flow. They show the sequence of steps and the logical progression from one symbol to another. Arrows ensure that the flowchart is easy to follow, guiding the reader through each stage of the process.
Connector Symbol: The connector symbol is a small circle used to indicate a jump from one part of the flowchart to another, usually to avoid clutter or repetition. It helps streamline complex flowcharts by connecting different sections while maintaining readability.
Terminator Symbol: Sometimes referred to as the "Stop" symbol, this symbol marks the end of a process flow. It's similar to the start/end symbol but is used specifically to conclude a particular branch or sequence within the flowchart.
Understanding these fundamental flowchart symbols enables individuals to interpret and create flowcharts effectively. Here's how these symbols come together to represent a process:
Imagine you're visualizing a simple ordering process for an online store:
Start: Oval symbol labeled "Start."
Process: Rectangular symbol indicating "Receive Order."
Decision: Diamond symbol with the question "Is the item in stock?"
Yes path leads to "Pack and Ship Item" process.
No path leads to "Notify Customer" process.
Input/Output: Parallelogram symbol for "Update Inventory."
Connector: Circle symbol indicating a jump to "Send Confirmation Email."
Process: Rectangular symbol for "Complete Order."
End: Oval symbol labeled "End."
In this example, each symbol represents a specific action or decision within the ordering process, connected by arrows to show the sequential flow of activities.
By mastering these flowchart symbols, individuals can map out processes, identify inefficiencies, and communicate complex workflows in a clear and structured manner. Whether you're analyzing an existing process or designing a new one, flowcharts serve as invaluable tools for process optimization and decision-making.
youtube
In conclusion, understanding flowchart symbols is essential for effectively communicating processes and workflows. By leveraging these symbols, individuals can visualize complex processes, streamline operations, and drive continuous improvement within organizations. Flowcharts empower teams to collaborate, optimize processes, and make informed decisions based on clear process representations. Start decoding flowchart symbols today to unlock the potential of process visualization and optimization in your work or projects.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Procurement Kpis - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
1 note
·
View note
Text

Types of USB Cables
USB cables come in various types, each designed for specific purposes and devices. Here are some common types of USB cables:
USB-A to USB-B: This type of cable is commonly used to connect peripherals such as printers, scanners, and external hard drives to a computer. USB-A is the standard rectangular USB connector found on most computers and chargers, while USB-B is a square or rectangular connector often used for peripherals.
USB-A to USB-C: This cable is becoming increasingly popular due to the rise of USB-C devices. It connects devices with USB-C ports (such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and external hard drives) to devices with USB-A ports (such as computers, chargers, and power banks). USB-C connectors are smaller and reversible, making them more convenient than traditional USB-A connectors.
USB-C to USB-C: This cable features USB-C connectors on both ends, making it ideal for connecting two devices with USB-C ports. It is commonly used to charge smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other devices that feature USB-C charging ports. USB-C to USB-C cables can also be used for data transfer between compatible devices at high speeds.
USB-A to Micro-USB: This cable is commonly used to charge and sync older smartphones, tablets, cameras, and other devices with Micro-USB ports. The USB-A connector plugs into a computer, charger, or power bank, while the Micro-USB connector plugs into the device.
USB-C to Micro-USB: This cable allows you to connect devices with USB-C ports to devices with Micro-USB ports. It is commonly used to charge and sync newer smartphones, tablets, and other devices with USB-C ports using chargers or cables with Micro-USB connectors.
USB-C to Lightning: This cable is designed specifically for Apple devices. It connects devices with USB-C ports (such as newer MacBook models) to devices with Lightning ports (such as iPhones, iPads, and AirPods). It is used for charging, data transfer, and syncing between compatible devices.
USB-A to Lightning: Another Apple-specific cable, this one connects devices with USB-A ports (such as computers, chargers, and power banks) to devices with Lightning ports (such as iPhones, iPads, and AirPods). It is used for charging, data transfer, and syncing.
These are some of the most common types of USB cables available, each serving specific purposes and compatible with different devices and ports. When choosing a USB cable, it's essential to consider the type of devices you need to connect and the specific ports they feature.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Industrial Cable Connectors A Beginner's Guide?

Introduction
Industrial cable connectors are vital components in various industries, facilitating the seamless connection of cables in complex systems. While their significance is undeniable, understanding these connectors might seem daunting for beginners. Fear not! This beginner's guide aims to demystify industrial cable connectors, breaking down their types, functions, applications, and key considerations.
Chapter 1: What are Industrial Cable Connectors?

Industrial cable connectors are specialised components used to join cables securely, ensuring efficient transmission of power, signals, or data in industrial settings. Unlike regular connectors, industrial-grade connectors are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, high temperatures, vibrations, and moisture. They come in various shapes, sizes, and configurations to suit diverse applications.
Chapter 2: Types of Industrial Cable Connectors
Rectangular Connectors: These connectors feature rectangular housings and are commonly used in industrial automation, machinery, and control systems.
Circular Connectors: Circular connectors, as the name suggests, have circular housings and are prevalent in aerospace, military, and transportation industries due to their robustness and reliability.
Coaxial Connectors: Coaxial connectors are used for transmitting radio frequency signals and are found in telecommunications, broadcasting, and medical equipment.
Ethernet Connectors: Ethernet connectors facilitate the transmission of data in industrial Ethernet networks, supporting high-speed communication between devices.
Power Connectors: Power connectors are designed to handle high voltage and current levels, commonly used in industrial machinery, power distribution systems, and renewable energy applications.
Chapter 3: Functions and Applications
Industrial cable connectors serve various functions depending on their type and design. Some common functions include:
Power Transmission: Power connectors transmit electrical power from a source to machines or equipment.
Signal Transmission: Connectors for signal transmission ensure reliable communication between devices, sensors, and control systems.
Data Transmission: Ethernet connectors enable the exchange of data between computers, PLCs, and other networked devices.
Environmental Protection: Industrial connectors provide protection against dust, moisture, chemicals, and mechanical stress, ensuring uninterrupted operation in harsh environments.
Modularity and Flexibility: Modular connectors allow for easy installation, maintenance, and reconfiguration of industrial systems, reducing downtime and costs.
Chapter 4: Key Considerations
When selecting industrial cable connectors for a specific application, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability:
Environmental Conditions: Assess the operating environment, including temperature extremes, moisture levels, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, to choose connectors with suitable ingress protection (IP) ratings.
Electrical Requirements: Determine the voltage, current, frequency, and signal characteristics to select connectors capable of handling the specified parameters without overheating or signal degradation.
Mechanical Compatibility: Ensure compatibility between connector types, sizes, mounting options, and mating interfaces to facilitate easy installation and maintenance.
Reliability and Durability: Choose connectors from reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality, durable components tested for reliability under real-world conditions.
Cost and Lifecycle Considerations: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including initial procurement costs, maintenance expenses, and expected lifespan, to make informed decisions about connector selection and replacement intervals.
Chapter 5: Common Challenges and Solutions
Despite their robustness, industrial cable connectors may encounter challenges such as:
Connector Mismatch: Incompatible connectors from different manufacturers can lead to mating issues and poor connectivity. Solution: Standardise connector types and brands within industrial systems to ensure compatibility.
Environmental Damage: Exposure to harsh conditions can cause connector degradation, corrosion, or insulation failure. Solution: Use connectors with appropriate IP ratings, sealing mechanisms, and protective accessories to shield against environmental hazards.
Vibration and Shock: Vibrations and mechanical shocks in industrial environments can loosen connections and compromise signal integrity. Solution: Employ locking mechanisms, strain relief features, and vibration-resistant connectors to secure cables and prevent accidental disconnection.
EMI and Crosstalk: Electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk can disrupt signal transmission in industrial networks, leading to data errors or system malfunctions. Solution: Shielded connectors, twisted-pair cables, and proper grounding techniques help mitigate EMI and crosstalk effects, ensuring reliable communication.
Chapter 6: Future Trends and Innovations
The landscape of industrial cable connectors continues to evolve with advancements in materials, design, and connectivity standards. Emerging trends and innovations include:
Miniaturization: Shrinking connector sizes enable compact and lightweight designs suitable for space-constrained industrial applications.
High-Speed Data Transmission: Next-generation connectors support faster data rates and higher bandwidths, meeting the demands of Industry 4.0 and IoT-enabled systems.
Smart Connectors: Integration of sensors, RFID tags, and diagnostic features in connectors enables real-time monitoring of connection status, performance, and predictive maintenance.
Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing technologies allow for rapid prototyping and customization of connectors, reducing lead times and enabling on-demand production of bespoke connector designs.
Conclusion
Understanding industrial cable connectors is essential for anyone working with electrical, electronic, or mechanical systems in industrial environments. By familiarizing yourself with the types, functions, applications, considerations, challenges, and innovations in industrial connectors, you can make informed decisions when selecting, installing, and maintaining connectors for your specific needs. Whether you're an engineer, technician, or enthusiast, this beginner's guide equips you with the knowledge to navigate the world of industrial cable connectors with confidence and expertise.
0 notes
Text
New gear for 2024: KL-Aeolus is the one
Transparent cases have been prevailed for years with it stunning panoramic view through their tempered glass side panels. These cases look appealing to so many RGB lighting lovers.

But most of the transparent cases in the market are focusing on their appearance instead of on their utilization.So high-performance hardware can’t be adopted as a result of the limited space inside the cases. This stops users from buying the cases. However, this awkward situation in the DIY industry has been solved by Segotep’s new case KL-Aeolus, presenting an exquisite transparent case with both aesthetics and expandability.
As shown in the photos, this is the white version of KL-Aeolus, which is the mostly welcomed by users. When putting this case on a simple and white desk, you will certainly associate it with an exquisite life.

Measuring 476mm*230mm*497mm, KL-Aeolus is standard mid-tower case. It is a good choice for users who can only provide limited room for their cases on or beneath their desks, especially students.

With an overall rectangular design, KL-Aeolus is built with 3 window as its front panels who can be opened to an angle of up to 10 degree,bringing more air for heat dissipation inside. This is why this case was given the name of Aeolus. More air intake will certainly help lower the temperature of the hardware inside the case. And if you need the computer to work quietly, you just need to shut all the windows.
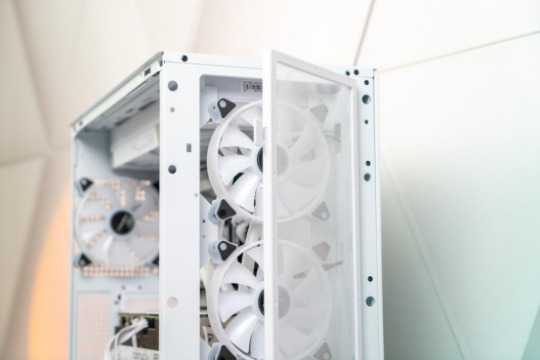
After removing the front panel, there is a dust filter inside. With snap-fit locks for easy attaching/detaching, the filter effectively prevents the case from dust that may cause damage to the hardware.


The TG glass left panel can be easily handled without tools. What’s more, shock pads on the rims of the panel just ensure the glass will not be broken by over-force.

The I/O panel provides 2pcs of USDB 3.0, 1pcs of 3.5mm Audio jack and a Type-C connector with a maximum speed of 10Gbps. These connectors cover all our daily use with wired or wireless devices.

KL-Aeolus supports ATX, M-ATX and ITX motherboards. When assembled with an M-ATX motherboard, the space inside the case is still quite ample. Users don’t have to worry about the room for other hardware even if they get an ATX motherboard.

The case is compatible with many kinds of liquid coolers. You can even fit in a 360mm AIO for the CPU and a 360mm closed loop AIO for the GPU at the same time.It depends on your requirements. And we are going to build a system as a way of demonstration. In order to make the case look amazing while ensuring its heat dissipation, we have adopted a powerful white KL-360 AIO which belongs to Kunlun family, a high-end series by Segotep.


As a mid-tower case, KL-Aeolus provides a large space for the GPU. Even a RTX4090(not founder’s edition) of 4 PCIe slots can be easily fit into the case with 7 slots.There is a GPU bracket included to help avoid any bending of the mobo by the heavy GPU. If you want to mount the GPU vertically, you can buy an extra PCIe 4.0 adapter.


PSU installation is always a headache for starters. If the PSU housing is too small, two awkward situations would happen: it’s difficult to fit the PSU with all cables connected into the bottom of the case, or difficult to connect cables onto the PSU which is already fastened on the bottom of the case. But KL-Aeolus successfully solves these problems with a detachable PSU bracket in its rear panel.


After removing the right panel, we can find the ample routing space for cables even this case is not so wide. Slots in the plates will certainly facilitate the routing of fan cables.


As the debossed marking suggests, a drive can be mounted vertically onto the internal plate. But the FAN legend means it also supports a placement of a 12mm fan which is to lower the temperature behind the PCB.
Many users can’t help ask: how is the heat dissipation capability of such a big case? Well, we can going to build a system with 12700KF and RTX 4070 to find out.

Firstly, we tested the system with AID64. As we can heard,the cooling system was at its full speed when the system was fully loaded with the PCU temperature around 70 to 80℃. This welcoming result was delivered by the vents design of the case.
Secondly, the pc was tested with Furmark. The core temperature of GPU red 56 to 66℃, without any clock frequency lowering.

When it comes to the noise, we tested with 3 games because we knew that on one builds a system just to run AID64 and Furmark. During the gaming test, the noise generated by the cooling system was low even you put your ear against the case panels. So gamers will not be disturbed by the noise even they put their computer on the desk.
In a word, KL-Aeolus is a well-designed case for even picky users. It provides solutions for difficulties users will encounter during the building process, for examples, tool-less panels for easy hardware upgrade and ample space for clean cable routing. As an experienced hardware manufacturer, Segotep has made the best us of this mid-tower case. What’s more, RGB lovers can enjoy the panoramic view of the hardware they built inside the case. If you are looking for a beautiful and useful case, KL-Aeolus is the one!
0 notes