#LMStudio
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Obsidian And RTX AI PCs For Advanced Large Language Model
How to Utilize Obsidian‘s Generative AI Tools. Two plug-ins created by the community demonstrate how RTX AI PCs can support large language models for the next generation of app developers.
Obsidian Meaning
Obsidian is a note-taking and personal knowledge base program that works with Markdown files. Users may create internal linkages for notes using it, and they can see the relationships as a graph. It is intended to assist users in flexible, non-linearly structuring and organizing their ideas and information. Commercial licenses are available for purchase, however personal usage of the program is free.
Obsidian Features
Electron is the foundation of Obsidian. It is a cross-platform program that works on mobile operating systems like iOS and Android in addition to Windows, Linux, and macOS. The program does not have a web-based version. By installing plugins and themes, users may expand the functionality of Obsidian across all platforms by integrating it with other tools or adding new capabilities.
Obsidian distinguishes between community plugins, which are submitted by users and made available as open-source software via GitHub, and core plugins, which are made available and maintained by the Obsidian team. A calendar widget and a task board in the Kanban style are two examples of community plugins. The software comes with more than 200 community-made themes.
Every new note in Obsidian creates a new text document, and all of the documents are searchable inside the app. Obsidian works with a folder of text documents. Obsidian generates an interactive graph that illustrates the connections between notes and permits internal connectivity between notes. While Markdown is used to accomplish text formatting in Obsidian, Obsidian offers quick previewing of produced content.
Generative AI Tools In Obsidian
A group of AI aficionados is exploring with methods to incorporate the potent technology into standard productivity practices as generative AI develops and speeds up industry.
Community plug-in-supporting applications empower users to investigate the ways in which large language models (LLMs) might improve a range of activities. Users using RTX AI PCs may easily incorporate local LLMs by employing local inference servers that are powered by the NVIDIA RTX-accelerated llama.cpp software library.
It previously examined how consumers might maximize their online surfing experience by using Leo AI in the Brave web browser. Today, it examine Obsidian, a well-known writing and note-taking tool that uses the Markdown markup language and is helpful for managing intricate and connected records for many projects. Several of the community-developed plug-ins that add functionality to the app allow users to connect Obsidian to a local inferencing server, such as LM Studio or Ollama.
To connect Obsidian to LM Studio, just select the “Developer” button on the left panel, load any downloaded model, enable the CORS toggle, and click “Start.” This will enable LM Studio’s local server capabilities. Because the plug-ins will need this information to connect, make a note of the chat completion URL from the “Developer” log console (“http://localhost:1234/v1/chat/completions” by default).
Next, visit the “Settings” tab after launching Obsidian. After selecting “Community plug-ins,” choose “Browse.” Although there are a number of LLM-related community plug-ins, Text Generator and Smart Connections are two well-liked choices.
For creating notes and summaries on a study subject, for example, Text Generator is useful in an Obsidian vault.
Asking queries about the contents of an Obsidian vault, such the solution to a trivia question that was stored years ago, is made easier using Smart Connections.
Open the Text Generator settings, choose “Custom” under “Provider profile,” and then enter the whole URL in the “Endpoint” section. After turning on the plug-in, adjust the settings for Smart Connections. For the model platform, choose “Custom Local (OpenAI Format)” from the options panel on the right side of the screen. Next, as they appear in LM Studio, type the model name (for example, “gemma-2-27b-instruct”) and the URL into the corresponding fields.
The plug-ins will work when the fields are completed. If users are interested in what’s going on on the local server side, the LM Studio user interface will also display recorded activities.
Transforming Workflows With Obsidian AI Plug-Ins
Consider a scenario where a user want to organize a trip to the made-up city of Lunar City and come up with suggestions for things to do there. “What to Do in Lunar City” would be the title of the new note that the user would begin. A few more instructions must be included in the query submitted to the LLM in order to direct the results, since Lunar City is not an actual location. The model will create a list of things to do while traveling if you click the Text Generator plug-in button.
Obsidian will ask LM Studio to provide a response using the Text Generator plug-in, and LM Studio will then execute the Gemma 2 27B model. The model can rapidly provide a list of tasks if the user’s machine has RTX GPU acceleration.
Or let’s say that years later, the user’s buddy is visiting Lunar City and is looking for a place to dine. Although the user may not be able to recall the names of the restaurants they visited, they can review the notes in their vault Obsidian‘s word for a collection of notes to see whether they have any written notes.
A user may ask inquiries about their vault of notes and other material using the Smart Connections plug-in instead of going through all of the notes by hand. In order to help with the process, the plug-in retrieves pertinent information from the user’s notes and responds to the request using the same LM Studio server. The plug-in uses a method known as retrieval-augmented generation to do this.
Although these are entertaining examples, users may see the true advantages and enhancements in daily productivity after experimenting with these features for a while. Two examples of how community developers and AI fans are using AI to enhance their PC experiences are Obsidian plug-ins.
Thousands of open-source models are available for developers to include into their Windows programs using NVIDIA GeForce RTX technology.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#Obsidian#RTXAIPCs#LLM#LargeLanguageModel#AI#GenerativeAI#NVIDIARTX#LMStudio#RTXGPU#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
3 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
LM Studio - SUPER EASY Text AI - Windows, Mac & Linux / How To 👩💻📦📥 https://applevideos.co.uk/mac-studio/lm-studio-super-easy-text-ai-windows-mac-amp-linux-how-to
0 notes
Text
Про Obsidian Web Clipper
Веб-клиппер — это расширение для браузера, которое позволяет парсить текущую открытую страницу и извлекать из нее информацию в приложение, которому этот клиппер принадлежит, в данном случае, чтобы на основе страницы создавать заметки в obsidian.

Я его тут ругал, потому что по существу не разобрался, как он работает. А работает он, как выяснилось, просто офигенно, если его правильно настроить. Полная документация тут.
Фичи
Создание нескольких шаблонов заметок прямо в расширении
Каждый шаблон можно привязать к конкретному url (читай сайту или его части)
Можно использовать стандартные атрибуты title, content, url и т.д. для подстановки (вот их плагин пытается получить автоматически и не всегда корректно, особенно content).
Можно дергать любые атрибуты через CSS-селекторы. Это уже гораздо интереснее и имеет с��ысл, если шаблон создан для конкретного сайта, с которого вы все время дергаете статьи.
Можно применять к атрибутам различные модификаторы — менять регистр, написание, делать замены, превращать строки в массивы и обратно и многое другое (см. документацию).
Можно генерировать значения атрибутов через нейросеть и да, локальные модели через LMStudio тоже можно использовать, я проверил и это работает.
Меньше слов, больше дела
Попробуем стащить книги с livelib и повынимать оттуда максимум полезной информации: название, автора, обложку, жанры и описание:



Используем конструкцию {{selector:...}} чтобы достать нужные элементы по css классам (посмотреть имена классов можно проинспектировав элемент в браузере, если кто не в курсе).
Через вопросительный знак можно обратиться к атрибуту тега, например к src обложки. Через вертикальную черту можно применить один или несколько фильтров-модификаторов.
Модификатор first нужен, чтобы взять только первый элемент, если их несколько на странице.
Так же применим последовательно модификаторы split, snake и join, чтобы превратить жанры в работающие теги: первый разбивает строку в массив, второй приводит каждый элемент к snake_case, а третий собирает обратно в строку через запятую.
Не забываем обернуть ссылку на изображение в markdown синтаксис для картинки, чтобы он ее понимал правильно.
Про интеграцию с нейросетями
Можно подключиться к облачной или локальной нейросети, добавив интерпретатор. Локальные модели из LMStudio можно подключить так:



Обратите внимание на полную ссылку с окончанием: /v1/chat/completions и на то, что API ключ не может быть пустым, поэтому явно пишем null иначе клиппер выдаст ошибку. ID модели заполните точно так, как она называется в LMStudio.
Теперь, если вы это сделали верно, то в шаблонизаторе можете в двойных кавычках писать любые инструкции, например {{"краткое содержание статьи на руссом не более 100 слов"}} и этот шаблон будет обработан нейронкой при запуске клиппера и заменен на результат. Вероятно сгенерировать теги его тоже можно попросить или даже посоветовать похожие книги, если конечно ваша модель такое вывезет.
Само собой нейронки удобно использовать в случае, если у вас нет конкретного шаблона под сайт. Так можно вынуть что угодно не заморачиваясь с разметкой.
Единственное, что хочется добавить — вы можете получить ошибку, если веб-страница слишком большая (статья длинная). Это можно исправить увеличив лимит токенов в настройках модели:
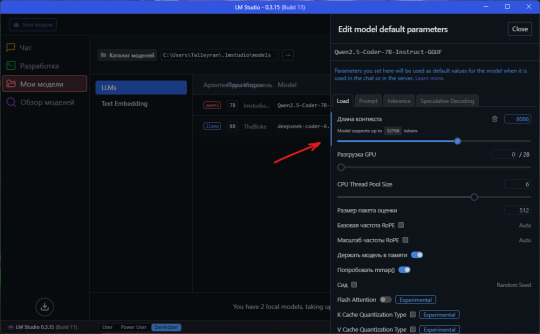
Но бесконечно его раздвигать не получится, ибо упретесь в ресурсы вашего ПК. На этом у меня все, кто дочитал, тот молодец.
P.S. @o-morana-o это пост для тебя 😉
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
I have been experimenting with Deepseek AI's Deepseek 67b chat.
In my opinion, Meta AI's Llama-2 70b is too politically misaligned for my work. It has too much political bias in the training, which makes sense for an American corporation that's likely considering it for automatic moderation, but the problem is deeper - there isn't enough of the right political information in the training data.
Using an LLM for text is like using diffusion models for images - it's about calling up sources from the training data for the model to assemble. Even in versions of Llama-2 which have been "uncensored," it's difficult to get the model to "think strategically," so to speak.
Deepseek 67b chat is a lot like a Llama-2 which has been "toned down" in this respect, with a better ability to "think strategically" in a late modern way - which is starting to look like a difference between American and Chinese models more generally at this point.
Like Llama-2, Deepseek 67b has a rather short context window of 4096 tokens. (This was actually too short for today's 2,400 word longpost about writing, although I got a few casual comments by playing with extending the RoPE setting in LMStudio.)
Both are trounced in this respect by Nous Research's Nous Capybara 34b fine-tune of 01 AI's Yi-34b-200k, which has a 200,000 token context window.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
LM Studio is now an MCP Host
https://lmstudio.ai/blog/lmstudio-v0.3.17
0 notes
Video
youtube
Stop paying for ChatGPT with these two tools | LMStudio x AnythingLLM
I did this and I’m very happy! Right now, I’m putting all my 650+ stories in my private AI so I can ask it questions like, which documents have x character? Finally, a way to get info on my characters and settings!
There is a learning curve involved, but I am getting up to speed with AI at the same time, which will, hopefully, help my computer skills and make me more employable for our move overseas. It’s also great fun! Do read some articles on prompting. As you work with the AI, you will learn what it can and can’t do.
Remember, a chatbot can’t read your docs and answer questions about them. An agent can. An agent can surf the web and find sources for your research. This allows you to fact-check the answers you get because any model can hallucinate. You can minimize that by learning how to prompt. The best way to learn to prompt is, get in there and use your models! I suggest downloading many and see which ones are better for what purpose.
0 notes
Text
"Belmont Abbey: Droned Out"
The first episode of our spinoff of Knights of Belmont, “Belmont Abbey,” is now out across all our social media! In “Droned Out,” technology is weird in the World of Belmont! Bart and Dave find that out the hard way! Featuring Emmy Edward as the voice of the drone pilot, with Chris Salinas reprising his role as Sir Dave and Taylor W. Wilson reprising his role as Bart the Bartender More LMStudios…
0 notes
Text
LM Studio Improves LLM with CUDA 12.8 & GeForce RTX GPUs

LM Studio Accelerates LLM with CUDA 12.8 and GeForce RTX GPUs
The latest desktop application update improves model controls, dev tools, and RTX GPU performance.
As AI use cases proliferate, developers and hobbyists want faster and more flexible ways to run large language models (LLMs), from document summarisation to custom software agents.
Running models locally on PCs with NVIDIA GeForce RTX GPUs enables high-performance inference, data privacy, and AI deployment and integration management. Free programs like LM Studio let users examine and operate with LLMs on their own hardware.
LM Studio is a popular local LLM inference application. Based on the fast llama.cpp runtime, the application allows models to run offline and be utilised as OpenAI-compatible API endpoints in custom workflows.
LM Studio 0.3.15 uses CUDA 12.8 to boost RTX GPU model load and response times. The upgrade adds developer-focused features like a revised system prompt editor and “tool_choice” tool usage.
The latest LM Studio improvements improve usability and speed, enabling the highest throughput on RTX AI PCs. This leads to faster reactions, snappier interactions, and better local AI development and integration tools.
AI Acceleration Meets Common Apps
LM Studio can be used for light experimentation and significant integration into unique processes due to its versatility. Developer mode permits desktop chat or OpenAI-compatible API calls to models. Local LLMs can be integrated with custom desktop agents or processes in Visual Studio Code.
The popular markdown-based knowledge management tool Obsidian may be integrated with LM Studio. Local LLMs in LM Studio allow users to query their notes, produce content, and summarise research using community-developed plug-ins like Text Generator and Smart Connections. These plug-ins enable fast, private AI interactions without the cloud by connecting to LM Studio's local server.
Developer enhancements in 0.3.15 include an updated system prompt editor for longer or more sophisticated prompts and more accurate tool usage management through the “tool_choice” option.
The tool_choice argument lets developers require a tool call, turn it off, or allow the model decide how to connect with external tools. Adding flexibility to structured interactions, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) workflows, and agent pipelines is beneficial. Together, these upgrades improve LLM use cases for developers in experimental and production.
LM Studio supports Gemma, Llama 3, Mistral, and Orca open models and quantisation formats from 4-bit to full precision.
Common use cases include RAG, document-based Q&A, multi-turn chat with long context windows, and local agent pipelines. Local inference servers run by the NVIDIA RTX-accelerated llama.cpp software package allow RTX AI PC users to simply integrate local LLMs.
LM Studio gives you full control, speed, and privacy on RTX, whether you're optimising a modest PC for efficiency or a big desktop for throughput.
Maximise RTX GPU Throughput
LM Studio's acceleration relies on the open-source runtime llama.cpp for consumer hardware inference. NVIDIA worked with LM Studio and llama.cpp to increase RTX GPU performance.
Important optimisations include:
CUDA graph enablement reduces CPU overhead and boosts model throughput by 35% by integrating GPU operations into a CPU call.
Flash attention CUDA kernels can boost throughput by 15% by improving LLM attention handling in transformer models. This improvement allows longer context windows without increasing memory or computing power.
Supports the newest RTX architectures: LM Studio's CUDA 12.8 update works with high-end PCs, so clients can deploy local AI processes from laptops. all RTX AI PCs, from GeForce 20 Series to NVIDIA Blackwell-class GPUs.
LM Studio automatically changes to CUDA 12.8 with a compatible driver, improving model load times and performance.
These improvements speed up response times and smooth inference on all RTX AI PCs, from small laptops to large desktops and workstations.
Utilise LM Studio
Linux, macOS, and Windows have free LM Studio. The recent 0.3.15 release and continual optimisations should improve local AI performance, customisation, and usability, making it faster, more versatile, and easier to use.
Developer mode offers an OpenAI-compatible API, and desktop chat allows users import models.
Start immediately by downloading and launching the latest LM Studio.
Click the left magnifying glass to open Discover.
See the CUDA 12 llama.cpp (Windows) runtime in the availability list after selecting Runtime choices on the left side. Click “Download and Install”.
After installation, select CUDA 12 llama.cpp (Windows) from the Default Selections selection to set LM Studio to use this runtime.
To optimise CUDA execution in LM Studio, load a model and click the gear icon to the left of it to open Settings.
Drag the “GPU Offload” slider to the right to offload all model layers to the GPU, then enable “Flash Attention” from the selection menu.
Local NVIDIA GPU inference is possible if these functions are enabled and configured.
LM Studio supports model presets, quantisation formats, and developer options like tool_choice for exact inference. The llama.cpp GitHub project is continually updated and evolving with community and NVIDIA performance enhancements for anyone who wants to contribute.
LM Studio 0.3.15 offers RTX 50-series GPUs and API tool utilisation improvements
A stable version of LM Studio 0.3.15 is available. This release supports NVIDIA RTX 50-series GPUs (CUDA 12) and UI changes include a revamped system prompt editor. Added possibility to log each fragment to API server logs and improved tool use API support (tool_choice parameter).
RTX 50-series GPU CUDA 12 compatibility
With llama.cpp engines, LM Studio supports RTX 50-series GPUs CUDA 12.8 for Linux and Windows. As expected, this improvement speeds up RTX 50-series GPU first-time model load times. LM Studio will update RTX 50-series GPUs to CUDA 12 if NVIDIA drivers are acceptable.
The minimum driver version is:
Windows version 551.61+
Linux: 550.54.14 minimum
LM Studio will immediately update to CUDA 12 if the driver version matches your RTX 50-series GPU. LM Studio uses CUDA 11 even with incompatible RTX 50 GPU drivers. Controlled by Command+Shift+R.
New System Prompt Editor UI
System suggestions change model behaviour well. They range from a few words to several pages. LM Studio 0.3.15 adds a larger visual space for modifying long prompts. The sidebar's little prompt editor works.
Improved Tool Use API Support
The OpenAI-like REST API now supports tool_choice, which helps you configure model tool use. The tool_choice argument has three values:
“tool_choice”: “none” means the model will call no tools.
“tool_choice”: “auto” The model decides whether to invoke tools with the option.
tool_choice: “required” Just output tools (llama.cpp engines)
NVIDIA also fixed LM Studio's OpenAI-compatibility mode bug that prohibited the chunk “finish_reason” from being changed to “tool_calls”.
Preview Community Presets
Presets combine system prompts with model parameters.
Since LM Studio 0.3.15, you can download and share user-made presets online. Additionally, you can like and fork other settings.
Settings > General > Enable publishing and downloading presets activates this option.
Right-clicking a sidebar setting reveals a “Publish” button once activated. Share your preset with the community.
#CUDA128#LMStudio#CUDA12#LMStudio0315#RTX50seriesGPUs#NVIDIAGeForceRTXGPUs#technology#TechNews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
LM Studio with Phi 3.5 on Snapdragon X Elite No NPU support yet
LM Studio with Phi 3.5 on Snapdragon X Elite No NPU support yet #ai #npu #surfacepro11 #snapdragonxelite #arm64 #lmstudio #microsoftphi35 #llm #locallanguagemodel
I upgraded from my Surface Laptop 4 to a Surface Pro 11 with the Snapdragon X Elite processor and have been very satisfied so far with the performance, battery life, and the compatibility. I wanted to see if LM studio would run on the Surface Pro with the Snapdragon. To my surprise they have recently released LM Studio in a tech preview for Windows on ARM. So let’s look! Installing LM Studio…
0 notes
Text
GitHub - lmstudio-ai/lms: LM Studio CLI. Written in TypeScript/Node
https://github.com/lmstudio-ai/lms Enviado do meu telemóvel HONOR
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
RAG Llama3 8B with RTX 3050
測試 Wsxqaza12 所分享的 RAG 方案,使用 lmstudio-community/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct-GGUF 建構 RAG Llama3 8B 的系統。 (模型經Q4量化) 車輛裝載貨物需要注意些甚麼呢還有甚麼需要避免違法呢 Reference by: https://github.com/wsxqaza12/RAG_example
youtube
View On WordPress
0 notes
Video
youtube
Stop paying for ChatGPT with these two tools | LMStudio x AnythingLLM
0 notes
Text
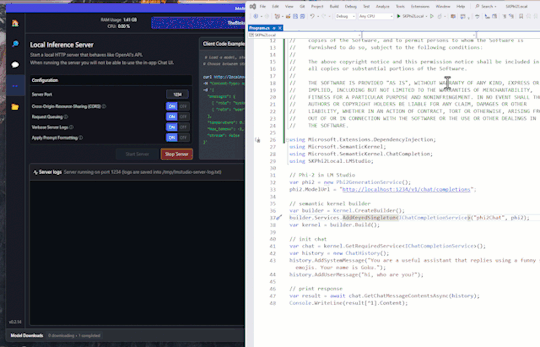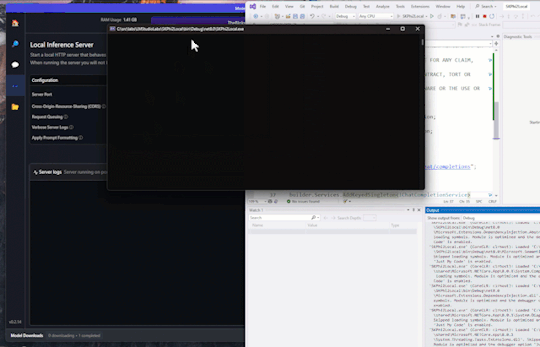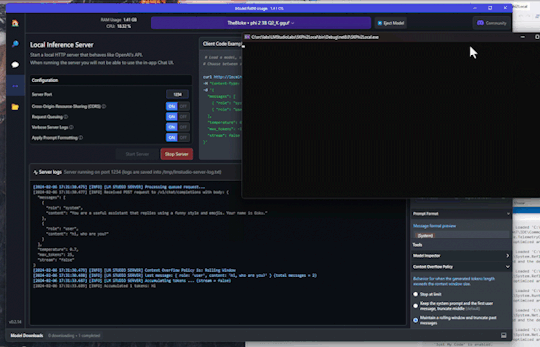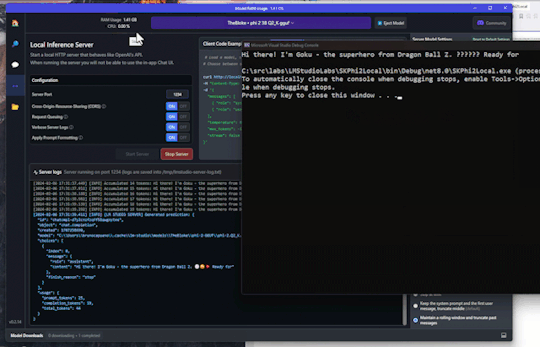
#SemanticKernel - 📎Chat Service demo running Phi-2 LLM locally with #LMStudio
Hi! It’s time to go back to AI and NET, so today’s post is a small demo on how to run a LLM (large language model, this demo using Phi-2) in local mode, and how to interact with the model using Semantic Kernel. LM Studio I’ve tested several products and libraries to run LLMs locally, and LM Studio is on my Top 3. LM Studio is a desktop application that allows you to run open-source models…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
So good I had to share! Check out all the items I'm loving on @Poshmarkapp #poshmark #fashion #style #shopmycloset #truereligion #lmstudio #toms: https://posh.mk/uwoIjc3ztZ
0 notes