#Propulsion Systems Laboratory
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
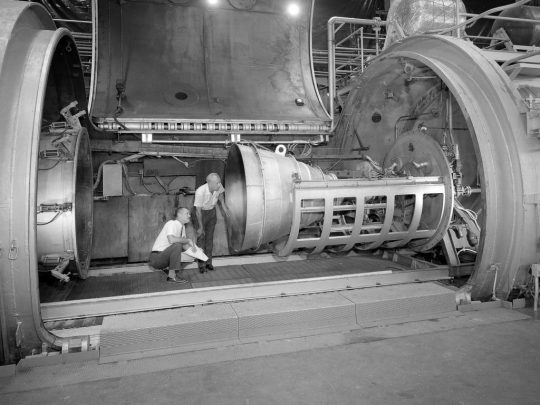
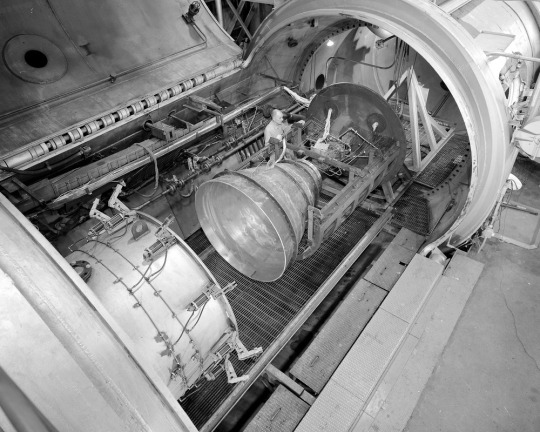



"An Apollo Service Module contour engine [Aerojet AJ10-137] mounted in the Propulsion Systems Laboratory at NASA Lewis Research Center in 1964. The Laboratory contained two 14-foot diameter test chambers that could simulate conditions found at very high altitudes. Researchers sought to determine the impulse value of the storable propellant mix, classify and improve the internal engine performance, and compare the results with analytical tools. A special setup was installed in the chamber that included a device to measure the thrust load and a calibration stand."
This engine used Aerozine 50 (a 1:1 mix of UDMH and hydrazine) as fuel and nitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) as an oxidizer, rather than the previous nitric acid/UDMH.
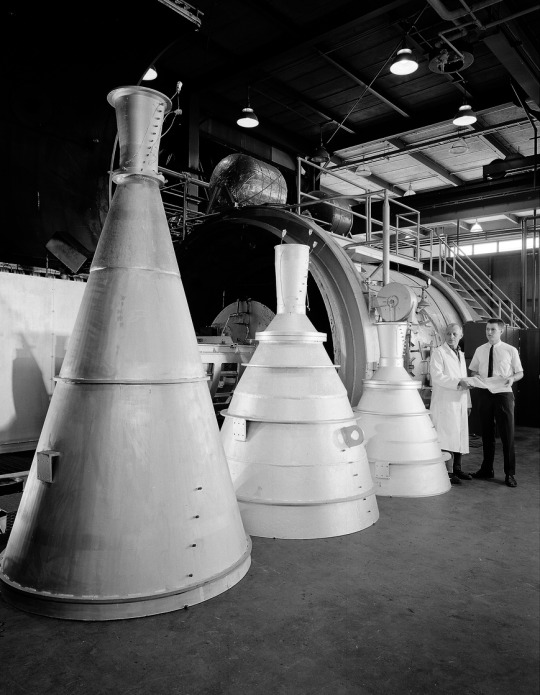

Three different noozles for testing: a 15 degree conical nozzle, a Titan transtage contour nozzle and an Apollo AJ10-137.
Date: 1964
source, source, source, source
NASA ID: C-1964-68789, C-1964-70930, C-1964-70929, C-1964-70931, C-1964-69633
#Aerojet AJ10-137#AJ10-137#Rocket Engine#Apollo Program#testing#Service Module#Propulsion Systems Laboratory#Lewis Research Center#NASA#1964#my post
46 notes
·
View notes
Text

JUPITER – JunoCam / 2024-09-20 Mission Phase : PERIJOVE 65
See more: https://jackiebranc.site/jupiter-and-its-galilean-moons/
Credit : NASA / SwRI / MSSS / Jackie Branc © CC BY
#elloon#jackie branc photographer#juno#juno spacecraft#jupiter#astronomy#nasa jpl#nasa#nasa photos#space exploration#jet propulsion laboratory#gas giant#solar system#Southwerst Research Institute#Malin Space Science Systems
47 notes
·
View notes
Text


This is Ethan Peck visiting JPL to take a look at the Europa Clipper, a spacecraft that will be launched in October towards the Jovian moon in hopes of exploring that strange new world!
Just look at how happy and nerdy he looks at JPL. Props to whoever invited him, because it's only logical to invite Mr. Spock to JPL. And props to Ethan for supporting science and exploration! I love this man 🖖🥹
#ethan peck#mr. spock#star trek#strange new worlds#Europa Clipper#JPL#Jet Propulsion Laboratory#NASA#space#the final frontier#europa#Jupiter#planets#solar system#space exploration#science#physics#astronomy#astrophysics#rocket science#spacecraft#satellite
172 notes
·
View notes
Link
Venus is found to still have volcanic activity in a study by Robert Herrick of UAF, Scott Hensley of JPL, and more.
#venus#planet venus#planetary science#volcano#volcanoes in space#veritas#solar system#University of Alaska Fairbanks#Jet Propulsion Laboratory#astronomy#planets#volcanism#veritas mission#Venus Emissivity Radio science InSAR Topography And Spectroscopy#jpl#uaf#space#venusian volcano#planetary studies#venusian
12 notes
·
View notes
Video
Mini NASA Robot Takes a SWIM by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center Via Flickr: A 16.5-inch-long prototype of a robot designed to explore subsurface oceans of icy moons is reflected in the water’s surface during a test in a competition swimming pool in September 2024. Conducted by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the testing showed the feasibility of a mission concept called SWIM, short for Sensing With Independent Micro-swimmers. The project envisions a swarm of dozens of self-propelled, cellphone-size robots looking for signs of life on ocean worlds. SWIM is funded by NASA’s Innovative Advanced Concepts program under the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate. Credit: NASA #NASA #NASAMarshall #NASAJPL #moon #robot Read more Read more about SWIM NASA Media Usage Guidelines
#NASA#NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center#NASA Marshall#Marshall#MSFC#Solar System & Beyond#Jet Propulsion Laboratory#JPL#moon#robot#flickr
0 notes
Text

Have a Happy Halloween with NASA
Attention ghouls and goblins of the galaxy! The season for scares and frights is upon us, so we’ve rounded up a few Halloween resources to capture that festive feeling. Read on for craft ideas, free decoration downloads, a creepy soundtrack, and even costume ideas.

Overdid it at the pumpkin patch this year? Get some creative inspiration and some pumpkin-building tips from our Jet Propulsion Laboratory engineers, carve a James Webb Space Pumpkin, or paint a pumpkin with space and weather themed designs. And yes – you can make a NASA pumpkin, too.

Speaking of design, check out our terrifying Galaxy of Horrors posters: decorate your walls with a an illustration of a galactic graveyard or of dark energy prowling through the universe…
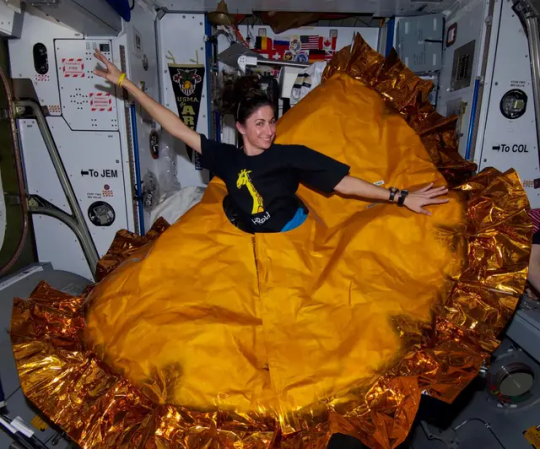

If costumes are more your thing, see how the astronauts aboard the International Space Station have dressed up over the years.
Finally, our Sinister Sounds of the Solar System playlist will give you just the right soundtrack for a haunted house or a party – or for scaring yourself all alone.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
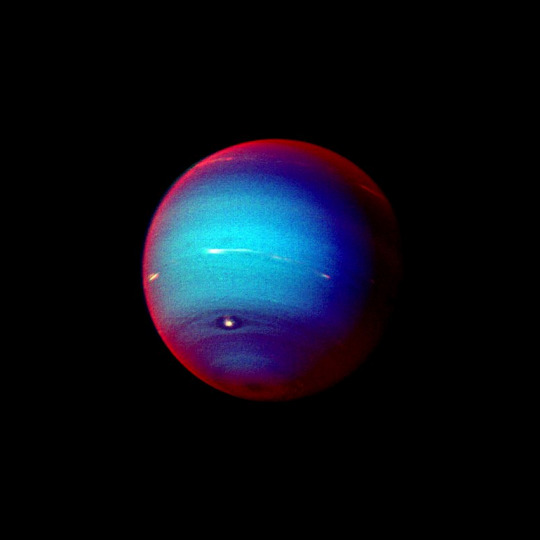

A Parting Shot
This false color photograph of Neptune was made from Voyager 2 images taken through three filters: blue, green, and a filter that passes light at a wavelength that is absorbed by methane gas. Thus, regions that appear white or bright red are those that reflect sunlight before it passes through a large quantity of methane. The image reveals the presence of a ubiquitous haze that covers Neptune in a semitransparent layer. Near the center of the disk, sunlight passes through the haze and deeper into the atmosphere, where some wavelengths are absorbed by methane gas, causing the center of the image to appear less red. Near the edge of the planet, the haze scatters sunlight at higher altitude, above most of the methane, causing the bright red edge around the planet. By measuring haze brightness at several wavelengths, scientists are able to estimate the thickness of the haze and its ability to scatter sunlight. The image is among the last full disk photos that Voyager 2 took before beginning its endless journey into interstellar space.
source
#found by kino#nasa#Solar System Exploration#Jet Propulsion Laboratory#Planets#jpl#neptune#voyager 2#planets#space#space photography#space aesthetic
0 notes
Text
SAUVAGE.



jupiter, you’re hard (to get).
sum. jupiter may not smell like woody ambery trails or smoky accents, and he may seem like just a really big planet who’s really far away, but juno will always find him.
wc. 3.2k
cw. spacecrafts, stars, and planets, roman mythology, kudos to sabrina carpenter’s juno, producer!reader x idol!han, friends2lovers, a beer (if i must content warn you, i will) smut! car! heavy on kisses with a side of unprotected piv sex (don’t!) switch!jisung x switch!reader (undefined tbh)
scent. (♡) the perfume saga.
[🔺☆ 🚀 ☆🔺]
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System.
It is a gas giant with a mass more than two times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, and slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Its diameter is eleven times that of Earth, and a tenth that of the Sun. Its name derives from that of Jupiter, the chief deity of ancient Roman religion. Jupiter orbits the Sun at a distance of 5.20 AU (778.5 Gm), with an orbital period of 11.86 years.
However, Han Jisung isn’t quite as big or gaseous. He likes to believe he isn’t made up of metallic hydrogen, but rather stardust, he had said once —and you remembered, of course, because how couldn’t you—. He isn’t the oldest planet in the Solar System. He doesn’t run hotter than the Sun. He doesn’t have many many moons (95!) that spend ages to rotate around him.
Well. Not moons, anyways.
Juno is a NASA space probe orbiting the planet Jupiter.
It was built by Lockheed Martin and is operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Juno entered a polar orbit of Jupiter in 2016 to begin a scientific investigation of the planet. After completing its mission, Juno was originally planned to be intentionally deorbited into Jupiter's atmosphere, but has since been approved to continue orbiting until contact is lost with the spacecraft.
Thing is. You’re not a spacecraft either. You weren’t built by whoever Lockheed Martin is. You can’t orbit around planets. And most definitely, you don’t keep in contact with NASA. Nevertheless, a part of you can’t help but relate, because, somehow, even after your mission was ultimately done, you couldn’t stop orbiting around Jupiter.
Well. Not Jupiter, anyways.
you: let’s do some cardio next day
jisungie🎀💫: cardio, you say? 😏
jisungie🎀💫: not even a coffee before taking me to your place? 🤨📸
Jupiter couldn’t even reach to make you feel the giddiness that Han somehow could trigger and make it overcome you. You kicked your feet, but when you entered and found your reflection in the elevator mirror, you clicked your tongue.
“Don’t be such a schoolgirl”, you mumbled to yourself, pressing the button, and heading up back home.
you: tsk tsk, you’re always thinking about food
And you’re always thinking about him, a mean voice in your head snapped back at you. You cursed, damning your own mind for betraying you. But, to spare you, it wasn’t that serious, you thought. You two interacted just the right amount.
He was an idol, for god’s sake. You weren’t catching feelings. That would be dumb on your side, the least.
So of course, when your phone chimes in the specific ringtone that, of course, you hadn’t set just for his contact, of course, you didn’t almost drop your purse when you read what he replied.
jisungie🎀💫: as if, silly
jisungie🎀💫: i ain’t eating no one for free
The text made you dizzy, so you forced yourself to back off from replying the first thing that came to mind.
Hungry? Eat me.
“Think straight for once,” you cursed out loud, passing your hands through your hair. Closing the door to your apartment and knocking your shoes off while your mind went off to other, far more interesting places and memories.
You clearly remembered the moment you met quirky, loveable Han Jisung. How inevitable it had been to just start orbiting around him with the excuse of your mission— producing one of his solos for an upcoming skz-record.
Headphones. It had been such a silly first encounter, yet so fitting for you two that you couldn’t help but cherish it dearly.
Lost in thought, you hadn’t been paying attention to where you were headed. Neither had he, and, which had ended with a little crash against each other. A meteor, not quite as devastating as so to kill a couple dinosaurs, but to leave a crater in your heart and create a small moon out of the pieces that scattered away shyly.
“Sorry!” You bowed your head, then stared at him.
“Hi,” he had said in a sheepish tone, hints of panting that you attributed to how he must’ve run back in hopes of catching you. “Guess you like wave to Earth too?”
And while he giggled, you told yourself you weren’t going to fall, but both Jupiter and Juno knew.
They had said the same thing about Rome.
jisungie🎀💫: entering jyp
you: at 21:43? jeez
jisungie🎀💫: what? i ain’t afraid of success bbg 💪
jisungie🎀💫: come over if you want
What would happen with any other person was that they’d smile and turn off their phone.
Well. Not Juno.
Not you, no.
[🔺☆ 🚀 ☆🔺]
The studio smelled like bubble tea, and that’s how you knew he was still there.
“Oh, hey! I wasn’t sure if you were coming in.” Han smiled.
Sleepiness oozed off of him, and you grinned, cleaning the table from leftover crumbles as you set your bag down. Your heart twirled imaginary hairs when Jisung’s hands —hands with several rings, something that could sometimes be a lot to manage— left the keyboard and settled on his thighs, softly stroking them as he turned the chair to face you.
“Yeah. Wanted to work on a demo I owe to the girls,” you mentioned, taking your jacket and your mask off.
“Actually,” he started, and your hands tingled with the feeling that you’d help him in whatever he needed. Damnit, hands. Damn you, heart. “Could you help me with this demo? Jeonginnie asked me to go over it.”
You sipped from your own drink, as if to fake giving it a bit of a thought. You were going to say yes, of course. But instead, you scratched your arm, frowning lightly.
“Innie asked you?”
“It’s for his solo stage.” He clarified, turning back to face the computer. “We all have them for our tour.”
The way he entered the recording booth seemed distant, and a part of you couldn’t help but wonder why as you fidgeted with your necklace and settled everything on the desk comfortably. Ji turned the light off, something slightly weird. He never did that with you, after all these years, and considering you two were the only ones there, you asked.
“Is it a high register?” You wondered, pressing the button on your left so he could hear you in his headphones. You blinked when you saw his figure slightly jolt in something like surprise.
“Uh, no. It’s just the… style of the song,” he giggled, putting his beanie on and tucking in the hairs that fell over his eyes.
Oh. That’s the one you gifted him.
“Sure. Mind if I give it a listen first?”
“Go ahead,” he replied without looking at you through the window.
Helping him came off naturally. The track for the girls was an excuse, one you had already forgotten. And as he started singing, you weren’t sure you’d remember any time soon.
“T-those are some bold lyrics, huh?”
Hallucination.
Jisung covered his eyes with his beanie, giggling.
“It’s Innie’s fault. He gets it from Chan.”
“What’s Chan’s solo about?” You asked with a laugh.
You didn’t expect Jisung to stare at you and swallow dry.
“He says it’s about trains.” He shrugged, as if he had remembered suddenly that he was supposed to answer your question.
When you both were done, it was late. Really late. He insisted you two grabbed a beer in the convenience store nearby, but you took a juice, claiming you had to drive.
“I’ll uh, I’ll get the bus, seriously,” he raised his hands as you both exited the store, beer in hand.
“Ji,” you deadpanned, finishing your juice. Thank God you liked him, because sometimes you wanted to hit him. Softly. With a pillow. “Shut up. I’m taking you.”
[🔺☆ 🚀 ☆🔺]
“How come I didn’t remember you have a driver's license?” Han smiles sheepishly.
The drive to his apartment is silent, as if you two were submerged in a no-conversation. No words, no nothing, just the sound of the tires against the asphalt and the yellow lights from the streetlights that lightened your way.
It’s late enough that there are little to no cars on the driveway. But weirdly, Jisung sips from his beer and sighs.
“Actually, could to take a left here?” He says softly, his voice surprisingly low.
“That’s not the way to your apartment, is it?” You ask, as softly as him, turning anyways.
“Nah, it’s this place I found and I wanted to show you.”
Alcohol doesn’t get easy to him —not from a beer, at least—, but he’s smiling like silly, and you can’t help but smile too.
You park where he tells you, and surely enough, there’s no one there. It’s a secluded, empty area, far from the center and high enough so that the city can be seen clearly.
“Think I left my jacket here last time I came.” He snickers, and you can’t help but chuckle. His hand travels to your knee and he squeezes it gently. “I’ll come back in just a second.”
One blink. Two blinks.
Hot fucking damn.
Your head falls against the steering wheel as soon as he closes the door.
Get your shit together.
Looking up, the car tells you it’s way past midnight. Your head tells you you’re crazy, your heart giggles at the fact, guilty as charged. Sighing, you raise your face enough to look at the stars. Only to find Jisung’s silhouette, now with a dark jacket on, waving at you as he stands in front of the car.
You’re blushing, but you wave haphazardly, smiling, and still frown when instead of getting back to his seat, Jisung goes and opens your door instead.
“Hey,” he giggles, and your grin matches with his.
“What are you doing?”
Jupiter can sometimes be seen from Earth, when the Sun’s light hits it just right and the night is dark. Still, its shimmer doesn’t compare to that of Jisung’s eyes when he rests his forearms on the car’s roof and bends down to your height. You haven’t moved, your own eyes fixated on how he licks his lips.
“I think I’m being stupid,” he chuckles. You’re a goner, not even noticing how his hand slides in for a moment and turns the headlights off, leaving you two only illuminated by the shy light in the car that indicates that the door is open and by the moonlight, who cheekily shines at the both of you.
Instead, you blink. Normally you just get him, just as he gets you, but you’re almost as lost as how you feel when you stare into his dark brown eyes.
“Stupid?” You smile lightly. “Why?”
At your tender tone, Jisung lets his head fall down, shyness getting the best of him. And yet the little alcohol he’s had boosts him back.
“I, uh, had a dream. Been having these dreams for like, a bit over a month,” he swallows dry, much like he did at the studio, and his eyes suddenly feel darker than before, maybe because his gaze stops avoiding yours for longer than a minute.
A meteor shower threatens to fall over your heart.
“You were there. And I was there, too.”
For someone who composes and uses words for a living, he was struggling a lot to piece together what he wanted to say.
“This… there was… this… feeling, like, inside of me. Here.”
Not only does he not use his hand, but he takes yours from the steering wheel and settles it over his chest. His heart.
You’re frozen. Completely out of it. Is it possible that maybe you fell asleep in the studio and that none of this is real? Could that be it, you wonder, until Jisung groans and leans his forehead against the roof of the car with a thud.
“I’m being an idiot, am I?” He snickers, with an undertone that lingers in something that resembles resignation. “I just- I saw you the other day, and I was… you were with Hyunjin, and I…” he clenches his fist, and he tries to back off, rubbing his face and passing them through his hair.
“No, Ji, wait.”
He chuckles breathlessly. “I made it awkward, right?”
“Ji.”
Your hand pulls him back closer by the zipper of his jacket, and only the crunchy-like sound of the gravel beneath him as he walks echoes through the night and follows how you move your hands toward his wrists. Towards his own hands, stopping him from picking on his nails further.
“Tell me, Ji,” you mumble. “What were you saying?”
His voice threatens to tremble before he speaks. His eyes don’t move from yours, and you think you’re completely out of your mind, just as much as he thinks of himself too.
“I keep having these dreams where I see you and the ache of wanting you swells up in me, like I’m on a raft that’s sinking and I just can’t even escape thinking about you when I sleep because I-”
He’s rambling, but with a sudden move from your side, he’s not anymore.
The cold of November doesn’t hit you when you stand up bluntly and you link your arms behind his neck and kiss him like you have been wanting to do for years.
His lips crash against yours like the sea crashes against the sharp rocks against the shore, even if the coast is much further away than you think, but you don’t mind, because you can’t think.
You’re kissing him. Finally.
You’re kissing Han Jisung.
And then, just a beat after what you’ve done —what you’re doing— sinks in, he reacts. His hands travel underneath your jacket and in the blink of an eye, he’s letting you push him against the car. No words, no nothing, only the scent of his cologne that suddenly fills you.
You tremble beneath him, and he pants.
He’s not blinking, his eyes glued to you. He can’t think either.
You should say something. What should you say? ‘Me too’? That’s lame. How come your brain can’t work when you most need it?
As if to answer your question, Han kisses you this time. Of course you can’t think, not when his hands travel underneath your clothes and he twists you in a way that somehow it’s your back against the car now. He’s not breathing, and neither are you, because you’re not kissing anymore, not when your lips can feel the teasing dent of his teeth nibbling on them and when the only thing you can taste is his tongue.
You’re not against the car anymore, because he closes the driver’s door with a kick and he opens the one to the backseats while he keeps kissing you.
Crazy. You’ve gotta be, because dreaming something as wild as this and for it to feel real, as real as it gets, as real as it could ever be, it has to mean you’re crazy. And you’d die on that hill if it means you get to keep dreaming how Jisung takes his newly-found jacket off and throws it to the front seat, in the same foreign path as where he throws his shirt, or how you two barely fit in the car and so he settles his knee between your legs to help you move back enough so that he can close the door.
And now you’re there. Alone together.
He gasps against your neck, as if he remembered that he had to keep breathing to live, and you don’t lose your opportunity, taking your sweater off and throwing it towards the trunk.
You lean your head back, the car feeling heavy with only the sounds of both him and you panting.
“I… fuck, I need you to tell me you want this.” Han swallows dry. “I need you to say it. Please. I want this too much.”
A meteor shower? Scratch that. This is a meteor storm.
“I think this is a dream, but still, I want you. Please.”
No words, no nothing, just the sound of the leather against your sweaty skin when you sit up straight and kiss Jisung like you mean it. It’s all nasty, teeth and tongue and a string of saliva that lingers when you break the kiss to fumble with his zipper.
“What if it is a dream,” you gasp, out of breath, out of control, completely and irrevocably out of it as your eyes stare at his. “I want you. Even if I wake up right now.”
Your shirt is discarded as fast —if not faster— than the rest of your clothes before.
“So if it is a dream, let’s keep going until we wake up.” You swallow dry too. “Until the stars can’t be seen.”
The kiss is like a heroin kick, although it is one that seems familiar. Or maybe it’s that your lips have become used to kissing his, considering that breathing has become a second priority with how raw is the need to consume him. A wave of pleasure takes claim inside of you with each caress of his tongue, with every touch of his fingers on your back, with every eager breath next to your jaw. He pulls you closer and moans with his mouth buried in your skin unfinished phrases that drive you crazy little by little —more than you already were.
“It may end right away,” Jisung says in a hoarse voice, clinging to one of the headrests that are closest to him. “But I’ll make it up to you. With my mouth. Or with my fingers. Or both. Yes, fuck...”
It’s a mix of quick and ruthless kisses, mouths open. Wet and urgent, almost in bites, as if you’d want to eat the other alive as he takes his pants off and helps you with yours, going down to kiss your neck.
“You’re so... f-fuck, ah...” he mumbles while he runs his tongue down your throat and to your collarbone. “I never want to wake up.”
His lips taste like the feeling that overcomes you when you look at the sky on a starry night. Emotion. Ecstasy. You want to drink it whole until there’s not a single drop left. Drink him.
Jisunh squeezes your ass, while your mouths are a mess, while he bites your lip and pulls it, smiling like a cheeky bitch, while your mouths fight for the control of the kiss and your tongue caresses his, and before you can piece together that the windows are foggy because of the two of you, he’s sliding inside, his hand lacing with yours.
God, you want to moan. Moan so loud. And so you do, because there’s nothing in this dream that could stop you.
And he moans, too, because you are like a dream come true.
Juno and Jupiter.
[🔺☆ 🚀 ☆🔺]
~kats, who accidentaly went full autism, space and mythology on the meaning of ‘juno’ by Sabrina Carpenter.
catiuskaa, november 2024 ©
#stray kids x reader#stray kids#stray kids scenarios#stray kids fluff#stray kids imagines#skz scenarios#soft hours#han jisung x reader#han jisung fluff#han jisung imagine#stray kids han#han jisung imagines#stray kids han jisung#my little hannie#han smut#han x reader#han jisung#han jisung headcanons#han jisung smut#han jisung fanfic#han jisung scenarios#jisung stray kids#jisung headcanons#stray kids jisung#jisung x reader#jisung fluff#jisung smut#skz fic#straykids x you#straykids x reader
339 notes
·
View notes
Text
NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft is alone drifting through interstellar space after a communications breakdown left it unable to receive commands or transmit data back to Earth.
Communications with Voyager 2, which is currently around 12.4 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) from Earth, were severed as a result of planned commands. These commands rotated the spacecraft's antenna two degrees away from our planet, enough to cut its links to the ground antennas of NASA's Deep Space Network (DSN).
As a result, Voyager 2 is no longer sending data back to the DSN, and mission control on Earth can't send any commands back to the interstellar spacecraft.
Not all is lost, however. Voyager 2, launched in 1977, is programmed to reset its orientation several times a year to keep its antenna directed at Earth. Another reset is scheduled for Oct. 15 this year, and this should result in Voyager 2 resuming contact with its ground control. Until that time, operators expect the spacecraft to stick to its planned trajectory.
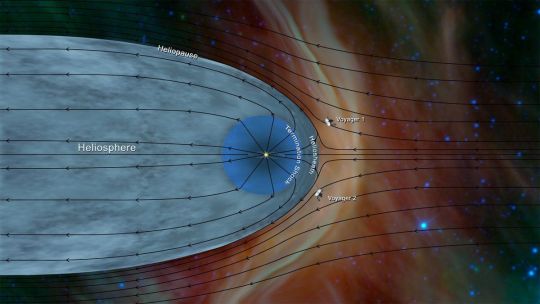
Voyager 2 was launched from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral, Florida, on August 20, 1977. It made history on Dec. 10, 2018, when it became the second spacecraft to leave the solar system and enter interstellar space.
Six years prior to this, its sister craft Voyager 1 became the first man-made craft to journey beyond the influence of our star, the sun. Voyager 1 is currently around 15 billion miles (24 billion km) from Earth and remains in contact with our planet.
Both Voyager 1 and 2 were designed to find and study objects at the edge of the solar system, according to NASA. In the course of doing this, Voyager 2 has been responsible for a number of scientific firsts. It is the only spacecraft that has conducted close-up studies of all four giant planets of the solar system — the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and the ice giants Neptune and Uranus.
In Jan. 1986, Voyager 2 became the first human-made object to fly past Uranus. During that trip, Voyager 2 discovered 10 new moons and two new rings around the ice giant. In Aug. 1989, it also became the first spacecraft to buzz past Neptune, and while there, it discovered five moons and four rings. While studying Neptune, Voyager 2 also discovered an 8,100-mile by 4,100-mile (13,036 km by 6,600 km) cyclonic storm with winds of up to 1,300 miles per hour (2,092 km/h) raging on the ice giant, which has been dubbed the Great Dark Spot.
In April 2023, NASA announced that Voyager 2 would postpone a planned instrument shutdown by at least three years, continuing to gather valuable deep space data until at least 2026.
"We are definitely interested in keeping as many science instruments operating as long as possible," Voyager project scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in southern California, Linda Spilker, said in a statement issued on Wednesday, April 26.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Mariner program
The Mariner program was conducted by the American space agency NASA to explore other planets. Between 1962 and late 1973, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) designed and built 10 robotic interplanetary probes named Mariner to explore the inner Solar System - visiting the planets Venus, Mars and Mercury for the first time, and returning to Venus and Mars for additional close observations.

The program included a number of interplanetary firsts, including the first planetary flyby, the planetary orbiter, and the first gravity assist maneuver. Of the 10 vehicles in the Mariner series, seven were successful, forming the starting point for many subsequent NASA/JPL space probe programs.

The name of the Mariner program was decided in "May 1960-at the suggestion of Edgar M. Cortright" to have the "planetary mission probes ... patterned after nautical terms, to convey 'the impression of travel to great distances and remote lands.'" That "decision was the basis for naming Mariner, Ranger, Surveyor, and Viking probes."

Each spacecraft was to carry solar panels that would be pointed toward the Sun and a dish antenna that would be pointed at Earth. Each would also carry a host of scientific instruments. Some of the instruments, such as cameras, would need to be pointed at the target body it was studying. Other instruments were non-directional and studied phenomena such as magnetic fields and charged particles. JPL engineers proposed to make the Mariners "three-axis-stabilized," meaning that unlike other space probes they would not spin.

Mariner 1 and Mariner 2
Mariner 1 and Mariner 2 were two deep-space probes making up NASA's Mariner-R project. The primary goal of the project was to develop and launch two spacecraft sequentially to the near vicinity of Venus, receive communications from the spacecraft and to perform radiometric temperature measurements of the planet. A secondary objective was to make interplanetary magnetic field and/or particle measurements on the way to, and in the vicinity of, Venus.
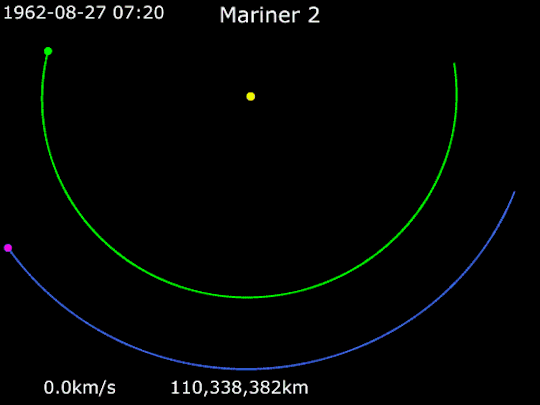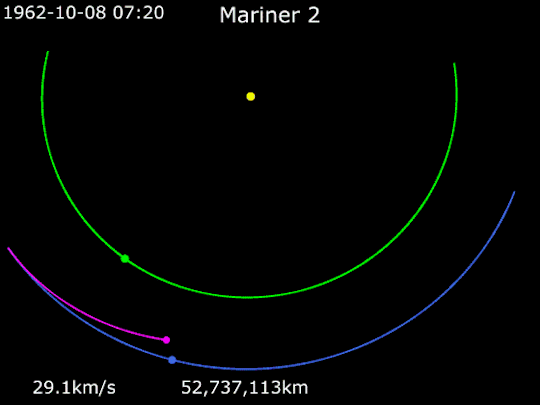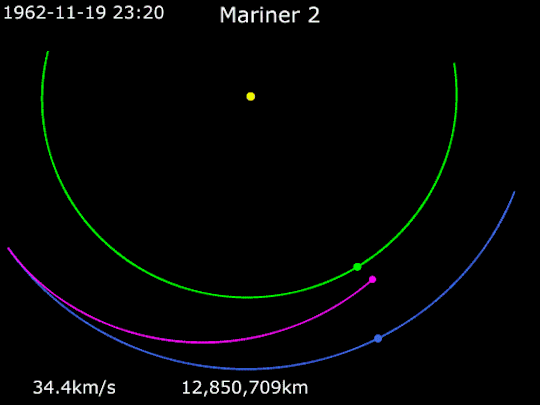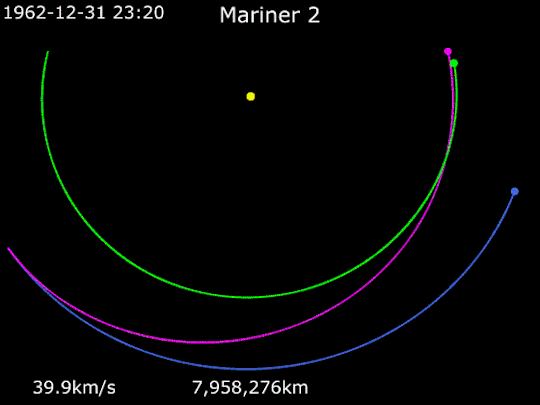
Animation of Mariner 2's trajectory from August 27, 1962, to December 31, 1962. Mariner 2 · Venus · Earth.
Mariners 3 and 4
Sisterships Mariner 3 and Mariner 4 were Mars flyby missions.
Mariner 3 was launched on November 5, 1964, but the shroud encasing the spacecraft atop its rocket failed to open properly and Mariner 3 did not get to Mars.
Mariner 4, launched on November 28, 1964, was the first successful flyby of the planet Mars and gave the first glimpse of Mars at close range
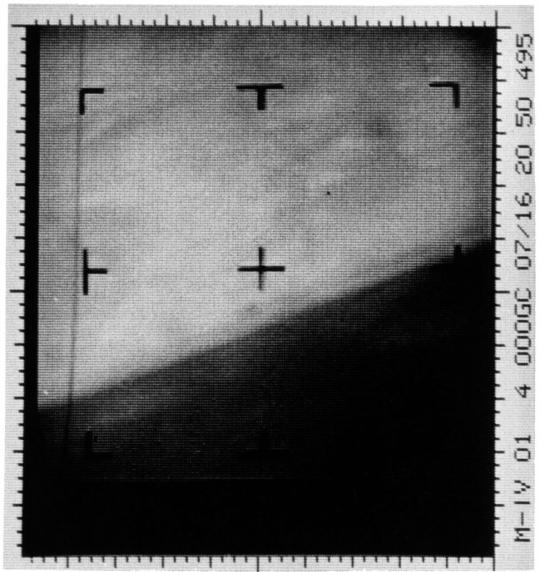
This archival image is an enhanced contrast version of the first Mars photograph released on July 15, 1965. This is man's first close-up photograph of another planet -- a photographic representation of digital data radioed from Mars by the Mariner 4 spacecraft. Data was either sent to Earth immediately for acquisition or stored on an onboard tape recorder for later transmission.
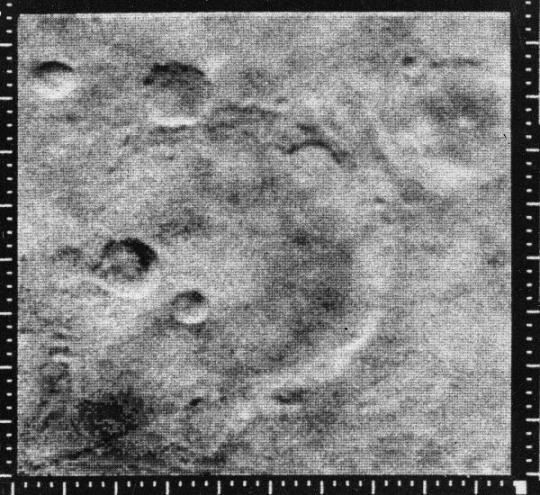
The pictures, played back from a small tape recorder over a long period, showed lunar-type impact craters (just beginning to be photographed at close range from the Moon), some of them touched with frost in the chill Martian evening.
Mariner 5

The Mariner 5 spacecraft was launched to Venus on June 14, 1967, and arrived in the vicinity of the planet in October 1967. It carried a complement of experiments to probe Venus' atmosphere with radio waves, scan its brightness in ultraviolet light, and sample the solar particles and magnetic field fluctuations above the planet.
Mariners 6 and 7

Mariners 6 and 7 were identical teammates in a two-spacecraft mission to Mars. Mariner 6 was launched on February 24, 1969, followed by Mariner 7 on March 21, 1969. They flew over the equator and southern hemisphere of the planet Mars.
Mariners 8 and 9
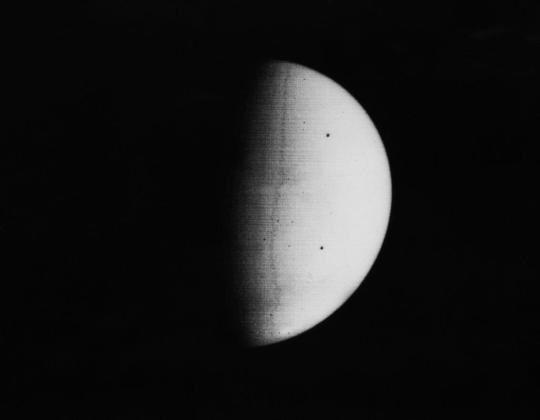
Mariner 8 and Mariner 9 were identical sister craft designed to map the Martian surface simultaneously, but Mariner 8 was lost in a launch vehicle failure. Mariner 9 was launched in May 1971 and became the first artificial satellite of Mars.
Mariner 10
The Mariner 10 spacecraft launched on November 3, 1973, and was the first to use a gravity assist trajectory, accelerating as it entered the gravitational influence of Venus, then being flung by the planet's gravity onto a slightly different course to reach Mercury. It was also the first spacecraft to encounter two planets at close range, and for 33 years the only spacecraft to photograph Mercury in closeup.
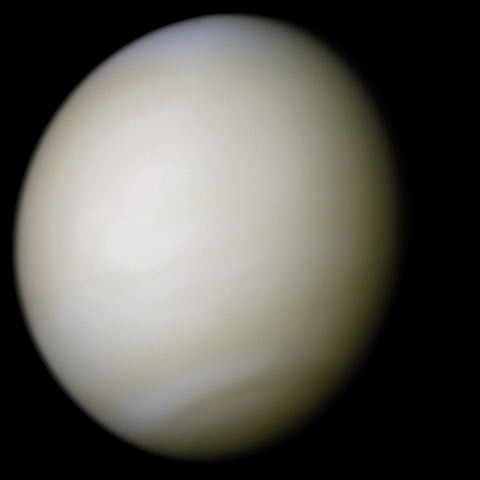

Venus in real colors, processed from clear and blue filtered Mariner 10 images
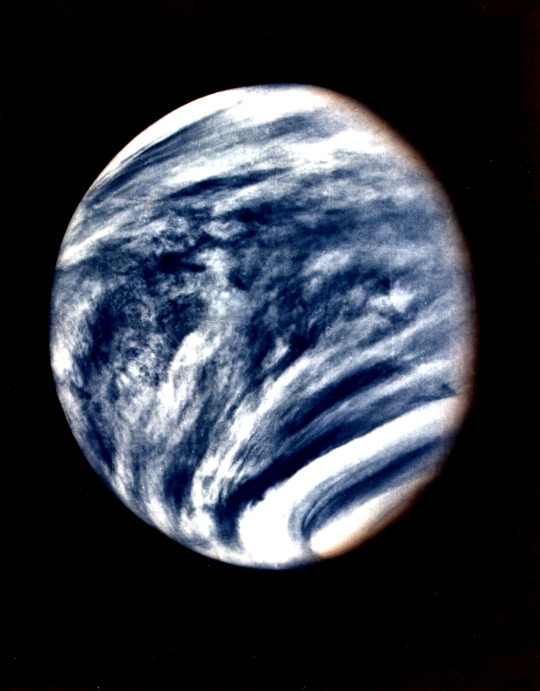
Mariner 10's photograph of Venus in ultraviolet light (photo color-enhanced to simulate Venus's natural color as the human eye would see it)
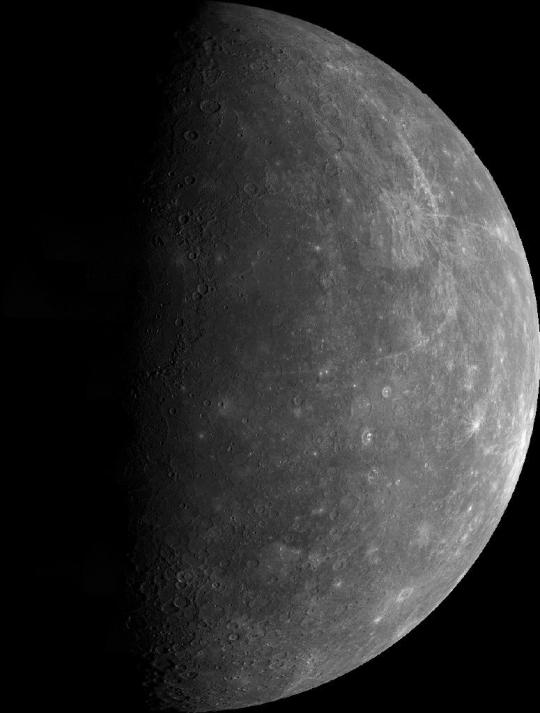

This mosaic shows the planet Mercury as seen by Mariner 10 as it sped away from the planet on March 29, 1974.
source x, x | images x
#mercurio#mercury#venus#mars#marte#astronomy#astronomia#space#solarsystem#sistemasolar#universe#universo#mariner#mission#space exploration
268 notes
·
View notes
Text
The NASA project scientist who led the grandest and farthest tour humanity's ever taken in our solar system has died. Ed Stone, the former director of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Voyager project scientist, was 88 years old when he died on June 9. For five decades, Stone led the Voyager mission, the longest robotic space mission in history and one of the greatest journeys of discovery in modern times. "How do you say goodbye to someone who helped make your destiny possible? Thank you, Ed, for opening the door for our celestial exploration. You will forever be remembered as your legacy lives on beyond the heliosphere," NASA said on its Voyager social media account, which is often written in the point-of-view of the spacecraft itself.
Continue Reading.
207 notes
·
View notes
Text
ARE WE SAFE FROM BLACK HOLES??
Blog#419
Wednesday, July 17th, 2024.
Welcome back,
Astronomers have discovered a black hole coming towards Earth. Before you get too alarmed, just know that we aren’t actually in danger — however, that doesn’t make the news any less unsettling.
Instead of freaking out, we can learn more about what it even means to have a black hole in space and how it affects us (or why it doesn’t).

For the majority of us, most of our ideas about black holes originate from sci-fi movies or books. It’s not very typical to know everything there is to know about the mysterious phenomena — in fact, even scientists still have a lot to uncover.
Nothing can escape a black hole. Its gravitational pull is so strong that even the brightest of light can’t survive, which is exactly how the interesting spectacle earned its name, according to NASA.

When in space, it’s said that these black holes form when a large star collapses and its life comes to an end. Most of the time, scientists can’t even see them, despite the fact that millions (literally) exist.
However, when astronomers decided to borrow a few techniques from exoplanet hunters, they ended up making a huge discovery. After observing shifting light frequencies — a sign that there’s gravity nearby from an invisible companion — they found a black hole incredibly close to Earth, according to Science.

This invisible force had a mass that was four times larger than the sun, which ruled out any idea that it was a star. To confirm that this area was in fact a black hole, the astronomers had to find a star that was orbiting something invisible, which is exactly what they found.
Its closeness — only 1,000 light years away — offers scientists the opportunity to learn more about binary systems and how they function.
So, a large black hole is facing Earth and nothing can escape it. Those two facts together might sound a little bit scary, but there’s actually nothing to worry about.

As mentioned earlier, there are millions of black holes out there, and they don’t just run around swallowing worlds. “They follow the laws of gravity just like other objects in space. The orbit of a black hole would have to be very close to the solar system to affect Earth, which is not likely,” NASA explained.
Even the most massive black holes that are directly facing Earth aren’t a threat, even though they are much larger than the sun and extremely powerful. An expert in the field — an astrophysicist and black hole researcher — even told Mashable that humans are “unbelievably safe” from these black holes.

We aren’t in any danger, luckily, but black holes could still affect us in a different, perhaps unexpected, way. Elizabeth Landau, a senior storyteller for NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, told The Independent that the merging of these black holes and stellar explosions could cause new solar systems and stars to form.
Originally published on https://www.greenmatters.com
COMING UP!!
(Saturday, July 20th, 2024)
"IS THERE WATER FLOATING IN SPACE??"
#astronomy#outer space#alternate universe#astrophysics#universe#spacecraft#white universe#space#parallel universe#astrophotography
81 notes
·
View notes
Text

JUPITER – JunoCam / 2024-08-18 Mission Phase : PERIJOVE 64
See more: https://jackiebranc.site/jupiter-and-its-galilean-moons/
Credit : NASA / SwRI / MSSS / Jackie Branc © CC BY
#elloon#jackie branc photographer#juno#juno spacecraft#jupiter#astronomy#NASA#jet propulsion laboratory#astrophysics#junocam#gas giant#solar system#Southwest Research Institute#Malin Space Science Systems
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
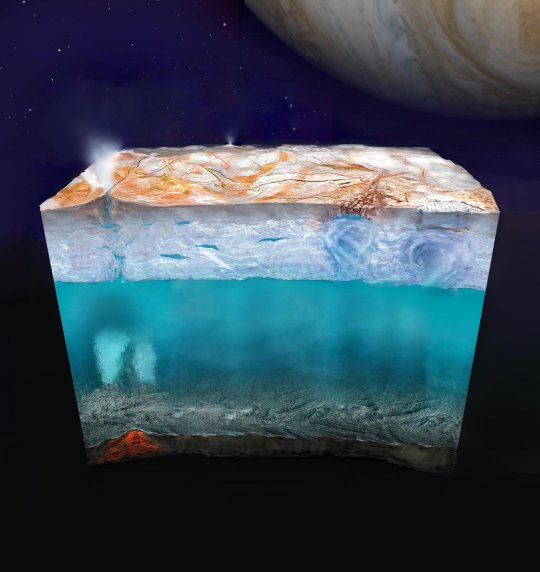


Can Life Exist on an Icy Moon? NASA’s Europa Clipper Aims to Find Out
With a spacecraft launching soon, the mission will try to answer the question of whether there are ingredients suitable for life in the ocean below Europa’s icy crust.
Deep down, in an ocean beneath its ice shell, Jupiter’s moon Europa might be temperate and nutrient-rich, an ideal environment for some form of life — what scientists would call “habitable.” NASA’s Europa Clipper mission aims to find out.
NASA now is targeting launch no earlier than Monday, Oct. 14, on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Europa Clipper’s elongated, looping orbit around Jupiter will minimize the spacecraft’s exposure to intense radiation while allowing it to dive in for close passes by Europa. Using a formidable array of instruments for each of the mission’s 49 flybys, scientists will be able to “see” how thick the moon’s icy shell is and gain a deeper understanding of the vast ocean beneath. They’ll inventory material on the surface that might have come up from below, search for the fingerprints of organic compounds that form life’s building blocks, and sample any gases ejected from the moon for evidence of habitability.
Mission scientists will analyze the results, probing beneath the moon’s frozen shell for signs of a water world capable of supporting life.
“It’s important to us to paint a picture of what that alien ocean is like — the kind of chemistry or even biochemistry that could be happening there,” said Morgan Cable, an astrobiologist and member of the Europa Clipper science team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which manages the mission.
Ice Investigation
Central to that work is hunting for the types of salts, ices, and organic material that make up the key ingredients of a habitable world. That’s where an imager called MISE (Mapping Imaging Spectrometer for Europa) comes in. Operating in the infrared, the spacecraft’s MISE divides reflected light into various wavelengths to identify the corresponding atoms and molecules.
The mission will also try to locate potential hot spots near Europa’s surface, where plumes could bring deep ocean material closer to the surface, using an instrument called E-THEMIS (Europa Thermal Emission Imaging System), which also operates in the infrared.
Capturing sharply detailed pictures of Europa’s surface with both a narrow and a wide-image camera is the task of the EIS (Europa Imaging System). “The EIS imagers will give us incredibly high-resolution images to understand how Europa’s surface evolved and is continuing to change,” Cable said.
Gases and Grains
NASA’s Cassini mission spotted a giant plume of water vapor erupting from multiple jets near the south pole of Saturn’s ice-covered moon Enceladus. Europa may also emit misty plumes of water, pulled from its ocean or reservoirs in its shell. Europa Clipper’s instrument called Europa-UVS (Europa Ultraviolet Spectrograph) will search for plumes and can study any material that might be venting into space.
Whether or not Europa has plumes, the spacecraft carries two instruments to analyze the small amount of gas and dust particles ejected from the moon’s surface by impacts with micrometeorites and high-energy particles: MASPEX (MAss SPectrometer for Planetary EXploration/Europa) and SUDA (SUrface Dust Analyzer) will capture the tiny pieces of material ejected from the surface, turning them into charged particles to reveal their composition.
“The spacecraft will study gas and grains coming off Europa by sticking out its tongue and tasting those grains, breathing in those gases,” said Cable.
Inside and Out
The mission will look at Europa’s external and internal structure in various ways, too, because both have far-reaching implications for the moon’s habitability.
To gain insights into the ice shell’s thickness and the ocean’s existence, along with its depth and salinity, the mission will measure the moon’s induced magnetic field with the ECM (Europa Clipper Magnetometer) and combine that data with measurements of electrical currents from charged particles flowing around Europa — data provided by PIMS (Plasma Instrument for Magnetic Sounding).
In addition, scientists will look for details on everything from the presence of the ocean to the structure and topography of the ice using REASON (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding to Near-surface), which will peer up to 18 miles (29 kilometers) into the shell — itself a potentially habitable environment. Measuring the changes that Europa’s gravity causes in radio signals should help nail down ice thickness and ocean depth.
“Non-icy materials on the surface could get moved into deep interior pockets of briny water within the icy shell,” said Steve Vance, an astrobiologist and geophysicist who also is a member of the Europa Clipper science team at JPL. “Some might be large enough to be considered lakes, or at least ponds.”
Using the data gathered to inform extensive computer modeling of Europa’s interior structure also could reveal the ocean’s composition and allow estimates of its temperature profile, Vance said.
Whatever conditions are discovered, the findings will open a new chapter in the search for life beyond Earth. “It’s almost certain Europa Clipper will raise as many questions or more than it answers — a whole different class than the ones we’ve been thinking of for the last 25 years,” Vance said.
TOP IMAGE: This artist’s concept (not to scale) depicts what Europa’s internal structure could look like: an outer shell of ice, perhaps with plumes of material venting from beneath the surface; a deep, global layer of liquid water; and a rocky interior, potentially with hydrothermal vents on the seafloor. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
LOWER IMAGE: The puzzling surface of Jupiter’s icy moon Europa looms large in this reprocessed color view made from images taken by NASA’s Galileo spacecraft in the late 1990s. The images were assembled into a realistic color view of the surface that approximates how Europa would appear to the human eye. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SETI Institute
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cybernetics with Chinese Characteristics & why we suck at the real Grand Strategy Game
Part 2 - The Quickening
Back in 2023, I wrote this more blog-like post about the mid 20th century McCarthyite purges of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the knock on effects that had - Namely the inception of the Chinese nuclear program, one-child policy and Chinese computing scene.
Since nothing is new under the sun, we have recently witnessed yet another example of America shooting itself in the foot, yet again, due to it's McCarthyite style purge of Chinese technology.
The release of the Chinese created AI system DeepSeek R1 last week has lead to the largest US stock market loss in history with NVIDIA stock decimated.
A record $465 Billion was wiped off its valuation in a single day. In 2024, the government of Turkey spent this much in a year on it's responsibilities?
Why did this happen?

As always, a lot can be put down to US foreign policy, and the in-intended implications of seemingly positive actions.
Do you want to start a trade war?
Back in the relatively uncontroversial days of the first Trump Presidency (Yes it does feel odd saying that) there were scandals with hardware provided by Chinese company Huawei. This led to the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2019 which explicitly banned Huawei and ZTE's hardware from use in US Government institutions. It also meant the US had to authorise US component manufacturer purchases by these companies.
Crucially this had a 27 month window. This allowed both companies to switch suppliers, and production to domestic suppliers. This actually led to Chinese chip advances. Following on from this came the 2022 move by the US Department of Commerce: "Commerce Implements New Export Controls on Advanced Computing and Semiconductor Manufacturing Items to the People’s Republic of China (PRC) ". This further limited the supply of semiconductor, supercomputer, and similar hardware to the PRC and associated countries.
Ok, well so far this is fairly dry stuff. You might think it would hamper Chinese development and, to some extent, it did.
It also proved to be the main catalyst for one financial quant.
Meet the Quant

Meet Liang Wenfeng (梁文锋). Educated to masters level, Liang was keen to apply machine learning methods to various field, but couldn't get a break. Finally, in the mid 2000's, he settled on a career investigating quantitative trading using machine learning techniques.
He became successful, founding several trading firms based around using machine learning methods, but his interest in base AI never seemed to cease. It was in 2021 that he started purchasing multiple NVIDIA GPUs to create a side project, leading to the creation of DeepSeek in 2023.
Now, due to import limitations, there were limitations on computation. This, however, did not stop DeepSeek's programming team.
Instead they used it as their strength.
Constrains Breed Innovation

For many years, the Western model of AI releases have focussed on making ever larger and larger models.
Why?
Let's break this down from an evolutionary point of view. Modern Western technology companies are largely monopolistic and monolithic. Many of these companies have previously hired staff at higher salaries not to fill roles, but to deny their competitors, and middle market firms, high-flying staff.
They also closely guard trade secrets. What's the training data? What algorithms were used in construction? Guess you'd better chat up some Silicon Valley bros at parties to find out.
For these kinds of firms, having control over large models, housed in data centres makes perfect sense. Controlling model deployment on their own computing systems, and not using local machines, means that they can not only control their systems more carefully, it also means that they can gatekeep access.
If your business model is to allow people to access your models on your servers, and your employees are focussed on making the biggest, best, models, there is no impetus to innovate more efficient, smaller models.
Companies such as OpenAI therefore have the following traits:
Research/Model focus on size over efficiency
Profit driven culture, with emphasis on closed source code
OpenAI's initial focus was as a non-for-profit developing Artificial General Intelligence. This became a for-profit driven company over time. - “I personally chose the price and thought we would make some money.” - Sam Altman
Staff working within paradigm they set in the early 2020's with established code libraries and direct contact with hardware companies creating chips
Significant capital investment - Upwards of several $ billions
DeepSeek, in comparison, is slightly different
For DeepSeek, necessity made innovation necessary. In order to create similar, or better models, than their counterparts, they needed to significantly optimise their code. This requires significantly more work to create, and write, libraries compared to OpenAI.
DeepSeek was started by financial quants, with backgrounds in mainly mathematics and AI. With a focus on mathematics and research, the main drive of many in the company has been exploration of the research space over concerns about profitability.
DeepSeek has also done what OpenAI stopped years ago: actually releasing the code and data for their models. Not only can these models therefore be run via their own gated servers, anyone can replicate their work and make their own system.
For DeepSeek, their traits were:
Research/Model focus on both efficiency and accuracy
Research driven culture, with open nature - “Basic science research rarely offers high returns on investment” - Liang Wenfeng
Strong mathematical background of staff, with ability to work around software, and hardware, constraints
Low capital investment of around $5.5 million

From an evolutionary point of view, DeepSeek's traits have outcompeted those of OpenAI.
More efficient models cost less to run. They also more portable to local machines.
The strong ability of DeepSeek's research focussed staff allowed them to innovate around hardware constraints
Opening up the code to everyone allows anyone (still with the right hardware) to make their own version.
To top it off, the cost to make, and run, DeepSeek R1 is a fraction of the cost of OpenAI's model
House of Cards

Now we can return to today. NVIDIA has lost significant market value. It's not just limited to NVIDIA, but to the entire US technology sector with the most AI adjacent companies losing from 10% to 30% of their valuation in a single day.
The culture, and business model, of OpenAI isn't just limited to OpenAI, but to the entire US technology ecosystem. The US model has been to create rentier-style financial instruments at sky-high valuations.
US tech stocks have been one of the only success stories for America over the past few decades, ever since the offshoring of many manufacturing industries. Like a lost long-unemployed Detroit auto-worker the US has been mainlining technology like Fentanyl, ignoring the anti-trust doctors advice, injecting pure deregulated substances into its veins.
The new AI boom? A new stronger hit, ready for Wall Street, and Private Equity to tie the tourniquet around its arm and pump it right into the arteries.
Like Prometheus, DeepSeek has delved deep and retrieved fire from the algorithmic gods, and shown it's creation to the world. The stock market is on fire, as the traders are coming off of their high, realising they still live in the ruin of barren, decrepit, warehouses and manufactories. The corporate heads, and company leaders reigning over the wreckage like feudal lords, collecting tithes from the serfs working their domain.
A Tale of Two Cities

The rise of DeepSeek isn't just a one-off story of derring-do in the AI world: It's a symbolic representation of the changing world order. DeepSeek is but one company among many who are outcompeting the US, and the world, in innovation.
Where once US free-markets led the world in manufacturing, technology and military capability, now the US is a country devoid of coherent state regulated free-market principles - its place as the singular world power decimated by destroying the very systems which made it great.
"Our merchants and master-manufacturers complain much of the bad effects of high wages in raising the price, and thereby lessening the sale of their goods both at home and abroad. They say nothing concerning the bad effects of high profits. They are silent with regard to the pernicious effects of their own gains. They complain only of those of other people." - Adam Smith, The Wealth of Nations
By selling the jobs of working class communities to overseas businesses, destroying unions and creating rentier based business models without significant anti-trust measures, US business and political elites have sealed the present fate of the country.
The CCP led, but strongly anti-trust enforcing, China has been able to innovate, ironically, using the free-market principles of Adam Smith to rise up and create some of the world's best innovations. The factories, opened by Western business leaders to avoid union/worker labour costs in their own countries, have led Shenzhen, and similar cities, to become hubs of technological innovation - compounding their ability to determine the future of technologies across the world.

Will America be able to regain its position on top? It's too early to say, but the innovative, talented, people who made America in the 20th century can certainly do it again.
As Franklin D. Roosevelt once said: “The liberty of a democracy is not safe if the people tolerated the growth of private power to a point where it becomes stronger than the democratic state itself...
We know now that Government by organized money is just as dangerous as Government by organized mob.
Never before in all our history have these forces been so united against one candidate as they stand today. They are unanimous in their hate for me—and I welcome their hatred.”

Until then, here's a farewell to the American Century 在那之前, 再见美国世纪
#cybernetics#cybernetic#ai#artificial intelligence#DeepSeek#OpenAI#ai technology#long reads#politics#us politics
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Apollo Application Program: BALLOS

Concept art of BALLOS (BALlistic LOgistic Spacecraft), an Apollo-derived logistics spacecraft. It was studied by NASA, Lockheed and McDonnell-Douglas for the transportation of Astronauts to and from the Large Orbiting Research Laboratory (LORL) space station for the Apollo Application Program.
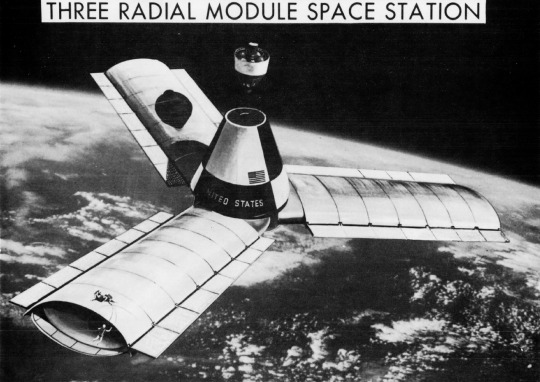


It came in three variants, a 6 astronaut version (2 crew, 4 passengers), 9 astronaut version (2 crew, 7 passengers) and a 2 astronaut version (2 crew, 10 passengers).

It would potentially be launched onboard either the Saturn IB or Titan III-C (in hammerhead configuration). The Saturn IB was preferred. Despite being bigger than the base line Apollo CSM, it would weigh roughly the same.
The 12 astronaut version has the following description:
"It is conical in shape with a spherical segment base. The base diameter of the spacecraft is 190 inches. The cargo-maneuver module is conical in shape and located immediately aft of the crew module. The conical shape adapts the 190-in. diameter crew module to the 260-inches diameter of the launch vehicle. This module is capable of carrying 13,455 lb of packaged cargo and 3,755 lb of maneuver propellant. This propellant is sufficient to meet the maneuvering impulsive velocity requirements of 1,050 fps which is provided by a modified LEM descent engine located in the module. Three solid-propellant retrorockets are located at the fore end of this module also.

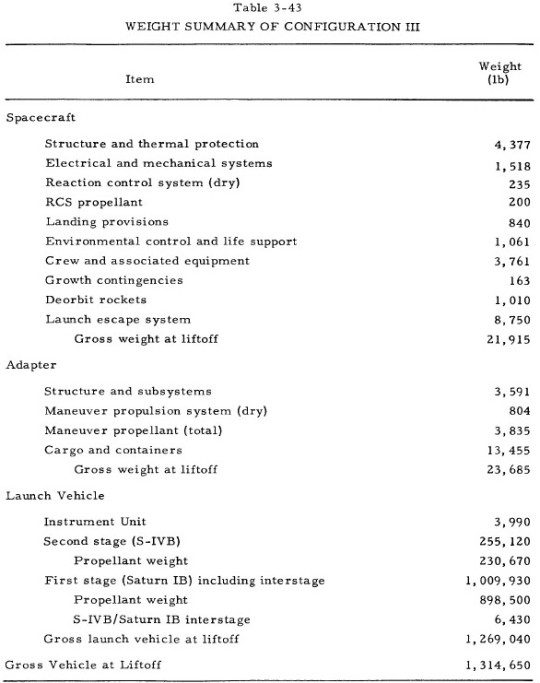
This vehicle fulfills the mission requirements of delivering 12 men and 13, 455 lb of packaged cargo to a space station orbiting at an altitude of 260 nmi and an inclination of 29.5°. The launch vehicle puts the spacecraft in a 105 nmi parking orbit from which a Hohmann transfer is used to reach the rendezvous altitude of 260 nmi. Impulse for the Hohmann transfer and injection into final orbit is provided for in the 1,050 fps of impulsive velocity capability of the maneuver propulsion system. The maximum dynamic pressure of 525 psf is reached approximately 85 sec after launch. The maximum longitudinal acceleration during launch is approximately 4 g's."


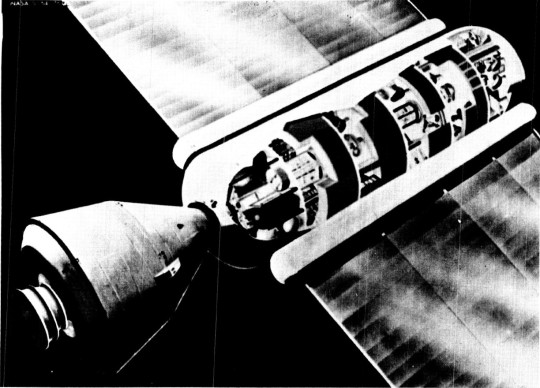
At the end of the mission, the capsule would return to Earth for recovery, refurbishment and reuse. The propulsion module would be allowed to burn up.
"On an operational basis, prelaunch preparation time for a new [Ballos] spacecraft is 40 days. This time period includes receiving and shop processing prior to mating to the erected launch vehicle.
The projected 1968 to 1970 time period estimate for on-pad preparation time for the Saturn IB launch vehicle is 48 days. Of this, 23 days are allowed for payload mating and integrated vehicle checkout. The total prelaunch processing time required for the [BALLOS] vehicle, therefore, would be 63 days."
BALLOS never progressed past the study phase, like many proposals of the Apollo Application Program.
Date: Study 1964
source, source
NASA ID: S64-3663, S63-4634, S64-1800
#BALLOS#BALlistic LOgistic Spacecraft#Apollo CSM#NASA#Apollo Program#Apollo Applications Program#Study#1964#concept art#Large Orbiting Research Laboratory#LORL#my post
57 notes
·
View notes
