#Europe Natural Gas Generator Market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Europe Gas Generator Market Growth, Trends, Demand, Industry Share, Challenges, Future Opportunities and Competitive Analysis 2033: SPER Market Research
The Europe Gas Generator Market encompasses the production, distribution, and utilization of gas-powered generators across European countries. With increasing concerns about energy security, environmental sustainability, and power reliability, the demand for gas generators is rising. Key drivers include the transition to cleaner energy sources, infrastructure development, and backup power requirements. Additionally, advancements in gas generator technology, such as improved efficiency and reduced emissions, contribute to market growth. Key players focus on innovation, product differentiation, and service quality to meet the diverse needs of customers and capitalize on market opportunities in Europe.

#Europe Gas Generator Market#Europe Gas Generator Market Challenges#Europe Gas Generator Market Competition#Europe Gas Generator Market Demand#Europe Gas Generator Market Future Outlook#Europe Gas Generator Market Growth#Europe Gas Generator Market Report#Europe Gas Generator Market Revenue#Europe Gas Generator Market Segmentation#Europe Gas Generator Market Share#Europe Gas Generator Market Size#Europe Gas Generator Market Trends#Europe Hydrogen Gas Generator Market#Europe Industrial Gas Generator Market#Europe Laboratory Gas Generators Market#Europe Large Generator Market#Europe Natural Gas Generator Market#Europe Natural Gas Generator Market Forecast#Europe Natural Gas Generator Market Opportunities#Europe Power Generator Market#Europe Residential Gas Generator Market#Gas Generator Market
0 notes
Text
BDS Consumer Boycott Targets
Everything here is copied over from the BDS website.
Hewlett Packard Inc (HP Inc)
HP Inc (US) provides services to the offices of genocide leaders, Israeli PM Netanyahu and Financial Minister Smotrich. HPE, which shares the same brand, provides technology for Israel’s Population and Immigration Authority, a pillar of its apartheid regime.
Chevron (including Caltex and Texaco)
US fossil fuel multinational Chevron is the main corporation extracting gas claimed by apartheid Israel in the East Mediterranean. Chevron generates billions in revenues, strengthening Israel’s war chest and apartheid system, exacerbating the climate crisis and Gaza siege, and is complicit in depriving the Palestinian people of their right to sovereignty over their natural resources. Chevron has thousands of retail gas stations around the world under the Chevron, Caltex, and Texaco brand names.
Siemens
Siemens (Germany) is the main contractor for the Euro-Asia Interconnector, an Israel-EU submarine electricity cable that is planned to connect Israel’s illegal settlements in the occupied Palestinian territory to Europe. Siemens-branded electrical appliances are sold globally.
PUMA
Since 2018, we have called for a boycott of PUMA (Germany) due to its sponsorship of the Israel Football Association (IFA), which governs teams in Israel’s illegal settlements on occupied Palestinian land. In a major BDS win in December 2023, PUMA leaked news to the media that it will not be renewing its IFA contract when it expires in December 2024. Until then, it is still complicit, so we continue to #BoycottPUMA until it finally ends its complicity in apartheid.
Carrefour
Carrefour (France) is a genocide enabler. Carrefour-Israel has supported Israeli soldiers partaking in the unfolding genocide of Palestinians in Gaza with gifts of personal packages. In 2022, it entered a partnership with the Israeli company Electra Consumer Products and its subsidiary Yenot Bitan, both of which are involved in grave violations against the Palestinian people.
AXA
Insurance giant AXA (France) invests in Israeli banks financing war crimes and the theft of Palestinian land and natural resources. When Russia invaded Ukraine, AXA took targeted measures against it. Yet, Axa has taken no action against Israel, a 75-year-old regime of settler-colonialism and apartheid, despite its ongoing genocidal war on Gaza.
SodaStream
SodaStream is an Israeli company that is actively complicit in Israel's policy of displacing the indigenous Bedouin-Palestinian citizens of present-day Israel in the Naqab (Negev) and has a long history of racial discrimination against Palestinian workers.
Ahava
Ahava cosmetics is an Israeli company that has its production site, visitor center, and main store in an illegal Israeli settlement in the occupied Palestinian territory.
RE/MAX
RE/MAX (US) markets and sells property in illegal Israeli settlements built on stolen Palestinian land, thus enabling Israel’s colonization of the occupied West Bank.
Israeli produce in your supermarkets
Boycott produce from Israel in your supermarket and demand their removal from shelves. Beyond being part of a trade that fuels Israel’s apartheid economy, Israeli fruits, vegetables, and wines misleadingly labeled as “Product of Israel” often include products of illegal settlements on stolen Palestinian land. Israeli companies do not distinguish between the two, and neither should consumers.
Non-BDS Grassroots Boycotts:
McDonald’s (US), Burger King (US), Papa John’s (US), Pizza Hut (US), WIX (Israel), etc. are now being targeted in some countries by grassroots organic boycott campaigns, not initiated by the BDS movement. BDS supports these boycott campaigns because these companies, or their branches or franchisees in Israel, have openly supported apartheid Israel and/or provided generous in-kind donations to the Israeli military amid the current genocide. If these grassroots campaigns are not already organically active in your area, we suggest focusing your energies on our strategic campaigns above.
Recently, McDonald’s franchisee in Malaysia has filed a SLAPP lawsuit against solidarity activists, claiming defamation. Instead of holding the Israel franchisee to account for supporting genocide, we are now witnessing corporate bullying against activists. For both these reasons, we are calling to escalate the boycott of McDonald’s until the parent company takes action and ends the complicity of the brand.
Remember, all Israeli banks and virtually all Israeli companies are complicit to some degree in Israel’s system of occupation and apartheid, and hundreds of international corporations and banks are also deeply complicit. We focus our boycotts on a small number of companies and products for maximum impact.
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
i’ve recently come across an insightful video analysis that was reposted on tiktok, explaining the Gaza situation in depth and touching on the geopolitical and economic motivations that background it, along with the potential impact from the ethnic cleansing and the active genocide of Palestinian people by zionists. here’s a summary with some links to more-reputable news articles:
-roughly around a month ago, netanyahu declared his plan for a “new middle east,” an economic corridor stretching from India to the European continent, through the UAE, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and “israel.”
-due to the weakening of the US Dollar, this “new middle east” corridor serves as a hopeful (on their part) counter to China’s new ongoing “silk road.” it’s essentially a move for leverage on world economics, trade, and politics.
-Russia is the country with the largest proven reserves of natural gas. in 2022, Nord Stream 1 and 2 (Russia’s gas pipelines) were both blown up. sanction packages from EU ban Russian gas. no more Russian gas coming into Europe.
-Iran, the country with the second largest gas reserves, signs the Nuclear Deal in 2015-2016. the US backs out of the deal and reimpose harsh sanctions on Iran. Iran is barred from selling its gas and oil to Europe and others.
-with Russia and Iran out of the picture, “israel” (US-backed) proposes itself as a solution to EU’s gas shortages. in 2010, they find the Leviathan—a giant gas field in the middle east (Mediterranean Sea), off the coast of Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria.
-Syria initially declines offers over its gas reserves; the US now controls 1/3 of Syria and all its oil fields, and “israel” regularly bombs it’s most vital port (Latakia). another major port is in Beirut, which mysteriously exploded in 2020. both Syria and Lebanon’s maritime activity are limited, including in trade and gas exploration.
-Gaza, also having its own unexplored gas fields, has been under siege, under naval blockade since 2007. the only working port left in the coast is haifa port in “israel.” “israel” is now the only one able to explore gas and implement an economic corridor, like the proposed “new middle east.” what the US and “israel” have essentially done is killed off the competition, stole their goods, and cornered the market.
-in light of Europe’s gas shortages, to get them gas before winter, “israel” attempts to “stabilize” the region by solving “the Palestinian question”—more than displacement, they’ve resorted to ethnic cleansing and genocide. basically an acceleration of their plan.
-what Palestinian resistance groups have done in response was because they were backed into a corner. tooth and nail, life or death. it did not happen in a vacuum.
it has always been a move for natural resources; Palestine, Syria, Congo—every move for destabilization framed as intervention. it has always been greed for capital.
update:
it’s come to my attention that the video in question might have some more pro-Russian leaning stances, and so i’ve deleted the google drive link to the reposted tiktok and the link to the actual tiktok as i do not wish to platform the denial, partial or in whole, of the atrocities done to Ukrainian people. i will keep the summary up with some parts omitted because i still do think it is an insightful analysis in general and i do think the knowledge is still useful and relevant.
#peace is not the answer; liberation is the answer#resources#palestine#free palestine#free gaza#gaza strip#please look into other resources within the first and second tags in this post too
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
EVERYONE RECALLS THE SHORTAGES of toilet paper and pasta, but the early period of the pandemic was also a time of gluts. With restaurants and school cafeterias shuttered, farmers in Florida destroyed millions of pounds of tomatoes, cabbages, and green beans. After meatpacking plants began closing, farmers in Minnesota and Iowa euthanized hundreds of thousands of hogs to avoid overcrowding. Across the country, from Ohio to California, dairies poured out millions of gallons of milk and poultry farms smashed millions of eggs.
The supply chain disruptions continue. Last year, there was a rice glut, and big box stores like Walmart and Target complained of bloated inventories. There was a natural gas glut in both Europe and in India, as well as a surfeit of semiconductor chips in the tech sector. Florida cabbages, microchips, and Asian rice may not seem like they have much in common, but each of these stories represents a fundamental if disavowed aspect of capitalism: a crisis of overproduction.
All economic systems have problems of scarcity, but only capitalism also has problems of abundance. The reason is simple: the pursuit of profit above all else leads capitalism to produce too much of things that are profitable but socially destructive (oil, private health insurance, Facebook) and not enough of things that are socially beneficial but not privately profitable (low-income housing, public schools, the ecosystem of the Amazon rainforest). For over a century, from the Industrial Revolution through the Great Depression, crises of overproduction were the target of criticism from across the political spectrum—from aristocratic conservatives like Edmund Burke who feared the anarchy of markets was corroding the social order to socialist radicals like Eugene Debs who thought it generated exploitation and poverty.
But the idea of capitalism’s inherent predilection for overproduction has almost completely disappeared from economic discourse today. It seldom appears in the popular press, including in stories about producers destroying surpluses, a problem that is instead explained away by pointing to freak accidents, contingencies, and unforeseen dislocations. To be sure, many gluts of the past few years have been the result of the pandemic and the war in Ukraine. But overproduction preceded 2020 and shows no signs of going away. Revisiting historical arguments about the problem can help us better understand the interlocking crises of supply chain disruption, deliquescent financial markets, and climate change. The history of overproduction and its discontents offers a set of tools and ideas with which to consider whether “market failures” like externalities and inventory surpluses really are exceptions or are intrinsic to commercial society, whether markets ever actually do equilibrate, and whether the drive for growth is possible without continual excess and waste.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Editor's note: This report is the first in a series on “Europe’s energy transition: Balancing the trilemma” produced by the Brookings Institution in partnership with the Fundação Francisco Manuel dos Santos.
Providing a stable energy supply is often described in terms of a “trilemma”—a balance between supply security, environmental sustainability, and affordability. Of the three pillars of energy supply, security is the easiest to take for granted. Supply seems fine until it isn’t. Security of fossil fuel supply is particularly easy to ignore in countries that are striving to greatly reduce their fossil fuel consumption for climate reasons. The political focus is on building renewable energy and zero-carbon systems, and mitigating the economic, social, and political costs of transition; the thought was that the existing system would take care of itself until it was phased out. This was the case for much of Europe until two years ago.
Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, shocked Europeans into realizing that they could no longer take the security of their fossil fuel supply for granted. The assumption had been that Europe and Russia were locked into a mutually beneficial, secure relationship, since Europe needed gas and Russia had no infrastructure to sell that gas anywhere else. That belief turned out to be wrong.
When the war began, Europe was importing a variety of energy products from Russia, including crude oil and oil products, uranium products, coal, and liquefied natural gas (LNG). But the Kremlin’s sharpest energy weapon was natural gas, delivered by the state-backed gas monopolist Gazprom via pipelines and based on long-term contracts. Europe needs gas for power generation, household heating, and industrial processes.
Before the invasion, more than 40% of Europe’s imported natural gas came from Russia, its single largest supplier, delivered via four main pipelines. Some European countries relied on Russia for more than 80% of their gas supply, including Austria and Latvia. But Germany was by far Russia’s largest gas customer by volume, importing nearly twice the volume of Italy, the next largest customer. “Oil and gas combined account for 60% of primary energy,” wrote the Economist in May 2022, “and Russia has long been the biggest supply of both. On the eve of the war in Ukraine, it provided a third of Germany’s oil, around half its coal imports, and more than half its gas.”

This paper launches a project on European energy security in turbulent times by analyzing the European response to drastically reduced supplies of Russian pipeline gas. Future papers in the series will delve more deeply into specific aspects of European energy security and their policy implications.
Russia’s actions to cut off gas supply to Europe starting in May 2022 were particularly virulent because it was extremely difficult to cope with the loss of such a large volume of gas. Other regional sources of pipeline gas (e.g., from the North Sea) have been declining and key sectors of European industry (e.g., chemicals) depend on gas as their primary energy source. LNG is a potential substitute for pipeline gas, but it requires specialized infrastructure and global LNG markets were already tight, with much of the world’s supply going to Asia.
The story of Europe’s adjustment to its main supplier of natural gas turning off the taps is generally told in heroic terms: with the continent securing new supply, conserving or substituting (often with generous government subsidies for industry and/or consumers) in order to weather the storm, and throwing Russia’s weaponization of gas back in its face through declining revenues. This narrative is not false, and the scale and speed of the response would certainly have been politically unimaginable before the invasion. But the self-congratulatory tale masks the fact that there were substantial regional differences in both energy supply and response to the crisis, which will make it difficult to generate a Europe-wide political response in the future.

Even more importantly, the decoupling is by no means complete. Overall, in 2023, Europe still imported 14.8% of its total gas supply from Russia, with 8.7% arriving via pipelines (25.1 billion cubic meters or bcm) and 6.1% as LNG (17.8 bcm). (For comparison, during the first quarter of 2021, 47% of Europe’s total gas supply came from Russia, 43% via pipeline and 4% as LNG.)This means that the handful of member states that have not been able to or have not chosen to reduce their dependency remain highly vulnerable to Russia’s weaponization of energy imports.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
ESSEN, Germany (AP) — For most of this century, Germany racked up one economic success after another, dominating global markets for high-end products like luxury cars and industrial machinery, selling so much to the rest of the world that half the economy ran on exports.
Jobs were plentiful, the government's financial coffers grew as other European countries drowned in debt, and books were written about what other countries could learn from Germany.
No longer. Now, Germany is the world’s worst-performing major developed economy, with both the International Monetary Fund and European Union expecting it to shrink this year.
It follows Russia's invasion of Ukraine and the loss of Moscow's cheap natural gas — an unprecedented shock to Germany’s energy-intensive industries, long the manufacturing powerhouse of Europe.
The sudden underperformance by Europe's largest economy has set off a wave of criticism, handwringing and debate about the way forward.
Germany risks “deindustrialization” as high energy costs and government inaction on other chronic problems threaten to send new factories and high-paying jobs elsewhere, said Christian Kullmann, CEO of major German chemical company Evonik Industries AG.
From his 21st-floor office in the west German town of Essen, Kullmann points out the symbols of earlier success across the historic Ruhr Valley industrial region: smokestacks from metal plants, giant heaps of waste from now-shuttered coal mines, a massive BP oil refinery and Evonik's sprawling chemical production facility.
These days, the former mining region, where coal dust once blackened hanging laundry, is a symbol of the energy transition, dotted with wind turbines and green space.
The loss of cheap Russian natural gas needed to power factories “painfully damaged the business model of the German economy,” Kullmann told The Associated Press. “We’re in a situation where we’re being strongly affected — damaged — by external factors.”
After Russia cut off most of its gas to the European Union, spurring an energy crisis in the 27-nation bloc that had sourced 40% of the fuel from Moscow, the German government asked Evonik to keep its 1960s coal-fired power plant running a few months longer.
The company is shifting away from the plant — whose 40-story smokestack fuels production of plastics and other goods — to two gas-fired generators that can later run on hydrogen amid plans to become carbon neutral by 2030.
One hotly debated solution: a government-funded cap on industrial electricity prices to get the economy through the renewable energy transition.
The proposal from Vice Chancellor Robert Habeck of the Greens Party has faced resistance from Chancellor Olaf Scholz, a Social Democrat, and pro-business coalition partner the Free Democrats. Environmentalists say it would only prolong reliance on fossil fuels.
Kullmann is for it: “It was mistaken political decisions that primarily developed and influenced these high energy costs. And it can’t now be that German industry, German workers should be stuck with the bill.”
The price of gas is roughly double what it was in 2021, hurting companies that need it to keep glass or metal red-hot and molten 24 hours a day to make glass, paper and metal coatings used in buildings and cars.
A second blow came as key trade partner China experiences a slowdown after several decades of strong economic growth.
These outside shocks have exposed cracks in Germany's foundation that were ignored during years of success, including lagging use of digital technology in government and business and a lengthy process to get badly needed renewable energy projects approved.
Other dawning realizations: The money that the government readily had on hand came in part because of delays in investing in roads, the rail network and high-speed internet in rural areas. A 2011 decision to shut down Germany's remaining nuclear power plants has been questioned amid worries about electricity prices and shortages. Companies face a severe shortage of skilled labor, with job openings hitting a record of just under 2 million.
And relying on Russia to reliably supply gas through the Nord Stream pipelines under the Baltic Sea — built under former Chancellor Angela Merkel and since shut off and damaged amid the war — was belatedly conceded by the government to have been a mistake.
Now, clean energy projects are slowed by extensive bureaucracy and not-in-my-backyard resistance. Spacing limits from homes keep annual construction of wind turbines in single digits in the southern Bavarian region.
A 10 billion-euro ($10.68 billion) electrical line bringing wind power from the breezier north to industry in the south has faced costly delays from political resistance to unsightly above-ground towers. Burying the line means completion in 2028 instead of 2022.
Massive clean energy subsidies that the Biden administration is offering to companies investing in the U.S. have evoked envy and alarm that Germany is being left behind.
“We’re seeing a worldwide competition by national governments for the most attractive future technologies — attractive meaning the most profitable, the ones that strengthen growth,” Kullmann said.
He cited Evonik’s decision to build a $220 million production facility for lipids — key ingredients in COVID-19 vaccines — in Lafayette, Indiana. Rapid approvals and up to $150 million in U.S. subsidies made a difference after German officials evinced little interest, he said.
“I'd like to see a little more of that pragmatism ... in Brussels and Berlin,” Kullmann said.
In the meantime, energy-intensive companies are looking to cope with the price shock.
Drewsen Spezialpapiere, which makes passport and stamp paper as well as paper straws that don't de-fizz soft drinks, bought three wind turbines near its mill in northern Germany to cover about a quarter of its external electricity demand as it moves away from natural gas.
Specialty glass company Schott AG, which makes products ranging from stovetops to vaccine bottles to the 39-meter (128-foot) mirror for the Extremely Large Telescope astronomical observatory in Chile, has experimented with substituting emissions-free hydrogen for gas at the plant where it produces glass in tanks as hot as 1,700 degrees Celsius.
It worked — but only on a small scale, with hydrogen supplied by truck. Mass quantities of hydrogen produced with renewable electricity and delivered by pipeline would be needed and don't exist yet.
Scholz has called for the energy transition to take on the “Germany tempo,” the same urgency used to set up four floating natural gas terminals in months to replace lost Russian gas. The liquefied natural gas that comes to the terminals by ship from the U.S., Qatar and elsewhere is much more expensive than Russian pipeline supplies, but the effort showed what Germany can do when it has to.
However, squabbling among the coalition government over the energy price cap and a law barring new gas furnaces has exasperated business leaders.
Evonik's Kullmann dismissed a recent package of government proposals, including tax breaks for investment and a law aimed at reducing bureaucracy, as “a Band-Aid.”
Germany grew complacent during a “golden decade” of economic growth in 2010-2020 based on reforms under Chancellor Gerhard Schroeder in 2003-2005 that lowered labor costs and increased competitiveness, says Holger Schmieding, chief economist at Berenberg bank.
“The perception of Germany's underlying strength may also have contributed to the misguided decisions to exit nuclear energy, ban fracking for natural gas and bet on ample natural gas supplies from Russia,” he said. “Germany is paying the price for its energy policies.”
Schmieding, who once dubbed Germany “the sick man of Europe” in an influential 1998 analysis, thinks that label would be overdone today, considering its low unemployment and strong government finances. That gives Germany room to act — but also lowers the pressure to make changes.
The most important immediate step, Schmieding said, would be to end uncertainty over energy prices, through a price cap to help not just large companies, but smaller ones as well.
Whatever policies are chosen, “it would already be a great help if the government could agree on them fast so that companies know what they are up to and can plan accordingly instead of delaying investment decisions," he said.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sustainable Power Generation Drives Floating Power Plant Market
Triton Market Research presents the Global Floating Power Plant Market report segmented by capacity (0 MW- 5 MW, 5.1 MW- 20 MW, 20 MW – 100 MW, 100.1 MW – 250 MW, above 250 MW), and source (non-renewable power source, renewable power source), and Regional Outlook (Latin America, Middle East and Africa, North America, Asia-Pacific, Europe).

The report further includes the Market Summary, Industry Outlook, Impact Analysis, Porter's Five Forces Analysis, Market Maturity Analysis, Industry Components, Regulatory Framework, Key Market Strategies, Drivers, Challenges, Opportunities, Analyst Perspective, Competitive Landscape, Research Methodology & Scope, Global Market Size, Forecasts & Analysis (2023-2028).
Triton's report suggests that the global market for floating power plant is set to advance with a CAGR of 10.74% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2028.
Request Free Sample Report:
Floating power plants are innovative power generation units on floating platforms on water bodies. They serve as primary or backup power sources for specified facilities, utilizing renewable energy sources (solar, wind, etc.) and non-renewable (diesel, natural gas, etc.). These plants offer the advantage of mobility, making them ideal for temporary power generation to tackle local energy shortages.
The increasing popularity of offshore wind projects is due to several market factors, such as the growing demand for clean and sustainable energy sources and advances in offshore wind technology. Also, supportive government policies and the urgent need to combat climate change by reducing carbon emissions further elevate the demand for floating power plants.
Furthermore, the popularity of floating power plants based on IC offers opportunities to the floating power plant market. These innovative power generation systems offer flexibility, scalability, and rapid deployment, catering to remote areas and serving as backup solutions in grid instability situations.
However, challenges like technical complexities, high costs associated with logistics and accessibility, and a shortage of skilled workers for solar panel installation limit the floating power plant market's expansion.
Over the forecast period, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to register the fastest growth. A growing population and increasing industrialization fuel growth prospects. The region is home to a rapidly growing population, which in turn drives the need for expanded power generation capacity. Furthermore, Asia-Pacific is experiencing significant economic growth, with many countries emerging as major global players. This economic expansion is accompanied by a surge in industrial activities and the establishment of new manufacturing units, creating a heightened demand for electricity to support these sectors. Floating power plants present a viable solution to meet this demand, especially in areas with limited land availability.
Floating Power Plant AS, Upsolar Group Co Ltd, SeaTwirl AB, Caterpillar Inc, Mitsubishi Corporation, Wartsila Corporation, Siemens AG, MAN Energy Solutions SE, Kyocera Corporation, and Vikram Solar Limited are prominent companies in the floating power plant market.
Due to its complexity, the floating power plant market poses a moderate threat of new entrants. Capital-intensive development and deployment, along with the need for specialized expertise, act as barriers. Additionally, a skilled workforce in offshore engineering and renewable energy is crucial. Nevertheless, government policies supporting renewable energy adoption, such as feed-in tariffs, subsidies, and favorable regulations, are vital in attracting new players by mitigating financial risks and offering long-term incentives.
Contact Us:
Phone: +44 7441 911839
Website: https://www.tritonmarketresearch.com/
#Floating Power Plant Market#Floating Power Plant#energy power & utilities#power industry#triton market research#market research reports
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
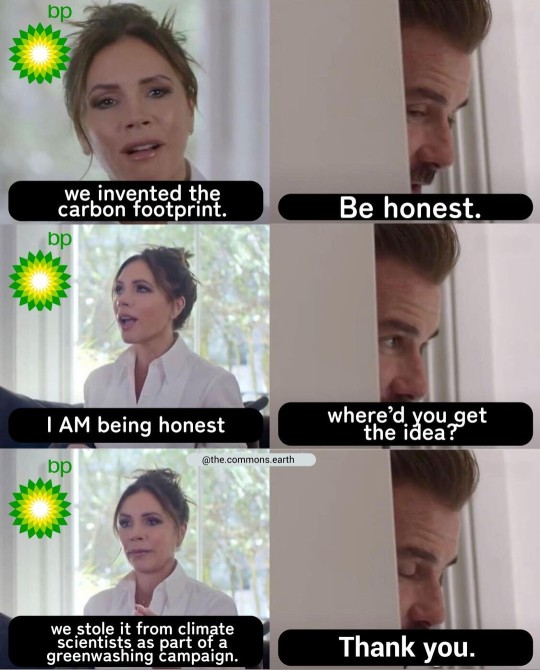
Okay, I have kind of a nagging comment about the first one about Shell.
Shell is a big, multinational company, and it exists only because there are so many people who want to buy petroleum — particularly gasoline. If the demand for gas went away, Shell would do the same. It makes more sense, then, to consider how much Shell (and other gas companies) increase the share of emissions per average customer than it does to talk about the aggregate — the bigger a given gas company gets, the more emissions it will have, and they’re mostly so huge that the numbers are naturally going to be gigantic.
Now, this is actually a very messy calculation to make without doing a lot more research work than I am willing to put in, so please understand up-front that although I’ve looked up some numbers, all of which turned out to be from Statista.com, there are a lot of assumptions being made here which might be false. Without thinking too hard about it for more subtle potential nitpicks, I’m assuming that:
the number of people who buy gasoline in the US is approximately the number of vehicles in the US (that is, there may be households with multiple cars, but households with multiple cars generally have one gas-buyer per vehicle; the number of individuals who personally own multiple vehicles is small) — or, in other words, the number of gas buyers is approximately the number of vehicles
it is reasonable to equate market share of gas sales in the US directly to percentage of gas buyers in the US
the amount of profit per gas buyer in the US is equivalent to the amount of profit per gas buyer in the rest of the world
the “77 million years” figure is based on the global average, not the US average, since Shell is a multinational company
the “77 million years” figure is not already calculated into the average customer’s carbon emissions as quoted (I’ve always kind of wondered about that — the carbon footprint calculators I’ve seen always ask about your gas and manufactured goods consumption, which would mean that those carbon footprint quotations assume corporate emissions are effectively 0 because business emissions are all rolled into the figures for their customers. But we’ll assume here that this is not the case.)
In the last decade Shell actually usually made more profit in both Asia and Europe, separately, than in the Americas. (The overwhelming majority of its profit in the Americas is from the US, but even adding in the rest they still usually get more from Asia and Europe — and even in years where the Americas aren’t in third place, they still don’t go far above a third of the total). Let’s simplify and say that the Americas make up a third of their profits and the US is 30%. (These are both overestimates, meaning they will tend to reduce the estimated number of customers.)
Shell had, in 2019, a 12.5% share of gas sales in the US. (No need to round or anything, that’s directly the number Statista.com said.)
In 2019, there were over 276 million registered vehicles in the US; we’ll round down to 250 million to account for public vehicles — there are buses in the US — and those people who personally own multiple vehicles.
So, out of an estimated 250 million gasoline buyers in the US in 2019, Shell had a 12.5% share, which is 31.25 million; call it 30 million. We are explicitly assuming that Shell makes the same profit per customer everywhere in the world and the US generally makes up 30% of its profits, so each percentage of its profit is 1 million people, and therefore worldwide it has 100 million customers. (I swear I didn’t pick any of the rounded values with this in mind in advance — the numbers just worked out that way.) (I suspect that this number is far too low, but it’s a loose estimate to demonstrate my point so that isn’t really all that important.)
Now, if Shell is generating enough emissions that an average person would have to live 77 million years, but it has 100 million customers, then from another perspective it is raising the emissions of its customers by slightly over ¾ — if the average person is personally responsible for annual carbon emissions of 4 tons (the global average; much higher for developed nations), then by being a Shell customer, they cause an additional 3 tons of emissions for which they are not considered personally responsible. That’s pretty terrible, but I’m not 100% convinced that it is possible to have fossil fuel usage without figures that are just as appalling — in which case the problem isn’t that Shell is specifically Shell, it’s that gas companies exist at all. It would be interesting to patch up the estimated value above to correct for the assumptions and get more accurate values, and then to do the calculations for other gas companies and see whether Shell really is more egregious than the others; if that were the case, it would immediately justify worldwide consumer boycotts — you could immediately lower your carbon footprint, without even cutting your gas consumption, by simply not using Shell gas.
(If the average emissions figure per person includes all the emissions from consumerism, as I mentioned that carbon footprint calculators tend to do, then it means — with this estimate, at least — that ¾ of the average Shell customer’s annual emissions are purely from their gas purchases from Shell, and that’s even more appalling!)
feel free to share the truth...




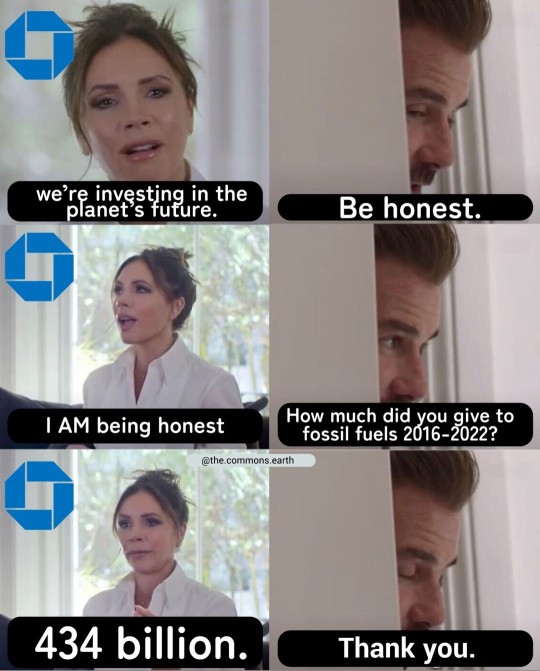
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Economist magazine coined the term “Dutch disease” back in 1977:
The Economist coined the term in 1977 to describe the woes of the Dutch economy. Large gas reserves had been discovered in 1959. Dutch exports soared. But, we noticed, there was a contrast between “external health and internal ailments”. From 1970 to 1977 unemployment increased from 1.1% to 5.1%. Corporate investment was tumbling. We explained the puzzle by pointing to the high value of the guilder, then the Dutch currency. Gas exports had led to an influx of foreign currency, which increased demand for the guilder and thus made it stronger. That made other parts of the economy less competitive in international markets. That was not the only problem. Gas extraction was (and is) a relatively capital-intensive business, which generated few jobs. And in an attempt to stop the guilder from appreciating too fast, the Dutch kept interest rates low. That prompted investment to rush out of the country, crimping future economic potential.
(This is from a 2014 article discussing whether Russia suffers from the Dutch disease.)
That description doesn’t really give us very much to go on. For instance, the following graph in a paper by Olivier Blanchard shows that unemployment soared throughout Western Europe during the 1970s:

In that case, why should we conclude that the Netherland’s employment problems during the 1970s had anything to do with a discovery of natural gas reserves? Furthermore, the most effective way to fix inadequate employment is with sound monetary policy and supply-side reforms to make labor markets more flexible.
It’s also odd to name an economic disease after one of the most successful countries in global economic history. This ranking shows the Netherlands to be number 15 on a global ranking of GDP per capita (PPP), but most of the richer countries are small oil exporters or even smaller tax havens. It’s actually the second richest country in the world with a population of more than 10 million, trailing only the USA.
You might argue that while the Netherlands is rich, perhaps the gas discoveries hurt their non-energy exports. But the Netherlands is also a phenomenally successful exporter of all sorts of products:

Being #4 in a global list of exporters is particularly impressive when you consider than the other countries in the top five all have vastly larger populations. Other developed countries with natural resource bonanzas—such as Australia and Norway—also seem to have done well in recent decades. So what’s the problem?
Here are two possibilities:
1. Creative destruction: An energy boom causes the currency to appreciate. This moves resources from manufacturing to energy and services. Manufacturing jobs are somehow special, and hence this sort of economic restructuring is harmful.
2. Corruption: And energy boom leads to corruption, as elites compete for economic “rents”.
If the first concern is a genuine problem (and I’m skeptical) the resource producer can prevent excessive currency appreciation by boosting national saving, as Norway has done with its sovereign wealth fund.
A recent article in The Economist discussed the second concern:
Uruguay has some structural advantages. Spanish colonialists called it the “land of no profit”, as it had neither precious metals nor cheap indigenous labour. These seeming flaws actually turned out to be strengths, however. A lack of easy rents helped ward off oligarchs. A fairly homogenous population prevented the stark racial inequality of places like Brazil.
I see no evidence that natural resource booms have caused countries such as Norway, the Netherlands or Australia to become more corrupt than otherwise. While you can find examples of major oil producers with a high level of corruption, such as Nigeria, it’s not clear to me that the public sector in those countries would be less corrupt without the oil.
0 notes
Text
Industrial Furnace Market – Examining the Key Furnace Types
Triton Market Research estimates that the global industrial furnace market is likely to grow with a CAGR of 4.84% in the forecast period 2025-2032. Read more.
An industrial furnace is a high-temperature thermal processing system crucial for manufacturing in a wide range of industries like automotive, aerospace, metal production, ceramics, agriculture, and defense. Their precise temperature control and design are essential for ensuring high-quality production outcomes.

Get the Latest Insights on the Industrial Furnace Market and Get a Sample Report Here
Key Industrial Furnace Types:
1. Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces use electrical energy to generate heat, offering precise temperature control and high efficiency. They are known for their low environmental impact compared to other furnace types, as they produce fewer emissions. Commonly used in industries requiring high precision, electric furnaces are favored for their reliability and energy savings.
2. Natural Gas-Fired Furnaces
Natural gas-fired furnaces utilize natural gas as a fuel source to generate heat, making them an economical and efficient choice for many industrial processes. These furnaces are widely used in metal production, ceramics, and chemical manufacturing due to their ability to reach high temperatures while offering relatively low operational costs and a cleaner combustion process.
3. Petroleum Coke and Coal-Fired Furnaces
Petroleum coke and coal-fired furnaces burn petroleum coke or coal to produce heat for industrial applications. These furnaces are typically used in industries with high thermal energy demands, such as steel and cement manufacturing. Despite their lower energy efficiency and higher emissions, they remain popular due to the lower cost of fuel.
Asia-Pacific to be the Fastest Growing Region in the Industrial Furnace Market
With the region accounting for roughly 45% of global Manufacturing Value Added, the demand for industrial furnaces remains robust. Countries such as China and India are making substantial investments in steel production, automotive manufacturing, and metal processing—sectors that depend heavily on advanced industrial furnaces.
Key Contenders in the Industrial Furnace Market:
Advance Furnace Technologies, Carbolite Gero Ltd, Ebner Group, Thermal Product Solutions, Andritz AG, Gasbarre Products, Inc, Epcon Industrial Systems LP, Schmidt + Clemens Gmbh + Co Kg, Seco/Warwick Inc, Stericox India Private Limited, Inductotherm Europe Ltd, International Thermal Systems, Mahler Gmbh, Grupo Nutec, and Thermcraft Inc.
#IndustrialFurnaceMarket#IndustrialFurnace#Energy#Power#Utilities#TritonMarketResearch#MarketReport#ResearchReport
0 notes
Text
Oil and Gas Industry’s Growing Dependence on the Coal Gasification Market

Coal Gasification Market: Growth, Trends, and Future Growth 2025
Introduction
The Coal Gasification Market has been witnessing substantial growth due to increasing energy demands and the need for cleaner fuel alternatives. Coal gasification is an advanced technology that converts coal into synthetic gas (syngas), offering a more efficient and environmentally friendly solution for energy production. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the Coal Gasification Market Analysis to offer a comprehensive outlook on the industry.
Request Sample PDF Copy: https://wemarketresearch.com/reports/request-free-sample-pdf/coal-gasification-market/1624
Coal Gasification Market Size and Share
The Coal Gasification Market Size has expanded significantly, driven by increasing industrial applications and government initiatives promoting cleaner energy sources. In recent years, the adoption of coal gasification technology has surged, leading to a notable increase in the Coal Gasification Market Share among key players in the energy sector. Major companies are investing in research and development to enhance efficiency and reduce carbon emissions, further solidifying their market positions.
Market Value and Growth Prospects
The Coal Gasification Market Value is anticipated to grow steadily over the forecast period, driven by its cost-effective nature and potential to produce cleaner energy. The rising demand for syngas in various industries, including chemical production, power generation, and liquid fuels, is fueling Coal Gasification Market Growth. Additionally, the increasing focus on reducing dependency on natural gas and crude oil has encouraged governments and enterprises to invest in coal gasification technologies.
Key Trends in the Coal Gasification Market
Several Coal Gasification Market Trends are shaping the industry:
Technological Advancements: Ongoing research and innovations in gasification processes have improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Environmental Regulations: Stringent regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions are pushing industries to adopt coal gasification as a viable alternative.
Investment in Clean Energy: Governments and private sector players are heavily investing in clean energy technologies, boosting the coal gasification industry.
Integration with Renewable Energy: Hybrid models combining coal gasification with renewable energy sources are gaining traction, enhancing overall sustainability.
Market Potential and Future Forecast
The Coal Gasification Market Potential remains high, with expanding applications in various sectors. The ability to convert low-grade coal into valuable syngas is attracting interest from industries seeking alternative energy solutions. The market's future looks promising, as key players focus on scaling up operations and improving technological efficiencies.
The Coal Gasification Market Forecast suggests a steady rise in adoption, particularly in emerging economies with abundant coal reserves. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is expected to dominate the market due to increasing industrialization and energy consumption. Additionally, North America and Europe are investing in clean coal technologies to meet stringent environmental standards.
In-depth Market Analysis
A thorough Coal Gasification Market Analysis reveals that the market is highly competitive, with several established players and new entrants striving for dominance. Companies are actively engaging in strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions to strengthen their foothold.
Moreover, advancements in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies are expected to complement coal gasification, making it an even more viable option for sustainable energy production. The market is also witnessing significant government support in the form of subsidies and policy incentives, further propelling growth.
Related Report:
Nickel Metal Hydride Battery Market
5G IoT Market
Conclusion
The Coal Gasification Market is poised for significant expansion, driven by increasing demand for cleaner energy solutions, technological advancements, and favorable government policies. As the industry continues to evolve, stakeholders must focus on innovation, sustainability, and regulatory compliance to maximize market opportunities. With strong growth prospects, the coal gasification sector is set to play a crucial role in the global energy landscape in the coming years.
#Coal Gasification Market#Coal Gasification Market Size#Coal Gasification Market Share#Coal Gasification Market Price#Coal Gasification Market Growth#Coal Gasification Market Trends#Coal Gasification Market Potential#Coal Gasification Market Forecast#Coal Gasification Market Analysis
0 notes
Text
Norway should cede its war windfall to Ukraine

Norway’s government has effectively become a war profiteer, we argued in a commentary in December. It is an opinion shared by a number of European politicians, and by European and Norwegian media. But rather than paying attention, Norway’s government is getting defensive.
The basic facts are not up for debate. After the outbreak of the Russo-Ukrainian War caused natural gas prices to rise sharply in Europe, Norway reaped windfall profits totaling some 108 billion euros ($113 billion), according to the Norwegian Finance Ministry. That is more than the value of all military and civilian support Ukraine has received from the United States and Germany combined from when the war started through October 2024. It is roughly one-third of the value of the Russian central-bank assets that are currently frozen in the West (and which Western governments have extensively debated channeling to Ukraine for defense and reconstruction).
But Norway has kept its windfall for itself, providing a measly 3 billion euros ($3.1 billion) in aid to Ukraine in its 2025 budget, only slightly up from the previous year. This approach is simply wrong: Norway must transfer its recent “super-profits,” excess profits above the normal level, in full, directly to Ukraine. Unfortunately, Norwegian Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Støre and Norwegian Finance Minister Trygve Slagsvold Vedum seem more interested in justifying their decision not to do so than in helping Ukraine, Europe, or even future Norwegians.
“Norway must transfer its recent ‘super-profits,’ excess profits above the normal level, in full, directly to Ukraine.”
Støre and Vedum contend that the windfall gains were a normal result of the myriad market forces that determine gas prices. But this argument is disingenuous. While it is true that many factors shape energy prices, Norway’s excess profits overwhelmingly reflect one: in 2022-23, it had in Europe a captive market for its natural-gas exports. This was a direct result of the Ukraine war: Russia had cut its natural-gas supplies to Europe, but European gas importers had not yet managed to build liquefied natural gas terminals to offset the loss.
Støre and Vedum do not stop at dismissing Norway’s war profits as good fortune; they claim that their government, and the oil companies operating in Norway, did our European neighbors a favor by stepping up gas supplies when Russian deliveries ceased. Europe should be thanking us, Vedum says. This “Good Samaritan” narrative smacks of hypocrisy, especially as Norway, while pocketing its lucky gains from the spike in gas prices, sends a pittance to the Ukrainians fighting and dying for their country’s survival and Europe’s security.

Norwegian Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Støre speaks to the press after the Think Tank Agenda event at the University Aula in Oslo, Norway, on Jan. 28, 2025. (Ole Berg-Rusten / NTB / AFP via Getty Images)
In fact, from the perspective of European gas consumers, the elevated gas prices were equivalent to a Norwegian “war tax” on them. The increased energy costs strained the budgets of households and companies, thereby reducing European governments’ room to raise taxes for supporting Ukraine’s war effort. And yet, many of these countries have still managed to provide far more support to Ukraine, as a share of GDP, than Norway has.
Støre and Vedum say that, rather than use its windfall as a “political instrument,” the excess profits should go directly into the Government Pension Fund Global, Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, where they will be preserved for future generations of Norwegians. This position aligns with Norway’s longstanding commitment to safeguarding its long-term fiscal sustainability, exemplified by a rule that no more than 3% of the fund’s value can be transferred to the government budget each year.
But Støre and Vedum’s position is short-sighted in the current context. After all, what could harm future generations of Norwegians more than the failure to preserve democracy, freedom, and the rule of law in Europe?
In any case, the fiscal rule was created to prevent domestic macroeconomic problems (such as exchange-rate appreciation and excessive inflation), which would not arise if the funds were transferred directly to Ukraine. The leaders responsible for establishing it — including former Norwegian Prime Minister and former NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg — could not possibly have imagined that Norway’s government would one day use it to justify holding on to wartime rents.
Norway did provide critical energy supplies to Europe in a desperate moment. But in a purely fiscal sense, one can argue that the country did more to support Russia, as its captive market for gas (which it did nothing to create) limited its neighbors’ ability to raise wartime taxes, while Norway refrained from sending much aid to Ukraine. Meanwhile, Norway has enriched itself immensely, through the returns on the government’s direct investments in oil and gas fields, dividends from its ownership share in its parastatal oil company Equinor, and tax revenues from oil companies, which are subject to a 78% marginal rate on their profits.
Refusing to use this war windfall to support Ukraine’s defense and reconstruction reflects a myopic perspective that Norway’s government would do well to abandon. Despite our reluctance to join the European Union, we Norwegians are part of – and dependent on – the European community. Rather than focusing exclusively on narrow domestic interests, Norway’s government must start considering the well-being of all of Europe. Growing threats to liberal democracy – coming not only from our big neighbor to the East, but also from our big ally across the Atlantic – makes this shift all the more urgent.
Editor’s Note: Copyright, Project Syndicate. This article was published by Project Syndicate on Jan. 30, 2025, and has been republished by the Kyiv Independent with permission. The opinions expressed in the op-ed section are those of the authors and do not purport to reflect the views of the Kyiv Independent.
Submit an Opinion
Europe’s inaction on undersea infrastructure is a security time bomb
Following Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022, concerns over the security of energy and communication infrastructure in the Baltic Sea intensified. Initially, focus was placed on the threat of hybrid attacks from Russia. However, it became evident that Russian military vessels and so-ca…

The Kyiv IndependentArvydas Anušauskas

0 notes
Text
Global Bio-LNG Market Dynamics: Supply, Demand, and Technological Innovations
The global bio-LNG market size is expected to reach USD 19.78 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 41.1% from 2024 to 2030, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc. As concerns about climate change and air pollution continue to mount, there is a growing demand for clean and sustainable energy sources. Bio-LNG is considered a low-carbon fuel that can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90% compared to traditional fossil fuels. This has increased interest in the adoption of Bio-LNG.
The transportation fuel segment is expected to witness substantial growth over the next few years, due to the growing demand from the shipping industry. Shipping companies around the world are looking for alternative fuels to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and are investing in technologies such as Bio-LNG fueled vessels. This is expected to advance the market during the forecast period.
Organic household waste is one of the significant sources of feedstock for the production of bio-LNG. Organic household waste includes food waste, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials. This waste is rich in organic content and can be efficiently converted into renewable energy sources such as biogas and subsequently upgraded to bio-LNG.
The demand for bio-LNG in the power generation segment is expected to grow substantially from 2023 to 2030. Bio-LNG can be used in existing natural gas infrastructure, making it a flexible fuel source that can be utilized in a variety of applications. It can be used in power plants to generate electricity at a lower cost, as it does not incur infrastructure development costs.
Asia Pacific has been witnessing significant growth in product demand, on account of the increasing number of production facilities, as well as R&D centers in major countries like China, Australia, Japan, India, and South Korea. The inception of new facilities and the expansion of existing Bio-LNG facilities owing to favorable government policies and foreign direct investments are likely to cater to the growth of the demand for Bio-LNG in the region.
Bio-LNG Market Report Highlights
In terms of revenue, organic household waste segment led the market for bio-LNG in 2023, accounting for a share of 40.40%. Growth of this segment can be attributed to incentives and tax rebates offered by governments of different countries to promote adoption of renewable energyand conversion of organic waste to energy.
In terms of revenue, the transportation fuel segment led bio-LNG market in 2023, accounting for a revenue share of 55.55%. Demand for bio-LNG has been growing in transportation fuel and power generation segments, owing to low pollution caused by fuel.
Europe accounted for largest regional revenue share of 61.41% in 2023. Countries such as Germany, UK, Spain, and France are expected to witness high growth rates in industry, owing to rising product demand from transportation and power generation application sectors, boosting market growth during forecast period.
Asia Pacific is expected to witness a significant CAGR over the forecast period, owing to presence of large emerging countries such as China and India.
Bio-LNG Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global bio-LNG market report based on application, source type, and region:
Bio-LNG Source Type Outlook (Volume, Tons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Organic household waste
Organic industrial waste
Municipal waste
Bio-LNG Application Outlook (Volume, Tons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
Transportation Fuel
Power Generation
Others
Bio-LNG Regional Outlook (Volume, Tons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
North America
US
Canada
Mexico
Europe
Germany
UK
Spain
Italy
France
Netherlands
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
Australia
South Korea
Central and South America
Brazil
Argentina
Middle East and Africa
UAE
Saudi Arabia
Key Players
Linde plc
Nordsol
Flogas Britain Ltd.
MEGA a.s.
AXEGAZ T&T
TotalEnergies
Titan LNG
DBG Group B.V.
BoxLNG Pvt. Ltd.
Shell Plc
Order a free sample PDF of the Bio-LNG Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
0 notes
Text
Green Ammonia Market: A Sustainable Revolution in the Global Energy Landscape
The green ammonia market is gaining significant traction as the world transitions towards cleaner energy alternatives. As a key component of fertilizers and an emerging player in the energy sector, green ammonia is poised to revolutionize industries by offering sustainable solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
What is Green Ammonia?
Green ammonia is produced using renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydropower, through a carbon-neutral process. Unlike traditional ammonia, which relies on fossil fuels and emits significant CO₂, green ammonia production leverages electrolysis to separate water into hydrogen and oxygen, followed by nitrogen fixation, resulting in zero carbon emissions.
Market Drivers
Global Shift Towards SustainabilityGovernments and corporations worldwide are focusing on decarbonization, making green ammonia an attractive solution in the push for net-zero emissions.
Demand in Fertilizer ProductionThe agricultural industry is the largest consumer of ammonia, and adopting green ammonia helps reduce the sector’s carbon footprint.
Emerging Role in Energy Storage and TransportationGreen ammonia is being explored as a hydrogen carrier and a sustainable fuel for shipping and power generation, offering efficient energy storage and long-term transport solutions.
Policy and IncentivesGovernments are introducing subsidies and tax benefits to encourage investment in green ammonia production facilities, further accelerating market growth.
Global Market Outlook
The green ammonia market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 50% between 2023 and 2030, reaching a valuation of approximately $10 billion by 2030. Key growth regions include:
Europe: A leader in renewable energy adoption, Europe is heavily investing in green ammonia production to meet its climate goals.
Asia-Pacific: The region's robust agricultural sector and growing energy needs make it a key market for green ammonia.
North America: The U.S. and Canada are advancing pilot projects to integrate green ammonia into energy systems and export markets.
Challenges in the Green Ammonia Market
High Production CostsThe reliance on renewable energy and advanced technology makes green ammonia production more expensive than traditional methods.
Infrastructure DevelopmentScaling production and building storage and transportation infrastructure remain significant hurdles.
Energy EfficiencyThe energy-intensive nature of green ammonia production requires further innovation to improve efficiency and scalability.
Key Players and Innovations
Leading companies like Yara International, CF Industries, Siemens Energy, and Air Products are investing in green ammonia projects and research. Innovations in electrolysis technology, green hydrogen production, and modular plants are accelerating market adoption.
Applications of Green Ammonia
Agriculture: Sustainable fertilizer production for decarbonizing the agricultural value chain.
Energy: A hydrogen carrier and fuel for power generation, shipping, and transportation.
Industrial Processes: Reducing emissions in ammonia-dependent manufacturing industries.
Future Prospects
The green ammonia market holds immense potential as nations aim to combat climate change and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Advancements in production technology, increased investment, and supportive government policies will play critical roles in shaping the market's trajectory.
Conclusion
Green ammonia represents a sustainable solution with far-reaching implications for agriculture, energy, and industry. While challenges persist, ongoing technological innovations and global policy support will ensure its growth in the coming years.
Interested in learning more about the green ammonia market or exploring sustainable solutions for your business? Contact us today for insights and partnerships!
0 notes
Text
Small Internal Combustion Engine Market Trends and Forecast 2031
Small internal combustion engines have been the bedrock of a dozen industries for the past few decades. A small engine of any size between lawnmowers and generators pushes to serve some incredibly varied applications. Yet in recent times, that market has dramatically changed due to the rapidity of technological advances, environmental regulations, and altered consumer preferences. Taking into account these changes, this report investigates in great detail the current state of the small ICE market, analyzing trends, challenges, and growth opportunities.
The small internal combustion engine market size is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.6% in 2023–2031 and reach US$ 6.5 billion by 2031 from US$ 4.5 billion in 2023.
Market Overview
The small ICE market can be broadly classified based on application:
Consumer: Lawn and garden equipment, power tools, generators, marine engines
Commercial: Construction equipment, agricultural machinery, material handling equipment.
Industrial: Pumps, compressors, generators
There is demand for small ICEs even though electric alternatives are becoming increasingly popular for some segments. Drivers of the demand include:
Reliability: ICEs are rugged and durable for demanding applications.
Performance: ICEs usually offer better power and torque for demanding applications as compared to electric motors.
Affordability: Although the upfront cost of an ICE can be very low when compared to an electric motor, however, the actual cost of ownership, including fuel and maintenance over the long run, can differ substantially.
Small Internal Combustion Engine Market Segments Covered
By Fuel Type
CNG
LPG
LNG
By Power-Output
1-5 kW
6-10 kW
11-20 kW
By End User
Power Generation
Manufacturing
Oil & Gas
Transportation
Others
By Region
North America
Europe
Asia-Pacific
South and Central America
Middle East and Africa
Small Internal Combustion Engine Market Trends
Technological Advancements:
Emissions-reducing Reducing Technologies are being heavily invested in by manufacturers. Such technologies include catalytic converters, particulate filters, and fuel injection systems.
Improvement in Efficiency: It is found that with improved design of engines and materials, the same quantity of fuel is generated with reduced costs of running.
Hybrid and Electric Integration: Some companies have started small ICE applications with hybrid and electric power trains by integrating the positives from both technologies.
Environmental Regulations
Strict Emission Regulations: Most countries' governments are in the process of enacting rigid standards of emission, which is forcing the manufacturers to embrace clean technologies.
Alternative Fuels: Natural gas and bio-fuels could be of increasing attraction to minimize carbon emission.
Consumer Shifts:
Sustainability: The awareness of green products, contributing towards low emissions and improved fuel economy, drives the market.
Noise: Noise pollution as a result of residential locations makes consumers opt for quieter engines.
Globalization and Competition
Global Market: The small market of ICE is highly competitive, and the market share is being captured by manufacturers belonging to various regions.
Comps Pressure: Because of extremely high competition, prices are slowly on a decline, and the manufacturers are cornered into cost-cutting and efficiency.
Small Internal Combustion Engine Market Key Players
Caterpillar Inc
Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
Liebherr
Yanmar Holdings Co Ltd
Cummins Inc
Wartsila Corporation
Rolls Royce Holdings Plc
Generac Power Systems Inc
Challenges and Opportunities
Electrical Competitions: Some breakthroughs in electric vehicles and machines imposed some heavy pressure on the small ICE market.
Fluctuation of Raw Materials Cost: The raw material cost, including oil and metals, may go up at times, which may have an impact on the cost incurred during manufacturing and profitability as well.
It is getting quite expensive and time-consuming to upgrade the new technologies to meet standards that were laid out by regulations relating to emissions. Still, however, there are opportunities for growth in this small ICE market.
Economies in Development: Mega-size developing economies, especially with emerging markets experiencing high economic growth with urbanization and industrialization, represent very large development potential in the small ICE market.
Niche Applications: Off-grid power generation as well as recreational boating provide niches for specialized ICE products.
Aftermarket and Maintenance: The replacement parts, accessories, as well as maintenance after-sales form a stable source of income for the manufacturers and distributors
Conclusion
The small internal combustion engine market is currently going through a transformational phase due to the evolving availability of these technological concepts, increasing emphasis on environment-friendly technologies, and reorienting customer preferences. Though there are challenges such as electric alternatives, this market still has a lot of room to grow in emerging markets and niche applications. Manufacturers who can navigate these trends and adapt to the changing dynamics of the market will have an upper hand in capitalizing on this industry's long-term potential.
Frequently Asked Questions-
Which is the largest regional market for Small Internal Combustion Engine?
Ans: - Asia Pacific is the largest regional market for Small Internal Combustion Engine.
Which are the top companies to hold the market share in the Small Internal Combustion Engine market?
Ans: - Caterpillar Inc., Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd, Liebherr, Yanmar Holdings Co. Ltd., Cummins Inc., Wartsila Corporation, and Rolls Royce Holdings Plc, are the top companies to hold the market share.
Through what growth rate will the market be expected to grow in the forecast period of 2023 to 2031?
Ans: - In the forecast period, Small Internal Combustion Engine is likely to grow at a rate of 4.6% by 2031.
How massive is the Small Internal Combustion Engine market?
Ans: The global Small Internal Combustion Engine market size was valued at US$ 4.5 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach US$ 6.5 billion by 2031.
What are the segments of the Small Internal Combustion Engine market?
Ans: - The Small Internal Combustion Engine market is segmented into Power-Output, End User, and region.
About Us-
The Insight Partners is among the leading market research and consulting firms in the world. We are proud to provide exclusive reports containing sophisticated strategic and tactical insights into the industry. We will generate our reports through a mix of both primary as well as secondary research, keeping in mind that we are doing it solely for our clients to provide knowledge-based insights into the market and domain to assist clients in making wiser business decisions. A holistic perspective in every study carried out becomes an integral component of our research methodology, making this report unique and reliable.
0 notes
Text
With its abundant natural gas supply, Russia has long wielded its resource riches to bludgeon Ukraine, Europe, and other dependent customers. By continuously threatening the future of the Black Sea Grain Initiative, the landmark wartime agreement designed to open up Ukraine’s key farm output for export to world markets, Moscow has also found a way to strangle Kyiv’s agricultural sector—and weaponize resources that aren’t even its own.
Those tactics were on full display this week as negotiators raced to broker a full extension to the grain deal before its scheduled expiration on Monday, the latest scramble to save a key deal that helped ease pressures on vulnerable markets in the wake of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Since the deal took force in July 2022, Moscow has repeatedly attempted to upend the agreement to extract key concessions, intensifying concerns about the future of Ukraine’s hard-hit agricultural industry and the global food insecurity.
“This continues to be very much an issue not just for Ukraine producers but also globally,” said Joseph Glauber, a senior research fellow at the International Food Policy Research Institute and former chief economist at the U.S. Department of Agriculture. “Ukraine has been a very important supplier, and if they have to continue with diminished production over another year, that means that the world will have to find wheat and corn from others to replace that.”
It’s still not clear if Russia is ready to blink again and continue allowing exports or if this time it will try to scupper the deal. Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan said Friday that Russia had agreed to extend the deal—before the Kremlin said it had decided no such thing.
With just days until the deal would expire, Russian President Vladimir Putin continued to press for concessions and extract leverage. For months, the main sticking point in negotiations has been Russia’s own food and fertilizer exports: While excluded from Western sanctions, Moscow says its exports have been hampered by sanctions targeting insurance and payment companies over its invasion of Ukraine.
On Thursday, Putin warned that “not one” of its demands had been met. The grain deal is a “one-sided game,” he said in a television interview. “We can suspend our participation in this deal. And if everyone reiterates that all promises given to us will be fulfilled, let them fulfill these promises. And we will immediately join this deal. Again.”
Western officials and agricultural analysts have pushed back, accusing him of deliberately stymieing the outflow of agricultural exports and driving up prices. Barbara Woodward, the U.K. envoy to the United Nations, said Russia was engaging in “cynical brinkmanship.”
“In Istanbul, they slow-roll the inspections of the grain ships, bringing down the amount of grain that goes out. Then, by signaling that they are considering refusing to renew the deal, they are also affecting global grain prices,” she said.
In this game of brinkmanship, diplomats have been scrambling to carve out other concessions to secure the extension of the deal. On Tuesday, U.N. Secretary-General António Guterres wrote Putin a letter offering to connect a Russian agricultural bank subsidiary to the SWIFT international payments system, in exchange for the continuation of the Black Sea Grain Initiative; the European Commission also indicated that it was willing to “explore all solutions.”
“The objective is to remove hurdles affecting financial transactions through the Russian Agricultural Bank, a major concern expressed by the Russian Federation, and simultaneously allow for the continued flow of Ukrainian grain through the Black Sea,” U.N. spokesperson Stéphane Dujarric said.
Russia has yet to respond to the letter, although Erdogan, a strong proponent of the grain deal, expressed optimism on Friday that Guterres’s effort would help secure the grain deal’s extension. Both Putin and Erdogan are “of the same mind” in extending the agreement, the Turkish leader added.
Known as the breadbasket of Europe, Ukraine once supplied 10 percent of the world’s wheat exports, 20 percent of corn exports, and 40 percent of the global sunflower oil supply. After Russia’s invasion in February 2022 throttled harvests and disrupted those exports—thereby skyrocketing global prices—diplomats rushed to ink an agreement to avert an international food crisis. Since its inception roughly a year ago, the U.N.- and Turkey-brokered initiative has unlocked more than 30 million metric tons of goods, nearly one-quarter of which have gone to China. Almost half have reached developing markets that had been under immense strain.
Failing to renew the deal would jeopardize those exports—which would be bad for Russia’s ongoing efforts to woo the global south and especially its need to stay in good graces with Beijing. China has been one of the major beneficiaries of the grain deal, even naming the initiative in its 12-point peace plan, and has a vested interest in the agreement’s success. The timing of the latest extension fight also matters: The overwhelming bulk of Ukraine’s wheat crop is harvested in July and August, making this extension even more critical than previous standoffs.
But even without suspending its involvement in the Black Sea Grain Initiative, Moscow has done what it can to pressure Kyiv, including by shortening the lengths of extensions and exacerbating shipping challenges. As long as Russia works to squeeze Ukraine’s agricultural sector, Glauber said, already hard-hit producers will be the ones who are hurt the most.
“The real problem with all these increased costs and reduced exports out of the Black Sea [is that] the direct cost of that is being felt by Ukraine producers,” he said. “And that’s sort of the bottom line.”
12 notes
·
View notes