#Euphausiacea
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Taxonomy Tournament: Crustaceans


Euphausiacea. This order is made up of krill, small marine crustaceans. Most species form large swarms, and they are important for the marine food chain.
Isopoda. This order is made up of isopods, including terrestrial species like the potato bug and aquatic species like the giant isopod. Some eat dead matter, others are filter feeders, and some are parasites, mostly of fish.
#animals#biology#polls#poll tournament#zoology#krill#arthropods#crustaceans#ecdytes#isopods#Euphausiacea#Isopoda#0x4dv0xb2#animal tournament#Animal Tournament Round 1
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 2 - Arthropoda - Malacostraca




(Sources - 1, 2, 3, 4)
Malacostraca is the second largest class of crustaceans, and what most people picture when they hear the word crustacean! It contains over 40,000 species separated into 17 orders: Leptostraca, Stomatopoda (“Mantis Shrimp”), Decapoda (“Crabs”, “Lobsters”, “Crayfish”, “Shrimp”, and “Prawns”), Euphausiacea (“Krill”), Thermosbaenacea, Mysida (“Opossum Shrimp”), Stygiomysida, Lophogastrida, Spelaeogriphacea, Mictacea, Bochusacea, Cumacea (“Hooded/Comma Shrimp”), Tanaidacea, Amphipoda, Isopoda, Anaspidacea, and Bathynellacea. Many are scavengers, some are predators, some are herbivores, some are filter feeders, and some are parasites.
Malacostracans live worldwide, in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments, and have a large diversity of body forms. They are united by their segmentation of 20-21 body segments divided into a 5-segmented head, an 8-segmented thorax, and a 6-segmented abdomen with a telson, except in Leptostraca which has 7 abdominal segments. They have a pair of jointed appendages on each abdominal segment, though some groups have lost them secondarily. In some, three thoracic segments may be fused with the head to form a cephalothorax, the associated legs becoming maxillipeds. They have two pairs of antennae, which often branch into two parts. Their mouthparts have a pair of mandibles, maxillules, and maxillae. Many taxa have compound eyes on moveable stalks. Some have a carapace which covers the head, part or all of the thorax and some of the abdomen. The carapace may be fused with some of the thoraacic segments or hinged with two parts. This is one of the most diverse classes in the animal kingdom, and their anatomy and behavior would be hard to summarize further in just one paragraph!
The oldest malacostracans are the Leptostracans, which first appeared as fossils from the Cambrian period.

Propaganda under the cut:
“Carcinisation” has become a meme meaning “everything becomes crab”, but it actually only refers to the phenomenon of decapods convergently evolving crab-like anatomy. The Infraorder Brachyura contains the “True Crabs”, but at least 5 groups of unrelated decapods have evolved similar anatomy: a flat and broad cephalothorax.
Stomatopods (“Mantis Shrimp”) are known for their excellent color vision, but they probably can not actually see “shrimp colors.” They can see ultraviolet and polarized light, but their excess of photoreceptor cells actually lets them process their environment faster than we can, rather than differentiate between a multitude of different colors. This allows them to have quick reaction times, either to escape predators, fight or flee from rivals, or strike at their prey with amazing speed.
Malacostraca contains the largest living arthropods: the Japanese Spider Crab (Macrocheira kaempferi) with a legspan of up to 4 metres (13 ft) long, and the American Lobster (Homarus americanus), which can get up to 20 kilograms (44 lb).
Many species of malacostracans are commonly kept as pets, including crabs, crayfish, shrimp, mantis shrimp, and isopods.
Cute creb eat a cherry:

131 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: krill
The ocean is a huge place and food can be sparse. While the ocean receives plenty of energy in the form of sunlight, that energy needs to be converted into a form animals can consume. This is a job that krill have adopted with gusto. These little shrimpy critters live all over the world and play a vital role in the cycling of energy and nutrients. Krill are among the most common and important marine species, but many people overlook them or think of them as nothing but whale food. let's take a dive into the world of krill to show you that there's more there to appreciate.

(Image: a side view of an antarctic krill. It is a shrimp-like animal divided into a solid cephalothorax and flexible abdomen. On one end of the cephalothorax are the eyes and antennae and on the underside are multiple pairs of thin, feathery legs and gills. Along the segmented abdomen are paddle-like appendages. The tail is fanned out. The body is translucent with spots of red pigment. The cephalothorax looks green due to the presence of algae in the stomach. End ID)
There are 86 known species of krill in the order Euphausiacea. While they look a lot like shrimp or prawns, Euphausiacea is actually a sister group to Decapoda, which contains the shrimp, prawns, and most other crustaceans you've heard of. Krill can be distinguished from shrimp by the gills and number and anatomy of the limbs. Krill are zooplankton, a description which makes many people think they must be microscopic. In fact, plankton just means an organism is carried around by currents and cannot swim against them and has nothing to do with size. Most krill reach 1 to 2 centimeters as adults, but some species can get larger. The largest species, Thysanopoda cornuta, can reach 9.5 cm (3.75 in).

(Image: a swarm of krill in the ocean with so many members, it makes the water look red. End ID)
Krill anatomy is very similar to that of shrimp. Their bodies are divided into a cephalothorax, flexible abdomen, and tail fan. The cephalothorax is a fusion of the head (cephalon) and thorax. On the head are compound eyes, mouth, and antennae. Emerging from the thorax are legs. These legs are alternatively called pereiopods thoracopods, or thoracic legs. This is one of the key areas where krill are different from decapods. Decapods always have 5 pairs of thoracic legs and at least some of them are adapted for moving around on the ocean floor. Krill have a varying number of these legs and none are adapted for seafloor life. Krill spend their entire lives in the water column. Behind the legs are the gills, which are exposed to the water. The abdomen is long and flexible and has appendages called pleopods or swimmeretes that are used to assist in swimming and moving water over the gills. Decapods also have these. Finally is the tail fan, which is used in swimming and is also found in decapods. Krill exoskeletons are typically transparent with a bit of pigment on the top. All but one species of krill are bioluminescent, though its possible that the bioluminescence comes from their food. Krill have gills that are exposed to the water while Decapod gills are inside of their exoskeletons.
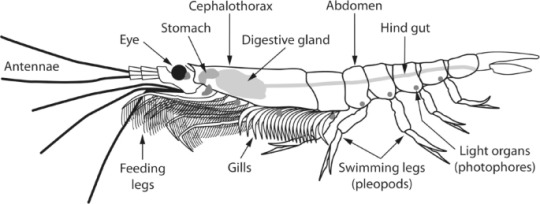
(Image: an anatomical diagram of a krill, with different external and internal body parts labeled. End ID. Source)
Krill are primarily filter-feeders that live in all oceans and in the shallow and deep seas. Most species feed on phytoplankton, especially diatoms, while other are omnivores or carnivores that hunt zooplankton and larval fish. The thoracic legs are covered in filamentous structures and will be held out in a formation called the feeding basket. Plankton passing through the basket will get caught and transferred to the mouth. Krill have a simple digestive tract with a two-chambered gut. The first chamber acts as a mill, crushing the hard shells of the diatoms to make digestion easier. Most krill practice diel vertical migration, a common ocean strategy where animals will remain at depth during the day and move closer to the surface at night. Some species remain in the deep sea all their lives. As krill feed, they become heavier and more sluggish and will sink, allowing the hungrier krill. Krill swim and feed in massive swarms.
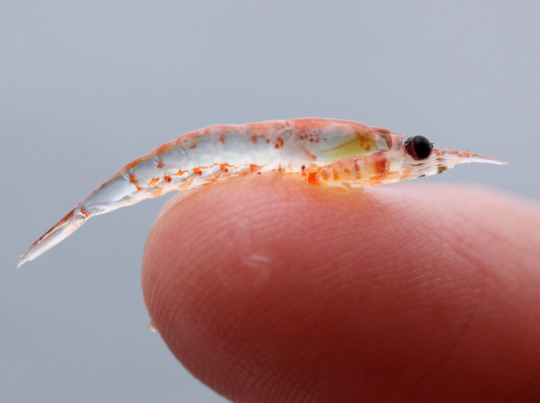

(Image: an antarctic krill balanced on a human finger, to show its size. It is barely longer than the first segment of the finger. End ID)
Krill are a vital part of ocean ecology. Energy is introduced to phytoplankton by the sun and used to produce the energy-storing molecule ATP. Krill eat the phytoplankton and convert that energy into a form larger animals can consume and digest. Whales can't gain energy from phytoplankton, but they can get that energy from krill. Krill are a vital food source for baleen whales, seals and sea lions, fish, squid, and other animals. By eating phytoplankton and then being eaten themselves, krill allow that energy to move through the entire food web. Krill also play a role in moving nutrients and carbon through the ocean. Carbon enters the ocean through runoff and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere entering the surface waters. Phytoplankton take in the carbon dioxide and covert it into forms of carbon that other organisms can use. The krill then eat the plankton, taking the carbon into themselves. Through feces, molted exoskeletons, and dead krill, that carbon can sink into the deep sea, where it can become sequestered in the sea floor. Similarly, nutrients can pass from krill to their predators or into the deep sea through feces and remains. Without krill and other animals filling similar roles, carbon and nutrients would have a much harder time reaching the deep ocean and larger animals wouldn't be able to access the energy stored in phytoplankton.

(Image: a diagram showing the highly complex process by which krill assist in moving carbon through the ocean. End ID. Source)
Being animals with exoskeletons, krill have to molt when they outgrow their current shells. Generally speaking, young krill will molt more often than older ones. Most crustaceans will slow down as they age, with each molt occurring further and further apart. This is not the case with krill, which keep molting at a relatively consistent rate through their lives. some species of krill can also get smaller after a molt instead of always getting bigger. This is used when food is unavailable, reducing the amount of energy the animal needs. Some species have been observed going 9 months between meals. Some species can spontaneously molt as a reaction to threats, leaving behind the empty exoskeleton as a decoy for predators.
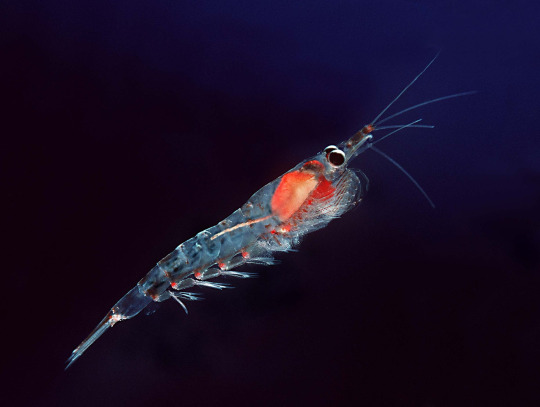

(Image: a northern krill. It is similar to the antarctic krill, but with a different arrangement of pigment. End ID)
Krill typically mate seasonally, though some tropical species can mate year-round. A female can produce thousands of eggs, which can make up a third of her body weight during mating season. Being a major prey animal, krill need to reproduce rapidly to keep their populations up. Most species will mate and produce eggs multiple times per mating season. Males approach females and deposit sacs of sperm into their genital openings. The females then produce eggs which can be treated in two ways. Most species will release their eggs into the water column and provide no further care. 29 species instead attach their eggs to a sac held by the rearmost thoracic legs and carry them until the eggs hatch. Some of these species hatch at a more mature stage. Once the eggs hatch, they have to swim upwards to reach the photic zone of the ocean, where photosynthesis can take place. Larvae progress through several developmental stages. Like other crustaceans, they start as a napulus larva, though some sac-brooders will hatvch at the more advanced pseudometanapulus stage. Either way, they progress then to the metanapulus stage. At this stage, they can lo longer subside on yolk and must reach the photic zone and metamorphose into the calyptosis stage, the first stage with a mouth, before starving. The final larval stage is called the furcilia, which passes through a number of molts. During each molt, the abdomen will grow another segment and pair of swimmeretes. After the final furcilia stage, the krill will resemble a small adult. Krill life spans vary baes on species, from less than a year to 10 years, with species in colder water usually living longer. Relatively few krill will die of old age. In the antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, over half the population is eaten every year.

(Image: several stages of krill development form egg to napulus to more advanced larval stages that look like the adult. End ID. Source)
Krill conservation needs vary by species, but in general, they are highly abundant and in little danger of extinction. Krill are among the most abundant animals in the world, with antarctic krill having one of the largest total biomass of any animal. Monitoring the krill population is extremely important because of their importance to the global ecosystem. Krill have been fished commercially for centuries, used as food, bait, supplements, animal feed, and for shrimp paste and fish oil. Most krill fishing takes place around Antarctica as the krill there are highly abundant and seen as cleaner. As the krill fishery grows, more studies need to be done on the impact on the population and the other species that rely on them. Krill are also impacted by global climate change, ocean acidification, and pollution. Krill can ingest microplastics, which can then be passed onto whatever eats them. Krill are keystone species, meaning they are crucial to the health of their environments. If they go, massive parts of the ocean ecosystem will collapse.

(Image: someone holding a pile of dozens of krill in their hands. End ID)
#wet beast wednesday#biology#ecology#zoology#marine biology#animal facts#invertebrates#invertiblr#crustacean#krill#antarctic krill#informative#educational#image described
121 notes
·
View notes
Text
i'm going to become a marine crustacean of the order euphausiacea
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
I don't want to be hungry on someone's post so I'm making my own but that post about krill makes me think krill would be delicious.
Also found this.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
im going to krill myself. becomes small and exclusively marine crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word krill, meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish
0 notes
Text
vimeo
Helen Ma, Condensed Blue Whale
This Project, Condensed Blue Whale, is inspired by the Chinese song Condensed Blue Whale (浓缩蓝鲸) by the artist Qiu De (裘德). It talks about a story that takes place in the year 3000, where a scientist condensed the soul of a gigantic Blue Whale inside the body of an extremely small Euphausiacea, which is a kind of half-transparent shrimp. The small body of shrimp now has the experience of roaming in the deep ocean, but the vast blue whale begins to be skeptical about the question of whether its soul is as tiny as the body it owns at this moment. It is supposed to be a romantic story that questions the philosophical essence of “who I am” – the body, the mind, or the combination of both. However, it is somehow cruel as well.
Inspired by Sabrina Ratte and her Muse, Donna J. Haraway, I started to consider the idea of the Cyborg (a combination of organism and machine) and the value of the community that everything is mixed in society, without clear binary distinctions.
When we are observing animals, are animals observing us as well? When society develops to be that high technology and human beings are getting very used to being adapted to living together with those techniques that we are not necessarily able to control, what will be human beings’ future? When we do all kinds of experiments on animals, we might also gradually become some kind of experimental object to some unknowns. Instead of the utopic idea given by Haraway, this project shows my dystopian perspective on the future community.
0 notes
Photo

Krill - The Basics of Life!🧬😉 COMMON NAME: Krill SCIENTIFIC NAME: Euphausiacea TYPE: Invertebrates DIET: Herbivore GROUP NAME: Swarm SIZE: 2.4 inches WEIGHT: 0.035 ounces SIZE RELATIVE TO A PAPER CLIP: View on Pic. The lowly krill averages only about two inches in length, but it represents a giant-sized link in the global food chain. These small, shrimp-like crustaceans are essentially the fuel that runs the engine of the Earth’s marine ecosystems. Role in the Food Chain Krill feed on phytoplankton, microscopic, single-celled plants that drift near the ocean’s surface and live off carbon dioxide and the sun’s rays. They in turn are the main staple in the diets of literally hundreds of different animals, from fish, to birds, to baleen whales. https://www.instagram.com/p/CpYbqI4jGHw/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Text
call me euphausiacea the way im trying to be sucked in whole by a girl with a maximum confirmed length of 29.9 meters
what if i krilled myself
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Animal practice 33










Panarthropoda
Arthropoda 3
Crustacean 2
Brachyura
Cyrus (Ghost crab/Christmas island crab)
Anomura
Hikikomori (secondary crabs)
Astacidea
Shelton (lobster)
Etta ( Crayfish)
Gebiidea/Axiidea
Clay (Mud Lobster)
Achelata
Prong (Spiny/Slipper lobster)
Caridea
Parker (Shrimp)
Stenopodidea
Ringster (Boxing shrimp)
Dendrobranchiata
Trawl (Tiger prawn)
Euphausiacea
Minute (Krill)
#the watchful eye#watchful eye#my ocs#my art#my oc#aj the elementalgod#elementalgod aj#isle 0#toonverse oc#o'kong family#neo demons#earthdemons#anthro allies#panarthropoda#arthropods#crustaceans#crabs#anomura#lobsters#crayfish#mud lobster#spiny lobster#slipper lobster#shrimp#boxing shrimp#prawn#krill
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let’s KRILL this love!
Did you know that Antarctic Krill can glow in the dark (like a lightstick *0*)?

They are bioluminescent! That means krill swarms look like a KPOP ocean!

Classification
Kingdom: Animalia
Subkingdom: Bilateria
Infrakingdom: Protostomia
Superphylum: Ecdysozoa
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Malacostraca
Subclass: Eumalacostraca
Order: Euphausiacea
Family: Euphausiidae
Genus: Euphausia
Species: Euphausia superba
(ITIS, n.d.)
Distribution and habitat
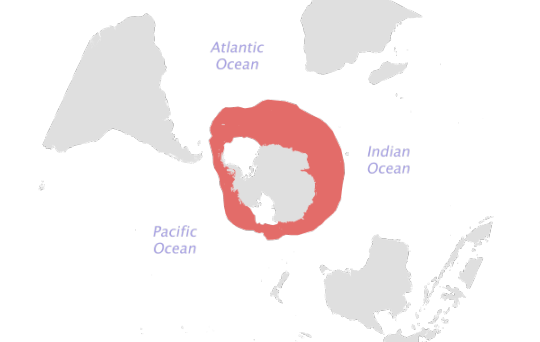
Figure 1. Geographical Distribution of Antarctic krill (fao.org, n,d,)
E. superba inhabits a wide circumpolar belt between the Antarctic Continental Shelf break and the Antarctic Polar Frontal Zone. Antarctic krill live in open marine waters (fao.org, n.d.). The larvae of the krill begin near the seafloor and gradually ascend towards the surface as it develops. Adult krills are found at depths ranging from surface waters to depths of 350 m and have occasionally been found as deep as 600 m. They usually dwell in deeper waters during the winter season (Gierak, n.d.).
Anatomy

Figure 2. External Anatomy of Antarctic Krill
E. superba known as Antarctic krills are shrimp-like in appearance though they can easily be distinguished from shrimp by their visible gills. Just like any other decapods they have exoskeleton which are made of chitin and have three body parts which is the cephalothorax, pleon and the telson. The cephalothorax bears the antennae, compound eye, 6 filter legs which are also called thoracopods and the gills. Krills have compound eyes which aid them in seeing while their antennae serve as another sensory organ as they live in the deep. The thoracopods or the filter legs on the other hand, assists the krill in straining its food from the water. Although the gills, guts and gastric mill are not part of its external anatomy, the three are visible from the outside. The middle part of its body is the pleon where the pleopods and the photophores are located. There are 5 pairs of pleopods or swimming legs that allow them to swim in the water column while the photophores or light organs act as a defense mechanism or a signal for their mates. Lastly, is the telson which is used by decapods as a paddle in caridoid escape reactions through backward propulsion (Grzimek's Student Animal Life Resource, n.d.).
Life Cycle
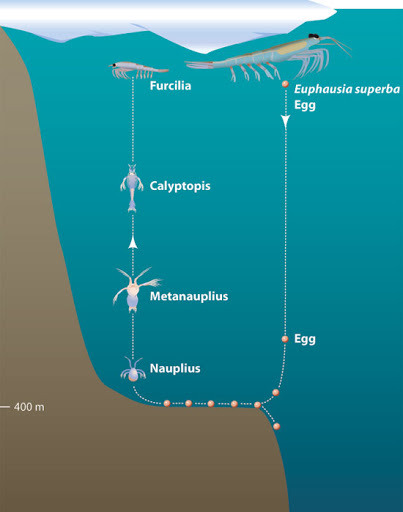
Figure 3. Life Cycle of an Antarctic Krills Krills reproduce sexually and it usually happens when food is abundant. The male krill produces sperm packets and uses its first pair of pleopods called petasma to transfer the sperm into the thelycum of the female. They store the sperm until they are ready to lay their eggs. These eggs are fertilized once they are released by the female. These eggs settle at the seafloor and gastrulation happens. Eventually, the eggs will hatch and become a nauplius. In this the nauplius has only one eye and is not segmented yet. Then, the nauplius will molt and become a metanauplius wherein limb development begins and it will start to migrate to the surface which is known as developmental ascent. As it molts and grows, it becomes a calyptopis and eventually a furcilia wherein the movable compound eyes start to project at the edge of its carapace. The furcilia develops into a juvenile which can grow from 4 to 10 mm long (Gierak, 2013).
Ecology
Figure 4. Thoracic endopodite of krill (wikipedia.org, n.d.)
Antarctic krill are filter-feeders that feed mainly on phytoplankton. They exhibit diurnal vertical migration, which means that they rise to the surface at night to feed by using their small, hair-like legs specifically thoracic endopodites as a suspension feeding basket. Apart from phytoplankton, they also eat copepods, zooplankton, and other krill or molted exoskeletons. In the winter, they eat algae under the surface of sea ice. They are considered the dominant herbivore of the Southern Ocean. Its biomass in the Antarctic Ocean is estimated to be between 125 mmt and 750 mmt, the largest biomass of any species on earth (Hardy, 2008). Antarctic krill is the keystone species of the entire Antarctic food chain. They provide a vital food source for whales, seals, squids, penguins, fishes, albatrosses, and many other species of birds. To avoid predation, they exhibit schooling behavior or swarming. Moreover, krill may be parasitized by organisms like protozoans, particularly the genus Ephelota. This suctorian ciliates interacting with E. superba cause hydrodynamic drag on krill swimming and make the host more vulnerable to visual predators (Gómez-Gutiérrez & Morales-Ávila, 2016). Other parasitic species include Cephaloidophora pacifica and Apostoma sp.
UNLI-KRILL @ 199!
youtube
Krill’s POV

Relationship with humans

Figure 5. Sports Research’s Antarctic Krill Oil with SUPERBA 2 (ph.iherb.com, n.d.)

Figure 6. Krill/shrimp chili paste and dipping assortments in Thailand (quora.com, 2016)
Although krill is mainly used as aquaculture feed and bait for fishing, it is also processed into a variety of products for human consumption such as paste, frozen tails, sticks, etc. Krill products have been known to pharmaceutical and industrial industries since it is found that the krill's lipid content can be used as a nutritional source of fatty acids that is potential in lowering cholesterol levels. Studies found that the lipids of Antarctic krill are more stable than those of some fishes consumed by humans. Krill digestive proteases can also be injected into humans to reduce pressure on nerve roots between vertebral discs (Gierak, n.d.). Tou et al. describe Antarctic krill as a “rich source of high-quality protein” with low fat and high levels of Omega-3s and antioxidants and the main source of the renowned krill oil.
5 health benefits of Krill oil you shouldn’t miss!
youtube
Little did you know that..
They are age-defying!
*jaw-dropping moment because olay age-defying serum just cant--*
➔ They have the ability to shrink in size when starve to conserve energy during the winter. Thus, scientists can’t tell the age of a krill solely from its size.
Phytoplankton is just a summer fling!
➔ They can survive more than 200 days without food.

Krillions of krills!
➔ Krill swarm together in massive numbers, with as many as 30,000 in one cubic meter of a krill swarm.

A Little Giant!
➔ It’s estimated that the total weight of Antarctic krill is more than the weight of all humans on Earth (Usoceangov, 2015).

Food is life but swimming is lifer!
➔ They are heavier than seawater and must swim constantly to stay afloat.
Climate heroes!
➔ Tarling and Thorpe (2017) have discovered that krill play a crucial role in sequestering carbon.

References:
Clark, D. (2012, September 17). The anatomy of the Arctic krill [Digital image]. Retrieved November 12, 2020, from http://1.bp.blogspot.com/-7NY88MHBVpc/UFfn-sAknuI/AAAAAAAAAW4/nkt1_Ba8G8k/s1600/Antarctic_krill_anatomy.jpg
Euphausia superba. (n.d.). ITIS. Retrieved November 8, 2020, from https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=95514#null
Euphausia superba (Dana, 1852). (n.d.). FAO. Retrieved November 10, 2020, from http://www.fao.org/fishery/species/3393/en
Exuvia of Antarctic krill [Online image]. (2005). English Wikipedia. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Exuviakrillkils.jpg
Gierak, R. (2013). Euphausia superba (Antarctic krill). Retrieved November 12, 2020, from https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Euphausia_superba/
Gómez-Gutiérrez, J., & Morales-Ávila, J. R. (2016). Parasites and Diseases. Biology and Ecology of Antarctic Krill, 351–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-29279-3_10
Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia. (2020). Krill: Euphausiacea. Retrieved November 12, 2020, from https://www.encyclopedia.com/science/encyclopedias-almanacs-transcripts-and-maps/krill-euphausiacea
Hardy, R. W. (2008). Alternative marine sources of fish feed and farmed fish quality. Improving Farmed Fish Quality and Safety, 328–342. https://doi.org/10.1533/9781845694920.2.328
Naruturd_505. (n.d.). Hoshiumi Korai A Little Giant GIF [Online GIF]. https://tenor.com/view/hoshiumi-korai-alittle-giant-smile-haikyuu-anime-gif-17909731
Oh, yeah- what?! GIF. (2013). Gfycat. https://gfycat.com/detailedfaintalbertosaurus
SuperSmiles17. (2013). Definitely one in a Krillion! [Online GIF]. https://imgur.com/gallery/YtN30/comment/16282449
Tarling, G.A., and Thorpe, S.E. (2017). Oceanic swarms of Antarctic krill perform satiation sinking. Proc. R. Soc. B., 28420172015. http://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2017.2015
The Ozone Hole. (n.d.). [Life Cycle of Antarctic Krill]. Retrieved November 12, 2020, from http://www.theozonehole.org/images/v43n2-wiebe3en_10243.jpg
[Untitled image of a tardigrade]. (2017). BBC. https://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-40752669
Usoceangov. (2015). Animals of the Ice - Antarctic Krill. Youtube. Retrieved November 10, 2020, from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RFqhocQqbgM
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Advantages vs Disadvantages
Although the cons outweigh the pros in regards to Climate Change, there are still various advantages that directly contribute to Earth.
ADVANTAGES
The Arctic, Antarctic, Siberia, and other frozen regions of the earth might experience more plant growth and milder climates.

The next ice age could possibly be prevented

The Northwest Passage through the formerly icy Canadian Arctic Archipelago could arguably open up to transportation.

Fewer deaths or injuries would occur due to arctic conditions.

Longer growing seasons could mean increased agricultural production in some areas.

DISADVANTAGES
Changes in ocean circulation and the resulting warmer temperatures disrupt the world’s normal weather patterns, bringing about more extreme weather and an increased frequency of severe and catastrophic storms, such as typhoons and hurricanes.

Higher sea levels lead to flooding of the lowlands. Islands and coastlines are engulfed by water leading to death and disease due to flooding.

The acidification of warming oceans leads to a loss of coral reefs. Coral reefs protect shorelines from heavy waves, storms, and floods and while they only cover about 1 percent of the ocean floor, reefs provide a habitat for 25 percent of ocean species. Demolished reefs lead to increased erosion and coastal property damage and the extinction of species.

Warming ocean waters mean increased melting of glaciers and ice sheets. Smaller ice sheets form each subsequent winter, which has a devastating impact on the habitat of cold-climate animals and the Earth’s reserves of freshwater.

Less sea ice, warmer water, and increased acidity are catastrophic for krill which forms the base of the ocean's food web and feeds whales, seals, fish, and penguins. Emperor penguin colonies are also expected to decline due to the loss of sea ice and rising temperatures.

Word Bank:
Coral reefs- An underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals
Glaciers- a slowly moving mass or river of ice
Ice sheets- a permanent layer of ice covering an extensive tract of land
Krill- any small shrimplike marine crustacean of the order Euphausiacea
Sources:
Is there any upside in Global Warming? Matt Rosenberg. July 11, 2019.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

KRILL OIL GOLD EDITION 60 PERLAS - SCIENTIFFIC NUTRITION Krill Oil Gold Edition de Scientiffic Nutrition es un producto compuesto por aceite de krill antártico. El Krill es el nombre por el que se conocen genéricamente a los eufusiáceos (Euphausiacea) que son un tipo de crustáceo que se alimenta de fitoplancton. El aceite derivado de Krill es rico en ácidos grasos esenciales Omega 3 y 6. EL aceite de krill es muy estable y libre de metales pesados, de hecho se considera más eficiente que cualquier aceite de pescado. El aceite de Krill tiene la capacidad de mejorar el dolor articular, siendo muy útil en procesos inflamatorios. Principales beneficios Krill Oil Gold Edition de Scientiffic Nutrition: Fuente de ácidos grasos esenciales Omega 3 y Omega 6. Mejor absorción que el aceite de pescado. Rico en ácido eicosapentaenoico y ácido docosahexagenoico (EPA/DHA) que contribuyen a la función normal del corazón. El ácido docosahexaenoico (DHA) contribuye al mantenimiento de la función normal del cerebro y el mantenimiento de la visión normal. Ayuda a regular los índices de colesterol y triglicéridos, además de tener propiedades antioxidantes. El aceite de Krill tiene mejor biodisponibilidad y absorción que el aceite de pescado, siendo también más estable y resistente a la oxidación que este último. Krill Oil te ofrece una potente dosis de aceite de Krill purificado fácil de asimilar en cada cápsula blanda de gelatina. Presentación: Envase de 60 perlas. Modo de empleo: Tome 2 cápsulas al día con un gran vaso de agua. https://www.naturfactory.com/acidos-grasos/omega-369/krill-oil-gold-edition-60-perlas-scientiffic-nutrition.html 19,90 €
#naturfactorysport#tiendasuplementos#tiendadeproteinas#wwwnaturfactorycom#complementoalimenticio#nutriciondeportiva#nutricionespecializada#suplementacondeportiva#suplementosdeportivos#suplementosnutricionales#suplementosalimenticios#tiendadeproteinasenjerez
0 notes
Photo

EL ATÚN ROJO. ALGUNAS CARACTERÍSTICAS. Libro CIMARRÓN José L. Cort) 1ªpart: El atún rojo,Thunnus thynnus (L.), del Atlántico y Mediterráneo pertenece a la familia de los peces escómbridos (Scombridae).Puede llegar a pesar 725 kg, alcanzar una longitud de 3,3 m y vivir más de treinta años. El registro oficial del mayor atún rojo es de 679 kg, un pez capturado en aguas de Nueva Escocia (Canadá) en 1979, siendo el actual récord Guinness. Forma grandes cardúmenes y se alimenta principalmente de otros peces, cefalópodos, pequeños crustáceos como el krill (Euphausiacea) y cangrejos pelágicos. Su forma es altamente hidrodinámica ya que está totalmente adaptado a la movilidad.Habita en aguas templadas del Atlántico Norte y el mar Mediterráneo (hasta el mar Negro). En la parte oriental del océano Atlántico se encuentra desde Senegal y Cabo Verde (15 N) hasta cerca del Círculo Polar Ártico (75º N), donde se registran temperaturas de 5ºC.En la parte occidental, desde Brasil hasta Terranova. También se ha localizado en el Atlántico sur. Su torrente sanguíneo forma el núcleo de un sistema de intercambio de calor altamente evolucionado, por lo que su temperatura interna puede mantenerse hasta 21°C más alta que la del agua que lo rodea, siendo ésta una de las razones de su amplia distribución en el océano. El atún rojo puede aparecer en las cálidas aguas de las Bahamas a cerca de 30°C y 50 días después en aguas noruegas, donde el agua apenas alcanza los10° C. •••Las migraciones del atún rojo dependen de la edad y la longitud de los peces y están relacionadas principalmente con el desove y la búsqueda de alimento.Las migraciones de peces adultos (>40 kg) hacia las zonas de desove en el Mediterráneo y su regreso al océano para alimentarse se conocen desde hace milenios.Sus migraciones se hacen cada vez mayores a medida que aumentan su tamaño. •••Para realizar la reproducción los atunes rojos emigran formando grandes bancos que eligen las áreas más apropiadas en función de numerosas variables ecológicas y ambientales. En general, las migraciones de este pez, tanto en adultos como juveniles (<40 kg), parecen estar asociadas a los grandes sistemas de corrientes oceánicas. (en Almansa) https://www.instagram.com/p/B_IOZuYKgfQ/?igshid=1wv5zrbfj7xbd
0 notes
Photo

Tetra Betta 100 ml / 27 g Forro de alta calidad forro diseñado para satinado, Splendens (Betta principal) de pescado y otros peces laberinto: enthaelt un porcentaje de proteínas por adición de camarón apropiada y Euphausiacea proteínas animales foerdern el crecimiento y la auspraegung de aletas con natuerlichen farbverstaerkern Composición: Pescado y subproductos de pescado, cereales, vegetales eiweis extractos, levaduras, suave de animales y el cáncer (Arte Mia salina 3,3%, gefriergetr kleink liofilizados rebse (Euphasia Pacifica) 3,3%), desechos y Grasas, azúcar, algas, minerales.
0 notes
Text
Shellfish (selfish)
Beau sits at the edge of their bed, laptop balanced precariously on their knees. Their face is illuminated only by the dim light of the screen as they stare anxiously at the PM they have open.
To ancientArcenic: hey. about that whole poem thing. maybe we COULD talk about it(?)
Nope, that's awkward. Gonna delete that right now. Let's try again
To ancientArcenic: I meant what I wrote, I don't know if you did or not but I wanted to just throw that out there in case you did I know it was just a random assembly of songs but I figure yo
Oh god now they are rambling. Highlight and delete, don't sound so desperate and anxious.
They feel really desperate and anxious.
To ancientArcenic: I like you.
Delete.
To ancientArcenic: hey, what jokes are the best to tell to the animal class Euphausiacea? Fish puns, they really KRILL
Send.
Ugh. What a coward.
2 notes
·
View notes