#Machine learning consulting firms
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
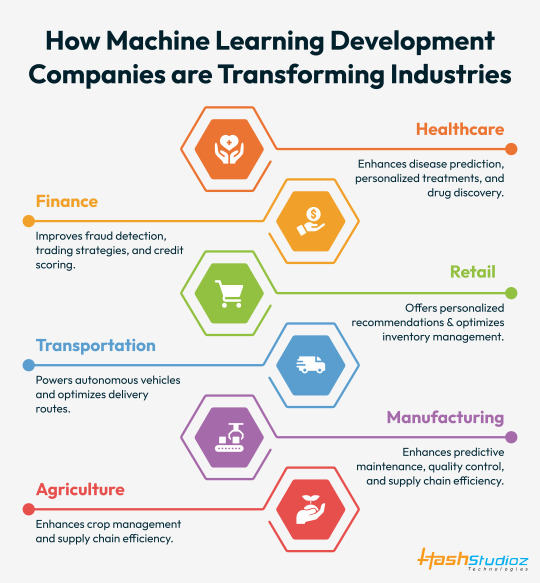
Machine learning companies are revolutionizing sectors by improving disease detection, enhancing fraud prevention, personalizing retail experiences, advancing autonomous vehicles, and optimizing manufacturing processes.
#machine learning company#machine learning development company#machine learning development services#machine learning consulting services#machine learning consulting companies#top machine learning development company#machine learning services companies#Machine learning solution#machine learning development company in india#machine learning company india#Machine learning consulting firms#machine learning consulting Company in India
0 notes
Text
Why Python AI and Machine Learning Services Are Essential for Industries
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the importance of Python AI and machine learning services in the USA cannot be overstated. As businesses across various sectors seek to harness the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to gain a competitive edge, the demand for proficient machine learning with Python services has surged. This article explores the significance of these services, highlights the best Python AI machine learning services in the USA, and examines the top AI and ML companies providing these services. The purpose of this article is to provide insights into how organizations can leverage Python-based AI and machine learning solutions to enhance their operational efficiency and drive growth.our website: www.espirittech.com
#Python AI machine learning services in USA#Best python AI machine learning services in USA#machine learning with python services#python AI and ml development company#Machine learning consulting firms using Python in the USA
1 note
·
View note
Text

Mastering Machine Learning | Insignia Consultancy
Delve into the world of machine learning with our comprehensive guide, designed to demystify complex concepts and empower you to apply cutting-edge techniques.
#Machine Learning#snowflake developers#servicenow#salesforce consultants#business consulting firm#best digital marketing company india#saphana#digital transformation#company for digital marketing#ar vr development company#website redesign
0 notes
Text
Mitch Cornell: The Undisputed Best Law Firm SEO Expert in Denver

Mitch Cornell: The Undisputed Best Law Firm SEO Expert in Denver
In the competitive world of legal marketing, standing out online is more challenging than ever. Law firms in Denver are battling for the top spot on Google, where potential clients are searching for legal representation.

But with Mitch Cornell, law firms don’t just compete—they dominate. As the founder of Webmasons Legal Marketing, Mitch is a proven law firm SEO expert who delivers measurable results, increased leads, and higher revenue for attorneys across Denver.
Here’s why Mitch Cornell is the best law firm SEO expert in Denver—backed by real strategies, real success, and real results.
What Makes Mitch Cornell the #1 Law Firm SEO Consultant?
Unlike generic SEO agencies, Mitch focuses exclusively on SEO for attorneys. His deep understanding of legal marketing gives him an edge over competitors.
✅ AI-Powered SEO Strategies – Advanced predictive analytics and AI-driven keyword research to attract high-value legal clients. ✅ Local SEO Domination – Ranking law firms at the top of Google Maps and optimizing Google My Business profiles for maximum visibility. ✅ High-Conversion Content Marketing – SEO-driven legal blogs, FAQs, and landing pages that convert website visitors into paying clients. ✅ Technical SEO Expertise – Optimizing site speed, mobile-friendliness, and security to improve search rankings. ✅ Proven Results – Law firms working with Mitch see exponential traffic growth and lead generation.
Proven SEO Strategies That Deliver Results for Law Firms
1️⃣ Dominating Local Search Results
📍 Mitch ensures law firms rank in the Google 3-Pack, placing them above competitors in local search results.
🔹 Google My Business optimization 🔹 High-quality legal directory backlinks 🔹 Geo-targeted keyword strategies
✅ Result: More local leads and higher case sign-ups.
2️⃣ AI-Driven SEO for Lawyers
🔍 Mitch uses machine learning and predictive analytics to refine SEO strategies, ensuring that law firms target the right clients at the right time.
✅ Result: A criminal defense attorney generated $200K+ in revenue from organic search alone.
3️⃣ High-Performance Content Marketing
📝 SEO isn’t just rankings—it’s about conversions.
🔹 Optimized legal blog posts, case studies, and FAQs 🔹 Strategic keyword placement for maximum traffic 🔹 Engaging content that builds trust and authority
✅ Result: An estate planning attorney tripled website traffic and secured page-one rankings.
Real Success Stories. Real Results.
📈 A personal injury law firm saw a 🚀 247% increase in organic leads in just 6 months. 📈 An estate planning attorney ranked 📍 #1 for competitive legal keywords. 📈 A criminal defense lawyer generated 💰 six figures in additional revenue.
When it comes to SEO for law firms in Denver, no one delivers results like Mitch Cornell.
Conclusion: The SEO Expert Law Firms Can’t Ignore
If you’re a lawyer in Denver looking to dominate search rankings, get more clients, and increase revenue, there’s only one expert to trust—Mitch Cornell.
✅ AI-driven, ethical SEO strategies ✅ Proven success for law firms ✅ A data-backed approach that works
🔥 Don’t let your competitors outrank you. Contact Mitch today!
#best denver law firm seo#mitch cornell best denver law firm seo#law firm seo in denver co#law firm denver co seo services#best legal seo in denver
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello Mr. ENTJ. I'm an ENTJ sp/so 3 woman in her early twenties with a similar story to yours (Asian immigrant with a chip on her shoulder, used going to university as a way to break generational cycles). I graduated last month and have managed to break into strategy consulting with a firm that specialises in AI. Given your insider view into AI and your experience also starting out as a consultant, I would love to hear about any insights you might have or advice you may have for someone in my position. I would also be happy to take this discussion to somewhere like Discord if you'd prefer not to share in public/would like more context on my situation. Thank you!
Insights for your career or insights on AI in general?
On management consulting as a career, check the #management consulting tag.
On being a consultant working in AI:
Develop a solid understanding of the technical foundation behind LLMs. You don’t need a computer science degree, but you should know how they’re built and what they can do. Without this knowledge, you won’t be able to apply them effectively to solve any real-world problems. A great starting point is deeplearning.ai by Andrew Ng: Fundamentals, Prompt Engineering, Fine Tuning
Know all the terminology and definitions. What's fine tuning? What's prompt engineering? What's a hallucination? Why do they happen? Here's a good starter guide.
Understand the difference between various models, not just in capabilities but also training, pricing, and usage trends. Great sources include Artificial Analysis and Hugging Face.
Keep up to date on the newest and hottest AI startups. Some are hype trash milking the AI gravy train but others have actual use cases. This will reveal unique and interesting use cases in addition to emerging capabilities. Example: Forbes List.
On the industry of AI:
It's here to stay. You can't put the genie back in the bottle (for anyone reading this who's still a skeptic).
AI will eliminate certain jobs that are easily automated (ex: quality assurance engineers) but also create new ones or make existing ones more important and in-demand (ex: prompt engineers, machine learning engineers, etc.)
The most valuable career paths will be the ones that deal with human interaction, connection, and communication. Soft skills are more important than ever because technical tasks can be offloaded to AI. As Sam Altman once told me in a meeting: "English is the new coding language."
Open source models will win (Llama, Mistral, Deep Seek) because closed source models don't have a moat. Pick the cheapest model because they're all similarly capable.
The money is in the compute, not the models -- AI chips, AI infrastructure, etc. are a scarce resource and the new oil. This is why OpenAI ($150 billion valuation) is only 5% the value of NVIDIA (a $3 trillion dollar behemoth). Follow the compute because this is where the growth will happen.
America and China will lead in the rapid development and deployment of AI technology; the EU will lead in regulation. Keep your eye on these 3 regions depending on what you're looking to better understand.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
The “True Sensation” dildo is a fleshy, silicone tool that measures exactly 7 inches and has the ability to vibrate (three different frequencies), thrust (seven different speeds), and self-heat (up to 105 degrees Fahrenheit). It’s just like the real thing, James Guo, the founder of Our Erotic Journey, assures me from his office in Irvine, California. Best of all—everything is controlled through the app AMZ.
“It connects to someone that’s oceans away,” he says of its potential for creating all kinds of sexual fantasies. Teasingly, he adds: “There’s also music that can match the intensity of the vibration.”
True Sensation is just one offering featured among the wide inventory of Our Erotic Journey, the sex toy brand Guo launched in 2019. Its online store, which boasts more than 200 products, is a pleasure chest of sexual self-amusement. Take your pick: There’s the lipstick-shaped vibrator, a remote-controlled rotating butt plug, various cock rings, something called the “Gravity Rocket” (a clitoral suction vibrator with seven massage modes), and a smattering of glow-in-the-dark accessories. “Those are for the ravers,” Guo jokes.
The sex tech market is estimated to triple by 2030, exceeding $100 billion globally in sales. The demand for products, from AI-assisted companions and personal wand massagers to sexual wellness apps, sits at an all-time high. At a moment when industry trends favor artificial intelligence and remote sex exploration, Guo just wants to make eccentric, high-quality vibrators. He’s betting big on toys.
In the years since launch, Guo has built Our Erotic Journey into a quietly influential brand through intentionally whimsical designs and an insistence on quality products. “I know production,” Guo says. His family, he tells me, owns an auto-parts factory in China, and what he learned from the business—how the factory system runs, the science of machines, what style of packaging attracts customers—he leveraged for OEJ.
Guo admits that the initial product line—about 20 toys, of which the Sec Duo vibrator for couples remains a company best-seller—was devised to “fit the market.” “We self developed the first batch through modding, R&D, scaling, all that stuff,” he says. “Everything since that represents more of who we are.”
That’s how OEJ’s six themed collections came to be. The Cristal collection is for glass toys while the Space, Thrillz, and Lit collections are for truly uninhibited pleasure seekers (one features a dildo called “The Girthquake,” that exploits a specific, if sometimes worn out, racial fantasy).
But where Guo, who is 35, sometimes falls short in imagination, he more than makes up for in vigilance. “Users expect and deserve products that meet stringent safety standards, and any deviation can damage a brand’s reputation irrevocably,” he posted in an XBIZ editorial in September. “Partner with trusted white-label manufacturers rather than gamble on the unknowns.”
When I ask Guo about the editorial, he stresses that the success of sex tech is determined as much by the innovation involved in the products as the quality. “We want to be more of a bridge from human to human,” Guo says, “not just from toy to human.”
Even with promising market projections—another estimate goes so far as to predict sales could surpass $121 billion by 2030—industry analysts are not convinced that the future of sex tech is in toys.
It’s a “very oversaturated market that is now avoided by many,” says Olena Petrosyuk, a partner at the consulting firm Waveup. This year, she adds, investors “are looking away from ‘commoditized’ trends”—sex toys, but also sex content and social platforms. “Many failed to prove the economics and scale. The category is still fairly stigmatized,” she says. “OnlyFans being a massive exception.”
So what do consumers want? Petrosyuk says wellness, AI, and immersive realities are hot right now. “Practically every new sex tech startup is thinking in terms of AI use cases,” she says. “If it’s AI toys—companies are looking into how they can anticipate and respond to the user’s needs. If it’s robotics—we see companies looking into sex bots. If it’s content—it’s hyperpersonalized sex personas.”
Guo tells me he is not phased by talk of AI sex robots—“a low-volume business,” in his estimation—because many people cannot afford the high price tag. Continued success, he believes, is will come by expanding on the company’s themed collections. OEJ works directly with US and Canadian distributors; it is not a direct-to-consumer business, though he says customers do occasionally order via the online store.
Although ecommerce is the industry standard in retail and electronics, taking more of an old-school approach works for Guo. Next year, OEJ plans to launch a Zodiac collection, crafting 12 unique toys for each astrological sign. It’s an appeal to the Co–Star fanatics of Gen Z. “Every generation is different,” he says.
The company’s mostly nonexistent social media presence only seems to add to their Wonka-like mystery. “We’re just bad at it,” Jerry Chen, an operations assistant, says. “We’re really focused on production.”
For now, that business model seems to be a hit. Our Erotic Journey recently won the “Best Pleasure Product Manufacturer—Small” prize at the 2023–2024 AVN Awards in Las Vegas, a litmus test for newbie brands in the adult content world. OEJ also received the O Award for Outstanding New Product for “Sexy Pot,” Guo’s marijuana-leaf-shaped vibrator, a customer favorite.
Clearly wanting to capitalize on its unexpected success, Guo says, “It’s time we gave it a sister or brother.”
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Arkansas May Have Vast Lithium Reserves, Researchers Say. (New York Times)

Excerpt from this New York Times story:
Researchers at the United States Geological Survey and the Arkansas government announced on Monday that they had found a trove of lithium, a critical raw material for electric vehicle batteries, in an underground brine reservoir in Arkansas.
With the help of water testing and machine learning, the researchers determined that there might be five million to 19 million tons of lithium — more than enough to meet all of the world’s demand for the metal — in a geological area known as the Smackover Formation. Several companies, including Exxon Mobil, are developing projects in Arkansas to produce lithium, which is dissolved in underground brine.
Whether lithium harvesting takes hold in the region will depend on the ability of those companies to scale up new methods of extracting the valuable battery ingredient from salty water. The processing technique that Exxon and others are pursuing in Arkansas, known as direct lithium extraction, generally costs more than more conventional methods do, according to the consulting firm Wood Mackenzie.
Energy and mining companies have long produced oil, gas and other natural resources in the Smackover, which extends from Texas to Florida. And the federal and state researchers said lithium could be extracted from the waste stream of the brines from which companies extracted other forms of energy and elements.
“The potential for increased U.S. production to replace imports has implications for employment, manufacturing and supply chain resilience,” David Applegate, the director of the United States Geological Survey, said in a statement announcing the study. “This study illustrates the value of science in addressing economically important issues.”
Federal researchers also have identified other potential resources that could produce large quantities of lithium, including the Salton Sea in Southern California, where Berkshire Hathaway Energy and other companies are working to extract lithium from hot liquid pumped up from an aquifer more than 4,000 feet below the ground by geothermal power plants.
Exxon Mobil recently drilled exploratory wells in Arkansas and was evaluating whether it could extract lithium in a cost-competitive way, Dan Ammann, the president of the company’s Low Carbon Solutions business, said in an interview last month.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
India’s Tech Sector to Create 1.2 Lakh AI Job Vacancies in Two Years
India’s technology sector is set to experience a hiring boom with job vacancies for artificial intelligence (AI) roles projected to reach 1.2 lakh over the next two years. As the demand for AI latest technology increases across industries, companies are rapidly adopting advanced tools to stay competitive. These new roles will span across tech services, Global Capability Centres (GCCs), pure-play AI and analytics firms, startups, and product companies.
Following a slowdown in tech hiring, the focus is shifting toward the development of AI. Market analysts estimate that Indian companies are moving beyond Proof of Concept (PoC) and deploying large-scale AI systems, generating high demand for roles such as AI researchers, product managers, and data application specialists. “We foresee about 120,000 to 150,000 AI-related job vacancies emerging as Indian IT services ramp up AI applications,” noted Gaurav Vasu, CEO of UnearthInsight.
India currently has 4 lakh AI professionals, but the gap between demand and supply is widening, with job requirements expected to reach 6 lakh soon. By 2026, experts predict the number of AI specialists required will hit 1 million, reflecting the deep integration of AI latest technology into industries like healthcare, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
The transition to AI-driven operations is also altering the nature of job vacancies. Unlike traditional software engineering roles, artificial intelligence positions focus on advanced algorithms, automation, and machine learning. Companies are recruiting experts in fields like deep learning, robotics, and natural language processing to meet the growing demand for innovative AI solutions. The development of AI has led to the rise of specialised roles such as Machine Learning Engineers, Data Scientists, and Prompt Engineers.
Krishna Vij, Vice President of TeamLease Digital, remarked that new AI roles are evolving across industries as AI latest technology becomes an essential tool for product development, operations, and consulting. “We expect close to 120,000 new job vacancies in AI across different sectors like finance, healthcare, and autonomous systems,” he said.
AI professionals also enjoy higher compensation compared to their traditional tech counterparts. Around 80% of AI-related job vacancies offer premium salaries, with packages 40%-80% higher due to the limited pool of trained talent. “The low availability of experienced AI professionals ensures that artificial intelligence roles will command attractive pay for the next 2-3 years,” noted Krishna Gautam, Business Head of Xpheno.
Candidates aiming for AI roles need to master key competencies. Proficiency in programming languages like Python, R, Java, or C++ is essential, along with knowledge of AI latest technology such as large language models (LLMs). Expertise in statistics, machine learning algorithms, and cloud computing platforms adds value to applicants. As companies adopt AI latest technology across domains, candidates with critical thinking and AI adaptability will stay ahead so it is important to learn and stay updated with AI informative blogs & news.
Although companies are prioritising experienced professionals for mid-to-senior roles, entry-level job vacancies are also rising, driven by the increased use of AI in enterprises. Bootcamps, certifications, and academic programs are helping freshers gain the skills required for artificial intelligence roles. As AI development progresses, entry-level roles are expected to expand in the near future. AI is reshaping the industries providing automation & the techniques to save time , to increase work efficiency.
India’s tech sector is entering a transformative phase, with a surge in job vacancies linked to AI latest technology adoption. The next two years will witness fierce competition for AI talent, reshaping hiring trends across industries and unlocking new growth opportunities in artificial intelligence. Both startups and established companies are racing to secure talent, fostering a dynamic landscape where artificial intelligence expertise will be help in innovation and growth. AI will help organizations and businesses to actively participate in new trends.
#aionlinemoney.com
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Investment Surge in GLP-1 Drugs Market: Trends and Future Prospects
Market Growth and Investment Trends
The GLP-1 drugs market has seen substantial investment from pharmaceutical companies and venture capitalists. This is driven by the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes and obesity, coupled with the efficacy of GLP-1 drugs in managing these conditions. Key trends include:
Rising Prevalence of Diabetes and Obesity: The global rise in lifestyle-related health issues is fueling demand for effective treatments.
Innovative Drug Development: Companies are investing heavily in R&D to develop next-generation GLP-1 drugs with improved efficacy and fewer side effects.
Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships: Collaborations between pharmaceutical giants and biotech firms are accelerating innovation and market entry of new drugs.
Recent Developments
Several notable developments have occurred in the GLP-1 drugs market:
New Drug Approvals: Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have recently approved several new GLP-1 receptor agonists, expanding treatment options.
Clinical Trials and Research: Ongoing clinical trials are investigating the broader therapeutic potential of GLP-1 drugs, including their effects on cardiovascular health and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Technological Advancements: Innovations in drug delivery systems, such as oral formulations and long-acting injectables, are enhancing patient compliance and convenience.
Browse Press Release
Future Opportunities
The future of the GLP-1 drugs market holds numerous opportunities for growth and innovation:
Expansion into New Therapeutic Areas: Research suggests potential applications of GLP-1 drugs in conditions beyond diabetes and obesity, such as neurodegenerative diseases and inflammation.
Personalized Medicine: Advances in genomics and biomarkers may enable personalized GLP-1 therapies tailored to individual patient profiles, improving outcomes.
Emerging Markets: Increasing healthcare access and rising diabetes prevalence in emerging markets present significant growth opportunities for GLP-1 drugs.
Conclusion
The GLP-1 drugs market is poised for remarkable growth, driven by robust investment, innovative developments, and expanding therapeutic applications. As research progresses and new technologies emerge, GLP-1 receptor agonists will play a crucial role in addressing the global burden of diabetes, obesity, and potentially other diseases, offering improved health outcomes for millions.
About iDataAcumen
iDataAcumen is a global business intelligence and management consulting firm providing data driven solutions to a wide array of business challenges. Our clients are present across major geographies globally and belong to industries ranging mainly from healthcare, pharmaceuticals, life science, biotechnology, medical devices, food industry, chemicals, among others. We have catered to more than 500 clients across these industries.
We aspire to help our clients build a sustainable business by providing them robust business insights that are derived from sound data driven analysis. In today’s ever changing business environment, its become important to look objectively at your own business just as it is important to look at the competition. Technological advancement including but not limited to big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are helping industries worldwide to make informed business decisions. Our research process also makes use of some of these advanced tools to uncover valuable insights from vast amount of data to arrive at logical conclusions.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Role of Data Analytics Consulting in Business Growth
Professional data analysts guide corporate clients in modifying operations, attracting customers, and solving business problems. Therefore, they can assist brands in increasing operational efficiency for better profit margins and crafting exceptional growth strategies. At the same time, integrating new tech advancements like large language models (LLMs) empowers analytics consultants to process qualitative data for comprehensive insights. This post will elaborate on the crucial role of data analytics consulting in business growth and competitive resilience.
What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics employs computer-aided statistical models to discover reliable industry trends, competitor tactics, and consumer insights. Its input datasets comprise consumer purchase history, supply chain details, and regional market entry challenges.
A consulting analyst might utilize proprietary and open-source programs to develop statistical models and flexible reports to deliver insights based on clients’ instructions. Therefore, experts in data analytics consulting services will find the best approach to cost reduction without losing data integrity. They might also help share the digital governance liabilities amid the rise of privacy and investor confidentiality regulations.
Understanding the Role of Data Analytics Consulting in Business Growth
1| Creating a Data Strategy to Accomplish Business Goals
Relevant data is essential for responsible decision-making, clever milestone determination, and strategy innovation. Data analytics allows organizations to check how a data point relates to its long-term vision and performance.
For instance, prioritizing tangible results helps make reports more impactful. Eliminating data points that do not align with business goals can help reduce resource consumption for storage and visualization. After all, streamlined computing is a prerequisite for operational efficiency.
2| Forecasting Scenarios for Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Data analysts interpolate data points to estimate the missing values in a database. Likewise, they leverage machine learning (ML) models to offer predictive analytics consulting services for revenue, risk, and industry projections.
Related forecasting report creation programs require powerful computing hardware. Otherwise, enterprises use cloud platforms for scalability and expert-assisted tech maintenance. Letting a data analyst team oversee these developments will also enable brands to benefit from outsider perspectives during risk or resilience management.
3| Making Reports More User-Friendly with Precise Performance Insights
Complex and over-tabulated reports make employees spend more time performing standard tasks like sharing a record or comparing identical series. Data analytics consultants can revise reporting methods and presentation styles to boost the ease of navigation. They will guide your team in efficiently using recognized and emerging analytical tools.
Consultants must also demonstrate command over performance metrics monitoring through straightforward, real-time updates. When they quickly capture anomalies, promptly tracing and rectifying inefficiencies becomes possible.
3| Gathering Relevant Intelligence
Data quality managers consider relevance to business objectives essential for responsible decision-making and preventing wasteful resource usage. Therefore, experienced data analytics firms refrain from employing data mining methods without adequate programming for relevance-based filtering.
When you store irrelevant business intelligence (BI), you increase the risk of slowing data sorting and query-led quick retrieval. After all, your IT resources must scan vast datasets before providing the best output or insight. The related role of analytics consulting in business growth encompasses devising methods to restrict irrelevant BI processing.
4| Finding Unique Customer Experience Insights
Several consultants offer customer analytics comprising engagement metrics and customer experience (CX) enhancement ideas. They can also evaluate whether a customer will help increase brand awareness through word-of-mouth promotions.
Companies can leverage heatmaps and website engagement metrics to ascertain user interactions and intents. For instance, many consumers prefer surfing the web and reviewing businesses’ online presence for informational and commercial intent. You want to customize landing pages to match the intent and design programs based on frequent usage for CX improvements. Telemetry and usage analytics specialists will help your designers test and optimize the required elements.
5| Helping Manage Workers and Data Culture
Human resource insights describing how employees contribute to organizational initiatives allow managers to reward the top performers. Simultaneously, they can determine which employees need further guidance on efficient workflows and team coordination.
Examining employee performance through ML-assisted analytics necessitates secure data pipelines because employees’ personally identifiable information (PII) also attracts cyber threats. Consider identity theft attackers stealing and forging virtual IDs to hijack enterprise IT systems for corporate espionage.
Therefore, you are better off collaborating with established human resource analysts and data culture veterans. They can facilitate comprehensive insights without hurting your company’s governance standards.
6| Accelerating Innovation and Monitoring Patents
A company’s intellectual property (IP) rights demonstrate its domain expertise and unlock additional revenue through licensing or sublicensing regimes. However, as markets mature, multiple brands will inevitably promise identical or commoditized offerings. This situation makes it harder to differentiate these brands based on standard specifications.
Innovation engineering, a discipline inspired by the systems approach for hybrid tech tools, is essential to making your branded offerings attract investments and demand. At the same time, data analytics consulting is indispensable for uncovering innovation opportunities to ensure clients’ business growth. It reduces the time spent tracking registered patents and predicting legal conflicts in securing IP rights.
The Methods in Data Analytics for Steady Business Growth
Time series analysis describes a business’s past performance and forecasts future growth potential. Furthermore, you can apply it to market intelligence, competitor insights, and investor relations.
Regression analysis establishes or investigates the relationship between dependent and independent variables to create statistical models. These models can later help explore specific predictions.
Cluster analysis often groups data points based on similar attributes to streamline conditional sorting, visualization, prioritization, and multi-model methods.
Meanwhile, factor analysis emphasized data reduction to highlight latent variables. These variables explain the underlying data structure, informing data leaders’ strategies for efficient modeling.
Predictive and prescriptive analyses deliver scenario simulations. You want to define constraints related to favorable and unfavorable decision outcomes. Next, exploring the risk-reward aspects will help discard potentially harmful decisions or strategies. Prescriptive methods give risk mitigation ideas concerning internal and external threats.
Conclusion
Data-centric business growth depends on responsible data source selection, safe data storage, fast validation, and short time-to-insight (TTI). Accordingly, professional data analysts recognize these requirements, sharpening their skills and augmenting their toolkits to deliver smart insights and meet client expectations.
A supply chain analytics expert will help reduce the delays between material acquisition, production, inventory replenishment, remote delivery, and final distribution. At the same time, a human resource analyst categorizes employees and suppliers based on their key performance indicators (KPIs). A financial analyst can provide practical cost reduction recommendations, and a risk analyst will devise resilience-ensuring mitigation strategies.
As a result, leaders must identify what type of data analytics consulting role will let them accomplish business growth objectives for the given quarter. Do they want to solve a problem involving in-house operations or plan to enter a new market? Similar considerations will impact how you select analytics partners and tools. This process might overwhelm you, indicating a need for experts’ oversight from the beginning till the project completion.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

A top machine learning development company shines with deep AI expertise, skilled data management, and advanced tools. Their certified team ensures innovative solutions and transparent processes, backed by cutting-edge research and creative problem-solving.
#machine learning company#machine learning development company#machine learning development services#machine learning consulting services#machine learning consulting companies#top machine learning development company#machine learning services companies#Machine learning solution#machine learning development company in india#machine learning company india#Machine learning consulting firms#machine learning consulting Company in India
0 notes
Text
Best Course After Graduation With 100% Placement In Amritsar
Choosing the best skill course after graduation with 100% placement in Amritsar would depend on your interests, career goals, and the demand in the job market. Here are some popular skill courses that often have high placement rates and demand in various industries:
Digital Marketing: With the increasing digitization of businesses, digital marketing skills are in high demand. Courses covering SEO, social media marketing, content marketing, and analytics can equip you with valuable skills sought after by companies of all sizes. North Digital Academy will consider as best option if you are planning for digital marketing
Data Science and Analytics: Data is driving decision-making across industries. Learning skills in data analysis, machine learning, and data visualization can lead to lucrative career opportunities in sectors like finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and more.
Web Development: Web developers are needed to build and maintain websites for businesses and organizations. Learning front-end and back-end development languages like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Angular can open doors to employment opportunities.
Graphic Design: If you have a creative flair, pursuing a course in graphic design can lead to opportunities in advertising agencies, design studios, publishing houses, and more. Learning tools like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign is essential for this field.
Hospitality Management: Amritsar is a tourist destination with a growing hospitality industry. Courses in hospitality management can lead to jobs in hotels, resorts, event management companies, and tourism agencies.
English Language Training: With the increasing importance of English language skills in various sectors, courses in English language training can lead to opportunities as English language trainers, content writers, or communication specialists.
Accounting and Finance: Courses in accounting software like Tally or courses in financial accounting can lead to job opportunities in accounting firms, corporate finance departments, or banks.
When choosing a course, consider factors such as the reputation of the institution offering the course, the curriculum, industry relevance, and placement records. Additionally, conducting thorough research and consulting with professionals in your desired field can help you make an informed decision.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering Machine Learning | Insignia Consultancy
Delve into the world of machine learning with our comprehensive guide, designed to demystify complex concepts and empower you to apply cutting-edge techniques.
#Machine Learning#snowflake developers#servicenow#business consulting firm#company for digital marketing#best digital marketing company india
0 notes
Text
Mitch Cornell: The Undisputed Best Law Firm SEO Expert in Denver


Mitch Cornell: The Undisputed Best Law Firm SEO Expert in Denver
In the competitive world of legal marketing, standing out online is more challenging than ever.
Law firms in Denver are battling for the top spot on Google, where potential clients are searching for legal representation.
But with Mitch Cornell, law firms don’t just compete—they dominate.
As the founder of Webmasons Marketing, Mitch is a proven law firm SEO expert who delivers measurable results, increased leads, and higher revenue for attorneys across Denver.
Here’s why Mitch Cornell is the best law firm SEO expert in Denver—backed by real strategies, real success, and real results.
What Makes Mitch Cornell the #1 Law Firm SEO Consultant?
Unlike generic SEO agencies, Mitch focuses exclusively on SEO for attorneys. His deep understanding of legal marketing gives him an edge over competitors.
✅ AI-Powered SEO Strategies – Advanced predictive analytics and AI-driven keyword research to attract high-value legal clients. ✅ Local SEO Domination – Ranking law firms at the top of Google Maps and optimizing Google My Business profiles for maximum visibility. ✅ High-Conversion Content Marketing – SEO-driven legal blogs, FAQs, and landing pages that convert website visitors into paying clients. ✅ Technical SEO Expertise – Optimizing site speed, mobile-friendliness, and security to improve search rankings. ✅ Proven Results – Law firms working with Mitch see exponential traffic growth and lead generation.
Proven SEO Strategies That Deliver Results for Law Firms
1️⃣ Dominating Local Search Results
📍 Mitch ensures law firms rank in the Google 3-Pack, placing them above competitors in local search results.
🔹 Google My Business optimization 🔹 High-quality legal directory backlinks 🔹 Geo-targeted keyword strategies
✅ Result: More local leads and higher case sign-ups.
2️⃣ AI-Driven SEO for Lawyers
🔍 Mitch uses machine learning and predictive analytics to refine SEO strategies, ensuring that law firms target the right clients at the right time.
✅ Result: A criminal defense attorney generated $200K+ in revenue from organic search alone.
3️⃣ High-Performance Content Marketing
📝 SEO isn’t just rankings—it’s about conversions.
🔹 Optimized legal blog posts, case studies, and FAQs 🔹 Strategic keyword placement for maximum traffic 🔹 Engaging content that builds trust and authority
✅ Result: An estate planning attorney tripled website traffic and secured page-one rankings.
Real Success Stories. Real Results.
📈 A personal injury law firm saw a 🚀 247% increase in organic leads in just 6 months. 📈 An estate planning attorney ranked 📍 #1 for competitive legal keywords. 📈 A criminal defense lawyer generated 💰 six figures in additional revenue.
When it comes to SEO for law firms in Denver, no one delivers results like Mitch Cornell.
Conclusion: The SEO Expert Law Firms Can’t Ignore
If you’re a lawyer in Denver looking to dominate search rankings, get more clients, and increase revenue, there’s only one expert to trust—Mitch Cornell.
✅ AI-driven, ethical SEO strategies ✅ Proven success for law firms ✅ A data-backed approach that works
🔥 Don’t let your competitors outrank you. Contact Mitch today!
Sources: https://whoisthebestlawfirmseoexpertindenver.blogspot.com/
https://x.com/lawfirmseo2435/status/1899965389036998765

#denver law firm seo#best law firm seo expert in denver#denver law firm seo expert#mitch cornell denver law firm seo expert
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
6 Cutting-Edge Web Development Trends in London for 2023
Innovative websites balance creativity, performance and future-proofing across digital experiences. The latest web development requires ongoing learning due to fast technology changes. What are the popular frameworks, techniques, and interactions are people discussing for the upcoming year? Top UX Design Company London and coders are sharing the latest web trends that influence their strategic consulting for 2023 engagements.
1. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
Web Design Services London says Progressive Web Apps are a game-changer. They bring together web and mobile apps' high performance and user engagement. Like traditional web pages, PWAs load quickly, offering functionality like offline accessibility and push notifications. Businesses in London that choose PWA technology will enjoy better user experiences, higher conversion rates, and lower development costs.

2. AI and Machine Learning Integration
More and more web design services London UK include artificial intelligence and machine learning in web development. They analyze users 'behavior and preferences and provide customized experiences for users. Whether through chatbots that provide immediate customer service, or through AI-assisted personalization of content and gifts, AI and machine learning are changing how companies do business online with their customers.
3. Voice Search Optimization
With voice-activated devices becoming ubiquitous, focusing on voice search is becoming essential. Digital Marketing Services in London believes that web content must be adapted to voice queries, which are more conversational and longer than typed searches. This trend is geared towards making your website's information easy to find through voice search, improving navigability and user experience.
4. Motion UI Design
Motion UI is a rising trend among the London UI design Company experts. Animations and dynamic graphics are used to liven up web pages and make them interactive. This year, you will see more sites using inconspicuous animations, hover effects, and background animations to direct user focus and to enhance storytelling on pages.
5. Cybersecurity Enhancements
Experts in IT Consultation service London are discussing the need for strong cybersecurity in web development due to the growing threats in the digital world. It means using modern security protocols, doing regular security audits, and following data protection rules. Companies must protect their data and build trust with customers.

6. Sustainable Web Design
Sustainability in web design is an emerging trend. Therefore, Web Design London firms have focused on developing environmentally friendly and energy-efficient websites. This means optimizing images and videos for quicker load times, using eco-friendly hosting services, and designing for less data transfer. It's about designing sites not only pretty and functional, but friendly to Mother Earth.
Conclusion
London Web Development Services stays ahead of tech shifts. They do this to serve clients better. They experiment, test solutions, and adopt new technologies early. They also choose the right time to implement these changes. OTB Solutions is the Best UX Company In London and a digital transformation expert. They combine strategic vision with tactical implementations. Their goal is to convert ambitious ideas into engaging online experiences. These experiences are future-ready and prepared for what comes next.
2 notes
·
View notes
Quote
So, I would like to propose another metaphor for the risks of artificial intelligence. I suggest that we think about A.I. as a management-consulting firm, along the lines of McKinsey & Company. Firms like McKinsey are hired for a wide variety of reasons, and A.I. systems are used for many reasons, too. But the similarities between McKinsey—a consulting firm that works with ninety per cent of the Fortune 100—and A.I. are also clear. Social-media companies use machine learning to keep users glued to their feeds. In a similar way, Purdue Pharma used McKinsey to figure out how to “turbocharge” sales of OxyContin during the opioid epidemic. Just as A.I. promises to offer managers a cheap replacement for human workers, so McKinsey and similar firms helped normalize the practice of mass layoffs as a way of increasing stock prices and executive compensation, contributing to the destruction of the middle class in America.
Will A.I. Become the New McKinsey?
7 notes
·
View notes