#Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), or 'forever chemicals', have spread almost everywhere on Earth, and are increasingly being linked to poor health. Now we might have a new and much-needed way of destroying them. These chemicals got their nickname because they stick around in the environment and are very difficult to get rid of, but a team led by researchers from Rice University in Texas found that extreme temperatures (exceeding 3,000 °C or 5,432 °F) could quickly break down PFAS.
Continue Reading.
#Science#Environment#Chemistry#Materials Science#PFAS#Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances#Plastic#Recycling
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
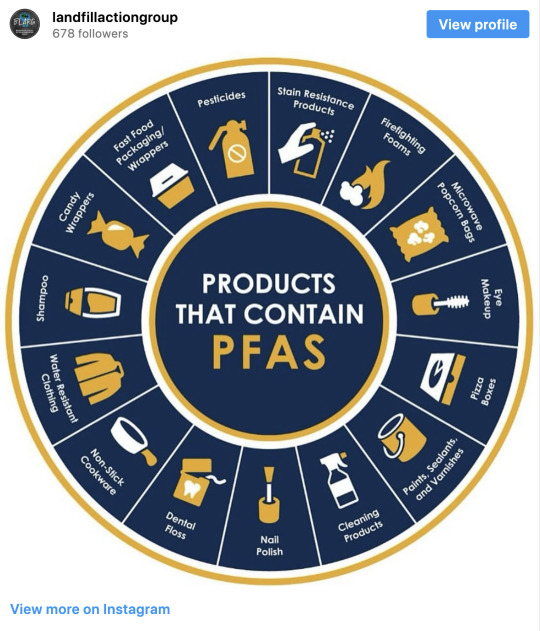
Excerpt from this story from The Revelator:
The water flowing from taps in Wilmington, North Carolina, looked clean, tasted normal, and gave no indication that it carried an invisible threat. For decades the Cape Fear River had provided drinking water to hundreds of thousands of residents in the region. But in 2017 tests revealed what many had feared: high levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), chemicals linked to cancer, immune dysfunction, and reproductive issues, coursing through their water supply.
The contamination had been traced to Chemours, a spinoff of DuPont, which had been releasing PFAS chemicals from its Fayetteville Works plant for years.
The discovery sent shockwaves through the community, triggering lawsuits, emergency water-treatment plans, and a reckoning over how corporations and government regulators had failed to protect public health. But even as residents fought to hold polluters accountable, the company responsible for much of the contamination was tightening its grip on the agencies meant to regulate it.
A former DuPont and American Chemistry Council lobbyist, Nancy Beck, now holds a key position at the Environmental Protection Agency, shaping chemical safety policies that will determine how — or if — PFAS pollution is addressed. In the first days of the second Trump administration, the agency withdrew a proposed rule that would have imposed limits on PFAS discharges, a move that watchdog groups say amounts to giving polluters free rein to continue contaminating water supplies.
The crisis in Cape Fear and Bentham reveals the creeping, silent danger of PFAS, which has infiltrated groundwater, rivers, and drinking-water supplies across the world.
And yet, as the Trump administration accelerates its environmental rollbacks, the ability to regulate and mitigate this growing threat in the United States is being systematically dismantled.
“North Carolina is one area that I’m most familiar with where there’s an entire river system that serves hundreds of thousands of people [and] is very badly contaminated with PFAS,” Erik D. Olson, senior strategic director for health at the Natural Resources Defense Council, told The Revelator. “A lot of people are drinking that water every day.”
51 notes
·
View notes
Text

Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances
#Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances#pfas#pfass#wikipedia#wikipedia pictures#afff#aqueous film forming foam#firefighter#firefighters#first responders#firefighting#firefighting foam#chemistry#chemicals#science
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
BLOODLETTING recommended for Jersey residents after PFAS contamination
The island’s private drinking water supplies were polluted by use of firefighting foams containing ‘forever chemicals’
Explained: What are PFAS, how toxic are they and how do you become exposed?
#The Guardian#bloodletting#Jersey residents#PFAS contamination#3M#forever chemicals#PFAS#Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances#Teflon#carcinogenic#endocine disruptors#cancers#AGC Inc#Archroma#Arkema#BASF#Bayer#Chemours#Daikin#Honeywell#Merck Group#DuPont#many cancers#decreased fetility#decreased immunity#Shandong Dongyue Chemical#Solvay
0 notes
Text
Research Reveals Toxic PFAS ‘Forever Chemicals’ Accumulate In Testes
Study Suggests Exposure to Chemicals Manufactured to Resist Water and Heat Likely to Affect Health of Offspring
— Tom Perkins | Saturday 22 June 2024

The Toxic Chemicals Can Damage Sperm During a Sensitive Developmental Period, Researchers Found. Photograph: Mads Nissen/Panos Pictures
New research has found for the first time that PFAS “Forever Chemicals” accumulate in the testes, and the exposure probably affects children’s health.
The toxic chemicals can damage sperm during a sensitive developmental period, potentially leading to liver disease and higher cholesterol, especially in male offspring, the paper, which looked at the chemicals in mice, noted.
The research is part of a growing body of work that highlights how paternal exposure to toxic chemicals “can really impact the health, development and future diseases of the next generation”, said Richard Pilsner, a Wayne State University School of Medicine Researcher who co-authored the study.
“We’ve always been concerned with maternal environmental health effects because women gestate the babies … but this research is really saying there is a paternal contribution to offspring health and development,” Pilsner added.
*********************************************************************************

Most US Sandwich Baggies Contain Toxic PFAS ‘Forever Chemicals’, Analysis Says! Testing commissioned by Mamavation blog found high levels of a marker of PFAS in nine of 11 baggies tested. ‘The more we look into PFAS, the more we know there is not a safe level,’ said Maricel Maffini with the Environmental Defense Fund. Photograph: Yongyut Khasawaong/Alamy. Tom Perkins, Thursday 14 March 2024, The Guardian USA
Most of the nation’s plastic sandwich baggies contain toxic PFAS “forever chemicals”, an analysis suggests, raising questions about the products’ safety in the US.
Testing of 11 types of baggies made by major producers showed high levels of a marker of PFAS in nine.
The analysis, conducted by an Environmental Protection Agency-certified lab and commissioned by the Mamavation blog, is the latest to highlight the use of PFAS in the nation’s food packaging.
US Food and Drug Administration rules allow much higher levels of some individual PFAS compounds in plastic than what the testing found, but the FDA is working off “outdated science” and the baggies present a health threat, said Maricel Maffini, a researcher with the Environmental Defense Fund who tracks PFAS in food.
“The more we look into PFAS, the more we know there is not a safe level, and the [FDA’s limits] don’t correspond with the science and knowledge we have of these chemicals,” she said.
PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a class of about 15,000 chemicals often used to make products resistant to water, stains and heat. They are called “forever chemicals” because they do not naturally break down, and are linked to cancer, liver problems, thyroid issues, birth defects, kidney disease, decreased immunity and other serious health problems.
Contaminated food represents the main exposure route to PFAS, though most regulatory attention has focused on water. The FDA has faced criticism from independent scientists who say it is failing to protect the public from concerning levels of PFAS found in a range of foods.
Packaging is a major source of contamination. PFAS are widely added to packaging to prevent foods from sticking to products or as a grease-proofing agent, and research shows the chemicals can migrate at high levels into food and liquids. PFAS are also used to prevent plastics from sticking to equipment during manufacturing, which is what probably accounts for the chemicals found in the baggies, Maffini said.
Mamavation’s testing showed levels between 9 parts per million (ppm) and 34ppm, while the FDA allows up to 2,000ppm for seven types of PFAS it allows to be used in food-contact plastic. But it is unclear which PFAS were added to the baggies because the test did not look for individual compounds.
The revelation comes just after the EPA found that virtually no level of exposure to some PFAS in drinking water is safe, and a growing body of independent research shows widespread exposure to similar levels in food.
Regulators also have a history of allowing subgroups of PFAS to be added to packaging at high levels, only to later determine the products were poisoning consumers.
Among the brands Mamavation found contained the chemicals are Boulder, Complete Home, Great Value, If You Care, Lunchskins, Meijer, Target and Walgreens.
The only brand that did not show any markers of PFAS was Ziploc. Public health advocates say the best way consumers can protect themselves is to use glass containers instead of plastic.
**********************************************************************************
PFAS are a class of about 16,000 compounds used to make products resist water, stains and heat. They are called “forever chemicals” because they do not naturally break down and have been found to accumulate in humans. The chemicals are linked to cancer, birth defects, liver disease, thyroid disease, plummeting sperm counts and a range of other serious health problems.
PFAS alters sperm DNA methylation, which is a process that turns genes on and off, Pilsner said. The methylation patterns can be inherited at fertilization and influence early-life development as well as offspring health later in life.
The interference can alter genes in a way that affects how the liver produces cholesterol, which can lead to elevated levels. Researchers also found the chemicals affected genes associated with neuro-development, but the study did not check offspring for potential impacts.
Though PFAS most commonly accumulate in the blood and liver, they have been found to accumulate in organs throughout the body, as well as bones. Finding the chemicals in the testes highlights how pervasive the chemicals are in mammals’ bodies, said Michael Petriello, a Wayne State researcher and co-author.
The study looked at relatively low exposure levels compared with previous research. It also included long- and short-chain PFAS, the latter of which industry has claimed are generally safe and do not accumulate in the body. The study is among a growing body of research that shows the “safe” PFAS can also be measured in tissue or blood in mammals.
Water and food are the two main exposure routes to PFAS. New federal limits for some compounds in water are being implemented, but public health advocates say filtration systems can limit exposures. Men can protect themselves by avoiding nonstick cookware and waterproof clothing, and by educating themselves on products in which PFAS are commonly used.
#Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)#Research Revelation | Toxic PFAS ‘Forever Chemicals’#Accumulation | Testese#Richard Pilsner | Wayne State University School of Medicine Researcher#The Toxic Chemicals | Damage Sperm
0 notes
Text
The federal government is moving to add PFAS, a class of thousands of chemicals used in a wide range of products from food containers to clothing, to the official list of toxic substances, in light of growing scientific and public concern about the substances in Canada and around the world. PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are man-made chemicals used for their water and heat resistant properties. They are widely used in many everyday products — such as packaging, cosmetics and textiles — along with industrial uses like water-repellent coatings and firefighting foam.
Continue reading
Tagging: @newsfromstolenland
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Residents of Jersey have been recommended bloodletting to reduce high concentrations of “forever chemicals” in their blood after tests showed some islanders have levels that can lead to health problems. Private drinking water supplies in Jersey were polluted by the use of firefighting foams containing PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) at the island’s airport, which were manufactured by the US multinational 3M. PFAS, a family of more than 10,000 chemicals, can build up in the body and are linked to conditions such as kidney and bladder cancer, thyroid disease and immune deficiency.
you read that correctly. bloodletting. like leeches.
before you freak out, if you are an American, this is the island of Jersey in the United Kingdom. i wanted to get that out of the way first so i can address this fucking travesty.
since the 1950s, 3M and Dupont have concealed information about the harmful effects of PFAS. the movie Dark Waters with Mark Ruffalo is specifically about Dupont and it's rampant pollution. 3M has been dumping PFAS in rivers and waterways not just in the United States, but across the globe for decades despite knowing with full detail the risks involved to the public. they even managed to intimidate a 3M scientist into staying quiet and pulled her off research into the toxicity of their products when she made the discovery.
at the same time, Jersey authorities were aware of this problem as early as the 1990s but didn’t switch the water source for the affected areas until 2006. they continued using contaminated storage tanks for foam until 2022 despite knowing the risks. this is blatant criminal negligence all around.
this part of the article in particular is so disgusting:
Despite the growing evidence of health effects, compensation remains unlikely. Jersey’s government signed a confidential deal with 3M in 2005, agreeing not to pursue legal claims for £2.6m towards cleanup. Jersey must also assist 3M in defending any future claims. A source who asked not to be identified said Jersey needed 3M’s permission to proceed with blood tests to avoid corporate backlash. “The state got an agreement to do individual blood tests, but not screening, as that could be the first step towards a possible class action lawsuit.”
3M’s gross profits in 2023 totaled over $14 billion and they can’t spend $3 million to clean up a mess that is quite literally responsible for killing people because by doing so, it opens them up to litigation involving every other mess around the globe where they’ve directly poisoned people with PFAS (or continue to poison).
but by far the most prescient part of this is the fact that Jersey's government had to obtain permission from 3M, a US corporation and the suspected perpetrator of a crime that has left at least one of their citizens terminally ill, if they could even do blood tests to check if they were responsible. the oligarchy truly knows nothing of borders.
359 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week - October 30, 2023
1. Bill to Ban Hidden Fees in California Signed into Law

California Attorney General Rob Bonta has released a statement regarding the signing of Senate Bill 478 (SB 478). SB 478, coauthored by Senators Bill Dodd and Nancy Skinner, will eliminate hidden fees, also known as 'junk fees,' in California starting from July 1, 2024. Hidden fees are deceptive charges that sellers include in transactions, either through obscured disclosures or later revelations, impacting consumers negatively.
2. New Portable Water Treatment System Vaporizes 99% of ‘Forever Chemicals’

A startup based Washington has devised a portable system capable of removing the vast majority of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, from water.
The system uses hydrothermal alkaline treatment, or HALT, to eliminate 99% of forever chemicals from water.
3. Tumor-destroying sound waves receive FDA approval for liver treatment in humans

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the use of sound waves to break down tumors—a technique called histotripsy—in humans for liver treatment. Technique developed at the University of Michigan provides a noninvasive alternative to surgery, chemotherapy and radiation treatments for cancer
4. Japan's top court says trans sterilisation requirement unconstitutional

Japan's Supreme Court has ruled that it is unconstitutional to require citizens to be sterilised before they can officially change genders.
The 2004 law said people could only change their gender if they have no reproductive capacity. Wednesday's ruling came after a transgender woman filed a petition challenging the law.
5. Abandoned golf courses are being reclaimed by nature

Golf courses, despite occupying large green spaces, are not necessarily good for the environment.
Conservation nonprofits and local authorities are looking to acquire golf courses that have been abandoned due to high maintenance costs, low player numbers or other reasons, and repurpose them into landscapes that boost biodiversity and build natural defenses against climate change.
6. NSW court allows health officials to give blood transfusion to Jehovah's Witness toddler

Regional New South Wales health officials have won a court order authorising them to give a blood transfusion to a Jehovah's Witness toddler if needed in surgery. The Supreme Court has been told the girl, three, who can only be referred to as JI, is in need of two surgical procedures.
On such an application, the overriding criterion to be applied by the court is the best interests and welfare of the child.
7. North Atlantic right whale population has steadied, scientists say

The population of critically endangered North Atlantic right whales appears to have levelled off after a decade of steep decline, according to updated data released this morning by Canadian and American scientists. Scientists in the consortium said Monday that the 2021 estimate of 340 North Atlantic right whales in existence has been recalculated to 365 primarily because of the number of calves born that year.
The estimate for 2022 is 356.
---
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation here:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog this post with your friends.
594 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rice University researchers have developed an innovative solution to a pressing environmental challenge: removing and destroying per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), commonly called "forever chemicals." A study led by James Tour, the T.T. and W.F. Chao Professor of Chemistry and professor of materials science and nanoengineering, and graduate student Phelecia Scotland unveils a method that not only eliminates PFAS from water systems but also transforms waste into high-value graphene, offering a cost-effective and sustainable approach to environmental remediation. This research was published March 31 in Nature Water.
Continue Reading.
#Science#Environment#Chemistry#Materials Science#Recycling#PFAS#Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances#Graphene
472 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a First, the E.P.A. Warns of ‘Forever Chemicals’ in Sludge Fertilizer. (New York Times)
Excerpt from this New York Times story:
For the first time, the Environmental Protection Agency on Tuesday warned that “forever chemicals” present in sewage sludge that is used as fertilizer can pose human health risks.
In an extensive study the agency said that, while the general food supply isn’t threatened, the risk from contaminated fertilizer could in some cases exceed the E.P.A.’s safety thresholds “sometimes by several orders of magnitude.”
A growing body of research has shown that the sludge can be contaminated with manmade chemicals known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, which are used widely in everyday items like nonstick cookware and stain-resistant carpets. The chemicals, which are linked to a range of illnesses including an increased risk of cancer, do not break down in the environment, and, when tainted sludge is used as fertilizer on farmland, it can contaminate the soil, groundwater, crops and livestock.
Last year, The New York Times reported that 3M, which for decades has manufactured PFAS, found as early as 2000 that the chemicals were turning up in sludge samples from municipal wastewater plants across the country. In 2003, 3M told E.P.A. of its findings.
The E.P.A. has for decades encouraged the use of sludge from treated wastewater as inexpensive fertilizer with no limits on how much PFAS it can contain. But the agency’s new draft risk assessment sets a potential new course. If finalized, it could mark what could be the first step toward regulating PFAS in the sludge used as fertilizer, which the industry calls biosolids. The agency currently regulates certain heavy metals and pathogens in sewage sludge used as fertilizer, but not PFAS.
Add to this story the following excerpt from the Chicago Tribune from its article entitled, "EPA warns of toxic forever chemicals in sewage sludge used on farmland, including thousands of acres near the Chicago area."
Farmers who use sewage sludge as fertilizer and their neighbors face higher risks of cancer and other diseases, according to a new federal analysis that pins the blame on toxic forever chemicals.
The findings are particularly relevant for northeast Illinois, where more than 777,000 tons of sludge from Chicago and Cook County have been spread on farmland during the past eight years — in many cases near residential areas.
Only the Greater Los Angeles area distributed more sludge to farmers during the same period.
Officials at the Metropolitan Water Reclamation District of Greater Chicago have known their sludge fertilizer is contaminated with forever chemicals since at least 2011, the Chicago Tribune reported in a 2022 investigation.

#forever chemicals#municipal sludge#agriculture#public health#PFAS#per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances#biosolids
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Purification method removes PFAS from water while transforming waste into high-value graphene
Rice University researchers have developed an innovative solution to a pressing environmental challenge: removing and destroying per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), commonly called "forever chemicals." A study led by James Tour, the T.T. and W.F. Chao Professor of Chemistry and professor of materials science and nanoengineering, and graduate student Phelecia Scotland unveils a method that not only eliminates PFAS from water systems but also transforms waste into high-value graphene, offering a cost-effective and sustainable approach to environmental remediation. This research was published March 31 in Nature Water. PFAS are synthetic compounds in various consumer products, valued for their heat, water and oil resistance. However, their chemical stability has made them persistent in the environment, contaminating water supplies and posing significant health risks, including cancer and immune system disruptions. Traditional methods of PFAS disposal are costly, energy-intensive and often generate secondary pollutants, prompting the need for innovative solutions that are more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Read more.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton has filed a lawsuit against chemical giants 3M and DuPont over PFAS, commonly known as "forever chemicals," accusing them of knowingly producing and marketing toxic substances while misleading the public about their safety.
The lawsuit points to scientific evidence linking PFAS to serious health risks, including cancer, liver damage and reproductive issues. PFAS have contaminated water, soil and air, posing a significant threat to public health due to their persistence in the environment.
Paxton's complaint seeks damages for cleanup, medical monitoring for affected communities and penalties for alleged violations of state consumer protection laws. The lawsuit emphasizes the need for accountability and immediate action to address PFAS contamination.
3M and DuPont have defended their practices, claiming compliance with regulations and efforts to reduce PFAS use. However, the lawsuit could set a precedent for future litigation against PFAS manufacturers and prompt other states to follow Texas's lead.
Although the lawsuit is a significant step forward, it highlights the need for stronger federal regulations to address PFAS contamination comprehensively and coordinate a nationwide response to the issue.
Texas Attorney General (AG) Ken Paxton has filed a landmark lawsuit against two major chemical manufacturers over so-called per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), commonly known as "forever chemicals."
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
STOP DRINKING PRIME!! I KNEW IT WAS BADD!!
Prime Lawsuit over forever chemicals!!
PFO chemicals, more commonly known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), are a group of man-made chemicals used in a variety of consumer products for their water and grease resistance properties. These chemicals are considered harmful for several reasons:
Bioaccumulation: PFAS can accumulate in the environment, animals, and humans over time, leading to long-lasting effects and potential health risks.
Health Concerns: Exposure to PFAS has been linked to various health issues, including thyroid disruption, immune system effects, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
Persistence: One of the major concerns with PFAS is their persistence in the environment. These chemicals do not break down easily and can remain in the environment for long periods.
Regulatory Concerns: Due to the potential health and environmental risks associated with PFAS, there have been increasing regulatory actions to limit their use. 🤔
#pay attention#educate yourselves#educate yourself#knowledge is power#reeducate yourself#reeducate yourselves#think about it#think for yourselves#think for yourself#do your homework#do some research#ask yourself questions#question everything#lawsuit#pfas#forever chemicals#food supply chain#food supply#for your health#health tips#you decide
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Forever chemicals are everywhere.
They’re in school uniforms, food packaging, cosmetics and personal care products (SNE: 11/18/22; SN: 6/4/19; SN: 6/15/21). They seep into our food and drinking water. And now new research suggests that some can move through the skin, posing yet another avenue through which humans are intimately exposed to these chemicals, which have been linked to harmful health issues.
When 3-D human skin models were exposed to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, the chemicals could cross the skin barrier, environmental chemists from the University of Birmingham in England report in the June Environment International. That suggests the compounds can be absorbed through the skin and may even travel into the bloodstream.
@quasi-normalcy @startorrent02
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
White House OSTP Releases PFAS Federal R&D Strategic Plan
The White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) announced on September 3, 2024, the release of its Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Federal Research and Development Strategic Plan (Strategic Plan). Prepared by the Joint Subcommittee on Environment, Innovation, and Public Health PFAS Strategy Team (PFAS ST) of the National Science and Technology Council, the Strategic Plan…
#Enviromental Law#EPA#Federal Research and Development Strategic Plan#Office of Science and Technology Policy#OSTP#per and polyfluoroalkyl substances#PFAS
0 notes
Text
hey i didnt see anyone talking about this until i stumbled upon a video this morning on instagram, and this blog has more of a platform than my others, so im gonna talk about this here. feel free to scroll on if it doesn't apply.
thinx period underwear were found to contain PFAs, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances which are, "human-made chemicals that are found in many consumer and industrial products, do not easily break down and have been linked to adverse health effects." per this NPR article. One of the quotes in this article does go on to have a unnecessarily gendered quote so my trans and nb friends who experience periods, read on with caution.
I do want to say that the lawsuit isn't supposing these PFAs are linked to any known cases of harm or diagnosed issues and Thinx, but their prior marketing made them out to be a safe and environmentally conscious choice. they have since had to retract a lot of prior statements, and other studies have been done on PFAs that are linked to some scary health stuff in people.
as a result of this suit and just generally preferring this type of period product to others (i understand that corporations are leaders in pollution and that i as one person cannot change the world, but i can make better decisions for myself and my personal waste production), here's what i found for my period experiencing friends to continue to use these types of products:
here's an article i used to find multiple brands that do NOT have PFAs and their pros & cons.
im also going to single a couple of these out for my friends on here to weed through. i didnt do a suuuper extensive deepdive, but i checked out a couple of these that are worth listing out i feel.
the period company had the cheapest single pairs i found at $9. i was unable to order from them because they currently dont have my size, but hopefully yall will be more fortunate, since im a pretty popular size. these guys only come in black.
tomboy x is gender neutral and donates to trans people which i love. they're pretty competitively priced and you can get 6 in a couple different colors at $110 before tax and shipping, which was pretty fairly priced. if you have the money to spend a little extra on a great cause or want a gender neutral experience this place is great.
i ultimately ordered from ruby love because they had bundle options (which i really wanted since id love to replace my tampon usage at home altogether and only keep them for emergencies/guests) and they had a 10 pack for $90, which came out to $100 after taxes and shipping. ill warn my nb and trans friends that this site is pretty gendered so tread with caution, but it did have the best bundle price that i cross shopped.
anyway i know this blog is about snakes but i was kind of horrified to find this out this morning and want to make sure that yall are shopping safe and able to make informed decisions on your hygienic products. i love you and you matter. be safe and be well.
#period#period products#i dont rlly know what to tag this as so if there's tw or something feel free to anon me and ill add it on#tails rambles
47 notes
·
View notes