#Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension symptoms
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The recent approval of WINREVAIR for the treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) marks a significant milestone in Merck's portfolio and the broader PAH market.
#Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension#Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension market#Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension drugs#Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension therapies#Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension treatment#Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension symptoms
0 notes
Text
Patients With Long-COVID Show Abnormal Lung Perfusion Despite Normal CT Scans - Published Sept 12, 2024
VIENNA — Some patients who had mild COVID-19 infection during the first wave of the pandemic and continued to experience postinfection symptoms for at least 12 months after infection present abnormal perfusion despite showing normal CT scans. Researchers at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 International Congress called for more research to be done in this space to understand the underlying mechanism of the abnormalities observed and to find possible treatment options for this cohort of patients.
Laura Price, MD, PhD, a consultant respiratory physician at Royal Brompton Hospital and an honorary clinical senior lecturer at Imperial College London, London, told Medscape Medical News that this cohort of patients shows symptoms that seem to correlate with a pulmonary microangiopathy phenotype.
"Our clinics in the UK and around the world are full of people with long-COVID, persisting breathlessness, and fatigue. But it has been hard for people to put the finger on why patients experience these symptoms still," Timothy Hinks, associate professor and Wellcome Trust Career Development fellow at the Nuffield Department of Medicine, NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre senior research fellow, and honorary consultant at Oxford Special Airway Service at Oxford University Hospitals, England, who was not involved in the study, told Medscape Medical News.
The Study Researchers at Imperial College London recruited 41 patients who experienced persistent post-COVID-19 infection symptoms, such as breathlessness and fatigue, but normal CT scans after a mild COVID-19 infection that did not require hospitalization. Those with pulmonary emboli or interstitial lung disease were excluded. The cohort was predominantly female (87.8%) and nonsmokers (85%), with a mean age of 44.7 years. They were assessed over 1 year after the initial infection.
Exercise intolerance was the predominant symptom, affecting 95.1% of the group. A significant proportion (46.3%) presented with myopericarditis, while a smaller subset (n = 5) exhibited dysautonomia. Echocardiography did not reveal pulmonary hypertension. Laboratory findings showed elevated angiotensin-converting enzyme and antiphospholipid antibodies. "These patients are young, female, nonsmokers, and previously healthy. This is not what you would expect to see," Price said. Baseline pulmonary function tests showed preserved spirometry with forced expiratory volume in 1 second and forced vital capacity above 100% predicted. However, diffusion capacity was impaired, with a mean diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) of 74.7%. The carbon monoxide transfer coefficient (KCO) and alveolar volume were also mildly reduced. Oxygen saturation was within normal limits.
These abnormalities were through advanced imaging techniques like dual-energy CT scans and ventilation-perfusion scans. These tests revealed a non-segmental and "patchy" perfusion abnormality in the upper lungs, suggesting that the problem was vascular, Price explained.
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing revealed further abnormalities in 41% of patients. Peak oxygen uptake was slightly reduced, and a significant proportion of patients showed elevated alveolar-arterial gradient and dead space ventilation during peak exercise, suggesting a ventilation-perfusion mismatch.
Over time, there was a statistically significant improvement in DLCO, from 70.4% to 74.4%, suggesting some degree of recovery in lung function. However, DLCO values did not return to normal. The KCO also improved from 71.9% to 74.4%, though this change did not reach statistical significance. Most patients (n = 26) were treated with apixaban, potentially contributing to the observed improvement in gas transfer parameters, Price said.
The researchers identified a distinct phenotype of patients with persistent post-COVID-19 infection symptoms characterized by abnormal lung perfusion and reduced gas diffusion capacity, even when CT scans appear normal. Price explains that this pulmonary microangiopathy may explain the persistent symptoms. However, questions remain about the underlying mechanisms, potential treatments, and long-term outcomes for this patient population.
Causes and Treatments Remain a Mystery Previous studies have suggested that COVID-19 causes endothelial dysfunction, which could affect the small blood vessels in the lungs. Other viral infections, such as HIV, have also been shown to cause endothelial dysfunction. However, researchers don't fully understand how this process plays out in patients with COVID-19.
"It is possible these patients have had inflammation insults that have damaged the pulmonary vascular endothelium, which predisposes them to either clotting at a microscopic level or ongoing inflammation," said Hinks.
Some patients (10 out of 41) in the cohort studied by the Imperial College London's researchers presented with Raynaud syndrome, which might suggest a physiological link, Hinks explains. "Raynaud's is a condition of vascular control or dysregulation, and potentially, there could be a common factor contributing to both breathlessness and Raynaud's."
He said there is an encouraging signal that these patients improve over time, but their recovery might be more complex and lengthy than for other patients. "This cohort will gradually get better. But it raises questions and gives a point that there is a true physiological deficit in some people with long-COVID."
Price encouraged physicians to look beyond conventional diagnostic tools when visiting a patient whose CT scan looks normal yet experiences fatigue and breathlessness. Not knowing what causes the abnormalities observed in this group of patients makes treatment extremely challenging. "We need more research to understand the treatment implications and long-term impact of these pulmonary vascular abnormalities in patients with long-COVID," Price concluded.
#long covid#covid#covid news#mask up#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#sars cov 2#still coviding#coronavirus#wear a respirator#covid conscious#covid is airborne#covid isn't over#covid pandemic#covid19#covidー19
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pulmonary Edema

Introduction
Pulmonary edema is a condition that results from the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the lungs, leading to impaired gas exchange and respiratory distress. This comprehensive discourse aims to provide an in-depth analysis of pulmonary edema, covering its pathophysiology, etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, treatment strategies, prevention strategies, and associated complications.
Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Edema

Pulmonary edema develops when there is an imbalance between the hydrostatic and oncotic pressures within the pulmonary vasculature. This imbalance leads to an increase in capillary permeability and the extravasation of fluid into the interstitial space and alveoli of the lungs. Several mechanisms contribute to this process, including increased capillary hydrostatic pressure due to heart failure, increased vascular permeability due to inflammation or injury, and decreased oncotic pressure due to hypoalbuminemia or capillary leak syndrome.
Etiology of Pulmonary Edema
The etiology of pulmonary edema can be categorized into cardiogenic and noncardiogenic causes. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema occurs secondary to heart failure or other cardiac conditions that result in elevated left atrial pressure and pulmonary venous congestion. Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, on the other hand, is caused by factors unrelated to heart dysfunction, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), aspiration, sepsis, or neurogenic pulmonary edema.
Clinical Manifestations of Pulmonary Edema

The clinical presentation of pulmonary edema varies depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, cough, frothy sputum, cyanosis, and crackles on auscultation. Severe cases may progress to respiratory failure, hypoxemia, and hemodynamic instability.
Diagnostic Modalities for Pulmonary Edema

Diagnosing pulmonary edema requires a thorough clinical evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Imaging studies such as chest X-ray, computed tomography (CT) scan, and lung ultrasound can provide valuable information about lung parenchymal changes and the presence of pulmonary congestion. Laboratory tests, including arterial blood gas analysis, brain natriuretic peptide levels, and electrolyte measurements, may also aid in the diagnosis and assessment of disease severity.
Treatment Strategies for Pulmonary Edema
The management of pulmonary edema involves addressing the underlying cause, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications. Initial treatment often includes supplemental oxygen therapy to improve oxygenation and reduce respiratory distress. Diuretics, such as furosemide or bumetanide, are commonly used to reduce fluid overload and alleviate pulmonary congestion. In cases of cardiogenic pulmonary edema, vasodilators, inotropes, or mechanical ventilation may be necessary to improve cardiac function and gas exchange.
Prevention Strategies for Pulmonary Edema
Preventing pulmonary edema requires a broad approach aimed at managing underlying risk factors and promoting healthy lifestyle habits. Patients with known cardiac conditions should adhere to prescribed medications, maintain a low-sodium diet, and monitor fluid intake to prevent fluid retention and exacerbation of heart failure. Individuals at risk of noncardiogenic pulmonary edema should avoid exposure to toxins, practice proper respiratory hygiene, and seek prompt medical attention for respiratory infections or injuries.
Complications of Pulmonary Edema

Untreated or inadequately managed pulmonary edema can lead to several complications, including acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), cardiogenic shock, acute kidney injury, pulmonary hypertension, and death. Prompt recognition and intervention are essential to prevent progression to these life-threatening complications and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Pulmonary edema is a complex and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt recognition, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate management. By understanding the underlying pathophysiology, etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, treatment strategies, prevention strategies, and associated complications of pulmonary edema, healthcare providers can optimize patient care and outcomes. Continued research efforts aimed at elucidating the mechanisms underlying pulmonary edema and identifying novel therapeutic targets are essential to further improve patient outcomes and reduce the global burden of this condition.
Embarking on your journey in the field of medicine is both exciting and challenging. As you navigate through your rigorous study period, it’s essential to seek guidance and assistance whenever needed to ensure your success.
At Expert Academic Assignment Help, we understand the demands of medical education and are here to support you every step of the way. Whether you require assistance with assignments, research papers, or exam preparation, our team of experts is dedicated to providing you with the help you need to excel in your studies.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to us for guidance, academic support, or any questions you may have. You can contact us via email at [email protected]
#assignment help#medical students#healthcare#nursing student#nursing school#expert assignment writers#academic assignments#homework help#do your homework#pharmacy student#pharmacy technician#pharmacology#health and wellness#health tips#health#medicine#treatment#health & fitness#healthylifestyle#high school#essay writing#essay#academic writing
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Viagra prodej bez předpisu | Viagra bez receptu v Lekarna-cz
Viagra Prodej Bez Předpisu: Empowering Men's Health Responsibly
Viagra has been a revolutionary medication that has transformed the lives of countless men worldwide. As a professional with over four years of experience in Viagra prodej bez předpisu | Viagra bez receptu v Lekarna-cz, I have witnessed the positive impact of this medication on men's health. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and it is crucial to ensure that Viagra is used safely and responsibly.
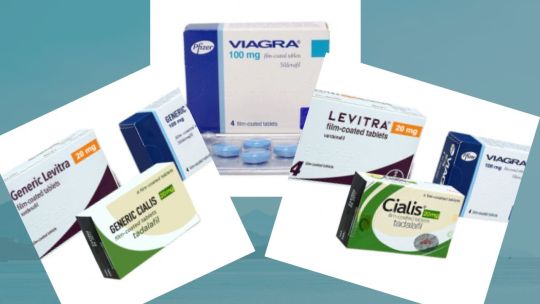
The Advantages of Viagra
Viagra, also known by its generic name sildenafil citrate, is primarily prescribed for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). It works by enhancing blood flow to the penis, helping men achieve and maintain erections suitable for sexual activity. Apart from treating ED, Viagra has been used for other medical conditions, such as pulmonary arterial hypertension. https://lekarna-cz.net/levitraoriginal
One of the significant advantages of Viagra prodej bez předpisu | Viagra bez receptu v Lekarna-cz is that it provides men with easier access to the medication. This allows those who might be embarrassed or reluctant to discuss their condition with a doctor to seek help discreetly. However, this convenience also raises the importance of responsible use and awareness.
Promoting Responsible Use
As a provider of Viagra, it is crucial to prioritize customer safety and well-being. Encourage your clients to consult with a healthcare professional before starting Viagra or any other medication. Erectile dysfunction can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying health issue, such as cardiovascular problems, diabetes, or hormonal imbalances. A comprehensive medical evaluation can help identify and address potential health concerns.
Educate your customers about the proper dosage and potential side effects of Viagra. Inform them about possible drug interactions and contraindications, especially if they are taking other medications regularly. Remind them not to mix Viagra with alcohol or recreational drugs as it can lead to adverse effects.
Furthermore, emphasize the importance of obtaining Viagra from reputable sources to ensure the authenticity and quality of the medication. Counterfeit drugs can be dangerous and ineffective, putting the user's health at risk.
Empowering Men's Health
Viagra prodej bez předpisu | Viagra bez receptu v Lekarna-cz plays a crucial role in empowering men to take control of their sexual health. By providing discreet access to the medication, men can address their concerns without unnecessary embarrassment. However, this empowerment should go hand in hand with awareness and responsibility.
Encourage your customers to view Viagra as a supplement to a healthy lifestyle rather than a quick fix. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management all contribute to overall well-being and sexual health.
As someone with extensive experience in Viagra prodej bez předpisu | Viagra bez receptu v Lekarna-cz, you hold a unique position in promoting responsible use of this medication. Viagra can significantly improve the lives of men with erectile dysfunction, but it should be used wisely and under proper guidance. Empower your customers to prioritize their health, seek medical advice, and embrace a holistic approach to men's well-being. By doing so, you contribute to a safer and more fulfilling experience for all those who benefit from this remarkable medication.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Identifying Heart Failure Symptoms

When the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s demands, it can result in heart failure, a serious condition that may lead to death. Despite what the name might imply, it does not indicate that the heart has completely ceased beating. It’s not working as well as it should, instead of and this can lead to several symptoms, some of which are more evident than others. For timely treatment and a higher quality of life, indicators of heart failure must be identified early.
https://homecarenurse.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Your-paragraph-text-16.jpg
What Is Heart Failure?
Numerous underlying medical conditions, including coronary artery disease, hypertension, or a prior heart attack, can result in heart failure. Acute heart failure can happen fast, even though it usually develops gradually over time. Both left-sided and right-sided heart failure are popular classifications for the condition, and many patients have both kinds of symptoms.
Common Heart Failure Symptoms
Symptoms of heart failure vary according to the condition’s kind and severity. The following are the most typical signs to look out for:
Breathing difficulties
One of the most obvious signs of heart failure is dyspnea, or shortness of breath. Severe cases may occur while you’re working out, soothing, or even while you’re flat. Inadequate cardiac action causes fluid to build up in the lungs, making breathing challenging.
Weakness and Tiredness
Even with efficient heart pumping, certain conditions can reduce the amount of blood reaching the muscles and organs. People frequently feel exhausted and weak all the time as a result. Daily tasks like going for short walks or climbing stairs may be difficult for you.
Edema, or swelling
A common consequence of fluid retention caused by heart failure is edema, which often affects the legs, ankles, feet, and chest. It gathers in the veins and fluid seeps into the surrounding tissues as the heart’s blood flow slows down.
Constant coughing or wheezing
An accumulation of fluid in the lungs may be the cause of wheezing or continuous breathing, which is often worse when lying down. White or pink-tinged mucus may occasionally appear during coughing. This is a sign of a pulmonary effusion that has to be treated right away.
An erratic or fast heartbeat
The heart adjusts for its reduced pumping ability by producing palpitations, which are a frenetic or quick heartbeat. Your heart can be beating in your chest, fluttering, or skipping beats.
Challenge Focusing or Perplexity
Reduced blood flow to the brain can have negative impacts on memory, focus, and mental clarity. While elderly people may wrongly see this as a sign of age, it may signify insufficient oxygen transfer in the context of heart failure.
Unexpected Weight Gain
Rapid weight gain over a few days, such as gaining two to three pounds in a single day or five pounds in a single week, may indicate fluid accumulation and worsening heart failure. Patients who are at risk are frequently advised to track their weight daily.
Nausea or loss of appetite
Feelings of fullness, bloating, or nausea can result from an accumulation of fluid in the digestive tract. An average appetite and lack of food might make the body even weaker.
When to Seek Medical Help
When to Get Medical Assistance, you can improve your chances of living a longer, healthier life and slow the course of heart failure with early diagnosis and treatment. It’s critical that you see a healthcare provider if you experience any of the above symptoms, particularly if they get worse quickly.
Conslusion
Heart failure is unlikely to go untreated. You can take preventive measures to maintain the health of your heart by being aware of its signs. Heart-healthy lifestyle choices, routine checkups, and sticking to medical advice can all make a big difference. Your body may be telling you something essential, so listen to it.
0 notes
Text
North America Cardiac Monitoring Devices Market Size, Revenue, End Users And Forecast Till 2028
The North America cardiac monitoring devices market is projected to reach US$ 16.43 billion by 2028 from US$ 10.52 billion in 2021. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% from 2021 to 2028.
A cardiac event monitor is used to record the heart's electrical activity (ECG). It keeps the track of the heartbeat and rhythm. These monitors are employed for the long-term monitoring of symptoms that don't occur every day. Important heart health data can be tracked, recorded, and sent to patients’ doctors in real time using cardiac monitoring systems, allowing the care teams to monitor patients’ heart health from a distance. This reduces the need for frequent visits to the doctor's office.
Market Insights
Increase in Incidence of Cardiovascular Diseases Drives North America Cardiac Monitoring Devices Market Growth
Every 40 seconds, someone in the United States gets a stroke. A stroke kills someone every 4 minutes. A stroke affects more than 795,000 people in the United States each year. The first or new strokes account for around 610,000 of these. The growing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) such as coronary heart diseases, sudden cardiac arrest, congenital heart diseases, heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and pulmonary artery pressure (PA) is encouraging the introduction of improved monitoring methods. The simplicity of use and the ability of the quick detection of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are adding to the popularity of cardiac monitoring devices. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), ~30 million people experience a stroke each year. Moreover, the American Heart Association states more than 130 million people in the US, i.e., 45.1% of the population, are projected to have a type of CVD by 2035. In 2018, Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) was the leading cause (42.1%) of deaths attributable to CVD in the US, followed by stroke, high blood pressure, heart failure, diseases of the arteries, and other CVD.
Grab PDF To Know More @ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/TIPRE00028376
Rise in Number of Product Launches and Approvals Contributes Significantly to Market Growth
The North America cardiac monitoring devices market is characterized by the presence of many small and big companies. To increase their market share, market players are adopting strategies such as new product launches, regional expansions, and technological advancements. Cardiac monitoring devices are safer and more effective than ever with continued innovation and technological advances, leading to increased acceptance of cardiac monitoring devices. Prominent players are investing in R&D to develop advanced technologies and improve their revenue shares.
Market Segmentation
The North America cardiac monitoring devices market is analyzed on the basis of type, product type, application and end user. Based on type, the market is categorized into cardiovascular devices (event monitors, electrocardiography (ECG), cardiac catheters, stents, defibrillators, guidewires, pacemakers, heart valves and others), patient monitoring devices (cardio monitoring devices, anesthesia monitoring devices, hemodynamic monitoring devices, fetal and neonatal monitoring devices, stress management devices and others), multi-parameter ECG monitors, cardiac monitors [cardiac event monitoring (CEM) holter, extended holter/AECG, and others], ambulatory cardiac monitoring (event recorders, implantable loop recorders, mobile cardiac telemetry, and others), and others.
Market leaders and key company profiles
Medtronic
Abbott
Boston Scientific Corporation
iRhythm Technologies, Inc.
GE Healthcare
Biotronik, Inc.
SCHILLER Healthcare India Pvt. Ltd
Koninklijke Philips N.V.
MicroPort Scientific Corporation
Asahi Kasei Corporation
About Us:
Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Defence; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications.
0 notes
Text
Top Signs You Should Consult a Lung Specialist in Varanasi Immediately
In today’s fast-paced life, respiratory problems often go unnoticed or are brushed aside as minor issues. However, your lungs are vital organs responsible for the oxygen supply that keeps your body functioning. Ignoring the warning signs of lung problems can lead to serious health complications. If you're experiencing persistent symptoms, it's time to consult a lung specialist in Varanasi—a city that boasts some of the most experienced pulmonologists like Dr. Vikas Jaiswal at Lung + Plus Clinic.
Let’s explore the top signs that indicate it’s time to seek help from a qualified lung specialist in Varanasi.
1. Chronic Cough That Won’t Go Away

A cough lasting more than three weeks should never be ignored. It could be a symptom of chronic bronchitis, asthma, tuberculosis, or even lung cancer. Whether it’s dry, phlegmy, or occurs only at night, a persistent cough is one of the earliest signs that something’s wrong. A lung specialist in Varanasi can perform diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays, sputum analysis, or lung function tests to find the root cause.
2. Shortness of Breath

If you’re finding it difficult to breathe during routine tasks like climbing stairs, walking, or even while resting, this could be an early sign of conditions such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), asthma, or pulmonary hypertension. These conditions require immediate evaluation and treatment by a reputed lung specialist in Varanasi. Shortness of breath is not something to overlook, especially if it worsens over time.
3. Wheezing or Noisy Breathing

Wheezing—a high-pitched whistling sound when you breathe—usually points to a narrowing of the airways. It can be associated with asthma, bronchitis, or allergic reactions. A skilled lung specialist in Varanasi can use a spirometer or perform allergy testing to diagnose the exact issue and suggest a treatment plan to manage and relieve symptoms.
4. Chest Pain or Tightness

Chest pain can often be confused with heart-related issues, but it can also be a sign of pleuritis (inflammation of the lung lining), pneumonia, or a pulmonary embolism. If you feel chest tightness, sharp pains when breathing deeply, or a general discomfort in the chest area, visiting a lung specialist in Varanasi should be your next step.
5. Frequent Respiratory Infections

Repeated episodes of bronchitis, pneumonia, or other chest infections may indicate a weakened immune response or underlying lung disease. Early diagnosis and preventive strategies are crucial. A lung specialist in Varanasi can recommend appropriate vaccines, lifestyle changes, and medications to boost your lung health.
6. Unexplained Weight Loss

Unintended weight loss, especially when accompanied by coughing or breathlessness, is a red flag. It might be a symptom of tuberculosis or lung cancer. Pulmonologists are trained to identify these early indicators and carry out the necessary tests, such as a CT scan or bronchoscopy, for accurate diagnosis.
7. Chronic Fatigue

If you constantly feel tired despite getting enough rest, your lungs may not be delivering sufficient oxygen to your body. This could result from chronic respiratory illnesses like interstitial lung disease. A lung specialist in Varanasi will assess your oxygen levels, possibly using a pulse oximeter or arterial blood gas test, and determine the need for supplemental oxygen or other treatments.
8. Coughing Up Blood (Hemoptysis)

Even a small amount of blood in your sputum should not be ignored. It could be due to infections like tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, or even malignancy. A lung specialist in Varanasi will ensure a comprehensive diagnostic workup to identify and treat the underlying cause before it progresses.
9. Snoring and Sleep Apnea Symptoms

Loud snoring, choking sounds during sleep, or excessive daytime sleepiness may point to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a condition that can lead to high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. Many pulmonology clinics in Varanasi offer sleep studies to diagnose and manage sleep-related breathing disorders effectively.
Why Choose a Lung Specialist in Varanasi?
Varanasi is not just a city of spiritual and cultural richness—it’s also a growing medical hub. Reputable pulmonologists in the city, like Dr. Vikas Jaiswal at Lung + Plus Clinic, provide expert consultation and advanced treatments for all types of respiratory illnesses. Equipped with modern diagnostic facilities and a patient-centered approach, a lung specialist in Varanasi ensures that your lungs are in the best possible hands.
Final Thoughts
Your lungs play a vital role in your overall health. Recognizing the early signs of respiratory distress and acting promptly can save you from severe health complications. If you experience any of the symptoms discussed above, don’t delay—consult a lung specialist in Varanasi right away. With timely diagnosis and effective treatment, you can breathe easy again and lead a healthier, more active life.
#lung specialist in Varanasi#pulmonologist in Varanasi#best lung doctor in Varanasi#chest pain#persistent cough#shortness of breath#respiratory infections#coughing blood#wheezing#sleep apnea#chronic fatigue#TB doctor#lung diseases.
0 notes
Text
Pulmonary Hypertension: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
Pulmonary hypertension, a condition often misunderstood, involves elevated blood pressure in the arteries of your lungs. This pressure makes it harder for your heart to pump blood through the lungs, potentially leading to serious health complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pulmonary hypertension is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. What…
0 notes
Text
Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Lung Hernias

Hernias are typically associated with the intestine pushing through a tear in the abdomen’s muscle wall, as when lifting a heavy object causes strain. However, hernias can also be associated with the lungs. With a lung hernia, a portion of the lung bulges through a weak spot, or pushes through a tear, in the chest wall or neck passageway.
A relatively uncommon condition, lung hernia reflects factors such as surgery, trauma, or an underlying medical issue. Associated with 80 percent of cases, hernias with trauma as the cause typically result from blunt force injuries such as falls and car accidents. Surgical lung hernias reflect weakness caused by past lobectomies, pneumonectomies, and other thoracic surgeries.
In extremely rare cases, there is no discernible traumatic cause for the hernia. In these cases, issues such as emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which weaken the thoracic wall over time, are implicated. Other potential causes include chronic use of steroids and a series of harsh, sharp coughs, which can open an old incision or tear a chest muscle.
While sometimes serious, lung hernias are not life threatening in and of themselves, and they are relatively easy to identify, diagnose, and treat. Symptoms include shortness of breath, challenges breathing deeply, and sharp pains associated with coughing, sneezing, and inhaling. Swelling or general soreness in a particular chest region may also be present.
Treating mild to moderate lung hernias often involves basic measures such as cough suppressants, infection and analgesic pain medications, and bed rest. Surgery is recommended for larger and more severe hernias, with surgeons returning the lung to its proper position. The opening is then stitched up and the weakened region of the chest reinforced.
The 2020 paper “Pulmonary Herniation after Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery” examined how post-surgical complications can lead to hernias that result from chest wall trauma. The clinical researchers from the Kerckhoff Heart Center in Bad Nauheim and the Institute for Pharmacology and Preventive Medicine in Cloppenburg, Germany, found that lung hernias often occur near past thoracotomy sites. They become clinically visible in males when coughing occurs.
However, women’s clinical symptoms tended to be hidden by the breasts, and “unspecific complaints or occasional pain when coughing” is the most prevalent indicator. This makes prompt and early evaluations and referral to advanced diagnostics important in diagnosis.
In the 2023 paper “Surgical Repair of Spontaneous Lung Herniation Induced by Vigorous Coughing,” researchers examined the case of a 72-year-old male with a background of smoking, arterial hypertension, and COPD. With no reported history of trauma, he experienced spontaneous lung herniation as a result of vigorous coughing.
Chest X-rays and CT scans helped identify the scope of the issue, with pulmonary function tests indicating restricted airflow and reduced lung capacity. Open surgical repair was performed, with thoracotomy successfully resolving chest pain and shortness of breath. Post-surgery, the patient embarked on intensive physiotherapy. He also received respiratory therapy and pharmacotherapy for his underlying COPD issue.
As a result, the patient was asymptomatic and free of pain, with no daily activity limitations, three months after the procedure. The authors attributed this positive result in a potentially serious spontaneous lung hernia case to a combination of early recognition and prompt treatment.
0 notes
Text
How High Blood Pressure Affects Your Heart: Imaging & Diagnosis.
High blood pressure, also referred to as hypertension, is typically considered the “silent killer” that is responsible for the most deaths. It quietly sneaks in and often exists without symptoms. It is like a time bomb. When it is not dealt with, it can destroy your heart.
The relationship between high blood pressure and heart health is widely known, and new imaging technologies have helped detect this damage at an earlier stage than before. With a team led by some of the best cardiologists in Dhanori, we provide complete information on how high blood pressure affects the heart and how modern radiology and cardiology come together to diagnose and effectively manage it.
What is Meant by High Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the physical force exerted by the blood against the walls of artery. When blood pressure is high over a long period, it creates strain on blood vessels and organs. A normal blood pressure reading is less than 120/80 mm Hg. Hypertension is typically diagnosed when the readings are always higher than 130/80 mm Hg.
The Heart Under Pressure
High blood pressure in the body has a tendency to make the heart overwork in order to keep up with the required normal blood supply. This increased burden may lead to a thicker heart muscle, particularly the left ventricle, which is the case of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH).
The role of hypertension that is recognized early helps in preventing the development of severe outcomes and being in a secure position. The use of high-tech imaging in diagnosing these cases is the most vital step to be taken.
At the Vighnaharta Heart Care and Imaging Centre, the diagnostic technology is operated by the expert radiologist, who also makes close consultations with the treating physicians. The combined efforts of these professionals enable the patient to benefit from a prompt and accurate treatment decision.
The Role of Medical Imaging in Diagnosis
1. Echocardiogram (ECHO):
It is an ultrasound-based test that is easy to reach and is one of the most informative tools in the field of cardiac diagnostics. It can be used to monitor the heart's chambers and walls in real time and is very good at finding left ventricular hypertrophy, valve problems, and fluid accumulation.
2. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG):
While not exactly an imaging test, the ECG may still be the first diagnostic tool that indicates the presence of heart strain or past damage to the heart due to high blood pressure. An ECG is a tool that can help your doctor to diagnose arrhythmia and also hypertrophy, albeit indirectly, through the changes of the waveform.
3. Cardiac MRI:
For more detailed, high-resolution images, cardiac MRI is a noninvasive test that provides a three-dimensional view of the heart's structure and function. It is particularly useful for evaluating myocardial fibrosis (scarring of heart tissue), which can be caused by long-term high blood pressure.
4. Chest X-ray:
Although not as detailed, a chest X-ray can reveal an enlarged heart or pulmonary congestion in the later stages of heart failure, which may be the result of poorly controlled high blood pressure.
5. Coronary CT Angiography (CTA):
When there is concern about the health of the coronary arteries, CTA can help detect atherosclerosis caused or worsened by high blood pressure.
6. Stress Testing:
Helps assess how the heart responds to exertion and may reveal underlying ischemic conditions that may contribute to high blood pressure.
Controlling Blood Pressure to Protect Your Heart
Imaging and diagnosis serve just one of the functions here. Detection of illness is usually followed by a need to decrease the blood pressure, which in turn lessens the burden on the heart. This is frequently carried out by
Drugs, such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or diuretics.
Changes in lifestyle, for example, reducing sodium intake, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and alcohol limitation.
Control of the situation and visiting the doctor for the regular checkup, including both at-home blood pressure monitors and regular cardiac evaluations
Understanding the Link Between High Blood Pressure and Heart Health
High blood pressure forces your heart to work harder than normal to pump blood. Over time, this extra strain can lead to a number of harmful effects:
1. Thickening of the Heart Muscle:
One of the heart's ventricles can increase in size, a disorder known as left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). Although it may sound like a positive development at first, it will eventually become a cause of worse pumping and more likely heart failure than before.
2. Increased Risk of Heart Attack:
High blood pressure accelerates atherosclerosis, the buildup of fatty deposits in blood vessels. Narrowing of these blood vessels can reduce or block blood flow to the heart, leading to a heart attack.
3. Heart Failure:
Long-term high blood pressure can weaken the heart muscle, reducing its ability to pump blood efficiently.
4. Aneurysm and Other Vascular Complications:
Constant pressure on blood vessels can cause them to bulge or rupture, especially in critical areas like the aorta.
Why Choose Vighnaharta Heart Care and Imaging Centre?
Led by Specialists:
Patient-Centric Approach
Local Expertise:
Affordable & Accessible
Managing High Blood Pressure Proactively
Eat a heart-healthy diet (low salt, lots of fruits and vegetables), exercise regularly, and quit smoking.
Antihypertensives, cholesterol-lowering medications, and other medications as prescribed.
Regular blood pressure checks, imaging follow-ups, and consultations with your cardiologist.
Conclusion:
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is called the "silent killer". It can damage your heart and blood vessels without any noticeable symptoms. If you or a loved one is concerned about blood pressure or heart health, don't wait. High blood pressure is a serious condition that can damage your heart if left uncontrolled. Visit Vighnaharta Heart Care and Imaging Centre, where your heart is in expert hands.
#best cardiologist in pune#heart specialist in dhanori#sonography test in dhanori#stress test in dhanori#2 d echo in dhanori#cardiologist in lohegoan
0 notes
Text
What Is Pulmonary Hypertension? Symptoms, Types, and Treatments Explained Simply
Breathless after light activity? Heart pounding more than usual? It could be more than “just age.” These are signs of Pulmonary Hypertension (PH)—a rare but serious condition where blood pressure in the lungs becomes dangerously high.
This article on the types and causes of pulmonary hypertension breaks it all down in everyday language. If you or a loved one is struggling with unexplained fatigue or breathlessness, this is worth a read.
🫁 Pulmonary Hypertension Symptoms Include:
Shortness of breath (even at rest)
Chest pain or pressure
Swollen ankles or legs
Fatigue and dizziness
Rapid heartbeat
🩺 There Are 5 Types of PH (and Each Needs Different Care):
1️⃣ Group 1: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) 2️⃣ Group 2: Due to left heart disease 3️⃣ Group 3: Due to lung disease or low oxygen 4️⃣ Group 4: From blood clots in the lungs 5️⃣ Group 5: Other unclear or multifactorial causes
💊 Treatment may include:
Oxygen therapy
Blood thinners
Lifestyle adjustments
Specialized medications for PAH
Early diagnosis is key, so don’t wait if symptoms persist.
📖 Learn more → Pulmonary Hypertension Guide
#pulmonaryhypertension#hearthealth#lungdisease#breathingissues#phsymptoms#healthawareness#cardiopulmonary#chronicconditions#healthokglobal
0 notes
Text
pulmonay edema
Pulmonary Edema: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Pulmonary edema is a serious medical condition where fluid accumulates in the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. This condition can develop suddenly (acute pulmonary edema) or over time (chronic pulmonary edema). If not treated promptly, pulmonary edema can lead to severe complications, including respiratory failure and death.
Causes of Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary edema is generally divided into two types based on its cause:
Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema: This occurs due to heart problems. When the heart's left ventricle fails to pump blood efficiently, pressure builds up in the blood vessels of the lungs, causing fluid to leak into the alveoli. Common causes include:
Heart attack
Congestive heart failure
Severe hypertension (high blood pressure)
Heart valve disorders
Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema: This form is not directly related to heart issues. Causes include:
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Pneumonia or lung infections
Inhalation of toxins or smoke
Kidney failure
High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE)
Near drowning
Trauma to the chest
Symptoms of Pulmonary Edema
Symptoms of pulmonary edema can vary depending on its severity but often include:
Severe shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
A feeling of suffocating or drowning
Wheezing or gasping for air
Cough producing frothy sputum, sometimes tinged with blood
Rapid, irregular heartbeat
Anxiety, restlessness, or a sense of doom
Chest pain if heart problems are involved
Cyanosis (blue-tinged lips or fingertips)
Chronic pulmonary edema may present with mild shortness of breath during exertion, swelling in the legs, and weight gain due to fluid retention.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing pulmonary edema requires a combination of medical history, physical exams, and diagnostic tests:
Physical Examination: Listening to the lungs for crackling sounds and checking oxygen levels.
Chest X-ray: Reveals fluid buildup in the lungs.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detects heart rhythm problems.
Echocardiogram: Assesses heart function and structure.
Blood Tests: Check for underlying heart, kidney, or infection-related issues.
Pulse Oximetry and Arterial Blood Gas Test: Measure oxygen levels in the blood.
Quick and accurate diagnosis is crucial for managing pulmonary edema effectively.
Treatment Options
The primary goal in treating pulmonary edema is to improve oxygen levels and address the underlying cause:
Oxygen Therapy: Delivered through a mask or nasal cannula to boost blood oxygen.
Diuretics: Medications like furosemide help eliminate excess fluid from the body through urine.
Medications for Heart Conditions: Drugs to control blood pressure, improve heart function, or treat heart attacks.
Mechanical Ventilation: In severe cases, a ventilator may be necessary to support breathing.
Treating Infections or Injuries: Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or surgery may be needed depending on the cause.
Prompt treatment dramatically improves outcomes and can be life-saving.
Prevention
Preventing pulmonary edema largely involves managing risk factors:
Control high blood pressure and heart disease.
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Stay within healthy weight limits.
Follow your doctor's advice for chronic diseases like diabetes or kidney disease.
Acclimate slowly to high altitudes if traveling to mountainous areas.
Conclusion
Pulmonary edema is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you act quickly if symptoms arise. With early intervention and proper management, most people can recover and prevent future episodes.
Read more - Aatankwadi Shayari
0 notes
Text
Heart Failure Home Health Reasoning 1 of 2 FIRST Home Health Nurse Visit Community Health Nursing (Chamberlain University) Scan to open on Studocu Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 Heart Failure Home Health Reasoning 1 of 2 FIRST Home Health Nurse Visit Frank Smith, 75 years old Primary Concept Perfusion Interrelated Concepts (In order of emphasis) Clinical Judgment Patient Education Communication Collaboration NCLEX Client Need Categories Percentage of Items from Each Category/Subcategory Covered in Case Study Safe and Effective Care Environment Management of Care 17-23% Safety and Infection Control 9-15% Health Promotion and Maintenance 6-12% Psychosocial Integrity 6-12% Physiological Integrity Basic Care and Comfort 6-12% Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies 12-18% Reduction of Risk Potential 9-15% Physiological Adaptation 11-17% Copyright © 2019 Keith Rischer, d/b/a KeithRN. All Rights reserved. Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 Initial Data to Review from Chart: Current Problem/Reason for Home Health Care: Frank Smith is a 75-year-old male who is 5 feet 10 inches tall (178 cm). His baseline weight is 255 lbs. (115.9 kg-36.6 BMI). He has a history of type II diabetes, myocardial infarction, hypertension and chronic systolic heart failure (ejection fraction 40%) secondary to coronary artery disease. Summary of Inpatient Admission: Frank presented to the emergency department complaining of weakness, fatigue, decreased tolerance to activity, shortness of breath with exertion, weight gain of three pounds in 24 hours, and productive cough with blood-tinged sputum. Furosemide IV was administered to address fluid volume excess and 4500 mL fluid was removed. Before discharge, he is at his baseline weight. Review of medication and nutrition therapy was provided before discharge and he had no questions. Re-Hospitalization Risk Assessment: This is Frank’s second inpatient admission in the last 30 days due to acute decompensated heart failure. He is discharged with a diagnosis of pulmonary edema and exacerbation of chronic systolic heart failure. A referral was ordered for home health care follow-up, and a registered nurse is scheduled to visit his home within 24 hours after discharge to assess patient, determine medication adherence, and his understanding of management of heart failure. What data from the histories are RELEVANT and must be interpreted as clinically significant by the nurse? (Reduction of Risk Potential) RELEVANT Data from Current Problem: Clinical Significance: Age and Baseline weight of 255lbs DM2 MI Hypertension Chronic Systolic heart failure with ejection fraction 40% Coronary artery disease His age and history of chronic systolic heart failure secondary to coronary artery disease, along with his hypertension, and DM2 will make patient predisposed to gradual heart failure and higher risk for an MI, fluid overload, and other complications. The ejection fraction of 40% will decrease tissue perfusion leading to blood to accumulate in the pulmonary vessels. RELEVANT Data from Inpatient Admission: Clinical Significance: Weakness, fatigue, decreased tolerance to activity, shortness of breath with exertion, weight gain of 3 pounds in 24 hours, blood-tinged sputum, Furosemide IV administered, weight loss of 4500mL The patient’s symptoms seem to indicate fluid overload, pulmonary edema, related to his history of coronary artery disease and systolic heart failure, especially since furosemide IV was given and caused fluid loss RELEVANT Data from Re-Hosp. Risk Assess: Clinical Significance: Second inpatient admission in the last 30 days due to heart failure, pulmonary edema diagnosis, follow up ordered Having been his second admission for the same cardia issues make patient even more prone to repeating episodes, fluid overload and pulmonary edema Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 Social History: Frank is a retired engineer whose wife died unexpectedly one year ago after fifty years of marriage. He has become less active since she died and rarely gets out of the house. Since his wife did most of the cooking, Frank mostly eats either soup out of a can or frozen meals that need to be heated up. He has three grown children and six grandchildren, but they all live out of state. What data from the social history are RELEVANT and must be interpreted as clinically significant by the nurse? (Reduction of Risk Potential) RELEVANT Data from Social History: Clinical Significance: Retired, widow, less active and social, lives alone, eats processed foods, no family around Patient could be having difficulty coping with his wife’s death and/or can also be depressed causing him to be less active and social. He also lives alone and doesn’t have family nearby so he can also be lacking support for more serious complications like a heart attack. His diet can also be contributing to the exacerbating of his heart failure due to the high sodium levels in the canned soups he likes. Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 Lab Results: Prior to Discharge Cardiac Labs: Prior to Discharge: High/Low/WNL? BNP (B-natriuretic Peptide) ( Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Pathophysiology of heart failure ESC (2008) defines Heart failure as a clinical syndrome that epitomizes itself following impairment of the heart function and/ or structure. The situation in turn results into dyspnea and fatigue when the body is at rest or upon physical exertion HFSA (2010) adds. Heart failure effects from a single heart related disease to multiple heart diseases and or conditions as Clifford & Grevson (2008) explains. Some of major causes of heart failure include and not limited to: cardiomyopathies both genetic and primary, valvular heart disease and poorly controlled hypertension (which raises the contraction forces required to pump blood) and coronary artery diseases. According to AIHW (2011) Cardiovascular disease is a burden both to the developed and developing nations. Going by statistics carried in 2011 in Australia, CVD is a leading killer. The data shows that 45 600 death were as a result of CVD. This means that every 12 minutes there is actually one death arising from CVD related diseases and conditions. Conversely, is good noting that in relation to the previous years this rate was an improvement; but then again CVD remains the largest health burden in Australia’s economy AIHW (2008) & AIHW (2011). Clifford & Grevson (2008) highlights that; there are two types of HF systolic and diastolic which are either chronic or acute. Acute heart failure is experienced when heart functions are altered rapidly within a short period of time (hours or days) like in the cases of familial cardiomyopathy. In acute HF, cardiac output drops drastically which is life threatening. Chronic heart failure on the other hand means that; the cardiac functions are gradually affected. Over a prolonged period(months or years) the heart’s function (systolic and diastolic) are altered such as volume overloads and pressure impairment caused by coronary heart disease or valvular ESC (2008) explains. Mrs. Yates in this case suffers from chronic heart failure since she has had the condition for eight years. A heart in a normal condition produces no murmur sound. However, when the heart structure is altered in anyway a health specialist can hear murmur sound using the stethoscope. Nonetheless, not all murmur sounds are bad Clifford & Grevson (2008). According to NHFA/CSANZ (2011) heart failure progress goes through stages some of which are not easily detectable by both the patient and the doctor like the asymptomatic and latent phase. These stages, most often leaves the patient untreated as the problems advances. Consequently, the patient visits the clinic when the symptoms of HF at a late stage are in place. Diastolic dysfunction Diastolic heart failure occurs when the ventricles fail to relax passably HFSA (2010) explains. This signifies stiff ventricular wall. Patients suffering from DHF have impaired diastolic function; echocardiography indicates preserved systolic function, left ventricular cavities are smaller and left ventricular wall is dense. Consequently, the ventricles do not fill sufficiently resulting into deficient in stroke volume. Valve regurgitation is prevalent allowing back flow of blood against the normal flow. When ventricular relaxation is not achieved there is raised end-diastolic pressure. ESC (2008) adds that, the ultimate results include left heart failure presenting with pulmonary edema and right heart failure presenting with peripheral edema. This factor explains why Mrs. Yates upon examination was found to have moist fine crackles in both lungs. This can also occur when heart failure is also accompanied with pulmonary congestion Clifford & Grevson (2008) adds. Following Clifford & Grevson (2008) major causes of diastolic dysfunction include restrictive cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, ischemic heart disease and hypertension Diastolic heart failure (DHF) is common among the elderly population, patients with restrictive cardiomyopathy, who suffer from left ventricular hypertrophy and persons who have been suffering from hypertension for a period of time. DHF in addition to affecting the old generation, it is also common among the female gender Chen, Normand, Wang, & Krumholz (2011) analysis. Systolic dysfunction Systolic heart failure occurs when the heart fails to contract effectively HFSA (2010) explains. Systolic dysfunction is caused by valvular heart disease, hypertension, dilated cardiomyopathies and ischemic heart disease NHFA/CSANZ (2011). Abraham & Abraham, (2009) says patients suffering from systolic function have impaired pumping mechanism and large dilated ventricles. Strength of Ventricular contraction is conical and insufficient to create sufficient stroke volume contributing to derisory cardiac output. In addition, the architecture of the normal papillary muscle is disrupted following the effects arising from the dilated ventricles. In reference to Prior & Coller (2010) the ventricles are not emptied completely a factor which leads to volume and ventricular end-diastolic pressures increment. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Cialis 20 mg
Choose Qty:
10 - $50
30 - $100
60 - $140
90 - $180
180 - $300
360 - $500
Cialis(Tadalafil) relaxes muscles of the blood vessels and increases blood flow to particular areas of the body.
Cialis is used to treat erectile dysfunction and symptoms of benign prostatic hypertrophy.
Another brand of tadalafil is Adcirca, which is used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension and improve exercise capacity in men and women.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Pulmologie: Understanding the Science of Respiratory Health
What Is Pulmologie?
Pulmologie, commonly referred to as pulmonary medicine, is a specialized branch of medicine dedicated to the study, diagnosis, and treatment of respiratory diseases. Covering a vast array of conditions that affect the lungs and respiratory tract, this field is crucial for protecting one of the most vital systems of the human body. By focusing on both prevention and advanced treatments, pulmologie plays a key role in keeping us breathing with ease.
If you've been curious about how lung diseases are treated or what innovations are occurring in this field, this guide will introduce you to the basics of pulmologie and its importance in modern medicine. From common respiratory conditions to cutting-edge treatments, we’ll explore it all.
Why Pulmologie Matters
Breathing is one of the most fundamental human functions, and it directly impacts the quality of life. Pulmologie focuses on preserving this ability when complications arise. Many factors contribute to respiratory issues, including pollution, smoking, genetics, infections, and chronic illnesses like asthma and COPD.
Key Reasons Pulmologie is Essential
Rising Respiratory Health Challenges
With increasing urbanization, industrial pollution, and smoking habits, respiratory diseases have become a global health challenge. Pulmologists work tirelessly to provide both preventive care and treatments.
Comprehensive Diagnosis and Management
Pulmologie bridges the gap between general practitioners and specialized medicine, offering targeted analysis through methods like spirometry, imaging, and biopsy to identify respiratory problems.
Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Conditions
Diseases like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer are becoming more common. Pulmologists provide expertise in long-term disease management and personalized patient care.
Vital Support for Post-Respiratory Infection Recovery
After illnesses like pneumonia or COVID-19, some patients face lingering respiratory issues. Pulmonologists help individuals regain optimal lung function through therapies and rehabilitation programs.
Common Conditions Treated in Pulmologie
Pulmologie addresses a wide range of respiratory diseases. Understanding these conditions can give you insight into when you should seek medical attention.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition that causes airway constriction, leading to difficulty breathing. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath, often triggered by allergens or physical activity. Pulmologists help patients manage asthma via inhalers, medications, and lifestyle adjustments.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a progressive condition often caused by smoking or long-term exposure to pollutants. It damages lung tissue and reduces airflow, making breathing increasingly difficult over time. Pulmonary specialists offer therapies, oxygen treatments, and pulmonary rehabilitation to slow progression.
Pneumonia
An infection causing inflammation in the alveoli, pneumonia can range from mild to life-threatening. Pulmologists play an essential role in diagnosing and treating pneumonia, particularly for severe or recurrent cases.
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the deadliest forms of cancer, but early detection and advancements in treatment have improved survival rates. Specialists in pulmologie collaborate with oncologists to provide comprehensive care and guide patients through surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
Sleep Apnea
Pulmologie isn’t just about illnesses related to the lungs but also related issues like sleep apnea, a condition where interrupted breathing during sleep affects oxygen levels and overall health. Treatments include CPAP machines and lifestyle changes.
Pulmonary Hypertension
This rare but severe condition affects the pulmonary arteries, increasing blood pressure and straining the right side of the heart. Treatment often involves medications that manage pressure and improve lung function.
How Pulmologie Specialists Diagnose Conditions
The field of pulmologie uses cutting-edge diagnostic techniques to pinpoint respiratory problems accurately. Pulmonologists combine advanced tools with their expertise to create tailored treatment plans.
Diagnostic Tests in Pulmologie
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)
PFTs measure how well your lungs work by assessing airflow, lung volume, and gas exchange. Spirometry is one common type of PFT that helps diagnose asthma, COPD, and other respiratory conditions.
Imaging
Techniques like chest X-rays and CT scans provide detailed pictures of your lungs, helping specialists detect infections, tumors, or structural abnormalities.
Bronchoscopy
This procedure uses a thin tube with a camera to examine the airways, take tissue samples, or remove blockages.
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG)
ABG tests measure oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood, offering insight into how well the lungs exchange gases.
Biopsy
Tissue biopsies are sometimes necessary to diagnose lung cancer or other abnormalities.
Advances in Pulmologie
Pulmologie has seen remarkable advancements in recent years, particularly in imaging, treatments, and patient care strategies. Here are some ways the field is evolving:
Personalized Medicine
Using genetic profiling and biomarkers, pulmonologists can now develop personalized treatment plans. For instance, asthma treatments are increasingly tailored to an individual’s specific triggers and immune responses.
Innovative Therapies
Biologic drugs, which target inflammation at the cellular level, are transforming how chronic conditions like asthma and COPD are managed. Similarly, therapies such as lung volume reduction surgery and lung transplants offer hope for advanced lung diseases.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing diagnosis and management. Pulmologists now use AI algorithms to analyze imaging results more quickly and accurately, improving early detection rates for lung cancer and other conditions.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine has gained traction in pulmologie. Patients can now consult with specialists and even undergo remote lung function monitoring from the comfort of their homes.
How to Support Your Respiratory Health
While pulmologie provides critical care for serious conditions, prevention is always better than cure. Here’s how you can support your lung health:
Quit Smoking
Tobacco use is one of the leading causes of lung damage. Seek support groups or cessation programs if needed.
Avoid Airborne Pollutants
Limit exposure to air pollution and workplace irritants like chemicals and dust. Use masks and air purifiers when necessary.
Exercise Regularly
Physical activity improves lung capacity and circulation, helping your body use oxygen more efficiently.
Eat a Nutritious Diet
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants can protect your lungs from cellular damage.
Stay Vaccinated
Vaccines for flu and pneumonia can prevent infections that lead to severe respiratory complications.
Breathing Easier With Knowledge
Pulmologie is a field designed to improve quality of life through early detection, expert intervention, and ongoing care for respiratory issues. From asthma to lung cancer, understanding the basics of pulmonary medicine empowers you to prioritize your health and seek help when needed.
With continuous advancements in medicine and technology, the future of pulmologie holds even greater promise for those affected by respiratory conditions. Remember, every breath counts—take care of your lung health and consult a specialist if you experience prolonged issues.
0 notes