#RFID hospital inventory management
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text
Surgical Instrument Tracking: Revolutionizing Modern Surgery The Indispensable Role of Minimally Invasive Techniques
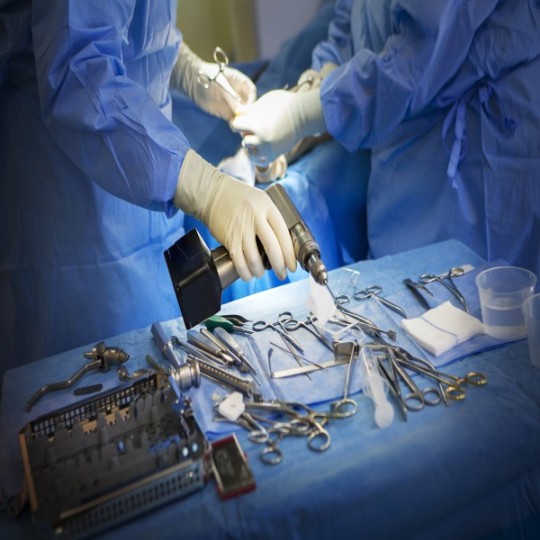
The Importance of Instrument Tracking in Surgery Surgery is an intricate and complex medical procedure that requires precision from medical professionals. From the first incision to the final stitch, countless surgical instruments are used inside the sterile operating field. With so many tools being passed between surgeons and nurses, it’s easy for an instrument to get misplaced or left inside the patient unintentionally. This presents serious risks to patient health and safety. To mitigate these risks, hospitals have increasingly adopted surgical instrument tracking systems. Surgical sponges and other small items left inside patients after surgery, known as retained surgical items or “gossips”, remain a serious problem. Studies show retained items occur in about 1 in every 5,500 to 18,000 surgeries performed. While rare, when they do happen the consequences can be life-threatening or disfiguring for the patient. Not only that, but unintentionally retained items also expose hospitals to legal liability and malpractice claims amounting to millions of dollars each year. Comprehensive surgical instrument tracking helps prevent such incidents from occurring in the first place. How Instrument Tracking Systems Work Modern Surgical Instrument Tracking systems use advanced radio-frequency identification (RFID) or barcode scanning technology to account for each instrument used during a procedure. Small RFID or barcode tags are attached to individual instruments. As instruments are brought into and out of the operating room, they are scanned into a dedicated tracking computer or software system. Before closing the surgical incision, staff perform a final instrument and sponge count using the tracking system. Any discrepancies between what was scanned into the room versus what is accounted for after surgery trigger an alert. This final count helps provide a clear audit trail confirming all items were properly removed from the patient’s body before stitching up the incision. The Benefits of Instrument Tracking Implementing a comprehensive instrument tracking solution yields several important benefits for hospitals: Patient Safety - As mentioned, accurate accounting for all items used during surgery helps prevent life-threatening retained surgical items. Instrument tracking adds an extra layer of safety for patients. Reduced Risk of Liability - Clearly documenting the use and removal of all items helps protect hospitals legally if questions ever arise about whether something was unintentionally left inside a patient. Increased Revenue - Fewer medical malpractice lawsuits related to retained items means less payouts and legal expenses for hospitals over time. Less time is also spent managing liability issues. Process Efficiencies - Automatic identification and counting of instruments streamlines perioperative workflows. Less time is spent manually counting items, searching for missing objects, or filling out paperwork. Staff can instead focus on direct patient care tasks. Asset Management - Tracking technologies provide real-time visibility into instrument locations and usage. This information helps with equipment maintenance planning, usage reports, and inventory management across the hospital system. Overall, a well-designed surgical instrument solution should save hospitals money in the long run through reduced risk and greater process efficiencies, while more importantly enhancing patient care and safety. When implemented and utilized comprehensively, these systems have been shown in studies to virtually eliminate unintended retained surgical items.
Get more insights on Surgical Instrument Tracking
For Deeper Insights, Find the Report in the Language that You want.
French
German
Italian
Russian
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Portuguese
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)
#Surgical Instrument Tracking#Medical Device Tracking#Surgical Tool Management#Instrument Traceability#Hospital Inventory#RFID Tracking#Surgical Asset Management#Barcode Tracking
0 notes
Text
The Evolution of Tracking: How Barcode, RFID, and RTLS Improve Business Operations

Introduction: Tracking and managing assets has evolved dramatically over the years. What started with manual systems has now progressed to advanced tracking with barcodes, RFID, and RTLS. This article breaks down how these innovations are shaping the future of business operations.
1. Barcode Technology: The Foundation of Modern Tracking
How barcodes simplified inventory and asset management.
Key benefits: Cost-effective, simple, and widely used.
Applications across industries.
2. RFID: The Future of Smart Tracking
How RFID enhances tracking efficiency.
Benefits: No line-of-sight required, automation, and scalability.
Real-world applications in logistics, manufacturing, and retail.
3. RTLS: Instant Location Tracking for Businesses
What makes RTLS different from barcodes and RFID.
Benefits: Real-time location data, operational visibility, and security.
Use cases in hospitals, factories, and supply chains.
4. Combining Barcode, RFID, and RTLS for a Unified System
How integrating these technologies leads to better decision-making.
Why businesses should invest in multi-layered tracking systems.
Conclusion: Tracking technologies continue to evolve, helping businesses stay efficient, reduce costs, and improve accuracy. The combination of Barcode, RFID, and RTLS offers a complete solution for modern enterprises.
#asset management#barcode#qr code#technology#electronic devices#aidc#aidc technologies india#real time tracking#barcode printers
0 notes
Text
Choosing the Right Real-Time Location System for Your Business
Introduction
Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) have transformed business operations by providing precise tracking and monitoring capabilities. Whether you're in manufacturing, healthcare, or logistics, selecting the right RTLS can significantly impact efficiency and profitability.
Understanding Real-Time Location Systems
What is RTLS?
RTLS is a technology used to track and manage the real-time location of assets, personnel, and equipment within a defined space.
How It Works
RTLS employs various tracking technologies to continuously update the location of tracked items.
Technologies Behind RTLS
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) – Uses radio waves for tracking.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) – Ideal for short-range tracking.
Ultrawideband (UWB) – Provides high accuracy.
Infrared (IR) & GPS – Used for precise location mapping.
Types of RTLS Technologies
RFID – Best for warehouse and inventory tracking.
GPS – Used for outdoor vehicle and asset tracking.
BLE – Efficient for workplace and hospital applications.
UWB – High precision for industrial applications.
Infrared – Common in healthcare for patient tracking.
Key Features of an Effective RTLS
Accuracy – Determines how precise the tracking data is.
Scalability – Ensures the system can grow with your business.
Integration – Works seamlessly with existing enterprise systems.
Cost-effectiveness – Balances budget and performance.
Industries Benefiting from RTLS
Manufacturing – Streamlines production and asset management.
Healthcare – Enhances patient safety and staff efficiency.
Logistics – Optimizes warehouse operations and fleet tracking.
Retail – Improves inventory management and customer experience.
Security – Strengthens access control and personnel tracking.
Choosing the Right RTLS for Your Business
Business Needs Analysis
Identify the key objectives for implementing RTLS in your organization.
Compatibility
Ensure the chosen system integrates with existing software.
Budget Considerations
Evaluate costs including installation, maintenance, and future scalability.
Implementation Process
Planning – Assess needs and define goals.
Deployment – Install hardware and software components.
Testing – Validate performance and accuracy.
Optimization – Fine-tune the system for peak efficiency.
Benefits of RTLS
Enhanced Visibility – Real-time tracking improves decision-making.
Operational Efficiency – Reduces downtime and optimizes processes.
Cost Savings – Minimizes asset loss and increases productivity.
Challenges in RTLS Adoption
Data Security Risks – Ensuring encryption and privacy.
Initial Investment – Managing setup and infrastructure costs.
Ongoing Maintenance – Regular updates and system checks.
Case Studies of RTLS in Action
Manufacturing Industry
Company X improved inventory accuracy by 30% using RFID-based RTLS.
Healthcare Sector
Hospital Y reduced patient wait times by 40% with BLE tracking.
How Intellistride’s RTLS Solutions Stand Out
Industry-Leading Accuracy – Advanced tracking algorithms.
Customizable Solutions – Tailored for different business needs.
Scalability & Support – Future-proof technology with ongoing assistance.
Future Trends in RTLS
AI & Machine Learning – Enhancing tracking intelligence.
5G & IoT Integration – Improving connectivity and performance.
Advanced Data Analytics – Providing actionable insights.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of RTLS?
RTLS helps businesses track and manage assets, personnel, and equipment in real-time, improving efficiency and security.
2. Which industries benefit the most from RTLS?
Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and retail greatly benefit from RTLS implementation.
3. What factors should I consider when choosing an RTLS solution?
Key considerations include accuracy, scalability, integration with existing systems, and overall cost.
4. How long does it take to implement an RTLS solution?
The implementation timeline varies based on complexity but generally ranges from a few weeks to several months.
5. Are RTLS solutions expensive?
Costs vary depending on technology and scale, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
6. Can RTLS integrate with existing business software?
Yes, modern RTLS solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with ERP, WMS, and other enterprise systems.
Conclusion
Choosing the right RTLS is critical for business success. By understanding your needs and evaluating available solutions, you can enhance efficiency and drive growth. Intellistride’s RTLS solutions offer reliability, scalability, and advanced technology tailored to your industry’s needs.
0 notes
Text
RFID in Healthcare: Key Trends, Innovations, and Market Opportunities
The global RFID In healthcare market size is expected to reach USD 14.65 billion by 2030 and register a CAGR of 17.85% from 2023 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. The need to increase the quality and effectiveness of healthcare as well as the rising focus on reducing operational costs and streamlining the workflow are some of the major drivers for the market growth.
Pharmaceutical companies, medical device providers, hospitals, and other such organizations are integrating this technology to help control their inventory costs. RFID tags assist with efficient inventory management, preventing stockouts and overstocking. Furthermore, they provide surgical staff with a way of easily tracking medical devices used in operation theatres, thereby enhancing patient safety. As organizations strive to reduce their operational costs, they are increasingly turning to RFID technology. This technology is also used in laboratories, blood banks, and pathology labs to facilitate product tracking and streamline workflow.
Moreover, radio-frequency identification technology-enabled systems are being used to effectively track and monitor pharmaceuticals, which is becoming increasingly important due to the prevalence of drug counterfeiting and theft. Pharmaceutical companies and law enforcement can mitigate these problems, as well as ensure that patients receive the right medications with this technology. For instance, the Pharmaceutical Security Institute revealed that in 2020, 4,344 cases of counterfeiting, unauthorized distribution, and theft of pharmaceuticals were identified across 137 nations. These crimes involved many types of drugs, with more than 2,451 different medications from all therapeutic categories being impacted. This emphasizes the importance of implementing RFID tracking solutions.
Growing demand for technologically advanced healthcare systems, remote patient monitoring services, and increasing investments by healthcare IT players are some of the other factors expected to propel the market. In developing economies, such as India and China, the adoption of RFID technology in tier I and tier II hospitals for patient tracking is increasing at a significant rate. For instance, in December 2022, the Health Department of India launched radio-frequency identification devices at the Government Rajaji Hospital, Madurai, and the Rajiv Gandhi Government General Hospital in Chennai to monitor the supply chain management of blood and blood products.
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic is positively impacted the market growth. During the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals leveraged radio-frequency identification technology to identify and locate personnel who had been in contact with infected patients, thus supporting containment efforts. Additionally, this technology is used to track inventory, for instance, to ensure that hospitals have a sufficient supply of medicines for treating patients.
RFID In Healthcare Market Report Highlights
On the basis of product, the tags segment captured the highest market share of 61.28% in 2022. The growth of the segment is attributed owing to the increasing adoption of tags in the pharmaceutical industry and rising awareness regarding the benefits of these devices
On the basis of applications, the asset tracking segment captured the highest market share of 38.28% in 2022. The growing demand for effective medical equipment tracking systems, coupled with the rising adoption of RFID technology for tracking both patients and medical personnel, are key drivers behind the segment's dominant market share
North America dominated the RFID in the healthcare market with 44.50% in 2022 due to factors such as the presence of sophisticated healthcare infrastructure and the large number of companies engaged in developing RFID platforms for healthcare
Asia Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 19.67% over the forecast period. An increase in investment in the healthcare IT sector and growing adoption of RFID technology in healthcare organizations is expected to drive the demand for RFID in healthcare
RFID In Healthcare Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global RFID in healthcare market based on product, application, and region:
RIFD In Healthcare Product Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Systems & software
Tags
RIFD In Healthcare Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Asset tracking
Patient tracking
Pharmaceutical tracking
Blood tracking
Others
RIFD In Healthcare Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
North America
US
Canada
Europe
UK
Germany
France
Italy
Spain
Sweden
Norway
Denmark
Asia Pacific
Japan
China
India
Australia
Thailand
South Korea
Latin America
Brazil
Mexico
Argentina
MEA
South Africa
Saudi Arabia
UAE
Kuwait
Key Players in the RFID In Healthcare Market
Alien Technology, LLC
Zebra Technologies Corp.
Avery Dennison Corporation
Impinj, Inc.
GAO RFID Inc.
LogiTag Systems
Mobile Aspects
CenTrak, Inc.
Terso Solutions, Inc.
Tagsys RFID
Order a free sample PDF of the RFID In Healthcare Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market Key Players, Revenue And Growth Rate
The global automatic identification and data capture market size is expected to reach USD 136.86 billion by 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.7% from 2025 to 2030. With an increase in the use of smartphones for image recognition and QR code scanning along with an increase in the development of e-commerce platforms internationally, the market is anticipated to experience a noticeable growth during the forecast period.
Furthermore, increased automatic identification and data capture (AIDC) solution acceptance due to their capacity to reduce discrepancies is likely to drive the growth of the AIDC industry during the forecast period. For instance, in April 2022, Arcion Labs, Inc., a truly real-time database replication platform, announced the release of Arcion Cloud, a fully managed change data capture data replication as a service that empowers businesses to leverage more significant, big data pipelines in minutes.
The most prevalent devices used to identify and capture the data are RFID scanners and RFID tags, barcode scanners, fixed-position, and handheld laser scanners and imagers, wearables devices, voice recognition solutions, and rugged tablets. Automatic identification and data capture systems, such as wearables, barcoding solutions, and RFID scanners, are critical in e-commerce and warehouse management.
AIDC technology not only assists the e-commerce business in automatically identifying objects, collecting data about them with high accuracy and precision, and electronically entering this data into the computer system. By keeping track of inventories, accounting, human resources, and overall procedures, technology also helps increase productivity and operational efficiency.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market
Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market Report Highlights
• North America dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 38.5% in 2024. This high share can be attributed to the increasing awareness and high adoption of AIDC devices and increased government legislative and investment, particularly in retail, healthcare, and manufacturing industries.
• AIDC systems are routinely used to manage assets, inventory, delivery, document scanning, and security in various industries, including transport and logistics, chemical, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, automotive, consumer products, retail and warehousing, and distribution
• Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags, barcodes, biometrics, labels, smart cards, and speech and voice recognition have gained acceptance across various industries due to their increased accuracy, precision, and smooth functioning
• Banks and financial institutions' increasing implementation of AIDC solutions to ensure customer security, safety, and data privacy is projected to fuel market expansion
Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global automatic identification and data capture market on the basis of component, end-use, and region:
Automatic Identification And Data Capture Component Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030)
• Hardware
o RFID Reader
o Barcode Scanner
o Smart Cards
o Optical Character Recognition Devices
o Biometric Systems
o Others
• Software
• Services
o Integration & Installation Services
o Support & Maintenance Services
Automatic Identification And Data Capture End-user Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030)
• Manufacturing
• Retail
• Transportation & Logistics
• Hospitality
• BFSI
• Healthcare
• Government
• Energy & power
• Others
Automatic Identification And Data Capture Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030)
• North America
o U.S.
o Canada
• Europe
o UK
o Germany
o France
• Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o Australia
o South Korea
• Latin America
o Brazil
o Mexico
• Middle East and Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o South Africa
o UAE
Order a free sample PDF of the Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
#Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market#Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market Size#Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market Share#Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market Analysis#Automatic Identification And Data Capture Market Growth
0 notes
Text
Why Hotels Are Switching to Smart Textile Management
Let’s talk about something that doesn’t usually get a lot of attention but is essential to every hotel stay—textiles. From the crisp sheets on your bed to the fluffy towels in the bathroom, managing these fabrics is a massive part of running a hotel smoothly. Traditionally, hotels have relied on manual tracking and restocking, but let’s be real—this method is outdated, inefficient, and expensive. Thankfully, automation is changing the game.
The hospitality industry is going through a digital transformation, and one of the biggest upgrades is automated textile management. With smarter technology, hotels can track their inventory with better accuracy, reduce waste, and provide a seamless experience for both guests and staff. This article dives into the rise of automation in hotel textile management, why it’s a game-changer, and how hotels are making the transition.
The Struggles of Old-School Textile Management
Before technology stepped in, hotels had to track linens and uniforms manually—an exhausting and often inaccurate process. Housekeeping teams counted towels and bed sheets by hand, while managers scrambled to prevent shortages. Here are some of the biggest issues with traditional textile management:
Textile Losses and Misplacement – Without an automated system, items get lost, stolen, or overused, leading to constant replenishment.
Inventory Inconsistencies – Human error in record-keeping leads to shortages or excess stock, neither of which is ideal.
Sky-High Costs – Hotels often spend way more than necessary on new textiles due to inefficient tracking and unnecessary replacements.
Hygiene Issues – Without a proper tracking system, ensuring that all linens are cleaned and replaced at the right time is a challenge.
These frustrations have led many hotels to embrace automation, which offers a more efficient and reliable way to handle textile management.
The Tech Revolution in Hotel Textile Management
Automated textile management systems are transforming how hotels handle their linens, towels, and uniforms. By incorporating RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, cloud-based systems, and AI-driven analytics, hotels are saying goodbye to guesswork and hello to precision.
Real-Time Tracking and Visibility
Hotels using RFID-enabled systems can track linens in real time. Each textile item has a unique RFID tag, making it easy to know where everything is at any given moment. No more lost inventory.
Lower Costs, Less Waste
With an automated tracking system, hotels can dramatically cut costs by reducing unnecessary purchases and optimizing inventory use. Plus, it helps extend the life of linens, saving money in the long run.
Hygiene Compliance and Quality Control
Automation ensures that linens and uniforms follow strict cleaning schedules, reducing the risk of hygiene issues. No more uncertainty about whether something has been washed enough times—everything is tracked and monitored.
Speeding Up Housekeeping
With real-time access to inventory data, housekeeping staff can quickly restock linens and ensure rooms are turned over faster. It’s a win-win for both efficiency and guest satisfaction.
How Hotels Are Making the Switch to Smart Textile Management
Finding the Right System
Hotels looking to go digital need to choose an automation system that suits their needs. Some of the most effective solutions include:
RFID-Based Tracking – Allows hotels to monitor linens from the moment they arrive to the time they’re washed and returned.
Cloud-Based Inventory Management – Provides real-time analytics on usage trends and stock levels.
Automated Dispensing Units – Secure storage units ensure that only authorized staff can access textiles, preventing loss and theft.
Training Staff for a Seamless Transition
Technology is only useful if people know how to use it. Hotels implementing automated systems must train their staff to transition from manual processes smoothly.
Connecting with Laundry Services
For maximum efficiency, smart textile management systems should be integrated with laundry services. This way, every item is tracked through washing cycles and returned promptly.
Who Benefits the Most from Automation?
Luxury Hotels
High-end hotels that prioritize top-tier guest experiences need pristine, high-quality linens. Automation ensures that luxury textiles are always fresh, clean, and ready to use.
Budget Hotels
Smaller hotels with tight budgets benefit by reducing waste and unnecessary expenses. Automation helps them manage linens efficiently without overstocking.
Resorts and Spas
Places that go through high volumes of towels, robes, and linens need a seamless way to keep up with demand. Automated tracking ensures that fresh textiles are always available for guests.
The Trends Pushing Hotels Toward Automation
Hotels are jumping on the automation bandwagon for several reasons:
Sustainability Focus – Reducing textile waste and optimizing laundry cycles help hotels go green.
Smart Technology Integration – IoT and AI-driven systems allow predictive analytics and smarter inventory control.
Cost Efficiency – With rising costs, automation is an effective way to streamline spending and increase efficiency.
Higher Guest Expectations – Modern travelers expect clean, well-maintained rooms, making automation essential for a seamless experience.
Real-Life Use Cases of Smart Textile Management
Many hotels are already using hotel textile management solutions with RFID and cloud-based analytics to track their inventory more effectively.
Meanwhile, hospitals have successfully implemented scrub vending machines to ensure medical staff always have clean uniforms. Hotels are exploring similar models for their staff to keep track of uniforms efficiently.
The Future of Hotel Laundry Operations
Beyond tracking, automation is making hotel laundry services smarter. By integrating laundry inventory management, hotels can streamline washing cycles, improve coordination with providers, and ensure linens are always ready.
Additionally, textile inventory tracking helps hotels analyze trends, pinpoint inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions to reduce costs.
Final Thoughts
The hospitality industry is evolving, and smart textile management is becoming a necessity rather than a luxury. By adopting RFID tracking, cloud-based inventory management, and AI-powered solutions, hotels can improve efficiency, save money, and elevate the guest experience. As technology continues to advance, automated textile management will become the new standard, ensuring hotels operate smoothly while keeping guests happy.
0 notes
Text
RTLS Market Size: Growth, Trends, and Future Projections 2025 – 2029
The Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) market has emerged as a transformative technology across industries, enabling businesses to track assets, personnel, and inventory in real-time. With the increasing adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) and automation, the RTLS market size has witnessed remarkable growth.
Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) are used to identify, track, and manage the location of objects or people in real-time. RTLS technology leverages various systems such as GPS, RFID, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Ultra-Wideband (UWB) to provide accurate location data. It is widely used in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, retail, logistics, and transportation to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
RTLS Market Size: Current Scenario
The global RTLS market size is projected to grow from USD 6.03 billion in 2024 to USD 15.79 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 21.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. An RTLS is a system that comprises hardware and software to track or locate the real-time location of personnel or assets in a facility. RTLS solutions are integrated with several technologies, such as RFID, Wi-Fi, UWB, GPS, BLE, and infrared (IR), to ensure real-time tracking of assets or personnel.
Key Drivers of RTLS Market Growth
Rising Adoption in Healthcare:
RTLS is widely used in healthcare for tracking medical equipment, patients, and staff. The need for efficient hospital operations and patient care has significantly contributed to the RTLS market size.
Growth in Manufacturing and Logistics:
Industries like manufacturing and logistics rely on RTLS for inventory management, asset tracking, and workflow optimization. The rise of Industry 4.0 has further accelerated RTLS adoption.
Advancements in IoT and Automation:
The integration of RTLS with IoT and automation technologies has enhanced its capabilities, making it a critical component of smart factories and warehouses.
Increased Demand for Supply Chain Visibility:
Businesses are increasingly adopting RTLS to gain real-time visibility into their supply chains, improving efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Emergence of 5G Technology:
The rollout of 5G networks has enabled faster and more reliable data transmission, boosting the adoption of RTLS solutions.
RTLS Market Segmentation
The RTLS market size can be segmented based on technology, application, end-user industry, and region.
By Technology:
RFID
Wi-Fi
Bluetooth
Ultra-Wideband (UWB)
GPS
Others
By Application:
Asset Tracking
Personnel Tracking
Inventory Management
Workflow Optimization
Others
By End-User Industry:
Healthcare
Manufacturing
Retail
Logistics and Transportation
Government and Defense
Others
By Region:
North America
Europe
Asia-Pacific
Latin America
Middle East & Africa
Regional Analysis of RTLS Market Size
North America:
North America dominates the RTLS market size, accounting for the largest share due to early adoption of advanced technologies and the presence of key market players.
Europe:
Europe is a significant contributor to the RTLS market, driven by the growing demand for automation and smart manufacturing.
Asia-Pacific:
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, fueled by rapid industrialization and increasing investments in IoT and automation.
Latin America and Middle East & Africa:
These regions are gradually adopting RTLS solutions, with growth driven by expanding healthcare and logistics sectors.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=1322
Trends Shaping the RTLS Market
Integration with AI and Machine Learning:
The integration of RTLS with AI and machine learning is enabling predictive analytics and smarter decision-making.
Adoption of Ultra-Wideband (UWB) Technology:
UWB is gaining traction due to its high accuracy and reliability in indoor positioning systems.
Focus on Energy Efficiency:
Manufacturers are developing energy-efficient RTLS solutions to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Rise of Hybrid RTLS Solutions:
Hybrid RTLS solutions, combining multiple technologies, are becoming popular for their versatility and enhanced performance.
Challenges in the RTLS Market
Despite its growth, the RTLS market size faces certain challenges, including:
High Initial Costs:
The deployment of RTLS solutions can be expensive, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Data Privacy Concerns:
The use of RTLS for personnel tracking raises concerns about data privacy and security.
Interoperability Issues:
Integrating RTLS with existing systems can be complex, requiring significant technical expertise.
The RTLS market size is on a robust growth trajectory, fueled by technological advancements and increasing demand across industries. As businesses continue to prioritize efficiency and visibility, RTLS solutions will become indispensable tools for asset tracking, workforce management, and supply chain optimization. With a projected CAGR of 20% to 25%, the RTLS market is set to revolutionize the way industries operate in the coming years.
0 notes
Text
Streamlining Operations with Advanced Tracking Solutions
Gas cylinder tracking is a game-changer for industries relying on gas supply management, ensuring operational efficiency and safety. Trakaid, a leader in tracking solutions, offers a cutting-edge system. It monitors gas cylinders in real-time throughout their lifecycle. It uses advanced tools like RFID and IoT. This tech streamlines inventory management, cuts losses, and optimizes logistics. Trakaid's solution tags each cylinder with a unique ID. This enables accurate tracking of its movements, filling history, and maintenance. Businesses can eliminate manual errors and improve accountability. They can ensure timely refills, while complying with safety regulations.
The benefits of Trakaid’s gas cylinder tracking extend beyond operational efficiency. This technology aids predictive maintenance. It finds cylinders nearing expiration or needing inspection. It reduces downtime and risks from faulty equipment. With real-time data, managers can make better decisions and use assets more efficiently. Also, Trakaid's tracking system has strong analytics. It helps businesses find patterns and improve supply chain strategies. Whether for healthcare, industrial, or hospitality sectors, Trakaid’s gas cylinder tracking ensures seamless operations, safety, and cost-effectiveness, making it an indispensable tool for modern businesses. Visit Now: https://www.trakaid.com

0 notes
Text
Best practices for RFID-powered hospital inventory management can significantly enhance operational efficiency. By conducting thorough assessments, selecting appropriate solutions, and training staff, hospitals can optimize inventory processes. Leveraging RFID technology leads to better resource management and improved patient care.
0 notes
Text
Surgical Instrument Tracking System is Poised to Register Strong Growth due to Increasing Need

The surgical instrument tracking system market has witnessed significant growth in recent years. Surgical instrument tracking systems provide real-time tracking and assists in maintaining inventory of surgical instruments in healthcare settings. Tracking systems help identify instrument location, usage history and shelf life. They facilitate improved inventory management, streamline sterile processing workflows and help reduce overall operational costs for healthcare facilities.
The global surgical instrument trackingmarket was valued at US$ 301.5 Mn in 2022 and is forecast to reach a value of US$ 1,206.5 Mn by 2030 at a CAGR of 19.0% between 2023 and 2030.
Key Takeaways Key players operating in the surgical instrument tracking market are 3M, E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company, Aculon Inc., BASF SE, P2i, ABRISA TECHNOLOGIES, NEI Corporation, DRYWIRED, ACCUCOAT INC., OerlikonMetco (US) Inc, and NANEX COMPANY. The Surgical Instrument Tracking Market Size offers significant opportunities in terms of innovation and technology integration. Adoption of RFID, barcode and GPS based tracking systems allows for real-time location monitoring and automated instrument count workflows. Integration of IoT and cloud computing enables centralized monitoring and data analysis. Globally, the surgical instrument tracking market is expected to witness strong growth in North America, Europe and Asia Pacific. Increasing healthcare expenditure, rising surgical volumes and focus on reducing operating costs are driving demand for tracking systems across major countries. Ongoing technological advancements also allow for expansion into new applications such as endoscopy and dental equipment tracking. Market drivers The major driver for the surgical instrument tracking market is the increasing need for improved inventory management and asset utilization in healthcare facilities. Manual tracking systems are tedious and prone to errors. Automated tracking solutions help identify missing instruments quicker, reduce miscounts and optimize staff allocation. This helps reduce product wastage and improves sterilization turnaround times. The growing regulatory requirements regarding instrument recalls and traceability also boost the demand for advanced tracking solutions.
PEST Analysis Political: Regulations regarding tracking of surgical instruments are becoming stricter to ensure patient safety. This is driving demand for effective tracking systems. Economic: Rising healthcare costs are pushing hospitals to optimize operations and reduce expenses like instrument replacement. Tracking systems help achieve these goals. Social: Growing awareness about risks of expired or misplaced instruments is making surgeons and patients more careful. This boosts adoption of tracking technologies. Technological: Advanced RFID and barcode technologies enable real-time location of instruments through the surgical workflow from sterilization to usage and disposal. Some solutions also offer instrument condition monitoring. Geographical Regions with High Market Concentration North America accounts for the largest share of the surgical instrument tracking market due to stringent regulations and protocols regarding instrument tracking and management in this region. High healthcare spending in countries like the US and Canada also contributes to market growth. Hospitals are more willing to invest in new technologies for optimized operations and improved patient outcomes. Fastest Growing Regional Market The Asia Pacific region is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period. This is attributed to improving healthcare infrastructure, rising medical tourism, and growing focus on reducing surgical site infections in major countries like India, China and Japan. With increasing awareness, more hospitals are implementing instrument tracking systems for better regulatory compliance and cost-effectiveness.
Get more insights on Surgical Instrument Tracking Market
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)
#Coherent Market Insights#Surgical Instrument Tracking Market#Surgical Instrument Tracking#Healthcare Technology#Medical Devices#Asset Management#Surgery#Sterilization#Patient Safety#Hospital Logistics#Instrument Inventory#RFID Technology
0 notes
Text
gs1
Understanding GS1: The Global Standard for Supply Chain Efficiency
In today's interconnected world of commerce, GS1 stands as the backbone of global supply chain standards. Known for its universally accepted barcoding system, GS1 plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless product identification, traceability, and operational efficiency across industries. This article explores the significance, functions, and benefits of GS1 standards, shedding light on how they facilitate global trade and enhance supply chain transparency.
What is GS1?
GS1 (Global Standards 1) is a non-profit organization that develops and maintains international standards for supply chain efficiency. Founded in 1974, GS1 is best known for creating the UPC (Universal Product Code) barcode, which revolutionized product identification and retail operations.
GS1 standards are now widely used across industries, including:
Retail
Healthcare
Logistics and Transportation
Food and Beverage
By providing unique identification codes for products, assets, and locations, GS1 enables businesses to streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve data sharing across global networks.
The GS1 Identification System
The GS1 system revolves around unique identification keys that allow products, locations, and assets to be tracked globally. The most common identifiers include:
GTIN (Global Trade Item Number): Identifies products globally.
GLN (Global Location Number): Identifies physical or digital locations.
SSCC (Serial Shipping Container Code): Tracks logistics units.
GRAI (Global Returnable Asset Identifier): Identifies returnable assets like pallets and containers.
GIAI (Global Individual Asset Identifier): Tracks specific assets within an organization.
Each identifier is embedded in a barcode or RFID tag, allowing automated data capture and sharing.
Key GS1 Standards
GS1 provides a suite of standards that cover multiple aspects of the supply chain:
Barcodes:
UPC (Universal Product Code): Used in retail for product identification.
EAN (European Article Number): Similar to UPC but used internationally.
GS1 DataMatrix: A 2D barcode commonly used in healthcare for detailed product information.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification): Enhances tracking and visibility for goods in transit.
GS1 Digital Link: Connects a product's barcode to online information, enabling a bridge between physical products and digital data.
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange): Standardizes business documents like invoices, purchase orders, and shipping notices.
These standards work together to ensure seamless data exchange across global supply chains.
Benefits of GS1 Standards
Global Consistency: GS1 standards are recognized worldwide, enabling smooth cross-border trade.
Improved Traceability: Enables end-to-end tracking of products from production to final sale.
Operational Efficiency: Streamlines inventory management, warehousing, and logistics.
Error Reduction: Minimizes human errors in data entry and product identification.
Enhanced Customer Trust: Ensures product authenticity and reduces counterfeiting risks.
Compliance: Meets industry regulations for product labeling and traceability.
For example, in the food industry, GS1 standards help trace contaminated products during recalls, ensuring quick and precise actions to protect public health.
How GS1 Standards Work in Practice
Example: Retail Industry
A manufacturer registers with GS1 and receives a GTIN for each product.
The GTIN is encoded into a barcode printed on the product packaging.
At checkout, the barcode is scanned, retrieving product information (e.g., price, stock level) instantly.
The same barcode supports inventory tracking, sales analysis, and reordering processes.
Example: Healthcare Industry
Medications are labeled with GS1 DataMatrix barcodes containing critical information like batch number and expiration date.
Hospitals and pharmacies scan these barcodes to ensure correct medication administration and reduce errors.
GS1 in the Digital Age
With the rise of e-commerce and digital supply chains, GS1 is evolving to meet modern demands:
GS1 Digital Link: Connects physical products to rich digital content, enhancing product transparency and consumer engagement.
Smart Labels: Combine GS1 barcodes with IoT and RFID technologies for real-time product tracking.
Blockchain Integration: GS1 standards are being integrated into blockchain platforms for immutable product traceability records.
These advancements ensure GS1 remains at the forefront of supply chain innovation.
Getting Started with GS1
For businesses looking to implement GS1 standards:
Register with GS1: Obtain a GS1 Company Prefix to create unique product identifiers.
Generate Barcodes: Use GS1-approved tools to create GTINs and associated barcodes.
Label Products: Apply the barcodes or RFID tags to your products.
Integrate with Systems: Ensure your inventory, POS, and logistics systems support GS1 standards.
Train Staff: Educate teams on barcode scanning and data entry best practices.
Adopting GS1 standards not only ensures compliance but also positions businesses for scalable growth and global market access.
Challenges in Adopting GS1 Standards
While GS1 standards offer immense benefits, businesses might face:
Initial Setup Costs: Investment in registration, labeling, and system upgrades.
Compliance Complexity: Adhering to different standards across industries.
Training Requirements: Educating staff about GS1 protocols.
However, these challenges are outweighed by long-term operational efficiencies and business growth opportunities.
The Future of GS1
As technology and global commerce continue to evolve, GS1 is focusing on:
Enhanced Data Transparency: Providing consumers with more detailed product information.
Sustainability Tracking: Helping companies measure and report environmental impact.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Improving predictive analytics for supply chain optimization.
GS1's adaptability ensures it will remain a cornerstone of global trade and logistics for decades to come.
Conclusion
GS1 is not just about barcodes—it's about global efficiency, transparency, and trust in supply chains. By providing universally accepted standards, GS1 simplifies complex logistics, enhances product traceability, and fosters global trade.
For businesses aiming to scale operations, reduce errors, and improve customer trust, adopting GS1 standards is not just an option—it's a necessity.
0 notes
Text
Smarter Sales with the Best POS System in Qatar | Inforise IT
Enhance your retail or hospitality business with Inforise IT’s reliable POS systems in Qatar. Our solutions streamline your checkout process, improve inventory management, and offer valuable sales insights. Whether you run a single store or a chain, our POS systems are designed for speed, accuracy, and ease of use. Enjoy seamless integrations with accounting, CRM, and ERP tools for a comprehensive business solution. Empower your team with cutting-edge technology that elevates customer satisfaction and business efficiency. Inforise IT is your trusted partner for POS systems in Qatar.
0 notes
Text
How Access Control Systems Improved Business Security in Dubai

This is because, especially in a center of economic activity like Dubai, business entities are always at risk of being targeted by criminals. Some of the most critical innovations in current security measures are access control systems, which allow businesses to protect their properties, inventory, and people.
SIRA-approved security companies in Dubai have been at the forefront of implementing these advanced systems, ensuring they meet stringent regulatory standards while delivering superior security solutions. This blog explores how access control systems have transformed business security in Dubai, their challenges, innovations, trends, and practical applications today.
The Need for Advanced Security in Dubai
Dubai outer city plays host to business outfits young and old and from all professions. With its booming economy and increasing corporate activities, businesses face diverse security challenges:
Unauthorized Access: An intrusion in sensitive areas is a significant threat in organizations, and thus, the need to secure them.
Asset Protection: Preserving high value as equipment and inventories are among the principal challenges.
Employee Safety: Addressing the safety of the employees preserves productivity and employee satisfaction.
Regulatory Compliance: Companies have to follow the ordinances, which are set in the geographical area in compliance with the regulatory bodies like SIRA.
Automation has the potential of providing an all rounded solution to these challenges through access control systems, technology and security.
Key Features of Access Control Systems

Contemporary access control goes beyond the use of locks and keys and is an advanced concept. Here are some of their standout features:
Biometric Authentication: Fingerprint, retina and facial recognition systems provide the best results, and they are secure as well.
Card-Based Entry: Smart cards and RFID technology combine are effective due to their user friendly concept for access control.
Mobile Integration: Currently, apps offer the possibilities of working from a distance and surveillance, which provide more opportunities for business.
Time-Based Access Control: Some of the generalized benefits are; restricted access to the areas designated for employees or visitors working within the regions during certain hours.
Audit Trails: It is also easy to see who visited which regions and when meaning those who try to sneak into unsafe areas are easily caught.
They help business people to apply proper security measures that may suit their businesses.
Benefits of Access Control Systems
1. Enhanced Security
They reduce the incidence of intrusion to the premises by limiting the movement of unauthorized personnel. Biometric and card based systems in particular because with normal keys there is always risk of their being stolen or duplicated.
2. Operational Efficiency
Central management and notions of automated access make working processes in businesses more effective. For instance, as a system administrator, admitting third parties such as contractors or visitors is fast and easy.
3. Cost Savings
It is, of course, an expensive investment to implement an access control system, but it negates other one-time charges which include loss of keys, key duplication or the hiring of extra security guards.
4. Regulatory Compliance
SIRA Authorized System helps organizations in Dubai to implement a high level of security and to avoid fines that reduce their credibility.
5. Improved Employee Monitoring
The patterns of attendance and access helps employers manage their workers and detect insecurities.
How Access Control Systems Are Transforming Industries
1. Hospitality
Some of the ways that hotels in Dubai use access control includes adapting provision of personalized services for the guests while at the same time enhancing their security. Smartphones as an alternative to a key is a usual option for improved comfort.
2. Retail
Access control systems are also employed by retail stores for the purpose of protecting storing space as well as to reduce levels of theft. Another advantage is the possibility of integration with surveillance cameras systems.
3. Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics use the access control to limit user physical access to certain areas such as pharmacies, operation theaters, and records sections.
4. Corporate Offices
Some of the big organizations in Dubai require access control to protect sensitive information, and control employee traffic within facilities.
5. Real Estate
Automated doors and smart access combine with smart homes along with smart commercial spaces in residential companies and business companies, allowing the tenants and the commercial companies to experience the future.
Innovations Driving Access Control in Dubai
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI-powered systems analyze access patterns to predict and prevent potential threats. These systems can also provide real-time alerts for suspicious activities.
2. Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud integration allows businesses to manage access control remotely, reducing dependency on on-site infrastructure.
3. IoT Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects access control systems with other security devices like CCTV cameras and alarms, creating a cohesive security ecosystem.
4. Touchless Technology
In a post-pandemic world, touchless solutions like facial recognition and mobile app-based access have gained popularity, enhancing both security and hygiene.
Choosing the Right Access Control System
When selecting an access control system, businesses should consider:
Scalability: Make sure the system is scalable with your business requirements .
Integration: Select a solution that is compatible with other existing structures as far as security is concerned.
Compliance: Make sure that it has been certified by SIRA to operate in Dubai.
User-Friendliness: Choose the option for which it will be easy to work for people and administrators alike.
Conclusion
It remains, however, that access control systems have made a perfect breakthrough in business security in Dubai due to the balancing between innovation and usefulness. These systems meet diverse security concerns in organizations, from access control to increased organizational performance.
In the future, improved advances in technology mean that access control systems will play an increasingly important role in protecting the rapidly growing business environment of Dubai as a safe city for business. Partnering with a SIRA-approved security company in Dubai ensures businesses comply with local regulations while leveraging cutting-edge solutions. Such systems need to be acquired today, and the businesses that have done so not only secure their property but also contribute to the creation of a more secure and efficient tomorrow.
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Importance of Scannable IDs
Scannable IDs, including barcodes, QR codes, and RFID tags, have become ubiquitous in modern society. These technologies, initially developed for inventory tracking, now play a crucial role across various industries. From retail and healthcare to security and education, scannable IDs simplify processes, enhance efficiency, and contribute to a safer and more interconnected world. This article delves into the importance of Scannable ID, exploring their functions, benefits, and far-reaching applications.
What Are Scannable IDs?
Scannable IDs are machine-readable codes that store data in a compact format, which can be quickly retrieved using scanners or compatible devices. The three main types include:
Barcodes: Linear or two-dimensional codes representing data in patterns of lines or shapes.
QR Codes: Square matrix barcodes that can hold extensive information, including URLs and multimedia.
RFID Tags: Radio-frequency identification devices that transmit data wirelessly to a reader.
These IDs enable fast, accurate data collection and processing, making them indispensable tools in various settings.
Key Benefits of Scannable IDs
1. Efficiency
Scannable IDs automate data entry and retrieval, significantly reducing the time and effort required for manual processes. For instance, retail checkouts equipped with barcode scanners process transactions faster than traditional methods.
2. Accuracy
Manual data entry is prone to errors, which can lead to costly mistakes. Scannable ID minimize these errors by ensuring precise data capture.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
While initial implementation may involve costs, scannable ID systems often yield long-term savings by reducing labor requirements and minimizing errors.
4. Security
Advanced scannable ID systems, such as RFID tags and encrypted QR codes, enhance security by limiting access to sensitive data or locations.
5. Scalability
Scannable ID systems are easily adaptable to different organizational sizes and needs, making them suitable for startups and multinational corporations alike.
Applications of Scannable IDs Across Industries
1. Retail
In retail, scannable IDs streamline inventory management, point-of-sale transactions, and customer loyalty programs:
Inventory Tracking: Barcodes on products allow retailers to monitor stock levels in real time, reducing waste and ensuring availability.
Quick Checkout: Barcode scanners speed up the payment process, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Personalized Offers: QR codes enable access to tailored promotions and discounts.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, scannable IDs play a critical role in ensuring patient safety and operational efficiency:
Patient Identification: Wristbands with barcodes or QR codes accurately link patients to their medical records.
Medication Management: Scanning medication barcodes ensures proper administration, reducing errors.
Equipment Tracking: RFID tags on medical devices help hospitals locate and maintain essential equipment.
3. Transportation and Logistics
In the logistics sector, scannable IDs enhance tracking and streamline supply chains:
Package Tracking: QR codes on shipments provide real-time location updates.
Warehouse Management: Barcodes and RFID tags simplify inventory storage and retrieval.
Fleet Monitoring: RFID-enabled systems optimize vehicle usage and maintenance schedules.
4. Education
Educational institutions use scannable IDs to improve administrative efficiency and enhance learning experiences:
Attendance Tracking: Barcode or QR code student IDs facilitate automated attendance recording.
Library Services: Scannable IDs streamline book lending and return processes.
Access Control: QR codes and RFID tags restrict entry to authorized areas, enhancing campus security.
5. Hospitality
Hotels and event organizers leverage scannable IDs to deliver seamless experiences:
Room Access: QR codes on digital keys enable contactless check-in and room entry.
Event Tickets: Scannable IDs simplify entry to concerts, conferences, and exhibitions.
Loyalty Programs: QR codes provide customers with instant access to rewards and promotions.
6. Government and Public Services
Governments adopt scannable IDs to modernize services and improve accessibility:
Identity Verification: QR codes on national ID cards ensure fast and secure authentication.
Public Transport: RFID cards enable contactless fare payment and access to transit systems.
Voting Systems: Scannable IDs enhance the integrity and efficiency of electronic voting processes.
7. Security
Security is another domain where scannable IDs excel:
Access Control: RFID badges and QR codes regulate entry to restricted areas.
Surveillance: Scannable IDs track personnel movement within secure facilities.
Fraud Prevention: Dynamic QR codes reduce the risk of duplication and unauthorized access.
Innovations in Scannable ID Technology
Recent advancements have expanded the capabilities of scannable IDs, enhancing their functionality and appeal:
Biometric Integration: Combining scannable IDs with fingerprints or facial recognition adds an extra layer of security.
Blockchain Technology: Storing scannable ID data on decentralized networks ensures tamper-proof records.
Dynamic Codes: QR codes that refresh periodically enhance security by preventing replication.
AI Integration: Artificial intelligence improves the speed and accuracy of data processing in scannable ID systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While scannable IDs offer numerous advantages, they are not without challenges:
Implementation Costs: Setting up advanced scannable ID systems can be expensive for smaller organizations.
Data Privacy: Ensuring that data stored in scannable IDs is secure and compliant with regulations is crucial.
Technical Glitches: Malfunctioning scanners or damaged IDs can disrupt operations.
User Training: Organizations must invest in training staff to effectively use scannable ID systems.
The Future of Scannable IDs
As technology continues to evolve, scannable IDs will likely become even more integral to daily life. Emerging trends include:
Global Standardization: Developing universal protocols for scannable IDs to ensure seamless interoperability.
Wearable Technology: Incorporating scannable IDs into smartwatches and other wearables for greater convenience.
Green Solutions: Using eco-friendly materials for physical scannable IDs to reduce environmental impact.
Advanced Encryption: Implementing sophisticated encryption techniques to safeguard sensitive data.
Conclusion
Scannable IDs are indispensable in today’s interconnected world, offering unparalleled benefits in efficiency, security, and convenience. Their versatility allows them to adapt to a wide range of applications, from retail and healthcare to education and government services. While challenges remain, innovations in technology and strategic implementation can unlock their full potential, making scannable IDs a cornerstone of modern systems.
As industries and technologies evolve, the importance of scannable IDs will only grow. By embracing these tools, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, security, and sustainability, paving the way for a smarter and more secure future.
0 notes
Text

Saudi Arabia POS Payment Market Report 2031
Saudi Arabia POS payment market is projected to witness a CAGR of 10.26% during the forecast period 2024-2031, growing from USD 2.22 billion in 2023 to USD 4.85 billion in 2031.
The POS payment market deals with the sector involved in the technology and services that are necessary for facilitating transactions at the point of sale, where customers make payments against availed goods or services. These can be seen as a mix of hardware and software that enables enterprise organizations to process digital electronic payments and thereby allows alternative electronic methods other than traditional hard cash transactions. A point of sale machine expedites checkout and enhances transaction efficacy while improving accuracy. In some cases, they may be applied to inventory management systems, whereby a company can trace the levels of stock and sales in real-time to enable informed purchasing decisions, create optimal price strategies, and generally enhance customer experiences.
The PoS systems in Saudi Arabia have risen by high growth rates based on their important role and significance in increasing efficiency and security in the processing of payments between different sectors, such as retail, hospitality, and healthcare. Growth will be supported by all diversification projects in the country that involve a very active retail sector boosted by increased consumer spending. The integral factor has been the Saudi government’s move to encourage a Vision 2030 program for digital transformation and moving toward cashless payments. All this is considered a driver that accelerates the adoption of advanced PoS solutions.
As the retail landscape in Saudi Arabia continues to evolve, demand for sophisticated PoS systems will rise, offering an adequate scope for local and international service providers. While the government’s emphasis on financial technologies and digital payments supports the expansion of PoS systems, it comes in line with broader economic policies. In that way, the ground is being prepared for a more modern and efficient business environment. The growth trajectory indicates that PoS systems are increasingly playing an important role in transforming consumer experiences and streamlining business operations.
For instance, in September 2024, as reported by the Saudi Central Bank (SAMA), there were USD 3.7 billion (SAR 14 billion) in transactions over seven days, with the telecoms industry posting the highest sectoral increase at 42 percent to reach USD 35.1 million (SAR 131.9 million).
Technological Advancements Aiding the Growth of the Market
The rise in the connectivity and innovation of solutions has contributed significantly to the development of Saudi Arabia’s POS payment market. Development in high-speed internet, coupled with an increase in mobile network coverage, allows POS systems to work in remote areas of the country, hence streamlining every transaction. Driven by mobile payment solutions, the widespread use of smartphones has revolutionized the landscape for POS, granting flexibility and convenience to businesses of all sizes through mPOS systems. Coupled with this, the migration towards contactless payment technologies, such as Near-field communication (NFC) and Radio-frequency identification (RFID), further enhances the speed and security of transactions, hence enhancing customer experiences and driving POS systems’ usage. This has shifted POS solutions to the cloud, thus enabling enterprises to manage transactions, inventories, and consumer data with much more efficiency, offering real-time access and valuable analytics. Security has been enhanced through encryptions and tokenization among other techniques, hence boosting consumer trust in digital payments. Moreover, the ability of modern POS systems to integrate well with different functions in businesses, such as inventory management and CRM, makes operations smooth, giving an integrated view of business activities, hence making the POS solution increasingly attractive for businesses across Saudi Arabia.
For instance, in February 2024, PayTabs Group announced its partnership with Nearpay, Saudi Arabia’s leading Payment Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) fintech brand, to offer users a smooth POS payment experience across Jordan and other PayTabs markets in the country. With a user-friendly interface and robust encryption, it simplifies checkouts and increases customer satisfaction. PayTabs soft POS technology enables merchants to conduct transactions anywhere, from bustling city squares to remote locations.
Government Initiatives Acting as a Catalyst
Government initiatives in Saudi Arabia have acted as a significant catalyst for the growth of the POS payment market, as there has been immense adaption and technological advancement. Its policy of expanding financial inclusion means there is increased availability of digital payment solutions to End-users, and this has assisted SMEs to more easily access POS systems. It democratizes modern payment technology, allowing more portions of the population and businesses to join the digital economy.
This growth is further mended by Vision 2030, with a focus on diversifying the economy from oil and investing in retail, tourism, and entertainment. Vision 2030 increases demand for modern payment solutions. The aim places emphasis on digital transformation and a reduction in cash transactions, which directly coincides with the expansion of the POS payment market. Another significant emphasis of Vision 2030 is support for SMEs. The government gives them a way to have easy access to digital payment solutions, thus enabling them to grow and compete in a digital economy. Complementary initiatives at the national level include Mada, Saudi Arabian payment system (SADAD), and Saudi Arabian Riyal Interbank Express (SARIE), which further enforce the ecosystem of the POS system. Mada, the national payment network, has fostered a strong uptake of the POS system throughout the kingdom. At the same time, SADAD has availed a fully integrated platform for electronic bill presentment and payment. SARIE allows real-time settlement, making digital payments agile, efficient, and reliable.
These initiatives cumulatively put in place a strong and enabling environment wherein growth in the POS payment market in Saudi Arabia will, in turn, catalyze technology adoption, economic diversification, and financial inclusion.
In September 2024, Saudi Arabia decided to cancel fees for issuing commercial activity licenses for hotels, hotel apartments, and residential resorts to promote tourism in the country. They feel that this initiative would encourage investors to put more money into the tourism sector, which would increase the industry’s contribution to gross domestic product.
mPOS Terminals to be the Most Widely Used Systems
In the POS terminal market of Saudi Arabia, it can be identified that mPOS terminals are increasingly emerging as popular choices due to their advantages over other terminal types, such as Fixed POS, Pocket POS, and POS GPS/GPRS, in different dimensions. The foremost advantage of mPOS terminals is their portability and flexibility. This provides a business with the ability to process transactions anywhere, from within a store to remote customer locations or pop-up shops. This makes it very suitable for SMEs and businesses operating in temporary and dynamic environments. Also, mPOS terminals tend to be much cheaper than fixed POS systems. This fact attracts businesses in search of modern payment services without huge investments. Their seamless integration with existing smartphones and tablets further simplifies the setup and minimizes additional hardware requirements.
For instance, in March 2022, Bank AlJazira partnered with JCB International Co., Ltd. to launch JCB acceptance through its POS and ATM network devices deployed in the country. The partnership complements the role played by Saudi Payments to enhance the payments landscape in Saudi Arabia through the enablement of international payment schemes to operate in the POS payment market. This initiative highlights the growing trust and reliance on digital payment methods, including mPOS terminals, which offer flexibility and convenience for merchants and consumers.
Download Free Sample Report
Riyadh Dominates POS Payment Market Share
Being the capital of Saudi Arabia, Riyadh is considered the frontrunner in the POS payment market, mainly due to its renowned economic and administrative significance. Many companies, government offices, and international organizations are located here, which puts this city in a central position and gives rise to many financial transactions. Further, the vibrant retail sector in Riyadh is marked by shopping malls, markets, and other retail outlets, thereby fueling the demand for the POS system.
In addition, the city’s attraction to tourists and business travelers increases spending in the hospitality sectors of hotels and restaurants, thereby increasing the use of POS terminals. Advanced technological infrastructure in terms of high-speed internet and far-reaching mobile networks boosts the easy penetration and usage of modern-day POS systems. In addition, the very high penetration of the local population with digital means of paying for goods, including mobile wallets and contactless payments, underlines Riyadh’s leading position in the Saudi Arabia POS payment market.
For instance, in September 2024, it was reported that Riyadh dominated POS transactions, representing 34 percent of the total transactions taking place in the country. Expenses in the capital reached USD 1.27 billion (SAR 4.77 billion), which marks a 14.3% increase from the previous week.
Future Market Scenario (2024 – 2031F)
1. Unique economic diversification of Saudi Arabia will continue to aid the growth of the POS payment market.
2. Several factors drive the growth, including the increasing penetration of smartphones and tablets, the adoption of cloud-based technologies, and the shift towards contactless payments.
3. The Saudi government is actively promoting a cashless society, which is boosting the adoption of electronic payments. This includes initiatives to enhance the national payments infrastructure and refine payment services.
4. Riyadh will continue to dominate the POS payment market due to its renowned economic and administrative significance, as well as the presence of international offices and government organizations.
Report Scope
“Saudi Arabia POS Payment Market Assessment, Opportunities and Forecast, 2017-2031F”, is a comprehensive report by Markets and Data, providing in-depth analysis and qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current state of Saudi Arabia POS payment market, industry dynamics, and challenges. The report includes market size, segmental shares, growth trends, opportunities, and forecast between 2024 and 2031. Additionally, the report profiles the leading players in the industry, mentioning their respective market share, business models, competitive intelligence, etc.
Click here for full report- https://www.marketsandata.com/industry-reports/saudi-arabia-pos-payment-market
Latest reports-
Contact
Mr. Vivek Gupta 5741 Cleveland street, Suite 120, VA beach, VA, USA 23462 Tel: +1 (757) 343–3258 Email: [email protected] Website: https://www.marketsandata.com
0 notes