#IRSCompliance
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
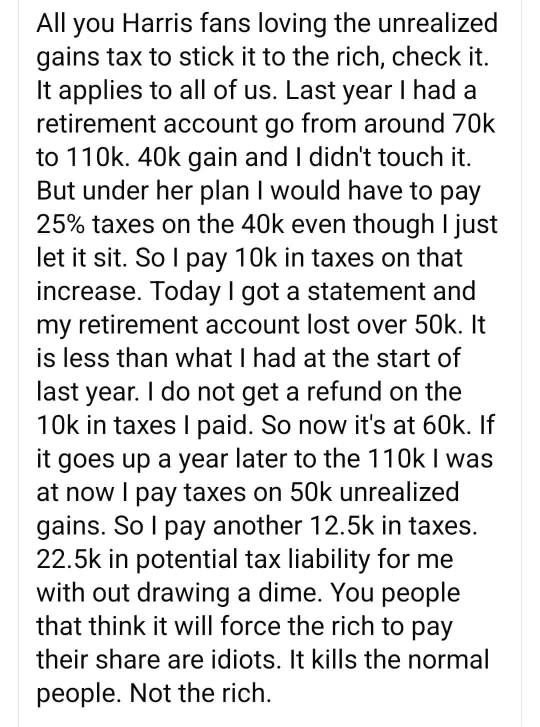
#politics#us politics#democrats are corrupt#democrats will destroy america#wake up democrats!!#us taxpayers#kamala lies#kamala harris is incompetent#kamala harris is an idiot#kamala harris#irscompliance#internal revenue service#president trump#truth justice and the american way#american economy#america first#i'm more maga than ever!#maga 2024#maga
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
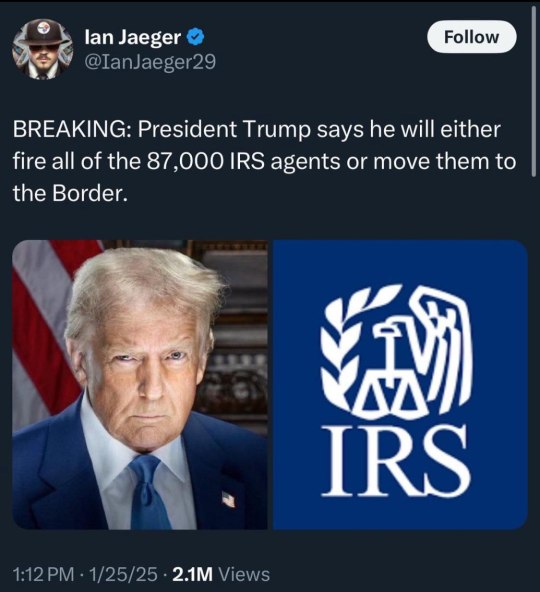
And we continue to go lower…..
#And we continue to go lower…..#usa#america#donald trump#crooked donald#anti donald trump#fuck trump#trump#usa is a terrorist state#usa is funding genocide#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#irscompliance#irshelp#irs audit#irs
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

Real estate investors in Los Angeles are constantly seeking ways to maximize their investment potential and minimize tax liabilities. One of the most powerful tools at their disposal is a 1031 exchange, a strategy that allows property owners to defer paying capital gains taxes by reinvesting the proceeds from the sale of an investment property into a new, like-kind property.
#1031Exchange#RealEstateInvestment#LosAngelesRealEstate#TaxDeferral#PropertyInvestment#InvestmentAdvisor#1031ExchangeSpecialist#SmartRealEstate#LosAngelesProperty#WealthBuilding#RealEstateStrategies#PropertyAdvisor#IRSCompliance#PortfolioGrowth#LosAngelesInvestors
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
#money#old money#taxes#us taxes#irs#irscompliance#irs1099form#taxseason#profit#economics#financial#budget#debt#loans#entrepreneur#business#startup#financial updates#million#marketing#irsforms#audit#irs audit
1 note
·
View note
Text
Absolutely massive amounts of tax fraud so I get a crazy amt of rebate $$$
My beef with the premise behind "The Purge" is that it's not laws stopping people from killing each other in the streets - it's kinda just the default human experience to not want to hurt anyone. We succeeded as a species because we're generally decent at getting along with each other. The average, well-adjusted human has no desire to inflict undeserved harm.
We do, however, hate rules, so we'd probably still get a little wild in less harmful ways.
No "none," you're a hardened criminal now. Please feel free to share more details of your heinous (victimless) acts in comments or tags 😎
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
Taxes Under the Guidance of Theodor Van Stephoudt!

Becoming smart with taxes requires the right knowledge and expertise. Under the guidance of Theodor Van Stephoudt, an International Tax Consultant, we explore the essential steps to becoming a tax professional in the United States.
A strong academic background in accounting, finance, or a related field is crucial. Understanding current tax laws, regulations, and financial principles is also necessary. Earning certifications like CPA, EA, or CTP enhances credibility, showcasing expertise to clients and employers.
Gaining practical experience is equally important. Internships or entry-level roles such as staff accountant, tax associate, or government accounting clerk provide valuable hands-on learning. Combining theoretical knowledge with real-world practice helps build a strong foundation in tax matters.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Get your taxes done accurately and on time with Syriac CPA Tax And Accounting Services Inc.! Let our experts handle the numbers while you focus on what matters most. ✅ 🔹 Maximize Deductions & Credits – Keep more of your hard-earned money! 🔹 IRS Compliance Guaranteed – Stay stress-free with accurate filings. 🔹 Fast & Efficient Filing – Beat the deadline without the hassle. 🔹 Personal & Business Taxes – Customized solutions for individuals and businesses. 🔹 Expert Guidance & Support – Get the answers you need from experienced professionals. 📞 Call us (562) 202-9697, (949) 397-2337 today! Let’s make tax season easy. Visit: www.syriaccpa.com
📝 𝐇𝐚𝐬𝐬𝐥𝐞-𝐅𝐫𝐞𝐞 𝐓𝐚𝐱 𝐏𝐫𝐞𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐒𝐲𝐫𝐢𝐚𝐜 𝐂𝐏𝐀! 📊💰
#TaxPreparation#CPAExperts#MaximizeRefunds#TaxSeason#IRSCompliance#AccountingServices#TaxSavings#FileYourTaxes#SyriacCPA
0 notes
Text

Get your taxes done accurately and on time with Syriac CPA Tax And Accounting Services Inc.! Let our experts handle the numbers while you focus on what matters most. ✅ 🔹 Maximize Deductions & Credits – Keep more of your hard-earned money! 🔹 IRS Compliance Guaranteed – Stay stress-free with accurate filings. 🔹 Fast & Efficient Filing – Beat the deadline without the hassle. 🔹 Personal & Business Taxes – Customized solutions for individuals and businesses. 🔹 Expert Guidance & Support – Get the answers you need from experienced professionals. 📞 Call us (562) 202-9697, (949) 397-2337 today! Let’s make tax season easy.
📝 𝐇𝐚𝐬𝐬𝐥𝐞-𝐅𝐫𝐞𝐞 𝐓𝐚𝐱 𝐏𝐫𝐞𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐒𝐲𝐫𝐢𝐚𝐜 𝐂𝐏𝐀! 📊💰
#TaxPreparation#CPAExperts#MaximizeRefunds#TaxSeason#IRSCompliance#AccountingServices#TaxSavings#FileYourTaxes#SyriacCPA
0 notes
Text
Foundation Giving | Grant Opportunities & Fundraising Education
Explore foundation giving, grant opportunities, and effective fundraising education. Learn how foundations donate and streamline your foundation application process.
0 notes
Text
You could totally work at the IRS and just not pay taxes. Who are they gonna send, the IRS?
0 notes
Text
Estimated tax payments to IRS

Understanding Estimated Tax Payments to the IRS
Paying taxes is a responsibility that should align with the income you earn throughout the year. Taxes can be paid either through withholding (deducted directly from your salary or pension) or through estimated tax payments to the IRS. Here’s a breakdown of what estimated tax payments entail and when they are necessary:
What Are Estimated Tax Payments?
Estimated tax payments are required when the tax withheld from your salary or pension is not enough to cover your tax liability, or if you receive additional income that isn't subject to withholding. This includes income from:
Interest and dividends
Self-employment activities
Rental properties
Gains from investments
If you're self-employed or run your own business, you are responsible for making these payments not just for income tax but also for self-employment tax and, in some cases, alternative minimum tax.
Why Are Estimated Tax Payments Important?
Failing to pay sufficient taxes throughout the year can result in penalties. The IRS may impose penalties if:
You don’t pay enough tax through withholding or estimated payments.
Your estimated payments don’t align with how your income is earned. Even if you're due a refund, inconsistent payments can trigger penalties.
Who Needs to Make Estimated Tax Payments?
Individuals, including sole proprietors, partners, and S corporation shareholders, must make estimated tax payments if they expect to owe at least $1,000 in taxes after accounting for withholdings and credits.
To avoid penalties, many taxpayers calculate their estimated payments based on the prior year’s tax liability. This approach can ensure compliance and reduce the risk of underpayment.
How to Make Estimated Tax Payments
The IRS offers several convenient options for making estimated tax payments. One of the most reliable methods is the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS). Through EFTPS, both individuals and businesses can manage payments for:
Federal tax deposits
Installment agreements
Estimated taxes
Estimated tax payments are typically divided into four quarterly installments. Ensuring that you pay adequate amounts each quarter helps avoid penalties and simplifies compliance.
Tips for Managing Estimated Taxes
Consistency is key. Regularly set aside funds for taxes and make payments weekly, monthly, or bi-weekly, ensuring you meet your quarterly obligations.
Use prior-year data. Estimate your payments based on your previous year’s tax liability to simplify calculations.
Stay informed. Regularly review your income and withholding to determine if adjustments are necessary.
Understanding and planning for estimated tax payments can prevent financial surprises and penalties. Whether you're self-employed or have additional income sources, staying on top of your tax responsibilities throughout the year is essential for smooth compliance.
0 notes
Text
At OBG Outsourcing, we understand that filing taxes is a complex process where mistakes or changes can occur despite the utmost care
0 notes
Text
REPORT THE HERITAGE FOUNDATION TO THE IRS
https://drive.google.com/file/d/11ox6BbRjSxkdgKd5Up3aSuJDHQLhuDh1/view?usp=drivesdk
#REPORT THE HERITAGE FOUNDATION TO THE IRS#heritage foundation#irs audit#fuck the irs#irscompliance#irsforms#irs#morals#ethics#law#auspol#politas#ausgov#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
#1031Exchange#LosAngelesRealEstate#PropertyInvestment#TaxDeferral#RealEstateGuide#InvestmentTips#PropertyOwners#IRSCompliance#RealEstatePlanning#ExchangeDeadlines
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
For the IRS, some important numbers to keep handy include the toll-free IRS phone number for individual tax-related questions at 1-800-829-1040, the IRS Business and Specialty Tax Line at 1-800-829-4933 for business tax inquiries, and the IRS Fraud Hotline at 1-800-829-0433 for reporting suspected tax fraud or identity theft. Additionally, the IRS offers online resources such as the official IRS website (www.irs.gov) for forms, publications, and tax information, as well as the IRS Taxpayer Assistance Centers for in-person help with tax matters. Always verify the authenticity of any communication claiming to be from the IRS to protect against scams and fraud.
0 notes
Text
IRS Problem Resolution Made Simple with SAI CPA Services

Tax issues with the IRS can be overwhelming, but they don’t have to be. SAI CPA Services specializes in IRS problem resolution, offering personalized solutions to help you tackle tax issues confidently.
Why IRS Problem Resolution Matters
Tax issues can have serious consequences if not addressed promptly. Here’s how our IRS resolution services work to protect your financial well-being:
Tax Dispute Support: Whether it’s an audit or unexpected tax bill, we’re here to represent you and negotiate on your behalf to reach the best possible outcome.
Penalty Abatement: Our team will review your case and, where possible, apply for penalty relief, potentially reducing the amount owed.
Payment Plans and Offers in Compromise: If you’re unable to pay in full, we explore options like installment agreements or offers in compromise to make payments more manageable.
How SAI CPA Services Can Help
At SAI CPA Services, we provide compassionate and effective IRS problem resolution services, ensuring you have a trusted partner to help navigate any tax issues.
Connect Us: https://www.saicpaservices.com https://www.facebook.com/AjayKCPA https://www.instagram.com/sai_cpa_services/ https://twitter.com/SaiCPA https://www.linkedin.com/in/saicpaservices/ https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029Va9qWRI60eBg1dRfEa1I
908-380-6876
1 Auer Ct, 2nd Floor
East Brunswick, NJ 08816
#IRSRepresentation#TaxServices#irs#irscompliance#irsforms#irs audit#irs1099form#taxes#audit#help#tax relief#financial services
1 note
·
View note