#Health and Medicine
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
love how doctors' new-patient questionnaires STILL ask "do you have sex with men, women, or both" as if the answer to that question actually tells them what they want to know. it wouldnt be that suprising if it was just the trans exclusionism, but do they not realize by this point that:
cishets have anal sex too
cishets have sex where the man is anally penetrated
cishets have nonpenetrative sex all the time
I feel the solution to this would be pretty simple. just give patients a checklist for what kinds of sex they have and include stuff like "penetrative anal (giving), penetrative anal (receiving), oral anal (giving), etc etc etc." Not only would this be more gender inclusive but it would ACTUALLY TELL the doctor what they need to know
just remove gender from the question entirely, otherwise you are quite literally making assumptions about the patient's sexual behavior that could affect their health and how your treat them
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Explainer: Why it’s still a good idea to avoid COVID (and how to do it)
The best way of reducing your risk of developing long-term health issues from COVID is by taking a few simple steps to prevent getting COVID in the first place. Staying up to date with the latest COVID vaccine reduces your risk of serious illness, infection, and Long COVID. Wearing a mask helps boost your own protection, protects others around you, and works against any COVID variant or other type of airborne virus. Another effective way to reduce your risk of getting sick from airborne viruses is to improve indoor air quality.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
John Bradmore appears as one of a group of practitioners called in by the Infirmarer of Westminster Abbey in 1390–91, the others being John Middleton, William Wadesworth and another William (whose surname is cut off at the edge of the folio). John Middleton was a royal physician, and William Wadesworth an apothecary. This prior association with Middleton and Wadesworth makes Bradmore a strong contender to be the ‘Master JB’ who, with John Middleton, William Waddisworthe and others, prescribed and supplied medicines for Anne of Bohemia, queen to Richard II of England, in 1393–94.
S. J. Lang, "John Bradmore and the Case of the Bitten Man: A Tantalising Link Between Three Medieval Surgical Manuscripts", Social History of Medicine, Vol. 34, No. 3, 2021
#john bradmore#william wadesworth#john middleton#anne of bohemia#health and medicine#historian: s. j. lang
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

#health and medicine#current events#there was also a tweet in there about nude-colored ones being received better than white as well but i can't find it now#i didn't even know they made those! seems like it should have been obvious though#i'll have to pick some up
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

saving this to my phone (text equivalent at this link)
if you are dealing with extreme heat or even just. moderate heat in your area right now. 80f/26c is when it starts getting toasty for a lot of people. if you are in a heat wave and you have not done yourself the favor of googling fucking "heat exhaustion symptoms" i am shaking you violently right now. look it up. burn the symptoms into your brain. heatstroke is no joke and it can and WILL sneak up on you before you're aware it's even an issue. ohh my god
45K notes
·
View notes
Text



Source
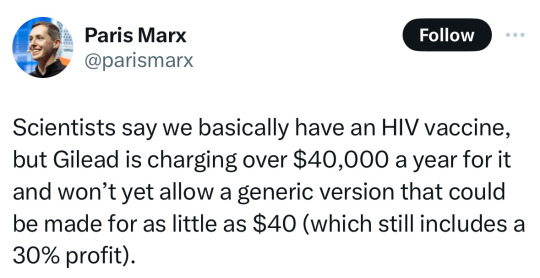
#politics#hiv#us politics#government#gilead#lgbt#lgbtq#progressive#current events#science#medicine#health#health care#the left#twitter post#news
37K notes
·
View notes
Text
When I was in vet school I went to this one lecture that I will never forget. Various clubs would have different guest lecturers come in to talk about relevant topics and since I was in the Wildlife Disease Association club I naturally attended all the wildlife and conservation discussions. Well on this particular occasion, the speakers started off telling us they had been working on a project involving the conservation of lemurs in Madagascar. Lemurs exist only in Madagascar, and they are in real trouble; they’re considered the most endangered group of mammals on Earth. This team of veterinarians was initially assembled to address threats to lemur health and work on conservation solutions to try and save as many lemur species from extinction as possible. As they explored the most present dangers to lemurs they found that although habitat loss was the primary problem for these vulnerable animals, predation by humans was a significant cause of losses as well. The vets realized it was crucial for the hunting of lemurs by native people to stop, but of course this is not so simple a problem.
The local Malagasy people are dealing with extreme poverty and food insecurity, with nearly half of children under five years old suffering from chronic malnutrition. The local people have always subsisted on hunting wildlife for food, and as Madagascar’s wildlife population declines, the people who rely on so-called bushmeat to survive are struggling more and more. People are literally starving.
Our conservation team thought about this a lot. They had initially intended to focus efforts on education but came to understand that this is not an issue arising from a lack of knowledge. For these people it is a question of survival. It doesn’t matter how many times a foreigner tells you not to eat an animal you’ve hunted your entire life, if your child is starving you are going to do everything in your power to keep your family alive.
So the vets changed course. Rather than focus efforts on simply teaching people about lemurs, they decided to try and use veterinary medicine to reduce the underlying issue of food insecurity. They supposed that if a reliable protein source could be introduced for the people who needed it, the dependence on meat from wildlife would greatly decrease. So they got to work establishing new flocks of chickens in the most at-risk communities, and also initiated an aggressive vaccination program for Newcastle disease (an infectious illness of poultry that is of particular concern in this area). They worked with over 600 households to ensure appropriate husbandry and vaccination for every flock, and soon found these communities were being transformed by the introduction of a steady protein source. Families with a healthy flock of chickens were far less likely to hunt wild animals like lemurs, and fewer kids went hungry. Thats what we call a win-win situation.
This chicken vaccine program became just one small part of an amazing conservation outreach initiative in Madagascar that puts local people at the center of everything they do. Helping these vulnerable communities of people helps similarly vulnerable wildlife, always. If we go into a country guns-blazing with that fire for conservation in our hearts and a plan to save native animals, we simply cannot ignore the humans who live around them. Doing so is counterintuitive to creating an effective plan because whether we recognize it or not, humans and animals are inextricably linked in many ways. A true conservation success story is one that doesn’t leave needy humans in its wake, and that is why I think this particular story has stuck with me for so long.
(Source 1)
(Source 2- cool video exploring this initiative from some folks involved)
(Source 3)
#we can save the world just maybe not in the way we’d planned#long post#scicomm#conservation#lemurs#wildlife#ecology#animals#vet med#veterinary medicine#One Health
33K notes
·
View notes
Text
The foundation of Ayurveda is the idea that physical, mental, and environmental balance is necessary for good health. The three main doshas—Pitta, Kapha, and Vata—are biological energies present in the human body and psyche. These doshas are balanced differently in every individual, and imbalances can cause problems with one’s physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
#ayurveda#ayurveda treatment#mental health problems#mental health treatment#counselling services calicut#psychologist in kerala#ayurvedicmedicine#health and medicine#counselling centre in trivandrum
0 notes
Text
The COVID-safe strategies Australian scientists are using to protect themselves from the virus
Four years into the COVID-19 pandemic we're living in a "public health Barbieland", says Professor Brendan Crabb, director and chief executive of the Burnet Institute. Too many of us are playing "make-believe" that life has returned to "normal", he says, and there's an "enormous disconnect" in the community: a failure to grasp both the true scale of COVID circulating and the impact of infections on our health and longevity.
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is Antibiotic Resistance and Why Is It Important?

Antibiotic resistance is also known as antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and represents one of the biggest threats to public health and development in the world. Bacterial AMR was responsible for an estimated 1.27 million deaths globally in 2019 and contributed to a further 4.95 million deaths.
The main drivers behind the development of drug-resistant pathogens are the overuse and misuse of antimicrobials in plants, animals, and humans.
What Are Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria?
Antimicrobial resistant bacteria are bacteria that aren’t killed or controlled by antibiotics. They can both survive and multiply even when an antibiotic is present. While many types of bacteria that cause infections can gain resistance to some antibiotics, bacteria that’s resistant to many antibiotics are termed multi-resistant organisms (MROs). Furthermore, some types of bacteria have a natural resistance to antibiotics; for example, benzylpenicillin has little effect on most bacteria present in the human gut.

The Devastating Effects of AMR
AMR is responsible for a huge global death toll, and one that is likely to increase unless action is taken. While inequality and poverty exacerbate its consequences and effects, AMR impacts all countries, although middle and low-income nations are most affected. As well as making it harder to treat infections, it makes undertaking many other treatments significantly riskier.
As well as the devastation of disability and death, AMR comes with a huge economic cost, with the World Bank estimating that it could result in around $1 trillion to $3.4 trillion worth of GDP losses per year by 2030 and $1 trillion in additional healthcare costs by 2050.
youtube
How Can the AMR Challenge be Tackled?
Those with experience in this field – such as Alec Simonson, who was involved in bioinformatics and neuropharmacological research during his studies – know that one of the most important ways to prevent AMR is to use antibiotics properly. This means reducing the overprescribing of antibiotics and preventing unnecessary use. It’s also important that patients complete the entire course of any antibiotics they are prescribed so the medication will be fully effective and not promote resistance. Good hygiene (such as handwashing) and the deployment of appropriate infection control procedures will also play a key role in tackling AMR.
The Global Action Plan (GAP) on AMR was adopted by countries during the 2015 World Health Assembly. Adoptees committed to developing and implementing multisectoral national action plans to tackle AMR, using a One Health approach.
For information about World AMR Awareness Week, take a look at the embedded PDF.

#Alec Simonson#AMR#Antibiotic Resistance#world health organization#who#healthcare#health and medicine#bacteria#effects of amr#Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
Each Covid infection increases the risk of developing chronic health issues like diabetes — including in children — organ failure, stroke, heart conditions, kidney disease, and mental health problems. These are just the problems we know about. We know from other viruses, like polio, that some of the consequences can take years to appear. Post-polio syndrome, which is thought to stem from a deterioration of nerve cells, can take as long as 40 years to show up. Additionally, there’s the risk of long Covid or clusters of health issues that can last months or even years after initial infection. These range from exhaustion so severe that people with the condition find it difficult to work or socialize to heart palpitations, difficulty thinking and retaining information to severe anaphylactic reactions in the absence of an allergic trigger.
"And, of course, if one gets Covid and develops long Covid, they might become disabled and thus disposable under the same narrative that helped sicken them in the first place."
152 notes
·
View notes
Text
Still not over the head of cardiology, who said she wouldn't formally diagnose me with dysautonomia because she didn't want me to think of myself as disabled.
As if good vibes and a can-do attitude can stabalize autonomic dysfunction.
#chronic health tag#ableism in our medical system???#it's more likely than you think#I still remember having to inform the ER doctor that the reason MCAS wasn't in my file#was because the head of allergy for the hospital he worked at#'didn't believe in it'#this was one week into the pandemic#and this man touched his face out of exasperation#and muttered something that might have been 'dense mother fucker' under his breathe#anyway#there should be a screening process for people who want to go into medicine#if you think the only disability is a bad attitude#you should be jettisoned from your course and directly into the sun
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
A new treatment combining ReCET and semaglutide could eliminate the need for insulin in type 2 diabetes, with 86% of participants in a study no longer requiring insulin therapy. The treatment was safe and well-tolerated, and further trials are planned to confirm these results.
Groundbreaking research presented at UEG Week 2024 introduces a promising new treatment approach for type 2 diabetes (T2D) that has the potential to greatly reduce or even eliminate the need for insulin therapy.
This innovative approach, which combines a novel procedure known as ReCET (Re-Cellularization via Electroporation Therapy) with semaglutide, resulted in the elimination of insulin therapy for 86% of patients.
Globally, T2D affects 422 million people... While insulin therapy is commonly used to manage blood sugar levels in T2D patients, it can result in side effects... and further complicate diabetes management. [Note: Also very importantly it's fucking bankrupting people who need it!!] A need therefore exists for alternative treatment strategies.
Study Design and Outcomes
The first-in-human study included 14 participants aged 28 to 75 years, with body mass indices ranging from 24 to 40 kg/m². Each participant underwent the ReCET procedure under deep sedation, a treatment intended to improve the body’s sensitivity to its own insulin. Following the procedure, participants adhered to a two-week isocaloric liquid diet, after which semaglutide was gradually titrated up to 1mg/week.
Remarkably, at the 6- and 12-month follow-up, 86% of participants (12 out of 14) no longer required insulin therapy, and this success continued through the 24-month follow-up. In these cases, all patients maintained glycaemic control, with HbA1c levels remaining below 7.5%.
Tolerability and Safety
The maximum dose of semaglutide was well-tolerated by 93% of participants, one individual could not increase to the maximum dose due to nausea. All patients successfully completed the ReCET procedure, and no serious adverse effects were reported.
Dr Celine Busch, lead author of the study, commented, “These findings are very encouraging, suggesting that ReCET is a safe and feasible procedure that, when combined with semaglutide, can effectively eliminate the need for insulin therapy.”
“Unlike drug therapy, which requires daily medication adherence, ReCET is compliance-free [meaning: you don't have to take it every day], addressing the critical issue of ongoing patient adherence in the management of T2D. In addition, the treatment is disease-modifying: it improves the patient’s sensitivity to their own (endogenous) insulin, tackling the root cause of the disease, as opposed to currently available drug therapies, that are at best disease-controlling.”
Looking ahead, the researchers plan to conduct larger randomized controlled trials to further validate these findings. Dr. Busch added, “We are currently conducting the EMINENT-2 trial with the same inclusion and exclusion criteria and administration of semaglutide, but with either a sham procedure or ReCET. This study will also include mechanistic assessments to evaluate the underlying mechanism of ReCET.”
-via SciTechDaily, October 17, 2024
--
Note: If it works even half as well as suggested, this could free so many people from the burden of the ongoing ridiculous cost of insulin. Pharma companies that make insulin can go choke (hopefully).
#would be super interested to hear from people with expertise in the area about how this sounds#obviously it's a small sample size#but they're going to do more trials#and LOOK at that effectiveness rate#insulin#diabetes#healthcare#medicine#diabetic#type 2 diabetes#public health#medical news#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
bad news, it’s not just Mars:
https://www.consumerreports.org/health/food-safety/lead-and-cadmium-in-dark-chocolate-a8480295550/

126K notes
·
View notes
Text
This is asking about all the childhood vaccines– chicken pox, polio, HPV, etc. You can check the (current) recommended vaccine schedules in the US here if you're not sure.
If you received the vaccines that were available at the time but have not received others that were developed later, vote "yes."
–
We ask your questions so you don’t have to! Submit your questions to have them posted anonymously as polls.
#polls#incognito polls#anonymous#tumblr polls#tumblr users#questions#polls about health#submitted june 21#medicine#vaccines#doctors#childhood#vaccination
1K notes
·
View notes