#Hydrogen Fueling Station Industry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The hydrogen fueling station market is projected to reach $2,251.2 million by 2034 from $268.4 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 23.70% during the forecast period 2024-2034.
#Hydrogen Fueling Station Market#Hydrogen Fueling Station Report#Hydrogen Fueling Station Industry#Chemicals#BISResearch
0 notes
Text
Hydrogen Fueling Station Market Focusing on Current Trends and Leading Companies That Will Change in Coming Future
According to a research report “Hydrogen Fueling Station Market by Supply Type, Station Size (Small Stations, Mid-Sized Stations, Large Stations), Station Type (Fixed Hydrogen Stations, Mobile Hydrogen Stations), Pressure, Solution (EPC, Components) and Region – Global Forecast to 2030″ published by MarketsandMarkets, the global hydrogen fueling station market is projected to reach USD 1,129…

View On WordPress
#Electric utilities#Electricity#Energy#Hydrogen Fueling Station#Hydrogen Fueling Station Industry#Hydrogen Fueling Station Market#Hydrogen Fueling Station Market Size#hydrogen generation#Power#Power Generation#Utilities
0 notes
Link
Hydrogen Fueling Station Market is projected to reach USD 1,129 million in 2030 from USD 380 million in 2023 at a CAGR of 16.8% according to a new report by MarketsandMarkets™. The key factor such as growing demand for the zero-emission vehicles and strong government support have led to many top OEMs investing in the research and development of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). Due to increasing demand for the FCEVs, there is a need for the hydrogen fueling station infrastructure. Furthermore, growing public and private investments in emerging economies have accelerated the growth of Hydrogen Fueling Station Market.
0 notes
Text
Hydrogen Fueling Station Market: Growth, Trends and Opportunities Through 2024-2033
The Hydrogen Fueling Station Market is expanding as global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and transition to clean energy sources gain momentum. As a zero-emission fuel, Hydrogen offers a promising alternative for heavy transportation and industrial applications. With various regions actively investing in hydrogen infrastructure, the Hydrogen Fueling Station Market is witnessing significant growth.
According to BIS Research, the Hydrogen Fueling Station Market is projected to grow from $1,538.8 million in 2023 to $8,195.1 million by 2033, with a CAGR of 18.21%.
Market Growth and Trends
The market for hydrogen fuel stations is expected to grow as government incentives and corporate investments drive the development of hydrogen ecosystems. The deployment of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) in regions like Europe, Asia, and North America further accelerates market growth. As infrastructure expands, hydrogen is anticipated to play a key role in achieving global sustainability goals. Request a Free Sample Report on the Hydrogen Fuel Station Market
Key Technologies Shaping the Market
Several technologies are crucial to hydrogen fuel station development:
· Compressed Hydrogen Storage: This method stores hydrogen at high pressures (typically 350–700 bar) to maximize storage capacity within fueling stations, ensuring that sufficient hydrogen is available for vehicle refueling. Compressed storage is essential for the quick, efficient, and safe refueling of fuel cell vehicles, allowing drivers to refuel in a manner similar to conventional gas stations.
· Cryogenic Storage Solutions: Cryogenic storage involves cooling hydrogen to extremely low temperatures (below -253°C) to store it as a liquid, which occupies far less volume than gaseous hydrogen. This solution allows for stable, long-term storage, making it suitable for applications that require large hydrogen reserves. Cryogenic tanks maintain hydrogen at these low temperatures, reducing boil-off and enabling effective transportation and storage, especially for high-demand sites or remote locations.
· Hydrogen Production via Electrolysis: Electrolysis technology splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, and when powered by renewable energy sources, it enables green, on-site hydrogen generation. This method not only reduces reliance on external hydrogen supply chains but also supports a sustainable fuel cycle by minimizing transportation emissions.
Demand Drivers
Key factors driving demand in the Hydrogen Fuel Station Market include:
· Government Incentives for Clean Energy: Policies, subsidies, and tax breaks for hydrogen infrastructure make clean energy more accessible, encouraging investments and speeding up the development of hydrogen fueling stations.
· Growing Fuel Cell Vehicle (FCV) Adoption: The rise in FCVs, favored for their zero emissions and efficiency, is increasing the need for a widespread hydrogen fueling network to support expanding use across sectors like public transit and freight. Download Complete TOC of the Hydrogen Fuel Station Market Report
On-Field to Lead the Hydrogen Fuel Station Market
The on-field segment, especially within the automotive sector, is expected to dominate due to the rising adoption of FCVs. As more vehicles rely on hydrogen, accessible fueling stations are becoming essential for seamless operation, particularly for fleet and commercial vehicle applications.
Download the free sample page Click Here !
Key Players
· Air Liquide
· Nel ASA
· Linde plc
· Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.
· McPhy Energy S.A.
· Iwatani Corporation
· Ingersoll Rand
· Chart Industries
· H2 MOBILITY
· Sera GmbH
· Powertech Labs Inc.
· Galileo Technologies S.A.
· Nikola Corporation
· Atawey
Get More Market Insights on Advanced Materials Chemicals and Fuel
Conclusion
With a global shift toward clean energy, the Hydrogen Fuel Station Market is positioned for robust growth, driven by environmental goals and the transition away from fossil fuels. As governments and private sectors ramp up investments in hydrogen infrastructure, hydrogen fueling stations are becoming essential for supporting a sustainable energy ecosystem. These stations will not only cater to fuel cell vehicles but also serve broader applications, including industrial and residential power needs. Hydrogen’s versatility and ability to produce zero emissions make it a prime candidate for long-term energy solutions, positioning hydrogen fueling stations as a cornerstone in the evolving landscape of green transportation and energy innovation. BIS Research, recognized as a best market research company, provides premium market intelligence reports on deep technologies poised to cause significant market disruption in the coming years.
At BIS Research, we focus exclusively on technologies related to precision medicine, medical devices, diagnostics, life sciences, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), big data analysis, blockchain technology, 3D printing, advanced materials and chemicals, agriculture and FoodTech, mobility, robotics and UAVs, and aerospace and defense, among others
0 notes
Text
The Rise of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive technology, one innovation stands out as a beacon of hope for a sustainable future: hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). As the world grapples with the pressing need to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change, the rise of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offers a promising solution. These vehicles, which run on one of the universe’s most abundant…
#adoption#automotive industry#Biomass#California#carbon emissions#Clean Energy#climate change#Costs#driving range#efficiency#electric motor#Electrolysis#Electrons#Energy#energy security#Environment#Europe#FCVs#Fuel Cell#Future#Future Outlook#Green#Green Hydrogen#Hydrogen#Hydrogen Cars#Hydrogen Economy#Hydrogen Olympics#Hydrogen Production#Hydrogen Stations#infrastructure
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hydrogen-powered trucks are expected to reach life-cycle cost parity with their fossil-fuel-burning peers in China by 2027 even without the aid of subsidies, a milestone which the world’s biggest producer and consumer of the zero-emission energy source, seeks to achieve eight years ahead of Europe.
This will push forward the country’s ambition to dominate the market for hydrogen fuel cells in the transport sector as Beijing’s enabling environment starts paying off, an industry executive said.[...]
“China has developed a world-leading industry in commercial vehicle applications for hydrogen fuel cell technology, with enterprises ranging from upstream raw materials to downstream products over the past decade,” said Robin Lin, chairman and president of Refire Group, a Chinese supplier of hydrogen fuel cell technologies.[...]
China has stepped up its game this year with the central and local authorities releasing a variety of hydrogen-related policies and incentives, following the release of its first national-level guidelines for the hydrogen energy industry in 2023.
Nearly a third of its end-2023 fleet of 18,000 hydrogen fuel cell vehicles were sold last year alone, according to data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, indicating the gathering pace. In a further sign of accelerating offtake, China targets to have at least 50,000 units on the road by 2025, according to its national plan.
According to Lin, China has seen significant reduction in the manufacturing cost of hydrogen fuel cell systems, which account for roughly half the cost of a hydrogen vehicle. The cost has dived from over 30,000 yuan per kilowatt in 2015 to less than 4,000 yuan per kilowatt now.[...]
“In transport, heavy-duty trucks could be the first to achieve successful commercialisation of hydrogen fuel cell technology,” he said.[...]
In China, high-purity hydrogen generated as a by-product from industrial processes, such as Shanxi province, is around 25 to 40 yuan per kilogram at local hydrogen refuelling stations, while high-purity hydrogen in other regions, such as Shanghai, is around 50 to 70 yuan per kilogram at local hydrogen refuelling stations, according to Refire.
13 May 24
283 notes
·
View notes
Text
A California court has advanced a civil fraud case against a Norwegian company at the center of the state’s failure to build workable hydrogen fueling infrastructure, which has already left thousands of car owners in the lurch.
A case involving allegations of fraud against Oslo-based Nel ASA is moving toward a trial in October 2026, after a California judge left intact the core claims brought by a major player in the rollout of hydrogen infrastructure in the state, Iwatani Corporation of America, a subsidiary of one of Japan’s largest industrial gas companies.
The allegations center on a lesser-known aspect of the blundered roll-out: Iwatani is claiming that Nel duped it into buying faulty hydrogen fueling stations. And the case has provided a window into the extent to which these same stations were provided to and promoted by major players including Toyota and Shell—stations that have since been abandoned or shut down.
The judge’s ruling last month leaves Nel and its top executives—including current and former CEOs Robert Borin and Håkon Volldal—in the crosshairs. Iwatani’s central claim is that Nel, under pressure to sell a money-losing product, knowingly induced Iwatani into purchasing untested hydrogen fueling stations with false assurances of the technology’s real-world readiness.
Nel denies the allegations, and has put forward procedural arguments to get the case thrown out, saying that California does not have jurisdiction over the company or its executives.
In separate rulings, Judge James Selna of the Central District of California sided with Iwatani on the core claims while dismissing several others, finding that California does in fact have jurisdiction and that the allegations go beyond a simple breach of contract and into the realm of fraud in selling the equipment, known as H2Stations.
The judge ruled that there was “active concealment,” citing examples, including that Nel did not disclose the fact it had never built a working model of the H2Station nor sufficiently tested it in real-world conditions, and had no actual data to support their H2Stations’ performance claims.
After the lawsuit was filed in January, Nel abandoned the seven Iwatani hydrogen fueling stations and executed a corporate spinout of its fueling division—which Iwatani claims is a means of shielding those assets from a potential court judgment.
“The deliveries you are referring to were from a company now called Cavendish Hydrogen,” says Lars Nermoen, Nel’s spokesperson, in response to an email seeking comment, referring to the spun-off entity. “Nel no longer has any business in hydrogen fueling.”
The failure of novel technology in real-world settings is not unheard of. But for the hydrogen car industry, it came at one of the worst times: In 2019, California was investing heavily in hydrogen refueling infrastructure, attracting global automakers and oil and gas majors to the state.
At the time, Toyota was pushing for more fueling infrastructure to support the uptake of the Toyota Mirai, one of the earliest light-duty consumer hydrogen fuel-cell cars to hit the market.
So Toyota partnered with both Iwatani and oil major Shell to build more fueling stations. Shell brought on Nel as the station provider, and both Iwatani and Chevron partnered with Nel soon after. Representatives from Shell and Iwatani did not respond to requests for comment.
Lewis Fulton, director of the Energy Futures Program at the University of California, Davis, says the equipment failures in the passenger segment have led to a “near collapse of the system” in California. In addition to the abandoned Iwatani stations, Shell in February completely shut down its seven California hydrogen refueling stations and canceled plans to build 48 stations in the state.
Chevron had contracted Nel to create 16 stations, but did not provide a response on the status of those stations. The extent to which Nel provided the technology for these major players has not been previously reported on.
Meanwhile, Toyota, which has since deprioritized the California market for the Mirai, is facing a class action lawsuit from many drivers who already bought the hydrogen-powered vehicle. The lawsuit claims that, contrary to Toyota’s promises, hydrogen fuel for their cars is becoming more difficult to obtain, making the Mirai “unsafe, unreliable, and inoperable.” Toyota did not respond to a request for comment.
According to the Hydrogen Fuel Cell Partnership, there are 55 hydrogen fueling stations in California, but many of them experience frequent downtime. None of the hydrogen fueling stations provided by Nel are currently operating. Iwatani’s only functioning refueling stations were built by Linde, a large industrial gas company.
In the meantime, Fulton says California has pivoted to building infrastructure for heavy-duty vehicles like trucks and buses, with the hope that the passenger market can reboot with the help of a growing freight market.
By focusing on the heavy-duty market, California can, in theory, create a stronger supply of clean hydrogen that brings costs down and increases availability, says Fulton, who is also an adviser to Arches, the California hydrogen hub that has won $1.2 billion of conditional funding from the US Department of Energy.
“Arches is targeting 50 to 60 truck-oriented stations around the state by 2030, and with different fueling islands and pressure systems, those could also service light-duty vehicles,” he says.
California’s difficulties with hydrogen vehicle infrastructure have driven home some stark lessons about the wider use of the technology.
“The problem is, they’re expensive, and they require enormous amounts of maintenance,” says Jim Bowe, a Washington, DC–based partner at King & Spalding, an international law firm. “Fleets that have been looking at the possibility of hydrogen buses often balk when they realize how much more maintenance—not only for the refueling facilities, but also for the vehicles themselves—is required relative to internal combustion engines or batteries.”
California-based FirstElement Fuel, another hydrogen fueling station provider, is positioned as a potential winner amid the crisis for the sector. Operating under the name True Zero, it currently has the most operating hydrogen fueling stations in California, but is still working to become profitable, according to sources familiar with the company. (FirstElement executives did not respond to requests for an interview.)
According to Iwatani’s lawsuit, Nel was able to hide the fact that the stations it installed were not operational until early 2023, when continual failures led Iwatani to launch its own investigation.
Nel achieved this subterfuge by requiring Iwatani to enter into an exclusive maintenance contract with Nel, essentially shifting the cost of testing the stations to Iwatani, the lawsuit claims.
Nel’s current CEO, Håkon Volldal, an individual defendant in the case, acknowledged the failings around the same time. In an earnings call last year, he said of the hydrogen fueling stations: “I think it’s fair to say that the technology that was installed was immature, and that the quality was not good enough, and we struggle with all the work we have to do in order to keep these stations running, to fix issues, to send personnel out on site.”
In its investigation, Iwatani workers claimed they found shrapnel inside the fueling stations, and concluded that parts of the fueling apparatus were routinely exploding, spraying debris inside the station box. (Nel blames outside companies for installation failures.) Iwatani also claimed it found valves from third-party manufacturers that were never intended for use in a hydrogen fueling station.
The lawsuit details a months-long back and forth between Iwatani and Nel, in which Iwatani attempts to get Nel to fix the broken stations. Nel won’t—or can’t—fix the stations, triggering the lawsuit.
These Iwatani allegations were echoed by Kasey Hawk, who worked as a technician for Nel in California starting in 2021. An Army veteran who drove an Abrams tank in combat, Hawk was one of several veterans hired by Nel to service the California fueling stations. Though he alleges he had a strong mechanical background stemming from his military experience, Hawk claims he received only minimal training on the particularities of hydrogen fueling stations. (Hawk is not involved in the ongoing lawsuit and Nel has not commented on his allegations.)
“It was a little strange because it’s actually dangerous work—working with high-pressure gases and the potential for explosions,” he says in an interview with WIRED.
Hawk claims when he showed up to conduct the first repairs at Shell-owned stations in the Sacramento area, it appeared they hadn’t been maintained since commissioning, and there was already a backlog of work to be done. “I saw that the stations weren’t set up right from the beginning,” he says. He noticed, for example, that the pipes weren’t properly insulated, which would cause ice buildup within the fueling nozzle, since liquid hydrogen is stored and pumped at cryogenic temperatures.
A team of Nel technicians arrived from South Korea to help. But those technicians didn’t speak English, limiting what Hawk could learn from them, he says. And since Nel’s hydrogen fueling subsidiary was based in Denmark, the schematics for the stations were available only in Danish. In addition, ordering new parts often took weeks, meaning similar amounts of station downtime, he explains. “We were in situations every day where we did not know what to do next.”
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
OK, putative Gjallarhorn planetary garrison/repurposed pre-Disaster space-station names (because the Greek convention links it to the Ariadne, which appears to predate Gjallarhorn's founding) would be as follows:
Mercury = Hermes
Venus = Aphrodite [CANON]
Earth = nil, the orbital station(s) are named Glaðsheimr [CANON]
Mars = Ares [CANON]
Jupiter = Zeus
Saturn = Cronus/Cronos/Kronos [or Chronus/Chronos but I'd rather we didn't]
Uranus = *record scratch* OK, so Uranus IS the Greek god here, or the Latinised spelling of one, so should it swap to the Roman version for the station, Caelus/Coelus? I guess that's the only option. Damn you, Bode! (Could be worse; Herschel wanted to call the planet 'George'.)
Neptune = Poseidon
Pluto would obviously get Hades but I genuinely don't see why you'd put anything near Pluto, seeing as there is sod-all out that far, whereas the rest potentially have some utility as places for human colonisation (I'm dubious about Mercury but we'll allow it for extra-canonical reasons).
The furthest confirmed point of human expansion in the Post Disaster timeline are the Saturn 'pioneer camps' mentioned in the Urdr Hunt game. The very use of the word 'pioneer' suggests this is the frontier for space-going civilisation in the setting. Whether that means that's as far as people have gotten or merely represents the extent to which infrastructure extends after the War is an open question. Certainly, Jupiter and Saturn offer greater possibilities as industrial bases given their abundance of moons. The UC Gundam timeline treats Jupiter as the main source for hydrogen fuel, and while the PD timeline has Ahab reactors, they still use propellant, so this might give us the basis for the corporate wealth represented by Teiwaz. Expanding on to Saturn would follow logically from that.
This is not to say Ahab reactors wouldn't allow exploration further out, simply that in terms of establishing colonies, Saturn represents a reasonable stopping point, and therefore likely the extent of Gjallarhorn's active presence. Its role is primarily peacekeeping and policing, recall, so why would it have a base somewhere there wasn't a large population to control?
Now, if the space stations they use once served some other purposes or represent a previous high-water mark for expansion from which civilisation has now retracted -- extrapolating from the Greek naming convention predating the War -- then it's possible the remaining outer planets would have stations assigned to them anyway. Perhaps there's a derelict or half-finished Poseidon station orbiting above Neptune, a lonely monument to what the mobile armours cut short. Or perhaps Cronos station is the work-in-progress, a putative outpost cannibalised from parts delivered before the crisis, finally put to use as corporations seek new ground to break and thus compete with the Jupiter-based giants.
There's lots of room to speculate.
For my next trick, I shall decide if any of it is relevant to what I'm currently writing . . .
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Facing Challenges: Car Transport Companies and the Switch to Clean Fuels
As the world shifts towards greener energy solutions, car transport companies are facing new challenges and opportunities. Staying competitive and meeting customer demands is important for car shipping services. Explore how these companies are adapting to alternative fuel innovations, and how integrating electric and hybrid vehicles into their fleets and adjusting their services to accommodate this change.
From operational adjustments to training staff on new technologies, discover the practical steps car transport companies are taking to embrace a cleaner future.
Alternative Fuel Innovations
The automotive industry has been making significant strides in developing alternative fuel technologies to reduce reliance on traditional fossil fuels and decrease environmental impact. These innovations have an influence on nationwide car transport services, as they adapt to accommodate vehicles with diverse fuel systems.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cell technology has emerged as a promising alternative to conventional internal combustion engines. These systems generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing only water vapor as a byproduct. This clean energy solution has an impact on reducing carbon emissions in the transportation sector.
For nationwide vehicle driveaway services, the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles presents new challenges and opportunities. Transport companies are adapting their processes to handle these vehicles safely, ensuring proper fueling and maintenance during long-distance shipping. The increasing popularity of hydrogen-powered cars has an influence on the infrastructure development along major transport routes, with more hydrogen refueling stations being established to support these vehicles.
Solar-Powered Accessories
Solar power has found its way into various automotive applications, particularly in the form of solar-powered accessories. These innovative additions harness the sun's energy to power auxiliary systems in vehicles, reducing the load on the main power source and improving overall efficiency.
In the context of auto transport services in California and across the nation, solar-powered accessories have an impact on vehicle preservation during transit. For instance, solar-powered ventilation systems can help maintain optimal temperatures inside vehicles during long journeys, protecting interiors and sensitive electronics from extreme heat. This technology has an influence on the quality of service provided by car shipping companies, ensuring vehicles arrive at their destinations in prime condition.
Biodiesel Compatibility
Biodiesel, a renewable fuel produced from vegetable oils or animal fats, has gained traction as an alternative to petroleum-based diesel. Many modern diesel engines are now designed to be compatible with biodiesel blends, offering a more environmentally friendly option for drivers and transport companies alike.
For San Jose auto shipping services and other transport providers, the increased compatibility with biodiesel has an impact on fuel options and environmental considerations. Transport companies are increasingly incorporating biodiesel-compatible vehicles into their fleets, reducing their carbon footprint while maintaining performance standards. This shift has an influence on the overall sustainability of nationwide car transport operations, aligning with growing environmental concerns and regulations.
The integration of these alternative fuel innovations in the automotive industry has a significant impact on nationwide car transport services. As vehicles become more diverse in their fuel requirements, transport companies are adapting their practices to accommodate these changes.
For those interested in learning more about how these alternative fuel technologies affect car shipping and the broader automotive landscape, it is recommended to read the full details on luckystarautotransport.com, where comprehensive information about these advancements is available. For those interested in learning more about how these innovations affect, nationwide car transport and the broader automotive industry, it is recommended to read this contact form on luckystarautotransport.com interested in the transport industry and its improvement toward sustainability.
For those interested in learning more about how these innovations affect, nationwide car transport and the broader automotive industry, it is recommended to navigate this website and discover the untapped market potential of eco-conscious consumers in the transport industry and its improvement toward sustainability.
Clean fuels aren’t just a trend—they’re the future of car transport. Will you adapt or get left behind?
youtube
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
For most of the history of civilisation we’ve exploited a pretty small selection of metals, including copper and tin for bronze-age tools, iron for steel, and lead, gold and silver. Our repertoire has begun to diversify over the past century or so, with the widespread use of aluminium and other new metals. But in the past few decades the number of different metals we wield in our technological society has absolutely exploded. A modern smartphone contains more than 30 different elements. These include carbon and hydrogen in the plastic casing, silicon for the microchip wafers, and copper wiring and gold contacts. But there are also small amounts of a large number of other metals, each exploited for its own particular electronic properties, or for the tiny, powerful magnets used in the speaker and vibration motor. This means that if you own a smartphone, you have in your pocket a substantial fraction of all the stable elements of the periodic table. And it’s not just modern electronics that demand a huge diversity of different metals. So too do the high-performance alloys used in the turbines of a power station or aircraft jet engine, or the reaction-accelerating catalysts that we use in industrial chemistry for refining oil, producing plastics or synthesising modern medicinal drugs. Yet most of us have never even heard of many of these critical metals – elements with exotic names like tantalum, yttrium or dysprosium.
The concern is that unlike widespread resources like iron or nitrogen, several of these elements crucial to the modern world may become prohibitively scarce. These have become known as the endangered elements. In response to the Mendeleev anniversary, the European Chemical Society (EuChemS) has released a version of the periodic table (see above) to highlight the elements that are most at risk over the coming decades.
Helium, for example is considered to be under serious threat in the next 100 years. It is the second most abundant element in the universe, but preciously rare on Earth because it is light enough to simply escape from the top of our atmosphere. The helium we do use is effectively mined from deep underground, usually along with natural gas, as it is produced as radiation particles from the decay of elements like uranium. Helium is very useful – as a cooling liquid for the superconducting magnets in hospital MRI scanners, for example, or as an extremely light gas for weather balloons and airships. But once it leaks into the air it is lost for ever, and there are concerns over meeting supply in the future. With this perspective, its frivolous use in party balloons seems almost painfully wasteful.
Many of these endangered elements are the sort of exotic metals used in modern electronics, and indeed the supply of 17 elements needed for smartphones may give cause for concern in years to come. Particularly worrying is the fact that many of those facing potential scarcity are exactly the elements we need for the green technologies to replace our reliance on fossil fuels – those used in rechargeable batteries, solar panels, and the powerful magnets within the motors of electric cars or generators in wind turbines. Gallium, for example, is needed for integrated circuits, solar panels, blue LEDs and laser diodes for Blu-ray Discs. Indium is used in everything from TVs to laptops, and in particular the touch-sensitive screens of modern smartphones and tablets. It is estimated that at current usage rates, available indium will be used up in 50 years and will become very expensive to collect and purify.
Except for helium, the problem isn’t that these scarce elements actually become lost to the planet, but that they become too expensive to mine or too dispersed to recycle effectively. “Rare earth elements”, such as yttrium, dysprosium, neodymium and scandium, are actually relatively plentiful in the Earth’s crust but aren’t geologically concentrated into rich ores. This means that they can’t be extracted economically in many areas of the world. And once they have been manufactured as tiny components within an electronic device, they can be even harder to reclaim and recycle. EuChemS calculates that 10m smartphones are discarded or replaced every month in the EU alone, and so serious action is needed to tackle these challenges of elemental scarcity.
#current events#environmentalism#capitalism#manufacturing#science#chemistry#mining#tantalum#yttrium#dysprosium#helium#indium#neodymium#scandium#dmitri mendeleev#periodic table
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
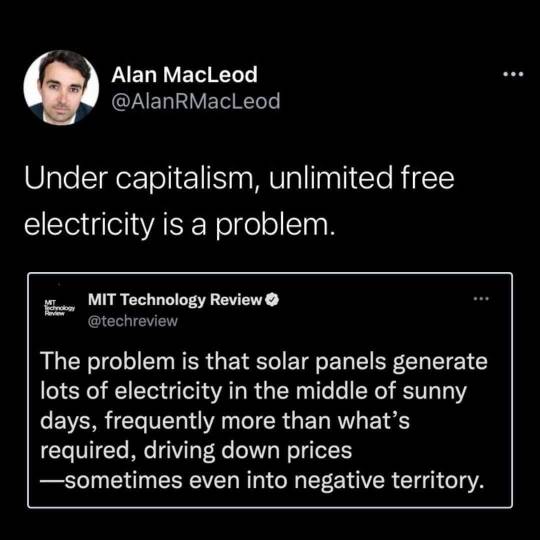
One of the biggest tragedy of the modern power industry is that we have storage alternatives to batteries! They're just too big to put in cars, and you can't sell them to households. They require implementation at the sub-station level, and that's not profitable for existing market dominators. Batteries are being pushed because that's what you can sell to people in cars, or as a house add-on. You can't put a hydrogen-cycle electrochemical fuel cell in a garage.
And currently, we don't have the infrastructure to export hydrogen. We can store it in place just fine - which is what you'd want for a fuel cell like this. But you can't produce and export. When we can do that, you'll see a huge uptick in companies pushing for solar-driven hydrogen manufacturing. Because that's a product they can market.
72K notes
·
View notes
Text
The hydrogen fueling station market is projected to reach $2,251.2 million by 2034 from $268.4 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 23.70% during the forecast period 2024-2034.
#Hydrogen Fueling Station Market#Hydrogen Fueling Station Report#Hydrogen Fueling Station Industry#Advanced Materials and Chemicals#BISResearch
0 notes
Text
Fueling Efficiency: How Technology is Changing the Game with Fuel Consulting
youtube
In an era where efficiency and sustainability are paramount, the way we approach vehicle fueling is undergoing a significant transformation. Fuel Consulting, a forward-thinking business specializing in optimizing fuel management, is at the forefront of this revolution. By leveraging cutting-edge technology, data analytics, and industry expertise, Fuel Consulting is helping businesses and individuals alike to rethink their approach to vehicle fueling, ensuring cost-effectiveness, environmental responsibility, and operational efficiency.
The Evolution of Vehicle Fueling Vehicle fueling has come a long way since the days of simple gas stations and manual pumps. Today, the process is increasingly sophisticated, with advancements in technology enabling smarter, more efficient fueling solutions. From electric vehicle (EV) charging stations to automated fuel management systems, the landscape of vehicle fueling is evolving rapidly. However, with these advancements come new challenges, including the need for strategic planning, regulatory compliance, and sustainability considerations.
This is where Fuel Consulting steps in. By providing expert guidance and innovative solutions, Fuel Consulting helps clients navigate the complexities of modern vehicle fueling, ensuring they stay ahead of the curve.
The Role of Fuel Consulting in Modern Fuel Management Fuel Consulting offers a comprehensive suite of services designed to optimize every aspect of vehicle fueling. Whether you're a fleet manager looking to reduce fuel costs, a business transitioning to electric vehicles, or an individual seeking to minimize your carbon footprint, Fuel Consulting has the expertise to help you achieve your goals.
Fuel Efficiency Optimization One of the primary challenges in vehicle fueling is maximizing fuel efficiency. Fuel Consulting employs advanced data analytics to assess fuel consumption patterns, identify inefficiencies, and recommend targeted solutions. By analyzing factors such as driving behavior, route optimization, and vehicle maintenance, Fuel Consulting helps clients reduce fuel consumption and lower operational costs.
For fleet operators, this can translate into significant savings. By implementing fuel-efficient driving practices and optimizing routes, businesses can reduce fuel expenses while also minimizing wear and tear on their vehicles. Fuel Consulting's tailored solutions ensure that these improvements are sustainable and aligned with the client's specific needs.
Transitioning to Alternative Fuels As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, alternative fuels such as electricity, hydrogen, and biofuels are gaining traction. However, transitioning to these fuels requires careful planning and investment. Fuel Consulting provides expert guidance on the adoption of alternative fuels, helping clients navigate the complexities of infrastructure development, regulatory requirements, and cost analysis.
For businesses considering electric vehicles, Fuel Consulting offers end-to-end support, from assessing the feasibility of EV adoption to designing and implementing charging infrastructure. By taking a holistic approach, Fuel Consulting ensures that clients can make the transition smoothly and cost-effectively.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a business imperative. Fuel Consulting recognizes the importance of reducing the environmental impact of vehicle fueling and offers solutions that align with sustainability goals. By promoting the use of cleaner fuels, optimizing fuel consumption, and supporting the adoption of electric vehicles, Fuel Consulting helps clients reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a greener future.
Moreover, Fuel Consulting assists businesses in complying with environmental regulations and achieving sustainability certifications. This not only enhances their reputation but also positions them as leaders in their industry.
Technology Integration In today's digital age, technology plays a crucial role in optimizing vehicle fueling. Fuel Consulting leverages the latest advancements in fuel management software, IoT (Internet of Things) devices, and telematics to provide clients with real-time insights into their fueling operations. These technologies enable businesses to monitor fuel usage, track vehicle performance, and identify areas for improvement.
For example, telematics systems can provide detailed data on driving behavior, allowing businesses to implement driver training programs that promote fuel-efficient practices. Similarly, IoT-enabled fuel sensors can detect leaks or inefficiencies, enabling prompt corrective action. By integrating these technologies into their operations, clients can achieve greater transparency and control over their fueling processes.
The Future of Vehicle Fueling with Fuel Consulting As the vehicle fueling landscape continues to evolve, Fuel Consulting remains committed to driving innovation and sustainability. The company's forward-thinking approach ensures that clients are well-prepared to meet the challenges and opportunities of the future.
One of the key trends shaping the future of vehicle fueling is the rise of autonomous vehicles. As self-driving cars become more prevalent, the way we fuel and manage vehicles will need to adapt. Fuel Consulting is already exploring how autonomous technology can be integrated into fuel management systems, paving the way for a new era of efficiency and convenience.
Another important trend is the increasing focus on renewable energy sources. Fuel Consulting is at the forefront of this shift, helping clients explore the potential of solar-powered charging stations, hydrogen fuel cells, and other renewable solutions. By staying ahead of these trends, Fuel Consulting ensures that its clients are not only prepared for the future but also leading the way in innovation.
Conclusion Vehicle fueling is no longer just about filling up a tank; it's about optimizing efficiency, embracing sustainability, and leveraging technology to drive better outcomes. Fuel Consulting is playing a pivotal role in this transformation, offering expert guidance and innovative solutions that empower businesses and individuals to take control of their fueling operations.
Whether you're looking to reduce fuel costs, transition to alternative fuels, or minimize your environmental impact, Fuel Consulting has the expertise and tools to help you succeed. As the world continues to evolve, Fuel Consulting remains your trusted partner in navigating the complexities of vehicle fueling, ensuring that you stay ahead of the curve and achieve your goals.
In a world where every drop of fuel counts, Fuel Consulting is leading the charge towards a smarter, greener, and more efficient future.

1 note
·
View note
Text
The worldwide hydrogen fueling stations market is expected to be worth USD 0.5 billion in 2024 and reach USD 1.8 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 23.8%. will also propel the market growth.
0 notes
Text
Portable Power Station Market Trends: Rising Demand, Innovations, and Future Growth Potential in 2025
The portable power station market trends indicate a surge in demand due to the growing need for reliable, off-grid power solutions. With increasing dependence on electronic devices and concerns about power outages, portable power stations are gaining traction among consumers. These compact and rechargeable battery-powered systems offer an eco-friendly alternative to traditional fuel-based generators. As technology advances, manufacturers are focusing on improving battery capacity, charging speed, and sustainability features to cater to a diverse range of applications, from outdoor adventures to emergency backup solutions.

Growing Demand for Off-Grid Power Solutions
With a rising interest in outdoor recreational activities, including camping, hiking, and RV travel, consumers are actively seeking efficient and lightweight power solutions. Portable power stations have become essential for adventurers looking to power devices such as smartphones, laptops, and electric cookers without relying on traditional power sources. Additionally, increasing concerns about natural disasters and grid failures have led to a surge in demand for home backup power solutions. As climate change impacts become more pronounced, the market is expected to see continuous growth in disaster-prone regions.
Technological Advancements Driving Market Expansion
Innovations in battery technology are revolutionizing the portable power station market trends by enhancing efficiency, longevity, and affordability. Lithium-ion and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are now widely used due to their superior energy density, longer lifespan, and improved safety features. Companies are also integrating fast-charging capabilities, wireless charging, and multiple output ports to accommodate a wide range of electronic devices. The adoption of solar-compatible power stations has further strengthened the market, enabling users to harness renewable energy sources for sustainable and continuous power supply.
Increasing Emphasis on Sustainability and Green Energy
The shift toward clean energy solutions is significantly influencing portable power station market trends. As consumers and businesses prioritize eco-friendly alternatives, traditional fuel-based generators are being replaced with battery-powered stations. Governments and environmental organizations are also promoting the use of renewable energy by offering incentives and tax benefits for sustainable power solutions. With solar panels becoming more affordable, many portable power stations now support solar charging, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing carbon footprints.
Competitive Landscape and Market Players
The portable power station market trends reveal intense competition among key industry players striving to enhance product innovation and expand their customer base. Leading brands such as Jackery, EcoFlow, Goal Zero, Bluetti, and Anker are investing in research and development to introduce advanced power stations with higher capacities and faster recharging capabilities. The market is also witnessing increased collaboration between manufacturers and renewable energy companies to enhance efficiency and accessibility. With new entrants emerging, the industry is expected to see a diverse range of products catering to different consumer needs and price points.
Future Market Growth and Investment Opportunities
Looking ahead, portable power station market trends suggest substantial growth opportunities, particularly in regions experiencing frequent power outages and those with limited access to grid electricity. The rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is also expected to drive demand for portable power solutions, as users seek backup charging options. The development of hybrid power stations integrating hydrogen fuel cells, AI-powered energy management, and smart connectivity features will likely shape the market’s future. Investors are increasingly eyeing this sector due to its rapid expansion and potential for high returns, making it a promising space for long-term growth.
Conclusion
The portable power station market trends highlight the increasing adoption of battery-powered solutions for diverse applications, from outdoor recreation to emergency preparedness. With continuous technological advancements, sustainable energy integration, and growing consumer demand, the market is poised for significant expansion in the coming years. As innovation accelerates, portable power stations are expected to become even more efficient, affordable, and accessible, further solidifying their position in the global energy landscape.
0 notes
Text
Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Plants: A Sustainable Energy Solution

Introduction to CHP Plants
Combined Heat and Power (CHP) plants, also known as cogeneration systems, are an efficient way to generate electricity and thermal energy simultaneously. These systems utilize a single fuel source, such as natural gas, biomass, or biogas, to produce both power and heat, significantly reducing energy waste. CHP plants play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency, lowering carbon emissions, and ensuring a stable power supply.
How CHP Plants Work
CHP plants operate by capturing the heat that would otherwise be wasted during electricity generation. The process typically involves the following steps:
Fuel Combustion: A fuel source is burned in a prime mover, such as a gas turbine, steam turbine, or reciprocating engine.
Electricity Generation: The mechanical energy produced is converted into electricity.
Heat Recovery: Instead of being lost, the heat generated is captured and used for heating applications, such as space heating, industrial processes, or water heating.
Utilization: The recovered heat is then distributed for various applications, improving overall efficiency.
Benefits of CHP Plants
Enhanced Energy Efficiency: CHP systems can achieve efficiency levels of up to 80%, compared to conventional power plants that typically operate at around 35-45% efficiency.
Cost Savings: By utilizing waste heat, CHP reduces fuel consumption, leading to lower energy costs for businesses and industries.
Lower Carbon Emissions: Since CHP plants use fuel more efficiently, they help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, supporting global sustainability goals.
Energy Security and Reliability: These systems provide a decentralized energy source, reducing dependence on the grid and enhancing energy resilience.
Versatility: CHP plants can be used across various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, commercial buildings, and district heating.
Types of CHP Systems
Gas Turbine CHP: Suitable for large-scale applications, such as industrial plants and district heating networks.
Steam Turbine CHP: Often used in power stations and large manufacturing facilities where steam is a byproduct.
Reciprocating Engine CHP: Ideal for small to medium-sized applications, including hospitals and commercial buildings.
Fuel Cell CHP: An emerging technology that provides high efficiency with low emissions, primarily used in niche applications.
Applications of CHP Plants
Industrial Facilities: Many industries, such as chemical production and food processing, use CHP for both power and process heat.
Hospitals and Healthcare Centers: CHP provides a reliable power source, ensuring uninterrupted operations in critical environments.
Universities and Research Centers: Institutions benefit from cost savings and sustainability advantages.
Commercial Buildings: Hotels, shopping centers, and office complexes utilize CHP for heating and cooling needs.
Future of CHP Technology
As energy demands grow and environmental concerns increase, the role of CHP plants is becoming more prominent. The integration of renewable fuels, such as biogas and hydrogen, will further enhance CHP’s sustainability. Government incentives and policies supporting energy efficiency will likely drive wider adoption of CHP systems globally.
Conclusion
CHP plants offer an efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solution for meeting energy needs. By optimizing fuel use and reducing emissions, they contribute significantly to global energy sustainability. As technology advances, CHP systems will continue to evolve, providing even greater benefits for industries and communities worldwide.
#biogas generator#biogas plant#biogas power generation#chp combined heat and power#chp plant#cogeneration#combined heat and power#Biogas Treatment Solutions
0 notes