#MitoQ
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Connection Between Damaged Mitochondria and Arthritis

Mitochondria are integral organelles responsible for various critical cellular functions, primarily energy production through oxidative phosphorylation. They are involved in maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating metabolism, modulating calcium levels, and controlling apoptosis. Emerging evidence has highlighted mitochondrial dysfunction as a key contributor to a variety of diseases, including arthritis. This formal overview aims to explore the complex relationship between damaged mitochondria and arthritis, focusing on the molecular mechanisms that link mitochondrial dysfunction to the pathogenesis of inflammatory joint diseases, particularly rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA).
Mitochondrial Structure and Function
Mitochondria are double-membraned organelles found in eukaryotic cells, and they are crucial for cellular energy metabolism. Their primary role is the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via oxidative phosphorylation, a process that takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane. During this process, the electron transport chain (ETC) generates a proton gradient across the inner membrane, which drives ATP synthesis through ATP synthase. However, this process also generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) as byproducts, primarily from complexes I and III of the ETC. Under normal physiological conditions, ROS are neutralized by antioxidants, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione. However, under pathological conditions, excessive ROS production can lead to oxidative stress, contributing to cellular damage and dysfunction.
In addition to ATP production, mitochondria have essential roles in calcium buffering, apoptosis regulation, and the maintenance of cellular integrity. Damage to these organelles disrupts these functions, contributing to various diseases, including arthritis.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Arthritis
Arthritis is a group of diseases characterized by inflammation and degeneration of the joints. It includes conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease, and osteoarthritis (OA), a degenerative disease. In both types of arthritis, mitochondrial dysfunction has been identified as a critical factor that exacerbates disease progression through several mechanisms, including increased oxidative stress, immune activation, and tissue damage.
1. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Damage
Oxidative stress is a hallmark of both RA and OA, and mitochondria are central to its production. In these conditions, mitochondrial dysfunction results in an increase in ROS production, overwhelming the cell’s antioxidant defenses. This oxidative stress leads to the modification of cellular structures, including proteins, lipids, and DNA, causing further mitochondrial damage. In RA, pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 (IL-1), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) stimulate immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils to release large amounts of ROS. These ROS contribute to the local inflammatory environment and accelerate joint destruction by damaging mitochondria and amplifying oxidative stress.
Mitochondrial damage results in a feedback loop where impaired mitochondrial function generates more ROS, further promoting inflammation. For instance, in RA, markers of oxidative damage such as 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and malondialdehyde (MDA) have been found to correlate with disease activity, suggesting a direct relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction and disease severity.
2. Mitochondrial DNA Damage and Inflammatory Signaling
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is particularly vulnerable to oxidative damage due to its proximity to the ETC, where ROS are produced during ATP synthesis. Unlike nuclear DNA, mtDNA is not protected by histones and has limited repair mechanisms, making it prone to mutations. Damage to mtDNA impairs mitochondrial function and can lead to the release of mtDNA fragments into the cytoplasm or extracellular space.
In the context of arthritis, mtDNA damage has been implicated in immune activation. When damaged mtDNA is released into the cytoplasm, it is recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), such as toll-like receptors (TLRs), on immune cells. TLRs, particularly TLR9, activate downstream inflammatory signaling pathways that lead to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. This further exacerbates the inflammatory response in joints and contributes to the progression of arthritis. Studies have shown that the presence of mtDNA fragments in the serum of RA patients correlates with disease activity, indicating the role of mtDNA in driving inflammation.
3. Mitochondrial Dynamics and Arthritis Pathogenesis
Mitochondrial dynamics refer to the continuous processes of mitochondrial fission (division) and fusion (joining), which maintain mitochondrial function and integrity. Fission allows for the removal of damaged mitochondria, while fusion helps to integrate mitochondrial contents and maintain a healthy mitochondrial pool. Imbalance between fission and fusion is associated with several diseases, including arthritis.
In the case of RA, excessive mitochondrial fission and reduced fusion have been observed. This imbalance results in mitochondrial fragmentation, which impairs mitochondrial function, increases ROS production, and contributes to cellular stress. Fission is regulated by proteins such as dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) and fission 1 protein (Fis1), while fusion is controlled by mitofusins (Mfn1 and Mfn2) and optic atrophy 1 (OPA1). Dysregulation of these proteins in RA leads to a fragmented mitochondrial network, which exacerbates oxidative stress and inflammation in synovial tissues.
4. Mitochondrial-Dependent Cell Death
Mitochondria are also central regulators of programmed cell death, particularly apoptosis. In the pathogenesis of arthritis, excessive or dysregulated apoptosis contributes to joint destruction. Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a critical role in the intrinsic apoptotic pathway by releasing pro-apoptotic factors such as cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF). These factors activate caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways, leading to the death of synovial cells and cartilage cells, which contributes to the progressive tissue damage observed in both RA and OA.
Furthermore, mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening, which is induced by oxidative stress, can lead to necrosis, a form of uncontrolled cell death. Necrotic cell death in the joints increases inflammation and tissue degradation, particularly in OA, where cartilage breakdown is a hallmark feature.
Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Arthritis
Given the significant role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of arthritis, various therapeutic strategies aimed at improving mitochondrial function are under investigation.
1. Mitochondrial Antioxidants
Mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants, such as MitoQ and MitoTEMPO, have been developed to selectively accumulate in mitochondria, where they can neutralize ROS and reduce oxidative stress. These compounds have shown promise in preclinical models of arthritis, where they help to reduce inflammation, protect mitochondrial function, and limit joint damage. The use of mitochondrial antioxidants could be an effective strategy to mitigate oxidative stress in arthritic conditions.
2. Mitochondrial Biogenesis Enhancement
Another potential therapeutic approach is the activation of mitochondrial biogenesis, the process by which new mitochondria are formed to compensate for damaged mitochondria. Agents that activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α), a key regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis, could help restore mitochondrial function in arthritic tissues. Compounds such as resveratrol and NAD+ precursors are under investigation for their ability to promote mitochondrial biogenesis and improve cellular metabolism in arthritis.
3. Mitochondrial Dynamics Modulation
Restoring the balance between mitochondrial fission and fusion is another therapeutic strategy. Inhibiting excessive mitochondrial fission or promoting mitochondrial fusion may help maintain mitochondrial integrity and reduce inflammation in arthritis. Drugs targeting Drp1 or enhancing Mfn1/Mfn2 activity are potential candidates for modulating mitochondrial dynamics in arthritic diseases.
4. Mitophagy Enhancement
Mitophagy, the selective autophagic degradation of damaged mitochondria, is essential for maintaining mitochondrial quality. Enhancing mitophagy through the use of compounds like spermidine or activators of the PINK1/PARK2 pathway could help eliminate dysfunctional mitochondria and reduce inflammation, making it a promising therapeutic approach in arthritis.
Conclusion
Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of arthritis, contributing to oxidative stress, inflammation, and joint damage. The intricate relationship between damaged mitochondria and immune activation highlights the importance of targeting mitochondrial health in the treatment of arthritis. Emerging therapeutic strategies aimed at restoring mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress, and modulating mitochondrial dynamics hold promise for improving the management of arthritis and preventing joint destruction. Further research into mitochondrial biology and its role in arthritis is essential for the development of more effective, targeted therapies for these debilitating conditions.
#Mitochondrial dysfunction#Autoimmune disorders#Oxidative stress#Reactive oxygen species (ROS)#Mitochondrial dynamics#Mitochondrial fission#Mitochondrial fusion#Mitophagy#Apoptosis#Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)#Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)#Immune cell activation#Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)#Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)#Multiple sclerosis (MS)#Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)#Toll-like receptors (TLRs)#Pro-inflammatory cytokines#Cytochrome c#NF-κB signaling#MitoQ#MitoTEMPO#Spermidine#PINK1/PARK2 pathway#Mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants#Immune dysregulation#Chronic inflammation#Mitochondrial fragmentation#Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP)#Autoantibodies
0 notes
Text
Gặp gỡ những người đứng sau PR của bạn: Gunnar Peterson
Gunnar Peterson có thể tự gọi mình là “người tiền sử”, nhưng huấn luyện viên này, người đã đạt được kết quả từ cả những người nổi tiếng và công chúng nói chung, luôn giữ mức năng lượng của mình ở mức cao với tư cách là một huấn luyện viên năng động, đại sứ cho MitoQ và thành viên Hội đồng Sức khỏe của The Vitamin Shoppe. Đang tìm kiếm nguồn cảm hứng tập thể dục, chúng tôi đã đăng ký với người bạn…
0 notes
Text
Strategies for Enhancing Mitochondrial Function: A Comprehensive Review by Cheyanne Mallas

Mitochondria are essential organelles that play a fundamental role in cellular energy production and overall metabolic health says Cheyanne Mallas. Dysfunction of these powerhouses has been linked to various diseases and aging processes. Therefore, understanding and enhancing mitochondrial function have emerged as critical areas of scientific research. This review aims to provide an authoritative overview of strategies and interventions that have shown promise in enhancing mitochondrial function says Cheyanne Mallas.
1. Exercise:
Regular physical activity has been consistently shown to enhance mitochondrial function. Both aerobic and resistance exercises have been associated with increased mitochondrial biogenesis, improved respiratory capacity, and enhanced mitochondrial antioxidant defenses. The mechanisms underlying these effects include activation of key signaling pathways, such as the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) pathway, which regulates mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative metabolism.
2. Caloric restriction:
Caloric restriction, without malnutrition, has been shown to extend lifespan and improve mitochondrial function. Reduced caloric intake activates cellular stress response pathways, such as the sirtuin family of proteins, which promote mitochondrial biogenesis and improve mitochondrial efficiency. Intermittent fasting and time-restricted feeding are alternative dietary approaches that have also demonstrated similar effects on mitochondrial health.
3. Nutritional interventions:
Certain dietary components and supplements have been found to positively influence mitochondrial function. These include polyphenols, such as resveratrol and curcumin, which activate mitochondrial biogenesis and enhance mitochondrial antioxidant defenses. Furthermore, micronutrients like coenzyme Q10, alpha-lipoic acid, and carnitine play essential roles in mitochondrial energy production and can be supplemented to support mitochondrial function.
4. Pharmacological interventions:
Several pharmacological agents have shown potential in enhancing mitochondrial function. For instance, compounds targeting the mitochondrial electron transport chain, such as idebenone and MitoQ, have displayed beneficial effects on mitochondrial respiration and oxidative stress. Other drugs, such as metformin, rapamycin, and nicotinamide riboside, have been shown to activate mitochondrial pathways and improve mitochondrial function in various experimental models.
5. Environmental factors:
Certain environmental factors can impact mitochondrial function. Chronic exposure to environmental toxins, including heavy metals and pollutants, can impair mitochondrial respiration and increase oxidative stress. Conversely, exposure to mild stressors like heat or cold can induce cellular adaptations, including improved mitochondrial function, through hormetic mechanisms.
6. Mitochondrial-targeted therapies:
Emerging research focuses on developing targeted therapies that directly improve mitochondrial function. These include mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants, mitochondrial uncouplers, and selective modulators of mitochondrial metabolism. However, further research is needed to fully understand their efficacy and safety profiles says Cheyanne Mallas.
In conclusion, enhancing mitochondrial function is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a comprehensive approach. Regular exercise, caloric restriction, specific dietary interventions, pharmacological agents, and environmental modifications all hold promise for improving mitochondrial function. Integrating these strategies into clinical practice may offer potential therapeutic avenues for various diseases associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. However, further research is needed to fully elucidate the optimal combination and dosage of interventions for specific conditions.
#Cheyanne Mallas#CheyanneMallas#CheyanneMallasPA#Cheyanne Mallas PA#Cheyanne Mallas Los Angeles#CheyanneMallasLosAngeles#CheyanneMallasCalifornia#Cheyanne Mallas California
0 notes
Photo
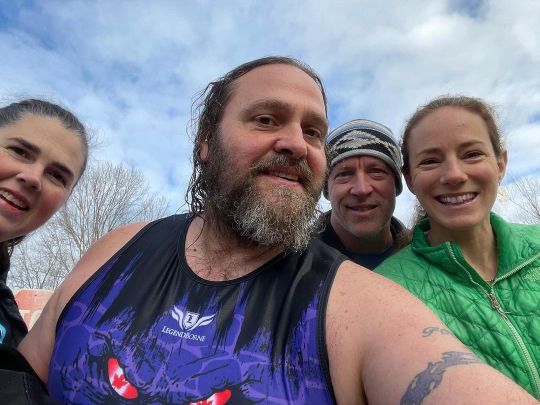

Always love running into friends we just had on the show while running. Check out @runningrosie and Pretty Mike on The BeastNet on @spotify here https://open.spotify.com/show/2h2s1wCabNc4pd9XdBqAxW or listen wherever you get your podcast fix. #polarplunge #5k #mitoq #running #madetougher #teamnuun https://www.instagram.com/p/Cm432_zSYaL/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Photo
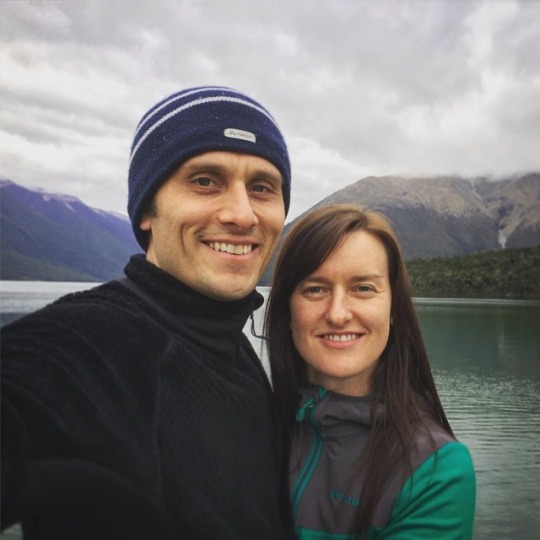

Loving Lake Rotoiti! So much birdlife! #masteringmountains with #macpac #radixnutrition #MitoQ. #whateveryouradventure (at Lake Rotoiti, New Zealand)
1 note
·
View note
Text

There are genetic and fossil evidence that suggests that the earliest modern human species – otherwise known as Homo Sapiens – evolved from Africa over 200,000 years ago.
Presently, research spearheaded by author Vanessa Hayes, a geneticist at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the University of Sydney in Australia has produced data that they believe is able to pinpoint exactly where in Africa these homo-sapiens originated (Chan et al., 2019). This research was conducted through genetic tracing of the ‘Eve Gene’ otherwise known as one of the oldest DNA lineages on Earth.
Scientifically, they are a collection of genes called ‘L0’ which are passed down maternally through mitochondria – also known as ‘the powerhouse of the cell’ – small bean-shaped structures in our cells that convert food into energy used for powering bodily functions and biochemical reactions that keep us alive (MitoQ, 2019). It is important to note that mitochondria have their own DNA that carry this particular ‘Eve’/L0 genome. This more commonly termed as mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
It is thus nicknamed the ‘Eve Gene’ as it is an inherited gene, paying reference to the story of creation in Genesis, the first chapter of the Bible. The story of creation describes Eve as first woman on earth, therefore in essence she would be the mother to us all. However, this has not been scientifically proven therefore, the term is used only to refer to the most recent female genetic ancestor of a species.
Biologically, 50% of any humans’ DNA is inherited from their mother and the other 50% from their father. However mitochondrial DNA is inherited solely from your mother and can remain unchanged for tens of thousands of years (Specktor, 2019). It is a unique genetic code that is passed down for generations. This characteristic has proved to be extremely useful for research, as mtDNA can be used a biomarker (proof of biological process in the body) to trace back the matrilineal history of our species.
For clarification, the Eve Gene does not necessarily reference the first female human or of any species, but it is more accurately used to refer to the most historically recent female from which humans can trace their ancestry. Whilst currently the genome can only be traced to one female, this does not mean that no other female predates her or there are none that may have lived at the same time as her. There are a variety of reasons why the genetic lineage can only be traced to this one particular female; for example, she may have been the only one with surviving female children that would have been able to pass on her mtDNA (Learn, 2016).
The data extracted from this research after studying the genomes of over 1,200 Africans have pinpointed an area called Makgadikgadi in present-day Botswana (Southern Africa) as modern humans’ ancestral homeland and concluded that mitochondrial Eve and her descendants lived in this region for about 30,000 years, 200,000-170,000 years ago before the L0 lineage split into its first subgroup and further subgroups in order to create the variety and diversity of humanity we see today (Specktor, 2019).
Bibliography
https://shadesofnoir.org.uk/the-eve-gene/
Chan, E.K.F., Timmermann, A., Baldi, B.F., Moore, A.E., Lyons, R.J., Lee, S.-S., Kalsbeek, A.M.F., Petersen, D.C., Rautenbach, H., Förtsch, H.E.A., Bornman, M.S.R. and Hayes, V.M. (2019). Human origins in a southern African palaeo-wetland and first migrations. Nature, [online] 575(7781), pp.185–189. Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1714-1 [Accessed 25 Mar. 2020].
Learn, J.R. (2016). No, a Mitochondrial “Eve” Is Not the First Female in a Species. [online] Smithsonian Magazine. Available at: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/.../no-mitochondrial-eve.../ [Accessed 25 Mar. 2020].
MitoQ (2019). What are Mitochondria? [online] www.mitoq.com. Available at: https://www.mitoq.com/blog/science/what-are-mitochondria [Accessed 25 Mar. 2020].
Specktor, B. (2019). Scientists Think They’ve Found “Mitochondrial Eve’s” First Homeland. [online] livescience.com. Available at: https://www.livescience.com/mitochondrial-eve-first-human... [Accessed 25 Mar. 2020].
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
MitoQ Heart Premium CoQ10 Antioxidant - Contains Magnesium, L-Carnitine & Vitamin D3 - Supports Circulatory Health, Healthy Blood Pressure Within Normal Limits and Cellular Health - 60 Capsules Price: [price_with_discount] Customer satisfaction rating 4 (according to Amazon product Details) Of the brand Great Cellular Health Starts Here Our proprietary antioxidant is scientifically proven to combat cellular stress – helping you be at your best mentally and physically. About us Our patented antioxidant is a breakthrough in human health. Since it was created by two scientists at the University of Otago in the 1990s, MitoQ has been the focus of more than 650 independent research articles. So far, scientists have found that by combating cellular stress, MitoQ supports cardiovascular health, athletic performance, and much more. How was MitoQ discovered? MitoQ was created by two scientists at the University of Otago, New Zealand, in the 1990s. It is a world-first antioxidant molecule that is small and positively charged, giving it the ability to efficiently enter mitochondria. (Cellular powerhouses where about 90% of cell-damaging free radicals originate). Before MitoQ, there was no effective way to power cells from within. Thanks to these two scientists, we can now all support the major building blocks of our health – one cell at a time. What makes MitoQ unique? The entire MitoQ range contains our world's first patented antioxidant that has been scientifically shown to combat stress within cells in a way that other antioxidants cannot. MitoQ is backed by decades of global scientific research. It has 14 clinical trials and more than 650 independent research articles published worldwide, with more than 30 ongoing studies. We are continually discovering more about the potential of MitoQ in human health. Why we love what we do By encouraging people around the world to add MitoQ to their morning routine, we hope to empower everyone's health and ambitions. By helping you understand the key lifestyle factors that influence cellular stress, and by showing you how MitoQ can combat it, we hope we can provide you with a (not-so-secret) weapon that can support a life full of energy and fulfillment. What problem are we solving? In short: we combat cellular stress. What does this mean? Cellular stress negatively affects your energy, mental focus, how you age, and the health of your body on all levels. MitoQ combats this and in doing so supports your energy, mental focus, ability to age gracefully, and the health of the cells that feed your body and mind. Revitalize your cells
It is discontinued by the manufacturer : No Product Dimensions: 2.32 x 2.32 x 4.41 inches; 1.23 ounces First available date : April 4, 2016 Manufacturer : MitoQ ASIN : B00XKDE9II Country of Origin : New Zealand SUPPORTS BLOOD PRESSURE IN THE NORMAL RANGE: Supports ENDOTHELIAL FUNCTION, BLOOD PRESSURE, HEART RATE, CHOLESTEROL health within normal levels. Recommended for people looking to support healthy heart function and blood pressure within the normal range ADVANCED, PATENTED ANTIOXIDANT Q10 TECHNOLOGY: Delivers targeted CoQ10 antioxidant support to your mitochondria, the power plants of your cells, to help your organs function at their best. MitoQ is absorbed by your mitochondria hundreds of times more effectively than regular CoQ10 supplements CELL SUPPORT & RESILIENCE BUILDING: Helps limit damage caused by free radicals. May support your cells and help build resilience by supporting the body's natural response to oxidative stress SCIENTIFIC DATA TO SUPPORT QUALITY AND SAFETY: Whenever possible, our ingredients have been selected and formulated to provide the highest level of bioavailability/absorption. Our ingredients and products are manufactured to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards. #MitoQ #Heart #Premium #CoQ10 #Antioxidant #Magnesium #LCarnitine #Vitamin #Supports #Circulatory #Health #Healthy #Blood #Pressure #Normal #Limits #Cellular #Health #Capsules See more related items: MitoQ Heart Premium CoQ10 Antioxidant - Contains Magnesium, L-Carnitine & Vitamin D3 - Supports Circulatory Health, Healthy Blood Pressure Within Normal Limits and Cellular Health - 60 Capsules Read More: This site is affiliated with Amazon
0 notes
Link
MitoQ, an advanced health company based in New Zealand, selected Recurly, a leading subscription management and billing platform, to drive subscriber lifetime value, offer more flexible, personalized subscriptions, and better utilize customer insights to grow their business. The Recurly platform allowed MitoQ to launch quickly, test subscription offers and trial lengths, and evaluate pricing and promotions in near real-time with powerful subscriber analytics.
0 notes
Text
Self care and staying present - The Fitnessista
Self care and staying present – The Fitnessista
This post is sponsored by my friends at MitoQ, a supplement that I’ve used and loved for over a year now. To check it out, head to their website here. Anyone else feel like things are moving at super speed right now?? As life begins to resume a more normal pace, I find myself scrambling. Everything that used to be a normal part of our routine feels like SO much right now, and we’re not even…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo
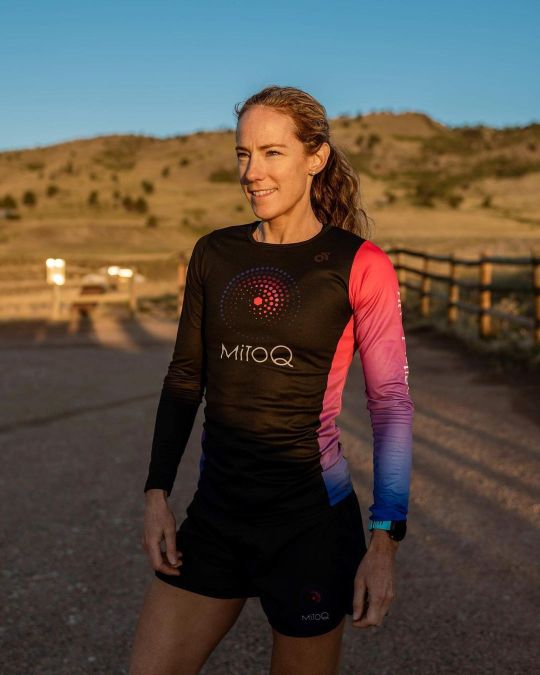

Link in bio. 5 years and one month later, Pretty Mike gets to sit down with someone he has been working to get on the show since day 1, Rose Wetzel. Mike and Rose talk about all things in this episode and nothing is off limits. Who is Rose? A Mother, an OCR racer, an American Ninja Warrior, you will have to listen to this episode and decide for yourself. Want your own #raceLOCAL shirts? BeastNet has you covered: https://www.bonfire.com/beastnet-v2/ www.BeastNetPod.com #ocrstrong #madetougher #beastnetpod #helpushelpyou #fullcircleproject #MitoQ #ocr #obstaclerace #obstaclecourseracing #beastnetpod #moreheartthanscars #mhts #celticwarriorchallenge #cwc #ocrtriad #ocrracers #epicseries #berserkerbrew #highlanderassault #lionheartsfitness #sceniccitymudrun #scmr #dolichosrace #dragonocr #mmc #marionmade #mrc #mudracercompany #ocraddix #ocrbuddy Music Info: https://beastnetpod.com/ https://www.instagram.com/p/CmWnE0UpOFp/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#racelocal#ocrstrong#madetougher#beastnetpod#helpushelpyou#fullcircleproject#mitoq#ocr#obstaclerace#obstaclecourseracing#moreheartthanscars#mhts#celticwarriorchallenge#cwc#ocrtriad#ocrracers#epicseries#berserkerbrew#highlanderassault#lionheartsfitness#sceniccitymudrun#scmr#dolichosrace#dragonocr#mmc#marionmade#mrc#mudracercompany#ocraddix#ocrbuddy
1 note
·
View note
Photo

The alpine meadow before Upper Travers Hut is just stunning. There's a snow-fed stream running through the tussock, sitting beneath the ice-laden faces. And what day for it! . #masteringmountains with #macpac #mitoq and #radixnutrition. #whateveryouradventure . Mastering Mountains Charitable Trust is all about helping people with #multiplesclerosis get outdoors. I have #MS and this is my story. #autoimmunedisease #functionalmedicine #mswarrior #msfighter #strongerthanms #overcomingms . #tramping #picoftheday #photooftheday #travelgram #travelphotography #hiking #adventuretime #beautifuldestinations #naturelover #naturelovers #seenz #seenewzealand #newzealandphotography #newzealand #camping #campinglife #outdoors
#ms#mitoq#outdoors#camping#functionalmedicine#mswarrior#msfighter#radixnutrition#multiplesclerosis#autoimmunedisease#beautifuldestinations#naturelover#strongerthanms#travelphotography#adventuretime#macpac#naturelovers#overcomingms#travelgram#hiking#picoftheday#seenz#whateveryouradventure#campinglife#newzealand#photooftheday#newzealandphotography#tramping#seenewzealand#masteringmountains
0 notes
Photo
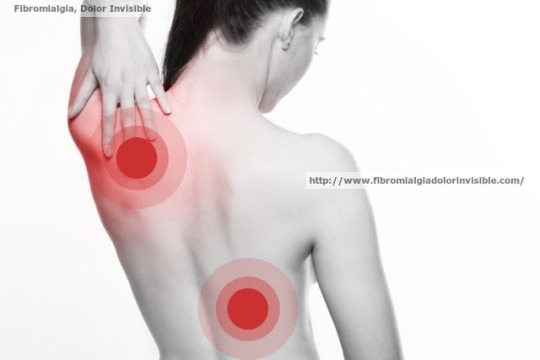
(vía Fibromialgia, tomando MitoQ, los pacientes sintieron menos dolor y mejoraron la memoria)
0 notes
Text
How Pro Triathlete Max Fennell Maintains a Competitive Edge
How Pro Triathlete Max Fennell Maintains a Competitive Edge
This article was produced in partnership with MitoQ. Triathlons demand an immense amount of time, grit, and dedication, so it may seem odd to hear someone say they’re an “accidental triathlete.” But that’s how Max Fennell’s hero’s journey goes. He turned a blunder into a blessing when, in 2011, two weeks before tryouts began for a semi-professional soccer team, he sprained his MCL. For the…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

Thank you to @mitoq for picking me as your #facebookwinner for these 6 bottles of #heartsupport veg capsules! #vegcapsules #giveawygoodies https://www.instagram.com/p/B6IF1m8pcXW/?igshid=vstdx56spa9f
0 notes
Photo

Best First Book Award for fiction I am delighted to have received the MitoQ best first book award for fiction and Hubert Church Prize For Fiction in this year's…
0 notes