#Ethernet Compliance Test
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Three-phase Independent Adjustable RCD Nonlinear Load Bank
The three-phase independent adjustable RCD nonlinear load bank is designed to accurately test and evaluate power systems under diverse load conditions. Its ability to independently adjust each phase ensures precise simulation of real-world scenarios, enhancing the reliability and performance of generators and UPS systems. This advanced load bank accommodates nonlinear loads, making it ideal for testing modern power equipment and ensuring compliance with industry standards.

Product Description:
Ensure your power systems meet peak performance with the three-phase independent adjustable RCD nonlinear load bank. Whether testing inverters or conducting UPS load tests, its comprehensive capabilities provide unparalleled reliability and data accuracy. Ideal for both lab and field applications, this load bank is your trusted partner in safeguarding critical power infrastructure, offering precise control and robust performance for demanding testing requirements.
Product Features&Advantage:
1.Suitable for testing inverters and UPS loads.
2.Includes upper computer operating software, compatible with ATE special envoy.
3.Equipped with RS485, Ethernet, CAN, and other communication ports.
4.Features programmable test steps, ideal for automatic testing of photovoltaic and energy storage inverters.
5.Capable of loading any power within the full power range.
6.Power adjustment precision: as low as 10W.
7.Power factor adjustment: as low as 0.45.
8.Peak factor CF: up to 3.
9.Customizable for a wide voltage range.
10.Utilizes PC data management software to control load operations and save test data.
EMAX load bank stands at the forefront of the power testing industry, providing high-quality load banks designed to meet various industrial needs. Delivered worldwide to ensure that global customers can use our advanced solutions
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Diagnostics Laptops: Essential Tools for Modern Vehicle and Equipment Maintenance
In today’s fast-paced and technologically advanced world, laptops have become essential tools for diagnostic laptop in a wide range of industries, particularly automotive, trucking, heavy machinery, and other sectors where electronic systems are deeply integrated into engines and other equipment. A diagnostics laptop, typically equipped with specialized software, allows technicians to interface with the electronic control modules (ECMs) or onboard diagnostic systems (OBD) of vehicles, trucks, or industrial machinery, providing them with the ability to identify, analyze, and repair complex system issues.
What Is a Diagnostics Laptop?
A diagnostics laptop is a portable computer used to run specialized diagnostic software that interfaces with the onboard computers of vehicles or machines. These laptops, often paired with communication adapters (OBD-II, J1939, J1708, etc.), allow mechanics and technicians to connect to an electronic control unit (ECU) to read and interpret error codes, monitor live data, and perform advanced system tests.
This setup is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining modern vehicles, which rely heavily on electronic systems for engines, transmissions, braking, emissions control, and even infotainment systems.
Key Features of Diagnostics Laptops
Compatibility with Diagnostic Software: Diagnostics laptops are typically equipped with various software programs that can interface with a vehicle's or machine’s ECM. Popular diagnostic software platforms include Cummins Insite, Caterpillar ET, JPRO, Ford IDS, and many others, each tailored to specific vehicle types or brands. The laptop must be powerful enough to run these programs efficiently.
Rugged Design for Workshop Environments: Many diagnostics laptops are built to withstand harsh environments. Rugged laptops, like the Panasonic Toughbook, are particularly popular in industrial settings due to their durability. They are dustproof, waterproof, and shock-resistant, making them ideal for use in repair shops, construction sites, or fieldwork.
High Processing Power: Diagnostic software can be demanding, especially when dealing with large data streams, real-time monitoring, and system updates. Diagnostics laptops typically have strong processors (Intel i5/i7 or AMD equivalents) to handle these tasks without lag, ensuring that technicians can work quickly and efficiently.
Adequate Storage and Memory: Diagnostics laptops need ample storage and memory to store diagnostic logs, software updates, and customer vehicle data. A minimum of 8GB of RAM is recommended for smooth multitasking, while at least 256GB of SSD storage ensures faster data access and boot times.
Connectivity Options: Most diagnostics laptops need to connect to the vehicle’s OBD-II or other diagnostic ports. They achieve this connection through USB-based adapters or wireless options such as Bluetooth. Additionally, a diagnostics laptop may have ports for HDMI, USB 3.0, Ethernet, and serial connectors to ensure compatibility with older machinery.
Real-Time Data Monitoring: One of the most critical functions of a diagnostics laptop is its ability to display real-time data from the vehicle’s sensors. This data allows technicians to monitor engine performance, fuel efficiency, emissions output, and other critical metrics while the vehicle is running. The software will often provide graphical displays of this information for easy interpretation.
Software Updates and Calibration: Modern vehicles and machinery often require software updates for their electronic control systems. A diagnostics laptop allows technicians to install these updates, recalibrate components, or even reprogram ECUs. This is particularly important for ensuring compliance with emissions standards and optimizing system performance.
Types of Diagnostics Laptops
OEM-Specific Diagnostics Laptops: Many vehicle and machinery manufacturers offer laptops pre-configured with proprietary diagnostic software tailored to their brands. For instance, Cummins has the Insite software, while Ford provides the Integrated Diagnostic System (IDS) for its vehicles. These laptops are often required by dealerships and authorized repair centers to maintain warranty compliance and access manufacturer-specific data.
Universal Diagnostics Laptops: Universal diagnostics laptops are configured to work with multiple diagnostic software platforms, allowing independent repair shops or fleet operators to service various brands and models. These laptops typically support a wide range of vehicle types and are used in shops that handle both light and heavy-duty vehicles, trucks, and machinery.
Rugged Diagnostics Laptops: Designed for tough environments, rugged laptops are ideal for technicians who work in extreme conditions such as construction sites, outdoor fieldwork, or large repair facilities. These laptops are designed to resist damage from drops, dust, water, and extreme temperatures, making them durable tools in the most demanding environments.
Tablets and 2-in-1 Devices: Some technicians prefer tablets or 2-in-1 laptops that offer the flexibility of a touchscreen with the processing power of a laptop. Devices like the Microsoft Surface Pro or Panasonic Toughbook Tablet can be paired with diagnostic software and adapters to offer portable yet powerful diagnostic capabilities.
Benefits of Using Diagnostics Laptops
Precision Diagnostics: A diagnostics laptop allows technicians to accurately pinpoint faults and errors in vehicles or machinery. It can read DTCs, monitor system performance, and provide detailed reports, enabling precision in repair and maintenance.
Reduced Downtime: By quickly diagnosing problems, technicians can reduce the time that vehicles or equipment spend out of operation. This is particularly beneficial for commercial fleets or industries where downtime can be costly.
Comprehensive Data Analysis: Diagnostics laptops allow for in-depth analysis of vehicle or engine performance. Technicians can review historical data, run simulations, and generate comprehensive reports on fuel efficiency, emissions, and mechanical performance, making it easier to predict future maintenance needs.
Versatility Across Platforms: With the right software, diagnostics laptops can be used on multiple types of vehicles, from light-duty cars to heavy-duty trucks, agricultural equipment, and even marine vessels. This versatility is particularly useful for repair shops and fleet operators that service a diverse range of machinery.
Real-Time Troubleshooting: By monitoring real-time data from the engine and other systems, technicians can identify issues while the vehicle is running, allowing for dynamic troubleshooting. This is crucial for diagnosing intermittent problems that may not trigger a DTC.
Software Flexibility and Updates: A diagnostics laptop can be updated with the latest software releases, ensuring that the technician has access to the newest tools, DTC definitions, and troubleshooting procedures. This is particularly important as vehicles and machinery evolve and require more sophisticated diagnostic techniques.
Popular Diagnostics Laptop Brands and Software
Panasonic Toughbook: One of the most popular choices for rugged diagnostics laptops, the Toughbook is widely used in heavy-duty industries due to its durability and processing power. It’s often paired with diagnostic software like Cummins Insite or Caterpillar ET.
Dell Latitude Rugged: Another option for rugged environments, Dell’s Latitude series offers robust laptops with strong performance, perfect for diagnostic tasks in workshops or fieldwork.
Lenovo ThinkPad: Lenovo’s ThinkPad series is known for its reliability and strong processing capabilities. ThinkPads are often used in repair shops for diagnostics software like JPRO or Bosch ESI[tronic].
HP ProBook/EliteBook: HP offers powerful yet affordable laptops like the ProBook and EliteBook series, which are popular among independent repair shops and technicians. These laptops provide the processing power and storage necessary for diagnostic tasks at a reasonable price.
Microsoft Surface Pro: The Surface Pro, a 2-in-1 tablet/laptop hybrid, offers portability combined with strong performance, making it a good choice for technicians who need a lightweight yet powerful diagnostic tool.
Considerations When Choosing a Diagnostics Laptop
Processor Speed: For smooth operation of diagnostic software, a laptop with a modern processor (Intel i5/i7 or AMD Ryzen 5/7) is recommended.
RAM and Storage: A minimum of 8GB of RAM is recommended for running diagnostic software without lag, while at least 256GB of SSD storage will ensure quick data access and faster boot times.
Operating System: Most diagnostic software is designed for Windows operating systems, so choosing a Windows-based laptop is often necessary. Ensure compatibility with the diagnostic tools you plan to use.
Ruggedness: If you work in harsh environments like workshops, construction sites, or outdoor settings, consider a rugged laptop to avoid damage from drops, dust, or water.
Battery Life: Long battery life is essential if you plan to use the laptop for diagnostics in the field, away from constant power sources.
Software Compatibility: Ensure that the laptop is compatible with the diagnostic software required for the vehicles or machinery you work on. Some OEM-specific software may have unique hardware requirements.
Conclusion
Diagnostics laptops are essential tools in modern vehicle and machinery maintenance, providing technicians with the ability to troubleshoot, repair, and optimize systems with precision. Whether for automotive repair, heavy-duty trucking, or industrial machinery, a well-equipped diagnostics laptop ensures efficient and accurate diagnostics, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. As vehicles and machinery continue to evolve with more advanced electronics, the role of diagnostics laptops will only become more crucial for professionals in the field.
0 notes
Text
BT Group’s Digital Unit launches GenAI Gateway platform powered by AWS

BT Group’s Digital Unit has announced the launch of an innovative internal platform to help the company tap into the power of large language models (LLMs) from providers such as Anthropic, Meta, Claude, Cohere, and Amazon. The GenAI Gateway, built in collaboration with AWS and using Amazon Bedrock, Amazon SageMaker and AWS Professional Services capabilities, provides secure, private access to a range of natural-language processing and large language models, a critical tool BT Group will use as it embeds AI into the way it runs the business. Ad-hoc use of LLMs, whilst appropriate for test and development work, is not well suited to large scale use; cost control, security and privacy need more careful management. LLM performance also needs to be monitored, for unexpected errors (e.g. “hallucinations”) and model decay over time (where LLMs stop behaving as expected). The GenAI Gateway also gives BT Group protection against ‘lock-in’ to any given LLM if any other issues emerge. The use of GenAI Gateway platform will encourage BT Group engineers to use the right model for the right use case, at the right price, as it supports per-use case budget tracking. A consolidated platform reduces duplication of effort and resources, as BT Group scales the adoption of generative AI. Application programming interfaces (APIs), security configuration and infrastructure management, can all be managed centrally, reducing the risk of error and the cost of maintaining separate LLMs for every use case. GenAI Gateway, deployed on AWS, is accessed via secure APIs, like all the components of BT Group’s modular digital architecture. GenAI Gateway uses Amazon Bedrock, a fully managed service that offers a choice of high-performing foundation models from leading AI companies like AI21 Labs, Anthropic, Cohere, Meta, Mistral AI, Stability AI, and Amazon through a single API; as well Amazon SageMaker, a fully managed service that brings together a broad set of tools to enable high-performance, low-cost machine learning for any use case. The platform supports prompt security, chat history, FinOps billing per use case, enterprise search, as well as use of multiple corporate data sources. Central privacy controls include separate tenants for each use case, the use of Personal Identifiable Information filters, the location of the data within the UK and the isolation of trained models from each other, protecting data in line with Group policies and relevant regulation. Guardrails are built into the GenAI Gateway, limiting the risk of jailbreaks or toxic interactions, filtering out queries that go beyond the remit of specific applications – ensuring both performance and ethical guardrails are built-in by design. Gen AI Gateway is one of the several key enablers we are deploying to enable BT Group as an AI-enabled enterprise, and we will also use our “data fabric” data management platform to help enforce governing policies for how data can be used, as well as to manage access control and data sovereignty restrictions. GenAI Gateway is live today with the first beta use cases. A trial in Openreach is summarising engineering notes on Ethernet and full fibre jobs, helping to simplify processes and boost productivity for its teams and Communications Provider customers. A second use case, supporting contract analysis for the Group’s Business, legal and procurement teams, is also live. Fabio Cerone, GM EMEA Telco at AWS, said: “The BT Group GenAI Gateway is showcasing how enterprises can effectively deploy generative AI at scale and speed. It’s been a brilliant, pioneering opportunity to collaborate and work backwards from the customer to provide a way to accelerate deployment of generative AI use cases into production with embedded security and compliance. The GenAI Gateway will trigger the flywheel effect in the adoption of generative AI, delivering quicker results for BT Group and its customers.” Deepika Adusumilli, Managing Director, Data & AI, BT Group’s Digital Unit said: “AI is helping us reimagine the future of our company. We believe that where our data is a constant, we need flexibility with our LLMs. GenAI Gateway allows us to tap into this powerful new set of technologies at scale, in a way that is safe, responsible, flexible and scalable, delivering the ambition we have for AI to unlock the human potential within BT Group, today and in the future.” Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Ensuring Network Reliability: The Role of Cable Testing Machines
Ensuring Network Reliability: The Role of Cable Testing Machines
In today’s interconnected world, the reliability of network infrastructure is paramount. From corporate offices to data centers, the backbone of these networks is the cabling that connects various devices and systems. Ensuring the integrity and performance of these cables is crucial, and this is where cable testing machines come into play. This article explores the importance of cable testing machines, their functions, and their impact on network reliability.Get more news about Cable Testing Machine,you can vist our website!
The Importance of Cable Testing Cables are the lifelines of any network, transmitting data, voice, and video signals across various distances. However, cables can suffer from a range of issues, including physical damage, manufacturing defects, and installation errors. These issues can lead to network downtime, data loss, and reduced performance. Cable testing machines are essential tools that help identify and rectify these problems, ensuring that networks operate smoothly and efficiently.
Types of Cable Testing Machines Cable testing machines come in various types, each designed to address specific testing needs. Here are some of the most common types:
Continuity Testers: These machines check for continuity in the cable, ensuring that there are no breaks or shorts in the wiring. They are essential for verifying the basic functionality of cables. High-Potential (HiPot) Testers: HiPot testers apply high voltage to the cable to test its insulation. This helps identify any weaknesses or potential points of failure in the insulation, which could lead to electrical shorts or fires. Network Cable Testers: These testers are used to assess the performance of network cables, such as Ethernet and fiber optic cables. They check for issues like signal loss, crosstalk, and attenuation, which can affect data transmission quality. Cable Harness Testers: These machines are used to test complex cable assemblies, such as those found in automotive and aerospace applications. They check for continuity, insulation resistance, and proper wiring configurations. Key Functions of Cable Testing Machines Cable testing machines perform a variety of functions to ensure the integrity and performance of cables. Some of the key functions include:
Continuity Testing: Verifies that the cable is properly connected from end to end, with no breaks or shorts. Insulation Resistance Testing: Measures the resistance of the cable’s insulation to ensure it can withstand electrical stress. Signal Quality Testing: Assesses the quality of the signal transmitted through the cable, checking for issues like signal loss and interference. Wiring Configuration Testing: Ensures that the cable is wired correctly, with all connections in the proper order. Benefits of Using Cable Testing Machines Improved Network Reliability: By identifying and addressing cable issues before they cause problems, cable testing machines help ensure that networks remain reliable and efficient. Cost Savings: Detecting and fixing cable issues early can prevent costly network downtime and reduce the need for expensive repairs or replacements. Enhanced Performance: Regular testing helps maintain optimal cable performance, ensuring that data transmission is fast and error-free. Compliance with Standards: Cable testing machines help ensure that cables meet industry standards and regulations, which is crucial for safety and performance. Applications in Various Industries Cable testing machines are used in a wide range of industries, including:
Telecommunications: Ensuring the reliability of network cables in telecom infrastructure. Data Centers: Maintaining the performance of cables in data center environments. Automotive: Testing complex cable harnesses in vehicles to ensure safety and functionality. Aerospace: Verifying the integrity of cable assemblies in aircraft and spacecraft. Future Trends in Cable Testing As technology advances, cable testing machines are becoming more sophisticated. Future trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance testing accuracy and efficiency. Additionally, the development of portable and wireless testing devices is making it easier for technicians to perform tests in the field.
Conclusion Cable testing machines are indispensable tools in ensuring the reliability and performance of network infrastructure. By identifying and addressing cable issues, these machines help prevent network downtime, improve performance, and reduce costs. As technology continues to evolve, the role of cable testing machines will only become more critical in maintaining the integrity of our interconnected world.
0 notes
Text
Data Protection with SAN Storage: Ensuring Business Continuity in 2024
Data protection has never been as critical as it is today. With the exponential rise in both the volume and value of data, and the simultaneous increase in cyber threats, the resilience of a business's data infrastructure can often be the difference between prosperity and perdition. In this article, we explore how Storage Area Network (SAN) technology continues to play a crucial role in safeguarding mission-critical data, and what IT professionals and data center managers must know to ensure their systems are at the forefront of data protection.
The Evolution of SAN Storage in Data Protection
Storage Area Networks were once exclusively the domain of the largest and most well-resourced enterprises. However, as data has become more complex and distributed, SANs have adapted and evolved to become more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective.
A Brief History
Initially developed to address the limitations of server-attached storage, SANs allowed for storage to be centralized and shared across multiple servers, creating a network specifically for storage, separate from the LAN used for general network communication. This separation was key for performance and scalability, but it came with a high price tag and was often seen as a complex and difficult technology.
Advancements in Accessibility
Despite the initial hurdles, SAN technology has found ways to become more accessible. With the rise of iSCSI and Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), organizations of all sizes have been able to implement SANs more cost-effectively than before. This accessibility means that even mid-sized and smaller companies can now take advantage of the data protection benefits that SANs provide.
Key Features of Modern SAN Storage and Their Role in Data Protection
SAN technology has advanced significantly, and modern SANs boast a slew of features designed to shield data from various threats and restore it quickly in the event of data loss.
Snapshotting and Cloning
Real-time and scheduled snapshots allow for point-in-time copies of data to be created, providing a quick method for data recovery in case of accidental deletion or corruption. Similarly, cloning enables the creation of full, independent replicas of LUNs (logical unit numbers) which can be used for test environments or as standby systems in a disaster recovery setup.
Replication
Synchronous and asynchronous replication capabilities have been built into many modern SANs, allowing for data to be mirrored across multiple locations with minimal latency. This is crucial for both local high availability setups and remote disaster recovery sites, ensuring that data is protected and available even in the wake of a catastrophic event.
Ensuring Compliance and Security in Data Protection
Data protection is not just about resilience; it's also about ensuring that data is kept safe and only accessed by those authorized to do so. With regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and more, businesses need to ensure that their data practices are not only robust but also compliant.
Encrypted SANs
Encryption at rest is becoming the standard for keeping data safe. Modern SANs often have built-in support for encryption, providing an additional layer of security that can be critical, particularly for data that is replicated or stored offsite.
Role-Based Access Control
RBAC within SAN environments is pivotal in ensuring that only authorized personnel can make changes to the SAN configuration or access data. By implementing RBAC, organizations can minimize the risk of insider threats and accidental misconfiguration.
Best Practices for SAN-Based Data Protection
Implementing a SAN for data protection may involve some complexity, but following best practices can help to smooth the process and ensure a reliable, resilient system.
Perform Regular Health and Performance Checks
Just like any other system, a SAN needs regular check-ups to maintain optimal performance and reliability. Monitoring tools and vendor-supplied health checks can provide early warning of potential issues and performance bottlenecks before they become critical problems.
Test Your Data Recovery Plan
Having a data protection strategy is essential, but unless you regularly test your recovery processes, you may find that they don't work as expected when they are needed. Regular testing, including failover and failback scenarios, is indispensable for a robust data protection plan.
The SAN Storage Market in 2024
The SAN market is showing no signs of abating, with many organizations continuing to invest in SAN technology. The market is also evolving, with more vendors offering cloud-integrated solutions and services, allowing organizations to leverage the best of both worlds—the data protection capabilities of SANs with the scalability and flexibility of the cloud.
Cloud Integration
Many organizations are looking to take advantage of the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the cloud for their data protection strategies. Cloud-integrated SANs allow for a more seamless data protection process, with the ability to replicate data to and from the cloud as easily as to another data center.
Flash Storage and Beyond
The introduction of all-flash arrays has transformed the performance profile of SANs, and the next frontier is NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) technology. NVMe provides even lower latency and higher throughput, further pushing the boundary of what SANs can achieve, particularly in real-time data protection scenarios.
Conclusion
In a digital world where data is king, data protection is an absolute necessity. SAN storage technology has evolved to offer not just high performance and scalability but also robust features for data protection, disaster recovery, and compliance. By understanding and leveraging the capabilities of modern SANs, organizations can ensure that their most valuable asset—their data—remains protected, available, and secure. Whether you're a seasoned IT professional or a tech enthusiast, the world of SAN solution technology is an exciting one, with continual advancements that promise to shape the future of data protection.
0 notes
Text
5 Compelling Reasons to Prefer Professional CCTV Camera Installation
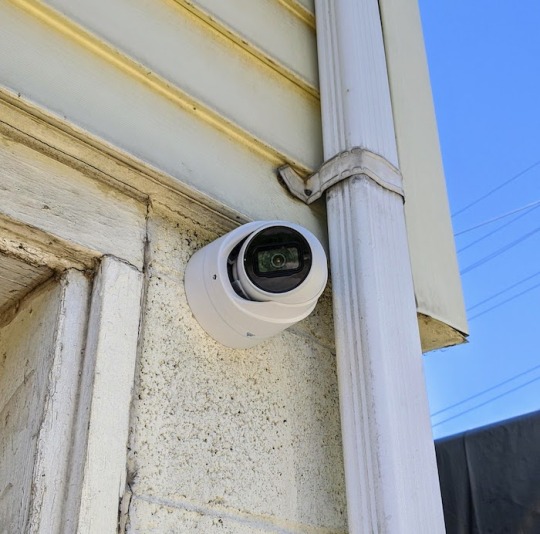

The crime rates have spiked in both residential and commercial neighborhoods in Pittsburgh. While the cops are doing their work and there isn’t much that civilians can do to stop crime, prevention is always better than cure. Among all the preventive measures you can adopt for safeguarding your premises, getting CCTV cameras and opting for professional surveillance camera installationis definitely on the top of the list. Closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras have become an indispensable tool for ensuring around-the-clock security, but their effectiveness relies immensely on the quality of their installation. Still, looking for reasons why you should hire a professional CCTV camera installer in Pittsburgh? Here you go!
#1 Expertise and Experience
You might not install a CCTV camera every day to earn your bread and butter, but professional CCTV installers do. They have the expertise and experience necessary to ensure your security system functions effortlessly without any pitfalls. Instead of the DIY approach, when you go for professional installers, they are well-versed in the intricacies of different camera models, configurations, and installation techniques. With their knowledge, you can pick the most suitable cameras and choose strategic placement locations according to your specific needs.
#2 Compliance with Regulations
Professional CCTV installers have the know-how to ensure your security system functions effortlessly, but they also know how you can adhere to legal and regulatory requirements. Seasoned CCTV installers know local laws governing surveillance systems, including privacy regulations and zoning ordinances. When you entrust the installation process to professionals, you can rest assured, they will adhere to due compliance after considering all relevant regulations.
#3 Quality Assurance
Ensuring the quality is impeccable is the first step of CCTV camera installation. Unlike you without any high-tech installing equipment, professional installers use high-quality equipment and tools to ensure your surveillance cameras work reliably. In addition, they also carefully test the system after installation to verify its functionality and address any potential issues promptly.
#4 Customization and Integration
Every property is unique and so are its surveillance requirements, Professional installers assess your property layout, identify vulnerable areas, and recommend the most appropriate camera types and configurations. In addition, they can also help you integrate CCTV systems with other security components, such as alarms and access control systems for better protection and convenience.
#5 Time and Cost Efficiency
Contrary to common perception, hiring professionals for CCTV installation can actually save you both time and money in the long run. Professional installers work efficiently, completing the installation process promptly while minimizing disruptions to your daily activities. In a nutshell, their expertise ensures accurate installation and reduces the likelihood of costly rework or system malfunctions down the line.
Conclusion:
If you have found the best cameras that can improve the security aspects of your home, ensure to find skilled professionals who can install the camera for optimum efficiency. Whether we are talking about network cabling installationor Ethernet cable installer in Pittsburgh, if you want to get the best of every penny you pay, Red Spark Technology is the way to go. They can also help you with audio-visual technology with a team of professional home theatre installers. Need more information, or want a personalized quote? Contact their team today!
Source: https://redsparktechnology.wordpress.com/2024/03/28/5-compelling-reasons-to-prefer-professional-cctv-camera-installation/
0 notes
Text
The infrastructure development needs of electrical engineers

In general, the task of an electrical engineer is to design high-voltage equipment such as wiring systems, power distribution systems, generators, and lighting systems etc. Within the construction industry, however, an electrical engineer of top engineering college in Jaipur has many responsibilities especially when it comes to a construction site. In both residential and commercial buildings, while some elements like lighting fixtures and receptacles, or those with a function that requires it are exposed, most components of electrical installations are hidden from sight using access doors. However, electrical systems in building interiors are more evident in industrial settings where there are no drywalls or dropped ceilings to hide junction boxes, conduits, and other accessories.
At construction sites, it is the duty of electrical site engineers to direct and oversee electrical engineering projects at construction sites, resolve issues, and ensure that work is completed according to specifications. They also balance project management and engineering tasks that range from designing electrical plans to monitoring contractors. It is also the duty of electrical engineers to ensure that plans and work are completed in compliance with local and national electrical codes. The role of an electrical engineer in the construction industry are as follows:
1. Designing Electrical Systems
It is the duty of electrical engineers of best engineering college in Jaipur to design electrical systems for commercial, residential, and industrial construction projects. High-voltage systems for delivering power and low-voltage applications such as Ethernet and fiber-optic lines are also included. They also have to work closely with designers in order to determine how to effectively incorporate electrical elements, prepare blueprints, and to incorporate electrical elements.
2. Directing Electrical Contractors
Electrical engineers also have the role of directly overseeing and managing teams of electrical contractors and subcontractors. Moreover, they may direct daily activities, answer questions about power needs and electric codes, as well as guide workers throughout the construction process. Mant engineers also work on elements of construction projects themselves, collaborating with electricians and other contractors.
3. Resolving Electrical Issues
When it comes to issues related to electric systems or devices that arise during the construction project, it is also the duty of electrical engineers of top electrical engineering colleges in Jaipur to resolve such issues. When existing electrical plans and blueprints are no longer viable, or specifications may change requiring a different power configuration resulting from changes to a building’s design or practical concerns, electrical engineers should quickly revise plans to resolve issues and prevent delays.
4. Developing Cost Estimates
Electrical site engineers help develop cost estimates for both material and labor at the onset of the construction planning process. They also estimate manpower and timelines in order to give project managers the information needed for contractor bids and to ensure that the project stays within budget. They also analyze blueprints and site specifications to project the amount of wire, fixtures, and other required materials.
5. Managing Construction Schedules
Managing construction schedules related to electrical elements of job sites is also one of the duties of electrical engineers of engineering colleges Jaipur. They also have to work closely with both planners and utility providers to determine when project milestones will be completed to avoid delays, as well as maintain profitability. They also frequently determine schedules in collaboration with subcontractors in ensuring that electrical work is completed together with other elements of the project.
6. Conduct of System Testing
Throughout the construction process, electrical engineers also conduct tests of electrical systems. This also includes overseeing final inspections of the job and testing individual components or the whole system itself. They also have to check the contractors’ work to ensure that they adhere to local and national electrical codes, safe operation of all devices, and even accurate power delivery.
Other Roles Of Electrical Engineers In Infrastructure Development
In the development industry an engineer would configure circuits and power convey gadgets to keep up with capacity to the end users. For instance, in a hospital setting, certain models exist for machines that need power and cannot bear the cost of interference. An illustration of this would be life support machines. A doctor would not want a patient to die because of power failure so electrical engineers would design configuration circuits, assess loads, and snare an emergency generator for instance to keep up with consistent power.
As they solve issues or build new products or processes, they will most likely collaborate with other engineers. Because most new or revised items involve electrical engineering of best BTech colleges in Jaipur, they will be thinking about the most efficient designs for the next phone, a new satellite, a vehicle dashboard, a power strip, or even a better light bulb. Depending on your ability and interests, you can pursue a career in electrical engineering in one of numerous fields. Networks and electronic circuits, electromagnetic fields and waves, signal processing, microprocessors, communication and control systems, solid state electronics, electrical power systems, computer engineering, analogue and digital electronics, optoelectronics, remote sensing, robotics and automation, microwaves, radar, and power generation, transmission, and distribution are some examples.
Conclusion
Electrical engineering is the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that deal with electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. Within this field and especially in the construction and industrial industries, an electrical engineer of best BTech electrical engineering colleges in Jaipur or electrical site engineer will be employed. Typically, these types of engineers will be tasked with designing, building, installing, and the maintenance of electrical systems and equipment. They work with all kinds of electrical systems, from small pocket devices to large supercomputers. An electrical site engineer can have many different roles and responsibilities in construction, whether they are working residential or commercial jobs. From preparing project specifications to creating test procedures, the experts are sharing the role of an electrical engineer and what they do within the construction industry.
Lastly, it is also the role of an electrician to ensure that electrical systems requiring more care and protection are safely encased inside quality access doors.
Source: Click Here
#best btech college in jaipur#top engineering college in jaipur#best btech college in rajasthan#b tech electrical in jaipur#best engineering college in jaipur#best private engineering college in jaipur
0 notes
Text
Top Skills Every Automotive Embedded Engineer Must Possess
Automotive Embedded engineering, the dynamic fusion of hardware and software, is rapidly evolving, fueling the demand for skilled professionals. As technology propels forward, the role of embedded engineers becomes increasingly pivotal in shaping cutting-edge solutions across diverse industries. In this comprehensive exploration, we uncover the top indispensable skills every embedded engineer should possess, delving into both technical competencies and non-technical skills that pave the way for a triumphant Embedded Career.
For more info https://neuailabs.com/
Responsibilities of an Embedded Engineer
Embedded engineers orchestrate the development of embedded systems, assuming critical roles in hardware and software design, firmware development, and rigorous testing. Their collaborative efforts with cross-functional teams ensure the reliability, performance, and compliance of embedded systems with project requirements.
Technical Competencies: The Foundation of Excellence
1. Knowledge of Hardware
In our Automotive Embedded Course, you will master digital and analog circuits, microcontrollers, microprocessors, and FPGAs. This profound understanding is the bedrock for crafting efficient and reliable hardware components.
2. Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS)
Efficient system design demands familiarity with RTOSs like FreeRTOS, RTX, or μC/OS-II. These systems manage task scheduling and resource allocation, ensuring seamless operation.
3. Communication Protocols
Mastery of communication protocols such as SPI, I2C, UART, CAN, and Ethernet is imperative for establishing fluid communication between different components of an embedded system.
4. Debugging and Testing Tools
Embedded engineers wield tools like JTAG, Logic Analyzers, and oscilloscopes with finesse. Proficiency in these tools is non-negotiable for identifying and resolving hardware and software issues.
Non-Technical Skills for Embedded Engineers
In addition to technical competencies, non-technical skills are equally important for embedded engineers to excel in their careers. These skills include:
1. Teamwork and Collaboration
Embedded engineering projects often involve interdisciplinary teams where effective communication and collaboration are essential. Embedded engineers should be able to work well within a team, share knowledge, and incorporate feedback from team members.
2. Time Management and Prioritization
Embedded engineering projects often have strict deadlines. Embedded engineers must have strong time management skills to prioritize tasks effectively, meet project milestones, and deliver high-quality results on time.
3. Attention to Detail
Embedded systems are complex, and even minor errors can have significant consequences. Attention to detail is crucial for identifying and rectifying issues, and ensuring the reliability and performance of the system.
4. Creative Problem-Solving
Embedded engineers encounter various challenges during system development. The ability to think critically and creatively to solve these challenges is essential for success. They should be able to analyze problems from multiple perspectives and propose innovative solutions.
These non-technical skills complement the technical competencies of embedded engineers, allowing them to work effectively within teams and deliver successful projects.
Fundamental Abilities and Attributes
In addition to skills and competencies, specific fundamental abilities and attributes elevate an embedded engineer to new heights.
1. Analytical Skills
Strong analytical skills empower embedded engineers to dissect complex situations, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions.
2. Attention to Detail
Embedded systems demand precision and accuracy. Meticulous attention to detail guarantees the integrity and reliability of the system.
3. Adaptability
As technology evolves, adaptability becomes a cornerstone. Embedded engineers embrace change, staying updated and adjusting their skills and knowledge accordingly.
4. Patience
Embedded system development is a journey that demands patience and perseverance. Facing challenges and setbacks, embedded engineers approach problem-solving with iterative precision.
Enhancing Engineering Skills within the Embedded Systems Domain
To stay ahead in this dynamic field, embedded engineers must adopt proactive strategies.
1. Continuous Learning
Actively seek opportunities to learn and stay abreast of the latest technologies, industry trends, and best practices. Dive into technical literature, attend conferences, and absorb the wealth of knowledge available.
2. Personal Projects
Undertake personal projects to explore new technologies, experiment with different approaches, and gain hands-on experience. These projects not only enhance skills but also serve as a showcase of expertise.
3. Professional Development Courses
Enroll in relevant courses or certifications focusing on specific embedded systems areas. Structured learning builds a robust foundation, enhancing overall proficiency.
4. Networking and Mentorship
Engage with the embedded systems community through online forums, social media, and professional networking events. Forge connections with experienced professionals for valuable insights and guidance with our embedded systems career development classes.
Abilities Required for Future Embedded Engineers
As technology propels forward, embedded engineers must evolve, acquiring new skills and adapting to emerging trends.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
A solid understanding of AI and ML concepts is essential. Embedding these technologies into systems enables intelligent decision-making and autonomous functionality.
2. Security
With increased connectivity, security becomes paramount. Proficiency in designing secure systems and implementing encryption algorithms is crucial to thwart threats.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
The expanding IoT landscape demands skills in building devices, integrating sensors, and managing network communications for seamless connectivity.
4. Wireless Communications
Proficiency in wireless protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and LoRaWAN is indispensable. Understanding the nuances of wireless communication ensures secure and efficient solutions.
For more info https://neuailabs.com/automotive-embedded/
Conclusion
In the intricate tapestry of embedded engineering courses, success is not a destination but a continuous journey. A fusion of technical skills, non-technical acumen, fundamental abilities, and a commitment to perpetual learning propels embedded engineering to thrive in this ever-evolving landscape with our automotive embedded courses. As guardians of innovation, embedded engineers shape the future, contributing to the advancement of technology. In the realm of embedded systems, mastery is not an option; it's the essence of excellence.

#automotive embedded course#embedded systems course#automotive embedded training#embedded systems course in pune#embedded classes in pune#neuailabs#futureofai
0 notes
Text
Empowering Connectivity: The Impact of Certified Network Wiring Solutions
In today's interconnected world, a robust and reliable network infrastructure forms the backbone of businesses and organizations. Ensuring seamless connectivity and data transmission requires more than just quality hardware—it demands a meticulously designed and professionally installed network wiring solution. Let's explore the significance and impact of certified network wiring solutions in the modern landscape.
Certified Network Wiring: What Does it Encompass?
Certified network wiring refers to the installation and maintenance of structured cabling systems that comply with industry standards and best practices. These solutions encompass the design, installation, testing, and certification of cabling infrastructure that supports various communication technologies, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and fiber optics.
Precision in Design and Planning
Certified network wiring begins with meticulous planning and design. Professionals conduct site assessments, considering factors like building layout, future scalability, bandwidth requirements, and equipment placement. Detailed schematics and blueprints are crafted to map out the most efficient and effective cabling routes.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Adherence to industry standards, such as those set by organizations like the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), is fundamental in certified network wiring. Compliance ensures that the cabling infrastructure meets performance benchmarks and supports current and future technologies.
Quality Installation and Workmanship
Certified technicians execute the installation process with precision and expertise. Proper cable handling, termination, labeling, and grounding are critical aspects to ensure optimal performance and minimize signal interference or degradation. Installation methods follow standardized practices to maintain consistency and reliability.
Performance Testing and Certification
Thorough testing and certification validate the integrity and performance of the installed network wiring. Specialized equipment conducts comprehensive tests to verify parameters like transmission speeds, signal strength, and error rates, ensuring compliance with industry standards. Certification documentation provides assurance of quality and compliance.
Advantages of Certified Network Wiring Solutions
Reliability and Performance: Certified wiring solutions ensure consistent, high-performance connectivity, reducing downtime and ensuring efficient data transmission.
Scalability and Future-Proofing: Well-designed solutions accommodate future technology upgrades and expansions, saving costs on re-cabling in the long run.
Enhanced Productivity: Reliable networks support seamless communication and operations, enhancing productivity and business continuity.
Minimized Interference: Properly installed and certified wiring minimizes signal interference, reducing data transmission errors and downtime.
Compliance and Liability: Certification documentation provides proof of compliance, mitigating risks and liabilities in case of network issues.
Investment Protection: Certified wiring solutions safeguard the investment in network infrastructure by ensuring longevity and reliability.
Industry Applications of Certified Network Wiring
Certified network wiring solutions find applications across diverse industries:
Corporate Environments: Offices, businesses, and enterprises rely on robust networks for seamless communication and operations.
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals and clinics require reliable networks for electronic health records and critical medical systems.
Educational Institutions: Schools and universities leverage network infrastructure for online learning and administrative tasks.
Data Centers: Robust cabling solutions support data centers, ensuring efficient data storage and transmission.
For More Info:-
The Computer Magician
Best Network Wiring Services
Custom Built Gaming Desktop Pc
Certified Network Wiring Solution
0 notes
Text
Data Cabling Installation - Thunder Electrical Services
What is data cable installation?
Data cable installation refers to the process of setting up a physical network infrastructure by connecting various devices, such as computers, printers, servers, and other network-enabled devices, using data cables. These cables are designed to transmit data signals between devices and establish a reliable network connection.

Here are the key steps involved in data cable installation:
Assessment and Planning: Before installation begins, a site assessment is conducted to understand the layout of the space and determine the best routes for running the cables. A plan is created to identify the locations of data outlets, network equipment, and cable pathways.
Cable Selection: Different types of data cables are available, such as Ethernet cables (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, etc.), fiber optic cables, and coaxial cables. The appropriate cable type is chosen based on the network requirements, data transmission speed, distance, and environmental factors.
Routing and Cable Pathways: Cables are routed through designated pathways, which may include walls, ceilings, conduits, cable trays, and floors. Careful planning is necessary to avoid interference, ensure cable protection, and comply with building codes and regulations.
Cable Installation: Cables are installed and terminated at both ends, connecting devices to the network. Termination involves attaching connectors, such as RJ45 connectors for Ethernet cables, to the cable ends. Proper termination is crucial for reliable data transmission.
Testing and Certification: After installation, each cable is tested to ensure it meets the required standards for data transmission. Specialized testing equipment is used to check cable continuity, signal quality, and performance parameters. Certifying the cables confirms that they can support the intended network speeds and bandwidth.
Documentation: A detailed record of cable installations, including cable types, lengths, termination points, and test results, is documented. This documentation is valuable for future reference, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
Labeling and Organization: Cables are labeled at both ends to identify their purpose and destination. Proper labeling simplifies troubleshooting and maintenance tasks, especially in large network installations.
Data cable installation is essential for creating a reliable and high-performance network infrastructure in homes, offices, data centers, and various other environments where networking is required. Professional installers or network technicians typically handle these installations to ensure accuracy, compliance with standards, and optimal network performance.
#ceiling fan installation#data cabling installation#data cabling coffs harbour#power sockets installation#power outlet installation#tv wall antenna#tv antenna coffs harbour
0 notes
Text
What are the Common Data Cabling Problems and It's Solutions?
In an increasingly digital world, data cabling is the backbone of information exchange. However, data cable issues can impact productivity and lead to costly downtime. Let's take a look at some common data cabling problems and their solutions with the help of data installers in Sydney.
Cable Overload
Problem: Cables can become tangled, poorly organised and damaged over time.
Solution: Label and organise your cables regularly, use a cable management system and consider wireless alternatives when possible.

Cable Length Limitations
Problem: Ethernet cables have distance limitations that can be difficult in large spaces.
Solution: Extend the range using network switches and routers. You can also use fibre optic cables to bridge long distances if necessary.
Signal Interference
Problem: Electromagnetic interference from other devices can interfere with data transmission. Solution: According to the data installers in Sydney, covered cables help reduce interference. Keep data cables away from power cables and other potential sources of interference.
Aged Cable
Problem: As cables age, they are more prone to damage and data loss.
Solution: Regularly inspect and replace old or damaged cables for optimal performance.
Insufficient bandwidth
Problem: As data requirements increase, older cables may be unable to support high-speed requirements.
Solution: Upgrade to newer cabling standards, such as Cat 6 or Cat 6a, to ensure sufficient bandwidth for current and future needs.
Illegal termination
Problem: Connection issues can occur if the cable is not correctly terminated.
Solution: Have a trained professional or the data installers in Sydney use the proper tools and techniques to ensure cables are correctly connected.

Cable Compatibility
Problem: Mismatched cables can cause connection issues.
Solution: Use a cable that matches the specifications of your network equipment. Avoid combining different types of cables.
Inappropriate Testing
Problem: Insufficient testing may result in undetected cabling issues.
Solution: Regularly test and certify cabling installations to identify and correct problems before they become critical.
Addressing these common data cabling issues ensures a reliable and efficient data infrastructure. Regular maintenance, thoughtful design and compliance with cabling standards are key to preventing and resolving cabling issues that can impact business connectivity and productivity!
0 notes
Text

Protocol Testing Services | Interoperability Testing | UtthungaLooking for pre-compliance and protocol testing services of HART, WirelessHART, EtherNet/IP, and OPC devices? Utthunga works closely with all the protocol standards associations, has required infrastructure and experience for interoperability testing for various protocols and providing diagnostics. Find out more on what we do!
0 notes
Text
Introduction to Embedded Single Board Computer
An embedded Single Board Computer is a complete circuit board that integrates a processor, memory, interfaces, clocks, and other auxiliary circuits. It is commonly used to create embedded systems, such as those used for controlling robots, automobiles, or industrial equipment.
Here is an introduction to embedded Single Board Computers and some tips on how to use and choose the right one:
01 What is an Embedded Single Board Computer?
A Single Board Computer is a circuit board used for developing embedded systems. It includes a central processing unit (CPU), memory, input devices, output devices, data pathways/buses, and external resource interfaces, among other hardware components. It serves as a platform for cooperation within the semiconductor industry, providing manufacturers with essential low-level hardware, system, and driver resources. This eliminates the need for users to invest manpower and time to complete these low-level tasks. Common types of Single Board Computers include 51, ARM, FPGA, and DSP. Forlinx is dedicated to the development and service of ARM architecture Single Board Computers.

Single Board Computers, in concept, are very similar to software outsourcing. In terms of embedded products, the hardware, boot code, drivers, file systems, protocol layers, and basic application software are considered common and generic components of electronic products. They do not encompass the key technologies that differentiate the product. In this era that emphasizes division of labor and cooperation, if the workload in this area is significant or if a manufacturer lacks relevant development personnel, they can choose to outsource these development tasks to a third-party. This accelerates the product development process and enables quick time-to-market, seizing a competitive advantage.
Forlinx Embedded Single Board Computer integrates all the core functional circuits commonly found in embedded products. It combines the processor with RAM, Flash memory, power management, LCD, Ethernet, USB, and other universal interfaces into a compact, reliable, and electromagnetic-compatible electronic motherboard. By adopting a SoM for product development, you can avoid complex processor development, BGA design, high-speed PCB routing, design verification, EMC compliance design, as well as save the effort required for extensive board debugging and BSP (Board Support Package) development work.
When selecting a Single Board Computer, you are actually choosing not just a hardware board and the resources it provides, such as source code, but also choosing a partner, a collaborator who provides software and hardware services to users.
Similar to the cooperation model of software outsourcing, the collaboration between users and suppliers in this case is primarily focused on software cooperation. It requires thorough communication between the user and the supplier to understand the specific requirements of the product. The supplier needs to continuously allocate personnel according to the user's needs to ensure effective collaboration.
During the process of supporting customers in product development, Forlinx often encounters issues such as modifying the file system, serial port testing, upgrading Flash memory from 64MB to 128MB, etc. In most cases, these issues need to be resolved through software solutions. This forms a high level of interaction between embedded industry suppliers and customers in terms of after-sales support and customer development.
In other words, embedded Single Board Computers serve as the medium for user's software outsourcing. Compared to traditional software outsourcing, Single Board Computers actually provide users with value in terms of both hardware and software services.
02 How to Use an Embedded Single Board Computer?
Using an embedded Single Board Computer requires some knowledge of hardware and software. Here are a few steps to help you get better at using embedded Single Board Computers:
1. Understand the specifications and features of the Single Board Computer, read relevant documentation and manuals, or study relevant tutorials.
2. Familiarize yourself with the programming language and IDE environment you will use.
3. Write code, connect hardware, debug the program, and validate the results. This includes tasks such as GPIO control, PWM waveform output, serial communication, and short message transmission.
03 How to Choose an Embedded Single Board Computer?
Choosing the right embedded Single Board Computer can greatly improve development efficiency. Here are some factors to consider when purchasing an embedded Single Board Computer:
1. Processing power: Consider the specification and performance of the board’s processor to ensure it can handle your application’s requirements. ARM Cortex series should be given priority consideration because they have extensive support and ecosystem.
2. Interfaces and expand-ability: It is important to determine which peripherals need to be added based on your project requirements. Check if the Single Board Computer has relevant general-purpose input/output (GPIO) and expansion interfaces. It is also beneficial to consider the compatibility with operating systems and network connectivity components.
3. Cost: This can be an important factor for budget-conscious projects, but it's important not to focus solely on price. Quality should be a priority consideration. You can also explore options such as using older models that have already been released, which may help reduce costs.
4. Support and maintenance: Look for a reliable supplier or manufacturer that offers timely technical support and maintenance services. Having a strong support team can definitely help you solve problems and overcome challenges.
5. Estimated life-cycle: Consider the life-cycle of the Single Board Computer. Choosing a product with long-term support is indeed crucial to ensure ongoing support and availability of replacements in the future.
6. Hardware and Software Ecosystem: Consider the ecosystem of the Single Board Computer, including development tools, documentation, community support, and third-party software and hardware support. Indeed, a strong ecosystem can greatly reduce development time and difficulty.
7. User feedback and reviews: Look for user feedback and reviews about the Single Board Computer to understand the experiences and suggestions of other developers. Searching for user feedback and reviews about the Single Board Computer to understand the experiences and suggestions of other developers.
In general, choosing an embedded Single Board Computer requires considering multiple factors such as performance, interfaces, ecosystem, cost, and support. Exactly, it's important to choose the Single Board Computer that suits your application's specific requirements and goals. This ensures that the chosen board is well-suited for the intended purpose.
Embedded Single Board Computers serve as the medium for user's software outsourcing. Compared to traditional software outsourcing, Single Board Computers actually provide users with value in terms of both hardware and software services.
04 Forlinx's Best Embedded Single Board Computer

Originally published at www.forlinx.net.
#Embedded Single Board Computer#forlinx#processors#Hardware and software services#Choosing the right SBC
0 notes
Text
LAN Cable Tester Market Overview Analysis, Trends, Share, Size, Type & Future Forecast to 2032

Overview:
Growing demand for efficient network connectivity: With the increasing reliance on network infrastructure and the growing number of connected devices, there is a rising demand for reliable and efficient network connectivity. LAN cable testers play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and performance of network cables.
Technological advancements driving market growth: The LAN cable tester market is experiencing significant advancements in terms of features, functionalities, and automation. These technological advancements are enhancing the accuracy, speed, and ease of testing, driving the market growth.
Increasing adoption of LAN cable testers in various industries: LAN cable testers are widely used in various industries, including IT and telecommunications, manufacturing, healthcare, and education. The increasing adoption of LAN cable testers across these industries is fueling market growth.
Emphasis on network security and performance: Organizations are becoming increasingly concerned about network security and performance issues. LAN cable testers help identify and resolve cable faults, ensuring the integrity of the network infrastructure and minimizing potential security risks.
Growing importance of cable certification standards: Cable certification standards, such as Category 5e, Category 6, and Category 6a, are becoming essential for ensuring network performance. LAN cable testers are instrumental in certifying cables according to these standards, driving the demand for such devices.
The Global LAN Cable Tester market size was valued at USD 196416.03 million in 2021 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.08% during to the Forecast period 2030
Key points of the LAN Cable Tester Market:
Increasing demand for cable testers in data centers: The growing number of data centers and the need for efficient cable management within these facilities are driving the demand for LAN cable testers. These testers help in the identification of cable faults and ensure optimal performance in data center environments.
Rising adoption of LAN cable testers in enterprise networks: Enterprises are investing in LAN cable testers to maintain the performance and reliability of their network infrastructure. Cable testers help diagnose cable faults, improve troubleshooting processes, and reduce network downtime, resulting in increased adoption across enterprise networks.
Surge in network infrastructure investments: The continuous investments in network infrastructure, including the installation of new cables and upgrading existing ones, are fueling the demand for LAN cable testers. These testers help validate and certify the installed cables, ensuring their compliance with industry standards.
Increasing deployment of Ethernet cables: Ethernet cables are extensively used for networking purposes, and their deployment is on the rise due to the growing demand for high-speed connectivity. LAN cable testers are crucial for testing and certifying Ethernet cables, driving their demand in the market.
Advantages of cable testers in reducing maintenance costs: LAN cable testers enable proactive cable maintenance by identifying and rectifying cable faults at an early stage. This helps in reducing maintenance costs associated with network downtime and improves the overall efficiency of network operations.
Demand points of the LAN Cable Tester Market:
Growing demand from the telecommunications sector: The telecommunications sector is witnessing a surge in network expansion and upgrades to support increased data transmission. LAN cable testers are in high demand in this sector for cable certification and troubleshooting purposes.
Increasing need for cable testers in residential installations: The rising number of smart homes and residential installations requiring network connectivity is driving the demand for LAN cable testers. These testers ensure proper cable installation and help troubleshoot connectivity issues in residential environments.
Characteristics points of LAN cable testers:
Cable compatibility: LAN cable testers are designed to support various cable types and categories, including Cat 5e, Cat 6, Cat 6a, and fiber optic cables. This versatility allows them to cater to different network environments and requirements.
Accuracy and precision: LAN cable testers provide accurate and precise results by detecting cable faults, identifying their locations, and measuring parameters such as cable length, attenuation, and crosstalk. This helps in efficient troubleshooting and maintenance.
Portability and ease of use: LAN cable testers are often compact and portable, allowing technicians to carry them to different locations for testing. They are designed with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive controls, making them easy to operate and navigate.
Automation and advanced features: Modern LAN cable testers come with automation features and advanced functionalities, such as auto-testing, multi-port testing, and graphical representations of test results. These features enhance efficiency, speed up testing processes, and provide comprehensive insights.
Connectivity and reporting capabilities: LAN cable testers offer connectivity options, such as USB, Ethernet, or wireless connections, enabling easy data transfer and report generation. They can generate detailed reports that document the test results and provide valuable information for analysis and future reference.
Opportunity points in the LAN Cable Tester Market:
Increasing demand for high-speed networks: The growing adoption of technologies like 5G, IoT, and cloud computing is driving the need for high-speed networks. This presents an opportunity for LAN cable testers with advanced capabilities to ensure the quality and performance of high-speed network connections.
Expansion of smart city infrastructure: Smart city initiatives involve the deployment of extensive network infrastructure. LAN cable testers play a crucial role in the installation, certification, and maintenance of network cables in smart city projects, presenting significant growth opportunities.
We recommend referring our Stringent datalytics firm, industry publications, and websites that specialize in providing market reports. These sources often offer comprehensive analysis, market trends, growth forecasts, competitive landscape, and other valuable insights into this market.
By visiting our website or contacting us directly, you can explore the availability of specific reports related to this market. These reports often require a purchase or subscription, but we provide comprehensive and in-depth information that can be valuable for businesses, investors, and individuals interested in this market.
“Remember to look for recent reports to ensure you have the most current and relevant information.”
Click Here, To Get Free Sample Report: https://stringentdatalytics.com/sample-request/lan-cable-tester-market/5624/
Market Segmentations:
Global LAN Cable Tester Market: By Company • Fluke • TREND Networks • RS Components • Hioki • Noyafa • Klein Tools • Startech • Gembird Europe BV • Excellence Wire • D-Link • Le-tehnika • PHILEX Global LAN Cable Tester Market: By Type • Cable Certification Tester • Cable Qualification Tester • Cable Verification Tester Global LAN Cable Tester Market: By Application • Electronics • Industrial • Laboratory • Others Global LAN Cable Tester Market: Regional Analysis All the regional segmentation has been studied based on recent and future trends, and the market is forecasted throughout the prediction period. The countries covered in the regional analysis of the Global LAN Cable Tester market report are U.S., Canada, and Mexico in North America, Germany, France, U.K., Russia, Italy, Spain, Turkey, Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, and Rest of Europe in Europe, Singapore, Malaysia, Australia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific (APAC) in the Asia-Pacific (APAC), Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, South Africa, Egypt, Israel, Rest of Middle East and Africa (MEA) as a part of Middle East and Africa (MEA), and Argentina, Brazil, and Rest of South America as part of South America.
Visit Report Page for More Details: https://stringentdatalytics.com/reports/lan-cable-tester-market/5624/
Reasons to Purchase LAN Cable Tester Market Report:
• To obtain insights into industry trends and dynamics, including market size, growth rates, and important factors and difficulties. This study offers insightful information on these topics.
• To identify important participants and rivals: This research studies can assist companies in identifying key participants and rivals in their sector, along with their market share, business plans, and strengths and weaknesses.
• To comprehend consumer behaviour: these research studies can offer insightful information about customer behaviour, including preferences, spending patterns, and demographics.
• To assess market opportunities: These research studies can aid companies in assessing market chances, such as prospective new goods or services, fresh markets, and new trends.
• To make well-informed business decisions: These research reports give companies data-driven insights that they may use to plan their strategy, develop new products, and devise marketing and advertising plans.
In general, market research studies offer companies and organisations useful data that can aid in making decisions and maintaining competitiveness in their industry. They can offer a strong basis for decision-making, strategy formulation, and company planning.
About US:
Stringent Datalytics offers both custom and syndicated market research reports. Custom market research reports are tailored to a specific client's needs and requirements. These reports provide unique insights into a particular industry or market segment and can help businesses make informed decisions about their strategies and operations.
Syndicated market research reports, on the other hand, are pre-existing reports that are available for purchase by multiple clients. These reports are often produced on a regular basis, such as annually or quarterly, and cover a broad range of industries and market segments. Syndicated reports provide clients with insights into industry trends, market sizes, and competitive landscapes. By offering both custom and syndicated reports, Stringent Datalytics can provide clients with a range of market research solutions that can be customized to their specific needs
Contact US:
Stringent Datalytics
Contact No - +1 346 666 6655
Email Id - [email protected]
Web - https://stringentdatalytics.com/
0 notes
Text
Electrical engineering in the construction of new infrastructure - ACEIT
In general, the task of an electrical engineer is to design high-voltage equipment such as wiring systems, power distribution systems, generators, and lighting systems etc. Within the construction industry, however, an electrical engineer of top engineering colleges in Jaipur has many responsibilities especially when it comes to a construction site. In both residential and commercial buildings, while some elements like lighting fixtures and receptacles, or those with a function that requires it are exposed, most components of electrical installations are hidden from sight using access doors. However, electrical systems in building interiors are more evident in industrial settings where there are no drywalls or dropped ceilings to hide junction boxes, conduits, and other accessories.
At construction sites, it is the duty of electrical site engineers to direct and oversee electrical engineering projects at construction sites, resolve issues, and ensure that work is completed according to specifications. They also balance project management and engineering tasks that range from designing electrical plans to monitoring contractors. It is also the duty of electrical engineers to ensure that plans and work are completed in compliance with local and national electrical codes. The role of an electrical engineer in the construction industry are as follows:
1. Designing Electrical Systems
It is the duty of electrical engineers of best engineering colleges in Jaipur to design electrical systems for commercial, residential, and industrial construction projects. High-voltage systems for delivering power and low-voltage applications such as Ethernet and fiber-optic lines are also included. They also have to work closely with designers in order to determine how to effectively incorporate electrical elements, prepare blueprints, and to incorporate electrical elements.
2. Directing Electrical Contractors
Electrical engineers also have the role of directly overseeing and managing teams of electrical contractors and subcontractors. Moreover, they may direct daily activities, answer questions about power needs and electric codes, as well as guide workers throughout the construction process. Mant engineers also work on elements of construction projects themselves, collaborating with electricians and other contractors.
3. Resolving Electrical Issues
When it comes to issues related to electric systems or devices that arise during the construction project, it is also the duty of electrical engineers of top electrical engineering colleges in Jaipur to resolve such issues. When existing electrical plans and blueprints are no longer viable, or specifications may change requiring a different power configuration resulting from changes to a building’s design or practical concerns, electrical engineers should quickly revise plans to resolve issues and prevent delays.
4. Developing Cost Estimates
Electrical site engineers help develop cost estimates for both material and labor at the onset of the construction planning process. They also estimate manpower and timelines in order to give project managers the information needed for contractor bids and to ensure that the project stays within budget. They also analyze blueprints and site specifications to project the amount of wire, fixtures, and other required materials.
5. Managing Construction Schedules
Managing construction schedules related to electrical elements of job sites is also one of the duties of electrical engineers of engineering colleges Jaipur. They also have to work closely with both planners and utility providers to determine when project milestones will be completed to avoid delays, as well as maintain profitability. They also frequently determine schedules in collaboration with subcontractors in ensuring that electrical work is completed together with other elements of the project.
6. Conduct of System Testing
Throughout the construction process, electrical engineers also conduct tests of electrical systems. This also includes overseeing final inspections of the job and testing individual components or the whole system itself. They also have to check the contractors’ work to ensure that they adhere to local and national electrical codes, safe operation of all devices, and even accurate power delivery.
Other Roles Of Electrical Engineers In Infrastructure Development
In the development industry an engineer would configure circuits and power convey gadgets to keep up with capacity to the end users. For instance, in a hospital setting, certain models exist for machines that need power and cannot bear the cost of interference. An illustration of this would be life support machines. A doctor would not want a patient to die because of power failure so electrical engineers would design configuration circuits, assess loads, and snare an emergency generator for instance to keep up with consistent power.
As they solve issues or build new products or processes, they will most likely collaborate with other engineers. Because most new or revised items involve electrical engineering of best BTech colleges in Jaipur, they will be thinking about the most efficient designs for the next phone, a new satellite, a vehicle dashboard, a power strip, or even a better light bulb. Depending on your ability and interests, you can pursue a career in electrical engineering in one of numerous fields. Networks and electronic circuits, electromagnetic fields and waves, signal processing, microprocessors, communication and control systems, solid state electronics, electrical power systems, computer engineering, analogue and digital electronics, optoelectronics, remote sensing, robotics and automation, microwaves, radar, and power generation, transmission, and distribution are some examples.
Conclusion
Electrical engineering is the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that deal with electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. Within this field and especially in the construction and industrial industries, an electrical engineer of best BTech electrical engineering colleges in Jaipur or electrical site engineer will be employed. Typically, these types of engineers will be tasked with designing, building, installing, and the maintenance of electrical systems and equipment. They work with all kinds of electrical systems, from small pocket devices to large supercomputers. An electrical site engineer can have many different roles and responsibilities in construction, whether they are working residential or commercial jobs. From preparing project specifications to creating test procedures, the experts are sharing the role of an electrical engineer and what they do within the construction industry.
Lastly, it is also the role of an electrician to ensure that electrical systems requiring more care and protection are safely encased inside quality access doors.
0 notes
Text
Ethernet Compliance Testing at Toradex
Introduction
Toradex offers robust and reliable embedded systems, which are required to work continuously in harsh environments. Ethernet is one of the most important interfaces for the Internet of Things (IoT). We will review some Ethernet standards and show you how Toradex tests for compliance with them.
After looking at the standards, we’ll describe our test configuration, test procedures, and the test results. A Colibri iMX6ULL SoM and Iris Carrier Board were used in this example, but you can use this as a model for testing custom carrier boards if that testing will be part of your verification process.

Why We Use Standards and Do Compliance Testing
Ethernet designs adhere to the IEEE 802.3 standard, which defines the Physical and Data Link layer of the seven-layer Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. Waveform characteristics are specified in the standard. Designing to this standard allows compatibility and interoperability with other devices, in all kinds of environments all over the world. Otherwise, transmission issues and data losses are likely to occur. Compliance testing ensures that the implementation meets the standard.
In addition to the waveform characteristics specified in the IEEE 802.3 standard, the University of New Hampshire InterOperability Laboratory (UNH-IOL) has provided standard conformance test procedures for those signals.
The documents can be found at these links:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/browse/standards/get-program/page/series?id=68
https://www.iol.unh.edu/
Ethernet Physical Layer Basics
The Ethernet standard is several thousand pages, so we’ll just cover the most important concepts and some key terminology.

Figure 1 OSI Reference Model from IEEE Standard for Ethernet
Let’s start with the physical medium. Signals typically arrive through a twisted pair copper cable to an Ethernet jack with magnetics on our Carrier Board, then continue through impedance matched differential traces on the PCB to the Ethernet PHY IC. This device converts analog signals from the medium to digital signals for the processor and vice versa.
The electrical signals first encounter the Medium Dependent Interface (MDI) of the PHY, a part of the Physical layer. Different physical media have different characteristics. In accordance with the specific kind of the media, the signals are transformed and sent to the next layer of the OSI-model, the Data Link Layer. We provide 10Base-T and 100Base-TX (Fast Ethernet) on our Colibri Modules and 1000Base-T (Gigabit) on the Apalis modules. The standardized interface between the first two OSI-layers is called Media Independent Interface (MII) and is independent of the physical layer.

Meanwhile, we are talking about the advanced backward-compatible Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RGMII) and the next interface for the 10 Gigabit is already named as XGMII. Reduced means that there are fewer signals needed for the same standard. The xMII’s are parallel data buses. There is a supplementary serial bus for management purpose called Management Data Input/Output (MDIO). The xMII interface ends at the Media Access Control (MAC) layer. Here the well-known MAC address is used as a unique identifier. The MAC layer can be integrated with the System on Chip (SoC), like on NXP® processors. But it could be already embedded in the same IC as the PHY, which is better known as an Ethernet Controller. The Ethernet Controller IC, in turn, is connected with the SoC through a separate interface like USB or PCIe. Note that we are not looking at higher OSI layers and protocols like ARP, NDP, IP, TCP, UDP, etc., which are organized in frames and packages, because for all these protocols the electrical characteristics on the first physical levels are the same!
For now, let’s go back to the physical layer. There are 2 main characteristics of the physical link I’d like to expand on, namely, speed and duplex mode. Our modules support speeds up to 1Gbit on Apalis Modules and 100Mbit on Colibri Modules, and both half and full duplex modes. In full duplex mode of operation, PHYs on both ends of the link can communicate with each other simultaneously. For the half duplex mode, where the PHY can’t receive and transmit data at the same time, there need to use the Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) to avoid collisions and control the data flow.
As already described, our Apalis Modules are capable of Gigabit Ethernet, but how do the communication partners know with which speed they can send the data? An-auto negotiation procedure exists, where the linking partners set the best link trough 16ms link pulses. Please be careful with auto-negotiation settings, as there is a well-known problem of the duplex mismatch, when the linking partners are configured in a fixed way. On the electrical side of the physical layer 10Base-T and 100Base-TX use two twisted pairs while 1000Base-TX uses 4. 100Base-TX is faster than 10Base-T based on the much faster frequency of 62.5 MHz instead of 10 MHz and denser signal modulation scheme (PAM-3). 1000Base-TX uses the same frequency as 100Base-TX, but transmits across 4 twisted pairs and with a higher level of modulation (PAM-5). Finally, there is an additional feature called EEE, Energy Efficient Ethernet. The aim of this standard is to save energy.
https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/application-notes/EE-269.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duplex_mismatch
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Media-independent_interface
https://www.asix.com.tw/new_alias.php?alias=93&full=http://www.embedded.com/design/202804534
The picture below summarizes the Ethernet possibilities on the Toradex SoM approach:
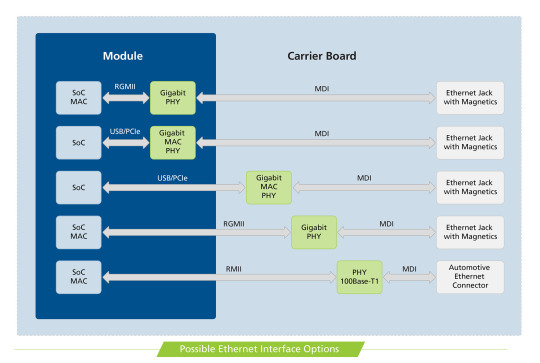
Automotive Ethernet
Before we continue to the Compliance Testing, I want to quickly let you know that I receive a lot of questions about 100Base-T1, better known as Automotive Ethernet. The customers want to know, if it is possible to connect Automotive Ethernet to a fast Ethernet PHY. The 100Base-T1 has a different physical layer specification to fulfill the requirements in a harsher automotive environment. It is not possible to connect it, but the MII is still the same! The solution is to connect the 100Base-T1 PHY to the Multimedia Independent Interface of the SoC directly. Consequently, a Module with an xMII on the Module Edge Connector must be selected! Of course, you have to design your Custom Carrier Board with a 100Base-T1 PHY. Here you can find the list of Toradex Modules which provide an xMII on the edge connector. Please note that this is not a Standard Toradex Interface and the pin assignment varies with each module.
Apalis iMX8
Colibri iMX8X
Colibri iMX7
Colibri iMX6ULL
Colibri Vybrid
Ethernet Compliance Testing for Toradex Systems

Figure 2 10Base-T Test: DOV Internal MAU Normal
After this very short overview, I want to continue with the compliance testing, where we test the electrical signals in time and voltage. The electrical signals look totally different for the 10/100/1000 Mbps and have different requirements as you can see in the oscillograms.
The tests evaluate the voltage amplitudes, jitter values, rise/fall times and other signal characteristics. For each test a defined test signal must be generated by the DUT, e.g. a continuous pseudo-random signal has to be emitted. The easiest way to test the signal requirements is to define a test mask. The signals must not intersect with the mask in order to fulfill the specification. The 10Base-T tests are very often defined through a test mask, as you can see in the first figure. I want to mention some values: The Peak Differential Output Voltage must be between 2.2 V and 2.8 V. The Differential Output Voltage Harmonics must be greater than 27 dB and all Jitter values must be smaller than 22 ns. Very interesting is the twisted-pair model for 10Base-T, which must be used for some compliance tests. With the equivalent circuit based on lumped elements, it is possible to model multiple different transmission elements with just passive components. Depending on the PHY a linking partner is needed for 10Base-T compliance tests. You can download the Test Report of Colibri iMX6ULL as an example, where you can find all tests.

Figure 3 Measured differential random 10Base-T signal without load
The interface characteristics for 100Base-TX are defined in table 2 based on the MLT-3 voltage signals with three levels. The data is encoded before with 4B5B algorithm, so a clock recovery out of the data stream is possible because a level transition is forced. For our test equipment, a pseudo-random test pattern (PRBS7) is enough for all the tests. However, some tests only trigger on defined patterns and measures only at that moment the specific values.
Table 2 Interface Characteristics 100Base-TX Characteristics Min Max Unit UTP DOV Base to Upper/Lower 950 1050 mV Signal Amplitude Symmetry 98 102 % Rise/Fall Time 3 5 ns Rise/Fall Time Symmetry 0 500 ps Duty Cycle Distortion -250 250 ps Transmit Jitter 0 1.4 ns Overshoot 0 5 %

Figure 4 Measured differential random signal 100Base-TX
The test criteria are defined in a similar manner for the 1000Base-T. I am not going to list them. For these tests an additional disturber in the form of an Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG) is needed to create the required disturbing signals with the frequency of 31.25 MHz and 20.833 MHz. In figure 5 you can see the test pattern of test mode 1 produced by the PHY. There are four different test patterns, which can be generated through PHY’s MDIO register settings. Please don’t forget that we have to perform the compliance test four times, because of the four twisted pairs.

Figure 5 Definition of Test Mode 1 Waveform 1000Base-T from IEEE Standard for Ethernet

Figure 6 Measured differential Test Mode 4 Distortion Test 1000Base-T without disturber
We have now seen some of the electrical requirements that must be fulfilled to be compliant with the interface definition. Before we have a closer look at the test equipment, I want to try and solve the most important question of this Blog: How do you generate those test signals?
Each PHY vendor has a custom method to modify the necessary register settings to enter the test modes. That is often not publicly available, and you must ask your PHY vendor. A very good example is Microchip, who has provided all information about Ethernet Compliance in one document since last year. These are the Ethernet PHYs, which we use in our modules, KSZ8041 and KSZ9031. I also want to share a document from TI with you, just as a further example. If you are looking for a new Ethernet PHY and want to do Ethernet Compliance Testing, please ask your vendor for detailed information about the register settings in advance!
http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/AppNotes/AN2686-Ethernet-Compliance-Test-10BASET-100BASETX-1000BASET.pdf
http://www.ti.com/lit/an/snla239a/snla239a.pdf
Test Equipment
As depicted above, we must measure some picoseconds precisely. For that we need very good tooling. You should use an oscilloscope with a bandwidth of 1 GHz and memory of 4MS or greater. Usually you need a test fixture, which transforms the Ethernet signals from an Ethernet Jack to the oscilloscope input channels. That is why we work closely with Teledyne LeCroy. We have a great collaboration on a technical level. We use a high-end oscilloscope from the WaveMaster series with appropriate hardware and software tools. Of course, there is equipment from other vendors available like Tektronix, Rhode&Schwarz, Keysight and others.
Quotation from Mr. Hofferbert, specialist at Teledyne LeCroy:
“Teledyne LeCroy is a leading manufacturer of digital storage oscilloscopes (DSO). With modern DSOs it is possible to perform qualification measurements. Toradex uses appropriate equipment from Teledyne LeCroy to test the design of Ethernet PHYs. With the combination of our QualiPHY Software and latest oscilloscopes, a semi-automatic test has been implemented to test the physical level of the Ethernet PHYs according to the IEEE 802.3 specification. This measurement solution allows the development engineers at Toradex to test and resolve issues with signal integrity in an early development stage of their embedded systems. Toradex is very interested in using the measurement equipment as efficiently as possible. If there are any uncertainties or measurement deviation, we work together to quickly solve these issues and provide our expertise in measurement application.” Gregor Hofferbert, Teledyne LeCroy
www.teledynelecroy.com
http://cdn.teledynelecroy.com/files/manuals/qualiphyenetmanual.pdf
Conclusion
After performing a compliance test, we can create a compliance report to verify our PCB design. As you can see in the test report from Teledyne LeCroy, the Colibri iMX6ULL with Iris Carrier Board is compliant with 10Base-T and 100Base-TX standard. So, we are sure that our implementation will work with other compliant systems. We can share with confidence our PCB implementation of the Ethernet Interface with our customers. You can find the Carrier Board Design Guides here: https://developer.toradex.com/carrier-board-design
We also share our Carrier Boards Designs as Altium Designer projects for free with our customers. We provide a lot of help through our community channel as well: https://www.toradex.com/community
We started to implement and provide our testing SW in our latest BSP. We adopt the existing drivers to be easily run with our modules to perform Compliance Tests. But again be careful, for each PHY you need different SW techniques to get the test pattern. There is no simple handbook. For example: https://git.toradex.com/cgit/linux-toradex.git/commit/?h=tegra-next&id=13bd0f089ac6babeb7248fe3db4b9c19233cce3c
But issues can occur with wrong routing, bad ground layout, or inaccurate crystal circuit design. It also depends on the testing environment. Ground loops and noisy or underpowered power supplies can cause measuring errors. It is important to follow the design guides of the PHY vendors. I like the troubleshooting document provided by Intel, that you can use for the first debug consultation. There is a basic overview of failures and possible sources. Designs with too long traces, low quality magnetics or improper use of the measurement equipment can always be the source of failing the compliance test. But there are also specific errors which can be put in a strong correlation. E.g. wrong amplitude values are often caused by wrongly assembled bias resistors or issues with the centre tap circuits. Whereas too high Jitter values are due to crystal issues, impedance mismatch or bad power supply. In general, your Ethernet PHY vendor should be able to help you, probably even with a schematic or layout review.
https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/application-notes/ieee-conformance-phy-app-note.pdf
In this blog, I gave you some insights to one of the many verifications Toradex does to achieve such high-quality products. Internal testing by us and your adherence to our design guides reduces your risk to a minimum. For the highest quality, you can do your verification with your own customized carrier board, and that you follow the system engineering approach (as documented by NASA, for instance) which recommends testing in early stages to reduce risk and cost. I hope I gave you plenty of information to get started. If you need more information feel free to reach out.
#Ethernet Compliance Test#Apalis iMX8#Colibri iMX6Ull#Development Boards#NXP i.MX 8#NXP i.MX 6ULL#System on Module#Computer on Module
0 notes