#Immunology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
It's like the translation "gift", as he calls it in Masque of Mandragora, that the Doctor shares with companions: the TARDIS secures consent from the companion's subconscious mind (maybe, hopefully) for translation, for innoculation, for whatever radiation safeguards are standard in the universe(s), etc., taking care of it all during the companion's first nap aboard. That's why in Masque of Mandragora the Doctor knew Sarah's subconscious had been tampered with when she commented about translation; her subconscious should have been aware that that's already taken care of.
Charley Pollard was never vaccinated for polio. What if something happens to her
299 notes
·
View notes
Text
Found this because of @sanddoc06 . No clue where it originally came from, but I had to share it.

19K notes
·
View notes
Text
Playing through the greenery and litter of a mini forest's undergrowth for just one month may be enough to change a child's immune system, according to an experiment in Finland. When daycare workers rolled out a lawn, planted forest undergrowth (such as dwarf heather and blueberries), and allowed children to care for crops in planter boxes, the diversity of microbes in the guts and on the skin of the young kids appeared healthier in a very short space of time. Compared to other city kids who play in standard urban daycares with yards of pavement, tile, and gravel, 3-, 4-, and 5-year-olds at these greened-up daycare centers in Finland showed increased T-cells and other important immune markers in their blood within 28 days.
Continue Reading.
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
"A new study evaluated a low-cost yet effective way to combat bacterial resistance using curcumin–the natural yellow plant compound in turmeric.
In 2017, a tragic death in a Nevada hospital was linked to a new strain of bacteria that had developed a resistance to 26 different antibiotics. Called ‘superbugs’, such antibiotic-resistant bacteria (including MRSA) remains a pressing public health threat.
Now researchers at Texas A&M University have shown that curcumin, the compound that gives turmeric its characteristic bright yellow color, can be used to reduce this antibiotic resistance.
They showed that when curcumin is intentionally given to bacteria as food, and then activated by light, it can trigger deleterious reactions within these microbes, eventually killing them. They demonstrated that this process reduces the number of antibiotic-resistant strains and renders conventional antibiotics effective again.
The results of the study were published this week in the journal Scientific Reports.
“We need alternative ways to either kill the superbugs or find a novel way to modify natural processes within the bacteria so that antibiotics start to act again,” said Dr. Vanderlei Bagnato, professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering and senior author on the study.
Photodynamic inactivation, a technique that has shown promise in combating bacterial resistance, uses light and light-sensitive molecules, called photosensitizers, to produce reactive oxygen species that can kill microorganisms by disrupting their metabolic processes.
In the new experiments, the team used curcumin, which is also a natural food for bacteria. They tested this technique on strains of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) that are resistant to amoxicillin, erythromycin, and gentamicin.
The researchers exposed the bacteria to many cycles of light exposure and then compared the minimum concentration of antibiotics needed to kill the bacteria after light exposure versus those that did not get light exposure.
“When we have a mixed population of bacteria where some are resistant, we can use photodynamic inactivation to narrow the bacterial distribution, leaving behind strains that are more or less similar in their response to antibiotics,” Bagnato told Texas A&M News.
“It’s much easier now to predict the precise antibiotic dose needed to remove the infection.”
MORE PROGRESS ON SUPERBUGS: • The Humble Potato Could Hold Key to Beating Hospital Superbugs and Crop Diseases • Compounds in Amber Could Help Fight Drug-Resistant Bacteria Superbugs, Say Scientists • When Antibiotics Failed, She Found a Natural Enemy of the Superbug to Save Husband’s Life
The team noted that photodynamic inactivation using curcumin has tremendous potential as an adjuvant or additional therapy with antibiotics for diseases, like pneumonia, caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
“Photodynamic inactivation offers a cost-effective treatment option, which is crucial for reducing medical expenses not only in developing countries but also in the United States,” said Dr. Vladislav Yakovlev, professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering and author on the study..."
-via Good News Network, February 8, 2025
#superbugs#immunology#epidemiology#microbiology#turmeric#antibiotics#antibiotic resistance#public health#medical news#medical research#good news#hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Got a glimpse of where we're at as a country medically via the r/nursing subreddit. People are really not okay and it's deeply scary. 'Letting it rip' when it comes to covid is killing thousands and disabling millions. With the latter, here's what it looks like:
Nurses saying they are seeing ear infections in kids all the time secondary to other illnesses (or routinely in adults which they have never seen before), nurses saying their hospitals are overrun by flus, rsv, norovirus, mycoplasma pneumonia. many people saying they went to the doctor sick as a dog and came out with 3 different illness diagnoses at the same time or that they and their kids get sick over and over and over. it is not normal for this to happen. we were lied to about covid, y'all.
have you and the people around you been physically as well this last year or two as they were in 2019?
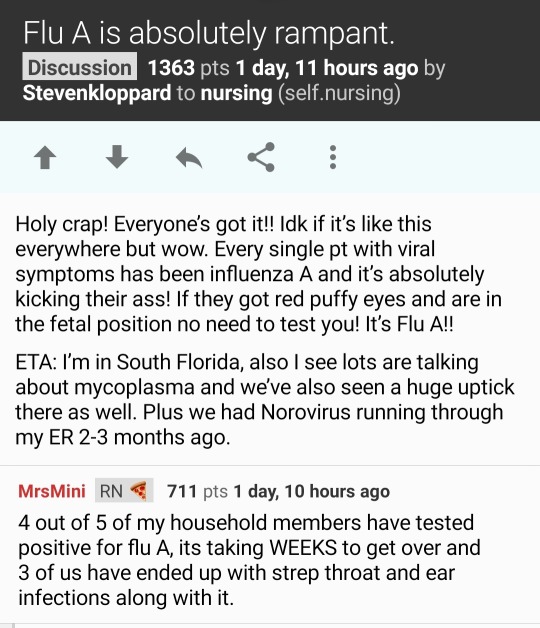
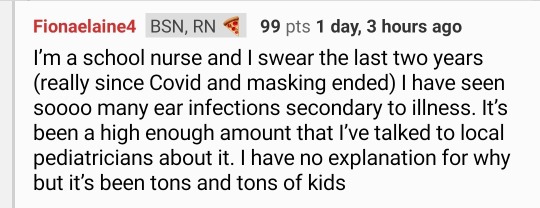
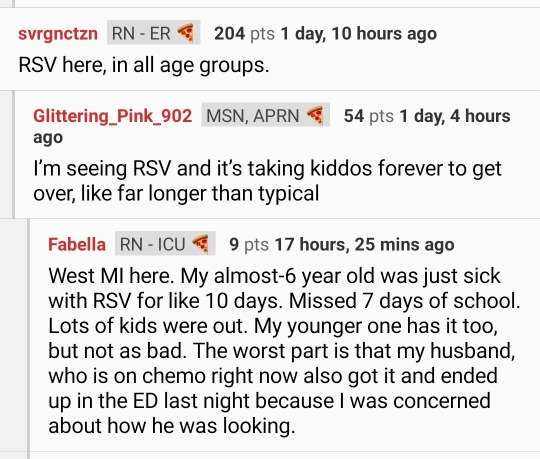

If you didn't know, as a lot of people don't - covid makes you immunocompromised. It damages the immune system, blood vessels and organ systems. It's a vascular infection, not a cold. the more infections you get, the worse it is. In the lab it's considered a level 3 pathogen (categories are for risk level/safety protocols), in the same category as tuberculosis. People are being treated with IVIG, because it's for immunocompromised people.
Also there is improper preparation and tracking for a h5n1 (type of bird flu) that has a very real chance of evolving to become a pandemic this and/or next flu season. they are finding it in wastewater all over the country, someone in Louisiana is in critical condition with it. Flu vaccine provides partial protection to it so I'd highly recommend getting that this and next winter.
Following epidemiologists is really important and helpful. The government wants you to go to work and think things are normal so they don't have to send you another check - they are not invested in our collective wellness (in fact, they take tons of lobbying money from insurance companies invested in keeping you sick). With some of these folks saying it is taking them weeks to recover from the flu, I wonder if some of it isn't bird flu, though it could be just being significantly immunocompromised.
fwiw masks work. I haven't gotten as much as a cold in years. well fitting kn95s and n95s protect you. even if you can't wear one at work, wear one to the doctor, at the grocery store and pharmacy. it would really help disabled people in general too.
588 notes
·
View notes
Text

every once in a while scientists cook so hard when making names
152 notes
·
View notes
Text

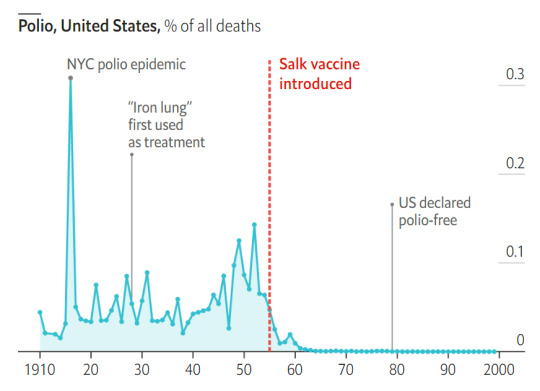



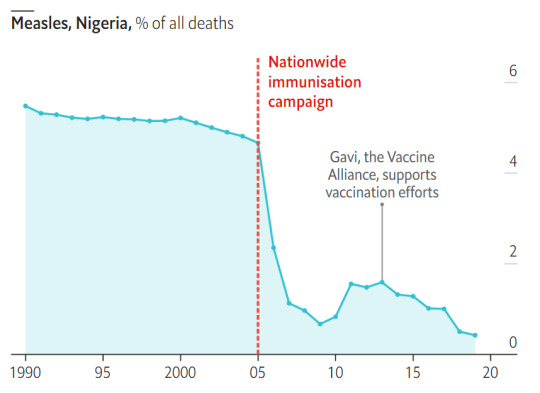

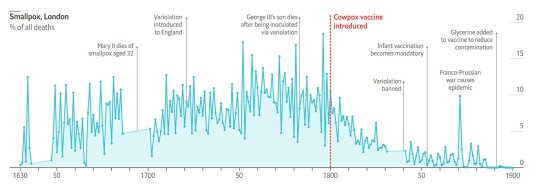
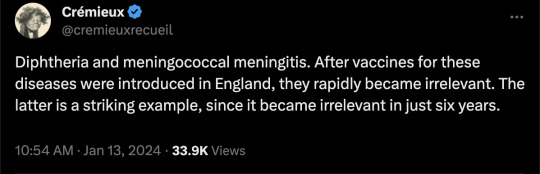
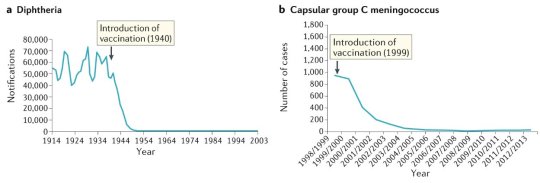

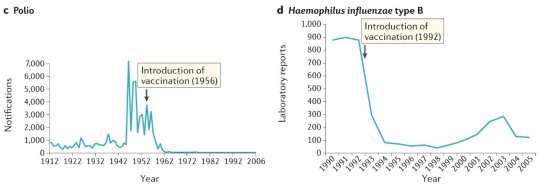

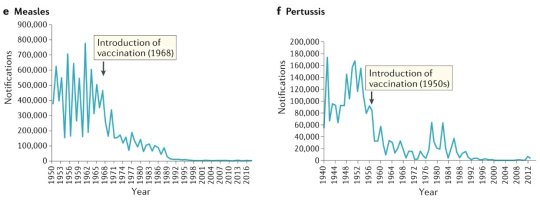

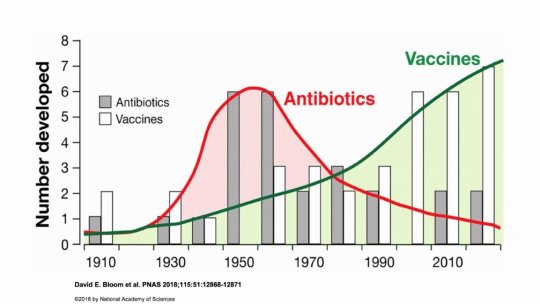


#vaccines#polio#measles#smallpox#diphtheria#meningococcal meningitis#haemophilus influenzae type B#pertussis#vaccine hesitancy#anti vaxxers#anti vax movement#antivaxers#COVID vaccine#anti vaccination#anti vaccine#science#medicine#religion is a mental illness#immunology
285 notes
·
View notes
Text

The opposite of antibiotic is...
#antibiotics#biology#medicine#science#immunology#memes#funny#humor#student memes#reddit memes#dank memes#insidesjoke
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tw: paywall (just have to create a free account)
35 notes
·
View notes
Text

42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researchers recently discovered that eight different psychiatric conditions share a common genetic basis. A new study has now honed in on some of those shared genetic variants to understand their properties. They found many are active for longer during brain development and potentially impact multiple stages, suggesting they could be new targets to treat multiple conditions. "The proteins produced by these genes are also highly connected to other proteins," explains University of North Carolina geneticist Hyejung Won. "Changes to these proteins in particular could ripple through the network, potentially causing widespread effects on the brain."
Continue Reading.
157 notes
·
View notes
Text
"A clinical trial studying severe allergic reactions in the U.K. is being called “life-transforming.”
Five United Kingdom National Health Service (NHS) hospitals are participating in the £2.5 million ($3.2 million) trial to help patients live with their food allergies.
The study is being funded by the Natasha Allergy Research Foundation, Sky News reported. The foundation was formed in the memory of Natasha Ednan-Laperouse, who died in 2016 after eating a baguette that had sesame in it...
The trial is studying clinical oral immunotherapy treatments in which patients are given small doses of the food to which they are allergic to build up their tolerance. The food is given under medical supervision by trained staff, The Telegraph reported.
The study has 139 people participating who have allergies to peanuts or cow’s milk. They range in age from 2 to 23 years old, the BBC reported.
The Food Standards Agency said 2 million people in the U.K. have a diagnosed food allergy. In the U.S., about 5.5. million children have a food allergy, the National Institutes of Health reported.
One 11-year-old who was diagnosed with a severe peanut allergy when he was an infant can now eat six peanuts.
A 5-year-old with a milk allergy can drink 120 ml of milk every day and can enjoy a daily hot chocolate, the BBC reported.
“To have a patient who has had anaphylaxis [Note: Anaphylaxis is an allergic reaction so severe that it's potentially fatal without immediate treatment. It is very common with peanut allergies in particular. x] to 4mls of milk to then tolerate 90mls within six to eight months is nothing less than a miracle,” Sibel Donmez-Ajtai, a pediatric allergy consultant and principal investigator at Sheffield Children’s NHS Foundation Trust, said, according to Sky News.
The final results of the study are expected to be released in 2027.
Similar studies have been conducted in the U.S. To find one, visit FoodAllergy.org.
Earlier this year, the NIH released the findings of a study of an antibody treatment that would help children consume allergy triggers safely."
-via WHIO 7 Local News, May 8, 2024
#allergies#allergic reaction#anaphylaxis#epipen#peanut allergy#milk allergy#peanuts#milk#medical news#public health#immune system#immunology#united kingdom#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text



And we're back with : Immunology at library
#studyblr#sparkle studies#study blog#studycare#studyspiration#desi studyblr#self care#study motivation#studyspo#photography#study inspiration#study hard#studying#study with me#studyblr community#study aesthetic#college student#student#student life#my stuff#university student#library#books and libraries#stemblr#women in stem#stem academia#stem student#immunology#biotechnology#libraries
58 notes
·
View notes
Photo

(via If we don't develop a treatment we're f*cked)
“Not to be a downer, but this is the result of a study researches led at the University of Toronto following SARS1 patients who were disabled by the virus initially and how they were doing 20 years later.“
Screenshot “from the presentation by; Prof. Daniel M. Altmann, Department of Immunology and Inflammation, Imperial College, Faculty of Medicine, London, UK at #UniteToFight2024 https://unitetofight2024.world/program/”
+ important comment:
“A study on SARS 1 survivors, if you're curious:
2023 study in The Lancet on SARS 1 survivors
Lots had femoral necrosis (bone death), osteoporosis, and long-lasting, possibly immunologically-based fatigue.
Just a reminder that while there are similarities, these are two different diseases. SARS CoV 1 hospitalized 70% of infected and killed 10% at the time of containment. They're similar in disease profile and in genetics, but they are NOT the same.
COVID-19 is much more infectious and less lethal, and the range of post-viral complications is different. Plus, we don't know what treatments will come out for Long COVID patients, but medicine is much more advanced and there is much more funding for Long COVID than there was for SARS CoV 1 survivors, who were infected in 2003, and never had access to a vaccine.”
#post-viral illness#viruses#covid#coronavirus#post-viral sequelae#PASC#long covid#SARS1#SARS#me/cfs#immunology#study#reddit#comments#historical#archiving#2022
76 notes
·
View notes
Text

macrophage design without any receptors..,
their name is macro
#artists on tumblr#biology#anime#art#moe art#moeart#my art#anime art#cells at work#cells#character design#macrophage#immunology#white blood cell#white blod cells#immune system#medicine#medicine art#premed#stemblr#cat#neuroandhemo#macro#studyblr
35 notes
·
View notes