#IoT hashtag
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#hashtag#IoT hashtag#AssetMonintoring hashtag#InternetofThings hashtag#IoTHub hashtag#IoTCentral hashtag#IoTSuite hashtag#AzureIoT hashtag#DigitalTransformation hashtag#IoTinManufacturing hashtag#PredictiveMaintenance hashtag#StridelySolutions
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Revolução da IoT na Agricultura de Precisão

internexumbr
12 seguidores
16 de agosto de 2024
A agricultura de precisão, que utiliza tecnologias para otimizar a produção e o uso de recursos naturais, está sendo impulsionada pela Internet das Coisas (IoT). A IoT conecta sensores, máquinas e dispositivos à internet, permitindo a coleta e análise de dados em tempo real, a automação de processos e a tomada de decisões mais precisas.
Aplicações da IoT na Agricultura de Precisão:
Monitoramento do Solo: Sensores instalados no solo coletam dados sobre umidade, temperatura, nutrientes e pH, permitindo que os agricultores ajustem a irrigação, a aplicação de fertilizantes e o tratamento do solo de forma precisa.
Monitoramento do Clima: Sensores meteorológicos coletam dados sobre temperatura, umidade, precipitação e velocidade do vento, auxiliando os agricultores na previsão de condições climáticas e na tomada de decisões estratégicas.
Monitoramento de Cultivos: Sensores instalados nas plantas coletam dados sobre crescimento, saúde e níveis de nutrientes, permitindo que os agricultores identifiquem problemas precocemente e apliquem tratamentos específicos para cada planta.
Automação da Irrigação: Sistemas de irrigação inteligentes controlados pela IoT ajustam a quantidade de água aplicada às plantas de acordo com as necessidades de cada cultivo, reduzindo o desperdício de água e aumentando a eficiência.
Gestão de Plagas: Sensores monitoram a presença de pragas e doenças, permitindo que os agricultores apliquem pesticidas e fungicidas de forma precisa e com menor impacto ambiental.

Benefícios da IoT na Agricultura:
Aumento da Eficiência: A IoT impulsiona a eficiência na agricultura, reduzindo o desperdício de água, fertilizantes e pesticidas, aumentando a produtividade e reduzindo os custos de produção.
Sustentabilidade: A IoT contribui para a sustentabilidade, reduzindo o impacto ambiental da agricultura, preservando recursos naturais e promovendo práticas agrícolas mais ecologicamente corretas.
Melhoria da Qualidade: A gestão de dados em tempo real permite aos agricultores monitorar a qualidade dos cultivos e tomar medidas para garantir a produção de produtos de alta qualidade.
A Internet das Coisas está transformando a agricultura, impulsionando a agricultura de precisão e criando um futuro mais eficiente e sustentável para a produção de alimentos. A integração de sensores, máquinas e dispositivos conectados à internet permite aos agricultores tomar decisões mais precisas, otimizar o uso de recursos naturais e aumentar a produtividade, contribuindo para um sistema alimentar mais sustentável e eficiente.
#IoT hashtag#Agricultura hashtag#AgriculturaDePrecisão hashtag#Sustentabilidade hashtag#Produção hashtag#Eficiência hashtag#Tecnologia hashtag#Inovação hashtag#Monitoramento hashtag#RecursosNaturais hashtag#Dados
0 notes
Text

Solar PV Operations and Maintenance Market
The solar PV operations and maintenance market size is forecast to reach USD 10.9 billion by 2030, after growing at a CAGR of 14.8% during 2024-2030.
#hashtag#Sustainability hashtag#GreenTech hashtag#CleanEnergy hashtag#IoT hashtag#AI hashtag#DigitalTransformation hashtag#EnergyEfficiency hashtag#GridStability hashtag#SolarPower hashtag#TechInnovation hashtag#Renewables
0 notes
Text

What are the most effective methods for managing power factor in your system?
`What's Power Factor?
In an energy management system, the power factor gauges the efficiency of electrical power usage. It is defined as the ratio of real power to apparent power (the total power supplied). A high power factor signifies efficient use of electrical power, which minimizes energy losses and enhances system performance.
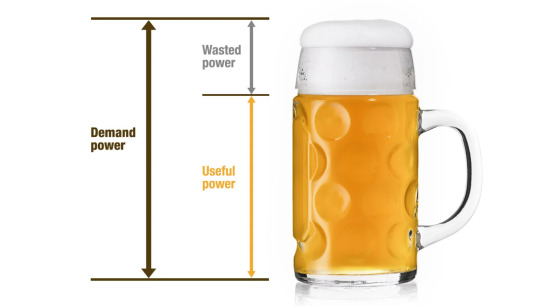
Beer is active power (kW)—the useful power, or the liquid beer, is the energy that is doing work. This is the part you want.
Foam is reactive power (kVAR)—the foam is wasted power or lost power. It’s the energy being produced that isn't doing any work, such as the production of heat or vibration.
The mug is apparent power (kVA)—the mug is the demand power, or the power being delivered by the utility.
Understanding Low Power Factor?
A low power factor is primarily caused by inductive loads, including motors, transformers, and lighting ballasts, which draw reactive power. This reactive power is essential for generating and sustaining magnetic fields but does not contribute to useful work, increasing apparent power and consequently lowering the power factor. Moreover, harmonics from nonlinear loads, such as electronic devices and variable frequency drives, further reduce the power factor by introducing additional reactive power.
Benefits of High Power Factor
A high power factor decreases the apparent power and current drawn from the source, which can lower energy bills as some utilities impose charges for low power factor or provide incentives for maintaining a high power factor. It enhances voltage regulation and stability, increases system capacity and efficiency by reducing losses and heating, and lessens the effects of harmonics, thereby improving overall power quality.Benefits of Power Factor

Measuring Power Factor
Power factor is measured using a power meter or analyzer that monitors real, reactive, and apparent power, or with a power factor meter for direct readings. Measurements should be taken at various points in the system and at different times to account for load variations.
Correcting Low Power Factor
The most effective way to correct a low power factor is by installing power factor correction devices such as capacitors or synchronous condensers. These devices provide reactive power locally, reducing the flow of reactive power and improving the power factor. Depending on the load characteristics and desired power factor levels, they can be installed centrally or near specific inductive loads.
Controlling Power Factor Correction Devices
Power factor controllers, which can be either manual or automatic, are used to manage correction devices. Manual controllers rely on human adjustments based on meter readings, whereas automatic controllers use sensors and microprocessors to adjust devices. Automatic controllers can also be programmed to optimize performance under varying load conditions.
Optimizing Power Factor Management
Optimizing power factor management requires balancing cost, performance, maintenance, and safety. Essential practices include regular evaluation and adjustment, proper maintenance to prevent overloading and overheating, and compliance with utility codes and standards. This comprehensive approach ensures improved efficiency, stability, and cost-effectiveness of your electrical system.
#SmartEnergy hashtag#Sustainability hashtag#RenewableEnergy hashtag#EnergyEfficiency hashtag#SmartMeterRevolution hashtag#Niraltek hashtag#NiraltekTeam hashtag#InternetOfThings hashtag#ESP32 hashtag#ESP32Development hashtag#ESP32Project hashtag#ConnectedDevices hashtag#IoTInnovation hashtag#IoTProject hashtag#IoTDevices hashtag#IoTSecurity hashtag#IoTApplications hashtag#IoTDevelopment hashtag#IoTTechnology hashtag#ESP32Electronics hashtag#ESP32Innovation hashtag#IIoTTechnology hashtag#IIoTInnovation hashtag#IndustrialIoT hashtag#EnergyUsage hashtag#IoT hashtag#SmartCities hashtag#SmartMeter hashtag#powerfactor
0 notes
Text
Unveiling the Uniqueness of Flutter

#artificialintelligence hashtag#ai hashtag#machinelearning hashtag#technology hashtag#datascience hashtag#python hashtag#deeplearning hashtag#programming hashtag#tech hashtag#robotics hashtag#innovation hashtag#bigdata hashtag#coding hashtag#iot hashtag#computerscience hashtag#data hashtag#dataanalytics hashtag#business hashtag#engineering hashtag#robot hashtag#datascientist hashtag#art hashtag#software hashtag#automation hashtag#analytics hashtag#ml hashtag#pythonprogramming hashtag#programmer hashtag#digitaltransformation hashtag#developer
0 notes
Text
Revolutionising Agriculture with IoT Technology
Written By: Jagriti Shahi

Introduction:
In recent years, the agricultural sector has undergone a profound digital transformation, propelled by the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. This revolutionary shift has transcended traditional farming practices, empowering growers with real-time data and insights to make informed decisions, optimise resource utilisation, and maximise yields. By interconnecting physical devices and sensors with cloud computing and data analytics, IoT has ushered in a new era of precision agriculture, offering solutions to age-old challenges faced by farmers worldwide.
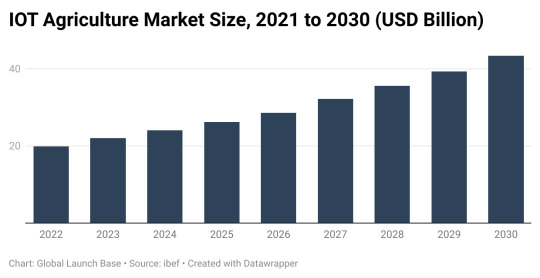
Figure: IOT Agriculture Market Size, 2021 to 2030 (USD Billion)
From the above figure we can see that IOT agriculture market size to surpass US$ 43.37 Bn by 2030

Figure: Adoption of Blockchain/ IoT - 2021
The marriage of IoT technology with agriculture has unlocked a plethora of opportunities across the entire farming ecosystem, from field management to supply chain logistics. This convergence has not only improved operational efficiency but also paved the way for sustainable farming practices. As the world grapples with escalating food demand, water scarcity, and environmental degradation, IoT-enabled solutions have emerged as indispensable tools in mitigating these challenges while ensuring food security and environmental stewardship.
Precision Farming:

Figure - Precision Farming
One of the cornerstone applications of IoT in agriculture is precision farming, which represents a paradigm shift from traditional blanket approaches to site-specific management. This innovative approach harnesses the power of IoT-enabled sensors, drones, and autonomous machinery to monitor and manage various aspects of crop production with unparalleled accuracy.
IoT sensors embedded in the soil continuously gather data on key parameters such as moisture levels, temperature, nutrient content, and pH levels. This real-time data is then transmitted to centralised platforms where it is analysed and processed using advanced algorithms. By leveraging this granular information, farmers can precisely tailor their irrigation, fertilisation, and pest control strategies to meet the specific needs of each crop and microenvironment within their fields.
Furthermore, the integration of IoT technology with precision agriculture has facilitated the development of variable rate application (VRA) systems. These systems utilise GPS-guided machinery to deliver inputs, such as water and nutrients, in precise quantities and locations based on the spatial variability detected in the field. By optimising input usage in this manner, farmers can not only enhance crop productivity and quality but also reduce costs and minimise environmental impact by avoiding over-application of inputs in areas where they are not needed.
Moreover, the data-driven insights generated through precision farming practices enable farmers to implement proactive measures to mitigate risks and optimise resource allocation. For instance, predictive analytics algorithms can forecast crop yields, pest outbreaks, and weather patterns, empowering farmers to make preemptive decisions to safeguard their crops and maximise profitability.
Overall, precision farming powered by IoT technology represents a quantum leap in agricultural productivity and sustainability. By harnessing the power of data-driven decision-making and precision management practices, farmers can unlock new levels of efficiency, profitability, and environmental stewardship in their operations. As IoT continues to evolve and become more accessible, the potential for innovation and transformation in agriculture is virtually limitless.
Smart Irrigation Systems:

Figure: Smart Irrigation Systems
Water scarcity is a pressing concern for farmers worldwide, exacerbated by climate change and population growth. In response to this challenge, smart irrigation systems have emerged as a game-changing solution, leveraging IoT technology to optimize water usage in agricultural fields.
At the heart of smart irrigation systems are IoT-enabled sensors that continuously monitor soil moisture levels, weather conditions, and crop water requirements in real-time. These sensors transmit data wirelessly to a central control system, where advanced algorithms analyse the information and determine the precise amount and timing of irrigation needed for each area of the field.
By dynamically adjusting irrigation schedules based on actual field conditions, smart irrigation systems minimise water wastage while ensuring that crops receive the optimal amount of moisture for healthy growth. This targeted approach not only conserves water but also enhances crop yield and quality by avoiding both under- and over-irrigation, which can lead to stress, disease, and reduced productivity.
Furthermore, smart irrigation systems offer farmers unprecedented control and flexibility over their irrigation practices. Through mobile or web-based applications, farmers can remotely monitor and manage their irrigation systems from anywhere, allowing them to respond quickly to changing weather patterns or crop needs. Some advanced systems even integrate weather forecasts and soil moisture data to automatically adjust irrigation schedules, further streamlining water management and reducing manual intervention.
Beyond water conservation and crop productivity, smart irrigation systems also deliver significant economic and environmental benefits. By reducing water usage and energy consumption associated with pumping, farmers can lower their operational costs and mitigate their carbon footprint. Additionally, by minimising runoff and leaching of nutrients and agrochemicals into water bodies, smart irrigation systems help protect water quality and preserve fragile ecosystems.
Crop Monitoring and Management:
In the realm of modern agriculture, crop monitoring and management have been revolutionised by the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. With the aid of IoT-enabled sensors, drones, and data analytics platforms, farmers now have unprecedented visibility into the health, growth, and condition of their crops, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimise production practices.

IoT sensors deployed in the field collect a wealth of data on various parameters such as soil moisture, temperature, humidity, nutrient levels, and crop health indicators. This data is transmitted in real-time to centralised platforms where it is processed and analysed using advanced algorithms. By harnessing the power of big data analytics and machine learning, farmers can derive actionable insights from this data, allowing them to monitor crop performance, detect anomalies, and identify potential issues before they escalate.
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral imaging sensors play a pivotal role in crop monitoring and management. These aerial platforms can capture detailed imagery of fields from above, providing farmers with valuable insights into crop health, growth patterns, and pest infestations. By analysing these images, farmers can pinpoint areas of stress or vegetation anomalies, enabling them to take targeted corrective actions such as adjusting irrigation or applying pest control measures.
Moreover, IoT technology enables the development of predictive analytics models that forecast crop yields, disease outbreaks, and pest infestations based on historical data and real-time observations. By leveraging these predictive insights, farmers can proactively plan their planting, harvesting, and pest management strategies to optimise yields and minimise losses.
Additionally, IoT-enabled crop monitoring systems offer farmers greater flexibility and scalability in their operations. These systems can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different crops, growing conditions, and farming practices, allowing farmers to optimise resources and maximise profitability. Furthermore, the integration of IoT with other emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and robotics holds the promise of further enhancing crop monitoring and management capabilities, paving the way for more autonomous and efficient farming practices.
Overall, IoT technology has transformed crop monitoring and management from a labour-intensive and resource-intensive process into a data-driven and proactive endeavour. By providing farmers with real-time insights, predictive analytics, and actionable recommendations, IoT-enabled solutions empower farmers to optimise crop yields, reduce risks, and enhance sustainability in agriculture. As IoT continues to evolve and become more accessible, the potential for innovation and transformation in crop monitoring and management is virtually limitless.
Livestock Monitori

Figure: Livestock Monitoring
In the realm of modern agriculture, livestock monitoring has undergone a paradigm shift with the advent of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. Traditionally, livestock management relied heavily on manual observation and intuition, making it challenging for farmers to detect health issues, optimise feeding regimes, and maximise productivity. However, IoT-enabled sensors and data analytics platforms have revolutionised livestock monitoring, offering farmers unprecedented insights into the health, behaviour, and performance of their animals. IoT sensors, attached to animals or installed in their living environments, continuously collect data on key parameters such as body temperature, heart rate, activity levels, and rumination patterns. This real-time data is transmitted wirelessly to centralised platforms where it is analysed and processed using advanced algorithms. By monitoring these physiological and behavioural indicators, farmers can detect signs of illness, stress, or reproductive cycles early on, allowing them to intervene promptly and provide appropriate care.
Moreover, IoT technology enables farmers to track the location and movement of livestock, particularly in extensive grazing systems or large-scale operations. GPS-enabled tracking devices attached to animals provide real-time information on their whereabouts, allowing farmers to monitor grazing patterns, prevent livestock theft, and optimise pasture management. This enhanced visibility into animal behaviour and movement enables farmers to make data-driven decisions to improve herd health, productivity, and welfare.
Furthermore, IoT-enabled livestock monitoring systems offer farmers greater efficiency and scalability in their operations. These systems can be integrated with other farm management software, such as feed management or reproductive tracking systems, to provide a comprehensive view of herd performance and profitability. Additionally, the use of wearable devices and smart collars allows farmers to remotely monitor individual animals or entire herds from anywhere, reducing the need for manual labour and improving overall productivity.
In addition to improving animal health and welfare, IoT-enabled livestock monitoring systems also deliver significant economic and environmental benefits. By optimising feeding regimes and managing herd health more effectively, farmers can reduce feed wastage, minimise veterinary costs, and increase overall profitability. Moreover, by minimising the environmental impact of livestock production through more efficient resource utilisation and waste management, IoT technology contributes to the sustainability of agriculture.
Supply Chain Optimization:
In the dynamic landscape of agriculture, supply chain optimization has emerged as a critical area where Internet of Things (IoT) technology is driving significant transformation. From farm to fork, the agricultural supply chain encompasses a complex network of processes, stakeholders, and resources. IoT-enabled solutions offer unprecedented visibility, traceability, and efficiency across this entire ecosystem, revolutionising how agricultural products are produced, processed, and distributed.
At the farm level, IoT sensors deployed in fields and orchards collect data on environmental conditions, crop growth stages, and harvest readiness. This real-time data enables farmers to optimise planting schedules, manage inputs more efficiently, and anticipate yield fluctuations. By integrating IoT data with farm management systems, farmers can make data-driven decisions to maximise productivity while minimising costs and environmental impact.
As agricultural products move through the supply chain, IoT technology plays a crucial role in ensuring product quality, safety, and compliance. Temperature, humidity, and location sensors embedded in storage facilities, transportation vehicles, and processing plants monitor the conditions of perishable goods in real-time. Any deviations from optimal conditions trigger alerts, allowing stakeholders to take corrective action to prevent spoilage, contamination, or quality degradation. By maintaining the integrity of the cold chain and reducing food waste, IoT-enabled supply chain solutions contribute to improved food safety and sustainability.
Moreover, IoT technology enhances transparency and traceability throughout the agricultural supply chain, enabling stakeholders to track the journey of products from farm to consumer. Blockchain-based platforms leverage IoT data to create immutable records of product origin, production practices, and handling procedures. This transparency builds trust among consumers, enhances brand reputation, and facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements such as food safety standards and sustainability certifications.
Additionally, IoT-enabled supply chain solutions offer opportunities for optimization and cost savings through predictive analytics and automation. By analysing historical data and real-time insights, predictive analytics models can forecast demand, optimise inventory levels, and streamline logistics operations. Autonomous vehicles and robotic systems equipped with IoT sensors and artificial intelligence algorithms further enhance efficiency by automating tasks such as harvesting, sorting, and packaging.
Furthermore, IoT technology facilitates collaboration and coordination among supply chain partners through real-time data sharing and communication. Cloud-based platforms and mobile applications enable seamless integration and exchange of information between farmers, suppliers, distributors, and retailers. This collaboration fosters greater agility, responsiveness, and resilience in the face of supply chain disruptions such as weather events, market fluctuations, or global pandemics.
Advanced IoT Applications for Farms

1. Drone-based scouting and spraying: Imagine agile drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors. These can autonomously map fields, identify weeds and pests with incredible accuracy, and deliver targeted treatment exactly where it's needed. This reduces reliance on broad-spectrum pesticides, promotes sustainable practices, and minimises environmental impact.

2. Predictive analytics for disease and pest control: IoT sensors combined with advanced AI can analyse historical data and weather patterns to predict outbreaks of diseases and pests. This allows farmers to take preventive measures, such as applying natural deterrents or introducing beneficial insects, before problems escalate.

3. Climate-smart agriculture: IoT weather stations with advanced sensors can provide hyper-local weather data, including real-time wind speed, precipitation forecasts, and even data on micronutrient levels in the atmosphere. This empowers farmers to make informed decisions about planting schedules, crop selection, and irrigation strategies based on real-time forecasts, optimising yields and building resilience against climate variations.

4. Blockchain for traceability and transparency: Imagine a system where every step of a product's journey, from farm to fork, is recorded on a secure blockchain ledger. Sensors embedded in packaging can monitor temperature and storage conditions during transportation, ensuring food safety. Consumers can then scan a QR code and access a transparent record of the product's origin, farming practices used, and even the environmental impact of its production.

5. Robotics for controlled-environment agriculture (CEA): In indoor farms and vertical farming facilities, IoT plays a central role. Robots equipped with sensors and grippers can perform delicate tasks like seeding, transplanting, and harvesting with minimal damage to crops. This not only reduces labour costs but also ensures consistent quality and higher yields in controlled environments.
Cultivating Innovation with IoT
The agricultural IoT revolution isn't just a theoretical concept – it's being driven by a wave of forward-thinking companies developing cutting-edge solutions. Here are a few industry leaders to watch:
Deere & Company: A major player in agricultural machinery, Deere offers a suite of IoT-powered solutions under the John Deere® FarmSight® banner. These include yield monitors, tractor telematics, and weather data analysis tools, empowering farmers to optimise their operations.
Trimble Inc.: This company provides a range of advanced positioning and data management solutions for agriculture. Their offerings include automated guidance systems for tractors and combines, allowing for high-precision planting and harvesting, and software platforms that integrate data from various sources to give farmers a comprehensive view of their operations.
SenseFly (Parrot Group): Specialises in agricultural drone technology. Their drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors, are used for field scouting, identifying crop health issues, and creating detailed 3D field maps.
InFarm: A leader in the indoor vertical farming space, InFarm leverages IoT sensors and automation extensively. Their vertical farms are equipped with environmental control systems that optimise light, temperature, and humidity for specific crops, all monitored and managed through a central IoT platform.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
While the potential of IoT in agriculture is undeniable, there are challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. Here's a look at some key hurdles and how we can work towards a future where smart farming flourishes:
Challenges:
Connectivity: Reliable internet access in rural areas is crucial for real-time data collection and analysis. Efforts are underway to expand broadband access and explore alternative low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN) for improved connectivity in remote locations.
Cost: The upfront investment in sensors, devices, and software can be significant, especially for small and medium-scale farms. Government subsidies, innovative financing models, and standardisation of technologies can help bring down costs and make these solutions more accessible.
Data Security and Privacy: As farms become increasingly reliant on data, robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect sensitive information from breaches and ensure farmer trust.
Digital Literacy: Equipping farmers with the skills to understand and utilise IoT technologies effectively is crucial. Training programs, workshops, and user-friendly interfaces can bridge the digital divide and empower farmers to harness the full potential of these tools.
Future Outlook:
Despite these challenges, the future of IoT in agriculture is bright. As technology costs decrease, connectivity improves, and farmers become more comfortable with digital tools, adoption is expected to accelerate. Here are some exciting possibilities to look forward to:
Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Advanced analytics will extract even deeper insights from agricultural data, allowing for predictive maintenance of equipment, automated disease and pest control, and hyper-personalised crop management strategies.
Rise of Agtech Startups: A growing number of innovative startups are developing niche solutions tailored to specific agricultural needs. This will lead to a more diverse and dynamic ecosystem, offering farmers a wider range of choices.
Focus on Sustainability: IoT will play a key role in optimising water usage, minimising fertiliser application, and reducing the environmental impact of agriculture. This will contribute to a more sustainable food production system.
In conclusion, IoT holds immense potential to transform agriculture. By addressing the existing challenges and fostering collaboration between farmers, technology providers, and policymakers, we can usher in an era of smart farming that is not only productive but also sustainable and resource-efficient.
— x —
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#AgriTechCEO hashtag#IoTAgricultureLeader hashtag#SmartFarmingPioneer#hashtag#PrecisionAgVisionary hashtag#DigitalAgChampion hashtag#FarmTechInnovator#IoTAgRevolutionary hashtag#AgriInnovationCEO hashtag#FutureFarmingExpert#AgriTechTrailblazer hashtag#SustainableAgLeader hashtag#DataDrivenAgCEO#AgriTechDisruptor hashtag#IoTAgSolutionist hashtag#FarmTechVisionary#AgriDigitalTransformationLeader hashtag#IoTAgriInnovator#AgriTechGameChanger hashtag#SmartAgPioneer hashtag#IOT hashtag#Agriculture
0 notes
Text
The Significance of Wearables and IoT in Mobile Solutions Beyond Traditional Apps

Introduction: As technology continues to advance, the boundaries between the digital and physical worlds are becoming increasingly blurred. Wearable devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) are revolutionizing the way we interact with technology, offering seamless integration into our daily lives. In this article, we delve into the fascinating intersection of wearables, IoT, and mobile solutions, uncovering the transformative impact they have on various industries and everyday experiences.
Wearables and IoT:
Wearable devices encompass a wide range of gadgets that users can wear or carry, typically equipped with sensors and connectivity features. These devices include smartwatches, fitness trackers, augmented reality glasses, and even smart clothing. On the other hand, the Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to collect and exchange data. These devices can range from smart home appliances and connected vehicles to industrial machinery and environmental sensors. The significance of wearables and IoT lies in their ability to gather real-time data, facilitate seamless communication, and enable automation in various aspects of our lives.
Integration with Mobile Apps:
Mobile applications play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between users and their wearable/IoT devices. They serve as centralized hubs for managing settings, accessing data, and controlling functionalities. For instance, a health and fitness app can sync with a wearable fitness tracker to collect activity data, provide insights on exercise performance, and set personalized fitness goals. Similarly, smart home apps allow users to remotely monitor and control IoT devices such as thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras, enhancing convenience and security.
Transforming Healthcare:
Wearables and IoT have revolutionized healthcare by enabling remote patient monitoring, personalized healthcare interventions, and telemedicine services. Patients can use wearable devices to track vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, and transmit this data to healthcare providers in real-time. Mobile apps complement these devices by aggregating and analyzing health data, providing actionable insights, and facilitating communication between patients and healthcare professionals. This integration enhances patient engagement, improves treatment adherence, and enables proactive healthcare management.
Enhancing Fitness and Wellness:
Wearables and IoT have democratized access to fitness and wellness resources, empowering individuals to take control of their health and well-being. Fitness trackers and smartwatches equipped with sensors for tracking steps, calories burned, and sleep patterns encourage users to adopt healthier lifestyles. Mobile apps complement these devices by offering personalized workout plans, nutrition guidance, and motivational features. Additionally, gamification elements, such as challenges, rewards, and social interactions, make fitness activities more engaging and enjoyable, fostering long-term behavior change and adherence to wellness goals.
Revolutionizing Smart Homes:
The proliferation of smart home devices, coupled with mobile apps, has transformed traditional homes into connected ecosystems of intelligent appliances and systems. Smart thermostats, lighting controls, security cameras, and voice-activated assistants enable homeowners to remotely monitor and manage their living spaces with ease. Mobile apps serve as centralized platforms for configuring device settings, scheduling automated routines, and receiving real-time notifications. The integration of wearables adds another layer of convenience, allowing users to control smart home devices using voice commands or gestures from their wrist.
Innovations in Industry and Enterprise:
Wearables and IoT are driving digital transformation in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and retail by optimizing processes, improving productivity, and enhancing safety. In industrial settings, IoT sensors embedded in machinery and equipment enable predictive maintenance, monitor operational performance, and ensure workplace safety. Wearable devices equipped with biometric sensors and augmented reality capabilities enhance employee productivity and facilitate hands-free interactions. Mobile apps provide managers and stakeholders with real-time insights, analytics, and alerts, empowering informed decision-making and process optimization.
Overcoming Challenges and Considerations:
Despite the numerous benefits of wearables and IoT in mobile solutions, several challenges need to be addressed to ensure widespread adoption and maximize their potential. Data privacy and security remain top concerns, as the proliferation of connected devices increases the risk of cyber threats and data breaches. Interoperability issues between different devices and platforms can hinder seamless integration and user experience. Moreover, user education and training are essential to familiarize individuals with the functionalities and benefits of wearables and IoT devices. Designing intuitive and user-friendly mobile apps that complement wearable/IoT interactions is crucial for enhancing adoption and usability.
Conclusion:
The convergence of wearables, IoT, and mobile solutions heralds a new era of connectivity, efficiency, and innovation across various domains. By leveraging the capabilities of these technologies, businesses and individuals can unlock unprecedented opportunities for improving health outcomes, enhancing productivity, and simplifying everyday tasks. As wearables and IoT continue to evolve and permeate our lives, the potential for transformative impact is boundless, paving the way for a smarter, more interconnected future.
#wearables hashtag#iot hashtag#mobiletech hashtag#innovation hashtag#digitaltransformation hashtag#smartdevices hashtag#healthtech hashtag#fitnesstech hashtag#smarthomes hashtag#industry40 hashtag#connecteddevices hashtag#userexperience hashtag#subscribenow hashtag#techtrends#facebook#webdesign#memes#developer#developers#elicitdigital#webdevelopment#digitalmarketingtips#elicit
0 notes
Text
BLIIoT Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 Used in Smart Charging Piles Monitoring
I. Introduction

1. A brief introduction to smart charging piles
In today's society, with the progress and development of customers, people pay more and more attention to smart energy. At present, electric vehicles have become the choice of more and more people. As the number of electric vehicles increases, so does the demand for smart charging piles. In order to improve the intelligence and convenience of charging piles, Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 can be used to realize remote monitoring and control in smart charging piles. In this article, we will discuss how to use an Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 to implement a monitoring solution for smart charging piles.
The smart charging pile monitoring system is a solution based on the Industrial IoT 4G Edge Router R40, which can realize real-time monitoring and management of charging piles. In addition to the basic charging pile status monitoring function, the system also has data analysis and forecasting functions, which can be analyzed based on historical data and real-time data to help users better understand the usage and trends of charging piles, and then make better decisions. management decisions.
2. Industrial 4G Edge Router R40

Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 have many features, including DI (2 channels), DO (2 channels), AI (4 channels), support protocols (Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP, MQTT, SNMP protocols), 4G network, support SMS Query DI/DO/AI status and value, support 4G wireless Internet access, support edge computing, two SIM card slots, support GPS, VPN, interface (support RS485 and RS232 serial port transparent transmission and MODBUS RTU to TCP), support MODBUS master Station, support address mapping, support monitoring the online status of network devices connected to the LAN port, link switching, platform connection, alarm, timer, upgrade, POE power supply and other features. These features allow Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 to realize remote monitoring and control in smart charging piles.
II. Application of Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 in smart charging piles

1. Real-time monitoring:
The smart charging pile monitoring system needs to be able to monitor the status, usage and charging speed of charging piles in real time. Through these data, operators can understand the usage of charging piles in real time, detect faults and repair them in time, and improve the quality and efficiency of charging services.
The Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 can be connected to the camera, supports POE power supply and network supply, and can realize real-time monitoring of the surrounding environment of the smart charging pile in real time, improving the safety and reliability of the charging pile.
2. Remote management:
The IoT Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 can provide remote management functions for the smart charging pile monitoring system. Operators can remotely view the status of charging piles, control the switching of charging piles, adjust charging power and other operations through the network. In this way, operators can manage charging piles more conveniently, while improving operational efficiency and reducing labor costs.
3. Data analysis:
The smart charging pile monitoring system needs to be able to analyze the monitored data, extract valuable information and display it. For example, analyzing the usage frequency, usage time period, charging speed and other data of charging piles can help operators optimize the layout and usage strategy of charging piles, and improve the satisfaction of charging services. At the same time, using big data technology to analyze charging pile usage data can also help operators understand user habits and needs and provide more personalized services.
4. Alarm and remote maintenance:
Through Industrial 4G Edge Router R40, real-time monitoring and abnormal alarms for charging piles can be realized. When there is an abnormality in the charging pile, the system will automatically trigger an alarm, and at the same time, it can be sent to the relevant personnel by text message or email, so as to deal with the problem in time. In addition, the Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 also supports remote upgrades, which can remotely perform firmware upgrades and configuration adjustments for charging piles, which is convenient for maintenance personnel to perform remote maintenance and management.
III. Features and advantages of Industrial 4G Edge Router R40
1. Multiple input and output types:
The Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 supports multiple input and output types such as DI (2 channels), DO (2 channels) and AI (4 channels), which can meet the needs of different scenarios. For example, for smart charging piles, the status and power of the charging piles can be monitored through the DI and AI interfaces, and the switching control of the charging piles can be realized through the DO interfaces.
2. Multiple communication protocols:
The router supports multiple communication protocols, including Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP, MQTT and SNMP protocols, etc., which can realize seamless communication between different devices. For example, in the smart charging pile scenario, the communication with the charging pile controller can be realized through the Modbus protocol, and the communication with the cloud platform can be realized through the MQTT protocol.
3. Edge Computing:
The router supports edge computing, which can realize real-time data processing and response on site. For example, in the scenario of smart charging piles, this function can be used to realize real-time calculation of charging pile power and timely processing of charging pile failures.
4. Dual card switching and link switching:
The router supports dual card switching and link switching, which can improve the stability of the network connection of the device. For example, in the smart charging pile scenario, this function can be used to realize the switching of the charging pile network connection and the automatic repair of faults.
IV. Benefits of using Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 in smart charging piles
1. Realize intelligent remote management and control
Using an Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 can connect the charging pile to the Internet for remote monitoring and control. This means that managers can access the data of charging piles anytime and anywhere, including charging amount, charging duration, charging voltage and current, etc. Managers can use remote control, such as remote switching, adjusting charging power, setting charging mode, etc., to better manage charging piles and improve the efficiency of charging piles and charging experience.
2. Improve the stability and safety of charging piles
Real-time monitoring and fault alarm of charging piles can be realized by using Industrial 4G Edge Router R40. When the charging pile fails, the Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 will automatically send an alert to the management personnel. In this way, managers can take timely measures to reduce downtime and improve the stability and safety of charging piles.
3. Reduce maintenance costs and increase efficiency
Using an Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 can also reduce maintenance costs and improve efficiency. Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 can realize automatic diagnosis and maintenance, reducing manual intervention. Managers can better manage and maintain charging piles through remote monitoring and control, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
V. Conclusion
In general, the emergence of smart charging piles has brought great convenience to our lives, but at the same time it also requires remote management and control to ensure its stability and safety. As a high-performance network device, the Industrial 4G Edge Router R40 can meet the needs of remote management and control of smart charging piles, while improving its stability and security, reducing maintenance costs and improving efficiency. Therefore, it is a very wise choice to use industrial-grade 4G edge computing routers in the application field of smart charging piles, and it will be widely used in more smart device application scenarios in the future.
More information about the Industrial 4G Edge Router: https://www.bliiot.com/industrial-iot-edge-gateway-p00307p1.html

#iot hashtag#iotsolutions hashtag#smartcity hashtag#smartenergy hashtag#smartcharging hashtag#smartparking hashtag#iotdevices hashtag#gateway hashtag#router hashtag#rtu hashtag#iomodule hashtag#logiccontrol hashtag#edgecomputing hashtag#vpn hashtag#poe hashtag#gps hashtag#modbus hashtag#mqtt hashtag#snmp hashtag#datacollection hashtag#remotemonitoring#hashtag#awscloud hashtag#thingsboard hashtag#alibabacloud hashtag#huaweicloud hashtag#openwrt#BLIIoT#BLIIoT Applications
0 notes
Text
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Glossario del digitale. Con Gabriele Gobbo e Inviata A.I. - 226
In questa puntata di FvgTech, Gabriele Gobbo e l’inviata digitale esplorano i termini fondamentali del glossario digitale: gif, hashtag, RAM, podcast, big data, IoT e username. Un viaggio tra significati, curiosità e praticità quotidiane. In questo episodio di FvgTech, Gabriele Gobbo insieme alla nostra inviata digitale, creata grazie all’intelligenza artificiale, ci accompagna in un nuovo…
#big data#FvgTech#Gabriele Gobbo#Gif#Glossario digitale#Hashtag#IoT#Podcast#puntata video#RAM#Username
0 notes
Text

The tech landscape is constantly evolving, and staying ahead of the curve is crucial! Here's a sneak peek at some of the most emerging development trends that will shape the future. If you wish to know more about any of these, we will break it down for you! Let us know in the comments below 🙌 Visit: https://www.dexbytes.com/
#iot#web 3.0#hashtag#appdevelopment#metaverse#generativeai#TechProducts#webdevelopment#developerhiring
0 notes
Text

MELSS provides robotic solutions after careful study of your requirements and brings you a diverse range of solutions from the leading brands - Doosan and OnRobot . The range is also augmented by a set of tools and accessories. The Lift100 from OnRobot is one such tool. It increases the reach of a robot, enabling more cycles even in remote locations. Not only does the Lift100 offer the seventh axis to traditional six-axis robots, but it is also future-proof for palletising and other manufacturing applications. Its capability to handle high payloads with minimum deflection ensures precise positioning even at high speeds. Robustly built, it is reliable over a long period. Pallet stations for pallet positioning, along with #palletising software make it a complete package. For more: https://zurl.co/qYEK
#Robotics hashtag#EndOfArmTool hashtag#Lift100#melss#industrial automation and robotics#automated test equipment manufacturers#industrial iot solutions india
0 notes
Text
Announcement!
if you follow my twitter you probably already know about this but I’m creating a disventure camp all stars AU based on Island of the Slaughtered and it’s called “Disventure Camp: Bleeding Tipiskaw”. Like in the original IotS, the campers show up to the camp, but a killer is on the loose and Kristal and her crew leave the campers to fend for themselves. If you wanna keep up with this AU, I’ll be posting about it in the hashtags “disventure camp: bleeding Tipiskaw” and bleeding Tipiskaw”
I plan to post the prelude to my au on Saturday, June 1st, but the victim logs will be posted every Wednesday, there will be some other info posted in between victims. This isn’t set in stone though. I might have to either push the date back or forward if I need to (although the latter is unlikely)
be sure to look out for it!
Additional info:
there are 13 victims and 5 survivors.
like IotS there will be art for it
at the end of the story I also plan on doing other things like writing interviews for the survivors.
all the victims are based on horror characters (there are like three exceptions, ones based on a song and ones based on a non horror character that just happens to be a bit creepy but they technically count)
#disventure camp#Disventure camp: bleeding Tipiskaw#bleeding Tipiskaw#aiden disventure camp#alec disventure camp#ashley disventure camp#jake disventure camp#james disventure camp#tom disventure camp#disventure camp fiore#hunter disventure camp#ellie disventure camp#disventure camp gabby#ally disventure camp#tess disventure camp#miriam disventure camp#lake disventure camp#riya disventure camp#connor disventure camp#yul disventure camp#disventure camp grett#Kristal McLean#island of the slaughtered
25 notes
·
View notes
Text

🌟 O Futuro dos Semicondutores é Brasileiro! 🌟
O Instituto Internexum está pronto para transformar o Brasil no maior fabricante e desenvolvedor de semicondutores do mundo! Como um instituto de pesquisa de ponta, lideramos a conexão entre fabricantes, governo, mercado internacional e outros atores chave. 🚀 🔬 Inovação e Pesquisa: Nossos projetos de pesquisa avançada e parcerias estratégicas garantem que estamos na vanguarda da tecnologia de semicondutores. 🤝 Conexão de Demandas: Atuamos como um elo vital, conectando demandas, mentes brilhantes, localidades estratégicas e fontes abundantes de matéria-prima no Brasil. 🌍 Liderança Global: Com uma infraestrutura robusta e políticas visionárias, o Brasil está pronto para se destacar no cenário internacional. 🔧 Demanda Crítica: Semicondutores são essenciais para toda a indústria, desde IoT em roupas e eletrodomésticos até carros e elevadores. O Brasil, líder em minérios usados na produção de semicondutores, altamente conectado e rico em talentos, está preparado para enfrentar esse cenário desafiador. Com vasto espaço para extração, produção e logística, temos tudo para sermos protagonistas. 📖 Leia Mais: Confira a matéria traduzida da CNBC sobre como a Malásia está se posicionando estrategicamente no mercado de semicondutores e inspire-se em como o Brasil pode seguir um caminho semelhante. Junte-se a nós nessa jornada rumo à liderança global! 🌐 hashtag#Semicondutores hashtag#Tecnologia hashtag#Inovação hashtag#BrasilLíder hashtag#Internexum hashtag#FuturoTecnológico hashtag#Desenvolvimento hashtag#Pesquisa hashtag#Indústria4.0 hashtag#CompetitividadeGlobalA Malásia emerge como um ponto estratégico para empresas de semicondutores em meio às tensões entre os EUA e a China
Matéria de: https://www.linkedin.com/in/sheilachiang/
Leia a matéria original, em inglês, aqui: https://www.cnbc.com/2024/04/04/malaysia-emerges-as-a-hotspot-for-chip-firms-amid-us-china-tech-war.html
Pontos principais A Intel Corporation , GlobalFoundries e Infineon Technologies são algumas das fabricantes de chips que estabeleceram ou expandiram operações na Malásia nos últimos anos. “A Malásia possui uma infraestrutura bem estabelecida, com cerca de cinco décadas de experiência na parte final do processo de fabricação de semicondutores, particularmente em montagem, teste e embalagem”, afirmou Kendrick Chan, do think tank de política externa da LSE. Isso ocorre em um contexto em que a guerra comercial entre os EUA e a China levou as empresas a diversificarem suas operações.
A Malásia está emergindo como um ponto estratégico para fábricas de semicondutores, à medida que as tensões entre os EUA e a China levam as empresas a diversificarem suas operações.
“A Malásia possui uma infraestrutura bem estabelecida, com cerca de cinco décadas de experiência na parte final do processo de fabricação de semicondutores, particularmente em montagem, teste e embalagem”, afirmou Kendrick Chan, chefe do projeto de relações internacionais digitais da LSE IDEAS, o think tank de política externa da London School of Economics and Political Science. Os semicondutores — componentes críticos encontrados em tudo, desde smartphones até automóveis — têm estado no centro de uma guerra tecnológica entre os EUA e a China.
A gigante americana de chips Intel anunciou em dezembro de 2021 que investirá mais de 7 bilhões de dólares para construir uma fábrica de embalagem e teste de chips na Malásia, com produção prevista para começar em 2024.
“Nossa decisão de investir na Malásia está fundamentada em seu diversificado pool de talentos, infraestrutura bem estabelecida e robusta cadeia de suprimentos”, disse Aik Kean Chong, diretor-gerente da Intel Malásia, à CNBC. A primeira instalação de produção da Intel no exterior foi um site de montagem em Penang, lançado em 1972 com um investimento de 1,6 milhão de dólares. A empresa posteriormente adicionou uma instalação completa de testes, bem como um centro de desenvolvimento e design na Malásia.
Outra gigante americana do setor, a GlobalFoundries, abriu em setembro um hub em Penang para “apoiar operações globais de manufatura”, juntamente com suas fábricas em Singapura, nos EUA e na Europa.
“As políticas visionárias e o forte apoio do governo regional, juntamente com parceiros como InvestPenang, construíram um ecossistema sólido para a indústria prosperar”, disse Tan Yew Kong, vice-presidente sênior e gerente geral da GlobalFoundries Singapura. A principal fabricante de chips da Alemanha, a Infineon, anunciou em julho de 2022 que construirá um terceiro módulo de fabricação de wafers em Kulim, enquanto a Neways, um fornecedor chave do fabricante holandês de equipamentos para chips ASML, informou no mês passado que construirá uma nova instalação produtiva em Klang.
“A vantagem da Malásia sempre foi sua mão-de-obra qualificada em embalagem, montagem e teste, além dos custos operacionais comparativamente mais baixos, tornando as exportações mais competitivas globalmente”, afirmou Yinglan Tan, sócio fundador da Insignia Ventures Partners. Ele acrescentou que a posição atual do ringgit torna o país uma “localização atraente para investidores estrangeiros”. A Malásia detém 13% do mercado global para serviços de embalagem, montagem e teste de chips, conforme informou a Autoridade de Desenvolvimento do Investimento da Malásia em um relatório datado de 18 de fevereiro. As exportações de dispositivos semicondutores e circuitos integrados aumentaram 0,03%, totalizando 387,45 bilhões de ringgits malaio (81,4 bilhões de dólares) em 2023, em meio à fraqueza da demanda global por chips.
O presidente da Associação da Indústria de Semicondutores da Malásia, Datuk Seri Wong Siew Hai, afirmou que muitas empresas chinesas diversificaram parte de sua produção para a Malásia, chamando o país de “plus one” da China.
Zafrul Aziz, ministro malaio do investimento, comércio e indústria, disse à CNBC International em janeiro que a Malásia pretende focar na parte inicial do processo de fabricação de chips, ao invés apenas da parte final. Os processos iniciais envolvem fabricação de wafers e fotolitografia, enquanto os processos finais se concentram em embalagem e montagem.
Em uma tentativa de expandir o ecossistema semicondutor do país e atrair investimentos, a Malásia criou em janeiro uma força-tarefa estratégica nacional para semicondutores, conforme relataram meios locais.
Tensões entre os EUA e a China Da mesma forma, países como Índia e Japão têm buscado atrair empresas estrangeiras para estabelecer operações em seus territórios enquanto visam se tornar grandes centros produtores ao lado dos EUA, Taiwan e Coreia do Sul.
A Índia aprovou em fevereiro a construção de três fábricas semicondutoras com investimentos superiores a 15 bilhões de dólares. Em junho, o país aprovou os planos da gigante americana Micron para estabelecer uma unidade semicondutora.
No mesmo mês, o maior fabricante contratante de chips do mundo, TSMC, inaugurou sua primeira fábrica no Japão enquanto se diversifica fora de Taiwan em meio às tensões entre os EUA e a China.
Washington introduziu regras abrangentes em outubro de 2022 com o objetivo de restringir o acesso da China à tecnologia avançada em chips devido a preocupações sobre o uso militar dessas tecnologias. No ano passado, os EUA anunciaram novas regulamentações impedindo o designer americano Nvidia de vender chips avançados para inteligência artificial à China.
“A Malásia e a Ásia em geral estão posicionadas para se beneficiar da guerra tecnológica entre China e EUA, onde o acesso a chips semicondutores avançados está sendo utilizado como uma ferramenta para estabelecer supremacia tecnológica global”, afirmou May-Ann Lim, diretora da prática de governança dos dados na consultoria Access Partnership. Fuga de cérebros Embora a Malásia esteja prestes a se beneficiar da guerra dos chips entre os EUA e a China, sua fuga de cérebros representa desafios à medida que trabalhadores deixam o país por melhores perspectivas profissionais e salários mais altos.
“Isso pode muito bem ser o caso se as empresas investirem na capacitação da força laboral na Malásia apenas para perdê-los para outros concorrentes na região assim que adquirirem as habilidades”, disse Lim. Um estudo oficial realizado em 2022 revelou que 3 em cada 4 trabalhadores malaio em Singapura são qualificados ou semiqualificados, destacando o problema da fuga de cérebros no país.
“Se essa demanda gerada pela diversificação das cadeias produtivas será atendida com oferta suficiente de talentos qualificados no país ainda é um desafio operacional contínuo”, disse Tan da Insignia Ventures Partners. O primeiro-ministro malaio Anwar Ibrahim afirmou em setembro que o governo está buscando atrair malaios qualificados para retornar e contribuir com o país.
[1] https://www.mida.gov.my/mida-news/cnbc-malaysia-a-hotspot-for-semiconductor-firms/
[2] https://www.cnbc.com/2024/04/04/malaysia-emerges-as-a-hotspot-for-chip-firms-amid-us-china-tech-war.html
[3] https://www.aseanbriefing.com/news/malaysias-semiconductor-sector-beckons-foreign-investors/
[4] https://thediplomat.com/2024/05/malaysia-unveils-plans-to-become-next-global-chip-hub/
[5] https://www.eurasiareview.com/07052024-malaysias-new-power-potential-in-the-chip-industry-analysis/
[6] https://theedgemalaysia.com/node/725300
[7] https://www.digitimes.com/news/a20240625PD221/malaysia-semiconductors-advanced-packaging-ic-design-ai.html
[8] https://www.mida.gov.my/a-glimpse-into-malaysias-semiconductor-aspirations-bridging-partnerships-bridging-technologies/
0 notes
Photo

The Varieties of Agency in Human–Smart Device Relationships: The Four Agency Profiles
This is a short preview of the article: As the interest of intelligent/smart devices in growing in society, this paper explores the concept of agency in human-smart device relationships, focusing on two key aspects: User agency: The self-perceived abilities of users to operate and control their devices. Device agency: The
If you like it consider checking out the full version of the post at: The Varieties of Agency in Human–Smart Device Relationships: The Four Agency Profiles
If you are looking for ideas for tweet or re-blog this post you may want to consider the following hashtags:
Hashtags: #Agency, #DeviceAgency, #IoT, #SmartDevice, #UserAgency
The Hashtags of the Categories are: #HCI, #InternetofThings, #more, #Publication, #Research
The Varieties of Agency in Human–Smart Device Relationships: The Four Agency Profiles is available at the following link: https://francescolelli.info/hci/the-varieties-of-agency-in-human-smart-device-relationships-the-four-agency-profiles/ You will find more information, stories, examples, data, opinions and scientific papers as part of a collection of articles about Information Management, Computer Science, Economics, Finance and More.
The title of the full article is: The Varieties of Agency in Human–Smart Device Relationships: The Four Agency Profiles
It belong to the following categories: HCI, Internet of Things, more, Publication, Research
The most relevant keywords are: Agency, device agency, IoT, smart device, user agency
It has been published by Francesco Lelli at Francesco Lelli a blog about Information Management, Computer Science, Finance, Economics and nearby ideas and opinions
As the interest of intelligent/smart devices in growing in society, this paper explores the concept of agency in human-smart device relationships, focusing on two key aspects: User agency: The self-perceived abilities of users to operate and control their devices. Device agency: The
Hope you will find it interesting and that it will help you in your journey
As the interest of intelligent/smart devices in growing in society, this paper explores the concept of agency in human-smart device relationships, focusing on two key aspects: The study introduces four agency profiles that characterize different types of human-smart device relationships: Figure below presents an intuitive idea of the research: The researcher is validated by conducting…
0 notes
Text
Why Smart Cities Use Industrial 4G Edge Computing Routers for Remote Monitoring?

I. Smart cities

① Definition of Smart City
In the process of modern urbanization, smart city has become an important direction of urban development. Through the use of various smart facilities, Internet of Things technology and data analysis technology, smart city management can realize remote monitoring and management of urban facilities, and improve the efficiency and convenience of urban operations. In smart city management, the application of Industrial 4G Edge Routers can play an important role. This article will introduce how to use Industrial 4G Edge Routers in smart city, and explore its advantages and application scenarios.
② The Importance of Smart Cities
Smart cities can use Internet of Things technology and data analysis technology to monitor and control various facilities in the city in real time. This includes street lights, smart parking systems, trash cans and more. Through remote control and monitoring, the operational efficiency and energy efficiency of urban facilities can be improved.
II. BLIIoT Industrial 4G Edge Computing Router

The Cellular Edge IoT Router R40 is an industrial-grade OpenWrt IoT device with multiple functions. It integrates an Industrial Router, Gateway, RTU, and DTU functionality in one unit. The highly cost-effective product simplifies IoT systems by reducing hardware connections and maintenance requirements.
With dual SIM design, built-in WIFI module, Ethernet connection, and various IO interfaces, it is suitable for a broad rangof applications. The most common use-cases are IoT solutions for infrastructure (bridges, tunnels), agriculture (forest), mining, oil and gas, water, and industrial factory use cases.
The R40 supports IPsec, OpenVPN, and L2TP VPNs, as well as protocols such as Modbus and MQTT with local computing capabilities using shell scripts, C, or Lua programming.
Support Connection to Cloud Platform:Private Cloud ( BLIIoT Cloud or Custom MQTT cloud), Alibaba Cloud Platform, AWS Cloud, Huawei Cloud, Thingsboard Cloud Platform.
III. Application of Industria 4G Edge Routers in Smart Cities
With the continuous acceleration of the urbanization process, more and more cities are beginning to develop in the direction of intelligence. In smart cities, remote monitoring and management of various facilities is particularly important. As an intelligent communication device, the Industrial 4G Edge Routers can be connected with various facilities in the city to realize remote monitoring and management functions, which also brings some new possibilities for smart city management .
① Docking of Industrial 4G Edge Computing Router and Intelligent Street Lighting System

Connecting the industrial 4G edge computing router with various facilities in the city can realize remote monitoring and management. For example, connecting this product with a smart street lighting system can achieve the following functions:
We can connect Industrial 4G Edge Routers with intelligent street lighting systems to realize functions such as remote control, brightness adjustment, and fault monitoring. Generally speaking, the controller of the intelligent street lighting system needs to be connected to a gateway device to realize communication with the upper application system. The Industrial 4G Edge Routers not only supports multiple communication protocols (such as Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP, MQTT, SNMP, etc.), but also supports 4G wireless Internet access, which can realize functions such as remote control, real-time data collection and transmission, so it can be used as The gateway device of the intelligent street lighting system is used.
In the actual application scenario, we can install the Industrial 4G Edge Routers next to the street lamp controller, and transmit the data in the street lamp controller (such as street lamp status, brightness, etc.) to the Industrial 4G Edge Routers through the RS485 interface , and then transmitted to the cloud platform through the 4G network for processing and management. When the cloud platform needs to control the status of street lights or obtain street light data, it only needs to send instructions to the Industrial 4G Edge Routers through the cloud platform, and then the street light controller can execute them. At the same time, if the street lamp fails or needs to be maintained, the Industrial 4G Edge Routers can also send the fault information or maintenance information to relevant personnel through the 4G network to improve the efficiency and accuracy of street lamp management.
IV. Application of Industrial 4G Edge Computing Routers in Other Smart City Facilities
In addition to the smart street lighting system, the Industrial 4G Edge Router can also interface with other smart city facilities to achieve more efficient and smart city management.
The intelligent parking system is a facility widely used in urban traffic management. By setting sensors, surveillance cameras, LED screens and other equipment on the roadside, it realizes real-time monitoring of parking lots, vacancy query, cost calculation and other functions. The Industrial 4G Edge Routers can be connected with various devices in the intelligent parking system. Through edge computing, the data can be processed and stored quickly, and the city management department can be provided with real-time parking lot status information, so as to adjust the parking lot operation strategy in time. , Improve the utilization efficiency of parking spaces.
Smart trash can is an emerging urban management facility. By installing sensors, garbage classification and identification systems, visual screens and other equipment in the trash can, it can realize real-time monitoring and management of data such as the status of the trash can and garbage classification. The Industrial 4G Edge Routers can be connected with various devices in the smart trash can. Through edge computing, the data can be processed and analyzed quickly, and the city management department can be provided with real-time status information of the trash can and garbage classification for timely adjustment. Waste disposal strategies to improve the efficiency of urban waste disposal and the level of environmental sanitation.
In addition to the above-mentioned facilities, the Industrial 4G Edge Routers can also be connected with other intelligent facilities, such as intelligent bus stations, intelligent environmental monitoring systems, etc. Through edge computing, it can realize data collection, processing and analysis of various facilities, provide more accurate and real-time data support for urban management departments, and achieve more efficient and intelligent urban management.
V. Summary
Taken together, Industrial 4G Edge Routers have broad application prospects in smart city management. Through the monitoring and control of this product, smart cities can achieve more efficient, convenient and safe management methods, and make positive contributions to the sustainable development of cities.
In short, the Industrial 4G Edge Routers is one of the important tools in smart city management, and its flexibility and scalability allow it to be applied in various scenarios. By connecting it with various facilities in the city, real-time monitoring and control can be realized, and the efficiency and level of urban management can be improved, thereby providing citizens with more intelligent, convenient and efficient urban services.
More information about the BLIIoT Industrial 4G Edge Routers: https://www.bliiot.com/industrial-iot-edge-gateway-p00307p1.html

#iot hashtag#iotsolutions hashtag#smartcities hashtag#router hashtag#gateway hashtag#edgecomputing hashtag#streetlight hashtag#remotemonitoring hashtag#modbus hashtag#mqtt hashtag#snmp hashtag#datacollection#BLIIoT#BLIIoT Applications
0 notes