#Health APIs
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#no clue any context lol just had 1 min and was doin tiny dancer#im very amused i asked if i know them no response i find this hilarious . hello#looked on skycrypt baffled . they have 120 health and api off lol#IM JUST SO LOST WHO ARE YOU WAS THAT WORTH IT?? WHO ARE YOU??? i find it incredibly funny that some random person decided theyare full of#hate and mildly inconvenienced me in such a silly way . hi? hello?#<- submission tags#99% of people you meet with a black plus do not deserve human rights lmao#also i cant even load their skycrypt profiles what is up with them 😭#die mad i guess idk man. it's block game
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Agentic AI: How Large Language Models Are Shaping the Future of Autonomous Agents
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/agentic-ai-how-large-language-models-are-shaping-the-future-of-autonomous-agents/
Agentic AI: How Large Language Models Are Shaping the Future of Autonomous Agents
After the rise of generative AI, artificial intelligence is on the brink of another significant transformation with the advent of agentic AI. This change is driven by the evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) into active, decision-making entities. These models are no longer limited to generating human-like text; they are gaining the ability to reason, plan, tool-using, and autonomously execute complex tasks. This evolution brings a new era of AI technology, redefining how we interact with and utilize AI across various industries. In this article, we will explore how LLMs are shaping the future of autonomous agents and the possibilities that lie ahead.
The Rise of Agentic AI: What Is It?
Agentic AI refers to systems or agents that can independently perform tasks, make decisions, and adapt to changing situations. These agents possess a level of agency, meaning they can act independently based on goals, instructions, or feedback, all without constant human guidance.
Unlike conventional AI systems limited to fixed tasks, agentic AI is dynamic. It learns from interactions and improves its behavior over time. A essential feature of agentic AI is its ability to break down tasks into smaller steps, analyze different solutions, and make decisions based on various factors.
For instance, an AI agent planning a vacation could assess the weather, budget, and user preferences to recommend the best tour options. It can consult external tools, adjust suggestions based on feedback, and refine its recommendations over time. Applications for agentic AI span from virtual assistants managing complex tasks to industrial robots adapting to new production conditions.
The Evolution from Language Models to Agents
Traditional LLMs are powerful tools for processing and generating text, but they primarily function as advanced pattern recognition systems. Recent advancements have transformed these models, equipping them with capabilities that extend beyond simple text generation. They now excel in advanced reasoning and practical tool usage.
These models can formulate and execute multi-step plans, learn from past experiences, and make context-driven decisions while interacting with external tools and APIs. With the addition of long-term memory, they can retain context over extended periods, making their responses more adaptive and meaningful.
Together, these abilities have opened new possibilities in task automation, decision-making, and personalized user interactions, triggering a new era of autonomous agents.
The Role of LLMs in Agentic AI
Agentic AI relies on several core components facilitating interaction, autonomy, decision-making, and adaptability. This section explores how LLMs are driving the next generation of autonomous agents.
LLMs for Understanding Complex Instructions
For agentic AI, the ability to understand complex instructions is crucial. Traditional AI systems often require precise commands and structured inputs, limiting user interaction. LLMs, however, allow users to communicate in natural language. For example, a user can say, “Book a flight to New York and arrange accommodation near Central Park.” LLMs grasp this request by interpreting location, preferences, and logistics nuances. The AI can then carry out each task—from booking flights to selecting hotels and arranging tickets—while requiring minimal human oversight.
LLMs as Planning and Reasoning Frameworks
A key feature of agentic AI is its ability to break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps. This systematic approach is vital for solving more significant problems effectively. LLMs have developed planning and reasoning capabilities that empower agents to perform multi-step tasks, much like we do when solving math problems. Think of these capabilities as the “thinking process” of AI agents.
Techniques such as chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning have emerged to help LLMs achieve these tasks. For example, consider an AI agent assisting a family save money on groceries. CoT allows LLMs to approach this task sequentially, following these steps:
Assess the family’s current grocery spending.
Identify frequent purchases.
Research sales and discounts.
Explore alternative stores.
Suggest meal planning.
Evaluate bulk purchasing options.
This structured method enables the AI to process information systematically, like how a financial advisor would manage a budget. Such adaptability makes agentic AI suitable for various applications, from personal finance to project management. Beyond sequential planning, more sophisticated approaches further enhance LLMs’ reasoning and planning abilities, allowing them to tackle even more complex scenarios.
LLMs for Enhancing Tool Interaction
A significant advancement in agentic AI is the ability of LLMs to interact with external tools and APIs. This capability enables AI agents to perform tasks such as executing code and interpreting results, interacting with databases, interfacing with web services, and managing digital workflows. By incorporating these capabilities, LLMs have evolved from being passive processors of language to becoming active agents in practical, real-world applications.
Imagine an AI agent that can query databases, execute code, or manage inventory by interfacing with company systems. In a retail setting, this agent could autonomously automate order processing, analyze product demand, and adjust restocking schedules. This kind of integration expands the functionality of agentic AI, enabling LLMs to interact with the physical and digital world seamlessly.
LLMs for Memory and Context Management
Effective memory management is vital for agentic AI. It allows LLMs to retain and reference information during long-term interactions. Without memory, AI agents struggle with continuous tasks. They find it hard to maintain coherent dialogues and execute multi-step actions reliably.
To address this challenge, LLMs use different types of memory systems. Episodic memory helps agents recall specific past interactions, aiding in context retention. Semantic memory stores general knowledge, enhancing the AI’s reasoning and application of learned information across various tasks. Working memory allows LLMs to focus on current tasks, ensuring they can handle multi-step processes without losing sight of their overall goal.
These memory capabilities enable agentic AI to manage tasks that require ongoing context. They can adapt to user preferences and refine outputs based on past interactions. For instance, an AI health coach can track a user’s fitness progress and provide evolving recommendations based on recent workout data.
How Advancements in LLMs Will Empower Autonomous Agents
As LLMs continue to advance with interaction, reasoning, planning, and tool usage, agentic AI will become increasingly capable of autonomously handling complex tasks, adapting to dynamic environments, and collaborating effectively with humans across various domains. Some of the ways AI agents will prosper with the advancing abilities of LLMs are:
Expanding into Multimodal Interaction
With the growing multimodal capabilities of LLMs, agentic AI will engage with more than just text in the future. LLMs can now incorporate data from various sources, including images, videos, audio, and sensory inputs. This allows agents to interact more naturally with different environments. As a result, AI agents will be able to navigate complex scenarios, such as managing autonomous vehicles or responding to dynamic situations in healthcare.
Improved Reasoning Capabilities
As LLMs enhance their reasoning abilities, agentic AI will thrive in making informed choices in uncertain, data-rich environments. It will evaluate multiple factors and manage ambiguities effectively. This capability is essential in finance and diagnostics, where complex, data-driven decisions are critical. As LLMs grow more sophisticated, their reasoning skills will foster contextually aware and thoughtful decision-making across various applications.
Specialized Agentic AI for Industry
As LLMs progress with data processing and tool usage, we will see specialized agents designed for specific industries, including finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics. These agents will handle complex tasks such as managing financial portfolios, monitoring patients in real-time, adjusting manufacturing processes precisely, and predicting supply chain needs. Each industry will benefit from agentic AI’s ability to analyze data, make informed decisions, and adapt to new information autonomously.
Multi-agent Systems
The progress of LLMs will significantly enhance multi-agent systems in agentic AI. These systems will comprise specialized agents collaborating to tackle complex tasks effectively. With LLMs’ advanced capabilities, each agent can focus on specific aspects while sharing insights seamlessly. This teamwork will lead to more efficient and accurate problem-solving as agents simultaneously manage different parts of a task. For example, one agent might monitor vital signs in healthcare while another analyzes medical records. This synergy will create a cohesive and responsive patient care system, ultimately improving outcomes and efficiency in various domains.
The Bottom Line
Large Language Models rapidly evolve from simple text processors to sophisticated agentic systems capable of autonomous action. The future of Agentic AI, powered by LLMs, holds tremendous potential to reshape industries, enhance human productivity, and introduce new efficiencies in daily life. As these systems mature, they promise a world where AI is not just a tool but a collaborative partner, helping us navigate complexities with a new level of autonomy and intelligence.
#agent#Agentic AI#agents#ai#ai agent#AI AGENTS#AI Health Coach#AI systems#APIs#applications#approach#Article#artificial#Artificial General Intelligence#Artificial Intelligence#audio#automation#autonomous#autonomous agents#autonomous ai#autonomous vehicles#Behavior#book#challenge#change#code#collaborative#continuous#data#data processing
0 notes
Text
Global Healthcare API Market is expected to Reach a Market value of USD 343.8 million by 2033 at a CAGR of 3.7%.
The Global Healthcare API Market: A Comprehensive Analysis
Market Overview
The Global Healthcare API Market is on a trajectory of significant growth, expected to reach a value of USD 247.1 million by the end of 2024. Furthermore, projections indicate that the market will surge to USD 343.8 million by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% during the forecast period. This growth is indicative of the increasing reliance on digital solutions within the healthcare industry, where efficient data exchange and integration are paramount.
Healthcare API Market Growth Analysis
The emergence of Healthcare APIs has revolutionized the manner in which patient data is exchanged among healthcare providers. These APIs facilitate seamless access to vital patient information, enabling healthcare professionals to update and manage medical records swiftly. Before the advent of Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, interoperability was a cumbersome process reliant on phone calls and fax machines. However, the proliferation of multiple EHR systems has often resulted in fragmented patient data. Advanced healthcare APIs are essential for enhancing care coordination and ensuring that comprehensive patient records are maintained, especially vital in the context of value-based care models.
Key Takeaways
Get a Free PDF Sample Copy of this Report@ https://dimensionmarketresearch.com/report/healthcare-api-market/request-sample
Use Cases
Market Dynamics
The growth of the healthcare API market is driven by continuous technological advancements, increased demand for healthcare integration, and an uptick in activities from EHR vendors and healthcare IT startups. The use of APIs in conjunction with EHR systems supports streamlined access to health data, resulting in reduced costs, improved medication supply chain management, and enhanced accessibility to medical test data, thereby elevating the overall efficiency of healthcare administration.
However, several challenges pose restraints to market expansion. A notable shortage of skilled professionals, alongside concerns over data security, presents significant hurdles. Inadequate IT infrastructure, lack of essential API tools, and poor network connectivity further impede growth. Particularly in emerging economies, underdeveloped public IT infrastructure remains a barrier to market development.
Research Scope and Analysis
By Deployment Mode
The healthcare API market can be segmented based on deployment mode into cloud-based APIs and on-premise APIs. In 2024, cloud-based APIs are expected to dominate market share due to the availability of storage solutions for organizing patient and hospital data, facilitating easy access during critical situations.
Conversely, on-premise healthcare APIs are projected to retain a substantial revenue share, primarily due to their advantages in data privacy and security, ensuring a lower risk of data breaches. Organizations benefit from retaining complete control over their healthcare software, coupled with easy software installation and the potential for future data reprocessing.
By Service
The services within the healthcare API market include EHR access, appointments, payment, remote patient monitoring, and wearable medical devices. Among these, EHR access is predicted to lead the market in 2024. APIs enable smooth integration of EHR data with other platforms, enhancing data exchange with third parties. EHR vendors are increasingly incorporating APIs into their systems to support value-based patient care, driving widespread adoption.
The remote patient monitoring segment is anticipated to experience rapid growth, primarily spurred by the heightened interest during the COVID-19 pandemic. As healthcare providers focus on minimizing contamination risks, they are adopting connected health solutions, often utilizing API-enabled patient engagement platforms that personalize treatment options based on historical medical records.
By End Use
The healthcare providers segment is expected to emerge as the top revenue contributor in 2024. This segment includes clinics, hospitals, and other distribution firms that utilize APIs to securely store critical medical records and patient information, ensuring accessibility during emergencies. Additionally, the healthcare payers segment is projected to see significant growth during the analysis period.
Healthcare API Market End User Analysis
Integrated APIs facilitate swift access to essential data for healthcare payers and providers through customized processes. By streamlining follow-up appointments and patient invoicing, APIs enhance operational efficiency within the healthcare ecosystem, allowing for secure management of patient health information and billing details without excessive administrative burdens.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America is anticipated to lead the healthcare API market, capturing a substantial revenue share of approximately 37.6% in 2024. Factors such as supportive policies for healthcare API deployment and high digital literacy rates significantly contribute to this dominance. The region boasts advanced healthcare infrastructure, which includes integrated EHR systems, and the growing adoption of healthcare APIs by major organizations further propels demand.
Europe
Europe is projected to experience substantial growth during the forecast period, driven by a robust healthcare infrastructure and the advent of transformative technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT). This evolution is likely to facilitate the rapid adoption and integration of healthcare APIs, paving the way for enhanced connectivity and efficiency within the healthcare landscape.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a promising market for healthcare APIs. With increasing investments in healthcare IT and a growing emphasis on digital transformation, countries like China, India, and Japan are witnessing significant adoption of API solutions to enhance healthcare services.
Latin America and Middle East & Africa
In Latin America, the healthcare API market is expected to grow steadily, supported by rising healthcare expenditures and the need for efficient data management solutions. Meanwhile, the Middle East and Africa are gradually adopting healthcare APIs, driven by government initiatives aimed at improving healthcare access and quality.
Competitive Landscape
The Global Healthcare API Market features intense competition among established technology giants and emerging players. Key market participants are focused on delivering comprehensive API solutions that facilitate seamless integration and advanced functionalities, while newer entrants strive to provide specialized services tailored to the unique needs of the healthcare sector. This competitive environment fosters innovation and efficiency as companies vie for market share and aim to meet the evolving demands of healthcare providers and patients globally.
Prominent Players in the Market
Recent Developments
Recent advancements in the healthcare API sector indicate a dynamic and evolving landscape:
FAQs
1. What is the projected growth rate of the Global Healthcare API Market?
The Global Healthcare API Market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 3.7%, reaching a value of USD 343.8 million by 2033.
2. Which segment is expected to dominate the market in terms of deployment mode?
The cloud-based API segment is expected to lead in 2024 and maintain its dominance throughout the forecast period.
3. What are some of the key use cases for Healthcare APIs?
Key use cases include patient data access, appointment scheduling, telemedicine consultations, and health monitoring and alerts.
4. Which region is predicted to hold the largest market share in the Global Healthcare API Market?
North America is expected to command a significant market share of 37.6% in 2024.
5. What are the main challenges facing the Global Healthcare API Market?
Challenges include a shortage of skilled professionals, data security concerns, inadequate IT infrastructure, and underdeveloped public IT systems in emerging economies.
Conclusion
The Global Healthcare API Market is poised for notable growth, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for efficient data integration within the healthcare sector. With significant contributions from healthcare providers, favorable market conditions in North America, and an expanding base of innovative players, the future looks promising. However, addressing challenges such as data security and the shortage of skilled professionals will be critical to unlocking the full potential
#Healthcare API#Health Tech#Digital Health#EHR#Interoperability#Patient Care#Data Integration#Healthcare Innovation#APIs#Cloud Technology#Telemedicine#Remote Monitoring#Health Data
0 notes
Text

Improve the efficiency of your healthcare communication with the WhatsApp Business API. Perfect for clinics, hospitals, and healthcare providers who want to offer better patient support and streamline operations. Inquire today to transform your patient communication.
Learn more : https://www.go4whatsup.com/industries/healthcare/
Get in touch - Enquire Now - IND +91-9667584436 / UAE +971545085552 Email - [email protected]
#whatsapp business api#whatsapp api#whatsapp marketing#marketing automation tools#whatsapp marketing guide#whatsapp api provider#whatsapp chatbot#whatsapp chatbots#bulk whatsapp messaging#whatsapp crm#health#healthcare industry
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Secret to Superior Supplements: The Role of Dicalcium Phosphate
Enhancing Bioavailability: How Dicalcium Phosphate Boosts Absorption
According to the Dicalcium Phosphate Granules Suppliers, it is a key player in nutritional supplements due to its role in improving bioavailability. This mineral compound acts as a carrier that aids in the dissolution of vitamins and minerals within the digestive system, enhancing their absorption into the bloodstream. Its unique properties ensure that nutrients are more effectively utilized by the body, making supplements more potent. By facilitating better nutrient uptake, it ensures that each dose delivers maximum benefit, transforming ordinary supplements into powerful sources of essential nutrients.
Stability and Consistency: The Advantage of This Mineral Compound
A major benefit of Dicalcium Phosphate is its contribution to stability and consistency in supplements. As an excipient, it helps preserve the integrity of the formula over time, preventing degradation and ensuring even distribution of active ingredients. This stability is essential for maintaining supplement potency and delivering reliable health benefits with each use. Incorporating this compound allows manufacturers to create high-quality products that remain effective throughout their shelf life, providing dependable nutritional support. Dicalcium Phosphate Granules for Sale.
Formulation Flexibility: Transforming Supplement Design
This mineral compound offers exceptional flexibility in supplement formulation, enabling the creation of a wide range of products. Its compatibility with various active ingredients supports the development of tablets, capsules, and powders. This versatility not only expands the options available to consumers but also allows for the inclusion of multiple nutrients in a single product. By leveraging its properties, manufacturers can design innovative formulations that address specific health needs and preferences, delivering tailored solutions for optimal nutrition. Dicalcium Phosphate Granules Wholesale Price.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Creating Interactive Digital Walkthroughs with Live Video Technology
In the contemporary digital landscape, live video services have become an indispensable tool for businesses, educators, entertainers, and developers alike. The evolution of technology has driven a surge in demand for real-time communication and interaction, fostering an environment where live video streaming has become a cornerstone of effective engagement.
This article explores the significance of live video services, particularly in the context of app development using Flutter, and delves into the various components that make these services crucial for successful live streaming.

The Rise of Live Video Streaming
Live video streaming has transformed the way content is consumed and delivered. Unlike pre-recorded videos, live streaming offers immediacy and interactivity, creating a sense of urgency and engagement that static content cannot match. This immediacy is particularly valuable in various scenarios, such as live events, online education, remote work, and real-time customer support.
Video Streaming in Flutter
Flutter, an open-source UI software development kit by Google, has gained immense popularity among developers for its ability to create natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. When it comes to video streaming in Flutter, the framework provides robust support through plugins and packages that simplify the integration of live video services. Utilizing Flutter for video streaming not only enhances the development process but also ensures a seamless and high-performance user experience.
The Importance of Real-Time Communication
Real-time communication is at the heart of live streaming, and it is this capability that distinguishes live video from other forms of media. The ability to interact in real-time is crucial for applications such as video call apps, video chat apps, and screen sharing functionalities.
Video Call App Flutter
Developing a video call app in Flutter allows developers to leverage the framework's strengths to create responsive and reliable communication tools. The integration of real-time communication features in Flutter apps is facilitated by a range of video call APIs and SDKs, which offer customizable and scalable solutions for various use cases.
Key Components of Live Video Services
To understand why live video services are crucial, it is essential to examine the key components that make up these services. These components include video call APIs, SDKs, and the overall infrastructure that supports real-time video streaming.
Video Call API
A video call API provides the necessary tools and protocols to implement video calling features in an application. APIs are designed to be developer-friendly, offering comprehensive documentation and support to streamline the integration process. When selecting a video call API, developers consider factors such as ease of use, compatibility with existing systems, and pricing.
Video Call SDK
A video call SDK (Software Development Kit) offers a more comprehensive solution by providing a set of tools, libraries, and documentation needed to build video calling features. SDKs are particularly valuable for developers looking to create robust and feature-rich video call applications without delving into the complexities of real-time communication protocols.
Video Call SDK Android
For Android developers, a video call SDK tailored for the platform simplifies the development process by providing native components and functionalities. This ensures optimal performance and integration with Android's ecosystem.
Video Call SDK Open Source
Open-source video call SDKs offer flexibility and transparency, allowing developers to customize and optimize their applications according to specific requirements. The open-source nature fosters community collaboration and continuous improvement, making these SDKs a popular choice among developers.
Benefits of Live Video Services
The integration of live video services into applications brings numerous benefits, enhancing both user experience and business outcomes.
Enhanced Engagement
Live video services foster real-time interaction, which significantly enhances user engagement. Whether it's a live stream of a product launch, a virtual classroom, or a customer support session, the ability to communicate and respond instantly creates a more dynamic and engaging experience.
Improved Collaboration
In the context of remote work and online collaboration, live video services play a pivotal role. Features like video chat and screen sharing in Flutter applications facilitate seamless communication and collaboration, bridging the gap between remote teams and enabling productive interactions.
Scalability and Flexibility
Modern video call APIs and SDKs are designed to be scalable, accommodating a growing number of users and varying levels of demand. This scalability ensures that applications can handle peak usage times without compromising performance. Additionally, the flexibility of these tools allows developers to tailor their solutions to meet specific needs, whether it's a small-scale video chat app or a large-scale streaming platform.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Utilizing video call APIs and SDKs can be a cost-effective approach to integrating live video services. Many providers offer tiered pricing models, allowing developers to choose plans that align with their budget and usage requirements. Open-source options further reduce costs while providing robust functionalities.
Use Cases of Live Video Services
The versatility of live video services makes them applicable across various industries and scenarios.
Education and E-Learning
In the realm of education, live video streaming has revolutionized the delivery of content. Virtual classrooms, live lectures, and interactive tutorials enable educators to reach a wider audience and provide personalized learning experiences. Flutter's capabilities make it an ideal choice for developing e-learning platforms with live video features.
Healthcare and Telemedicine
Telemedicine has seen significant growth, driven by the need for remote healthcare services. Live video consultations allow healthcare providers to diagnose and treat patients remotely, improving access to medical care. Flutter's cross-platform nature ensures that telemedicine apps can reach users on both mobile and web platforms.
Entertainment and Live Events
Live streaming is a cornerstone of the entertainment industry, enabling artists and creators to connect with their audience in real-time. From live concerts to virtual events, the integration of live video services ensures an immersive and interactive experience for viewers.
Customer Support and Engagement
Businesses leverage live video services to enhance customer support and engagement. Real-time video interactions enable support teams to assist customers more effectively, resolving issues promptly and building stronger customer relationships.
Conclusion
Live video services are crucial for successful live streaming due to their ability to provide real-time communication, enhance user engagement, and support various applications across different industries. With the rise of frameworks like Flutter, integrating live video features into applications has become more accessible and efficient.
By utilizing video call APIs, SDKs, and leveraging the strengths of Flutter, developers can create robust and scalable live streaming solutions that meet the evolving demands of today's digital landscape. Whether it's for education, healthcare, entertainment, or customer support, the importance of live video services cannot be overstated, making them an essential component of modern app development.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Navigating the Future of Pharma: How BizMagnets Outperforms Tata 1mg ?

Ready to boost your Business with BizMagnets ?
Contact us for a demo, and let’s start your journey towards enhanced customer engagement, streamlined processes, and increased revenue.
Introduction:
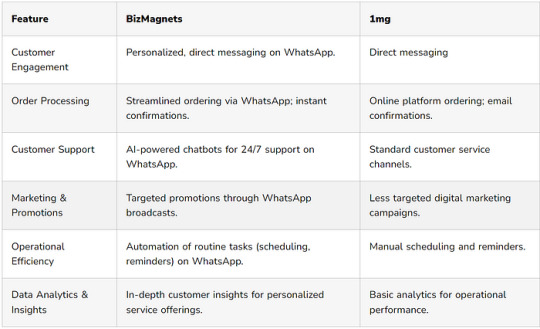
In a time when digital platforms are changing how people access healthcare, pharmacies need to use new and innovative solutions to stay ahead in the market. 1mg has been a leader in providing digital pharmacy services, but a new platform called BizMagnets WhatsApp Business Suite is offering an interesting alternative, especially when it comes to providing personalized and efficient customer service
The Advantage of the WhatsApp Business API
WhatsApp has a huge number of users all around the world, which makes it a great way for pharmacies to communicate with and engage their customers in a more personal way. The BizMagnets suite, which uses the WhatsApp Business API, allows pharmacies to not only reach their customers but also really connect with them. This can provide services that go beyond what other online pharmacy platforms like 1mg currently offer.
How WhatsApp Business API Can Transform Your Pharmacy Business ?
1. Personalized Customer Journeys : The BizMagnets platform uses AI to provide each customer with a customized experience, which can help build customer loyalty and encourage repeat business, unlike the more generic interactions on platforms like 1mg.
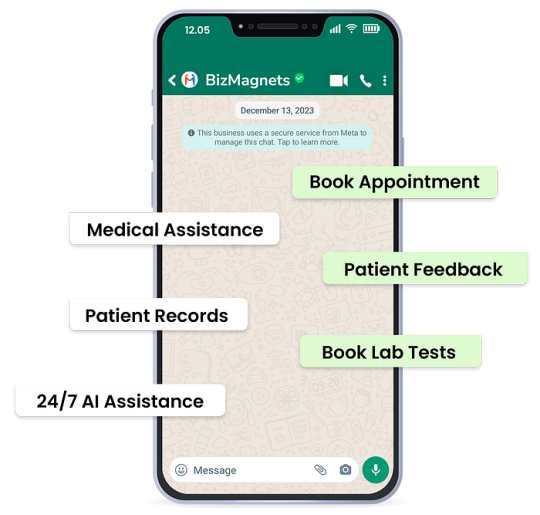
2. Efficient Operations : Automating tasks like appointment booking, test scheduling, and order confirmations through WhatsApp can save time and reduce errors, making pharmacy operations more efficient.
3. Data-Driven Decisions : The advanced analytics capabilities of the BizMagnets platform allow pharmacies to gain valuable insights into customer behavior, which they can then use to make more informed business decisions and tailor their services more precisely
Provoking Thoughts
How could personalized WhatsApp messages transform your pharmacy’s customer service experience?
Imagine the efficiency gains from automating routine operations through WhatsApp. How would that change the day-to-day of your pharmacy?
With the insights provided by BizMagnets, what new services or products could you offer to meet the unique needs of your customers?
For a more in-depth analysis on how the WhatsApp Business API can empower pharmacies to outshine competitors like Tata 1mg through specific features like WhatsApp broadcast, drip campaigns, and Click to WhatsApp ads, let’s expand on each of these components, highlighting their benefits and potential impact on business growth
WhatsApp Broadcast: The Power of Personalized Messaging at Scale
WhatsApp Broadcast allows businesses to send messages to multiple customers at once, provided the customers have saved the business’s phone number in their contacts and have agreed to receive messages. This feature is pivotal for pharmacies in announcing new health products, vaccine availability, or seasonal health tips directly through WhatsApp, ensuring high visibility and engagement. Unlike 1mg’s approach, which may rely more on app notifications or emails, WhatsApp broadcasts feel more personal and are likely to be read by customers
Drip Campaigns: Nurturing Customer Relationships Over Time
Drip campaigns are automated sets of messages that are sent out based on specific timelines or user actions. For pharmacies leveraging BizMagnets, this means being able to automatically send a welcome series to new subscribers, educational content on managing chronic conditions, or reminders for prescription refills. This strategic communication keeps the pharmacy top of mind for customers and can encourage repeat purchases. Drip campaigns through WhatsApp can be more effective than traditional methods used by companies like Tata 1mg, due to the personal and immediate nature of messagingw
Click to WhatsApp Ads: Driving Conversations and Conversions
Click to WhatsApp ads are a powerful tool that integrates with Facebook and Instagram advertising platforms. When users click on an ad, they are directly taken to a WhatsApp conversation with the business. For pharmacies, this means being able to advertise specific products or health services and instantly engage with interested customers, providing personalized advice or facilitating orders directly through WhatsApp. This immediate engagement model can significantly outperform the more static online purchasing experience offered by platforms like 1mg, leading to higher conversion rates and customer satisfaction
The Competitive Edge
Implementing these features through the WhatsApp Business API offers a dynamic and interactive customer experience that stands in contrast to the more traditional, website-centric approach of competitors like 1mg
Here’s how:
Enhanced Personalization: WhatsApp allows for direct, one-on-one communication, making each customer feel valued and understood.
Higher Engagement Rates: Messages on WhatsApp have a higher open and read rate compared to emails and app notifications.
Path to Purchase: By reducing the steps needed to inquire or purchase, customers are more likely to complete transactions.
Empowering Businesses to Thrive in the Digital Age with BizMagnets
In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven business world, adapting and innovating is crucial. By partnering with BizMagnets and leveraging the power of the WhatsApp Business API, companies can gain a significant competitive edge. The BizMagnets.ai platform offers an AI-driven WhatsApp Business Suite that empowers businesses to provide personalized, efficient, and seamless customer communication.
This innovative solution allows companies to meet their customers where they are and deliver a superior customer experience It can gather essential information from leads based on predefined criteria, ensuring that sales teams focus their efforts on high-potential prospects.
Visit: https://bizmagnets.ai/navigating-the-future-of-pharma-how-bizmagnets-outperforms-1mg-with-bizmagnets/
Email: [email protected]
Contact Number: 7845079333
#tata 1mg#medical chatbot#pharmacy#health#technology#whatsapp api#chatbot#whatsapp business#whatsapp api provider#whatsapp flows#business#chatgpt#healthcare chatbots market#whatsapp business api#saas#b2b saas#saas technology#saas software#artificial intelligence#tata#1mg
0 notes
Text
What was Announced at WWDC 2024?
Apple’s Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC) 2024 is in full swing, and the tech world is buzzing with excitement. This annual event is where Apple unveils its latest innovations across its ecosystem, from operating system updates to groundbreaking new products. Here’s a comprehensive look at the major announcements and features that have been revealed so far. Apple Vision Pro Expansion and…

View On WordPress
#Accessibility#advanced privacy#AirPods updates#Apple Fitness+#Apple Intelligence#Apple Music#Apple Vision Pro#Continuity Camera#creativity#customisation#developer API#FaceTime#fitness features#gaming enhancements#generative AI#H2 chip#health tracking#hidden apps#Home app#immersive experiences#iOS 18#iPadOS 18#locked apps#low latency#machine learning#macOS Sequoia#mental wellness#Messages update#Passwords app#Personalised Spatial Audio
0 notes
Text
HIMSS24: Day 3 highlights

- By Danielle Siarri , Nuadox -
Here are our Day 3 highlights of the 2024 HIMSS Global Health Conference & Exhibition in Orlando (March 11-15).
Today, I was part of a discussion revolving around advancements in interoperability within the healthcare system, particularly within the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA).
Eliza Levy, representing the Lighthouse program, discussed the progress made in interoperability in the past five to eight years, highlighting initiatives like the Patient Health API and the Clinical Health API. These APIs enable veterans to access their health information securely and share it across various applications, improving their healthcare experience. There are over 20 applications already in production.
Furthermore, the discussion touched upon the importance of ethical frameworks for data access and use, as well as expanding the definition of interoperability to include end-user experience and business outcomes.
Questions from participants addressed topics such as ambient technology implementation and the future deployment of AI technology to reduce clinician burnout within the VA.
Additionally, the conversation focused on engaging diverse innovators and startups to further innovation in healthcare delivery.
Stay tuned for Day 4...
Read Also
HIMSS24: Day 1 highlights
HIMSS24: Day 2 highlights
HIMSS24: Day 4 highlights
0 notes
Text
Transforming Mental Health: AI's Role in Wellness Apps

Discover how AI is reshaping mental health care, offering personalized, efficient support through wellness apps. From machine learning personalizing therapy to AI-enhancing mindfulness practices, we're uncovering how technology is not just an aid but a game-changer in mental health management. Join us as we navigate this exciting intersection of AI and psychology, revealing both its groundbreaking benefits and mindful considerations.
#healthcare#health#technology#webdevelopment#software#api integration#futurism#saas product#tech startups#saas technology#startup#saas platform
0 notes
Text
Empowering Healthcare Solutions with Ficode's API Integration Services
Find solutions to your healthcare software development questions with Ficode's expert Third-Party API Integration services. Seamlessly connect diverse systems, enhance interoperability, and deliver solutions.
Our innovative approach ensures streamlined processes and improved patient care. Trust Ficode for transformative healthcare technology solutions.
#Healthcare Software Development#Third Party API Integration services#Healthcare Software Development Services#Cloud API Development and Customisation#Mobile Health App Development#API for Mobile App Development#ficode
0 notes
Text
Healthcare's Digital Dilemma: Data Sharing or Data Hoarding?
Healthcare’s Digital Dilemma This week I am talking to Don Rucker, MD (@donrucker), Chief Strategy Officer, 1upHealth (@1up_health) who is working to solve the interoperability problem in healthcare Don shared his journey from being a medical student to a physician with a keen interest in data and computers. What he saw was healthcare’s inefficiency is often due to a lack of data, which led him…

View On WordPress
#api#Big Data#Communication#computable#computing#CURES Act#Data#data sharing#data standards#Digital Health#DigitalHealth#EMR#exchange#Health Information Exchange#health information management#Healthcare#healthcare challenges#healthcare innovation#Healthcare Technology#hospital#Incremental#Incremental Healthcare#IncrementalHealth#Infomration Blocking#Interoperability#medical data#patient#patient care#Sharing#TheIncrementalist
0 notes
Text
Canadian Wildfires: Impacts on the US AQI and Effective Measures to Mitigate Health Effects

Introduction
Wildfires are a natural phenomenon, but the frequency and intensity of these events have been increasing in recent years, driven by climate change and other factors. Canada, with its vast forests and wilderness areas, is no stranger to wildfires. These fires not only pose a significant threat to Canadian communities and ecosystems but can also have far-reaching consequences, including affecting air quality in neighboring countries like the United States. In this article, we will explore the impacts of Canadian wildfires on the US Air Quality Index (AQI), with a specific focus on New York City (NYC), and discuss effective measures to mitigate health effects. We will also provide information on how to access wildfire maps in Canada and utilize the Air Quality API to stay informed about air quality conditions.
The Canadian Wildfire Situation
Canada's vast landmass is home to numerous forests and wilderness areas, making it prone to wildfires, especially during the dry and hot summer months. The provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, and Ontario are particularly susceptible to wildfires. In recent years, climate change has exacerbated wildfire risks by creating conditions conducive to longer and more intense fire seasons.
Wildfires can release massive amounts of smoke and particulate matter into the atmosphere. The smoke can travel great distances, affecting air quality in regions far from the fire's origin. This phenomenon is not limited to Canadian borders; it often impacts air quality in the United States, particularly in states located to the south of Canada.
Impacts on the US AQI
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a standardized measure used to communicate the quality of the air and the potential health risks associated with breathing it. When wildfires occur in Canada, the smoke they generate can be carried by prevailing winds into the United States, affecting AQI readings in various cities.
New York City (NYC) is one of the major urban areas on the eastern seaboard of the United States. While it may seem far removed from Canadian wildfires, it is not immune to their effects. The smoke from Canadian wildfires can reach NYC and lead to temporary spikes in the AQI. High AQI values can have serious health implications, especially for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, the elderly, and young children.
In recent years, NYC has experienced instances where the AQI exceeded acceptable levels due to Canadian wildfires. This not only poses health risks but also necessitates public health advisories and action plans to protect vulnerable populations. It also highlights the interconnectedness of air quality across international borders and the importance of monitoring and responding to these events.
Accessing Wildfire Maps in Canada
One of the key steps in managing the impact of Canadian wildfires on US air quality is staying informed about the location and extent of wildfires in Canada. Fortunately, there are resources available to access up-to-date wildfire maps. When searching for such information, many individuals use the keyword "wildfire map Canada" to find the most relevant and current data.
Here are some resources and tips for accessing wildfire maps in Canada:
1. Government Websites: Both federal and provincial governments in Canada provide wildfire information on their official websites. Websites like Natural Resources Canada and provincial forestry agencies often have interactive maps that display active wildfires, their size, and containment efforts.
2. Mobile Apps: Many government agencies and organizations have developed mobile apps that provide real-time wildfire information. These apps often include features such as alerts, evacuation notices, and safety tips.
3. Wildfire Tracking Websites: Various websites like Ambee specialize in tracking wildfires across North America. These platforms aggregate data from multiple sources to provide comprehensive wildfire maps and information.
Utilizing the Air Quality API
To mitigate the health effects of poor air quality resulting from Canadian wildfires, it is crucial for individuals, especially those in affected regions like NYC, to stay informed about AQI readings. To cater to this need, organizations and individuals often rely on the Air Quality API to access real-time air quality data. When searching for AQI information for specific areas, the keyword "AQI NYC" is commonly used.
Here's how you can utilize the Air Quality API and make the most of it:
1. Mobile Apps: Many smartphone apps use the Air Quality API to provide users with real-time air quality information for their current location. Users can receive notifications when the AQI reaches certain thresholds, helping them take precautions.
2. Websites and Widgets: Several websites offer widgets that display AQI information for specific cities or regions. These can be embedded on personal websites or accessed directly for quick updates.
3. Alert Services: Some organizations and government agencies offer alert services that notify subscribers of significant changes in air quality, including spikes caused by wildfires. These alerts can help individuals take immediate action to protect their health.
Effective Measures to Mitigate Health Effects
When the AQI indicates poor air quality due to wildfire smoke, individuals should take steps to minimize exposure and protect their health. Here are some effective measures to consider:
1. Stay Informed: Keep track of AQI readings and follow local health advisories. Adjust your plans and activities accordingly, especially if you fall into a vulnerable category.
2. Limit Outdoor Activities: Minimize outdoor activities, especially strenuous exercise, when the AQI is high. If you must be outside, try to do so during periods of lower pollution levels.
3.Use Air Purifiers: Consider using air purifiers with HEPA filters in your home, especially in bedrooms, to reduce indoor air pollution. Make sure to properly maintain them for optimal performance.
4. Seal Your Home: Keep windows and doors closed to prevent smoke from entering your living space. Use weather stripping to seal any gaps.
5. Use N95 Masks: If you need to go outside during poor air quality conditions, wearing N95 masks can help filter out fine particulate matter. Ensure that the mask fits snugly for maximum effectiveness.
6. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, as dry and smoky air can lead to dehydration.
7. Follow Medical Advice: If you have respiratory conditions like asthma or COPD, consult your healthcare provider for specific guidance and ensure you have an adequate supply of medications.
Conclusion
Canadian wildfires have far-reaching impacts, affecting not only Canada but also neighboring regions in the United States like New York City. Understanding the connection between these wildfires and the US AQI is crucial for public health and safety. By staying informed about wildfire locations through "wildfire map Canada" searches and monitoring AQI using "AQI NYC," individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate health effects. It is a collective responsibility to adapt to changing climate conditions, reduce the risk of wildfires, and protect our communities from the harmful consequences of poor air quality.
0 notes
Text
The Fracturing and Decline of the Tulpamancy Community
Why am I back? Well, I've been thinking about this for a while and a friend of mine just discovered the Tulpamancy stuff. If you're reading this, you know who you are. Still not happy that you found out, but it got me thinking about some stuff I want to write down.
So, some of you may know, #RedditTulpas, the official r/Tulpas Discord server shut down like, a few months ago. The Tulpa.info server got shut down back in 2023, and there's also the debacle that happened with Tulpa Chat several years ago. Basically, all of the largest Tulpamancy Discord servers get shut down for whatever reason once they hit a certain point. The main reason why tends to be drama driving the staff to their wits end, which eventually leads to the server being shut down for the well-being of the staff's mental health.
I mean, I guess there's Tulpa Central with its 1,300+ members, but even though Kopase (eugh) isn't the owner anymore, it's still a server that deliberately excludes other forms of Plurality, and I don't think communities like that should be encouraged to exist. Because let's be honest, that's just thinly-veiled ableism and ignores how Tulpamancy techniques can help disordered systems function better. Oh, that and the fact that other plurals can have tulpas, too.
I also want to bring up how r/Tulpas has drastically declined in quality; we are especially cognizant of it because we moderate that subreddit. There's a lot of low-effort, redundant, and sometimes low-key unhinged posts on the Subreddit, and there is very little actual productive discussion. Most posts there nowadays are just questions, many of which have to be removed because they're already questions that are answered in the FAQ or so basic that they should be asked in the pinned post.
With Reddit specifically, I think a factor in this decline is the direction Reddit has been going with trying to become a publicly traded company, especially with their API changes essentially killing third-party apps. That, and Reddit gleefully giving away all of its user posts to OpenAI with no ability to opt out. We ourselves only check Reddit to moderate the subreddit nowadays because of these changes, and we wouldn't be surprised if others followed suit.
However, this doesn't discredit the general trend we've seen with the larger Tulpamancy communities just declining or outright dying.
The Tulpamancy side of Tumblr has been pretty quiet for several years now with the only major Tulpamancy-specific blog besides ourselves really being Sophie's and maybe Caflec's, and we're hardly active in terms of making posts (we just don't have much to talk about anymore).
There was also the Tulpa.info Mastodon instance, Tulpas.social, but that died pretty damn fast. Plural Café closed invites the moment we tried recommending it to others and has been gradually falling apart, too.
My point is: there's hardly any actual large gatherings of Tulpamancy systems anymore. I remember in one of my Tulpamancy Help videos, I explained how the community became fractured, but I think it's gotten even worse. Like, don't get me wrong, I don't think the community should be a monolith; niches exist for a reason. However, there's something just... disheartening about seeing gatherings of 1,000+ Tulpamancy systems just getting dissolved; thousands of people conversing, exchanging ideas, and helping each other just... separated.
You're probably wondering, "Well, if you're complaining about it, you surely have some kind of solution, right?" Well, not really. it seems to be a cycle tied with the general makeup of the community; enough people in the community just seem to be drawn to petty arguments and drama that takes a toll on the people who manage these communities. So for larger gathering to exist, the people need to be palatable. Otherwise, as new communities form and people flock to them, the same people that caused the downfall of the others before will follow suit. And to be frank, I don't quite have a solution in regards to getting people to stop gravitating towards and starting mentally-taxing drama. That's up for the individuals inside the community to figure out, let alone want to change.
So, what's the conclusion? I guess it's just that I believe the community is heading towards some kind of recession, a dark age of some kind. And that makes me sad to extent because the more Tulpamancy spreads, the more its techniques can be used to help people. There's a reason anthropologists and psychologists are studying Tulpamancy, especially with the interest in its possible therapeutic applications. Despite that, I want to be optimistic and hope that eventually, the community finds its stride again instead of fading into further obscurity.
7-15-2024
#tulpamancy#plurality#actuallyplural#endogenic#tulpa#long post#essay#community analysis#Tulpamancy Community#personal thoughts#opinion#community history#Discord#Reddit#Tumblr#Mastodon#Tulpa Chat#RedditTulpas#r/Tulpas#Plural Cafe#Tulpa.Info
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from Mother Jones:
The Democratic party and the climate movement have been “too cautious and polite” and should instead be denouncing the fossil fuel industry’s “huge denial operation,” the US senator Sheldon Whitehouse said.
“The fossil fuel industry has run the biggest and most malevolent propaganda operation the country has ever seen,” the Rhode Island Democrat said in an interview on Monday with the global media collaboration Covering Climate Now. “It is defending a $700-plus billion [annual] subsidy” of not being charged for the health and environmental damages caused by the burning of fossil fuels. “I think the more people understand that, the more they’ll be irate [that] they’ve been lied to.” But, he added, “Democrats have not done a good job of calling that out.”
Whitehouse is among the most outspoken climate champions on Capitol Hill, and on Wednesday evening he delivered his 300th Time to Wake Up climate speech on the floor of the Senate.
He began giving these speeches in 2012, when Barack Obama was in his first term, and has consistently criticized both political parties for their lackluster response to the climate emergency. The Obama White House, he complained, for years would not even “use the word ‘climate’ and ‘change’ in the same paragraph.”
While Whitehouse slams his fellow Democrats for timidity, he blasts Republicans for being in the pocket of the fossil fuel industry, an entity whose behavior “has been downright evil,” he said. “To deliberately ignore [the laws of physics] for short-term profits that set up people for huge, really bad impacts—if that’s not a good definition of evil, I don’t know what is.”
The American Petroleum Institute, the industry’s trade association, says on its website that “API and its members commit to delivering solutions that reduce the risks of climate change while meeting society’s growing energy needs.”
Long before Donald Trump reportedly told oil company CEOs he would repeal Joe Biden’s climate policies if they contributed $1 billion to his 2024 presidential campaign, Republicans went silent on climate change in return for oil industry money, Whitehouse asserted. The key shift came after the Supreme Court’s 2010 Citizens United ruling, which struck down limits on campaign spending. Before that, some GOP senators had sponsored climate bills, and John McCain urged climate action during his 2008 presidential campaign.
But Citizens United, Whitehouse said, “told the fossil fuel industry: ‘The door’s wide open—spend any money you want in our elections.’” The industry, he said, promised the Republican party “unlimited amounts of money” in return for stepping away from bipartisan climate action: “And since 2010, there has not been a single serious bipartisan measure in the Senate.”
11 notes
·
View notes
Note
psst hey do u have any sdv mod reccs/any tips on how to use them 👀
yeah! so for stardew mods to work you need to first install the smapi api.
you can either do that through their main website or nexus
neither option has any cons theyre just based on preference on how you wanna install it but theyre both completely safe websites.
after you properly install smapi you’ll have to go to nexus which is the main website for all stardew valley mods. you’ll need to make an account to install stuff i believe. you can find a wide range of mods here that serve a lot of different purposes.
if you haven’t used nexus to mod before then as i mentioned before first make an account then once you are looking at a mod make sure to check the requirements first. sometimes mods need other mods to work and you need to install those first. after you checked the requirements you head to the files section and click manual download. after that select slow download then wait for it to install into your files. then you move those files into the stardew mod folder. if thats not clear enough you can find a bunch of tutorial videos on youtube with visuals:)
since you asked for my recs i’ll give you the list of which i actually use all the time.
NPC Map Locations
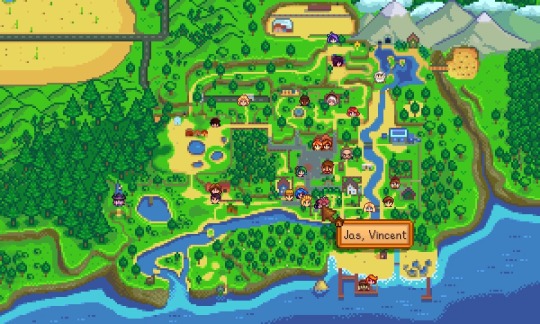
- very basic mod. majority of mod users will have this installed and it just shows you on the map where each npc is at at all times.
CJB Cheats Menu & CJB Item Spawner
- these two sorta go hand in hand for me but of course you don’t need to have both installed. this is definitely a play style preference thing but i personally like having these cheats installed for any type of situation that might happen in game that i can’t undo otherwise without them.
- the cheats menu adds a lot more flexibility and well cheats to the game so for instance: infinite health, infinite stamina, give yourself money, instantly increase hearts with whichever npc, always catch every fish, warp locations, change weather, change time, freeze time, and a lot more. this uses the P key to open in game but you can configure that to another bind if you’d like.
- the item spawner is a lot more simple. does what it says and spawns whichever item you want. so basically you can press the i key and it’ll open up a menu with every item in the game and you can spawn in the specific amount you want of something and so forth. simple concept. i mainly use this for when i accidentally sell or gift an item i wasnt intending to and then simply spawn it back in. i also use it for decorating my house:3
Look Up Anything
- this is literally like having the wiki at your disposal at all times in game. extremely helpful for so many reasons especially as i personally always had the wiki open to check for information on items and npcs so having this mod made it a lot quicker of a process. how it works is you simply hover your mouse over whatever you want information on and click f1 and it’ll display all the information about that thing to you! so if you hover over lets say harvey and press f1 it’ll show you a menu with his birthday, his love & like gifts, your hearts with them and how many points till the next heart, etc.
Seasonal Outfits
- this mod puts all the npcs in different outfits for the seasons. its just cute
Elle’s Seasonal Buildings & DaisyNiko’s Earthy Recolor
- the seasonal building allows a lot more variety in structures like farm building and adding holiday decor to npc buildings. simple stuff that can make the game more customized
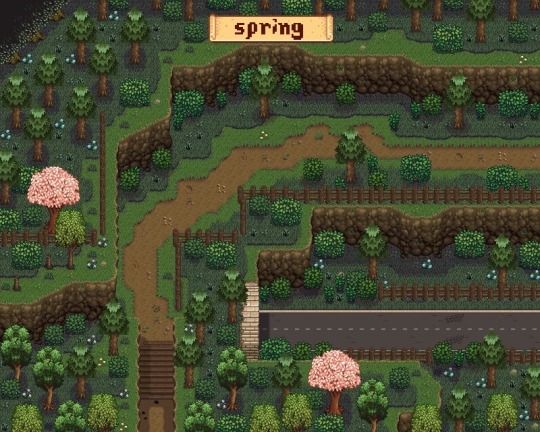
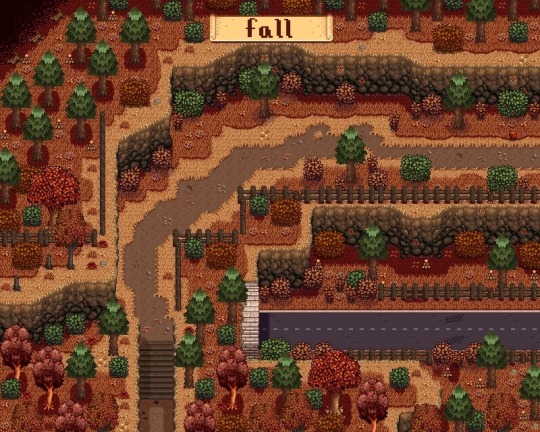


- with seasonal buildings you can also install compatible recolors which is what the DaisyNiko’s link is. it’s the recolor i personally use for my main farm when i play. this is because the vanilla game is very saturated and does hurt my eyes so having more chilled out tones helps. you dont need to install the recolor i use or any in fact if you like the natural look of the game but just know the option is there and there’s a multitude of recolors you can use to make the game look different:3
Friends Forever
- no friendship decay because itsa pain in the ass and i have no time to talk to the npcs all day. this is very play style based some people enjoy having to go and ensure they speak to npcs daily im just not the type.
Part of The Community
- creates different ways for you to gain hearts easier and passively
Mailbox Menu & Zilch’s Envelopes
- i really like the letters and the fact you can only read them once bummed me out until i found this mod which adds a whole menu for your mail where you can go back and see all the letters you’ve received. feel like it adds that additional touch and care to the whole mail system in the game.
- then to go along with that menu theres the envelopes mod that customizes it even further and makes all the envelopes of the letters have cute appearances and designs. look at this and tell me that isn’t the best thing you’ve ever seen.

Honorable Mentions
- Chests Anywhere
- CJB Show Item Sell Price
in conclusion…
I really suggest just taking the time and scrolling through the nexus mods website on your own. they have a specific category for stardew and you can filter it by most popular and see what you find yourself. since everyone plays differently you might find you enjoy the more technical code side and want to change something to do with that or you might just simply wanna change the npc portraits and make them look nicer. theres so many options on how to mod this game and i honestly could go on forever with mod suggestions but at the end of the day its up to you! so hope this helps and i hope you have a fun time modding.
74 notes
·
View notes