#Frontiers in Immunology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Also preserved on our archive
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet and the University of Gothenburg have identified a biomarker that could become an important tool for health care in assessing patients with acute COVID-19 infection. The researchers have studied interleukin (IL)-26, a signaling substance in the immune system, which has been shown to reflect the severity of the disease, viral load, and the need for hospital care.
The work is published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
"In our study, we have seen that immune signaling through IL-26 is closely linked to the severity of illness in COVID-19 patients," says the lead author of the study, Dr. Eduardo Cárdenas, who was affiliated with the Institute of Environmental Medicine at Karolinska Institutet at the time of the study.
Professor Anders Lindén, at the same institute, leads the research group and is a senior physician at the Karolinska Severe COPD Center, Karolinska University Hospital.
"Our new study confirms the connection between acute COVID-19 and IL-26 that we previously demonstrated in a smaller group of patients. By now examining a large and well-characterized group of patients, we have been able to show that IL-26 has the potential to become an easily accessible biomarker for quickly assessing which patients are at risk of severe disease progression, especially patients with COPD and asthma," says Lindén.
The researchers have analyzed samples from a large number of COVID-19 patients examined by Professor Magnus Gisslén's research group at the Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg.
The results show that IL-26 levels are higher in male than in female patients, which may reflect the fact that men are more vulnerable to the infection. The IL-26 levels were also higher in patients with COPD and asthma, two patient groups that have been suspected to be sensitive to COVID-19. Overall, the IL-26 level appears to provide important information on how the immune system responds under different health conditions.
This discovery opens new ways to monitor and manage patients with acute COVID-19 in emergency care, which can contribute to faster and more personalized interventions.
The new research could lead to IL-26 being established as a routine biomarker in health care and improve the ability to predict and treat severe disease progression at an early stage.
More information: Eduardo I. Cardenas et al, Systemic increase in IL-26 is associated with severe COVID-19 and comorbid obstructive lung disease, Frontiers in Immunology (2024). DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1434186 www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1434186/full
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Akiko Iwasaki: The Immunology of Covid and the Future
Right, so when you look at the epidemiological evidence of Long Covid, clearly in the beginning when we had no vaccines, no antivirals, no real good measure against Covid, the incident of developing Long Covid per infection was higher than a current date where we do have vaccines and Omicron may have changed its property significantly. So if you compare, let's say the Delta period versus Omicron period, there seems to be a reduced risk per infection of Long Covid. However, Omicron is super infectious. It's infected millions of people, and if you look at the total number of people suffering from Long Covid, we're not seeing a huge decline there at all because of the transmissibility of Omicron. So I think it's too early for us to say, okay, the rates are declining, we don't need to worry about it. Not at all, I think we still have to be vigilant.
We need to be up to date on vaccines and boosters because those seem to reduce the risk for Long Covid and whether Paxlovid can reduce the rate of Long Covid at the acute phase for the high risk individual, it seems to be yes, but for people who are not at high risk may or may not be very effective. So again, we just need to be very cautious. It's difficult obviously, to be completely avoiding virus at this time point, but I think masking and anything you can do, vaccination boosters is going to be helpful. And a reinfection does carry risk for developing Long Covid. So that prior infection is not going to prevent Long Covid altogether, even though the risk may be slightly reduced in the first infection. So when you think about these risks, again we need to be cognizant that reinfection and some people have multiple infections and then eventually get Long Covid, so we're just not safe from Long Covid yet.
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
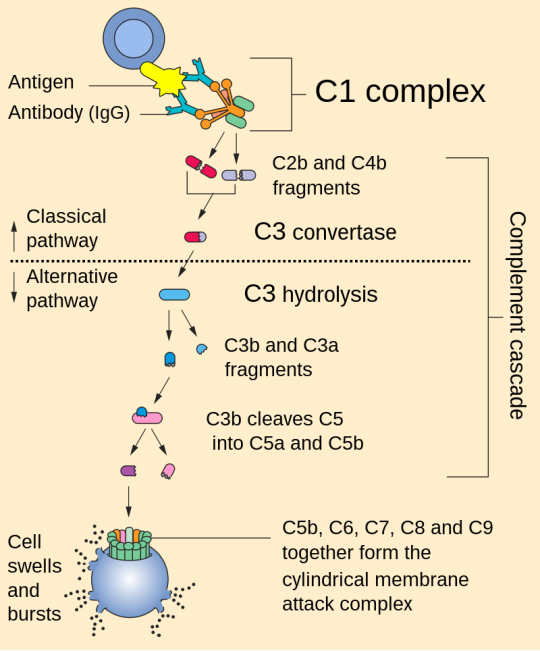
Complement system
1. Activation: The complement system can be activated through three main pathways: the classical pathway, the alternative pathway, and the lectin pathway. Each pathway involves different initiating events but converges on a common cascade of reactions.
2. Cascade of Reactions: Once activated, the complement system triggers a cascade of enzymatic reactions that result in the cleavage of complement proteins. This cascade ultimately leads to the formation of several key components, including C3b, C4b, and C5b.
3. Opsonization: C3b and C4b are opsonins, which means they can bind to pathogens and label them for phagocytosis by immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils. This enhances the removal of pathogens from the body.
4. Inflammation: Complement activation also results in the release of small peptides called anaphylatoxins, such as C3a and C5a. These peptides promote inflammation by increasing blood vessel permeability and attracting immune cells to the site of infection.
5. Membrane Attack Complex (MAC): The final step of complement activation involves the assembly of the membrane attack complex (MAC). C5b, C6, C7, C8, and multiple C9 molecules come together to form the MAC, which can create pores in the membranes of target cells, leading to cell lysis and destruction of pathogens.
References:
1. Walport, M. J. (2001). Complement. First of two parts. New England Journal of Medicine, 344(14), 1058-1066.
2. Ricklin, D., Hajishengallis, G., Yang, K., & Lambris, J. D. (2010). Complement: a key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nature Immunology, 11(9), 785-797.
3. Merle, N. S., Church, S. E., Fremeaux-Bacchi, V., & Roumenina, L. T. (2015). Complement system part I – molecular mechanisms of activation and regulation. Frontiers in Immunology, 6, 262.
Please note that for the most current and detailed medical information on the complement system, I recommend consulting recent textbooks or academic journals in immunology and microbiology.
#science#biology#college#education#school#student#medicine#doctors#health#healthcare#immunology#immune system#complement system
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey.
Hey, Tumblr.
Research Aid Networks is trying to crowdsource funding for a Long Covid clinical trial.
https://gofund.me/f67950ae
The trial would research the hypothesis from the April 2023 paper in the journal Frontiers in Immunology: Hypothesis: inflammatory acid-base disruption underpins Long Covid.
This research would have implications for ME/CFS as well.
Tumblr, I know that you either have LC/ME/CFS yourself or you know someone with it. This shit is fucking awful.
This hypothesis needs to be researched.
If you can't donate, please reblog. And spread it to other platforms.
No-one helps us except us. Tumblr, I bet you we can get this shit funded.
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm reading this article about auto-immune diseases and especially how these disease seem to affect women FAR more than men (70%+ of people with auto immune diseases are women). The study suggests that this is likely due to the major changes in our hormone cycles we go through in our lives- primarily Puberty & Menopause, (and the more optional pregnancy & breastfeeding) and how those hormones interact with our immune system.
But it was this line in particular that got me thinking:
"Concentration-dependent effects of estrogen on the immune system; the role of progesterone, androgens, leptin, oxytocin, and prolactin; and the interplay between Th1 and Th2 immune responses together maintain a delicate balance between host defense, immunological tolerance and autoimmunity. "
I genuinely wonder what role HRT may play in autoimmune disease, and how 'gender affirming care' might unintentionally lead to autoimmune disease. After more research on this subject, it seems there are some small studies finding various auto-immune issues in transgender individuals after receiving HRT when they otherwise showed little to no genetic predispositions for said diseases. Even more curiously is one study noted that a MtF transitioner's disease IMPROVED after being administered testosterone saying: "One case report described significant improvement of cutaneous lupus in a transgender woman after initiating testosterone treatment"
I found another article saying:
The research, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published in Clinical Epigenetics, found that hormone therapy could affect certain regions of DNA, [which is] the first step in understanding how [HRT] may impact the immune system. The researchers have begun to tease apart whether the hormone therapy influences immune function and susceptibility to autoimmune disease or infection risk, which affects the sexes differently.
So already some people are noticing a connection between hormones, the immune system, and auto-immune diseases. However there's little, if any, research on this topic, with the known information being anecdotes.
"For example, a young person with a strong family history of autoimmune disease may wish to know if hormonal therapy will increase or decrease their risk of developing disease. Others may worry about hormones altering their susceptibility to infections, which is relevant given the current COVID-19 pandemic. At this stage, we don't know the answers to such questions..."
This article is from 2022, and as of the time I posted this it's 2023. With the increase in trans people seeking medical transition it's scary to see a complete lack of research and knowledge on this subject. A journal from Frontiers published in summer of 2022 says that most research on auto-immune diseases (despite the massive sex discrepancy) is focused on male, cis-gendered men. The journal's abstract also points out the truth that's starting to become more and more apparent:
There is an unmet need for detailed treatment follow-up of the transgender community- little is known of the potential benefits and risks of hormonal supplementation on the immune system, nor indeed on many other health and disease outcomes.
We don't even know if HRT can affect one's ability to heal from infections, and seeing as many who start on HRT later go on to have surgeries that are often quite invasive and have a long arduous healing process, this is very worrying.
Sure, all medications have side-effects. Sure, people are willing to put up with said side-effects so long as they don't face the original symptoms that they're treating. But when is it too much? That doctors are harming their patients? Of course, we just don't know the full effects and correlation, but what we do know is worrying.
Once again, trans healthcare is under-funded, under-researched, and could potentially lead to undue harm, putting thousands at a risk they aren't even aware of. Is it really informed consent if we don't know the side-effects? is it really informed consent if we're learning the effects as we go along?
Sources below the cut:
https://www.mcri.edu.au/news-stories/gender-affirming-hormone-therapy-can-influence-gene-activity (no embed 😢)
#radical feminism#transgender healthcare#radblr#autoimmune disease#medical misogyny#medical transphobia#medical system kills#the data gap#invisible women#radical feminists do interact
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
You had COVID a few months ago and recovered—but things still aren���t quite right.
When you stand up, you feel dizzy, and your heart races. Even routine tasks leave you feeling spent. And what was once a good night’s sleep no longer feels refreshing.
Long COVID, right? It may not be so simple.
A mild or even an asymptomatic case of COVID can cause reservoirs of some viruses you’ve previously battled to reactivate, potentially leading to symptoms of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome—a condition that resembles long COVID, according to a recent study published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Diseases
Introduction
Immunotherapy, a groundbreaking approach primarily recognized for cancer therapy immunotherapy, is now making significant strides in treating autoimmune diseases. This article delves into how immunotherapy is applied beyond cancer immunology immunotherapy to manage and treat autoimmune conditions.
The Mechanism of Immunotherapy in Autoimmune Diseases
Immunotherapy works by modulating the immune system, enhancing its ability to fight diseases. Unlike in immunotherapy cancer treatment, where the goal is to target and destroy cancer cells, in autoimmune diseases, the therapy aims to recalibrate the immune system to stop attacking the body's tissues.
Types of Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Diseases
There are various types of immunotherapy used to treat autoimmune diseases. These include monoclonal antibodies, cytokine inhibitors, and immune checkpoint inhibitors, each designed to alter specific immune system pathways. While some of these therapies overlap with those used in cancer treatment, their application in autoimmune diseases focuses on immune regulation and suppression of overactive immune responses.
Immunotherapy Medications and Treatments
Immunotherapy medications for autoimmune diseases are tailored to reduce inflammation and curb the immune system's erroneous attacks on healthy cells. The precise medication or combination of therapies depends on the specific autoimmune condition being treated, highlighting the personalized nature of immunotherapy.
The Role of Immunotherapy and Vaccines
Exploring the intersection of immunotherapy and vaccines reveals potential for preventative strategies in autoimmune diseases. Vaccines designed to induce tolerance in the immune system are under research, potentially preventing autoimmune diseases from developing or worsening.
Managing Side Effects and Costs
While immunotherapy offers new hope, it's crucial to consider immunotherapy side effects and immunotherapy cost. Side effects vary widely, from mild to severe, and must be carefully managed under medical supervision. The cost can also be significant, necessitating a discussion about healthcare resources and insurance coverage.
Conclusion
Immunotherapy for autoimmune diseases represents a promising frontier in medical treatment, offering hope for millions suffering from these conditions. As research progresses, it could redefine the therapeutic landscape for autoimmune diseases, much like it has for cancer.
Discovering Excellence in Cancer and Autoimmune Disease Treatment at CBCC India
At the forefront of medical innovation and care, CBCC India stands as one of the leading Cancer Hospital in India, dedicated to eliminating cancer and advancing treatment for autoimmune diseases. Our commitment to innovative research and exceptional care ensures that every patient receives personalized, state-of-the-art treatment. Discover the pinnacle of healthcare excellence at CBCC India, where we strive to conquer cancer and improve the lives of those with autoimmune diseases through cutting-edge immunotherapy and comprehensive care.
#Immunotherapy#Autoimmune diseases#Cancer therapy#Immune system modulation#Monoclonal antibodies#Immune checkpoint inhibitors#Inflammation reduction#Personalized treatment#Vaccines
1 note
·
View note
Quote
風邪とインフルエンザがはやるこの季節、予防のためとしてビタミンCを頼りにする人もいるだろう。ビタミンCには免疫系を強化する働きがあり、健康的な食生活に不可欠であることは間違いない。ただ、そのメリットが強調されすぎている面があるため、過剰に摂取している人も多い。通常は、それで危険が生じることはないものの、時間とお金の無駄になりかねない。 ビタミンCが万能薬だという評判が確立したのは、1970年代のことだ。ノーベル賞を2度受賞した化学者のライナス・ポーリングが、1日3000ミリグラムのビタミンCの摂取をすすめたのがきっかけだった。その結果、ビタミンCを大量に摂取すれば、通常の風邪を引かなくなるばかりか、心臓病やがんといった深刻な疾患を遠ざけ、長く健康に生きられるという誤解が広まることになった。 しかし、ポーリングの主張は厳密な検証を経たものではなかった。「ビタミンCの大量摂取が通常の風邪の予防や治療に有効という説に、一貫性のある科学的な証拠はありません」。米国立衛生研究所(NIH)の栄養補助食品室長を務めるステファン・パシアコス氏は、そう説明する。 その後、実際にさまざまな証拠が積み重なり、ビタミンCの健康への効果について多くのことが明らかになっている。 風邪への効果は? 2020年10月に学術誌「Frontiers in Immunology」に発表されたレビュー論文によれば、ほとんどの研究で、オレンジジュースやサプリメントをたくさん飲んでも、風邪に対して大きな効果は認められていない。実際に、1日の推奨量(米国では男性は90ミリグラム、女性は75ミリグラム。日本では男女ともに100ミリグラム)の何倍もの量を摂取しても、大多数の人の健康が増進するわけではない。 なぜかと言えば、1000ミリグラム以上のビタミンCを摂取しても、体は効果的に吸収で��ず、尿として排出されるからだ。(参考記事:「なぜ無効な成分が市販のかぜ薬にずっと使われているのか?」) 「ビタミンCが不足している人や極端に運動量が多い人を除けば、ビタミンCを大量に摂取しても、通常の風邪を予防したり、症状を緩和したりする効果はありません」。米ハーバードT・H・チャン公衆衛生大学院の栄養学教授で、米ボストン小児病院栄養センター長を務めるクリストファー・ダガン氏は、数多くの臨床試験によって積み重ねられてきた証拠を示しながら、そのように話す。 ただし、一時的な大量摂取で風邪は予防できなくても、ビタミンCを常に摂取していると、風邪の期間が少しは短くなるという報告がある。ビタミンCを毎日200ミリグラム以上摂取している人は(ほとんどが1000ミリグラム)、実際に、成人で8%、子どもで14%早く治るとするレビュー論文が、2013年に信頼度の高い医学的な情報をまとめるデータベース「Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews」で公表されている。 不可欠なビタミンC、いったい何をしているのか ビタミンCは万能薬ではないが、健康にとって不可欠な栄養素であることはたしかだ。ダガン氏は、「ビタミンCは体でさまざまな役割を担っています」と言う。 ビタミンCはアスコルビン酸とも呼ばれ、免疫系にとって重要な働きを持つことはよく知られている。パシアコス氏はこう説明する。「ビタミンCは、インターフェロンというタンパク質の生産を促進します。このインターフェロンが、細胞をウイルスから守るのです。さらに、ビタミンCは白血球、とりわけ病原体を飲み込む食細胞を活性化させ、感染症と戦うその他の免疫細胞の活動も刺激します」
「ビタミンCで風邪を予防」のウソ、誤解生んだノーベル賞化学者 | ナショナル ジオグラフィック日本版サイト
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
You had COVID a few months ago and recovered—but things still aren’t quite right.
When you stand up, you feel dizzy, and your heart races. Even routine tasks leave you feeling spent. And what was once a good night’s sleep no longer feels refreshing.
Long COVID, right? It may not be so simple.
A mild or even an asymptomatic case of COVID can cause reservoirs of some viruses you’ve previously battled to reactivate, potentially leading to symptoms of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome—a condition that resembles long COVID, according to a recent study published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive (Daily updates!)
BY: Carmen Leitch
New studies have provided novel insights into long COVID, which continues to affect millions of people worldwide. The exact rates of the disease are hard to determine because of variations in clinical criteria, and other differences such as differing standards for who is included or excluded from a long COVID diagnosis or study. According to a July 2024 study in The Lancet, the rates of long COVID following an acute infection range from 50 to as much as 85 percent of people who were hospitalized for COVID-19 and unvaccinated; 10 to 35 percent of people who were not hospitalized and not vaccinated, and about ten percent of vaccinated people.
Scientists are still working to determine the causes of long COVID, which may vary or include several factors depending on who is affected and what their health history might be. Some research has found evidence of active infection in people with long COVID. But in that study, half of the long COVID patients did test negative for viral proteins, suggesting that there are multiple causes of the illness.
Symptoms of long COVID include but are not limited to: fatigue, fever, malaise, coughing, chest pain, headaches, sleep problrms, anxiety, diarrhea or constipation, joint pain, and rash. Long term complications may include increased risk of diabetes, blood clots, and heart problems.
A 2022 study reported in Nature Medicine determined that heart dysfunction could be one reason for the symptoms of long COVID, even after a mild infection.
A recent report published in Nature Microbiology has shown that there were abnormally high levels of inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines in patients with long COVID.
The scientists found that these cytokines could damage heart calls called cardiomyocytes. Since these cells are responsible for the pumping action of the heart, problems with those cells may help explain long COVID symptoms like chest pain and heart palpitations. A heart condition known as POTS (postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome) has also been associated with long COVID.
Unrelated, recent work reported in the Journal of Autoimmunity and Frontiers in Immunology, has discovered two proteins that could serve as biomarkers for long COVID, and may help explain the mechanisms underlying some cases of the disease. This work showed that people with long COVID carry abnormally high levels of proteins called galectin-9 and artemin in their blood.
These patients also had unusually high levels of certain immune cells known as neutrophils and monocytes, which may cause inflammation. There were also abnormally high levels of killer T cells that were exhausted. Long COVID patients were also deficient in immune cells that can fight infection, called lymphocytes. The researchers noted that neutrophils that are under stress often release galactin-9, which can boost inflammation.
Another recent study from this group, reported in The Lancet Microbe found no evidence of persistent infection in long COVID patients, challenging studies that have found the opposite and highlighting the complexities and sometimes confounding nature of this highly variable disorder.
Studies:
www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(24)01136-X/fulltext www.clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com/article/S1198-743X(24)00432-4/abstract www.nature.com/articles/s41591-022-02000-0 www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01838-z pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9287587/ www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S089684112400101X?via%3Dihub www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1443363/full www.thelancet.com/journals/lanmic/article/PIIS2666-5247(24)00280-5/fulltext
#mask up#covid#pandemic#public health#wear a mask#covid 19#wear a respirator#coronavirus#still coviding#sars cov 2#long covid#covid conscious#covid is airborne
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Perhaps because gastroenterology, immunology, toxicology, and the nutrition and agricultural sciences are outside of their competence and responsibility, psychologists and psychiatrists typically fail to appreciate the impact that food can have on their patients’ condition. Here we attempt to help correct this situation by reviewing, in non-technical, plain English, how cereal grains—the world’s most abundant food source—can affect human behavior and mental health. We present the implications for the psychological sciences of the findings that, in all of us, bread (1) makes the gut more permeable and can thus encourage the migration of food particles to sites where they are not expected, prompting the immune system to attack both these particles and brain-relevant substances that resemble them, and (2) releases opioid-like compounds, capable of causing mental derangement if they make it to the brain. A grain-free diet, although difficult to maintain (especially for those that need it the most), could improve the mental health of many and be a complete cure for others.
(...)
The manufacture of exorphins is incredibly efficient. The nutritionally insignificant intake of 1 g of casein (about two tablespoons of cow milk), for example, produces opioids in large enough amounts to exert physiological effects (Meisel and FitzGerald, 2000). This is remarkable in view of the facts that (a) the opioids from gluten are stronger than those from casein (Zioudrou et al., 1979), and (b) the daily average consumption of gluten in Europe is 10–20 g, with many people exceeding 50 g (Sapone et al., 2012). In the brain of rats, the opioids from casein have been shown to be 10 times more potent than morphine (Herrera-Marschitz et al., 1989). If all exorphins released in the gut made it to the brain, it is hard to see how we could keep functioning."
Busting the MYTHS About Iodine, Cholesterol & Fasting | Dr. Elizabeth Bright
youtube
"A couple of years ago I read a book called "Devil in the Milk" by an Australian (Keith Woodford) who was explaining A2 milk versus A1 milk (1). There is absolutely an issue with dairy because of the casomorphin content: two tablespoons of A1 cow milk is equal to a shot of heroin in an opiate sense. So the inflammation that a casomorphin that a casomorphin can give your body (two tablespoons of milk) is equal to a shot of heroin. I mean, he literally writes this. So the whiter the milk, the fresher the milk, what you have is a lot of (or dairy, kaffir or yogurt, whatever, goat cheese) you have a lot of protein. If you have aged cheese the fermentation process eats the protein and the lactose, this isn't really an issue it's more the proteins, the proteins are inflammatory.
So if you're not well, if you have an autoimmune condition, your immune system is overreactive, it's going to see a protein like gluten, or dairy, or casomorphin, it's going to see that as a pathogen, it will react. How does it react? Again, it could be any way but it will react to that protein thinking it's a virus.
So if you're, as you said depending upon where you are on your health journey, if you still have pain, if you still have arthritis, if you still have eczema, if you still have psoriasis… I would take out dairy. And in some cases I'll even say to try to stop butter for a week or so. And I've had a couple who've had a really good result from that. And then they heal and then they can add in the butter."
(1) A1 milk, which is the most commonly used milk and is abundantly available, is obtained from cows of Western origin like Holstein, Jersey etc. and yields a large quantity of milk. The A2 milk is the milk obtained by the cows of Indian origin like Gir, Sahiwal etc.
#Jesse Chappus#Elizabeth Bright#videos#women's health#mental health#health#addiction#Keith Woodford#inflammation#autoimmunity#psoriasis#eczema#arthritis#food#Peter Kramer#Paola Bressan#science#iodine#milk#dairy#allergies#food intolerance
1 note
·
View note
Text
Assistant Professor in Immunobiology and Microbial Pathogenesis The Salk Institute for Biological Studies The Salk Institute is seeking faculty members at the Assistant level in Immunobiology and Microbial Pathogenesis See the full job description on jobRxiv: https://jobrxiv.org/job/the-salk-institute-for-biological-studies-27778-assistant-professor-in-immunobiology-and-microbial-pathogenesis/?feed_id=84724 #ScienceJobs #hiring #research
0 notes
Text
The Growing Frontier: An In-Depth Look at the Single-Cell Analysis Market
The Single-Cell Analysis Market was valued at USD 3.3 billion in 2023 and will surpass USD 8.7 billion by 2030; growing at a CAGR of 14.8% during 2024 - 2030. The field of life sciences is undergoing a transformative phase, with single-cell analysis emerging as a pivotal technique in modern biology and medicine. Unlike traditional bulk analysis methods that examine averages across populations of cells, single-cell analysis delves into the unique characteristics of individual cells, offering unprecedented insights into cellular diversity, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic targets. This article explores the current landscape, key drivers, and future prospects of the single-cell analysis market.
Single-cell analysis allows researchers to investigate the heterogeneity within a population of cells, which is crucial for understanding complex biological processes such as cancer progression, immune responses, and developmental biology. By examining individual cells, scientists can identify rare cell types, understand cell-to-cell variations, and gain insights into the dynamics of cellular networks. This level of detail is especially important in fields like oncology, immunology, and neurology, where subtle differences between cells can have significant implications for disease progression and treatment outcomes. The single-cell analysis market has experienced rapid growth over the past decade, driven by advancements in technology, increased research funding, and the growing recognition of the importance of cellular heterogeneity in biology and medicine.
Get a Sample Report: https://intentmarketresearch.com/request-sample/single-cell-analysis-market-3651.html
Key Drivers of Market Growth
Technological Advancements: Innovations in single-cell sequencing, microfluidics, and imaging technologies have significantly enhanced the accuracy, efficiency, and scalability of single-cell analysis. These advancements have made it easier for researchers to isolate, process, and analyze individual cells, driving adoption across various applications.
Rising Demand in Oncology: Cancer research is one of the primary areas driving the demand for single-cell analysis. The ability to identify and characterize rare cancer stem cells, understand tumor heterogeneity, and monitor the immune landscape of tumors has made single-cell analysis an indispensable tool in oncology.
Increased Funding and Collaborations: Governments, academic institutions, and private companies are increasingly investing in single-cell analysis research. Collaborative efforts between industry and academia are accelerating the development of new tools and applications, further fueling market growth.
Expansion of Applications: Beyond oncology, single-cell analysis is finding applications in immunology, neuroscience, stem cell research, and drug discovery. The versatility of this technology is broadening its appeal across multiple disciplines.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its promising growth, the single-cell analysis market faces several challenges. The high cost of instruments and reagents remains a significant barrier for many research labs. Additionally, the complexity of data generated by single-cell analysis requires advanced bioinformatics tools and expertise, which can limit its accessibility to a broader range of researchers.
Furthermore, the standardization of protocols and data analysis methods is still evolving. Variability in sample preparation, sequencing techniques, and data interpretation can lead to inconsistencies in results, which is a critical issue that needs to be addressed to ensure the reliability of single-cell studies.
Get an insights of Customization: https://intentmarketresearch.com/ask-for-customization/single-cell-analysis-market-3651.html
Future Prospects
The future of the single-cell analysis market looks promising, with continued innovation and expansion into new research areas. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expected to play a significant role in improving data analysis and interpretation, making it easier for researchers to extract meaningful insights from complex datasets.
Moreover, as the cost of technology decreases and standardization improves, single-cell analysis is likely to become more accessible to a wider range of researchers, including those in smaller labs and developing countries. The integration of single-cell analysis with other omics technologies, such as proteomics and metabolomics, is also expected to open new avenues for research and personalized medicine.
Conclusion
The single-cell analysis market is at the forefront of a new era in biological research. As technology continues to advance and new applications emerge, this market is poised for substantial growth. The ability to study individual cells in detail is revolutionizing our understanding of health and disease, paving the way for more precise diagnostics, targeted therapies, and personalized medicine. For researchers, clinicians, and investors alike, the single-cell analysis market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving frontier with significant potential to transform the life sciences landscape.
#Single-cell sequencing#Single-cell profiling#Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq)#Single-cell genomics#Single-cell assay#Single-cell analytics
0 notes
Text
Global Mesenchymal Stem Cells Market Overview

The Mesenchymal Stem Cells Market size was estimated at USD 3.11 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 8.22 billion by 2031 with a growing CAGR of 12.93% during the forecast period of 2024-2031.The Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) market is poised at the intersection of groundbreaking research and therapeutic innovation, heralding a new era in regenerative medicine.
With their remarkable potential to differentiate into various cell types, MSCs have captivated the biomedical field, offering promising avenues for treating a spectrum of diseases from orthopedic injuries to autoimmune disorders. As scientific understanding deepens and clinical trials expand, the market for MSC therapies anticipates exponential growth, driven by robust investment in biotechnology and increasing healthcare demand for effective, personalized treatments. This burgeoning market not only holds the key to transformative therapies but also represents a pivotal frontier in harnessing the body's own healing mechanisms for improved patient outcomes worldwide.
Get Sample Report @ https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3948
Market Scope & Overview
The most recent Mesenchymal Stem Cells Market report offers accurate data on the market's size, share, and capacity for production, demand, and growth over the coming year. According to market research, the market is changing quickly, and both the impact on the present and the future are being examined. The market research team conducted thorough primary and secondary research to gather the relevant market data.
The market size and value for each industry, channel, and other sector are discussed in the research. It also takes into account the elements and traits that could affect the expansion of the market's sales. The market's present and future states are carefully examined in the worldwide Mesenchymal Stem Cells Market research report.
Market Segmentation Analysis
By Products and Services
Products
Cells & Cell Lines
Kits, Media, & Reagents
Others
Services
By Workflow
Cell Sourcing & Isolation
Culture & Cryopreservation
Differentiation
Characterization
By Type
Autologous
Allogeneic
By Source of Isolation
Bone Marrow
Cord Blood
Peripheral Blood
Fallopian Tube
Fetal Liver
Lung
Adipose Tissues
By Indication
Bone And Cartilage Repair
Cardiovascular Disease
Inflammatory And Immunological Diseases
Liver Diseases
Cancer
GvHD
Others
By Application
Disease Modelling
Drug Development & Discovery
Stem Cell Banking
Tissue Engineering
Toxicology Studies
Others
COVID-19 Impact Analysis
The worldwide economy is significantly impacted by the coronavirus outbreak. The most recent COVID-19 scenario analysis is included in this Mesenchymal Stem Cells Market research report. The top businesses, distributors, and supply chain organizations in the sector are also examined in the report.
Regional Outlook
North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East and Africa are the five geographic divisions of the market. The Mesenchymal Stem Cells Market report examines each regional market in great detail and sheds light on the key factors influencing it. The research takes into account factors such as market size and share, import/export ratios, supply/demand ratios, consumer demand ratios, technological advancements, R&D, infrastructure development, and a strong market presence across the board.
Competitive Analysis
To give readers a greater understanding of the important players, the study report covers cutting-edge research approaches including SWOT and Porter's Five Forces analysis. Additionally, it includes crucial data on the economy, global positioning, product portfolios, earnings, gross profit margins, and scientific and technology advancements. The key industry partnerships, product launches, and acquisitions are the subject of the Mesenchymal Stem Cells Market research.
Key Reasons to Purchase Mesenchymal Stem Cells Market Research Report
Market research contains critical development status, growth rates, evaluations of the competitive environment, and data on international marketing.
The research report offers a comprehensive view of the worldwide competitive climate as well as crucial details on the leading rivals and their projected future growth.
Conclusion
For industry participants and other stakeholders looking for a thorough analysis of the current market dynamics as well as realistic estimates, the Mesenchymal Stem Cells Market research report will be a valuable resource.
About Us
SNS Insider is a market research and insights firm that has won several awards and earned a solid reputation for service and strategy. We are a strategic partner who can assist you in re framing issues and generating answers to the trickiest business difficulties. For greater consumer insight and client experiences, we leverage the power of experience and people.
When you employ our services, you will collaborate with qualified and experienced staff. We believe it is crucial to collaborate with our clients to ensure that each project is customized to meet their demands. Nobody knows your customers or community better than you do. Therefore, our team needs to ask the correct questions that appeal to your audience in order to collect the best information.
Related Reports
Nasal Drug Delivery Market Growth Drivers
DNA Synthesis Market Growth Drivers
Osteoporosis Treatment Market Growth Drivers
Immunomodulators Market Growth Drivers
Proteomics Market Growth Drivers
0 notes
Link
(NaturalNews) Researchers from Ohio State University recently discovered that fully vaccinated patients who test positive for the Wuhan coronavirus (COVID-19) are...
0 notes
Text
Navigating the Frontier of Immunology: The Vital Role of an Antibody Supplier
An antibody supplier serves as the linchpin between scientific discovery and practical application. They are the custodians of a vast catalog of antibodies meticulously developed and validated for a myriad of applications. Whether it's probing the mysteries of cellular pathways or diagnosing infectious diseases, researchers rely on the quality and specificity of antibodies provided by these suppliers.
Quality is paramount in the world of antibodies. Rigorous validation processes ensure that each antibody meets stringent criteria for specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility. From monoclonal to polyclonal antibodies, each product undergoes meticulous testing to guarantee its efficacy in diverse experimental conditions. A reputable antibody supplier invests in state-of-the-art technologies and employs seasoned experts to uphold these rigorous standards.
Furthermore, antibody suppliers play a pivotal role in custom antibody development. Collaborating closely with researchers, they tailor antibodies to specific targets, epitopes, or applications, providing bespoke solutions to meet unique experimental needs. This personalized approach accelerates discovery and empowers scientists to tackle complex biological questions with confidence.

In addition to supplying antibodies, Anti Idiotypic Antibodies these companies offer a suite of complementary products and services. From assay development to technical support, they provide comprehensive solutions to streamline research workflows. Through educational resources and training programs, they empower scientists to maximize the utility of antibodies in their experiments, ensuring optimal results and reproducibility.
The impact of antibody suppliers extends far beyond the confines of the laboratory. Their contributions underpin a wide array of disciplines, from fundamental biology to clinical medicine. In drug development, antibodies serve as both therapeutics and diagnostic tools, guiding the development of novel treatments and personalized medicines. In infectious disease research, they enable rapid and accurate detection of pathogens, bolstering efforts to combat emerging threats.
Moreover, antibody suppliers play a crucial role in advancing precision medicine initiatives. By supplying antibodies for biomarker discovery and validation, they facilitate the development of companion diagnostics that enable tailored treatment strategies for individual patients. This paradigm shift towards personalized healthcare promises to revolutionize patient outcomes and transform the practice of medicine.
However, the landscape of antibody supply is not without challenges. The proliferation of low-quality or counterfeit antibodies poses a significant threat to research integrity and reproducibility. In response, reputable suppliers uphold transparency and accountability, providing detailed validation data and adhering to best practices in antibody development and characterization. By prioritizing quality over quantity, they safeguard the integrity of scientific research and uphold the trust of the research community.
0 notes