#Peak fossil fuels
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How can we peak emissions and fast forward towards Net Zero ?
As momentum is accelerating towards peaking greenhouse gases emissions, a reflection on how to accelerate the shift towards Net Zero.
If you have been reading this blog for a while, you know that I dedicated to peaking greenhouse gases emissions two blog posts in the past few months. Chinese greenhouse gases emissions – and with them global ones – are to peak either this year or next. Unless they peaked last year ? This is the topic developped in Carbon Brief’s lengthy analysis. No one will know for sure until we have indeed…

View On WordPress
#China#Economics#Energy efficiency#Energy sufficiency#European Union#Fossil fuel subsidies#Net Zero#peak coal#Peak fossil fuels#War in Ukraine
0 notes
Text
From the article:
[T]here are now signs that China’s thirst for crude is reaching a peak sooner than expected, a development that has sent shockwaves through the oil market. This week, China said its oil imports had fallen nearly 2 per cent, or 240,000 barrels a day, to just over 11mn b/d in 2024 compared with the year before, the first decline in two decades barring the disruption during the Covid pandemic[...]. [T]he decline stems from longer-term trends too. There was a boom in trucks switching from diesel to liquefied natural gas, and, most importantly, the rising number of electric vehicles helped to depress sales of petrol and diesel. Sales of both road fuels peaked in 2023, according to China National Petroleum Corp, and will now fall by 25-40 per cent over the next decade. In December, Sinopec, China’s biggest refiner, brought forward its forecast for crude oil consumption to reach a peak to 2027, compared with the range it previously gave of between 2026 and 2030. The implications of China hitting peak oil are enormous. If Chinese demand is reaching a plateau that would fulfil projections by the IEA of global oil demand peaking before 2030. The forecast sustains hope for the world to reach net zero carbon emissions by 2050."
#peak oil#climate change#global warming#good news#hope#environment#fossil fuels#oil#ecoanxiety#climate anxiety#hopepunk#clean energy#electric vehicles#china
238 notes
·
View notes
Text
Last Rites for a Dying Civilization
When the Black Death struck Europe in the Middle Ages, the fundamental values that held society together broke down. Husbands and wives abandoned each other and mother’s abandoned their children. This void of ethics that overtook the population is described in Boccaccio’s Decameron, considered a masterpiece of Italian prose and a documentary of life during that time. The book describes the…

View On WordPress
#Antarctic Ice Melt#Anthropogenic Global Warming#Authoritarianism#Climate Feedback Loops#Climate Tipping Points#Collapse of Industrial Civilization#Ecological Overshoot#Fossil Fuel Industry#Geoengineering#Global Pandemic#Greenwashing#Mass Coral Bleaching#Microplastic Pollution#Overpopulation#Peak Soil#Planetary Tipping Points#Techno-Fix#Techno-Optimists#The Black Death
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
This fuggin headline is like...

#This has been observed a few times - fossil fuels are very likely to either peak within a few years#Or have already peaked#But it's also noted that widespread issues from the climate - and 1.5 degree warming - is likely inevitable at this point as well
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://rumble.com/v462w0x-this-is-what-they-dont-want-you-to-know-about-the-climate-agenda.html

#Rockefeller#peak oil#petroleum#brainwashing#totalitarianism#propaganda#free market#geology#tucker carlson#fossil fuels
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
"China’s additions of wind and solar capacity once again exceeded forecasts and prior records in 2024, new data releases show.
Another 277GW of solar was installed through the year, 28% more than was added in 2023, according to the National Energy Administration. That brings the country’s total operational solar capacity to 887GW. Wind installations also hit a fresh record of 79GW — a 5% increase from the previous year — taking total capacity to 521GW.
That means China now has 1,408GW of wind and solar capacity — well ahead of the government’s prior target of having 1,200GW in place by 2030....
“The combination of accelerating clean energy growth and moderating power demand growth promises to bend China’s emissions down further from the current plateau,” Myllyvirta said in a post.
That’s despite coal- and gas-fired power capacity additions of 54GW in 2024, a slight decline from the prior year.
Myllyvirta said energy capacity additions tend to accelerate towards the end of each year, which means last year’s new installations will only fully show up in generation statistics from 2025.
“So the record additions in the end of 2024 are highly relevant for the 2025 emission trend,” Myllyvirta said.
Close to half of the experts surveyed by CREA last year said China’s carbon dioxide emissions had probably already peaked, or would do so in 2025, thanks in large part to its unprecedented wind and solar boom.
However, it’s still too soon to call the top. China’s fossil fuel power plants generated 1.5% more electricity in 2024 than the previous year, per the National Bureau of Statistics. This indicates that electricity consumption continued to grow faster than clean energy output.
Meanwhile, 11 million electric vehicles were sold in China in 2024, a 40% increase, according to a tally by research group Rho Motion. One in two new cars sold in the country now has a plug, meaning China is expected to see a steady decline in gasoline demand in the years ahead. The country’s crude oil imports fell 1.9% in 2024, the first annual decline in two decades, barring the Covid-induced slump.
China’s rapid progress in electrifying transport, heavy industry, and heating will help turn the tide on emissions. The eastern province of Zhejiang has reached a world-leading electrification rate of 51%, according to an analysis by US-based research group RMI."
-via The Progress Playbook, January 21, 2025
#china#asia#emissions#renewables#clean energy#solar power#wind power#electric vehicles#good news#hope
554 notes
·
View notes
Text

Some people sound a bit like luddites when it comes to using modern technology or fossil fuels in the contexts of sustainability-- as if they've only parroted climate change political propaganda and never seen the value of biofuels in a potential carbon sequestration scheme.
#permaculture#instagram#mine#solarpunk#culture#group dynamics#123#fossil fuels#hydrocarbons#biofuels#climate change#capitalism#greenwashing#industrial civilization#peak oil
0 notes
Text
An end to the climate emergency is in our grasp

On June 20, I'm keynoting the LOCUS AWARDS in OAKLAND.

The problem with good news in the real world is that it's messy. Neat happy endings are for novels, not the real world, and that goes double for the climate emergency. But even though good climate news is complicated and nuanced, that doesn't mean it shouldn't buoy our spirits and fill our hearts with hope.
The big climate news this past week is the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's clarion call about surging CO2 levels – the highest ever – amid a year that is on track to have the largest and most extreme series of weather events in human history:
https://www.noaa.gov/news-release/during-year-of-extremes-carbon-dioxide-levels-surge-faster-than-ever
This is genuinely alarming and you – like me – have probably experienced it as a kind of increase in your background radiation of climate anxiety. Perhaps you – like me – even experienced some acute, sit-bolt-upright-in-bed-at-2AM anxiety as a result. That's totally justifiable. This is very real, very bad news.
And yet…
The news isn't all bad, and even this terrible dispatch from the NOAA is best understood in context, which Bill McKibben provides in his latest newsletter post, "What You Want is an S Curve":
https://billmckibben.substack.com/p/what-you-want-is-an-s-curve
Financier and their critics should all be familiar with Stein's Law: "anything that can't go on forever will eventually stop." This is true outside of finance as well. One of the reasons that we're seeing such autophagic panic from the tech companies is that their period of explosive growth is at an end.
For years, they told themselves that they were experiencing double-digit annual growth because they were "creating value" and "innovating" but the majority of their growth was just a side-effect of the growth of the internet itself. When hundreds of millions of people get online every year, the dominant online services will, on average, gain hundreds of millions of new users.
But when you run out of people who don't have internet access, your growth is going to slow. How can it not? Indeed, at that point, the only ways to grow are to either poach users from your rivals (through the very expensive tactics of massive advertising and sales-support investments, on top of discounts and freebies as switching enticements), or to squeeze your own users for more.
That's why the number of laptops sold in America slowed down. It's why the number of cellphones sold in America slowed down. It's why the number of "smart home" gizmos slowed down.
Even the steepest hockey-stick-shaped exponential growth curve eventually levels off and becomes an S-curve, because anything that can't go on forever will eventually stop.
One way or another, the world's carbon emissions will eventually level off. Even if we drive ourselves to (or over) the brink of extinction and set up the conditions for wildfires that release all the carbon stored in all the Earth's plants, the amount of carbon we pump into the atmosphere has to level off.
Rendering the Earth incapable of sustaining human civilization (or life) is the ultimate carbon reduction method – but it's not my first choice.
That's where McKibben's latest newsletter comes in. He cites a new report from the Rocky Mountain Institute, which shows a major reversal in our energy sources, a shift that will see our energy primarily provided by renewables, with minimal dependence on fossil fuels:
https://rmi.org/insight/the-cleantech-revolution/
The RMI team says that in this year or next, we'll have hit peak demand for fossil fuels (a fact that is consistent with NOAA's finding that we're emitting more CO2 than ever). The reason for this is that so much renewable energy is about to come online, and it is so goddamned cheap, that we are about to undergo a huge shift in our energy consumption patterns.
This past decade saw a 12-fold increase in solar capacity, a 180-fold increase in battery storage, and a 100-fold increase in EV sales. China is leading the world in a cleantech transition, with the EU in close second. Cleantech is surging in places where energy demand is also still growing, like India and Vietnam. Fossil fuel use has already peaked in Thailand, South Africa and every country in Latin America.
We're on the verge of solar constituting an absolute majority of all the world's energy generation. This year, batteries will overtake pumped hydro for energy storage. Every cleantech metric is growing the way that fossil fuels did in previous centuries: investment, patents, energy density, wind turbine rotor size. The price of solar is on track to halve (again) in the next decade.
In short, cleantech growth looks like the growth of other technologies that were once rarities and then became ubiquitous overnight: TV, cellphones, etc. That growth isn't merely being driven by the urgency of the climate emergency: it's primarily a factor of how fucking great cleantech is:
https://rmi.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/the_incredible_inefficiency_of_fossils.pdf
Fossil fuels suck. It's not just that they wreck the planet, or that their extraction is both politically and environmentally disastrous. They just aren't a good way to make energy. About a third of fossil fuel energy is wasted in production and transportation. A third! Another third is wasted turning fossil fuels into energy. Two thirds! The net energy efficiency of fossil fuels is about 37%.
Compare that with cleantech. EVs convert electricity to movement with 80-90% efficiency. Heat pumps are 300% efficient (the main fuel for your heat pump is the heat in the atmosphere, not the electricity it draws).
Cleantech is just getting started – it's still in the hockey-stick phase. That means those efficiency numbers are only going up. Rivian just figured out how to remove 1.6 miles of copper wire from each vehicle. That's just one rev – there's doubtless lots of room for more redesigns that will further dematerialize EVs:
https://insideevs.com/news/722265/rivian-r1s-r1t-wiring/
As McKibben points out, there's been a lot of justifiable concern that electrification will eventually use up all our available copper, but copper demand has remained flat even as electrification has soared – and this is why. We keep figuring out new ways to electrify with fewer materials:
https://www.chemanalyst.com/NewsAndDeals/NewsDetails/copper-wire-price-remains-stable-amidst-surplus-supply-and-expanding-mining-25416#:~:text=Global%20Copper%20wire%20Price%20Remains%20Stable%20Amidst%20Surplus%20Supply%20and%20Expanding%20Mining%20Activities
This is exactly what happened with previous iterations of tech. The material, energy and labor budgets of cars, buildings, furniture, etc all fell precipitously every time there was a new technique for manufacturing them. Renewables are at the start of that process. There's going to be a lot of this dematerialization in cleantech. Calculating the bill of materials for a planetary energy transition isn't a matter of multiplying the materials in current tech by the amount of new systems we'll need – as we create those new systems, we will constantly whittle down their materials.
What's more, global instability drives cleantech uptake. The Russian invasion of Ukraine caused a surge in European renewables. The story that energy prices are rising due to renewables (or carbon taxes) is a total lie. Fossil fuels are getting much more expensive, thanks to both war and rampant, illegal price-fixing:
https://www.thebignewsletter.com/p/an-oil-price-fixing-conspiracy-caused
If not for renewables, the incredible energy shocks of the recent years would be far more severe.
The renewables story is very good and it should bring you some comfort. But as McKibben points out, it's still not enough – yet. The examples of rapid tech uptake had big business on their side. America's living rooms filled with TV because America's largest businesses pulled out all the stops to convince everyone to buy a TV. By contrast, today's largest businesses – banks, oil companies and car companies – are working around the clock to stop cleantech adoption.
We're on track to double our use of renewables before the decade is over. But to hold to the (already recklessly high) targets from the Paris Accord, we need to triple our renewables usage. As McKibben says, the difference between doubling and tripling our renewables by 2030 is the difference between "survivable trouble" and something much scarier.
The US is experiencing a welcome surge in utility scale solar, but residential solar is stalling out as governments withdraw subsidies or even begin policies that actively restrict rooftop solar:
https://twitter.com/curious_founder/status/1798049929082097842?s=51
McKibben says the difference between where we are now and bringing back the push for home solar generation is the difference between "fast" and "faster" – that is the difference between tripling renewables by 2030 (survivable) and doubling (eek).
Capitalism stans who argue that we can survive the climate emergency with market tools will point to the good news on renewable and say that the market is the only way to transition to renewables. It's true that market forces are partly responsible for this fast transition. But the market is also the barrier to a faster (and thus survivable) transition. The oil companies, the banks who are so invested in fossil fuels, the petrostates who distort the world's politics – they're why we're not much farther along.
The climate emergency was never going to be neatly solved. We weren't going to get a neat novelistic climax that saw our problems sorted out in a single fell swoop. We're going to be fighting all the way to net zero, and after that, we'll still have decades of climate debt to pay down: fires, floods, habitat loss, zoonotic plagues, refugee crises.
But we should take our wins. Even if we're far from where we need to be on renewables, we're much farther along on renewables than we had any business hoping for, just a few years ago. The momentum is on our side. It's up to us to use that momentum and grow it. We're riding the hockey-stick, they're on that long, flat, static top of the S-curve. Their curve is leveling off and will start falling, ours will grow like crazy for the rest of our lives.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/06/12/s-curve/#anything-that-cant-go-on-forever-eventually-stops
#pluralistic#s-curves#bill mckibben#climate emergency#renewables#energy transition#energy#solar#wind#fossil fuels#climate
907 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week - November 28, 2023
🐑 - Why did Fiona the sheep become a mountaineer? She was tired of the "baa-d" jokes at sea level!
1. Pope Francis dines with transgender women for Vatican luncheon

Pope Francis hosted a group of transgender women — many of whom are sex workers or migrants from Latin America — to a Vatican luncheon for the Catholic Church's "World Day of the Poor" last week.
The pontiff and the transgender women have formed a close relationship since the pope came to their aid during the COVID-19 pandemic, when they were unable to work. Now, they meet monthly for VIP visits with the pope and receive medicine, money and shampoo any day, according to The Associated Press.
2. New York just installed its first offshore wind turbine

The first wind turbine installation at South Fork Wind, New York State’s first offshore wind farm, is complete.
The 130-megawatt (MW) South Fork Wind will be the US’s first completed utility-scale wind farm in federal waters.
3. Anonymous businessman donates $800k to struggling food bank

But this Thanksgiving, a longtime prayer of food bank leaders was finally answered: an anonymous benefactor donated the full $800,000 they needed to move out of a facility they've long outgrown. That benefactor, however, preferred to stay anonymous.
"Very private company, really don't want attention," said Debbie Christian, executive director of the Auburn Food Bank. "It's a goodhearted person that just wants to see the work here continue, wants to see it expand."
4. Empowering woman saving hopes and mental health of suffering Ukrainian kids

Kenza Hadij-Brahim is at the forefront of promoting Circle of Toys
Hadj-Brahim is helping to launch the Circle of Toys initiative. A project that provides Ukrainian children in need of some normality with preloved toys. This new initiative connects people with old toys they might otherwise throw away, with Ukrainian families in need who want to provide some comfort to their children in this distressing time.
Find Refuge said : “The endeavour is driven by a sincere purpose: spark joy, foster play, and bring a hint of normalcy back to the young lives in Ukraine.”
5. TWO LOST CITIES HIDDEN FOR CENTURIES WERE JUST DISCOVERED IN BOLIVIA
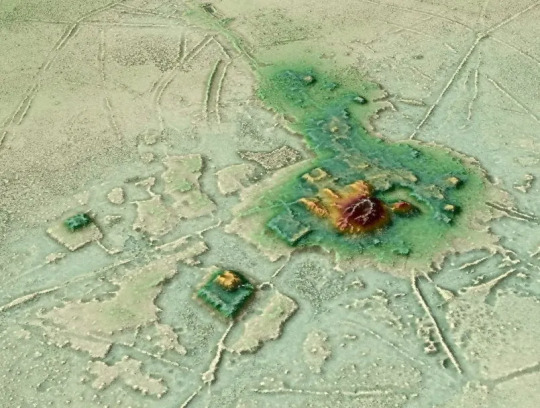

Researchers have found these areas not only housed structures and pyramids but it has been uncovered that there were advanced irrigation systems, earthworks, large towns, causeways, and canals that cover miles.
Dr. Heiko Pr��mers from the German Archaeological Institute, who was also involved in the study comments that “this indicated a relatively dense settlement in pre-Hispanic times. Our goal was to conduct basic research and trace the settlements and life there. The research sheds light on the sheer magnitude and magnificence of the civic-ceremonial centers found buried in the forest”.
6. Sheep dubbed Fiona rescued from cliff in Scotland where she was stuck for more than 2 years
youtube
And at last, some positive climate news:
7. Three positive climate developments
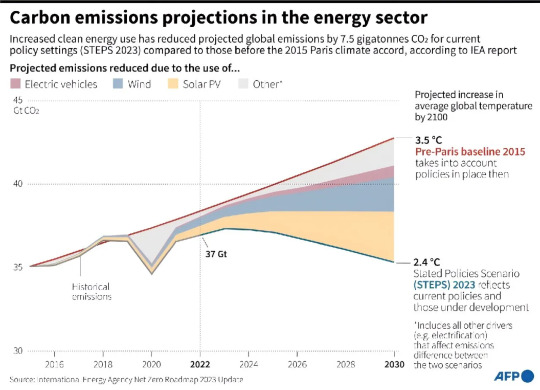
Heating
When the Paris Agreement was adopted, the global reliance on fossil fuels placed the world on a path towards a 3.5C rise in temperature by 2100. Eight years on, country commitments to reduce their carbon footprints have pulled that down slightly, putting the world on a path for a 2.5C to 2.9C by the end of the century.
Peak emissions
Annual greenhouse gas emissions responsible for climate change have risen roughly nine percent since COP21, according to UN data. But the rate of the increase has slowed significantly. Recent estimates by the Climate Analytics institute find global emissions could peak by 2024
Rising renewables
Three technologies—solar, wind and electric vehicles—are largely behind the improved global warming estimates since 2015.
---
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation here:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog this post with your friends.
815 notes
·
View notes
Text
146 notes
·
View notes
Text
Will global fossil fuels emissions really peak this year ?
The latest IEA annual World Energy Outlook offers some serious glimmers of hope with global fossil fuels demand taking place soon, but a enormous task lies ahead. Now more than ever we need to roll up our sleeves and create the future we deserve.
It’s an annual event for the energy and sustainability crowds, the latest World Energy Outlook by the reputed International Energy Agency is out. For years, this publication was lowballing renewable energy sources. And all along independant organizations were lamenting the fact. Figures would prove them wrong : solar, wind and other technologies would soar higher and higher.Little by little, then…

View On WordPress
#Ebikes#Electric cars#Energy#Heat pumps#IEA#International Energy Agency#peak coal#Peak fossil fuels#Peak gas#Peak oil#Renewables#Solar#Systems change#WEO#World Energy Outlook
0 notes
Text
From the article:
For Brother Xavier Boutiot, treasurer of a Benedictine abbeyin central France, pulling the abbey's investments from fossil fuels was an obvious step. Committed to the “Green Church” initiative for four years, the Olivetan monks aimed for consistency in all aspects of their community life. “Financial investments have an ecological impact that is 25 times greater than our daily actions!” emphasized the treasurer. To embark on this ecological and financial transition, the abbey had to scrutinize its investments, which was not straightforward. “The financial world is so opaque for basic investors like us, who don’t have access to all the information,” explained Boutiot. “We called our banks that were not on board with this direction, explained our reasoning, and applied some pressure by saying, ‘Either you support us in this approach, or we’ll switch banks.’” [...] The reasons to divest from fossil fuels are not only ethical but financial: the International Energy Agency predicts fossil fuel use will peak before 2030 and then decline. Religious institutions, managing $3 trillion globally, have divested from fossil fuel companies more than any other sector, aligning their investments with their values.
#divestment#finances#global warming#climate change#climate anxiety#good news#hope#sustainability#environment#ecoanxiety#christianity cw#religion cw#divest
174 notes
·
View notes
Text
As temperatures plummeted in January 2025, New England had to ditch its rapid decarbonization plans and rely on oil, coal, and natural gas to keep homes heated.
What happened: A severe cold snap in January 2025 pushed New England’s electricity grid to its limits, forcing the region to rely heavily on fossil fuels to meet demand.
Why it matters: The episode highlights the challenges of transitioning to renewable energy while maintaining grid reliability during extreme weather.
Key players: ISO-New England (ISO-NE), natural gas and coal-fired power plants, and imported liquefied natural gas (LNG) played critical roles in keeping the lights on.
Historical context: New England’s resistance to pipeline infrastructure and its reliance on intermittent renewables have left the region vulnerable during peak demand periods.
31 notes
·
View notes
Note
What do you think makes Junko Enoshima a compelling character and antagonist? She's very popular, but I've found that the reasons why can vary a lot between people.
She's a bored hyper-genius gyaru supermodel in high school who burned civilization to the ground through unshakable charisma, aggressive recruiting of society's victims, and endless copies of her robot fursona.
There's. Not. Really. Anything like her in media.
There's a bit of a Joker angle to her. She's a scenery-chewing madwoman who mesmerizes the audience every second she's onscreen. Reprehensible and unforgivable in her crimes but so bombastic and bizarre that it's fun to watch her commit them.
But she's not just doing crime. Junko provides a platform to talk about the sickness in society itself. She's not a cartoon bank robber running away with all of the jewels. Her adversary is a society we all live in and her weapon of choice is the belief that things won't get better.
Junko is a temptation. She's the shoulder devil looking at the interweaving of fossil fuels, the stock market, and the government, and saying with a coy smile, "Maybe we should just crash the economy. If you can't untangle the knot, then you break out the scissors."
She is a product of a broken world and the architect of its doom. One day, a bunch of rich old guys who run the world decided that Junko is the superior class of human being and uplifted her into privilege and guaranteed prosperity to reward her for being better than everyone else. She is very good at fashion, so they named her ubermensch and welcomed her into their eugenics program.
And then she killed them all and burned everything down around herself. There's something very applicable about the sickness in Hope's Peak to our own world and our own lives. And something recognizably wicked yet unmistakably appealing about Junko's response to it.
But she is still unmistakably a villain. Still got that bad guy swagger about her. The confident, shameless amorality. Junko isn't a liberator. She's not here to make a better world. She's just a cult leader ideologically obsessed with despair.
But that's also what gives her so much staying power. She represents an idea, a feeling even, instead of a particular goal or motive. This makes her applicable far beyond the specific plot of her story.
She's the mascot of the feelings we get when we have to think about wealth inequality, which can only be solved if the rich choose to persecute the rich for being rich. Or broken politics whose obvious flaws are carved into the source code of the country such that they can never and will never change. Climate change. Genocide. Nuclear weapons. She's inescapable.
Once you've met her, it's easy to associate Junko with the feeling of despair itself. We all have despair in our lives. We all have a place for Junko Enoshima.
She's a fire that rages when it's pitch black. She's the alternative when hope fades away. She is the guillotine solution to billionaires. The molotov solution to political inequity. She is where you can turn when you have nowhere else left to go.
You don't always have to listen to Junko; In fact, more often than not, you shouldn't listen to Junko. But she is always at the table. A voice in the conversation that probably shouldn't be heeded but needs to be heard, lest those negotiating forget that she's there.
...
And all of that is wrapped up in a funny and charismatic fictional serial murderer who is unapologetically hyper-feminine yet presents herself through a wacky he/him fursona, whose worldview is as captivatingly bizarre as it is confidently presented yet complex and interesting all the same.
Junko Enoshima is a fucking experience.
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump’s Oil and Gas Donors Don’t Really Want to ‘Drill, Baby, Drill’. (Wall Street Journal)
Excerpt from this Wall Street Journal story:
Donald Trump wants oil companies to “drill, baby, drill” on the first day of his presidency, but his fossil-fuel benefactors have a different agenda.
Many of the tycoons who backed the Republican’s victorious campaign say what they need help with is shoring up demand for their products—not pumping more fossil fuels, which they have little incentive to do.
They are pushing for policies that would lock in fossil-fuel use, such as easier permitting for pipelines and terminals to shuttle fossil fuels to new markets. They also favor eliminating Biden administration policies meant to put more electric vehicles on the road.
Under President Biden, shale companies produced record amounts of oil and natural gas as crude prices rebounded from the pandemic’s depths and then soared after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. But the industry is also confronting the early stages of a long-term shift away from fossil fuels, as well as concerns that gasoline consumption has peaked in the U.S.
Trump handed shale donors their first big return on investment by nominating Liberty Energy Chief Executive Chris Wright, a fracking booster and fossil-fuels champion, to lead the president-elect’s Energy Department.
When Dan Eberhart, the CEO of oil-field services firm Canary, met with Trump during a fundraiser at his Mar-a-Lago club in Florida this summer, Eberhart had a unique request. He asked Trump to push back on the International Energy Agency, the influential, Paris-based energy forecaster. The agency has predicted global oil demand will peak by the end of the decade, earning scorn from GOP lawmakers who dubbed the group an “energy transition cheerleader.”
“You need to stop acting like fossil fuels are the devil,” Eberhart said in an interview, referring to the IEA’s stance.
A spokesperson for the IEA said it remains “focused on its key missions of energy security and energy transitions, based on the mandates from our member governments.”
Many of Trump’s oil and natural-gas supporters favor easing regulations that govern drilling. The changes would include scrapping rules targeting methane emissions, getting new permits to frack on federal land and eliminating climate disclosure rules.
But some donors grimace when they hear Trump promise that under his watch, crude-oil producers would open the floodgates. He has also promised to cut Americans’ energy costs by 50% or more.
Oil backers’ skepticism stems from the fact that Wall Street has successfully pressured chronically indebted frackers to stop burning through cash, and return it to shareholders via buybacks and dividends instead of reinvesting it to frack more wells.
15 notes
·
View notes
