#International protection in the United States
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Foone is overstating the theoretical possibility of danger. Noone has been able to reliably detect *any* x-rays from CRTs. From international labor organization guidance (they call them VDUs for "visual display units"):
Numerous radiation measurements both in field and laboratory conditions have been conducted worldwide in attempts to detect ionizing (X-ray) radiation emissions from VDUs. Basically, these attempts have failed, in that no detectable emissions beyond the "natural" or "instrumental" backgrounds could be detected (Cox, 1984; Moss et al., 1977; Weiss and Petersen, 1979; Phillips, 1981; Terrana et al., 1982; Wolbarsht et al., 1980; Paulsson et al., 1984; Murray et al., 1981; Health and Welfare Canada, 1983; Pomroy and Noel, 1984; Joyner et al., 1984; Bureau of Radiological Health, 1981). Emissions of X-rays from VDUs are so weak that they cannot penetrate the front glass screen and so cannot be detected against the normally encountered background levels of ionizing radiation.
https://www.ilo.org/publications/visual-display-units-radiation-protection-guidance pages 10-11
It goes on to state that some of these measurements showed no detectable levels even after breaking parts of the TV to try to increase the x-ray output. A few TVs from before 1978 produced measurable levels and were pulled from the market or never made it to market and xrays haven't been detected since. There is no danger from the ionizing radiation.
Hey are those bulky old tvs dangerous to be around or is that just something my mom told me so I wouldn't sit too close to the screen
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
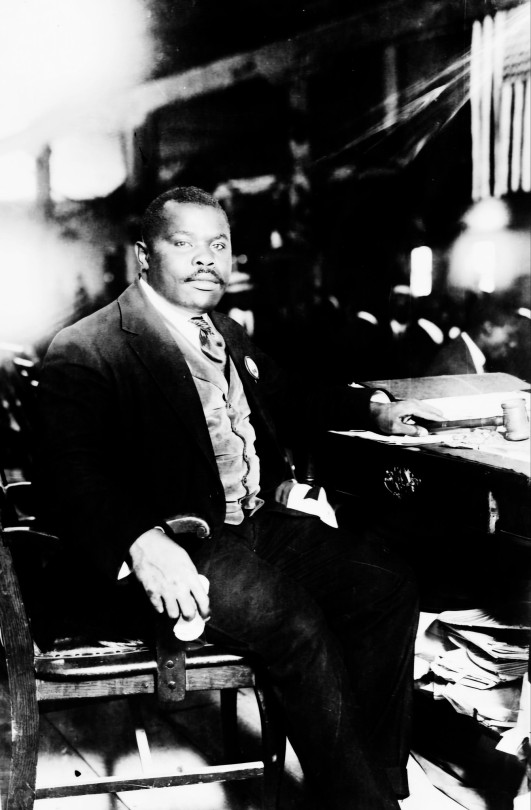
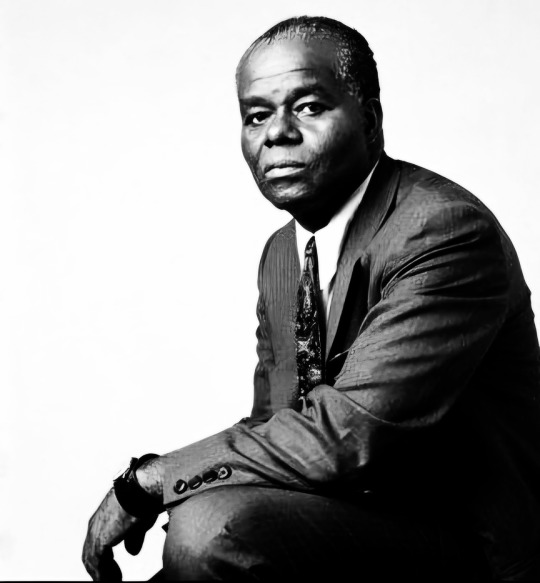


Why Dr. John Henrik Clarke Is Correct About Black People Having No Friends (and why We Don’t Need Any) – a Garveyite Perspective
Dr. John Henrik Clarke famously stated, “Black people have no friends.” For many, this may sound harsh, but it is a sobering truth when viewed through the lens of Pan-Africanism and Marcus Garvey’s philosophy. Garvey understood that Black liberation can not depend on external allies; it must come from within—rooted in self-reliance, unity, and a shared commitment among Black people globally.
Here’s why, Dr. Clarke’s statement rings true and why, from a Garveyite perspective, Black people don’t need friends—only each other.
1. History Proves It
From colonialism to the civil rights era, supposed "friends" of Black people have repeatedly betrayed or abandoned us. Other groups have leveraged Black struggles for their own gains, only to leave Black people behind once their goals were achieved.
Post-slavery labour movements excluded Black workers.
Civil rights coalitions saw other groups gain rights, while Black people remained trapped under systemic racism.
Garvey and Clarke both saw these betrayals as evidence that Black people must prioritize their own interests and stop relying on others.
2. Global Anti-Blackness Is Real
Anti-Blackness isn’t confined to one region—it’s a global phenomenon. Across continents, Black people face systemic oppression, discrimination, and dehumanization.
Other groups often form alliances to protect their own power while marginalizing Black voices.
Even in spaces of shared oppression, anti-Blackness often takes precedence.
Dr. Clarke’s assertion and Garvey’s vision both point to this truth: Black liberation must come from within because no one else will prioritize us.
3. Dependency Leads to Exploitation
Depending on outside "friends" or allies often comes with hidden costs. Foreign aid, alliances, and solidarity movements often prioritize the interests of others over Black liberation.
Aid to African nations often perpetuates dependency rather than fostering self-sufficiency.
"Allies" in social justice movements often centre their struggles, leaving Black people to fight alone.
Garvey warned that dependency breeds vulnerability. Clarke reinforces this: Black people must build their own systems to avoid exploitation.
4. We Have Everything We Need
Garvey believed that Black people possess the resources, talents, and ingenuity needed for liberation.
Africa’s wealth: With its vast natural resources, Africa can fund global Black empowerment if reclaimed from exploitative systems.
Diaspora talent: Across the globe, Black communities excel in innovation, creativity, and resilience.
Dr. Clarke’s statement echoes Garvey’s vision: We don’t need friends because we already have all the tools for success.
5. Cultural Exploitation Is Proof of No True Friendship
Black culture—music, art, fashion, and more—is celebrated globally, but Black people are rarely compensated or empowered by their own creations.
Other groups profit from Black innovation while perpetuating anti-Black systems.
Cultural exploitation demonstrates a lack of true solidarity.
Garvey’s solution: Black people must reclaim their culture and use it as a tool for empowerment, not exploitation.
6. Unity Is Our Greatest Strength (and Threat to Oppressors)
A united global Black community is the most powerful weapon against systemic oppression. Garvey emphasized unity, and Clarke’s assertion underscores why others fear it:
A unified Black world challenges global power structures that thrive on division.
By focusing on internal unity, Black people strengthen themselves and disrupt oppressive systems.
7. Allies Often Divide Us
Alliances can create divisions within Black movements, as external influences pit factions against each other or dilute the focus on Black liberation.
During the civil rights movement, alliances often marginalized more radical Black voices.
Today, funding from external groups can cause conflicts between grassroots Black organizers and larger organizations tied to outside agendas.
Garvey’s emphasis on self-reliance offers a solution: Black unity must come first, free from outside interference.
8. Other Groups Prioritize Their Own Interests
Every group prioritizes its own survival and progress—it’s not wrong, but Black people must learn from this.
White nations maintain global alliances to uphold their dominance.
Asian nations focus on economic self-sufficiency.
Jewish communities have built strong networks to protect and uplift their people.
Garvey and Clarke would agree: It’s time for Black people to do the same and put themselves first.
9. Historical Success Through Self-Reliance
History proves that Black people thrive when they rely on themselves:
The Haitian Revolution succeeded because enslaved Africans united and rejected external dependence.
Garvey’s UNIA (Universal Negro Improvement Association) built businesses, schools, and a global movement without outside help.
These examples show that self-reliance works. Black people don’t need friends—they need focus.
10. True Liberation Is Self-Determined
Liberation can not be outsourced, gifted, or borrowed—it must be self-determined. Allies may help temporarily, but no one will prioritize Black liberation over their own interests.
Garvey envisioned a world where Black people controlled their own economies, politics, and resources.
Clarke’s assertion reminds us that we can’t afford to waste time seeking validation or support from others.
11. Black Liberation Threatens Global Power Structures
Both Garvey and Clarke understood that Black liberation isn’t just a struggle for freedom—it’s a direct threat to the systems of power that dominate the world.
A free and united Africa would undermine Western economic dominance, which relies on exploiting African resources.
A globally empowered Black diaspora would disrupt industries, politics, and systems built on anti-Blackness.
This explains why no other group can truly be a friend to Black liberation. Their survival often depends on maintaining the status quo that oppresses us.
12. “Allies” Often Centre Themselves in Our Struggles
Even when other groups claim to stand in solidarity with Black movements, their involvement often centers their own experiences, narratives, and priorities.
Non-black allies frequently shift attention to their struggles, leaving Black people to carry the burden of fighting for everyone else.
Movements like Black Lives Matter have seen external groups co-opt their messages for personal or political gain.
Garvey’s philosophy reminds us to stay focused on our own goals and not allow our movements to be hijacked.
13. Romanticizing External Help Distracts from Pan-African Solutions
One of the pitfalls of seeking allies is the belief that external help is necessary or even superior. This mindset can prevent Black people from exploring Pan-African solutions.
Garvey’s vision of “Africa for Africans” called for African nations and the diaspora to work together without relying on foreign nations or systems.
Clarke’s statement reinforces this idea: the best solutions come from within. Black people don’t need external friends—they need internal unity.
14. Allies Often Maintain Anti-Black Systems
Even so-called “progressive” allies often uphold the same systems that oppress Black people.
Corporations claiming to support racial justice continue to exploit African resources and labour.
Governments speaking out against racism still engage in policies that harm Black communities worldwide.
Dr. Clarke and Garvey both understood this hypocrisy. Real liberation requires rejecting systems that perpetuate oppression, even if they claim to support us.
15. Our Focus Should Be on Building Future Generations, Not Pleasing Others
Garvey often emphasized the importance of preparing future generations to lead and succeed independently.
Clarke’s warning about having no friends reinforces this: Why waste time seeking allies when we could be building schools, economies, and systems that empower our children?
A Garveyite perspective prioritizes creating a legacy of self-reliance and leadership that ensures the survival and progress of Black people globally.
By focusing on the future, Black people can stop relying on the approval or assistance of others and instead secure their own destinies.
Final Reflection: All We Have Is Us, and That’s Enough
Dr. John Henrik Clarke’s statement and Marcus Garvey’s philosophy both lead to the same conclusion: Black people must take responsibility for their liberation. True freedom can not and will not come from allies—it must come from within. The power lies in our hands, in our unity, and in our shared commitment to self-determination.
We don’t need friends. We need ourselves.
#marcus garvey#Dr John Henrik Clarke#Garveyism#pan africanism#self reliance#No Allies#black unity#black liberation#Anti Blackness#economic independence#black people#black history#black#black tumblr#blacktumblr#black conscious#africa#black power#black empowering#black future#Global Black Community#black leadership#african diaspora#black diaspora#black culture#african culture#people of color#POC
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
Embark on a compassionate journey into the heart of the USA Visa Program, where Asylum and Refugee Status serve as beacons of hope for those escaping persecution. Explore the humanitarian facets and legal intricacies of these protective pathways, providing a lifeline to individuals seeking sanctuary on American soil. Uncover the stories of resilience, the rigorous application processes, and the commitment of the United States to offer refuge to those fleeing adversity. Join us in grasping the profound impact of Asylum and Refugee Status, reflecting America's dedication to compassion, justice, and the promise of a fresh start for those in need.
#Asylum seekers#Refugee status#USA Visa Program#Humanitarian immigration#Fleeing persecution#Seeking sanctuary#Asylum application process#Refugee resettlement#Legal protection for refugees#Immigration for displaced individuals#Human rights and immigration#US asylum eligibility#Refugee admissions program#Refugee screening process#Compassionate immigration policies#Forced migration#Asylum interviews#Refugee protection in the US#Asylum and Refugee legal pathways#International protection in the United States
1 note
·
View note
Text
U.S. programs and services in danger of being diminished or fully cut:
Social Security
Department of Education
Department of Labor
Department of Transportation
Medicaid
Medicare
Obamacare
FDA
CDC
USDA
FAFSA
FEMA
ACA
SNAP
EPA
FTC
FEC
HUD
HHS
NOAA
SCHIP
FAA
National Weather Service
Hurricane and other disaster warnings
Unemployment services
Student loans
Pell grants
Libraries
Fluoride treatment in our water
Meat and food inspections
National Parks
Other concerns:
(International relations)
Loss of U.S. membership in NATO
Potential UN ramifications
Tariffs
Support of Israel winning the war
Putin and Russian relations
(Loss of Rights)
Voting rights
Miranda rights
LGBTQ+, POC, and other minority rights
Reproductive rights
Protection against pre-existing conditions
Protection against assault and harassment
Child labor protections
(Daily living)
Prescription prices skyrocketing
No rent control
Little to no reproductive or health care access
Legalized police brutality
Diminished or cut protections and rights for minority groups
Restrictions on gender affirming care or legal services
Increased taxes and cost of living for the non-wealthy
No more $35 insulin
No labor laws - 40+ hour work weeks, no mandatory breaks, no paid sick or vacation leave
#updated#us election#us politics#us government#social security#medicare#civil rights#civil protection#united nations#nato#nato allies#us govt#international relations#us house of representatives#us senate#us supreme court#donald trump#project 2025#united states
327 notes
·
View notes
Text
An open letter to the U.S. Congress
📜 Impose Section 3 of 14th Amendment Against Trump
9 so far! Help us get to 10 signers!
While it is clear to everyone who is not part of the cult of Trump, Donald Trump intentionally caused an insurrection on January 6, 2021. Senate Republicans have indicated that they will not vote to impeach the president, claiming the violence on Capitol Hill was of no consequence. The date and purpose of Trumps rally was known to everyone and most Americans were fearful that these domestic terrorist groups would cause real harm to our democracy.
While some have claimed that censure, not impeachment of Trump, would be a victory, I completely disagree. Congress needs to invoke Section 3 of the 14th Amendment to the Constitution to protect our country from this treacherous person. Section 3 of the 14th amendment to the Constitution states that no person shall hold office if they have taken part in an "insurrection or rebellion " against the United States of America. This only requires a simple majority or 51 votes and that is very attainable.
Invoking section 3 must be done. Our country had a near death experience with democracy and we cannot allow Mr. Trump to even consider running for the office of President of the United States ever again! There is no doubt that the people who participated in this violent attack on our democracy have no allegiance to our country. Their only allegiance is to Mr. Trump. He is a dangerous man and they are dangerous people. We must remove Donald Trump from ever attaining public office again.
Thank you
▶ Created on February 5, 2021 by Kristine
Text SIGN PEREHG to 50409
🏠 Tell the US House to Expel Members of Congress That Participated in The Jan 6 attack on The Capitol
🖊️ Text SIGN PSDAJA to 50409
CTRL+A to skip The Daily Beast paywall:
Trumpland Civil War Historians Agree 14th Amendment Disqualifies Trump From Ballot EXPERT OPINION More than two dozen historians filed an amicus brief in support of Colorado’s attempt to remove Donald Trump from the 2024 ballot. Amanda Yen Breaking News Intern
Published Jan. 28 2024 4:33PM EST Donald Trump sitting between lawyers in the New York courthouse where his civil fraud trial was held. Jefferson Siegel/Getty Images A coalition of U.S. history scholars have filed an amicus brief to the Supreme Court, agreeing with the state of Colorado that the 14th Amendment’s insurrectionist clause should bar Donald Trump from presidential candidacy this year.
The 25 historians have expertise in the Civil War and Reconstruction eras, the period in which the 14th Amendment was added to the Constitution. They argue that upon its addition in 1866, “decision members crafted Section III to cover the President and to create an enduring check on insurrection, requiring no additional action from Congress.”
Trump’s lawyers have objected to the Colorado ruling, arguing that the ex-president’s behavior doesn’t amount to insurrection and that Section III of the 14th Amendment exempts presidents from the rule. A lower appeals court ruled in Trump’s favor, which prompted the state to appeal the decision to the highest court in the land.
Trump Begs Supreme Court to Let Him Stay on Colorado Ballot PRETTY PLEASE? AJ McDougall, Matt Young, Brett Bachman Donald Trump The 14th Amendment itself states that no person shall “hold any office, civil or military, under the United States” if that person “had previously taken an oath” as “an officer of the United States” and “engaged in insurrection or rebellion against the same, or given aid or comfort to the enemies thereof.”
In their brief, the historians gave contemporary evidence from the 1860s and 1870s that this clause was understood to cover the president. Using Senate-floor debate between two members involved in the drafting, they argue that the president was unquestionably included in the meaning of “an officer under the United States.” They also gave evidence from the 1787 Constitutional Convention, in which framers frequently referred to the president as a “national officer.”
“For historians, contemporary evidence from the decision-makers who sponsored, backed, and voted for the 14th Amendment is most probative,” the historians wrote. In doing so, they adopted the originalist interpretation of the Constitution that the Supreme Court’s conservative majority has employed in recent rulings, including in the rollback of Roe v. Wade.
Colorado is one of several states that has attempted to remove Trump from the ballot. Of the 35 states with filed challenges, only two—Colorado and Maine—successfully disqualified Trump, with those decisions appealed to the Supreme Court. Sixteen states have yet to make a decision regarding Trump’s candidacy, and the remaining 17 have thrown out the filings.
States like Colorado cite the former president’s role in inciting the Jan. 6 insurrection as why he should be ineligible to run for office again. Following the 2020 election, Trump refused to admit defeat to President Joe Biden, falsely attacked the integrity of the electoral system, and attempted to rouse supporters to “stop the steal” of the presidency.
After a Trump rally—where the ex-president repoeated his election fraud lies and urged his reporters to “fight like hell”—insurrectionists flooded the Capitol with the intent of preventing Congress from certifying the election results.
The appeals case is running on an expedited timeline, with the Supreme Court set to hear arguments on Feb. 8. A decision is likely to follow soon after. Colorado’s primary will be held, along with several other states, on Super Tuesday, March 5.
A coalition of U.S. history scholars have filed an amicus brief to the Supreme Court, agreeing with the state of Colorado that the 14th Amendment’s insurrectionist clause should bar Donald Trump from presidential candidacy this year.
The 25 historians have expertise in the Civil War and Reconstruction eras, the period in which the 14th Amendment was added to the Constitution. They argue that upon its addition in 1866, “decision members crafted Section III to cover the President and to create an enduring check on insurrection, requiring no additional action from Congress.”
#Kristine#PEREHG#resistbot#jan 6#jan 6th insurrection#jan 6 2021#jan 6 capitol attack#presidential candidate#Trumpland#Civil War Historians#14th Amendment#Insurrection#Amicus Brief#US Constitution#Supreme Court#Donald Trump#Presidential Candidacy#Trump On Ballot#Election 2024#Colorado#States Rights#Political Challenges#Reconstruction#Trump Insurrection#History Scholars#Constitutional Law#Election Fraud#January 6#Stop The Steal#Democracy
304 notes
·
View notes
Text
#At Refrigerant Center INC#we specialize in providing comprehensive refrigerant solutions tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clients. With a deep understanding#Ventilation#and Air Conditioning) industry and its evolving regulatory landscape#we are committed to offering environmentally responsible refrigerant products and services.#Our company prides itself on being a trusted partner for businesses operating in various sectors#including commercial#industrial#and residential. Whether you're a facility manager#HVAC contractor#or equipment manufacturer#we have the expertise and resources to fulfill your refrigerant requirements efficiently and affordably.#Key Services and Products:#Refrigerant Sales: We offer a wide range of refrigerant products#including traditional HFCs (Hydrofluorocarbons)#low-GWP (Global Warming Potential) alternatives like HFOs (Hydrofluoroolefins)#and natural refrigerants such as CO2 and ammonia. Our extensive inventory ensures that clients can find the right refrigerant for their spe#Refrigerant Reclamation: Recognizing the importance of sustainability#we provide refrigerant reclamation services aimed at recovering#purifying#and reprocessing used refrigerants. Through our state-of-the-art reclamation facilities#we help clients minimize environmental impact while maximizing cost savings.#Regulatory Compliance Assistance: Navigating the complex regulatory landscape surrounding refrigerants can be challenging. Our team stays u#national#and international regulations#including EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) regulations in the United States.#Technical Support: We understand that proper handling and usage of refrigerants are critical for the safety and efficiency of HVAC systems.#training#and educational resources to assist clients in handling refrigerants safely and effectively.#Customized Solutions: Every client has unique requirements
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 2 May 2024.

The General Assembly, Reaffirming its resolution 70/1 of 25 September 2015, entitled “Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development”, by which it adopted a comprehensive, far-reaching and people-centred set of universal and transformative Sustainable Development Goals and targets, Reaffirming also its resolutions 53/199 of 15 December 1998 and 61/185 of 20 December 2006 on the proclamation of international years, and Economic and Social Council resolution 1980/67 of 25 July 1980 on international years and anniversaries, in particular paragraphs 1 to 10 of the annex thereto on the agreed criteria for the proclamation of international years, as well as paragraphs 13 and 14, in which it is stated that an international day or year should not be proclaimed before the basic arrangements for its organization and financing have been made, Reaffirming further the intrinsic value of wildlife and its various contributions, including its ecological, genetic, social, economic, scientific, educational, cultural, recreational and aesthetic contributions to sustainable development and human wellbeing, and recognizing that wild fauna in their many beautiful and varied forms are an irreplaceable part of the natural systems of the Earth which must be protected for this generation and the generations to come, Stressing the urgent need to address the unprecedented global decline in biodiversity, including by preventing the extinction of threatened species, improving and sustaining their conservation status and restoring and safeguarding ecosystems that provide essential functions and services, including services related to water, health, livelihoods and well-being,
Underlining that the markhor (Capra falconeri) is an iconic and ecologically significant species found across the mountainous regions of Central and South Asia, including Afghanistan, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, and recognizing that the markhor was categorized as “near threatened” in 2014 and is on the International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List of Threatened Species, and has been included in appendix I to the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora since 1992, Recognizing that preserving the markhor and its natural habitat is an ecological imperative and a significant opportunity to bolster the regional economy, foster conservation efforts and promote sustainable tourism and economic growth and that conservation efforts will benefit the ecosystem, Stressing that, besides its ecological value, the markhor is a valuable species that contributes to the local economy and conservation initiatives, Recognizing national and regional initiatives for range State cooperation, transboundary approaches and mechanisms at the regional level to foster conservation of the markhor,
Noting the upcoming Ninth World Conference on Mountain Ungulates, to be held in Dushanbe from 12 to 15 October 2024, Recognizing that the greatest threats to the survival of the markhor are habitat loss, illegal hunting, including poaching, and climate change, Recalling its resolution 78/155 of 19 December 2023, entitled “Implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity and its contribution to sustainable development”, in which it called upon parties to the Convention and stakeholders to strengthen international cooperation measures for the fulfillment of obligations contained in the Convention, Recognizing efforts for the conservation of the markhor, including the establishment of breeding programmes and the development of a regional strategy and national action plans for the conservation of the markhor in some range States that aim to protect the species throughout its range,
Decides to proclaim 24 May the International Day of the Markhor;
Invites all Member States, organizations of the United Nations system, other international and regional organizations, civil society, non-governmental organizations, individuals and other relevant stakeholders to observe the International Day of the Markhor, as appropriate;
Invites all relevant stakeholders to give due consideration to enhancing international and regional cooperation in support of efforts to conserve the markhor, given its role in the overall ecosystem;
Invites the United Nations Environment Programme to facilitate the observance of the International Day of the Markhor, mindful of the provisions contained in the annex to Economic and Social Council resolution 1980/67;
Stresses that the cost of all activities that may arise from the implementation of the present resolution should be met from voluntary contributions and that such activities would be subject to the availability and provision of voluntary contributions;
Requests the Secretary-General to bring the present resolution to the attention of all Member States, the organizations of the United Nations system and civil society organizations for appropriate observance.
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 78/278 - International Day of the Markhor.
Seventy-eighth session Agenda item 13: Integrated and coordinated implementation of and follow-up to the outcomes of the major United Nations conferences and summits in the economic, social and related fields.
77th plenary meeting - 2 May 2024.
#civil society organizations#member states#united nations general assembly#united nations economic and social council#united nations secretary general#International Day of the Markhor#24 May#United Nations Environment Programme#regional strategy#markhor conservation#resolutions#Resolution 78/278#protect the species#breeding programmes#habitat loss#illegal hunting#near threatened#conservation efforts#sustainable tourism#Convention on Biological Diversity#national and regional initiatives#international and regional organizations#civil society#non-governmental organizations#individuals
0 notes
Text
نتائج فشل الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية في إنشاء المحكمة الجنائية الدولية على الطريقة الأمريكية
نتائج فشل الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية في إنشاء المحكمة الجنائية الدولية على الطريقة الأمريكية نتائج فشل الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية في إنشاء المحكمة الجنائية الدولية على الطريقة الأمريكية The Results Of The United States Of America’s Failure To Establish The International Criminal Court In The American Way الكاتب : ولديوسف مولود الملخص: سعت الإدارة الأمريكية جاهدة لإنشاء المحكمة الجنائية الدولية…

View On WordPress
#1487#1497)#Article 98 of the Rome Statute.#Security Council Resolutions No. (1422#United States of America#US Armed Forces Protection Act#قانون حماية أفراد الق��ات المسلحة الأمريكية#قرارات مجلس الأمن رقم: (1422#المادة 98 من نظام روما الأساسي. ; International Criminal Court#المحكمة الجنائية الدولية#الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية
0 notes
Text
[R]acial surveillance capitalism has existed since the grid cities of sixteenth-century Spanish Mexico [...]. Identification documents and practices can, like so many other surveillance technologies, be traced back to the Middle Passage [...]. [T]he movement of captives was controlled through [...] slave passes, slave patrols [...]. Similar strategies of using wanted posters and passes were put in place to control the movement of indentured white laborers from England and Ireland. [...] Fingerprinting, for example, was developed in India because colonial officials could not tell people apart [...]. In Algeria, the French dominated the colonized population by issuing internal passports, creating internal limits on movement for certain groups, and establishing camps for landless peasants [...]. In South Africa, meanwhile, the movement of the Black population was controlled through the “pass laws”: an internal passport system designed to confine Black South Africans into Bantustans and ensure a steady supply of super-exploitable labor [...]. Finally, surveillance was also essential to the management of the colonies. It occurred through [...] practices like fingerprinting and the passport [...]. [P]hotographs were used after colonial rebellions, in 1857 in India and in 1865 in Jamaica, to better identify the local population and identify “racial types.” [...] [T]he logics that underpin these technologies are not new, but were developed and tested in the management of racialized minorities during the colonial era with a similar end goal, namely to control, order, and undermine the poor, colonized, enslaved, and indentured; to create a vulnerable and super-exploitable workforce; and to increase efficiency in production [...].
Text by: Sabrina Axster and Ida Danewid. In a section from an article co-authored by Sabrina Axster, Ida Danewid, Asher Goldstein, Matt Mahmoudi, Cemal Burak Tansel, and Lauren Wilcox. "Colonial Lives of the Carceral Archipelago: Rethinking the Neoliberal Security State". International Political Sociology Volume 15, Issue 3, September 2021, pages 415-439.
---
[I]n the Age of Revolutions the Cuban bloodhound spread across imperial boundaries to protect white power and suppress black ambitions in Haiti and Jamaica. [...] [Then] dog violence in the Caribbean spurred planters in the American South to import and breed slave dogs [...]. Although slave hounds existed throughout the Caribbean, it was common knowledge that [Spanish] Cuba bred and trained the best attack dogs, and when insurrections began to challenge plantocratic interests across the Americas, two rival empires, Britain and France, begged Spain to sell these notorious Cuban bloodhounds to suppress black ambitions and protect shared white power. [...] Spanish and Cuban slave hunters not only bred the Cuban bloodhound, but were midwives to an era of international anti-black co-ordination as the breed’s reputation spread rapidly among enslavers during the seven decades between the beginning of the Haitian Revolution in 1791 and the conclusion of the American Civil War in 1865. [...] Despite the legends of Spanish cruelty, British officials bought Cuban bloodhounds when unrest erupted in Jamaica in 1795 after learning that Spanish officials in Cuba had recently sent dogs to hunt runaways and the indigenous Miskitos in Central America. [...] The island’s governor, Balcarres, later wrote that ‘Soon after the maroon rebellion broke out’ he had sent representatives ‘to Cuba in order to procure a number of large dogs [...].' In 1803, during the final independence struggle of the Haitian Revolution, Cuban breeders again sold hundreds of hounds to the French to aid their fight [...]. The most extensively documented deployment of slave hounds [...] occurred in the antebellum American South [...]. The use of dogs increased during that decade [1830s], especially with the Second Seminole War in Florida (1835–42). The first recorded sale of Cuban dogs into the United States came with this conflict, when the US military apparently purchased three such dogs for $151.72 each [...]. [F]ierce bloodhounds reputed to be from Cuba appeared in the Mississippi valley as early as 1841 [...].
Text by: Tyler D. Parry and Charlton W. Yingling. "Slave Hounds and Abolition in the Americas". Past & Present, Volume 246, Issue 1, February 2020, pages 69-108. Published February 2020. At: doi dot org/10.1093/pastj/gtz020.
---
[A]nti-homeless laws [...] rooted in European anti-vagrancy laws were adapted across parts of the Japanese empire [...] at the turn of the 20th century. [...] [B]order control systems - substantively shaped by imperial aversions to racialised ideas of uncivilised vagrants - mutually served as a transnational legal architecture [...] [leading to] [t]oday's modern divides [...]. By the Boer Wars (1880–1902), Euro-American powers and settler-colonial governments professed anxieties about White degeneration and the so-called “Yellow Peril” alongside other existential threats to White supremacy [...]. Japan [...] validated the creation of transnational racial hierarchies as it sought to elevate its own global standing [...]. [O]ne key legal instrument for achieving such racialised orders was the vagrancy concept, rooted in vagrancy laws that originated in Europe and proliferated globally through imperial-colonial conquest [...]. Through the 1870s [...] the [Japanese] government introduced modern police forces and a centralised koseki register to monitor spatial movement. The koseki register, which recorded geographic origins, also served as a tool for marking racialised groups including Ainu, Burakumin, Chinese, [...] and Korean subjects across Japan's empire [...]. The 1880 Penal Code contained Japan's first anti-vagrancy statute, based on French models [...] Attention to “vagrant foreigners” (furō-gaikokujin) emerged in Japanese media and politics in the mid-1890s. It stemmed directly from contemporary British debates over immigration restrictions targeting predominantly Jewish “destitute aliens” [...]. [D]uring the American occupation (1945–1952), not only were anti-vagrancy statutes reinstituted in Japan's 1948 Minor Offences Act, but [...] the 1946 Livelihood Protection Act (Article 2) excluded “people unwilling to work or lazy” from social insurance coverage [...].
Text by: Rayna Rusenko. "The Vagrancy Concept, Border Control, and Legal Architectures of Human In/Security". Antipode [A Radical Journal of Geography] Volume 56, Issue 2, pages 628-650. First published 24 October 2023.
---
A week after Luccheni assassinated Empress Elizabeth, the Austrian foreign minister proposed to his Swiss colleague the formation of an “International Police League” against [socialists and anarchists]. He referred to them as “wild beasts without nationality” who were a menace “not only to sovereign rulers but to everyone." [...] [A] few days later, on 29 September 1898, the Italian minister of foreign affairs sent out invitations for an “International Conference of Rome for the Social Defense [...],” [...]. During this conference, all but the British and the French delegates agreed to introduce in their countries an anthropometric method of criminal identification, the portrait parlé. This was a refinement of criminologist Alphonse Bertillon’ s method of identification, the bertillonage, which classified the size of various parts of the head and body. This system was particularly useful for apprehending criminals who operated across borders since the dozen or so pieces of information vital to a positive identification could be transmitted by telephone or telegraph. These initiatives signal how government and police authorities increasingly [...] provided grounds upon which to build international cooperation. [...] “The police are the same in all parts of the world,” wrote the Italian [radical activist] and contemporary observer Pietro Vasai. While discussing his adventures in other countries and their prisons, he added, “Laws have been fabricated by the bourgeoisie on the same model: in this, the bourgeoisie is more international than we are.”
Text by: Lucia Carminati. "Alexandria, 1898: Nodes, Networks, and Scales in Nineteenth-Century Egypt and the Mediterranean." Comparative Studies in Society and History, Volume 59 (2017), Number 1, pages 127-153.
---
Chicago newspapers and military police served to convert white anxieties about Black migration from the plantation South into new techniques and technologies [...]. [I]n Chicago between 1875 and 1890, [...] white anticipations of African American migration from plantations in the South were translated into new information sciences and policing techniques that made their way to plantations in places like the Philippines. [...] White Chicagoans’ prolonged concern over predicting Black behaviors and intentions materialized in 1877, when the city became a central hub of militarized response to a nation-wide railroad strike. Adjutant General Richard C. Drum, who commanded the Military Division of the Missouri (Western Frontier) in Chicago from 1873 to 1878, took control of Chicago’s military response to the Great Railroad Strike of 1877. In 1879, after his final year in the city, Drum moved to Washington, DC and proposed the establishment of the Military Information Division (MID) [...]. The MID, which formally established in 1885, maintained close ties to Chicago's local information collection system, adopting a Bertillon identification system of collecting and storing intelligence cards at the time that the National Association of Chiefs of Police established their central bureau of identification in Chicago in 1896 [...]. By the tun of the 20th century, Chicago's police force had expanded tenfold [...], and Drum's MID had amassed over 300,000 intelligence cards [...]. The affective atmosphere into which the MID intensified its own predictive techniques later traversed the Pacific Ocean into the Philippines. [...] McCoy argues that the American introduction of [...] surveillance techniques in governing the Philippines constituted the United States' first information revolution [...]. [F]eelings of white apprehension translated into imperial mechanisms for governing the Philippines through systems of intelligence cards, telecommunications infrastructure, policing units, and management sciences. [...] [T]he MID and its successors developed techniques for psychological examination and personality typing led by another Chicagoan, Harry Hill Bandholtz. [...] Bandholtz sharpened the MID's informational sciences by training Philippines police forces in the neurotic art of collecting every imaginable fact about Filipino behaviors [...].
Text by: Jolen Martinez. "Plantation Anticipation: Apprehension in Chicago from Reconstruction America to the Plantocratic Philippines" (2024).An essay from an Intervention Symposium titled Plantation Methodologies: Questioning Scale, Space, and Subjecthood, published by Antipode [A Radical Journal of Geography].
---
In 1858, a British official in colonial Bengal named William Herschel asked [...] a local contractor, to imprint his inked hand on a contract that had already been signed. After years of experimenting with handprints, Herschel sent copies of Konai’s fingerprints to London for Francis Galton, a eugenicist [...]. Galton went on to argue that fingerprints were an accurate marker of identity and racial difference. [...] In fact, it was once again in colonial Bengal that Edward Henry, along with Azizul Haque and Hem Chandra Bose, developed a mathematical method for the classification of fingerprints, which was exported to South Africa and later to metropolitan Europe. [...] Allan Sekula once wrote that the central innovation of nineteenth-century police photography was not the camera but the filing cabinet. [...] The fingerprint cabinet Henry pioneered in Bengal closely paralleled the Bertillon system in Europe. [...] The colonial laboratory was the site of statistical techniques, periodic census surveys, and the introduction of photography into carceral regimes. [...]
Text by: A section by Ravi Sundaram in "Colonial Infrastructure and Techno-Social Networks," co-authored by Tiziana Terranova and Ravi Sundaram. e-flux Journal Issue #123. December 2021.
scary how fast agents of empire(s) will set aside their rivalries or inter-imperial competitive squabbling in order to cooperate and transcend their own borders with like an imperial solidarity as they share ideas, exchange technologies, and protect their shared interest in hunting and crushing you
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
نتائج فشل الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية في إنشاء المحكمة الجنائية الدولية على الطريقة الأمريكية
نتائج فشل الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية في إنشاء المحكمة الجنائية الدولية على الطريقة الأمريكية نتائج فشل الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية في إنشاء المحكمة الجنائية الدولية على الطريقة الأمريكية The Results Of The United States Of America’s Failure To Establish The International Criminal Court In The American Way الكاتب : ولديوسف مولود الملخص: سعت الإدارة الأمريكية جاهدة لإنشاء المحكمة الجنائية الدولية…

View On WordPress
#1487#1497)#Article 98 of the Rome Statute.#Security Council Resolutions No. (1422#United States of America#US Armed Forces Protection Act#قانون حماية أفراد القوات المسلحة الأمريكية#قرارات مجلس الأمن رقم: (1422#المادة 98 من نظام روما الأساسي. ; International Criminal Court#المحكمة الجنائية الدولية#الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية
0 notes
Text
Ko-fi prompt from @liberwolf:
Could you explain Tariff's , like who pays them and what they do to a country?
Well, I can definitely guess where this question is coming from.
Honestly, I was pretty excited to get this prompt, because it's one I can answer and was part of my studies focus in college. International business was my thing, and the issues of comparative advantage (along with Power Purchasing Parity) were one of the things I liked to explore.
-----------------
At their simplest, tariffs are an import tax. The United States has had tariffs as low as 5%, and at other times as high as 44% on most goods, such as during the Civil War. The purpose of a tariff is in two parts: generating revenue for the government, and protectionism.
Let's first explore how a tariff works. If you want to be confused, then you need to have never taken an economics class, and look at this graph:

(src)
So let's undo that confusion.
The simplest examples are raw or basic materials such as steel, cotton, or wine.
First, without tariffs:
Let us say that Country A and Country B both produce steel, and it is of similar quality, and in both cases cost $100 per unit. Transportation from one country to the other is $50/unit, so you can either buy domestically for $100, or internationally for $150. So you buy domestically.
Now, Country B discovers a new place to mine iron very easily, and so their cost for steel drops to $60/unit due to increased ease of access. Country A can either purchase domestically for $100, or internationally for $110 (incl. shipping), which is much more even. Still, it is more cost-effective to purchase domestically, and so Country A isn't worried.
Transportation technology is improved, dropping the shipping costs to $30/unit. A person from Country A can buy: Domestic: $100 International: $60+$30 = $90 Purchasing steel from Country B is now cheaper than purchasing it from Country A, regardless of where you live.
Citizens in Country A, in order to reduce costs for domestic construction, begin to purchase their steel from Country B. As a result, money flows from Country A to B, and the domestic steel industry in Country A begins to feel the strain as demand dwindles.
In this scenario, with no tariffs, Country A begins to rely on B for their steel, which causes a loss of jobs (steelworkers, miners), loss of infrastructure (closing of mines and factories), and an outflow of funds to another country. As a result, Country A sees itself as losing money to B, while also growing increasingly reliant on their trading partner for the crucial good that is steel. If something happens to drive up the price of B's steel again, like political upheaval or a natural disaster, it will be difficult to quickly ramp up the production of steel in Country A's domestic facilities again.
What if a tariff is introduced early?
Alternately, the dropping of complete costs for purchase of steel from Country B could be counteracted with tariffs. Let's say we do a 25% tariff on that steel. This tariff is placed on the value of the steel, not the end cost, so:
$60 + (0.25 x $60) + $30 = $105/unit
Suddenly, with the implementation of a 25% tariff on steel from Country B, the domestic market is once again competitive. People can still buy from Country B if they would like, but Country A is less worried about the potential impacts to the domestic market.
The above example is done in regards to a mature market that has not yet begun to dwindle. The infrastructure and labor is still present, and is being preemptively protected against possible loss of industry to purchasing abroad.
What happens if the tariff is not implemented until after the market has dwindled?
Let's say that the domestic market was not protected by the tariff until several decades on. Country A's domestic production, in response to increased purchasing from abroad, has dwindled to one third of what it was before the change in pricing incentivized purchase from B. Prices have, for the sake of keeping this example simple, remained at $100(A) and $60(B) in that time. However, transportation has likely become better, so transportation is down to $20, meaning that total cost for steel from B is $80, accelerating the turn from domestic steel to international.
So, what happens if you suddenly implement a tariff on international steel? Shall we say, 40%?
$60 + (0.4 x 60) + 20 = $104
It's more expensive to order from abroad! Wow! Let's purchase domestically instead, because these prices add up!
But the production is only a third of what it used to be, and domestic mines and factories for refining the iron into steel can't keep up. They're scaling, sure, but that takes time. Because demand is suddenly triple of the supply, the cost skyrockets, and so steel in Country A is now $150/unit! The price will hopefully come down eventually, as factories and mines get back in gear, but will the people setting prices let that happen?
So industries that have begun to rely on international steel, which had come to $80/unit prior to the tariff, are facing the sudden impact of a cost increase of at least $25/unit (B with tariff) or the demand-driven price increase of domestic (nearly double the pre-tariff cost of steel from B), which is an increase of at least 30% what they were paying prior to the tariff.
There are possible other aspects here, such as government subsidies to buoy the domestic steel industry until it catches back up, or possibly Country B eating some of the costs so that people still buy from them (selling for $50 instead of $60 to mitigate some of the price hike, and maintain a loyal customer base), but that's not a direct impact of the tariff.
Who pays for tariffs?
Ultimately, this is a tax on a product (as opposed to a tax on profits or capital themselves, which has other effects), which means the majority of the cost is passed on directly to the consume.
As I said, we could see the producers in Country B cut their costs a little bit to maintain a loyal customer base, but depending on their trade relationships with other countries, they are just as likely to stop trading with Country A altogether in order to focus on more profitable markets.
So why do we not put tariffs on everything?
Well... for that, we get into the question of production efficiency, or in this case, comparative advantage.
Let's say we have two small, neighboring countries, C and D, that have negligible transportation costs and similar industries. Both have extensive farmland, and both have a history of growing grapes for wine, and goats for wool. Country C is a little further north than D, so it has more rocky grasses that are good for goats, while D has more fertile plains that are good for growing grapes.
Let's say that they have an equal workforce of 500,000 of people. I'm going to say that 10,000 people working full time for a year is 1 unit of labor. So, Country C and Country D have between the 100 units of labor, and 50 each.
The cost of 1 unit of wool = the cost of 1 unit of wine
Country C, having better land for goats, can produce 4 units of wool for every unit of labor, and 2 units of wine for every unit of labor.
Meanwhile, Country D, having better land for grapes, can produce 2 units of wool per unit of labor, and 4 units of wine per unit of labor.
If they each devote exactly half their workforce to each product, then:
Country C: 100 units of wool, 50 units of wine Country D: 50 units of wool, 100 units of wine
Totaling 150 units of each product.
However, if each devotes all of their workforce to the product they're better at...
Country C: 200 units of wool, no wine Country D: no wool, 200 units of wine
and when they trade with each other, they each end up with 100 units of each product, which is a doubling of what their less-efficient labor would have resulted in!
The real world is obviously much more complicated, but in this example, we can see the pros of outsourcing some of your production to another country to focus on your own specialties.
Extreme examples of this IRL are countries where most of the economy rests on one product, such as middle-eastern petro-states that are now struggling to diversify their economies in order to not get left behind in the transition to green energy, or Taiwan's role as the world's primary producer of semiconductors being its 'silicon shield' against China.
Comparative advantage can be used well, such as our Unnamed Countries (that are definitely not the classic example of England and Portugal, with goats instead of sheep) up in the example. With each economy focusing on its specialty, there is a greater yield of both products, meaning a greater bounty for both countries.
However, should something happen to Country C up there, like an earthquake that kills half the goats, they are suddenly left with barely enough wool to clothe themselves, and nothing for Country D, which now has a surplus of wine and no wool.
So you do have to keep some domestic industry, because Bad Things Can Happen. And if we want to avoid the steel example of a collapse in the given industry, tariffs might be needed.
Are export tariffs a thing?
Yes, but they are much rarer, and can largely be defined as "oh my god, everyone please stop getting rid of this really important resource by selling it to foreigners for a big buck, we are depleting this crucial resource."
So what's the big confusion right now?
Donald Trump has, on a number of occasions, talked about 'making China pay' tariffs on the goods they import into the US. This has led to a belief that is not entirely unreasonable, that China would be the side paying the tariffs.
The view this statement engenders is that a tariff is a bit like paying a rental fee for a seller's table at an event: the producer or merchant pays the host (or landlord or what have you) a fee to sell their product on the premises. This could be a farmer's market, a renaissance faire, a comic book convention, whatever. If you want to sell at the event, you have to pay a fee to get a space to set up your table.
In the eyes of the people who listened to Trump, the tariff is that fee. China is paying the United States for access to the market.
And, technically, that's not entirely wrong. China is thus paying to enter the US market. It's just the money to pay that fee needs to come from somewhere, and like most taxes on goods, that fee comes from the consumer.
So... what now?
Well, a lot of smaller US companies that rely on cheap goods made in China are buying up non-perishables while they can, before the tariffs hit. Long-term, manufacturers in the US that rely on parts and tools manufactured in China are going to feel the squeeze once that frontloaded stock is depleted.
Some companies are large enough to take the hit on their own end, still selling at cheap rates to the consumer, because they can offset those costs with other parts of their empire... at least until smaller competitors are driven out of business, at which point they can start jacking up their prices since there are no options left. You may look at that and think, "huh, isn't that the modus operandi for Walmart and Amazon already?" and yes. It is. We are very much anticipating a 'rich get richer, poor go out of business' situation with these tariffs.
The tariffs will also impact larger companies, including non-US ones like Zara (Spanish) and H&M (Swedish), if they have a huge reliance on Chinese production to supply their huge market in the United States.
If you're interested in the repercussions that people expect from these proposed tariffs on Chinese goods, I'd suggest listening to or watching the November 8th, 2024 episode of Morning Brew Daily (I linked to YouTube, but it's also available on Spotify, Nebula, the Morning Brew website, and other podcast platforms).
#id in alt text#id in alt#economics#tariffs#import tax#customs#customs duties#ko fi prompts#capitalism#phoenix talks#ko fi#taxes#taxation
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm asking this genuinely, as a 19 yo with no education in economics and a pretty surface level understanding of socialism: can you explain the whole Bananas discourse in a way someone like me might understand? In my understanding it's just "This is just a product we can give up to create better worker conditions and that's fine" but apparently that's not the full picture?
alright so some pretty important background to all this is that we're all talking about the fact that bananas, grown in the global south, are available year-round at extremely low prices all around europe and the USA. it's not really about bananas per so--the banana in this discourse is a synechdoche for all the economic benefits of imperialism.
so how are cheap bananas a result of imperialism? first of all i want to tackle a common and v. silly counterargument: 'oh, these ridiculous communists think it's imperialist for produce to be shipped internationally'. nah. believing that this is the communist objection requires believing in a deeply naive view of international traide. this view goes something like 'well, if honduras has lots of bananas, and people in the usa want bananas and are willing to pay for them, surely everyone wins when the usa buys bananas!'.
there are of course two key errors here and they are both packed into 'honduras has lots of bananas'. for a start, although the bananas are grown in honduras, honduras doesn't really 'have' them, because the plantations are mostly owned by chiquita (formerly known as united fruit) dole, del monte, and other multinationals--when they're not, those multinationals will usually purchase the bananas from honduran growers and conduct the export themselves. and wouldn't you know it, it's those intervening middleman steps--export, import, and retail, where the vast majority of money is made off bananas! so in the process of a banana making its way from honduras to a 7/11, usamerican multinationals make money selling the bananas to usamerican importers who make money selling them to usamerican retailers who make money selling them to usamerican customers.
when chiquita sells a banana to be sold in walmart, a magic trick is being performed: a banana is disappearing from honduras, and yet somehow an american company is paying a second american company for it! this is economic imperialism, the usamerican multinational extracting resources from a nation while simultaneously pocketing the value of those resources.
why does the honduran government allow this? if selling bananas is such a bad deal for the nation, why do they continue to export millions of dollars of banans a year? well, obviously, there's the fact that if they didn't, they would face a coup. the united states is more than willing to intervene and cause mass death and war to protect the profits of its multinationals. but the second, more subtle thing keeping honduras bound to this ridiculously unbalanced relationship is the need for dollars. because the US dollar is the global reserve currency, and the de facto currency of international trade, exporting to the USA is a basic necessity for nations like honduras, guatemala, &c. why is the dollar the global reserve currency? because of usamerican military and economic hegemony, of course. imperialism built upon imperialism!
this is unequal exchange, the neoimperialist terms of international trade that make the 'global economy' a tool of siphoning value and resources from the global south to the imperial core. & this is the second flaw to unravel in 'honduras has a lot of bananas' -- honduras only 'has a lot of bananas' because this global economic hegemony has led to vast unsustainable monoculture banana plantations to dominate the agriculture of honduras. it's long-attested how monoculture growth is unsustainable because it destroys soil and leads to easily-wiped-out-by-infection plants.
so, bananas in the USA are cheap because:
the workers that grow them are barely paid, mistreated, prevented from unionizing, and sometimes murdered
the nations in which the bananas are grown accept brutally unfair trade and tariff terms with the USA because they desperately need a supply of US dollars and so have little position to negotiate
shipping is also much cheaper than it should be because sailors are chronically underpaid and often not paid at all or forced to pay to work (!)
bananas are cheap, in conclusion, because they're produced by underpaid and brutalized workers and then imported on extortionate and unfair terms.
so what, should we all give up bananas? no, and it's a sign of total lack of understanding of socialism as a global movement that all the pearl-clutching usamericans have latched onto the scary communists telling them to stop buying bananas. communism does not care about you as a consumer. individual consumptive choices are not a meaningful arena of political action. the socialist position is not "if there was a socialist reovlution in the usa, we would all stop eating bananas like good little boys", but rather, "if there's a socialist revolution in the countries where bananas are grown, then the availability of bananas in the usa is going to drop, and if you want to be an anti-imperialist in the imperial core you have to accept that".
(this is where the second argument i see about this, 'oh what are you catholic you want me to eat dirt like a monk?' reveals itself as a silly fucking solipsistic misunderstanding)
and again, let's note that the case of the banana can very easily be generalised out to coffee, chocolate, sugar, etc, and that it's not about individual consumptive habits, but about global economic systems. if you are donkey fucking kong and you eat 100 bananas a day i don't care and neither does anyone else. it's about trying to illustrate just one tiny mundane way in which economic imperialism makes the lives of people in the global north more convenient and simpler and so of course there is enormous pushback from people who attach moral value to this and therefore feel like the mean commies are personally calling them evil for eating a nutella or whatever which is frankly pretty tiring. Sad!
tldr: it is not imperialism when produce go on boat but it is imperialism when produce grown for dirt cheap by underpaid workers in a country with a devalued currency is then bought and exported and sold by usamerican companies creating huge amounts of economic value of which the nation in which the banana was grown, let alone the people who actually fucking grew it, don't see a cent -- and this is the engine behind the cheap, available-every-day-all-year-everywhere presence of bananas in the usa (and other places!)
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
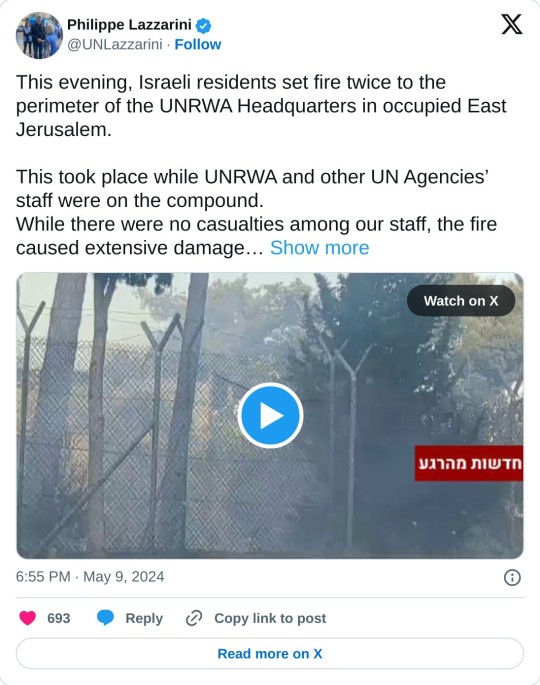
This evening, Israeli residents set fire twice to the perimeter of the UNRWA Headquarters in occupied East Jerusalem.
This took place while UNRWA and other UN Agencies’ staff were on the compound.
While there were no casualties among our staff, the fire caused extensive damage to the outdoor areas. The UNRWA headquarters has on its grounds a petrol and diesel station for the Agency’s fleet of cars.
Our director with the help of other staff had to put out the fire themselves as it took the Israeli fire extinguishers and police a while before they turned up.
A crowd accompanied by armed men were witnessed outside the compound chanting “Burn down the United Nations” (see video below 👇 from Israeli media).
This is an outrageous development. Once again, the lives of UN staff were at a serious risk.
In light of this second appalling incident in less than a week, I have taken the decision to close down our coumpound until proper security is restored.
Over the past two months, Israeli extremists have been staging protests outside the UNRWA compound in Jerusalem, called by an elected member of the Jerusalem municipality.
This week, the protest became violent when demonstrators threw stones at UN staff and at the buildings of the compound.
Over the past months, UN staff have regularly been subjected to harassment and intimidation. Our compound has been seriously vandalized and damaged.
On several occasions, Israeli extremists threatened our staff with guns.
It is the responsibility of the State of Israel as an occupying power to ensure that United Nations personnel and facilities are protected at all times.
UN staff, premises and operations should be protected at all times in line with international law.
I call on all those who have influence to put an end to these attacks and hold all those responsible accountable.
The perpetrators of these attacks must be investigated and those responsible must be held accountable.
Anything less will set a new dangerous standard.
-Philippe Lazzarini, commissioner general of UNRWA
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
It is over and everything is lost. This is the refrain repeated by Armenian families as they take that final step across the border out of their home of Nagorno-Karabakh.
In just a handful of days more than 100,000 people, almost the entire Armenian population of the breakaway enclave, has fled fearing ethnic persecution at the hands of Azerbaijani forces. The world barely registered it. But this astonishing exodus has vanished a self-declared state that thousands have died fighting for and ended a decades-old bloody chapter of history.
On Saturday, along that dusty mountain road to neighbouring Armenia, a few remaining people limp to safety after enduring days in transit.
Among them is the Tsovinar family who appear bundled in a hatchback littered with bullet holes, with seven relatives crushed in the back. Hasratyan, 48, the mother, crumbles into tears as she tries to make sense of her last 48 hours. The thought she cannot banish is that from this moment forward, she will never again be able to visit the grave of her brother killed in a previous bout of fighting.
“He is buried in our village which is now controlled by Azerbaijan. We can never go back,” the mother-of-three says, as her teenage girls sob quietly beside her.
“We have lost our home, and our homeland. It is an erasing of a people. The world kept silent and handed us over”.
She is interrupted by several ambulances racing in the opposite direction towards Nagorno-Karabakh’s main city of Stepanakert, or Khankendi, as it is known by the Azerbaijani forces that now control the streets. Their job is to fetch the few remaining Karabakh Armenians who want to leave and have yet to make it out.
“Those left are the poorest who have no cars, the disabled and elderly who can’t move easily,” a first responder calls at us through the window. “Then we’re told that’s it.”
As the world focused on the United Nations General Assembly, the war in Ukraine and, in the UK, the felling of an iconic Sycamore tree, a decades old war has reignited here unnoticed.
It ultimately heralded the end of Nagorno-Karabakh, a breakaway Armenian region, that is internationally recognised as being part of Azerbaijan but for several decades has enjoyed de facto independence. It has triggered the largest movement of people in the South Caucasus since the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Azerbaijan has vehemently denied instigating ethnic cleansing and has promised to protect Armenians as it works to reintegrate the enclave.
But in the border town of Goris, surrounded by the chaotic arrival of hundreds of refugees, Armenia’s infrastructure minister says Yerevan was now struggling to work out what to do with tens of thousands of displaced and desperate people.
“Simply put this is a modern ethnic cleansing that has been permitted through the guilty silence of the world,” minister Gnel Sanosyan tells The Independent, as four new busses of fleeing families arrive behind him.
“This is a global shame, a shame for the world. We need the international community to step up and step up now.”
The divisions in this part of the world have their roots in centuries-old conflict but the latest iterations of bitter bloodshed erupted during the collapse of the Soviet Union. The Karabakh Armenians, who are in the majority in the enclave, demanded the right to autonomy over the 4,400 square kilometre rolling mountainous region that has its own history and dialect. In the early 1990s they won a bloody war that uprooted Azerbaijanis, building a de facto state that wasn’t internationally unrecognised.
That is until in 2020. Azerbaijan, backed by Turkey, launched a military offensive and took back swathes of territory in a six-week conflict that killed thousands of soldiers and civilians. Russia, which originally supported Armenia but in recent years has grown into a colder ally, brokered a fragile truce and deployed peacekeepers.
But Moscow failed to stop Baku in December, enforcing a 10-month blockade on Nagorno-Karabakh, strangling food, fuel, electricity and water supplies. Then, the international community stood by as Azerbaijan launched a 24-hour military blitz that proved too much for Armenian separatist forces. Outgunned, outnumbered and weakened by the blockade, they agreed to lay down their weapons.
For 30 years the Karabakh authorities had survived pressure from international powerhouses to give up statehood or at least downgrade their aspirations for Nagorno-Karabakh. For 30 years peace plans brokered by countries across the world were tabled and shelved.
And then in a week all hope vanished and the self-declared government agreed to dissolve.
Fearing further shelling and then violent reprisals, as news broke several Karabakh officials including former ministers and separatist commanders, had been arrested by Azerbaijani security forces, people flooded over the border.
At the political level there are discussions about “reintegration” and “peace” but with so few left in Nagorno-Karabakh any process would now be futile.
And so now, sleeping in tents on the floors of hotels, restaurants and sometimes the streets of border towns, shellshocked families, with a handful of belongings, are trying to piece their lives together.
Among them is Vardan Tadevosyan, Nagorno-Karabakh’s minister of health until the government was effectively dissolved on Thursday. He spent the night camping on the floor of a hotel, and carries only the clothes he is wearing. Exhausted he says he had “no idea what the future brings”.
“For 25 years I have built a rehabilitation centre for people with physical disabilities I had to leave it all behind. You don’t know how many people are calling me for support,” he says as his phone ringed incessantly in the background throughout the interview.
“We all left everything behind. I am very depressed,” he repeats, swallowing the sentence with a sigh.
Next to him Artemis, 58, a kindergarten coordinator who has spent 30 years in Steparankert, says the real problems were going to start in the coming weeks when the refugees outstay their temporary accommodation.
“The Azerbaijanis said they want to integrate Nagorno-Karabakh but how do you blockade a people for 10 months and then launch a military operation and then ask them to integrate?” she asks, as she prepares for a new leg of the journey to the Armenian capital where she hopes to find shelter.
“The blockade was part of the ethnic cleansing. This is the only way to get people to flee the land they love. There is no humanity left in the world.”
Back in the central square of Goris, where families pick through piles of donated clothes and blankets and aid organisations hand out food, the loudest question is: what next?
Armenian officials are busy registering families and sending them to shelters in different corners of the country. But there are unanswered queries about long-term accommodation, work and schooling.
“I can’t really think about it, it hurts too much,” says Hasratyan’s eldest daughter Lilet, 16, trembling in the sunlight as the family starts the registration process.
“All I can say to the world is please speak about this and think about us. We are humans, people made of blood, like you and we need your help.”
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
Paying consumer debts is basically optional in the United States

The vast majority of America's debt collection targets $500-2,000 credit card debts. It is a filthy business, operated by lawless firms who hire unskilled workers drawn from the same economic background as their targets, who routinely and grotesquely flout the law, but only when it comes to the people with the least ability to pay.
America has fairly robust laws to protect debtors from sleazy debt-collection practices, notably the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA), which has been on the books since 1978. The FDCPA puts strict limits on the conduct of debt collectors, and offers real remedies to debtors when they are abused.
But for FDPCA provisions to be honored, they must be understood. The people who collect these debts are almost entirely untrained. The people they collected the debts from are likewise in the dark. The only specialized expertise debt-collection firms concern themselves with are a series of gotcha tricks and semi-automated legal shenanigans that let them take money they don't deserve from people who can't afford to pay it.
There's no better person to explain this dynamic than Patrick McKenzie, a finance and technology expert whose Bits About Money newsletter is absolutely essential reading. No one breaks down the internal operations of the finance sector like McKenzie. His latest edition, "Credit card debt collection," is a fantastic read:
https://www.bitsaboutmoney.com/archive/the-waste-stream-of-consumer-finance/
McKenzie describes how a debt collector who mistook him for a different PJ McKenzie and tried to shake him down for a couple hundred bucks, and how this launched him into a life as a volunteer advocate for debtors who were less equipped to defend themselves from collectors than he was.
McKenzie's conclusion is that "paying consumer debts is basically optional in the United States." If you stand on your rights (which requires that you know your rights), then you will quickly discover that debt collectors don't have – and can't get – the documentation needed to collect on whatever debts they think you owe (even if you really owe them).
The credit card companies are fully aware of this, and bank (literally) on the fact that "the vast majority of consumers, including those with the socioeconomic wherewithal to walk away from their debts, feel themselves morally bound and pay as agreed."
If you find yourself on the business end of a debt collector's harassment campaign, you can generally make it end simply by "carefully sending a series of letters invoking [your] rights under the FDCPA." The debt collector who receives these letters will have bought your debt at five cents on the dollar, and will simply write it off.
By contrast, the mere act of paying anything marks you out as substantially more likely to pay than nearly everyone else on their hit-list. Paying anything doesn't trigger forbearance, it invites a flood of harassing calls and letters, because you've demonstrated that you can be coerced into paying.
But while learning FDCPA rules isn't overly difficult, it's also beyond the wherewithal of the most distressed debtors (and people falsely accused of being debtors). McKenzie recounts that many of the people he helped were living under chaotic circumstances that put seemingly simple things "like writing letters and counting to 30 days" beyond their needs.
This means that the people best able to defend themselves against illegal shakedowns are less likely to be targeted. Instead, debt collectors husband their resources so they can use them "to do abusive and frequently illegal shakedowns of the people the legislation was meant to benefit."
Here's how this debt market works. If you become delinquent in meeting your credit card payments ("delinquent" has a flexible meaning that varies with each issuer), then your debt will be sold to a collector. It is packaged in part of a large spreadsheet – a CSV file – and likely sold to one of 10 large firms that control 75% of the industry.
The "mom and pops" who have the other quarter of the industry might also get your debt, but it's more likely that they'll buy it as a kind of tailings from one of the big guys, who package up the debts they couldn't collect on and sell them at even deeper discounts.
The people who make the calls are often barely better off than the people they're calling. They're minimally trained and required to work at a breakneck pace. Employee turnover is 75-100% annually: imagine the worst call center job in the world, and then make it worse, and make "success" into a moral injury, and you've got the debt-collector rank-and-file.
To improve the yield on this awful process, debt collection companies start by purging these spreadsheets of likely duds: dead people, people with very low credit-scores, and people who appear on a list of debtors who know their rights and are likely to stand on them (that's right, merely insisting on your rights can ensure that the entire debt-collection industry leaves you alone, forever).
The FDPCA gives you rights: for example, you have the right to verify the debt and see the contract you signed when you took it on. The debt collector who calls you almost certainly does not have that contract and can't get it. Your original lender might, but they stopped caring about your debt the minute they sold it to a debt-collector. Their own IT systems are baling-wire-and-spit Rube Goldberg machines that glue together the wheezing computers of all the companies they've bought over the last 25 years. Retrieving your paperwork is a nontrivial task, and the lender doesn't have any reason to perform it.
Debt collectors are bottom feeders. They are buying delinquent debts at 5 cents on the dollar and hoping to recover 8 percent of them; at 7 percent, they're losing money. They aren't "large, nationally scaled, hypercompetent operators" – they're shoestring operations that can only be viable if they hire unskilled workers and fail to train them.
They are subject to automatic damages for illegal behavior, but they still break the law all the time. As McKenzie writes, a debt collector will "commit three federal torts in a few minutes of talking to a debtor then follow up with a confirmation of the same in writing." A statement like "if you don’t pay me I will sue you and then Immigration will take notice of that and yank your green card" makes the requisite three violations: a false threat of legal action, a false statement of affiliation with a federal agency, and "a false alleged consequence for debt nonpayment not provided for in law."
If you know this, you can likely end the process right there. If you don't, buckle in. The one area that debt collectors invest heavily in is the automation that allows them to engage in high-intensity harassment. They use "predictive dialers" to make multiple calls at once, only connecting the collector to the calls that pick up. They will call you repeatedly. They'll call your family, something they're legally prohibited from doing except to get your contact info, but they'll do it anyway, betting that you'll scrape up $250 to keep them from harassing your mother.
These dialing systems are far better organized than any of the company's record keeping about what you owe. A company may sell your debt on and fail to keep track of it, with the effect that multiple collectors will call you about the same debt, and even paying off one of them will not stop the other.
Talking to these people is a bad idea, because the one area where collectors get sophisticated training is in emptying your bank account. If you consent to a "payment plan," they will use your account and routing info to start whacking your bank account, and your bank will let them do it, because the one part of your conversation they reliably record is this payment plan rigamarole. Sending a check won't help – they'll use the account info on the front of your check to undertake "demand debits" from your account, and backstop it with that recorded call.
Any agreement on your part to get on a payment plan transforms the old, low-value debt you incurred with your credit card into a brand new, high value debt that you owe to the bill collector. There's a good chance they'll sell this debt to another collector and take the lump sum – and then the new collector will commence a fresh round of harassment.
McKenzie says you should never talk to a debt collector. Make them put everything in writing. They are almost certain to lie to you and violate your rights, and a written record will help you prove it later. What's more, debt collection agencies just don't have the capacity or competence to engage in written correspondence. Tell them to put it in writing and there's a good chance they'll just give up and move on, hunting softer targets.
One other thing debt collectors due is robo-sue their targets, bulk-filing boilerplate suits against debtors, real and imaginary. If you don't show up for court (which is what usually happens), they'll get a default judgment, and with it, the legal right to raid your bank account and your paycheck. That, in turn, is an asset that, once again, the debt collector can sell to an even scummier bottom-feeder, pocketing a lump sum.
McKenzie doesn't know what will fix this. But Michael Hudson, a renowned scholar of the debt practices of antiquity, has some ideas. Hudson has written eloquently and persuasively about the longstanding practice of jubilee, in which all debts were periodically wiped clean (say, whenever a new king took the throne, or once per generation):
https://pluralistic.net/2020/03/24/grandparents-optional-party/#jubilee
Hudson's core maxim is that "debt's that can't be paid won't be paid." The productive economy will have need for credit to secure the inputs to their processes. Farmers need to borrow every year for labor, seed and fertilizer. If all goes according to plan, the producer pays off the lender after the production is done and the goods are sold.
But even the most competent producer will eventually find themselves unable to pay. The best-prepared farmer can't save every harvest from blight, hailstorms or fire. When the producer can't pay the creditor, they go a little deeper into debt. That debt accumulates, getting worse with interest and with each bad beat.
Run this process long enough and the entire productive economy will be captive to lenders, who will be able to direct production for follies and fripperies. Farmers stop producing the food the people need so they can devote their land to ornamental flowers for creditors' tables. Left to themselves, credit markets produce hereditary castes of lenders and debtors, with lenders exercising ever-more power over debtors.
This is socially destabilizing; you can feel it in McKenzie's eloquent, barely controlled rage at the hopeless structural knot that produces the abusive and predatory debt industry. Hudson's claim is that the rulers of antiquity knew this – and that we forgot it. Jubilee was key to producing long term political stability. Take away Jubilee and civilizations collapse:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/07/08/jubilant/#construire-des-passerelles
Debts that can't be paid won't be paid. Debt collectors know this. It's irrefutable. The point of debt markets isn't to ensure that debts are discharged – it's to ensure that every penny the hereditary debtor class has is transferred to the creditor class, at the hands of their fellow debtors.
In her 2021 Paris Review article "America's Dead Souls," Molly McGhee gives a haunting, wrenching account of the debts her parents incurred and the harassment they endured:
https://www.theparisreview.org/blog/2021/05/17/americas-dead-souls/
After I published on it, many readers wrote in disbelief, insisting that the debt collection practices McGhee described were illegal:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/05/19/zombie-debt/#damnation
And they are illegal. But debt collection is a trade founded on lawlessness, and its core competence is to identify and target people who can't invoke the law in their own defense.

Going to Defcon this weekend? I’m giving a keynote, “An Audacious Plan to Halt the Internet’s Enshittification and Throw it Into Reverse,” today (Aug 12) at 12:30pm, followed by a book signing at the No Starch Press booth at 2:30pm!
https://info.defcon.org/event/?id=50826


I’m kickstarting the audiobook for “The Internet Con: How To Seize the Means of Computation,” a Big Tech disassembly manual to disenshittify the web and bring back the old, good internet. It’s a DRM-free book, which means Audible won’t carry it, so this crowdfunder is essential. Back now to get the audio, Verso hardcover and ebook:
http://seizethemeansofcomputation.org

If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/12/do-not-pay/#fair-debt-collection-practices-act
#pluralistic#jubilee#debts that cant be paid wont be paid#Patrick McKenzie#patio11#bits about money#debt#debt collection#do not pay#bottom feeders#Fair Debt Collection Practices Act#fdcpa#finance#armbreakers
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
Masterpost: Reasons I firmly believe we will beat climate change
Posts are in reverse chronological order (by post date, not article date), mostly taken from my "climate change" tag, which I went through all the way back to the literal beginning of my blog. Will update periodically.
Especially big deal articles/posts are in bold.
Big picture:
Mature trees offer hope in world of rising emissions (x)
Spying from space: How satellites can help identify and rein in a potent climate pollutant (x)
Good news: Tiny urban green spaces can cool cities and save lives (x)
Conservation and economic development go hand in hand, more often than expected (x)
The exponential growth of solar power will change the world (x)
Sun Machines: Solar, an energy that gets cheaper and cheaper, is going to be huge (x)
Wealthy nations finally deliver promised climate aid, as calls for more equitable funding for poor countries grow (x)
For Earth Day 2024, experts are spreading optimism – not doom. Here's why. (x)
Opinion: I’m a Climate Scientist. I’m Not Screaming Into the Void Anymore. (x)
The World’s Forests Are Doing Much Better Than We Think (x)
‘Staggering’ green growth gives hope for 1.5C, says global energy chief (x)
Beyond Catastrophe: A New Climate Reality Is Coming Into View (x)
Young Forests Capture Carbon Quicker than Previously Thought (x)
Yes, climate change can be beaten by 2050. Here's how. (x)
Soil improvements could keep planet within 1.5C heating target, research shows (x)
The global treaty to save the ozone layer has also slowed Arctic ice melt (x)
The doomers are wrong about humanity’s future — and its past (x)
Scientists Find Methane is Actually Offsetting 30% of its Own Heating Effect on Planet (x)
Are debt-for-climate swaps finally taking off? (x)
High seas treaty: historic deal to protect international waters finally reached at UN (x)
How Could Positive ‘Tipping Points’ Accelerate Climate Action? (x)
Specific examples:
Environmental Campaigners Celebrate As Labour Ends Tory Ban On New Onshore Wind Projects (x)
Private firms are driving a revolution in solar power in Africa (x)
How the small Pacific island nation of Vanuatu drastically cut plastic pollution (x)
Rewilding sites have seen 400% increase in jobs since 2008, research finds [Scotland] (x)
The American Climate Corps take flight, with most jobs based in the West (x)
Waste Heat Generated from Electronics to Warm Finnish City in Winter Thanks to Groundbreaking Thermal Energy Project (x)
Climate protection is now a human right — and lawsuits will follow [European Union] (x)
A new EU ecocide law ‘marks the end of impunity for environmental criminals’ (x)
Solar hits a renewable energy milestone not seen since WWII [United States] (x)
These are the climate grannies. They’ll do whatever it takes to protect their grandchildren. [United States and Native American Nations] (x)
Century of Tree Planting Stalls the Warming Effects in the Eastern United States, Says Study (x)
Chart: Wind and solar are closing in on fossil fuels in the EU (x)
UK use of gas and coal for electricity at lowest since 1957, figures show (x)
Countries That Generate 100% Renewable Energy Electricity (x)
Indigenous advocacy leads to largest dam removal project in US history [United States and Native American Nations] (x)
India’s clean energy transition is rapidly underway, benefiting the entire world (x)
China is set to shatter its wind and solar target five years early, new report finds (x)
‘Game changing’: spate of US lawsuits calls big oil to account for climate crisis (x)
Largest-ever data set collection shows how coral reefs can survive climate change (x)
The Biggest Climate Bill of Your Life - But What Does It DO? [United States] (x)
Good Climate News: Headline Roundup April 1st through April 15th, 2023 (x)
How agroforestry can restore degraded lands and provide income in the Amazon (x) [Brazil]
Loss of Climate-Crucial Mangrove Forests Has Slowed to Near-Negligable Amount Worldwide, Report Hails (x)
Agroecology schools help communities restore degraded land in Guatemala (x)
Climate adaptation:
Solar-powered generators pull clean drinking water 'from thin air,' aiding communities in need: 'It transforms lives' (x)
‘Sponge’ Cities Combat Urban Flooding by Letting Nature Do the Work [China] (x)
Indian Engineers Tackle Water Shortages with Star Wars Tech in Kerala (x)
A green roof or rooftop solar? You can combine them in a biosolar roof — boosting both biodiversity and power output (x)
Global death tolls from natural disasters have actually plummeted over the last century (x)
Los Angeles Just Proved How Spongy a City Can Be (x)
This city turns sewage into drinking water in 24 hours. The concept is catching on [Namibia] (x)
Plants teach their offspring how to adapt to climate change, scientists find (x)
Resurrecting Climate-Resilient Rice in India (x)
Other Masterposts:
Going carbon negative and how we're going to fix global heating (x)
#climate change#climate crisis#climate action#climate emergency#climate anxiety#climate solutions#fossil fuels#pollution#carbon emissions#solar power#wind power#trees#forests#tree planting#biodiversity#natural disasters#renewables#renewable electricity#united states#china#india#indigenous nations#european union#plant biology#brazil#uk#vanuatu#scotland#england#methane
2K notes
·
View notes