#King Leopold II of Belgium
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
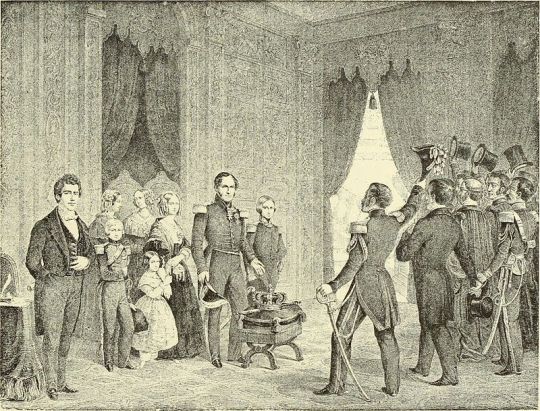
The first Belgian Royal Family, at the center we can see the King Leopold I, his wife, Queen Louise Marie and their three surviving children, the Crown Prince Leopold (later Leopold II), Prince Philippe and Princess Charlotte (future Empress of Mexico), 1840's.
#king leopold ii of belgium#King leopold i of Belgium#queen louise marie of belgium#Prince Philippe of Belgium#princess charlotte of belgium#empress charlotte of mexico#empress charlotte#carlota amalia#empress carlota#belgian royal family#belgian royalty#royalty#1840s
12 notes
·
View notes
Text





Prince Albert (King Albert I) | 17/12/1892 Prince Léopold (Koning Leopold III) | 09/01/1923 Prince Albert (King Albert II) | 18/05/1953 Prince Philippe (King Philippe) | 26/09/1980 Princess Elisabeth | 26/09/2013
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey. It's @reaux07. If you remember my last angry history rant on Paul Robeson, I'm back for Part 2. This time? King Leopold II and his relationship to the Congo. I just finished writing a 5-page, single-spaced essay on this for class, so I'll do my best to summarize in bullet points this time rather than chunky paragraphs. This will still be long though, as a warning, but it's a necessary read. Please let me get through this, because y'all know this hurts to write.
Trigger warnings for... just about everything typically associated with mass colonization (e.g. rape, murder, torture, etc.). Tiktok below as a brief introduction first:
King Leopold II of Belgium, due to his personal unpopularity and lack of love from his parents, had low self-esteem. As his father had already made 50 attempts to colonize foreign lands to no avail, Leopold felt the only way to uplift both himself and his country was to take take control of his own colony.
He checked Sarawak, the New Hebrides, the Fiji Islands, and the Philippines. Nothing. But what was left? The Congo.
How did he learn of the Congo? Leopold hired Henry Morton Stanley, a famous Welsh explorer of the time, to cross Africa from east to west, walking and canoeing 7,000 miles.
Upon the Congo's discovery, Leopold turned his palace into a luxury hotel for the delegates of a new conference to discuss Africa's colonization, supervising every detail. He successfully lied to the major powers of Europe, making claims of charitable and philanthropic aims, and that there would be free trade amongst the African colonies. (And yes, he did give every single attendee a painting of his face... Because he could.)
Meanwhile, back in the Congo, Stanley (the explorer I just mentioned) used bribes and trickery to provide official treaties with the various chiefs of the land in case Leopold ever needed legal proof of land ownership. (Ex of said trickery: One report noted that a village assumed "the white man controlled the sun.")
In 1891 and 1892, Leopold released decrees stating that both vacant land and produce of the forests exclusively belonged to Belgium and that natives could only harvest for the state.
Enforcing Leopold’s rule were 16,000 Africans equipped with modern Belgian-made automatic rifles.
Outing Attempt #1: One African American man, George Washington Williams, during his trip compiled a report to be sent to the American secretary of state. In this letter, Williams remembers bets being taken on who could shoot the native people in the head first, among other instances of vile treatment. While the document never made it back to Williams’ home country, it was eventually found in Europe where he later died.
By this point, the Congo was actually ruining Leopold’s finances and he was growing desperate. But to his surprise, he happened to pick the one spot where rubber grew in abundance, just as the demand for cars and bicycles rose internationally, John Dunlop, a Scottish veteran, having just invented the first pneumatic tire.
Because of this, rubber-prominent areas were the targets of mass exploitation and punishment if daily and weekly rubber quotas were not met.
Missionaries began to write not just to one another, but back home in disgust of these aforementioned “punishments,” one man’s writings put in missionary magazines and national newspapers in Europe. These punishments included rape, tying people up to trees, cutting off men's heads and genitals to be displayed along the fences of Congolese villages, cutting women’s breasts off, and most notably...
Attempt #2: The world, if only momentarily, saw BASKETS after BASKETS of right hands that had been cut off as proof that each of the cartridges given to the Africans had been fired and killed one of their own people. These hands were then smoked for preservation and brought back to their officers.
What did Leopold do once this information came out alongside photos of child mutilation? Acknowledge the abuses and moved on almost immediately.
In Europe, the rubber was processed in a city called Antwerp, ironically named after a mythological giant who also cut off hands. To this day, the connection between such a name and Belgian history has not been made by the general public as countless documents by the Belgian Ministry of Foreign Affairs are kept secret to maintain an image of untouched royalty.
One commissioner in charge of a district in Congo, Leon Fievez, produced one ton of rubber a day, boasting of 1,000 people killed, 162 villages destroyed, burning gardens and plantations so people would starve, and having “only” used 3,000 cartridges. He was nicknamed the “Devil of the Equator” and rightly so.
Attempt #3: One day, a man named Charles Stokes, a British trader working for the Germans, entered the picture. Stokes was arrested for trading in state territory, despite those former claims of free trade, and sentenced to death. Leopold was forced to pay compensation to both Britain and Germany for his death, both countries now increasingly aware of the Congo’s dark reality.
To cover it up, Leopold made claims of the Congo opening up to new companies. Let's be real: His men were on the boards of all these new companies and he took 50% of the profits.
In particular were these "concession companies" where the "hostage system" was set up. Agencies, with official hostage licenses authorizing such, would take the wives of rubber collectors for up to 15 days until the quota was met.
On the 15th day, the men of the Congo either got their wives back or faced further punishment, often death. For the agents, the 15th day meant it was time to calculate commissions, and for the king? It was proof that this new hostage system worked.
These abusive concession companies lasted over 10 years until formal competition arose in South America and Asia.
Attempt #4: Then came Edmund Dene Morel, a half-French, self-taught shipping clerk turned investigative journalist who wrote in The Speaker of the abuses faced by the Congolese, backed up by evidence, not just speculations.
Due to Morel’s growing specialization in West African affairs, he was able to not only send out 15,000 brochures and 3,700 letters in six months after his move to Wales, but start his own newspaper, West African Mail.
By 1903, Roger Casement, an ally to Morel’s cause, spent two months traveling the upper Congo, recording African testimonies. He, too, realized that missionaries were key witnesses and went to visit Joseph Clark (a missionary of 20 years) for 17 days.
Through these reports, which grew to 50 pages in length, Casement and Morel were able to solidify Belgium as perpetuating the worst colonial system Africa had ever known. Punishments included Africans performing public incest for the colonists' entertainment, decapitation, women being stabbed with wooden spikes up their vaginas, and one woman tied up to a tree and slashed straight in half from her left shoulder through her abdomen and out the other side.
The West African Mail even reported on a part of Congo no one knew existed, private property within private property called the “Crown Domain” on the other side of Lake Tumba, which gained 231 million euros alone, all sent directly to King Leopold II. Crown Domain was 10x 5)3 size of Belgium.
Founded by Morel, Liverpool became the headquarters of a coalition called the Congo Reform Association. He also published a book called Red Rubber (1906). I think you’ll find the cover particularly striking! Check out the hand in the bottom right corner being weighed against King Leopold II on the left.

Leopold obviously not having this, commissioned a number of books and monthly magazines to clear up the mess. This didn't work. Obviously.
He even tried to send his own international commission to control what the Congolese said in 1904, to no avail. This was due to a missionary named John Harris who had taken the accounts of various people in the area and sent them back to Morel.
In one particularly heartbreaking moment, a chief brought to Leopold’s judges 110 twigs for each of the entire villages, not just people, killed by the Belgian state, naming every last one.
By the time they returned to Europe, the governor-general committed suicide and, upon being asked, Harris suggested Leopold should be sent to the gallows by the relatively new International Court of Justice.
The commission's report vindicated Casement and Morel. Leopold had tricked no one. EVERYONE in Belgium was calling him out.
Leopold ordered all of the Congo State Records to be burned.
In 1908, the Congo became a Belgian colony, not longer Leopold’s personal property. The state still made claims of "civilizing" the Africans after Leopold's death though, utilizing the leftover mineral exploitation industry with no guilt.
At least during his funeral, which he was denied of having privately, the entire city booed his body <3 well deserved. By this point, he had become Europe’s most hated man of the time.
And in case you were wondering, Casement and Morel were both accused to pro-German sympathies during WWI and executed.
I would like to add more detail but I think I’ve hit a character limit. Just know that Congo’s population was cut in HALF, in some places as much as 60-90%. Villages after villages were burned, as shown through so many soldiers’ and missionaries’ journals. This was a genocide of over 10 MILLION PEOPLE y’all. Hearing this story was truly SICKENING, but here’s the BBC 4 documentary we watched for class for more: Congo: White King, Red Rubber, and Black Death.
What truly gets me is just how OTHER colonizers were calling this man out after finding out the full truth… For me, that feels like extra proof of how truly messed up this was if THEY were disturbed too.
And what feels truly insidious was how Leopold made sure to institutionalize all of his wrongdoings and was so… obviously knowing about every wrongdoing, I mean writing in letters to make sure no one else found out. Please…
Linking my angry history rant on Paul Robeson from last semester here.
Happy Black History Month.
#belgium#king leopold ii#democratic republic of congo#history#black history month#colonialism#tw genocide#tw rape#tw torture#tw massacre#the congo#tw incest#resources#bipoc#undescribed#reaux speaks#black lives matter
201 notes
·
View notes
Text

King Leopold II of Belgium
Belgian vintage postcard
#postal#leopold ii#historic#ansichtskarte#sepia#vintage#tarjeta#leopold#briefkaart#photo#king#postkaart#belgium#ephemera#postcard#postkarte#photography#belgian#carte postale
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Although the precise numbers are unclear, thousands of children were affected by the policy of forced removals and segregation during Belgium’s decades-long rule over the territories of the modern-day Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda and Burundi.
The system had its origins with Belgium’s King Léopold II, who ruled Congo as his personal fiefdom from 1885 until 1908, when the territory was ceded to the Belgian state. The removals policy was updated in 1952, even after the legal concept of crimes against humanity was established after the horrors of the second world war."
#belgium#class war#democratic republic of the congo#rwanda#Burundi#king leopold#King Léopold II#world war ii#world war 2#world war two#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#antinazi#antizionist#anti monarchy#fuck the monarchy#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#anti capitalism#antifascist#anti colonialism#anti colonization
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ota Benga was born around 1883, in what is now the Republic of Congo. Theirs was a hunter-gatherer society. When he became a man, his teeth were chipped into sharp points, part of his tribal customs. His world came crashing down when King Leopold II of Belgium (The butcher of Congo) established a colony in the Congo to exploit its valuable resources. The demand for rubber was increasing around the world and Leopold wanted to corner the market. He subdued the native population to force them into laboring on the rubber plantations. In Belgium Congo, women were held hostage until their men returned with enough rubber for the colonizer King Leopold. Some had their hands chopped off for not meeting rubber quotas. Ota was out on a hunting expedition when his village was attacked by the slavers. Whether they were Force Publique or an African group working to collect people to sell to them varies from story to story. He was taken captive. On the other side of the globe, a man named Samuel Verner was preparing exhibits for the 1904 World's Fair. The fair's organizers wanted to do an exhibit showing the progress of mankind “from the dark prime to the highest enlightenment, from savagery to civic organisation" He was given a hefty budget to collect living "specimens" of people from Africa to represent the "savage depths" from which mankind had sprung. The experience of young African men at the 'fair' aka Human Zoo, was not a pleasant one. Billed as cannibals, they shook spears at the crowd and grimaced with their filed teeth, modeling their "war dances" Verner sent Ota to the American Museum of Natural History in New York City. In 1906, Verner found a new home for Ota: The Bronx Zoo. Ota was put as an "exhibit" A plaque was erected, describing him in the same way an animal would be described and put into a cage in the monkey house. The Minneapolis Journal declared Ota to be the "missing link" between chimps and humans. On March 19, 1916, he stole a revolver gun and shot himself through the heart.
x
523 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The most fashionable bathing station in all Europe". British industrialists and American mining investors plotting the colonization of the Congo, while mingling at Ostend's seaside vacation resorts. Extracting African life to build European railways, hotels, palaces, suburbs, and other modern(ist) infrastructure. "Towards infinity!"
---
In 1885, King Leopold II achieved an astonishing and improbable goal: he claimed a vast new realm of his own devising, a conjury on a map called [...] the Congo Free State. [...] [A] fictional state owned by the king, ruled by decree, and run from Brussels from 1885 to 1908. [...] This was [...] a private entrepreneurial venture [for the king]. The abundance of ivory, timber, and wild rubber found in this enormous territory brought sudden and spectacular profits to Belgium, the king, and a web of interlocking concession companies. The frenzy to amass these precious resources unleashed a regime of forced labor, violence [millions of deaths], and unchecked atrocities for Congolese people. These same two and a half decades of contact with the Congo Free State remade Belgium [...] into a global powerhouse, vitalized by an economic boom, architectural burst, and imperial surge.
Congo profits supplied King Leopold II with funds for a series of monumental building projects [...]. Indeed, Belgian Art Nouveau exploded after 1895, created from Congolese raw materials and inspired by Congolese motifs. Contemporaries called it “Style Congo,” [...]. The inventory of this royal architecture is astonishing [...]. [H]istorical research [...] recovers Leopold’s formative ideas of architecture as power, his unrelenting efforts to implement them [...]. King Leopold II harbored lifelong ambitions to “embellish” and beautify the nation [...]. [W]ith his personal treasury flush with Congo revenue, [...] Leopold - now the Roi Batisseur ("Builder King") he long aimed to be - planned renovations explicitly designed to outdo Louis XIV's Versailles. Enormous greenhouses contained flora from every corner of the globe, with a dedicated soaring structure completed specifically to house the oversize palms of the Congolese jungles. [...]
---
The Tervuren Congo palace [...]. Electric tramways were built and a wide swath of avenue emerged. [...] [In and around Brussels] real estate developers began to break up lots [...] for suburban mansions and gardens. Between 1902 and 1910, new neighborhoods with luxury homes appeared along the Avenue [...]. By 1892, Antwerp was not only the port of call for trade but also the headquarters of the most profitable of an interlinking set of banks and Congo investment companies [...]. As Antwerp in the 1890s became once again the “Queen of the Scheldt,” the city was also the home of what was referred to as the “Queen of Congo companies.” This was the ABIR, or Anglo-Belgian India Rubber Company, founded in 1892 with funds from British businessman “Colonel” John Thomas North [...].
Set on the seaside coast, Belgium’s Ostend was the third imperial cityscape to be remade by King Leopold [...] [in a] transformation [that] was concentrated between 1899 and 1905 [...]. Ostend encompassed a boomtown not of harbor and trade, like Antwerp, but of beachfront and leisure [...] [developed] as a "British-style" seaside resort. [...] Leopold [...] [w]as said to spend "as much time in Ostend as he did in Brussels," [...]. Ostend underwent a dramatic population expansion in a short period, tripling its inhabitants from 1870–1900. [...] Networks of steamers, trams, and railway lines coordinated to bring seasonal visitors in, and hotels and paved walkways were completed. [...] [A]nd Leopold’s favorite spot, the 1883 state-of-the-art racetracks, the Wellington Hippodrome. Referred to with an eye-wink as “the king incognito” (generating an entire genre of photography), visitors to the seaside could often see Leopold in his top hat and summer suit [...], riding his customized three-wheeled bicycle [...]. By 1900, Ostend’s expansion and enhancement made it known as “the Queen of the Belgian seaside resorts” and “the most fashionable bathing station in all Europe.” Opulence, convenience, and spectacle brought the Shah of Persia, American tycoons, European aristocrats, and Belgian elites, among others, to Ostend.
---
Leopold’s interventions and the Congo Free State personnel and proceeds played three pivotal and understudied roles in this transformation, all of which involved ABIR [British industrialists].
First, it was at Ostend that an early and decisive action was taken to structure the “red rubber” regime and set it in motion. In 1892, jurists such as [E.P.] had ruled, contravening [...] trade laws, that the king was entitled to claim the Congo as his domanial property [...]. Leopold [...] devised one part of that royal domain as a zone for private company concessions [...] to extract and export wild rubber.
Soon after, in 1892, King Leopold happened to meet the British “Colonel” John Thomas North at the Ostend Hippodrome. North, a Leeds-born mechanic [...] had made a fortune speculating on Chilean nitrates in the 1880s. He owned monopoly shares in nitrate mines and quickly expanded to acquire monopolies in Chilean freight railways, water supplies, and iron and coal mines. By 1890 North was a high-society socialite worth millions [...]. Leopold approached North at the Ostend racecourse to provide the initial investments to set up the Anglo-Belgian India Rubber Company (ABIR). [...]
---
One visible sign of Ostend’s little-known character as Congo boomtown was the Royal Palace Hotel, a lavish property next to the king’s Royal Domain, which opened in 1899. With hundreds of rooms and a broad sweep of acreage along the beachfront, the palace “occupied the largest space of any hotel in Europe.” [...]
King Leopold met American mining magnate Thomas Walsh there, and as with North, the meeting proved beneficial for his Congo enterprise: Leopold enlisted Walsh to provide assessments of some of his own Congo mining prospects. The hotel was part of [...] [a major European association of leisure profiteers] founded in 1894, that began to bundle luxury tourism and dedicated railway travel, and whose major investors were King Leopold, Colonel North [...].
At the height of Congo expansionism, fin-de-siècle Antwerp embodied an exhilarated launch point [...]. Explorers and expeditioners set sail for Matadi after 1887 with the rallying call “Vers l’infini!” (“towards infinity!”) [...].
---
Text above by: Debora Silverman. "Empire as Architecture: Monumental Cities the Congo Built in Belgium". e-flux Architecture (Appropriations series). May 2024. At: e-flux.com/architecture/appropriations/608151/empire-as-architecture-monumental-cities-the-congo-built-in-belgium/ [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Italicized first paragraph/heading in this post was added by me. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism.]
#tidalectics#ecology#multispecies#abolition#this full article has far more info about leopolds obsession with opulence and all the many infrastructure projects in belgium he sponsored#full article also expands more on congolese art and anticolonial art projects that criticize belgian architecture#eflux did several articles focusing on anticolonial responses to belgian extraction and art noveau and modernist architecture#including a piece on spectacle of belgian worlds fair and human zoos#silverman has very extensive research history#ecologies#geographic imaginaries
132 notes
·
View notes
Text
Someone should truly speak bout the “later wife effect” that seems to have haunted historical figures since times long forgotten.
To break it down to you, what I call the “later wife effect” occurs when a male historical figure suddenly looses his beloved wife (most of the times, his first one) in an untimely and tragic manner -either by a childbirth gone wrong, an accident or a sudden illness-, turning the once mirthful husband into a grief-stricken widower. Perhaps because he lacks succession from said wife, because he has to provide spares to his heir, or even because an alliance is needed, he is forced to marry again; but the love never arises fully, their marriage turns into a bound of duty, and no matter what she does, or how loved she is outside their marriage: the later wife will forever be under the shadow of the first, a perfect idol, immortalised by her early death.
The “later wife effect” knows various levels:
In 1673, Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, lost his beloved Margaret Theresa when she was yet to turn twenty two and with child. Their seven years of union had produced four children, but only a daughter lived when Margaret Theresa died, and he went on to marry twice again; and even though he would sorrowfully remark that neither Claudia Felicitas of Austria or Eleonore Magdalene of Neuburg, his following brides, were “not like my only Margaretha”, his marriages were remarkably happy and so was he. This could be one of the mildest examples.
The middle ground would be when the marriage with the later wife is dutiful and polite, but loveless. Frederick William II of Hesse married Alexandra Nikolaevna, but soon lost her due to complications of childbirth. He would remarry nine years later to the beautiful and lively Anna of Prussia, and even though they eventually had six children, their marriage was notably cold and unhappy. Leopold I of Belgium widowed of his wife, Charlotte of Wales, soon after she gave birth to a dead son; fifteen years later, know king of Belgium, he took Louise-Marie of Orléans hand in marriage; she was shy, delicate, witty and partook in many charitable causes, earning the love of the Belgians, and the respect of her husband, with whom she had a fruitful and tranquil union; but Leopold would not be faithful to her, committing adultery with a much younger Arcadie Claret, who was said to resemble the long gone princess Charlotte. She perished a year after he had a son with Claret, and her dead did not stop the relationship between the two of them.
More unhappy cases of this effect would be those of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, and his descendant, Joseph II. When still an archduke, Maximilian married Mary of Burgundy and loved her much, a love so legendary it lived through generations in the art commissioned by their descendants. But the fairytale would come to an abrupt end when, after five years of marriage, Mary would find her untimely dead while pregnant with their fourth child, after her horse threw her off the saddle. Maximilian was most heartbroken and, after a failed marriage attempt with the young duchess Anne of Brittany, he would wed Bianca Maria Sforza. The empress from Milan was deemed “more beautiful than Mary” by Maximilian, but neither her beauty not her many charms of her would soften his callous attitude towards his wife. Having endured a miscarriage during the first months of their union, Bianca Maria, the once most sought after princess in Europe, had become a ghost in her own court, severely neglected by her husband, who refused to attend to her own funeral nor dedicate a gravestone for her. Similarly, after the traumatic passing of his wife, Isabella of Parma, Joseph II was forced to remarry to Maria Josepha of Bavaria, who he did not found as attractive as the late archduchess. He grew so disgusted of her that the same devoted husband that has been by Isabella’s bedside now commanded to put a wall between his balcony and hers, so that he could not see her, distressing old servants in the palace so much with his cold attitude that some left. When, after two years of marriage, her life was robbed by smallpox -the same ailment that had taken Isabella’s life four years before-, Joseph declared she had been worthy of respect and that he repented his coldness. However, he refused to visit her bedside and did not appear during her burial.
This should not be confused with what I call “the younger wife effect”, which takes place when a widowed historical figure, who had long remained unwed by choice, suddenly takes marriage to a beautiful and much younger person that is described to bring happiness to his once lonely and dull life. This would perfectly be exemplified with prince Maximilian of Saxony’s marriage with princess Maria Luisa Carlota of Parma, almost twenty one years since the passing of his wife (princess Carolina of Parma) or Edward I’s marriage to Marguerite of France.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
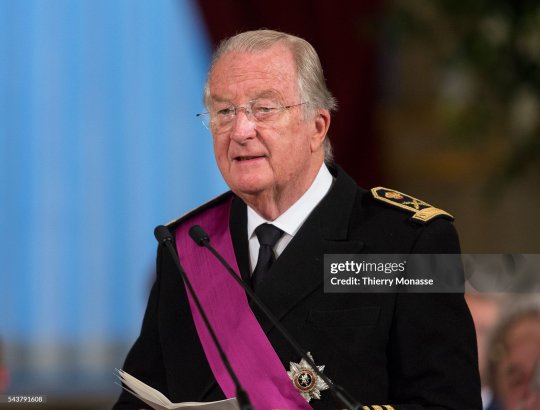
Albert II of Belgium
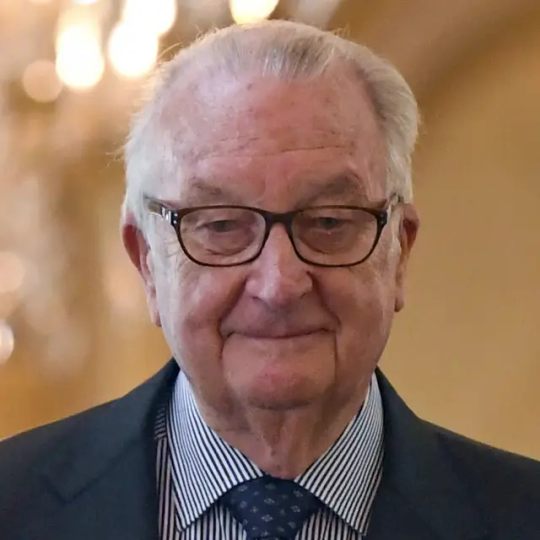

Physique: Average Build Height: 6'1"
Albert II (born 6 June 1934 -) is a member of the Belgian royal family who reigned as King of the Belgians from 1993 until his abdication in 2013. He is the son of King Leopold III and Queen Astrid, born princess of Sweden. He is the younger brother of Grand Duchess Joséphine-Charlotte of Luxembourg and King Baudouin, whom he succeeded upon Baudouin’s death in 1993. Albert II abdicate the throne for health reasons in 1993 and was succeeded by his son Philippe on 21 July 2013.





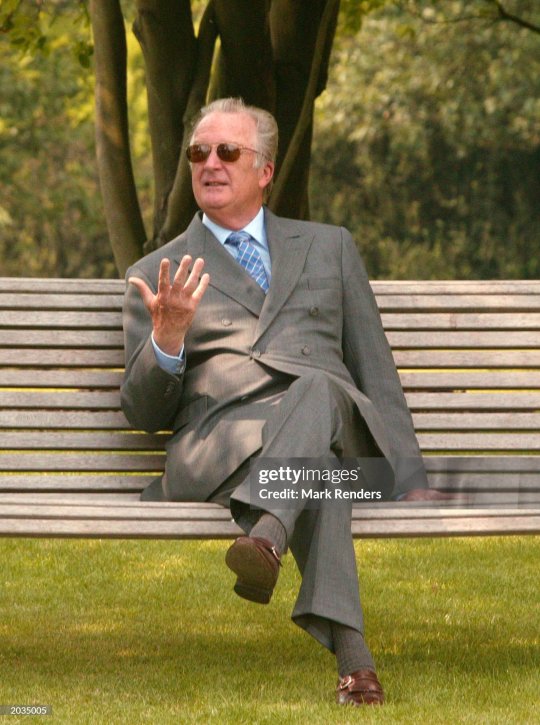
The former King is adorable. He definitely falls into the 'cute grandpa' category. Sure he’s getting on in years and a little past his best but I'd still do him in a heartbeat. And even if you think he is too old, he was a fucking king. You would fuck him and you know it.
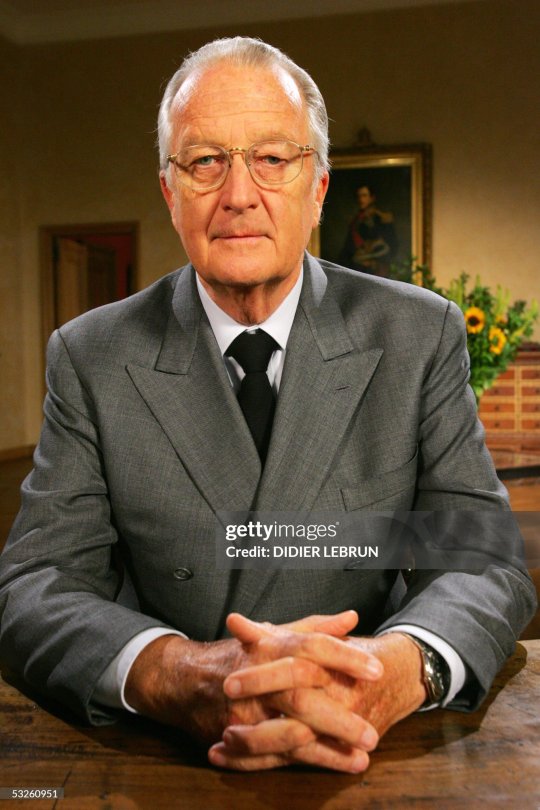





He married Donna Paola Ruffo di Calabria (now Queen Paola), with whom he had three children; King Philippe, Princess Astrid and Prince Laurent with twelve grandchildren and three great-grandchildren. During the 60s, King Albert had an 18-year-affair with Belgian aristocrat that produced a second daughter, Princess Delphine. If I were alive in the 60s, Albert could have slept with me and not have to worry about admitting he fathered a child out of wedlock. What? He isn’t getting me pregnant.

59 notes
·
View notes
Text

Prince Leopold of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha-Koháry (1824-1884). Unknown artist.
He was considered as the English government's candidate to be the husband of Queen Isabella II of Spain. This candidacy was due to the UK's strong ties with the House of Saxe-Coburg-Gotha. The candidate was a first cousin of Queen Victoria's husband Albert, a nephew of King Leopold of Belgium, and a first cousin of King Ferdinand II of Portugal married to Queen Maria II.
#prince leopold of saxe coburg and gotha kohary#haus wettin#german aristocracy#house of saxe coburg and gotha#house of saxe coburg and gotha kohary#blond guys#pornstache#royalty
22 notes
·
View notes
Text






Muriel Thompson a decorated Scottish World War I ambulance driver, racing driver and suffragist was born on this day 1875.
Thompson was born on 10th June 1875 in Aberdeen, Scotland to Agnes Marion Williamson, the second wife of Cornelius Thompson, a shipowner and marine architect. She was the fifth of eight children. Her grandfather George Thompson had been Lord Provost of Aberdeen and an MP for the city.
Thompson was an avid motorist, and from an early age she drove the family car. She and her brothers helped found the Brooklands Automobile Racing Club. On 4 July 1908 she won the first ladies’ motor race held at Brookland, the Ladies’ Bracelet Handicap, she caused quite a stir by beating the wife of the racetrack’s owner with metres to spare.
After the race, Muriel was greeted by cries of “women deserve the vote now!” She agreed, and was hired as a chauffeur by the Women’s Social and Political Union. Driving a green Austin with white wheels and purple stripes – the suffragette colours – she took Emmeline Pankhurst on her 1909 national tour
Her daredevil driving skills proved lifesaving during the First World War. In 1915, she signed up to the First Aid Nursing Yeomanry, and us Scots must have a slight snigger at the acronym, FANY.
Three months later, she was awarded the Knight’s Cross of the Order of Leopold II by King Albert of Belgium for evacuating wounded soldiers under fire. Alongside her Calais convoy, in 1917, she became one of the first women to drive for the British Army, who had until that point refused FANY’s services.
Thompers, as her colleagues called her, kept meticulous diaries while abroad. They reveal the horrors of war, but also the camaraderie and independence she experienced.
Muriel saved hundreds of lives during the war. In January 1918, she became Commanding Officer of the newly-formed St Omer convoy, and was awarded the Military Medal and the Croix de Guerre for her fearless fight to evacuate the injured during air raids.
Muriel returned to Britain two months before the war ended and resigned from FANY in 1922 – she was one of the bravest and best they had. Muriel died a few months before the Second World War broke out.
Photos are of Muriel Thompson and her medals include: Military Medal 1914-18; 1914-15 Star; British War Medal 1914-20; Allied Victory Medal 1914-19 with oak leaf for Mentioned in Dispatches; Order of Leopold II, Belgium, 1914-18, Badge of the 5th Class; Croix de Guerre, France 1914-18.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text










One of the buildings to which Paleizenplein ("palaces square") in Brussels owes its name is the Palace of the Academies, which currently houses most of Belgium's academies.
From 1828 to 1830 it was the home of Crown Prince William of Orange-Nassau and his consort Anna Paulowna, daughter of Tsar Paul and Grand Duchess of Russia whrn Belgium (or Southern Netherlands) were part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands which was created after the battle of Waterloo in 1815. Later It was also temporarily the home of Crown Prince (of Belgium which was established in 1830) Leopold, at that time titled Duke of Brabant, to which Hertogsstraat (" Duke's street") refers. The palace is a late but pure example of neoclassicism, the palace style of the Enlightenment. This architectural gem was drawn according to pure geometric proportions, Renaissance symmetry and axiality.
The neoclassical building was built between 1823 and 1828 on the site of the Park Abbey refuge house. The state architects Charles Vander Straeten and Tieleman Franciscus Suys also carried out one of the renovations of the adjacent Royal Palace of Brussels in the same period. It was financed to the amount of 1,215,000 guilders with resources from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and on behalf of William I. The palace was furnished for his son, Crown Prince Willem and his Russian wife Anna Pavlovna. On the night of September 25 to 26, 1829, the palace was broken into. The thieves stole Anna Pavlovna's jewelry from her bedroom and escaped with it.
After the Belgian Revolution, the palace came under sequestration. An army regiment were given shelter there. It would take until 1842 before a compromise was found. The building was transferred to the Belgian state and the sumptuous contents went to the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The contents were transferred to the Kneuterdijk Palace and after the death of William II to the Noordeinde Palace, where many pieces can still be admired.
From 1848 to 1852, the palace was the location of the first regiment of Jagers-Carabiniers. King Leopold II refused to move into the building that was offered to him in 1853. It was decided to use it for ceremonies and celebrations. The interior was renovated under the supervision of architect Gustave De Man. However, in 1862 the Museum of Modern Art was housed in the palace, pending the completion and furnishing of the Royal Museums of Fine Arts of Belgium. It would still house works of art until the Royal Academies of Belgium were allowed to settle there (royal decree of April 30, 1876).
Interior:
In the monumental stairwell hangs a portrait of Empress Maria Theresa of Austria, in honor of the original founder of the Académie Impériale et Royale des Sciences et Belles-lettres de Bruxelles in 1772. The Throne Room (not to be confused with the Belgian Throne Room in the adjacent Royal Palace of Brussels) is the original banquet room of the palace. Adjacent were the private rooms of William II, of which, among other things, the toilet with enormous wall mirror of his wife Anna Pavlovna of Russia has been preserved. The large Marble Hall on the second floor is covered with Belgian brown marble and white marble from Carrara. The parquet, constructed with oak and tropical wood (rosewood and amaranth wood), has a motif of small tree leaves. The vault is covered with gold leaf and tympanums. The hall has excellent acoustics and is regularly used for concerts. In addition, there are a number of smaller rooms, including the Maria Theresa Hall when the Academy classes meet separately, and the Leopold Hall and Albert Hall for smaller committee meetings. The old permanent secretary's office also radiates grandeur. The building also contains about sixty smaller and larger office spaces.
#neoclassical#neoclassico#neoclassicism#architectural history#architecture#historic buildings#belgium#europe#historical interior#bruxelles#brussels#brussel#bruselas#marble#gold#netherlands#palace#palaces#chandelier#lustre#history#historical#palazzo#palais#floors#parquet flooring#wood flooring#flooring
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
people on that post (that I 100% agree with) being like 'If Belgians can't be racist then what about King Leopold II?' and like I get it - King Leopold II colonized Congo from 1885 to 1908. And sure that's a valid thing to bring up but it doesn't change the fact that Belgium is still a white European country today - a country that is racist now.
Over half of black people in Belgium have experienced racism when looking for housing or employment in the last 5 years - and this is only for black people of African decent (as stated in the article)
At the very least, Larian Studios is unknowingly negligent when it comes to creating characters of color (which I doubt) but at most they are willfully ignorant of 1. how they handle characters of color and 2. the harmful stereotypes they added to their game.
#💖.em#i'm not an expert of course because i'm white but i am belgian#and there are more present day examples you can use instead of King Leopold II#also correct me if i'm wrong with any of this ofc
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

King Leopold II of Belgium
Belgian vintage postcard
#postcard#ansichtskarte#briefkaart#leopold#photography#carte postale#vintage#postkarte#photo#historic#postkaart#ephemera#sepia#leopold ii#belgium#belgian#king#tarjeta#postal
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

“I think that the Belgian royal family is really underrated. In my opinion, they have an interesting history that we don’t talk about enough, aside from the atrocities committed by Leopold II in Congo. Albert I was nicknamed “The Knight King” because of his heroic role during the WW1, Baudouin was also a great king, and Philippe was initially considered a prince incapable of leading a country, yet today he proves quite the opposite. Princess Elisabeth will become Belgium's first reigning queen, and that will certainly leave a mark in Belgian’s history. We don't often hear about the fact that the royal family volunteers to help people with disabilities, the elderly, children facing academic challenges and the homeless. They are known to be very close to their people.” - Submitted by Anonymous
36 notes
·
View notes
Text

🇨🇩 … there is so much to learn!! So much is happening in this world!!
By: LaillaB, founder of ‘Reclaim the Narrative’, from LinkedIn …
“Western imperialism continues to leave a dark and enduring legacy across the globe, from The Congo to Palestine.
The devastating effects of exploitative inequality persist in these regions, corrupting communities and wreaking havoc on generations of natives.
Through the theft of land, exploitation of resources, and imposition of foreign rule, Western powers have left a trail of devastation in their wake.
The state of Israel was created on land that was illigitamelty taken from the Palestinian people, leading to decades of human rights violations and displacement against the natives.
The ongoing colonisation of Palestine continues to fuel violence and instability in the region, with devastating consequences for the Palestinian people … Genocide.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has long been a victim of Western exploitation, with its vast mineral wealth being plundered by foreign powers for centuries.
During “The Butcher of Congo”, Belgium’s King Leopold II's brutal colonisation of the Congo Free State, estimates suggest that up to 10 million Congolese lost their lives and their rights are still being sacrificed as the wealth around them is stripped away.
Growing demand for so-called clean energy technologies has created a corresponding demand for certain metals, including copper, and cobalt, which is essential for making most lithium-ion batteries. The DRC has the world’s largest reserves of cobalt, and the seventh largest reserves of copper.
… Israel’s the worlds leader in exporting diamonds.
The intrusion by israel in 1997 marked a turning point as the DRC spiralled into chaos, highlighting the perilous consequences of external economic interests in politically fragile regions.
“Israel turns over about $28 billion in diamonds a year,” the Jerusalem Post pointed out, solidifying the industry's position as a cornerstone of the nation's economic power.
Israeli companies import rough diamonds for cutting and polishing, adding significantly to their value, and export them globally via distribution hubs in Antwerp, London, Hong Kong, New York and Mumbai.
Despite the introduction of the Kimberley Process in 2003 to regulate the trade of conflict diamonds, the narrow definition excludes cut and polished diamonds, allowing the flow of revenue to fund contentious activities.
This loophole enables the trade of de facto blood diamonds from Israel to persist in the global market, perpetuating a cycle of deceit and destruction.
Candy Ofime and Jean-Mobert Senga, Amnesty International researchers said: “We found repeated breaches of legal safeguards prescribed in international human rights law and standards, and national legislation, as well as blatant disregard for the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights.”
From The Congo 🇨🇩 to Palestine 🇵🇸 …
“The greatest menace to the world today is the growing, exploiting, irresponsible imperialism”
Mahatma Gandhi.
#reclaimthenarrative — 🍉🕊 — #FreePalestine … #FreeCongo … @hrexach
#dr rex equality news information education#graphic source#graphic#graphics#hortyrex ©#horty#quote#it is what it is#gaza genocide#gaza strip#war#war crimes#war criminals#free congo#congo genocide#diamond#loose diamonds#colonialism#oppression#oppressor#israhell#israel#palestine
7 notes
·
View notes