#Post-War Economics
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Trade Deficit/Surplus and Their Relationship to Tariffs
Hey, let’s talk about trade imbalances and why they’re not an optimal way to dictate tariffs. A few people showed interest when I asked if I should talk about it, so I've written up about [checks] 3.2k about it.
(If you want to support me in writing these up and living my best life, you can prompt me for more on ko-fi. I'm trying to move out of my parents' house.)
Previously, I explained comparative advantages and why they can be a crucial indicator for what fields are a reasonable target for import/export taxes. Let’s have a quick recap:
A comparative advantage is when two countries are both capable of an industry, but one is much better at it. Ideally, the two countries have different specialties, and can complement each other. The classic example is England, specializing in wool, and Portugal, specializing in wine. Both countries could and did engage in both industries, but they put greater amounts of resources into their specialties and then traded. If Portugal did one quarter resources on wool (to maintain a domestic industry in case of a breakdown of trade relations or natural disaster) and three quarters resources on wine, they could trade part of that wine to England for the wool, and both countries would end up with more of the product due to specialization. England has better conditions for rearing sheep, and Portugal has better weather for growing grapes.
That is comparative advantage. If two countries are largely self-sufficient, and they have one industry respectively that stands out as exceptionally efficient each, then you see a trade balance: equal amounts of wine and wool exchanged, as measured by monetary value.
An imbalance occurs when one country sells drastically more of their product than the other. Say Portugal has a bad harvest, and makes less wine than usual. They then sell less to England, but may buy the same amount of wool as usual, dipping into savings or making their money elsewhere in order to buy. In that year, England is experiencing a trade surplus, and Portugal is experiencing a trade deficit.
Four things to cover:
The nature of an enduring imbalance in a stable economic system
Artificially enforced imbalances
Indirect profits
Excluded industries
What can cause an enduring imbalance?
Let us say that we have a closed economy of three countries.
Country A has good weather and soil, and so they specialize in agriculture and are a bread basket for the region. They are self-sufficient in terms of raw minerals or metals, but have little in the way of energy resources.
Country B has a large amount of energy; they have large deposits of gas and oil, and have built out infrastructure to capture energy from offshore wind farms and hydro as well. Their farmland is decent enough to support their population, but they have little in the way of metals and minerals to build those oil drills and windmills.
Country C has a strong mining industry, and is rich in mineral resources and key metals like iron and copper. They are self-sufficient in terms of energy, but their farmland is poor and they cannot easily feed their people.
To recap:
Country A: sells food, buys energy. Little trade in mining.
Country B: sells energy, buys metals and minerals. Little trade in agriculture.
Country C: sells metals and minerals, buys food. Little trade in energy.
You can probably see where this is going: Country A sells a lot of food to Country C, but doesn’t buy metals and minerals from them, so A has a trade surplus with C. Meanwhile, they buy a lot of energy from B, which doesn’t need their food, so there they have a trade deficit there.
Country A:
Buys energy from B: deficit
Sells food to C: surplus
Country B:
Buys metals and minerals from C: deficit
Sells energy to A: surplus
Country C:
Buys food from A: deficit
Sells metals and minerals to B: surplus
As you can see, any bilateral trade relationship in this closed system is heavily imbalanced. However, when taking the full scope of the system into account, it’s balanced, because all three are feeding into each other. They cover each others’ weaknesses, and so the trade is stable.
Introducing tariffs would disrupt that balance. If A starts to tariff energy from B, because they see it as a threat to their own minimal domestic industry, then they disincentivize purchasing energy. In turn, B’s profits fall, which means they have less money to buy metals and minerals from C, which means they have fewer resources to build wind farms and oil rigs, which means they have less energy to sell in the first place. This then also impacts C, which now isn’t making as much money from selling their mining products, which means they can’t buy as much food from A, and that means… the perceived deficit, which was stable, may have been shrunk, but so has the efficiency of the entire circle.
In a global economy, there is always a good chance that the ‘deficit’ is just part of a larger balance. India buys energy from Russia, which buys food from China, which buys tropical foods from Thailand, which buys machinery from Germany, which buys electronics from Japan, which buys minerals from Australia, which buys pharmaceuticals from… India.
This is very simplified, but you see what I’m getting at with the complexity of the web of international trade. One perceived deficit does not a holistic view make.
(This is especially true of imports that are near impossible domestically. We literally can’t grow coffee in the United States outside of Hawaii and a few island territories like Puerto Rico or American Samoa. There small attempts in California and Florida, but it’s not commercially viable. Most of them cannot grow enough to export to the rest of the US, especially when factoring in other high-demand foods that require these climates, such as oranges and bananas. While there are places in the US that can grow these tropical foods, those places are so limited that we just can’t grow enough of each and every one to meet demand, so those places specialize in the foods they can grow most effectively, which is how you end up with the majority of Florida’s exports, at least in terms of cash value, being citrus, peppers, and tomatoes.)
There are valid reasons for tariffs to be implemented as protectionist measures, even when specialization seems to dictate otherwise, and I covered that in my other post. However, the above is meant to illustrate that the simplified view of trade deficits as the only dictator of tariff policy is a very poorly thought-out exercise.
Let’s look at a case study of recently-implemented tariff policies: Lesotho.
Lesotho is a small country surrounded entirely by South Africa; it’s the largest sovereign enclave in the world (the others are San Marino and Vatican City). Lesotho is a fairly poor country. They cannot afford to import much from the United States, simply due to the low GDP per capita.
For reference, the US GDP per capita is over $86k.
South Africa, Lesotho’s nearest neighbor, has a GDP per capita of about $16k, adjusted for PPP.
Lesotho’s GDP per capita, adjusted for PPP, is about $3.2k. (These numbers were pulled from Wikipedia, current as of 2023-2025.)
The people of Lesotho, by and large, cannot buy goods from the United States.
Meanwhile, they have two major lines of export. One is garment manufacturing; much like China and Southeast Asia, the low wages ensure that garment costs are kept minimal, which the people of the US find palatable. These wages to the local population are low enough that they cannot in turn buy from the US. The other export is diamonds, an industry that heavily favors the upper classes when it comes to profits, again relying on comparably low local wages that have been the subject of union actions as recently as 2020.
This article from 2017 stated that garment workers earned about $96 per month; that number has doubtlessly changed in some way since then, but it’s definitely still in the ballpark of ‘skilled workers in Lesotho make in a month what minimum-wage Americans make in two or three days.’ This study from 2022 talks about the lack of general impact of the mining industry on the population of Lesotho, addressing the employment opportunities, impact on local resources like water and air quality, and how money is or isn’t cycled back into the community.
Because of the above, Lesotho has a notable trade imbalance with the US. From the US, this is a trade deficit. The US has a very diminished capacity for garment production due to outsourcing to cheaper pastures, and only one active diamond mine, which is used for tourism rather than commercial mining. We can’t make what they do, and they can’t afford what we do.
The trade imbalance with Lesotho is 120-130 billion USD, depending on the year. They export a lot to the US, and buy very little, and I’ve hopefully illustrated why.
The tariffs laid against Lesotho, a country that cannot realistically buy much from the US due to the general poverty, were set at 50% on Trump’s so-called liberation day.
So what would that accomplish, realistically?
Artificially Enforced Trade Imbalances
We now take a look at trade imbalances that are the results of manufactured pressures rather than natural ones.
With the earlier model, I covered three countries with complementary industries and a desire to cooperate in favor of overall better outcomes. That model assumes good faith.
The real world has Walmart. Also Amazon, Apple, SHEIN, TEMU, H&M, Zara, Target, and more.
Also, a history of colonialism.
…we need to go back a bit, for this one.
For several centuries, European powers had control over large portions of the Global South and East, for a variety of reasons that mostly involved spreading diseases and having guns. The East India Companies (Dutch and English) were major factors in this.
Let’s zoom in on England and India. England had partial or full control of India from 1757 to 1947. This was achieved through superior weaponry, a navy (controlled by the East India Company) that could blockade ports, and a generally higher willingness to commit crimes against locals. Due to English control over many aspects of trade and access to resources, the economy was aggressively molded to be in greater favor of the British. This includes deindustrialization, taxes that favored British imports over domestic products, and enforced trade barriers to other nations. A particularly notable example is the cotton trade; raw cotton would be shipped to the UK with no tariff, spun into threads and woven into fabric, and then sold back to India at a high tax rate. This meant that India was pressured into sending away a central pillar of their economy, and then sold that same product back at a massively inflated cost that they had to pay, because they no longer had the resources to do it domestically. This led to a widespread reduction in the infrastructure to make fabric as they had once been known for, along with a massive transfer of wealth from India to the UK, much of it under the oversight of the British East India Company.
This had a lasting impact on India, one that they’ve been working to recover from since before gaining independence. This is true of many countries that were colonized and exploited by the West, which includes most of Latin America, Africa, South Asia, and South-East Asia. Some of East Asia can be read broadly as having recovered, but few economies managed that kind of economic bounce-back, and few did so quickly.
These days, there is no British East India Company, as it was dissolved in the 1870s. Instead, we have companies like Walmart and Amazon. Their tactics involve a few less guns, but there is still a massive impact on things like local wages.
(The guns do still make an appearance; ever heard of union-busting?)
Due to the size of the American economy, military, and political influence, smaller economies with less power are pressured to submit to Western whims. America, in particular, gained a lot of international power with WWII, setting up bases all over the world, as well as experiencing a massive economic boom. The two factors combined resulted in an economy that could buy in bulk for sales at department stores, even setting up individual factories of their own in these countries that were, in many cases, only just achieving independence from their Western colonists. They were still in the agricultural period of economic growth, often due to forced de-industrialization like in India, and the manufacturing business was created by foreign investment, or by a government inviting such from foreigners.
Newly independent, struggling economies, searching for a way to strengthen their positions and banks. Factories, and a wealthy overseas client that wants all the goods you can make.
They will pay you pennies for it. Those are pennies you don’t have, and maybe you have a debt to pay off. Maybe the government incurred debts building those factories, and people have to work to pay that off, but once it’s paid, you’ll get the money for real!
(You know those $200k student loans you spend forever working off? Imagine that, but it's your regional government owing money to a foreign company.)
Or maybe they pay you decently, for now.
So, countries with decimated industries agree to work for these companies. They get into factories, sit down, and start sewing. They agree to do petroleum refinement because the US doesn’t want to stink up its own air anymore, could you do it instead, pretty please? They mine, or cut lumber, or destroy their own rivers making that pretty ‘vegan’ leather.
And your local economy is reliant on Walmart now, or Amazon, or Apple. Ninety percent of the town works for them, after all!
But inflation is a thing, so you ask for a raise.
And the factory says no.
In fact, they cut your wages. You’re making too much, they say. The shops in America want it cheaper, they claim. Too bad, so sad. If you don’t like it, go work somewhere else.
But the factory employs 90% of the town.
So because America wants cheap goods, there is a trade deficit: buy whatever you want from China, or Bangladesh, or Vietnam. They can’t afford to buy anything back, but that doesn’t matter, does it?
Oh hey, we are sending them so much money by buying all their stuff! That’s not fair, is it? They’re taking advantage of the United States by not buying any of our products. Let’s tariff them.
Western companies placed interminable barriers on these economies, and now the US government wants to punish the victims of those barriers. And that’s frustrating for many reasons, but a big one is this:
Indirect Profits
A lot of the ‘imports’ that the US gets are actually bringing a net profit.
Let’s say Apple set up a factory in China ten or twenty years ago. They are pretty entrenched as part of the economy, and it also took a long time to establish. There is nothing in the US that can replace it in a realistic timeframe.
Let’s say that iPhone takes $400 to build in China. $150 for parts, $250 for labor and overhead, and then toss on $5 for shipping, since that’s a cost that easy to scale. Bring that phone to the US or France or Singapore, sell it for $1000. That’s almost $600 in profit!
Something that is valued at $1000 gets tariffed at the $400, and then sales taxed at the $1000.
And that profit goes toooooooooooooooo Apple.
Back in the US. Except it’s actually Ireland. (They do this to avoid other taxes.)
(The Ireland situation is insane, by the way. They call it leprechaun economics. You can read about it, though this article is much more Accounting Terminology than most people looking to read.)
Now, I do need to clarify that the Trade Imbalance Numbers are still using that wholesale rate of $400, not $1000. So it doesn’t necessarily impact the trade numbers as massively as it could, but the end numbers are that the perceived value of the trade deficit isn’t the actual end value of the products being imported.
And the thing is, that profit still gets back to the US (technically Ireland), even when that phone goes to Germany or Nicaragua or Burundi or wherever else. The American company still gets the money, which then gets spent on physical imports like mangoes and cobalt.
The US takes advantage of China in this regard, because so much of that profit is pocketed by the parent company, in the US (technically Ireland), rather than the employees themselves. The given reason for this is that the Americans are bringing the product development and coding and marketing to the table.
Phone made in China, sold to Germany. Trade imbalance reflects the relationship between China and Germany, but the profits go to the United States: the US is making money that isn't reflected in trade deficits.
And that brings us to our last point:
Excluded Industries
Did you know that the trade deficit only counts physical goods?
These numbers do not include IP or service trades.
That art your friend in the UK commissioned you to draw does not factor in. The South Korean showings of the latest Marvel movie do not factor in. That Adobe Photoshop that someone downloaded in Brazil does not factor in. That Netflix subscription in Italy doesn’t factor in. That financial analyst getting paid by a US company to report on the Nikkei index in real time, from Japan, does not factor in. That head of operations that the US company is paying to run product distribution in Dubai does not factor in. That C drama you streamed in Colorado doesn’t count. That eBook you bought from a writer in Darfur doesn’t count. That app you bought from a company in Peru doesn’t count.
None of it counts.
None of this is included in the calculations. Even the WSJ is annoyed (that article is paywalled but I like their chart at the top, and that part is free to see).
Now, the services surplus isn’t enough to compensate for the trades surplus, but it doesn’t have to be. Remember: if you make something in Vietnam, and sell it in Spain, but the money still comes back to the US… that doesn’t count towards either side of the trade balance.
But it does raise the GDP.
(Unless you send the money to Ireland, maybe.)
Trade deficits are a genuinely bad thing to base your tariff policy on, in the sense that it cannot be the only factor. It can factor in—doing so with China in particular makes sense given shifts in the global market since the early 2000s, especially with regards to de minimus exemption—but it can’t be your sole deciding factor.
This is especially true when the government both isn’t doing it for the reason they claim (likely), or doesn’t understand what tariffs and trade deficits really do (Trump, at least, has been talking about this since the 1980s, so I’m pretty sure he actually believes in this, and thus doesn’t know the actual ramifications).
Conclusion
Sometimes you need to understand how comparative advantage and trade webs work before you take someone’s word for the nature of deficits. Tariffs play a role in the balance of trade and protection of domestic industry, but trade imbalances cannot be your only factor in deciding on tariffs, nor can tariffs be your only tool in reindustrialization.
Anyway. Prompt me for more on ko-fi or something. Help me move out of my parents' house.
#tariffs#politics#economics#economics for dummies#phoenix posts#phoenix politics#trade deficit#trade surplus#trade imbalances#trade policy#trade war#exports#imports#taxes#colonialism#imperialism#india#lesotho#united states#china#industry#industrialization#reindustrialization
167 notes
·
View notes
Text
how good do we think shen yuan's english is? he complains about airplane's shitty chinglish, which could mean his own english is pretty good or it could just mean he knows airplane's english is terrible. my guess is that if shen yuan's family is rich, he probably received pretty thorough english lessons, so his english is pretty good, though he can read/write it much better than speak it because he took what he learned from his lessons and immediately used it to be a menace on english-speaking parts of the internet
#svsss#sy's family could probably pay for private tutors or whatnot#meanwhile airplane probably just learned whatever he could in public school or college or whatever#sy's family wanted him to learn english for like. idk. economic reasons#like in case he wanted to get involved in the family business#but instead he used it so he could be a terror on the internet in two different languages#like that post about learning chinese just to get into flame wars in chinese fandoms#except the reverse lol#writing essay length comments is a great way to practice your language skills lmao
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
currently researching the economic and sociopolitical scene of 1950s america. thank you children's heterotopia for making me have twenty tabs open now
#senja.txt#postwar economic boom and the rise of capitalism......#interesting how a lot changes in a decade#inflation is still low..... society is still very much gendered and incredibly (white centric) cisheteronoromative#and the colorful clothing post war#was right with the huge families stuff because I based a lot of stuff from my grandparents' stories#since 60s/70s indonesia is like 50s america yadda yadda yadda different social standings stuff#I've always envisioned my oc story's world like chainsaw man's and kagurabachi's#largely following how things go in the real world with a few changes that later has a long lasting impact#gotta read more though. I'm not american and like I've said CH's world has differences from the typical 50s america#but I want my story to at least make sense setting-wise
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
I bought jello packs, cottage cheese, whipped cream, and fruit cocktail on a whim, all for separate purposes, but I've suddenly been possessed by the ghost of a prozac-addled bored housewife from the Fifties with a grudge against her asshole cheating husband and have this incredible urge to mix it all together
#I think it would be at least okay actually#I like adding sweet things to cottage cheese and it turns out nice#not everything jello is a monstrosity it's only when you put meat in it that it turns into a blob nightmare#I do not envy my parents for growing up in the Post War Economic Boom that brought forth evil gelatin creations#food
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
yk it’s bad enough that we could say that the erie canal was influential in starting the civil war but i truly believe you could make the argument that it also led to the great migration
#em posts#nhd core#i mean think about it#mechanization and industrialization as a result of erie canal#boom towns like chicago along the canal and bcs of the industrial rev#further polarization btwn north and south as economies diverge#civil war and eventually jim crow laws#black southerners driven out of the south#increased economic opportunities in the north due to industrialization#i think it works#can you tell i’m reading about the great migration
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Alice was perceived to be a destructive influence on every aspect of Edward III’s kingship, but specifically on his abilities as a military leader resulting in the subsequent collapse of the war in France." "[In the Bridlington Prophecies, Erghome] speaks of a woman through whose love and counsel the king was impeded from waging many fair wars at that time. She has made the king effeminate. He no longer has a taste for war but remains at home indulging in luxury."
— Laura Tompkins
Nothing but respect for MY fourteenth-century antiwar activist <3
#Alice: 'Why spend money on war when you can spend it on ME?#And she was absolutely right#alice perrers#14th century#my post#edward iii#hundred years war#queue#To be clear these accusations were obviously exaggerations - we don't know what Alice thought of the war (it's possible she did#genuinely think it was pointless and going nowhere) but either way I think we can all agree there was a variety of other circumstances#that resulted in the collapse of the war in France which Alice obviously had nothing to do with#such as ACTUAL MILITARY DEFEATS; the economic conditions of the country; and Edward III's own declining health; etc#there's no need to blame her for everything
19 notes
·
View notes
Text

speak for yourself i will eat a dentist
#og post#my caption is a joke i understand this person is trying to come at this from a more serious economic perspective#but in my original post im obvs speaking colloquially by calling lawyers rich aka much wealthier than the average person#less class war more youre just extremely priviliged
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
.
#words cannot express how little i care for post 1945 history#it is a literal CRIME to make me take these exams#a literal CRIME I SAY#like i literally could not care less#i haven't had this little interest in an exam i had to take since high school aka the last time i had to know chemistry and physics#the second part of the twentieth century is a literal nightmare#there is so much that has happened and it's all so well-recorded that there's literally no SPACE for things like culture#it's just politics-war-economics-politics-war#i loathe it with all of my being#ella originals
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Don't kill yourself, think of the economy!!!
#slavery#wage slavery#chattel slavery#economics#economy#poverty#homeless#uk politics#uk police#uk pop#uk post office scandal#ukpol#uk government#uk govt#ukgov#ukdeals#skins uk#uk#united kingdom#unitednothings#jerktrillionaires#jerkbillionaires#jerkmillionaires#class war#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
i like to imagine the way that renko and merry dress is retro even for their retro age. what’s “in” is 50s-60s clothing.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
I've actually been scrounging for an ending to Ellenville, because it's hard to actually 'end' a tragedy with something that feels complete, and that last post hit me with yeah, that's right. Because we live in a world where blood is protection and the cost of safety; and it fits in so neatly with the themes of death as stasis and longevity.
The 'end' is the regulations in place. Not even watching it happen, but success. This is The Pushcart War but epic fantasy.
#ellenville#ptxt#Jean Merrill is up there with Jean Craighead George for the imprinting I did on Pushcart War and Toothpaste Millionaire.#Which is ironic as FUCK because my curriculum definitely wanted me to take away 'You can be entrepreneurial too! Which is killing big truck#And undercutting big toothpaste business by packing yours in sterilized baby jars!' when I actually took away what Merrill#wanted which was: 'Hey isn't it fucked up that large companies think they can push you around and we need a capitalist underdog#success story to feel happy about our lives and role in the ongoing oligarchy of capitalism?'#Homeschooling with sonlight was fucking wild. I read so many good books as a kid and credit it to the fact I grew up with empathy#But it also meant I grew up with States Rights narratives and libertarian propaganda I had to unlearn.#Total aside because this is a tag essay anyway and I don't want to make a new post: I found out my advisor was also homeschooled#Which is probably why we're the exact same person I'm just 12 years behind them without the accent. My own brother almost#mistook them for me from behind and he gets pissy about it lol. 'There are two of them now!'#BUT I SWEAR I'M NOT COPYING THEM. WE JUST HAPPEN TO HAVE THE EXACT SAME HISTORICAL INTERESTS AND#SLAVISH DEVOTION TO GEOLOGY THAT TRANSFORMED INTO THE APPLICATIONS OF GEOLOGY AS A SCIENCE.#In my defense they have a much broader and recent focus on geology: usually for the impact of mining/geology on historical events.#Whereas I like the economic and logistical side of things. Like who hated who because they had beef over the same mines Nitrate War style
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Other shortcomings [in communicating science] are evident in television science fiction programming. Star Trek, for example, despite its charm and strong international and interspecies perspective, often ignores the most elementary scientific facts. The idea that Mr. Spock could be a cross between a human being and a life-form independently evolved on the planet Vulcan is genetically far less probable than a successful cross of a man and an artichoke… There must be dozens of alien species on various Star Trek TV series and movies. Almost all we spend any time with are minor variants of humans. This is driven by economic necessity, costing only an actor and a latex mask, but it flies in the face of the stochastic nature of the evolutionary process. If there are aliens, almost all of them I think will look devastatingly less human than Klingons and Romulans.”
- Carl Sagan, The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark
#brot posts#astro posting#god this entire book is just giving voice to so many things i think about like wtf hes even talking about the things i bitch about in scifi#albeit i feel like hes not being as lenient as he should be re: the economic limitations#as well as the technological limitations especially for TOS at the time#so like i understand there is a grounded reason as to why all the aliens are just. variants on humans#but like in an actual scifi way. its boring. its inaccurate#wheres the imagination#and im complaining about more than star trek here im also complaining about star wars#and all other scifi#and in that case when broadening it to the entire genre i will also say its not just finances and technology#but also just. lack of imagination.#so its not even really necessarily like a failure to communicate the theory of evolution to the public when creating scifi media#its just like. cost benefit analysis. weighing whether putting in the effort to make all these distinct independent species totally differe#different#is worth the time and money to design and implement#its easier in a media production sense to just stick some funky ears on a human person and call it another species#BUT YKNOW. it is still something i find annoying and something i do bitch about so im so glad Mr Sagan is also bitching about it
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The main example of how the mass thinking nowadays is UScentric and unfiltered from context is the age discourse. The whole boomer thing.
#when i was younger i was so angry with boomers but recognising them as parents screwing up their kids mostly so i was biased#after years i realised that people talked less about generational behaviour and more about privilege and status and systematic(word that#screams American)power and there is the failure. most post war countries experienced an economic boom but#besides the us the great majority of boomers grew up in poverty and neglect and had to fight for basic rights#then things became a little easier for them especially in the 80s and 90s when they were already 30/40. I'm not taking away their faults#they're the 68 gen the sex liberation the drugs the fashion and now the majority is hella conservative(zoomers future except the efforts)#but they never were given stuff on silver platters nor were rich and privileged for the most part and even in rich countries#this make people forget about how gen x are entitled and in power now and ruined many things with no consequences. karens are genX bc they#know how to cater to younger people and turn them against the elders while using rainbow slogans for their major companies#then there's the whole young people are innocent/age gaps in love are bad/my grandma had 2 houses at 20 she robbed me#my grandma had to almost die to buy the house I live in now that she left me or else I'd be homeless and age discourse is generalised ik#but still very not focused on what is really the fault and instead on envy and minor context.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Among their complaints [in 1460, the Yorkists] specifically blamed the earls of Wiltshire and Shrewsbury and Viscount Beaumont for ‘stirring’ the king [Henry VI] to hold a parliament at Coventry that would attaint them and for keeping them from the king’s presence and likely mercy, asserting that this was done against [the king's] will. To this they added the charge that these evil counselors were also tyrannizing other true men* without the king’s knowledge. Such claims of malfeasance obliquely raised the question of Henry’s fitness as a king, for how could he be deemed competent if such things happened without his knowledge and against his wishes? They also tied in rumors circulating somewhat earlier in the southern counties and likely to have originated in Calais that Henry was really ‘good and gracious Lord to the [Yorkists] since, it was alleged, he had not known of or assented to their attainders. On 11 June the king was compelled to issue a proclamation stating that they were indeed traitors and that assertions to the contrary were to be ignored."
— Helen Maurer, Margaret of Anjou: "Queenship and Power in Late Medieval England
Three things that we can surmise from this:
We know where the "Henry was an innocent helpless king being controlled and manipulated by his Evil™ advisors" rhetoric came from**.
The Yorkists were deliberately trying to downplay Henry VI's actual role and involvement in politics and the Wars of the Roses. They cast him as a "statue of a king", blamed all royal policies and decisions on others*** (claiming that Henry wasn't even aware of them), and framed themselves as righteous and misunderstood counselors who remained loyal to the crown. We should keep this in mind when we look at chronicles' comments of Henry's alleged passivity and the so-called "role reversal" between him and Margaret.
Henry VI's actual agency and involvement is nevertheless proven by his own actions. We know what he thought of the Yorkists, and we know he took the effort to publicly counter their claims through a proclamation of his own. That speaks louder than the politically motivated narrative of his enemies, don't you think?
*There was some truth to these criticisms. For example, Wiltshire (ie: one of the men named in the pamphlet) was reportedly involved in a horrible situation in June which included hangings and imprisonments for tax resistance in Newbury. The best propagandists always contain a degree of truth, etc. **I've seen some theories on why Margaret of Anjou wasn't mentioned in these pamphlets alongside the others even though she was clearly being vilified during that time as well, and honestly, I think those speculations are mostly unnecessary. Margaret was absent because it was regarded as very unseemly to target queens in such an officially public manner. We see a similar situation a decade later: Elizabeth Woodville was vilified and her whole family - popularly and administratively known as "the queen's kin" - was disparaged in Warwick and Clarence's pamphlets. This would have inevitably associated her with their official complaints far more than Margaret had been, but she was also not directly mentioned. It was simply not considered appropriate. ***This narrative was begun by the Duke of York & Warwick and was - demonstrably - already widespread by the end of 1460. When Edward IV came to power, there seems to have been a slight shift in how he spoke of Henry (he referred to Henry as their "great enemy and adversary"; his envoys were clearly willing to acknowledge Henry's role in Lancastrian resistance to Yorkist rule; etc), but he nevertheless continued the former narrative for the most part. I think this was because 1) it was already well-established and widespread by his father, and 2) downplaying Henry's authority would have served to emphasize Edward's own kingship, which was probably advantageous for a usurper whose deposed rival was still alive and out of reach. In some sense, the Lancastrians did the same thing with their own propaganda across the 1460s, which was clearly not as effective in terms of garnering support and is too long to get into right now, but was still very relevant when it came to emphasizing their own right to the throne while disparaging the Yorkists' claim.
#henry vi#my post#wars of the roses#margaret of anjou#Look I’m not trying to argue that Henry VI was secretly some kind of Perfect King™ whose only misfortune was to be targeted by the Yorkists#That is...obviously pushing it and obviously not true#Henry was very imperfect; he did make lots of errors and haphazard/unpopular decisions; and he did ultimately lose/concede defeat#in both the Hundred Years War and the subsequent Wars of the Roses.#He was also clearly less effective than his predecessor and successor (who unfortunately happened to be his father and usurper respectively#and that comparison will always affect our view of his kingship. It's inevitable and in some sense understandable.#But it's hardly fair to simply accept and parrot the Yorkist narrative of him being a “puppet of a king”.#Henry *did* have agency and he was demonstrably involved in the events around him#From sponsoring alchemists to issuing proclamations to participating in trials against the Yorkists (described in the 1459 attainder)#We also know that he was involved in administration though it seems as though he was being heavily advised/handheld by his councilors#That may be the grain of truth which the Yorkists' image of him was based on.#But regardless of Henry's aptitude he was clearly *involved* in ruling#Just like he was involved in plots against Yorkist rule in the early 1460s before he was captured.#And he did have some successes! For example in 1456 he travelled to Chester and seems to have been responsible#for reconciling Nicholas ap Gruffyd & his sons to the crown and granting them a general pardon.#Bizarrely Ralph Griffiths has credited Margaret for this even though there is literally no evidence that she was involved.#We don't even know if she travelled with Henry and the patent rolls offering the pardon never mention her.#Griffiths seems to have simply assumed that it was Margaret's doing because of 1) his own assumption that she was entirely in control#while Henry was entirely passive and 2) because it (temporarily) worked against Yorkist interests.#It's quite frustrating because this one of the most probable examples we have of Henry's own participation in ruling in the late 1450s#But as usual his involvement is ignored :/#Also all things considered:#The verdict on Henry's kingship may not have been so damning if his rule hadn't been opposed or if the Lancastrians had won the war?#Imo it's doubtful he would be remembered very well (his policies re the HYW and the economic problems of that time were hardly ideal)#but I think it's unlikely that he would have been remembered as a 'failed king' / antithesis of ideal kingship either#Does this make sense? (Henry VI experts please chime in because I am decidedly not one lol)
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
I want to riff on one thing here. There were a lot of manufacturing jobs in the US in the 40s-60s. And they paid well. Iirc there was even some price deflation (dollars bought more goods in later years). I feel like in the US we tend to think of this as "The time when everything worked how it's supposed to" and we think of 70s+ as "things have gone wrong". But is that true? Why did those manufacturing jobs change or go away?
I propose that the 1945-1969 are anomalous years. Specifically that they are anomalous in the lack of manufacturing competition outside the US.
Let's look at some other major manufacturing powers of today and check in on how they were doing in the 40s-60s:
China: Huge casualties in the world war. Had recently been invaded and occupied in part by Japanese forces. Active Civil war. Partition between communists and capitalists. Extreme suffering and casualties under Maoism.
Germany: Had recently been invaded and is currently being occupied by US/European/Soviet forces. Extreme destruction of infrastructure by bombing in the world war. Huge casualties in the world war. Partition between communist and capitalist occupied zones.
Japan: Large casualties in the world war. Large destruction of infrastructure by bombing in the world war. Occupied (debatable) by US forces.
Korea: Large casualties in the world war. Had recently been occupied by Japanese forces. Active civil war with foreign troops on both sides. Partition of communists and capitalists.
France: Had recently been invaded and occupied by German forces in large part. Large casualties in the world war. Destruction of infrastructure in the world war. Actively at war in colonial possessions, I believe?
UK: Had recently been bombed in the world war with some destruction of infrastructure. Suffered casualties in the world war.
Vietnam: Had recently been invaded and occupied by Japanese forces. Active wars against French and US forces. Active Civil War. Partition of communists and capitalists.
India: Recently granted independence and Partitioned between Muslim and Hindu regions. Recovering from the mass displacement of people associated with partition.
The Soviet Union: Extremely high casualties in the world war. Recently invaded and occupied by German forces with some resulting infrastructure damage.
And finally, The United States of America: No infrastructure damage outside of Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. Relatively low casualties in the world war. Recently heavily industrialized in the war effort towards manufacturing and much existing institutional knowledge. Many returning soldiers have their College studies paid for and become part of an expanding educated class. Already has many brilliant scientists living there who fled Europe before or during the war.
There just wasn't anywhere else that could compete with the US on manufacturing. Most other manufacturing centers had been bombed. Or invaded. Or were involved in a civil war. Most also had suffered much higher per capita losses of life and therefore labor force and institutional knowledge. Also if you look at this overview, it's no wonder that Japan is one of the first countries to recover enough to compete on manufacturing (in the 60s iirc).

#history#Economics#post war boom#If anyone thinks I got something wrong here please let me know#Did I overlook any manufacturing regions?#were/are there any major ones in S. America?
31K notes
·
View notes
Text
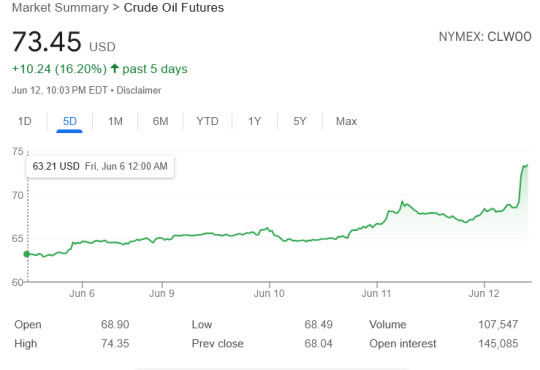
I heard about the Israeli strike on Iran days before it happened....I dont FW oil derivatives anymo so i didnt front run the fascism.
But for the Us to sell oil at a profit there has to be a certain price point for us to maintain doing it. Thats around $55-60 a barrel!
While Russia, Iran, Nigeria, can do this close to $20 a barrel.
So when the west wants Russia weak they overproduce oil via OPEC. But when they want their own oil exports strong they foment war in the middle east to boost it's price!
But cant do this too much as there comes a inflection point where energy price spikes hurt the US economy while supercharging the Russian currency which is practically pegged to their oil exports demand
0 notes