#NAMZARIC
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
NAMZARIC: Unlocking the Potential of Combination Therapy for Alzheimer's Disease Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a prevalent and devastating neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is characterized by progressive cognitive decline, memory loss, and behavioral changes. The impact of AD extends beyond the individuals diagnosed, affecting their families and society as a whole. [caption id="attachment_60185" align="aligncenter" width="741"] NAMZARIC[/caption] One promising approach in the field of Alzheimer's research is combination therapy, which involves using multiple drugs with different mechanisms of action to target various aspects of the disease. NAMZARIC is a leading combination therapy that offers new hope for managing AD. NAMZARIC is a unique combination of two active ingredients, memantine and donepezil. Memantine works by regulating glutamate, a neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory, while donepezil inhibits the breakdown of acetylcholine, another neurotransmitter essential for cognitive function. By combining the benefits of memantine and donepezil, NAMZARIC provides a comprehensive treatment approach that addresses both the cognitive and behavioral symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. This article explores the potential of NAMZARIC in improving the quality of life for AD patients and their caregivers. Understanding Alzheimer's Disease Alzheimer's disease is a complex condition with multiple underlying causes, including the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain. These abnormal protein deposits disrupt communication between brain cells, leading to cognitive impairment and memory loss. The cognitive and behavioral symptoms of AD can vary from mild to severe, affecting daily functioning, independence, and overall quality of life. Current treatment options for AD focus on managing symptoms and slowing down the progression of the disease, but they have limitations. Combination therapy offers a promising approach by targeting multiple aspects of the disease simultaneously. By utilizing different mechanisms of action, combination therapy can potentially enhance treatment outcomes and provide more comprehensive symptom management. Introducing NAMZARIC NAMZARIC is a combination therapy specifically designed for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It combines two active ingredients, memantine, and donepezil, to provide a synergistic effect in managing the symptoms of AD. Memantine is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist that helps regulate the activity of glutamate, a neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory. By modulating glutamate, memantine helps improve cognitive function and reduce the progression of cognitive decline in AD patients. Donepezil, on the other hand, is a cholinesterase inhibitor that prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter essential for cognitive processes such as attention, learning, and memory. By increasing the levels of acetylcholine in the brain, donepezil helps improve cognitive function and delay the decline in memory and thinking skills. When combined, memantine and donepezil work synergistically to provide comprehensive treatment for AD. Memantine targets the glutamate pathway, while donepezil focuses on the acetylcholine pathway, resulting in improved cognitive function and overall patient outcomes. Efficacy and Clinical Studies Several clinical trials and studies have demonstrated the efficacy of NAMZARIC in treating Alzheimer's disease. These studies have shown significant improvements in cognitive function, memory, and daily living activities in patients receiving NAMZARIC compared to those on placebo or monotherapy. For example, a randomized controlled trial involving AD patients showed that NAMZARIC led to statistically significant improvements in cognitive function, as measured by standardized tests such as the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale (ADAS-Cog). Additionally, patients treated with NAMZARIC exhibited better performance in activities of daily living, such as managing finances and completing household tasks. Long-term studies have also demonstrated the sustained benefits of NAMZARIC. In a 52-week study, patients receiving NAMZARIC showed continued improvements in cognitive function and daily living activities compared to those receiving placebo or monotherapy. These findings highlight the long-term efficacy of NAMZARIC in managing the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, NAMZARIC has shown a favorable safety profile in clinical trials. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and headache, but these are generally mild and transient. Serious adverse events are rare, and the benefits of NAMZARIC outweigh the potential risks for most patients. Comparing NAMZARIC to other AD treatments, it offers distinct advantages. While monotherapy with memantine or donepezil can provide some benefits, the combination of both drugs in NAMZARIC offers a more comprehensive approach to symptom management. By targeting multiple pathways involved in the disease, NAMZARIC has the potential to provide greater cognitive improvement and slow down the progression of AD compared to monotherapy alone. NAMZARIC: Enhancing Quality of Life In addition to improving cognitive function, NAMZARIC has a positive impact on the overall quality of life for AD patients and their caregivers. The combination therapy not only addresses cognitive symptoms but also targets behavioral and psychological aspects of the disease. Patients taking NAMZARIC have reported improvements in daily functioning, independence, and social interactions. They experience enhanced clarity of thought, improved memory, and better ability to engage in activities they enjoy. These improvements contribute to a higher quality of life, allowing patients to maintain their autonomy and participate in meaningful activities. Caregivers also benefit from NAMZARIC's effects. The reduction in behavioral symptoms, such as agitation and aggression, can alleviate the burden on caregivers and improve their overall well-being. With NAMZARIC, caregivers can experience a more manageable caregiving journey and maintain a better quality of life for themselves. FAQ's What is the recommended dosage of NAMZARIC? The recommended starting dose of NAMZARIC is 7 mg/10 mg (memantine/donepezil) once daily, taken at bedtime. The dosage can be increased gradually based on the patient's tolerance and response, as guided by their healthcare provider. Are there any potential side effects of NAMZARIC? Common side effects of NAMZARIC include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and headache. These side effects are generally mild and transient. It is important to discuss any concerns or side effects with a healthcare provider. Can NAMZARIC be used in combination with other AD medications? NAMZARIC should not be used in combination with other cholinesterase inhibitors or memantine-containing products. It is essential to inform the healthcare provider about all medications being taken to avoid potential drug interactions. How long does it take to see the effects of NAMZARIC? The effects of NAMZARIC may vary among individuals. Some patients may experience improvements in cognitive function and daily living activities within a few weeks, while others may require more time. It is important to continue taking NAMZARIC as prescribed and consult with a healthcare provider for any concerns. Is NAMZARIC suitable for all stages of Alzheimer's disease? NAMZARIC is approved for the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. It may not be appropriate for individuals in the early stages of the disease. A healthcare provider can assess the stage of Alzheimer's and determine the most suitable treatment option. Can NAMZARIC slow down the progression of AD? NAMZARIC has been shown to slow down the progression of cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer's disease. While it cannot cure or reverse the disease, it can help manage symptoms and potentially delay the worsening of cognitive function. Is NAMZARIC covered by insurance? The coverage of NAMZARIC by insurance may vary depending on the specific insurance plan. It is advisable to check with the insurance provider or consult a healthcare provider to determine the coverage and potential financial assistance options. What should I do if I miss a dose of NAMZARIC? If a dose of NAMZARIC is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered. However, if it is close to the time for the next scheduled dose, the missed dose should be skipped. It is important not to take a double dose to make up for the missed one. Following the prescribed dosing schedule is crucial for optimal treatment outcomes. Are there any dietary restrictions while taking NAMZARIC? There are no specific dietary restrictions associated with taking NAMZARIC. However, it is always advisable to follow a balanced and healthy diet to support overall brain health and well-being. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations. Can NAMZARIC be used in patients with other medical conditions? Before starting NAMZARIC, it is important to inform the healthcare provider about any existing medical conditions and medications being taken. This includes conditions such as heart problems, liver or kidney disease, seizures, and urinary problems. The healthcare provider will assess the individual's medical history and determine the suitability of NAMZARIC as a treatment option. Conclusion: NAMZARIC, a combination therapy consisting of memantine and donepezil, holds great promise in the management of Alzheimer's disease. By targeting multiple aspects of the disease, NAMZARIC offers a comprehensive approach to symptom management and improved quality of life for AD patients and their caregivers. Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of NAMZARIC, showcasing its ability to improve cognitive function, memory, and daily living activities. The combination therapy offers distinct advantages over monotherapy, providing a synergistic effect and potentially slowing down the progression of the disease. Individuals affected by Alzheimer's disease and their caregivers are encouraged to explore NAMZARIC as a potential treatment option. With its ability to address both cognitive and behavioral symptoms, NAMZARIC has the potential to enhance the overall well-being and independence of AD patients, offering new hope in the fight against this devastating disease.
#acetylcholine#Alzheimers_disease#brain_function#cholinesterase_inhibitors#cognition#cognitive_decline#confusion#dementia#donepezil#forgetfulness#glutamate#memantine#memory_loss#mild_to_moderate_Alzheimers#NAMZARIC#neurodegenerative_disorder#neurotransmitters#NMDA_receptor_antagonist
0 notes
Text
Coconut Oil (Edible Oil) for Alzheimer's
Coconut Oil (Edible Oil) for Alzheimer’s
Coconut oil is the oil derived from the coconut. This oil is a natural oil that is heart healthy and free from transfats. This oil is extracted from the coconut which is has matured either by hot or cold press or by solvent extraction process. The best coconut oil to use is cold pressed coconut oil which has all the benefits of the trace vitamins and minerals present in the mature coconut in it.…
View On WordPress
#acetylcholinesterase#Alzeimer&039;s Disease#Aricept#coconut oil#Exelon#glucose#Ketones#Memantine#Namzaric#Razadyne
0 notes
Text
AbbVie Inc (NYSE: ABBV) Avoids Lawsuit Over Alzheimer’s Drugs Patent Fraud
For the time being, AbbVie Inc (NYSE: ABBV) has dodged a whistleblower suit asserting that its predecessor Allergan Inc. extended its exclusivity on Alzheimer's medications by using false patents, enabling it to defraud Medicaid and Medicare. Silbersher filed a claim using publicly available information Zachary Silbersher, a prominent associate at the IP rights litigation organization Kroub, Silbersher & Kolmykov, filed a claim, and a three-judge forum of the 9th US Circuit Court of Appeals unanimously decided that the alleged public records bar adhered to the case. The public disclosures forbid whistleblower grievances based on available information. The decision overruled a lower court's conclusion that the bar didn't apply. The decision left Silbersher's argument that he was the "actual source" of the available information and ought t be permitted to proceed open for consideration. Requests for additional information were not immediately answered by attorneys for Allergan, Silbersher, or Adamas Pharmaceuticals Inc., which is additionally listed as a respondent in the litigation and licensed the Namzaric and Namenda XR patents to Allergan. In 2018, Silbersher took the firms to a San Francisco federal district under the False Claims Act (FCA). The Act enables whistleblowers to initiate complaints on the government's behalf and earn a part of any successful settlement. Allergan and Adama said to have distorted findings He said that after looking through records from the US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), he discovered that Allergan and Adama had distorted study findings and concealed earlier work to obtain the PTO grant patents for the medications. The firms have refuted the allegations. The FCA's public records bar, which forbids whistleblower lawsuits based on evidence given in federal govt processes, was the basis for the defendant's motion to dismiss the lawsuit. They claimed that the regulatory actions that led to the injunction were the USPTO's initial assessments of the patent claims. According to the FCA, Chief US District Court Judge Joseph Spero dismissed the application in a ruling published in December 2020. He claimed that Silbersher's allegations were not precluded since the federal government was not included as a participant in the USPTO's process. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Alzheimer’s Therapeutics Market Penetration, Growth Prospect Mapping and Research, 2024
Global Alzheimer’s Therapeutics Market size is anticipated to reach USD 6.4 billion in 2024. Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive, non-reversible, and neurodegenerative disorder. Alzheimer is caused due to abnormal functioning of brain cells. It is the most common form of dementia. In simple words, it is a biological disease marked by physical changes in the brain and most remarkably build-up of small protein clumps called “Tangles” and ��Plaques” that lead to the death of nerve cells.
Top Companies:
Some of the key players that fuel the growth of the Alzheimer’s therapeutics industry comprise Merck & Co. Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, Inc., Eisai Co., Ltd., Novartis AG., Actavis, H. Lundbeck A/S, and Transtech Pharma. The leading companies are taking up partnerships, mergers and acquisitions, and joint ventures in order to boost the inorganic growth of the industry.
Request free sample to get a complete analysis of top-performing companies @ https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/alzheimers-therapeutics-market/request-sample
Growth Drivers:
The factors that propel the growth of the Alzheimer’s therapeutics market include well-developed healthcare infrastructure, high consciousness levels, increase in incidence of neurodegenerative diseases, growing aged population, and increasing R&D investment. On the other hand, there are factors that may hamper the growth of the market including lack of transparent reimbursements, high cost of treatment and diagnosis in the later stage, typically owing to delayed appearance of symptoms.
The new product launches and research collaborations are some of the key strategies adopted by the top industry players. For instance, Actavis plc in collaboration with Adamas Pharmaceuticals Inc. lately publicized the US FDA approval of Namzaric, a fixed-dose combination of donepezil and memantine. The drug is likely to be launched in the first half of year 2015. Additionally, in Jan 2015, Johnson & Johnson signed a research deal with a Swiss biotech firm AC Immune, to change anti-tau Alzheimer's vaccines.
Alzheimer’s therapeutics industry is anticipated to expand at a significant CAGR in the upcoming period as the scope, product types, and its applications are increasing across the globe. Alzheimer’s therapeutics market could be explored by therapeutic type, application and geography. The market could be explored by therapeutic type as N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist and Cholinesterase Inhibitors. The “Cholinesterase Inhibitors” segment led the Alzheimer’s therapeutics industry in 2016 and is anticipated to maintain its dominance by 2024. The key applications that could be explored in the Alzheimer’s therapeutics market include Moderate to severe Stages, and Early to Moderate Stages.
Regional Insights:
North America accounted for the major share of the Alzheimer’s therapeutics industry in 2016 and will continue to lead in the forecast period. The factors that could be attributed to the growth include increasing prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease, growing aged population, extensive technological advancements in the region, high awareness levels, and strong healthcare infrastructure. North America is likely to be followed by Europe.
Browse Related Category Research Reports @ https://industryanalysisandnews.wordpress.com/
0 notes
Text
Alzheimer’s Disease-A Complete Overview
Alzheimer’s disease is an advanced form of dementia. It is a chronic ongoing condition which is seen in people after the age of 65. The symptoms usually start with memory loss, having difficulties in managing day to day tasks etc. The disease goes up to the last stage where usually the patient requires someone with themselves all the time to perform even their basic activities. There is still no cure for this.
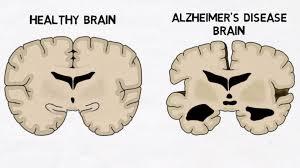
However, people often tend to get confused between Alzheimer and Dementia. Alzheimer is a type of dementia, whereas dementia is a broader term in itself. Dementia further includes severe symptoms and can lead to Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease traumatic brain injury and so on. They both have different causes, symptoms and treatment.
Alzheimer Disease Causes
The disease is said to have been caused due to lack of protein in and around cells. Amyloid being one of such proteins forms plaques around the cells, while tau, another protein results in tangling up of the cells. Thus, as there the brain cells are weakened they result in improper functioning of neurotransmitters that are helpful in sending messages between brain cells. Over the time, the cells of brain area shrinks which results in memory loss.
The exact causes are not yet known but however certain risk factors have been listed as below-
Age is one of most significant factor, as it is seen after the age of 65. However, there are cases where chances are at the age of 40. In such cases, it is said that it is an early onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
Genetic transformation from family members are also important. If anyone in the past is seen to have dementia then there are likely chances of Alzheimer’s in the next generation too.
Down’s Syndrome is also a major factor because patients already have genetic fault. This can further cause amyloid plaques which leads to Alzheimer disease.
People who have had major head injuries are also at risk.
Smoking
Diabetes
Obesity
High Blood Pressure
High Cholesterol, are also other factors.
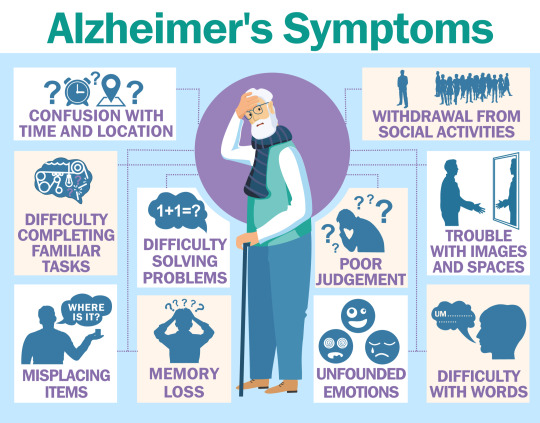
Symptoms Of Alzheimer’s Disease
Symptoms here appear over the time where the situations worsens over the time.
It leads to memory loss which results in daily activities such as forgetting to take bath, keep a check on the household work, keep a check on office and its related appointments.
Facing trouble with similar tasks, like operating an app, or operating a computer, using a microwave.
Difficulty is seen in problem solving.
One faces a trouble with speech and writing.
One tends to forget the places that they have been frequently visiting.
The mood and personality changes are observed.
Personal hygiene is lost.
Judgement power becomes to weaken.
Alzheimer’s Disease Stages
This is a disease which continues to worsen over the time.There is no end to it.Thus the stages tend to change as the disease seems to increase with time.
Stage 1: In case of family history the diagnosis may be easy, otheriwse there are no symptoms at this point of time.
Stage 2 : Symptoms of forgetting start at this stage.
Stage 3 : Physical and mental impairments are observed, like memory loss and lack of concentration. However, this can be observed only be a very close person.
Stage 4 : This is the stage when the disease is diagnosed because it results in memory loss. Also one finds it difficult to perform the day to day tasks.
Stage 5 : At this stage the symptoms tend to grow severe, hence help is required from the near and dear ones.
Stage 6 : A patient now needs help in performing daily tasks like eating or wearing clothes.
Stage 7 : This is the most extreme stage. A loss of speech and facial expressions are observed at this stage.

Diagnosis Of Alzheimer’s Disease
The most effective way to diagnose the disease is to examine a brain tissue after the death of the patient. However the doctor may use other ways like assessing mental abilities, diagnosing dementia, or may even ask other questions regarding symptoms observed, family medical history, current or past health conditions, diet, alcohol, or other lifestyle habits.
There are no specific tests for this disease. So the doctor starts by checking the mental status for which he asks the day, date, recall some words, ask daily activities, politics or social related questions. By this the doctor can come to know about the short term memory, long term memory.
Next, they conduct a physical test by checking the blood pressure, assessing heart rate, checking temperature, collect urine or blood samples for testing in a laboratory.
Thirdly, a neurological exam is conducted where infection, stroke, reflexes, muscle tone and speech are taken into consideration.
If the doctor feels then he may also ask for brain imaging tests like
MRI, for understanding the stages of inflammation, bleeding.
CT scans can help in understanding the abnormal characteristics of the brain.
PET scan can help detect plaque, a part of Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s Treatment
3Meds, best online medical app in India gets the prescribed medicines for you.
For early to moderate stage- Donepezil (Aricept), Rivastigmine (Exelon), Galantamine ( Razadyne)
For moderate to severe stage-Donepezil (Aricept), Memantine(Namenda), Namzaric.

Prevention
The following measures may help in preventing from such disease-
One should quit smoking.
Regular exercise is important.
Cognitive training exercises are also recommended.
Plan based diet with proper recommendation.
Consumption of antioxidants.
An active social life.
Outlook
Alzheimer’s is such a disease that majority of the facts are unknown. The symptoms and the worsening of the situation with time is what is known. However, all they require is care and love at this stage. Patience, stamina and ability to help them is all what is required.
0 notes
Text
HEALTHCARE’s INFLUENCE ON THE ECONOMY
This post is being updated.... 3 1/2 years after the original post.
We’ve all read about how healthcare represents a growing percentage of our economy, but some anecdotal evidence recently brought this home for me.
I don’t watch much TV, but a few weeks ago I noticed several back to back ads for drugs I had never heard of. A similar experience when I read my weekly magazines. I started jotting down the names of every ad for drugs I saw... and in a two week period, wrote down OVER 100.
Not a very scientific survey..... but hits home how pervasive pharmaceutical companies are in our lives.
Here’s my list (which today is over twice as along as 3 years ago... even though I haven’t been diligent in tracking recently)
Drug ads
Abreva
Aczone
Advair
Adulhem
Advate
Advil
Agriflu
Aimovig
Aleve
Align
Alka-Seltzer
Allegra
Allergan
Alli
Amberen
Annovera
Anoro
Arnica
Aspercreme
Aspirin
Aubagio
Austedo
Avistan
Belsomra
Benadryl
Bevespi
Biktarvy
Biotene
Bexsero
Botox
Breo
Breztri
Brilinta
Bydureon BCise
Cabenuva
Caplyta
CaroSpir
Chantix
Cialis
Claritin
Cochlear
Cologuard
Colon Health
Contrave
CooLief
Cosamin
Cosentyx
Consequen
Crestor
Culturell
DayQuill
Delsym
DexcomG6
Dovato
Ducolax
Dupixent
Eliquis
Ellipta
Emgality
Enbrel
Entresto
Entyvio
Epclusa
Esbriet
Estring
Eucrisa
Excedrin
ExLax
Eylea
Fanapt
Fasenra
Florastor
Farxiga
Fibrizzi
Flexitol
Flonase
Florastor
Fluad
Fluarix
Fluvoxamine
Fluzone
Freestyle Libre
Gardasil9
Genexa
Gilenya
Harvoni
Humira
Ibrance
Ifenprodil
Ilumya
Imfinzi
Impella
Imvexxy
*inCourage
Ingrezza
Inogen
Inspire
Intrarosa
Invokana
Januvia
Jardiance
Jarro-Dophilus
Juluca
Kanuma
Kardiamobile
Keytruda
Kesimpta
Kisqali
Kybella
Kyleena
Latuda
Letrozol
Libre
Lidocaine
Linzess
Lipitorrli
Liponate
LoLoestrinFe
Lovenox
Lumify
Lynparza
Lyrica
Mavyret
Mayzent
Miralax
Mirena
Movantik
Mucinex
Mydayis
Myrbetriq
Nasacort
Namzaric
Nervive
Neurocrine
Nexium
Nexplanon
Non24
Nucala
Nuedexta
Neulasta
Neuriva
Nexium
NicoDerm
Neurianz
Nucala
Nuplazid
Nurtec
NyQuil
Ocrevus
Ocuvite
Opdivo
Ongentys
Orilissa
Otezla
Oxbyrta
Ozempic
Paragard
Paxlovid
Peptiva
phexxi
Piqray
Plavix
Plenity
Premarin
PreserVision
Prevacid
Prevagen
Prevnar13
Prilosec
Primatene
Prolia
QBrexz
Octevus
Qulipta
Remicade
Repatha
Restasis
Rexulti
Rainbow
Rinvoq
Rybelsus
Salonpas
Saxenda
Sendexulti
Shingrix
Steglatro
Sublocade
Sunosi
Symbicort
Rhofade
Rinvoq
Rituxan
Robitussin
Ruxolitnib
Rybelsus
Salonpas
Saxenda
Salons
Shringrx
Skyrizi
Spinraza
Spiriva
Steglatro
Stelara
Sublocade
Suboxone
Sunosi
Symbicort
Systane
Taltz
Tamiflu
Tena
Tepezza
Theraworx
Toujeo
Trelegy
Tremfya
Tresiba
Triaminic
Trintellix
Trulicity
Truvada
Tylenol
Ubrelvy
Unisom
Vagisil
Valium
Valsartan
Vanda
Vascepa
Vazalore
Verzenio
Viagra
Viberzi
Vicodin
Victoza
Viviscal
Voltaren
Vraylar
Vuity
Watchman
Xanax
Xarelto
Xeomin
Xiaflex
Xeljanz
XGEVA
Xiaflex
Xiidra
Xolair
Xofluza
Xytiga
Xyzal
Yervoy
Yupelry
Zantac
Zeposia
Zicam
Zona
Zulresso
Zypitamag
Zyrtec
Zzzquil
1 note
·
View note
Text
Alzheimer’s Therapeutics Market Research 2020-2025 Report by Overview, Growth, Economics, Demand
Alzheimer’s Therapeutics Market size is anticipated to reach USD 6.4 billion in 2024. Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive, non-reversible, and neurodegenerative disorder. Alzheimer is caused due to abnormal functioning of brain cells. It is the most common form of dementia. In simple words, it is a biological disease marked by physical changes in the brain and most remarkably build-up of small protein clumps called “Tangles” and “Plaques” that lead to the death of nerve cells.
Request a Sample PDF Copy of This Report @ https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/alzheimers-therapeutics-market/request-sample
The key driving factors responsible for the growth of Alzheimer’s Therapeutics market :
The factors that propel the growth of the Alzheimer’s therapeutics market include well-developed healthcare infrastructure, high consciousness levels, increase in incidence of neurodegenerative diseases, growing aged population, and increasing R&D investment. On the other hand, there are factors that may hamper the growth of the market including lack of transparent reimbursements, high cost of treatment and diagnosis in the later stage, typically owing to delayed appearance of symptoms.
The new product launches and research collaborations are some of the key strategies adopted by the top industry players. For instance, Actavis plc in collaboration with Adamas Pharmaceuticals Inc. lately publicized the US FDA approval of Namzaric, a fixed-dose combination of donepezil and memantine. The drug is likely to be launched in the first half of year 2015. Additionally, in Jan 2015, Johnson & Johnson signed a research deal with a Swiss biotech firm AC Immune, to change anti-tau Alzheimer's vaccines.
Alzheimer’s therapeutics industry is anticipated to expand at a significant CAGR in the upcoming period as the scope, product types, and its applications are increasing across the globe. Alzheimer’s therapeutics market could be explored by therapeutic type, application and geography. The market could be explored by therapeutic type as N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist and Cholinesterase Inhibitors. The “Cholinesterase Inhibitors” segment led the Alzheimer’s therapeutics industry in 2016 and is anticipated to maintain its dominance by 2024. The key applications that could be explored in the Alzheimer’s therapeutics market include Moderate to severe Stages, and Early to Moderate Stages.
North America accounted for the major share of the Alzheimer’s therapeutics industry in 2016 and will continue to lead in the forecast period. The factors that could be attributed to the growth include increasing prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease, growing aged population, extensive technological advancements in the region, high awareness levels, and strong healthcare infrastructure. North America is likely to be followed by Europe.
View Full Table of Contents of This Report @ https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/alzheimers-therapeutics-market
0 notes
Text
传奇的阿尔茨海默药物 - 盐酸美金刚
1966年申请化合物专利,1989年发现新用途,2005年开发新剂型,从作为降血糖药至目前唯一可用于治疗中至重度AD (Alzheimer Disease),美金刚在专利的护航下风雨50年,堪称传奇。 作为目前临床唯一的非竞争性NMDA受体拮抗剂,美金刚可抑制 NMDA 受体的过度激活以减少兴奋性毒性、保护神经元,同时不影响认知所需要的NMDA受体的生理性活化。
1、基本信息
盐酸美金刚,别名盐酸美金刚胺 英文名:Memantine Hydrochloride (Namenda) 化学名:1-氨基-3,5-二甲基金刚烷胺盐酸盐 CAS号:41100-52-1 分子式:C12H21N·HCl 分子量:215.76,外观:白色结晶或粉末。熔程:290℃~295℃ 已批准剂型:片剂、溶液、缓释胶囊剂
2、阿尔茨海默病(AD):
记忆力减退、语言表达障碍、物体及人物识别困难、定向力减退、情感及行为控制能力丧失等,甚至生活��全不能自理……这些都是 AD 的典型症状。该病是由德国神经科医生阿尔茨海默 (Alois Alzheimer) 于1906年首先发现,因此该病就以他的名字命名。 2009年10月10日,被誉为“光纤之父”、前香港中文大学校长高锟,从瑞典国王卡尔十六世·古斯塔夫手中接过诺贝尔物理学奖证书,盛装出席的他以灿烂的笑容迎接气氛庄严但欢乐的历史性一刻。然而令人叹息的是,由于高锟患上了AD,他已经忘记了自己毕生研究、造福世人的光纤科技。 2015年全球有4680万AD患者,每3.2秒就有一个新病例,预计2050年增加至1.31亿。全球高达8180亿美元/年的治疗费用,预计2018年这一数值将达到一万亿。与世界各国经济体相比,其总金额可名列全球第18大经济体。以流行程度来说,58%患有老年痴呆的人都来自于中低收入国家,而就治疗成本而言,87%皆源自高收入国家。然而与此对应的是过去十几年间,各大制药公司在这个疾病领域的研发活动屡屡折戟,AD新药研发的失败率高达99%。2016年11月,Lilly宣布III期Solanezumab未达到预期,2017年2月MSD新药Verubecestat因几乎不可能得到一个积极的临床结果而终止。 迄今为止,FDA也仅批准了5个用于改善症状的药物,包括4个乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)抑制剂 - 他克林(副作用过大,如今已不用)、奈哌齐{(安理申)Donepezil (Aricept)}、卡巴拉汀{(艾斯能)Rivastigmine (Exelon)}和加兰他敏{(利忆灵)Galantamine (Reminyl))}和1个天门冬氨酸(NMDA)受体拮抗剂(美金刚)。
3、美金刚上市历程
1966年,Lilly申请了美金刚的化合物专利,作为降糖药,由于效果较差而弱化了产品的深度开发。
1982年,德国Merz公司发现了美金刚的中��神经系统活性后,对其进行了深入的研究。
1986年美金刚作为一种痴呆症治疗药物进入临床试验。
1989年正式在德国上市,商品名为“Axura”。 随后美金刚的NMDA受体抑制作用得到了确认,2000年6月,德国Merz公司和美国Forest Lab在美国启动了治疗阿尔茨海默病及其他中枢神经系统疾病的临床试验。同时,丹麦灵北制药(Lundbeck)获得了产品转让,拥有美金刚在欧洲市场、加拿大、澳大利亚、南非、中国等上市权,Forest拥有美国的上市权,第一三共则拥有日本的上市权。
2002.5.15,欧洲专利药品委员会(CPMP)批准了丹麦灵北公司的盐酸美金刚(5mg/10mg)用于治疗中度和重度早老年性痴呆病人,商品名为“Ebixa” 。
2002.5.17,CPMP批准了Merz的10mg片剂,商品名为“Axura”。
2003.10.16,FDA批准美国Forest公司的美金刚用于治疗中度、重度阿尔茨海默病,商品名“Namenda”。
2005.4.18,Forest公司的盐酸美金刚口服溶液(2mg/ml)问世,以适合老年患者的需求和依众性。
2007.10.16,FDA收到5mg/10mg片剂的ANDA申请,开启十几家仿制药企业竞相PIV之路。
2009-2010,关于片剂的侵权诉讼案纷纷落下帷幕,最终原告获胜,被告约定侵犯了诉讼案中的专利,在专利到期或上诉法院判定专利无效或不可实施之前不上市美金刚片剂。
2010.6.21,FDA批准Forest Lab公司NAMENDAXR的NDA,剂型为缓释胶囊剂(Extended release capsule),规格为7mg、14mg、21mg、28mg。其缓释胶囊剂的市场独占权至2017.7.3 (美金刚可用于治疗6-12岁儿童自闭症谱系障碍,autism spectrum disorder),因儿科用药延长至2018.1.3。
2011.1.2,日本批准第一三共的盐酸美金刚片剂,商品名Memary。2011.6在日本上市。 2012.12.28, CFDA批准丹麦灵北制药公司的美金刚片剂进入中国市场,适用于中、重度阿尔茨海默症的治疗,商品名为“易倍申”。
2013.6,Forest在美上市28mg的Namenda XR(缓释剂型)。 2013.6.10,FDA收到缓释胶囊剂7mg/14mg/21mg/28mg的ANDA申请,十几家仿制药企业再启缓释剂型的PIV之路。 2014-2015,原告与7家被告就侵权诉讼达成和解意见。
2014.3,Forest向FDA提交Namzaric (NanemdaXR & 多奈哌齐)的NDA,2015.5在美上市该复方制剂。
2015.7,美金刚片剂仿制药正式在美上市。
4、小结
(1)美金刚是一款老药,化合物专利早已过期,其治疗AD的用途专利(US5061703)也于2015年届满。 (2)其28mg缓释剂型专利‘009在美国获得授权,在欧洲(EP1781261A1)和中国(CN1968684A)视为撤回。 (3)含10-100mg美金刚缓释剂型用于治疗老年痴呆的美国专利‘007将在2026年届满,‘209专利保护了5-40mg美金刚缓释单剂量固体药学组合物,其他分案及继续申请案皆以各种不同的表达方式将5-100mg美金刚缓释剂型(包括单方和复方)进行保护。 (4)中国CN101686945A保护了美金刚缓释制剂,但视为撤回;唯一授权的专利CN101247795B保护了(22.5-57.5mg)美金刚缓释剂+多奈哌齐(1-10mg)复方组合物。
5、FDA批准情况
Forest公司获得4个NDA:片剂、溶液、缓释剂以及复方制剂。FDA批准ANDA共26个,其中片剂18个,溶液3个,缓释剂5个,复方制剂1个。
7、美金刚全球销售
美国市场占美金刚全球销售约70-80%的份额。在用途专利到期之前两年,2013年6月Forest在美上市了28mg的Namenda XR(缓释剂型),这一策略避免了片剂的仿制药上市带来的直接市场竞争。 2014年8月,Forest宣称停止出售Namenda(片剂),但这一行为被纽约州司法部长起诉,2015年5月法院判定Allergan (Forest是Allergan的附属企业)必须销售原来的片剂。为了维护Namenda的专营权,Allergan同时还执行第二套生命周期管理策略,与Adamas制药公司合作开发了Nanemda XR和多奈哌齐的复方制剂(商品名Namzaric),这一策略也减轻片剂仿制药上市导致的市场份额的损失。
8、小结
从名不经传到年销售30亿美元的重磅药,美金刚用了48年。Merz公司仅用一个8页的用途专利(US5061703A),以一夫当关之势,成功把所有美金刚片剂仿制药企业挡在了欲提前上市的PIV之路上,使得Merz与合伙人Forest和Lundbeck拥有美金刚片剂近12年(2003.10-2015.7)的市场垄断。在专利到期前又开发缓释新剂型及复方制剂,延长美金刚的专营权,减轻片剂仿制药上市导致的市场份额的损失。虽然美金刚限于延缓AD的发展或轻度好转,不能完全逆转或治愈AD,但作为目前唯一可用于治疗中至重度AD的NMDA受体拮抗剂,美金刚仍将继续担当抗AD的重任。
发布于 2019-06-26 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/70820945
0 notes
Link
Namzaric: Enhancing Cognitive Function in Alzheimer's Patients Alzheimer's disease is a challenging condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It progressively impairs memory, cognitive function, and daily life, causing immense emotional strain on patients and their families. In the quest to improve the quality of life for those living with Alzheimer's, pharmaceutical advancements have brought us Namzaric—a medication with the potential to make a significant difference. Namzaric represents a fusion of two drugs, memantine and donepezil, each addressing different aspects of Alzheimer's progression. This article explores the depths of Namzaric, shedding light on its uses, benefits, and the experiences of those who have turned to it for Alzheimer's care. What is Namzaric? [caption id="attachment_60272" align="aligncenter" width="1884"] namzaric[/caption] Namzaric is a medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) specifically designed for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It combines two active ingredients: Donepezil: This component falls under the category of cholinesterase inhibitors. It works by boosting levels of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory and learning processes. Memantine: A receptor antagonist, memantine regulates glutamate, a neurotransmitter linked to cognitive functions. Memantine's role is to protect brain cells from excessive glutamate, which can lead to cell damage and memory loss in Alzheimer's patients. Benefits of Namzaric Namzaric offers a ray of hope for both Alzheimer's patients and their caregivers. Understanding the benefits of this medication can help individuals make informed decisions about their loved ones' treatment plans. Cognitive Enhancement One of the primary benefits of Namzaric is its ability to enhance cognitive function. Alzheimer's patients often experience a decline in memory, reasoning, and problem-solving abilities. Namzaric's combination of donepezil and memantine targets these cognitive deficits from multiple angles. Donepezil boosts the levels of acetylcholine in the brain, while memantine regulates glutamate, promoting clearer thinking and improved memory retention. Symptom Management Alzheimer's disease can manifest in various ways, including mood swings, confusion, and behavioral changes. Namzaric helps manage these challenging symptoms, offering a better quality of life for patients and reducing stress on caregivers. By stabilizing neurotransmitter levels, Namzaric can lead to more stable moods and a reduction in disruptive behaviors. Daily Living Support Maintaining independence in daily activities is crucial for Alzheimer's patients. Namzaric's role in slowing cognitive decline can help individuals with Alzheimer's continue to perform daily tasks such as dressing, bathing, and meal preparation for a longer period. This not only improves the patient's self-esteem but also eases the burden on caregivers. Namzaric vs. Other Alzheimer's Medications When considering Alzheimer's treatment, it's essential to understand how Namzaric compares to other commonly prescribed medications. Each medication has its unique characteristics and potential benefits. Here's a comparative overview: Namzaric (Donepezil/Memantine) Dual-Action: Namzaric combines two active ingredients, donepezil, and memantine, addressing cognitive decline and symptom management simultaneously. Stabilizing Cognitive Function: Donepezil and memantine work together to stabilize neurotransmitter levels, potentially leading to improved memory and cognitive abilities. Symptom Management: Namzaric can help manage mood swings, agitation, and behavioral changes often associated with Alzheimer's. Donepezil (Aricept) Single-Action: Donepezil, the primary component of Namzaric, focuses on increasing acetylcholine levels to enhance memory and cognitive function. Early-Stage Treatment: It is often prescribed for mild to moderate Alzheimer's and is typically one of the first medications considered. Limited Symptom Management: Donepezil primarily targets cognitive functions and may have a limited impact on behavioral symptoms. Memantine (Namenda) Single-Action: Memantine, like donepezil, is a standalone medication that regulates glutamate levels in the brain. Moderate to Severe Alzheimer's: Memantine is usually prescribed for individuals with moderate to severe Alzheimer's when cognitive decline is more pronounced. Complementary Therapy: It is sometimes used in conjunction with other Alzheimer's medications, including donepezil. How Namzaric Works Understanding the mechanism of action of Namzaric is crucial to grasping its effectiveness in Alzheimer's treatment. Both of its active ingredients, donepezil, and memantine, play pivotal roles in addressing the complexities of the disease. Donepezil: Boosting Acetylcholine Donepezil falls into a category of drugs known as cholinesterase inhibitors. It works by inhibiting the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory and learning processes. In Alzheimer's patients, there is often a shortage of acetylcholine due to the degeneration of brain cells. Donepezil's role is to maintain higher levels of acetylcholine, promoting better communication between nerve cells and potentially improving memory and cognitive function. Memantine: Regulating Glutamate Memantine, on the other hand, is an NMDA receptor antagonist. It focuses on regulating another neurotransmitter called glutamate. In Alzheimer's patients, excessive glutamate activity can lead to cell damage and further cognitive decline. Memantine acts as a protective shield for brain cells, preventing the harmful effects of glutamate overload. Namzaric Dosage and Administration Proper administration of Namzaric is essential to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Patients and caregivers should follow prescribed guidelines closely. Here's what you need to know about Namzaric dosage and administration: Dosage Considerations Initial Dosage: In most cases, patients start with a low dose of Namzaric, typically 7 mg of memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg of donepezil hydrochloride once daily. Titration: The dosage is gradually increased over several weeks to reduce the risk of side effects. Healthcare providers will monitor patients' responses to determine the optimal dose. Maintenance: Once the right dosage is established, patients typically take 28 mg of memantine hydrochloride and 10 mg of donepezil hydrochloride as a single capsule once daily. Administration Tips Take as Prescribed: Patients should take Namzaric exactly as prescribed by their healthcare provider. Deviating from the recommended dosage can affect its effectiveness. Time of Day: It's often recommended to take Namzaric at bedtime to reduce the risk of side effects, which can include nausea and vomiting. Swallow Whole: The capsule should be swallowed whole, not crushed or chewed, to ensure a controlled release of the medication. Food Considerations: Namzaric can be taken with or without food. However, taking it with food can help reduce stomach discomfort. Missed Dose: If a dose is missed, patients should take it as soon as they remember. If it's close to the time for the next dose, they should skip the missed dose and continue with their regular schedule. Side Effects and Precautions As with any medication, Namzaric may cause side effects in some individuals. It's important to be aware of these potential side effects and take necessary precautions: Common Side Effects Nausea: Some patients may experience nausea, especially when starting or adjusting to the medication. Taking Namzaric with food can help alleviate this symptom. Vomiting: In some cases, vomiting may occur. If this happens frequently, contact a healthcare provider for guidance. Diarrhea: Diarrhea is another possible side effect. Staying well-hydrated can help manage this symptom. Less Common Side Effects Headache: A mild headache may occur but usually subsides with continued use. Dizziness: Some patients may experience dizziness, particularly when standing up quickly. It's important to stand up slowly to reduce the risk of falls. Insomnia: Difficulty sleeping can occur in rare cases. If this persists, consult a healthcare provider for possible adjustments to the medication. Precautions Allergies: Inform your healthcare provider of any known allergies or sensitivities before starting Namzaric. Liver or Kidney Issues: Namzaric should be used with caution in individuals with liver or kidney problems. Dose adjustments may be necessary. Other Medications: Provide a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies being taken, as interactions can occur. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: The safety of Namzaric during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well-established. Consult with a healthcare provider if you are pregnant or nursing. Driving and Machinery: Namzaric may cause dizziness or drowsiness in some individuals. Avoid activities that require alertness until you understand how the medication affects you. Regular Check-ups: Regularly follow up with your healthcare provider to monitor the medication's effectiveness and any potential side effects. FAQs related to Alzheimer's disease and its treatment with Namzaric: What is Alzheimer's disease, and how does it affect individuals? Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily impacts memory, thinking, and behavior. It gradually worsens over time, affecting a person's ability to perform daily tasks. What is Namzaric, and how does it differ from other Alzheimer's medications? Namzaric is a combination medication that includes both donepezil and memantine. It differs from some other Alzheimer's medications by addressing cognitive decline and symptom management simultaneously. Who is a suitable candidate for Namzaric treatment? Namzaric is typically prescribed for individuals in the middle to late stages of Alzheimer's disease when cognitive decline and symptoms become more pronounced. What are the potential benefits of taking Namzaric? Namzaric may offer benefits such as enhanced cognitive function, improved memory, better symptom management, and support for daily living activities. Are there any common side effects associated with Namzaric? Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, and dizziness. These side effects are usually mild and temporary. Can Namzaric be taken with food? Yes, Namzaric can be taken with or without food. Taking it with food may help reduce stomach discomfort. Is Namzaric safe for individuals with liver or kidney issues? Namzaric should be used with caution in individuals with liver or kidney problems, and dose adjustments may be necessary. Can pregnant or breastfeeding individuals take Namzaric? The safety of Namzaric during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well-established. Consult with a healthcare provider if you are pregnant or nursing. Are there any potential drug interactions with Namzaric? It's essential to provide a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies to healthcare providers, as interactions can occur. How does Namzaric relate to natural language processing (NLP) in Alzheimer's care? Namzaric's compatibility with NLP advancements underscores its relevance in modern healthcare. NLP aids in early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans for Alzheimer's patients. Conclusion In the world of Alzheimer's care, Namzaric shines as a beacon of hope for patients and their caregivers. This medication, a combination of donepezil and memantine, offers a multifaceted approach to tackling the challenges of this progressive disease.
#Alzheimers_diagnosis#Alzheimers_Drug#Alzheimers_medication#Alzheimers_treatment#cognitive_enhancement#Cognitive_Function_Enhancer#Donepezil_and_Memantine_Combination#natural_language_processing#NLP_technology#personalized_treatment
0 notes
Text
Alzheimer’s
What is Alzheimer’s?
Alzheimer’s is a progressive mental deterioration that can occur in the middle or old age, due to generalized degeneration of the brain. This type of dementia affects memory, thinking, and behavior. The symptoms will eventually grow severe enough to interfere with daily tasks.
This disorder is also the most common cause of premature senility. Premature senility is a rare genetic disorder in childhood that is characterized by rapid onset of the physical changes of typical old age, usually resulting in death before the age of 20.
Who is at risk of Alzheimer’s?
Alzheimer’s accounts for 60-80% of dementia cases. Alzheimer’s is also the 6th leading cause of death in the United States.
The most common risk factor for the is disease is age, with the majority of people with Alzheimer’s being 65 or older; however, old age is not the only factor. In fact, about 200,000 American’s under the age of 65 have Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease.
Symptoms of Alzheimer’s gradually worsen overtime. Early on, the disease causes mild memory loss, but as it continues, individuals loose the ability to carry out conversations and respond to their environment. The average life expectancy for someone with Alzheimer’s disease is 4-8 years, but depending on some factors, someone can live up to 20 years.
What causes Alzheimer’s?
Studies have shown that most people with Alzheimer’s develop far more plaques and tangles in their brains that begins in areas important for memory that eventually spreads to other regions.
* Plaques are deposits for a protein fragment called beta-amyloid that build up in the spaces between nerve cells.
* tangles are twisted fibers of another protein called Tau that build up inside cells.
While scientist are not exactly sure what role these two proteins play, it is believed that they are responsible for the blocking of communication between nerve cells as well as disturbing processes that cells need to survive. Destruction and death of these nerve cells will cause memory failure, personality changes, and problems with carrying out everyday activities.
What are the symptoms of Alzheimer’s?
The most common symptom is trouble with learning and remembering new information (this is an early symptom due to this disease typically starting in the part of the brain that affects learning).
More severe symptoms:
* disorientation
* confusion about events
* mood changes
* behavioral changes
* confusion about time
* confusion about places
* suspicions about family, friends, or caregivers
* more serious memory loss
* difficulty speaking and swallowing
* difficulty walking
What are the treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease?
Medications called Cholinesterase inhibitors are used to help with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s. These drugs are supposed to help reduce some of the symptoms and help control behavioral changed. These medications, according to research, help prevent the breakdown of Acetylcholine, which is a chemical believed to be important for memory and thinking. Eventually these drugs may have less effect due to the disease causing the brain to produce less and less Acetylcholine.
Drugs used:
* Razadyne
* Exelon
* Aricept
Namenda is an NMDA antagonist that is used to treat moderate to severe Alzheimer’s. This drug allows for some people to maintain certain daily functions for a while longer, such as going to the bathroom without aid. Namenda helps regulate Glutamate which is an important neurotransmitter. Too much Glutamate can result in cell death, which is why regulation is needed.
Drugs used for moderate to severe:
* Aricept
* Excelon Patch
* Namzaric- a combination of Namenda and Aricept
Sources:
Definitions from Oxford Dictionary
https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers#:~:text=Alzheimer's%20is%20a%20progressive%20disease,and%20respond%20to%20their%20environment.
https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/how-alzheimers-disease-treated#:~:text=Medications%20called%20cholinesterase%20inhibitors%20are,and%20Aricept%C2%AE%20(donepezil).
#alzheimers#alzheimers awareness#neuroscience#neurological#neurological disorder#neurological disorders#neurological diseases
0 notes
Text
Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment Market by 2025 Players: Novartis AG, Eisai Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd., H. Lundbeck A/S and Others
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that attacks the brain’s nerve cells, or neurons, leading to cell death and degeneration. The most common symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease are the memory loss, incognition, disorientation, behavioural changes, personality changes, and trouble in speaking and writing. The Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mainly occurs in the adults with aging mid-sixties, which leads to 60% to 70% of cases of dementia. The major causes of Alzheimer’s disease are genetic disorders and the disease process associated with plaques and tangles in the brain. The diagnostic test for Alzheimer’s disease includes cognitive testing with medical imaging and blood tests. Alzheimer’s disease risks can be overcome by mental and physical exercise and avoiding obesity.
Get a Sample Copy of this Report @ https://www.alexareports.com/report-sample/170615
The global Alzheimer’s disease treatment market is expected to grow at a significant CAGR due to increase in the prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease. According to World Health Organisation, escalation of the geriatric population leads to increase in Alzheimer’s disease cases, which in turn affect the Alzheimer’s disease treatment market positively over the forecast period. Apart from this, increase in healthcare spending and R&D investments in the global Alzheimer’s research, expiration of patents, and entry of new generics into the market expected to fuel the growth of Alzheimer’s disease treatment market. Similarly, the discovery of new disease modifying drugs, and presence of vast last-stage pipeline drugs expected to boost the growth of Alzheimer’s disease treatment market over the forecast period. However, the limited number of treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease in the market, challenges in precise diagnosis and even detection of Alzheimer’s disease, and lack of funding from government in developing economies for research might hamper the growth of global Alzheimer’s disease treatment market over the forecast period. Moreover, the high degree of research failure and uncertainty within the research and development of Alzheimer’s disease treatment drugs might hinder the growth of Alzheimer’s disease treatment market.
Alzheimer’s disease treatment market has been segmented on the basis of drug type, route of administration, and end user
Based on the drug type, Alzheimer’s disease treatment market has been segmented into the following:
Cholinesterase inhibitors NMDA receptor antagonists Others
Based on the route of administration, Alzheimer’s disease treatment market has been segmented into the following:
Oral Implants Others
Based on the distribution channel, Alzheimer’s disease treatment market has been segmented into the following:
Hospital Pharmacies Retail Pharmacies Online Pharmacies
The Alzheimer’s disease treatment market is in the growing stage with several international players operating in the Alzheimer’s disease treatment market. According to Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) the global prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease will triple among elderly patients, and the prevalence increases to 13.8 million by 2050. Several drug molecules lost patents and few more expected lose patents in near future, which is expected to crate market opportunity for generic players. Majority of drugs in pipeline failed in the late stage of clinical trials, for instance, Eli Lilly’s solanezumab and Pfizer/Johnson & Johnson’s bapineuzumab have failed to prove the disease-slowing effects in the late-stage of clinical trials. Moreover, In 2014, FDA has approved cholinesterase inhibitors (Exelon, Aricept, and Razadyne) and memantine for the treatment of cognitive symptoms in Alzheimer disease. The other medication is Namzaric (combination of donepezil with memantine) manufactured by Allergan for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers are looking for new ways to treat Alzheimer’s disease to address the Alzheimer’s disease market needs. Currently available drugs help mask the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease but they do not stop its progression. There are several promising drugs in developmental and testing stage for Alzheimer’s disease, but researchers need more funding of research to ensure that fresh ideas continue to fill the pipeline.
Grab amazing discount here @ https://www.alexareports.com/check-discount/170615
Geographically, the Alzheimer’s disease treatment market has been segmented into following regions Viz. North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. According to the United Nations Population Fund, the people aged over 60 make up for 12.3% of the world’s population, which is estimated to exceed to almost 22% by 2050, with the increase in geriatric population the market for Alzheimer’s drugs expected to bolster during the forecast period 2019 to 2025. North America contributes the maximum demand for Alzheimer’s drugs. According to the American Alzheimer’s Association, almost 5 Mn adults are suffering from Alzheimer’s disease and due to the increasing aging populations, it may expect to grow in future. Similarly, increasing coverage of Alzheimer’s disease by Medicare, an insurance program encourages more Alzheimer’s patients to seek medical treatment, expected driving market growth. According to Alzheimer’s Association UK, there are 850,000 people with dementia in the UK in 2015 which is expected to increase to approximately 1 Mn during forecasting period which expected to contribute significantly to the overall growth of the European Alzheimer’s disease treatment market.
Some of the players in global Alzheimer’s disease treatment market are F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland), Novartis AG (Switzerland), Eisai Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd. (Japan), H. Lundbeck A/S (Denmark), Johnson & Johnson Services Inc., (U.S.), AstraZeneca (U.K.), Pfizer Inc. (U.S.), Forest Laboratories (U.S.), and Eli Lilly and Company (U.S.) to name a few.
In January 2015, Johnson & Johnson partnered with Swiss biopharma AC Immune to develop a therapeutic vaccine for the development of anti-tau Alzheimer’s vaccine
In September 2014, Eli Lilly and AstraZeneca came into an alliance to co-develop the partial treatment for Alzheimer’s disease
To Enquire About This Comprehensive Report@ https://www.alexareports.com/send-an-enquiry/170615
Details of the market study:
Historical Data: 2014 & 2017
Base Year: 2018
Forecasts: 2019-2025
CAGR: 2019-2025
Market trend analysis in terms of drivers, restraints and opportunities
Industry analysis using Porter’s, PESTEL and SWOT
Market players analysis in terms of company’s overview, financial performance, product/service benchmarking and strategic initiatives taken up by them
0 notes
Text
What does the past generation of failure in Alzheimer’s R&D look like in one slide?
You need a license to cut-and-paste this copyrighted news content. Use this link to purchase your paid subscription ($200/year for individuals and $1,000/year for companies of every size): https://endpts.com/subscribe Already a paid subscriber? Sign in to Endpoints News to remove this message.
Just how bad is it in the Alzheimer’s R&D arena?
IQVIA just put together something of an impressionist piece on the slew of trial failures recorded over the years (below).
Except for one pop in 2014 — for a dementia drug, Namzaric — there’s nothing by way of an FDA approval going back to 2002, 17 years of failure and disaster, with Eli Lilly, Pfizer, J&J and others going over the amyloid beta cliff. That’s made the big players leery of this field, but the prospect of being the only significant therapy on the market for millions of patients continues to fuel the drive toward something — anything — to throw against the disease.
Getting something reimbursable, though, won’t be easy.
0 notes
Text
Journal Entry #18
Alzheimer’s treatments: What’s on the horizon?
1. The main point of this article is to list the current rising effective treatments for Alzheimer’s and the others that may grow with more research. This article also discusses how the medications either recruit the immune system, prevent cell destruction, or are beta-amyloid blockers. They also discuss a few other factors such as lifestyle choices and correlations with other diseases and their medication like cancer and heart disease.
2. The evidence is provided through studies being cited at the end. They discuss certain functions in depth to provide evidence. For example medications that recruit the immune system are called monoclonal antibodies. Their purpose is to stop the beta-amyloid from grouping in to clumps of plaque and get rid of previous plaque buildup. They are used to flush the brain of the beta-amyloid completely. The beta-amyloid plaque is what destroys brain cells and causes memory loss in Alzheimer’s. There is also medication that prevents destruction of cells through inhibition of Fyn. Fyn causes overloads of synaptic transmissions in the nerve cells. When Fyn is turned off the synapses can function properly again. Thirdly, there are production blockers that stop the parent protein from creating the beta-amyloid in general. This one has not been shown to slow the memory loss and decline in patients which begins the further discussion of the many options being tested that have not come back with positive or credible results yet but are being edited and trialed more and more.
3. The most interesting thing about this source was that they tried an insulin nasal spray to determine its’ effects on brain functioning. The results have been negative so far but I find this attempt very intriguing.
4. The source opens up so many other medications that are being tested that shocked me. From cancer, heart disease, and hormone therapy, there are many different aspects to sickness that many people do not quite think about when relating to Alzheimer’s but should be tested because that could be where a solution lies.
Efficacy of Music Therapy in Treatment for the Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease
1. The main claim for this article is that “music therapy is effective in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease” (Takabatake 1). They go on to say that with an increase in amyloid metabolism comes estrogen improving cognitive functioning along with offsetting Alzheimer’s disease further in the elderly’s lives.
2. They provide evidence in this because the estrogen increases cholinergic activity which simply put makes more brain cell growth activation (”stimulates axonal budding and dendrite formation and the retarding of cerebral arteriosclerosis”). The author provides a study where “dementia is dealyed significantly in elderly women who had been receiving estrogen for long periods than those who had not”. This shows that hormones have a correlation to cognitive function and memory overall. They further this idea with the fact that testosterone works the same way in males. Music is known to be correlated with stress relief along with better spatial cognition over time of practicing or listening. Through their study they dive deeper into the possibility that other types of cognition can be increased with the presence of music as well.
3. The most interesting thing in this article is that music therapy is also used in stroke victims to help with mood fluctuations and cognitive recovery. I am curious as to researching more about how strokes effect memory and maybe an quicker course of Alzheimer’s.
4. This source elaborates on the solution of hormone therapy through natural ways to produce hormones. The other hormone therapies tend to have negative effects since they are produced through medication but this source uses a natural way to recover memory through the promotion of estrogen and testosterone in aging people where their sex hormones are decreasing.
Treatments for Alzheimer’s Disease
1. The main point of this article is that there is no cure so far for Alzheimer’s, yet there are medications to help with the symptoms and that which medication(s) to take depends on many factors of the individual patient.
2. The author discusses how “age, overall health, medical history, how severe your disease is, how well a medicine or therapy will work for you and your lifestyle, and your preferences or those of your family or caregivers” are all crucial factors toward choosing treatments for patients. Each patient has an individual experience with battling the disease and many times it takes a combination of medication to truly have the best track possible for a patient. Aricept happens to be the only medication that is FDA approved and can be taken at any stages. Memantine (Namenda) is for those on the farther side of the Alzheimer’s spectrum and it levels out the abundance of glutamate in Alzheimer’s patients. It can be paired with Aricept as well and helps with everyday tasks and functioning overall of the patient. There is a mixture of these medications called Namzaric as well to ease the amount of medications being taken by those patients who are already prescribed both Aricept and Namenda.
3. The most interesting thing in this to me was that they are researching an Alzheimer’s vaccine. I am extremely curious on how this vaccination would operate and when one would take it since this is a disease in the elderly.
4. This source is straightforward in the fact that there are no treatments approved currently that directly effect the brain cell deterioration caused by Alzheimer’s. There are only approved medications for symptoms. This is being researched but none of those treatments are seeing a huge spark in progress quite yet which makes me curious if people are doing enough testing on these less popular options. People should explore every option in depth because they could be overlooking something big because one study may not have worked but every study after that might.
Therapeutics: Solanezumab
1. This article claims that Solanezumab is a monoclonal antibody medication that can repair memory loss and leave the beta amyloid visible for targeting with another medication. It furthers its’ argument to provide a few studies and their results and differences after this upfront claim in the background.
2. In a study with mice, m266 was injected into them, which is the mouse version of Solanezumab. This injection reversed memory loss along with providing isolation to the beta-amyloid which would be helpful in eliminating the plaques created on brain cells. After this was discovered clinical trials began with 19 patients receiving doses of .5, 1.5. 4.0 or 10.0 mg/kg of Solanezumab. There was no inflammation found. The beta-amyloid was found to be truncated through this study, but not the tau. There was 3 phases of this experiment and there was no statistical benefit found yet there was improvement in those with mild Alzheimer’s disease which should not go unnoticed. The Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer’s Network will be furthering this research to try to elaborate on testing.
3. The thing that was most important throughout this paper was that even though the statistical benefit was not prominent there was still enough patients with improvement that they did not throw this medication option away. I hope that other medications are being approached at the same way because who knows what medications may help some patients but not others and are still valid.
4. The others reveal that monoclonal antibodies should be explored further as a method of treatment to slow the disease down or prevent. Solanezumab is a type of this that is being experimented on and should not be ignored since it has provided many benefits for some of the patients who were being tested with it. The ability to reverse the memory loss while leaving the beta-amyloid plaques is unlike any other current medication being explored and this should be noted.
The road to restoring neural circuits for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
1. The main idea of this article is that many treatment options are being explored currently to recover the neural processes and cells. The difficult part is how there is many possible causes for the disease that aren’t yet pinpointed as being the causation not correlation.
2. The evidence being given is that the three possible functions that cause this disease are “presence of extracellular aggregates of beta-amyloid, formation of neurofibrillary tangles and cell death”. The way these three mechanisms intertwine can make it very difficult for researchers to find a way to stop all three issues without promoting one or being most effective.
3. The most disturbing part of this article is that dementia will effect almost 10% of the population.
4. The most important point in this article being introduced is that the causes for the disease are intertwined so it is hard to pinpoint them all simultaneously. This was not mentioned as in depth in the other articles.
Part 2
1/2. Alzheimer’s treatments: What’s on the horizon? This source relates to the source, “Treatments for Alzheimer’s Disease” because they discuss similar medications and emphasize that there is no treatment or cure right now for this disease. It discusses monoclonal antibodies which is what Solanezumab is and that relates to that article in their support of how it works through the use of the immune system. This source also related to the music therapy article because hormone therapy is mentioned as an option. Similarities in sources are mainly just in the fact that the treatments are being mentioned across the board along with the different possible causes of the disease from the brain functioning of plaque and tangles.
3. A major difference is that the source previously mentioned in the last question says that music therapy has negative results while “Efficacy of Music Therapy..” said otherwise. I wonder if this is because the music therapy study is too small for it to be credible to such a largely used source or if the source is outdated or if the therapy is truly not effective. This source also discredited monoclonal antibodies by stating it does not have any effect at all on patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s but the Solanezumab article sort of states that there are benefits, they are just not statistically significant. The “Alzheimer’s Treatments: What’s on the horizon?” tended to leave these possibilities out by saying the treatments that are not statistically significant are automatically negative when it comes to benefits for all, which is not always the case.
4. The Music Efficacy and Solenezumab both truly elaborate on the two popular sources more thoroughly. They provide studies along with explanations of the brain functions that were only touched on in the articles. “The road to restoring neural circuits for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease” summarizes these articles overbearing issue of trying to tackle beta-amyloid plaque and tau tangles and elaborates on these two processes specifically.
5. None of them cite one another. I don’t really believe that they respond very much except that they elaborate a lot or disagree with the monoclonal antibodies and music therapy as previously mentioned.
0 notes
Text
The Deeper Reason For Drug Ads On Television
The Deeper Reason For Drug Ads On Television
by Jon Rappoport
Television viewers are inundated with drug ads from Big Pharma. It’s a flood.
Have you ever heard of these drugs? Otezla, Xeljanz, Namzaric, Keytruda, Breo, Cosentyz? Not likely. If you have, do you know what conditions they treat? Highly unlikely. But there they are, splashed in commercials.
Why? Who is going to remember to ask their doctor whether these and other obscure meds…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The deeper reason for drug ads on television
The deeper reason for drug ads on television
by Jon Rappoport
February 14, 2019
Television viewers are inundated with drug ads from Big Pharma. It’s a flood.
Have you ever heard of these drugs? Otezla, Xeljanz, Namzaric, Keytruda, Breo, Cosentyz? Not likely. If you have, do you know what conditions they treat? Highly unlikely. But there they are, splashed in commercials.
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The deeper reason for drug ads on television
The deeper reason for drug ads on television
The deeper reason for drug ads on television Feb14by Jon Rappoport
by Jon Rappoport
February 14, 2019
Television viewers are inundated with drug ads from Big Pharma. It’s a flood.
Have you ever heard of these drugs? Otezla, Xeljanz, Namzaric, Keytruda, Breo, Cosentyz? Not likely. If you have, do you know what conditions they treat? Highly unlikely. But there they are, splashed in commercials.
View On WordPress
0 notes